A Study of the Interaction between Xanthine Oxidase and Its Inhibitors from Chrysanthemum morifolium Using Computational Simulation and Multispectroscopic Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Extraction of C. morifolium Flowers
2.3. Solvent-Solvent Partitioning
2.4. Identification of C. morifolium Metabolites
2.5. Xanthine Oxidase (XO) Inhibitory Assay
2.6. Molecular Docking
2.6.1. Preparation of Protein
2.6.2. Preparation of Ligand
2.6.3. Molecular Docking Simulation
2.7. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.8. Fluorescence Quenching Assay
2.9. Circular Dichroism (CD) Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Multivariate Data Analysis
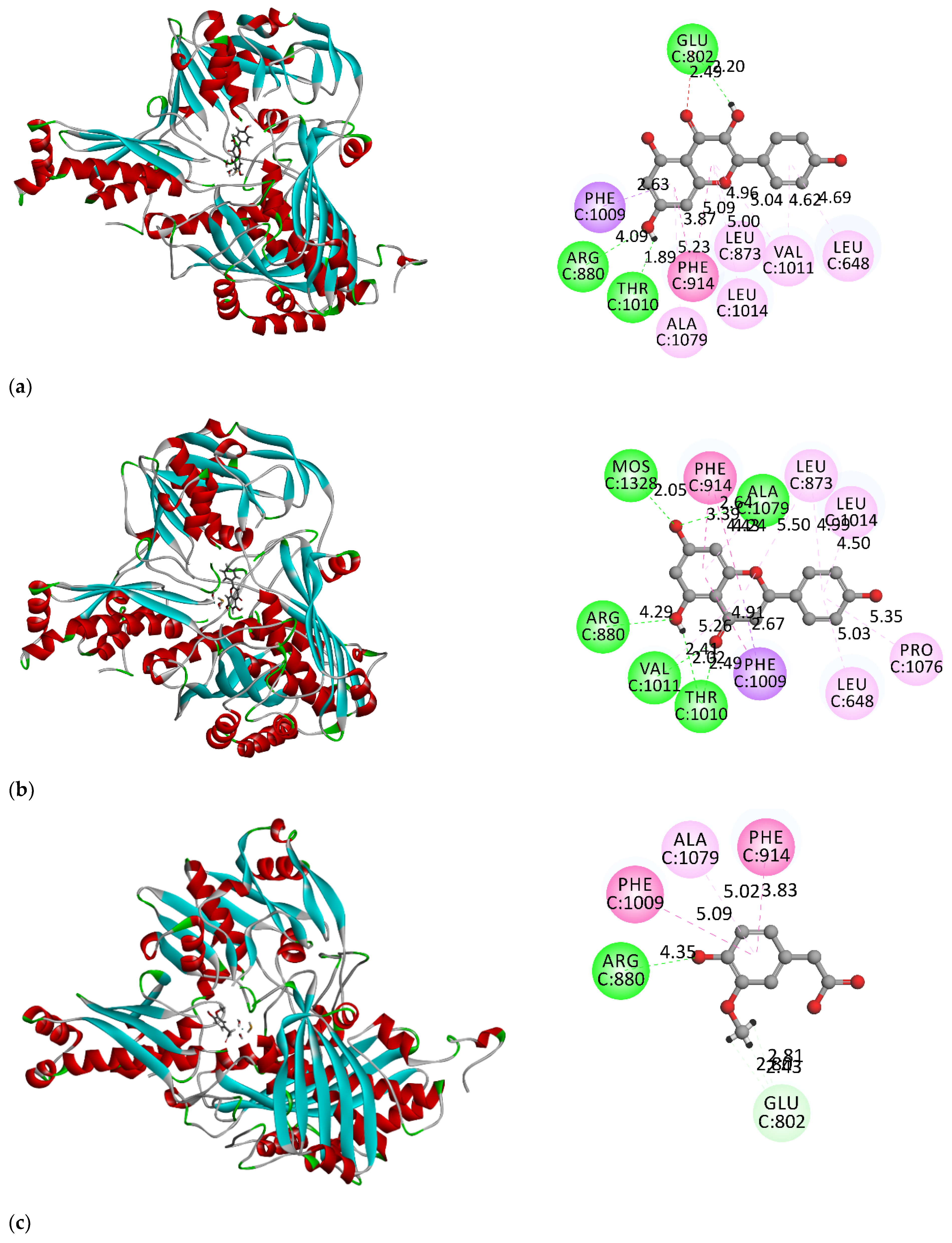
3.2. Molecular Docking Simulation
3.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
3.4. XO Inhibitory Activity
3.5. Fluorescence Quenching of XO
3.6. Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enroth, C.; Eger, B.T.; Okamoto, K.; Nishino, T.; Nishino, T.; Pai, E.F. Crystal structures of bovine milk xanthine dehydrogenase and xanthine oxidase: Structure-based mechanism of conversion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10723–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battelli, M.G.; Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Bolognesi, A. Xanthine oxidoreductase-derived reactive species: Physiological and pathological effects. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3527579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.; Fernandes, E.; Roleira, F. Progress towards the discovery of xanthine oxidase inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, A.; Hamzah, R.U.; Jigam, A.A.; Yahya, A.; Kabiru, A.Y.; Muhammad, H.; Sakpe, S.; Adefolalu, F.S.; Isah, M.C.; Kolo, M.Z. Inhibitory activity of xanthine oxidase by fractions Crateva adansonii. J. Acute Dis. 2012, 1, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Hase-Aoki, K.; Horiuchi, H.; Zhao, L.; Kasahara, Y.; Kondo, S.; Becker, M.A. Selectivity of febuxostat, a novel non-purine inhibitor of xanthine oxidase/xanthine dehydrogenase. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 1835–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, P.; Ying, L.; Calomme, M.; Hu, J.P.; Cimanga, K.; Poel, B.V.; Pieters, L.; Vlietinck, A.J.; Berghe, D.V. Structure-activity relationship and classification of flavonoids as inhibitors of xanthine oxidase and superoxide scavengers. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Chen, C.S.; Chen, C.T.; Liang, Y.C.; Lin, J.K. Molecular modeling of flavonoids that inhibits xanthine oxidase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Pan, J.; Gong, D. Novel insights into the inhibitory mechanism of kaempferol on xanthine oxidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, K.E.; Chin, Y.S.; Ismail, I.S.; Tan, H.Y. Rapid characterisation of xanthine oxidase inhibitors from the flowers of Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. Using metabolomics approach. Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.L.; Loh, K.E.; Tan, S.-A.; Tan, H.Y.; Yue, C.S.; Wee, S.P.; Tey, Z.T. Anti-hyperuricemic effect of ethyl acetate sub-fractions from Chrysanthemum morifolium Ramat. dried flowers on potassium oxonate-induced hyperuricemic rats. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.P.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Mo, H.Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Li, P. Screening for selective inhibitors of xanthine oxidase from Flos Chrysanthemum using ultrafiltration LC–MS combined with enzyme channel blocking. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 961, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Tram, L.H.; Hanh, T.T.H.; Binh, P.T.; Dang, N.H.; Van Minh, C.; Dat, N.T. Inhibitors of α-glucosidase, α-amylase and lipase from Chrysanthemum morifolium. Phytochem. Lett. 2013, 6, 322–325. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, S.P.; Bhakuni, R.S. Secondary metabolites of Chrysanthemum genus and their biological activities. Curr. Sci. 2005, 89, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar]
- Graziani, V.; Scognamiglio, M.; Belli, V.; Esposito, A.; D’Abrosca, B.; Chambery, A.; Russo, R.; Panella, M.; Russo, A.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Metabolomic approach for a rapid identification of natural products with cytotoxic activity against human colorectal cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarque, D.P.; Dusi, R.G.; de Sousa, F.D.; Grossi, S.M.; Silvério, M.R.; Lopes, N.P.; Espindola, L.S. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approach in the isolation of bioactive natural products. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, M.A.; Perez de Souza, L.; Serag, A.; Fernie, A.R.; Farag, M.A.; Ezzat, S.M.; Alseekh, S. Metabolomics in the context of plant natural products research: From sample preparation to metabolite analysis. Metabolites 2020, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Lim-Wilby, M. Molecular docking. In Molecular Modeling of Proteins; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 365–382. [Google Scholar]
- Salmaso, V.; Moro, S. Bridging molecular docking to molecular dynamics in exploring ligand-protein recognition process: An overview. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ciancetta, A.; Dudas, S.; Duca, S.; Lottermoser, J.; Jacobson, K.A. Structure-guided modification of heterocyclic antagonists of the P2Y14 receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 4860–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastelli, G.; Degliesposti, G.; Del Rio, A.; Sgobba, M. Binding estimation after refinement, a new automated procedure for the refinement and rescoring of docked ligands in virtual screening. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 73, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Pauff, J.M.; Hille, R. X-ray crystal structure of a xanthine oxidase complex with the flavonoid inhibitor quercetin. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1693–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Isha, A.; Lam, K.W.; Ismail, I.S. Molecular docking analysis of selected Clinacanthus nutans constituents as xanthine oxidase, nitric oxide synthase, human neutrophil elastase, matrix metalloproteinase 2, matrix metalloproteinase 9 and squalene synthase inhibitors. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2016, 12, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, R.; Open Source Drug Discovery Consortium; Lynn, A. g_mmpbsa A GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1951–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A web-based graphical user interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.; Reed, T.A. A set of constructed type spectra for the practical estimation of peptide secondary structure from circular dichroism. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 254, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.R.; Fan, S.Y.; Shi, W.G.; Zhong, B.H. Discovery of xanthine oxidase inhibitors and/or α-glucosidase inhibitors by carboxyalkyl derivatization based on the flavonoid of apigenin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2778–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Lee, F.W.; Chen, C.S.; Huang, S.T.; Tsai, S.H.; Huang, S.H.; Lin, C.M. Structure-activity relationship of C6-C3 phenylpropanoids on xanthine oxidase-inhibiting and free radical-scavenging activities. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohos, V.; Pánovics, A.; Fliszár-Nyúl, E.; Schilli, G.; Hetényi, C.; Mladěnka, P.; Needs, P.W.; Kroon, P.A.; Pethő, G.; Poór, M. Inhibitory effects of quercetin and its human and microbial metabolites on xanthine oxidase enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauff, J.M.; Cao, H.; Hille, R. Substrate orientation and catalysis at the molybdenum site in xanthine oxidase crystal structures in complex with xanthine and lumazine. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8760–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampogu, S.; Rampogu Lemuel, M. Network based approach in the establishment of the relationship between type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications at the molecular level coupled with molecular docking mechanism. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6068437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunta, M.J.R. Docking and Ligand Binding Affinity: Uses and Pitfalls. Am. J. Model. Optim. 2016, 4, 74–114. [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner, W.; Karch, R.; Knapp, B.; Ilieva, N. Relaxation estimation of RMSD in molecular dynamics immunosimulations. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2012, 2012, 173521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamp, L.K.; Chapman, P.T.; Barclay, M.; Horne, A.; Frampton, C.; Merriman, T.R.; Wright, D.F.; Drake, J.; Dalbeth, N. Relationships Between Allopurinol Dose, Oxypurinol Concentration and Urate-Lowering Response—In Search of a Minimum Effective Oxypurinol Concentration. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2020, 13, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y. Effect of luteolin on xanthine oxidase: Inhibition kinetics and interaction mechanism merging with docking simulation. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 3766–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.M.J. Fluorescence measurements of receptor–ligand interactions. In Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology, Practical Neurochemistry Methods; Springer Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 134–148. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Zhang, G.; Liao, Y.; Pan, J.; Gong, D. Dietary flavonoids as xanthine oxidase inhibitors: Structure–affinity and structure–activity relationships. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7784–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, L.; Chen, Z.; Fei, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, T. Spectroscopic analysis on the interaction of ferulic acid and tetramethylpyrazine with trypsin. Luminescence 2014, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z. Studies on the interaction between scopoletin and two serum albumins by spectroscopic methods. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 2719–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hadizadeh, M.; Keyhani, E.; Keyhani, J.; Khodadadi, C. Functional and structural alterations induced by copper in xanthine oxidase. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2009, 41, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Ma, Y. Mechanistic and conformational studies on the interaction of food dye amaranth with human serum albumin by multispectroscopic methods. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Contribution | Ligand Bound to XO | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaempferol | Apigenin | Homovanillic Acid | Trans-Cinnamic Acid | Allopurinol | Oxypurinol | |
| van der Waals energy, ∆Evdw (kJ/mol) | −148.688 ± 9.848 | −150.419 ± 10.214 | −88.825 ± 8.976 | −60.021 ± 9.090 | −80.751 ± 10.305 | −93.728 ± 9.469 |
| Electrostatic energy, ∆Eele (kJ/mol) | −31.383 ± 12.940 | −39.748 ± 10.267 | −47.019 ± 20.694 | −12.039 ± 11.900 | −52.820 ± 10.830 | −45.434 ± 21.075 |
| Solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) energy, ∆GSA (kJ/mol) | −15.812 ± 0.928 | −15.576 ± 0.705 | −12.120 ± 0.563 | −10.185 ± 0.967 | −8.452 ± 0.531 | −9.248 ± 0.581 |
| Polar solvation energy, ∆Gpolar (kJ/mol) | 147.669 ± 22.135 | 168.773 ± 13.730 | 134.437 ± 20.071 | 60.813 ± 21.158 | 190.432 ± 24.162 | 124.437 ± 26.528 |
| Binding energy, ∆Gbind (kJ/mol) | −48.214 ± 17.032 | −36.970 ± 15.249 | −13.527 ± 14.262 | −21.433 ± 12.833 | 48.409 ± 16.107 | −23.974 ± 12.030 |
| Inhibitor | Temperature (K) | KSV (×106 L mol−1) | Kq (×1014 L mol−1 s−1) | Ka (×105 L mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaempferol | 298 | 0.0977 | 0.3489 | 5.740 |
| 304 | 0.3964 | 1.416 | 2.903 | |
| 310 | 0.2779 | 0.9925 | 4.776 | |
| Apigenin | 298 | 0.1302 | 0.4650 | 1.875 |
| 304 | 0.3324 | 1.187 | 2.855 | |
| 310 | 0.1821 | 0.6504 | 2.325 | |
| Homovanillic acid | 298 | 0.0491 | 0.1754 | 1.783 |
| 304 | 0.0931 | 0.3325 | 3.746 | |
| 310 | 0.6988 | 2.4957 | 2.410 | |
| Trans-cinnamic acid | 298 | 0.1800 | 0.6429 | 1.247 |
| 304 | 0.2823 | 1.008 | 2.765 | |
| 310 | 0.2784 | 0.9943 | 2.865 |
| Inhibitor | Molar Ratio (XO:Inhibitor) | α-Helix (%) | β-Sheet (%) | Random Coil (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaempferol | 1:0 | 19.7 | 65.0 | 15.4 |
| 1:5 | 17.1 | 71.7 | 11.2 | |
| 1:10 | 0.0 | 65.8 | 34.2 | |
| Apigenin | 1:0 | 19.7 | 65.0 | 15.4 |
| 1:5 | 10.8 | 67.0 | 22.2 | |
| 1:10 | 36.7 | 63.3 | 0.0 | |
| Homovanillic acid | 1:0 | 19.7 | 65.0 | 15.4 |
| 1:5 | 36.3 | 63.7 | 0.0 | |
| 1:10 | 5.1 | 67.9 | 27.0 | |
| Trans-cinnamic acid | 1:0 | 19.7 | 65.0 | 15.4 |
| 1:5 | 36.4 | 63.6 | 0.0 | |
| 1:10 | 10.4 | 66.9 | 22.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wee, S.P.; Loh, K.E.; Lam, K.W.; Ismail, I.S. A Study of the Interaction between Xanthine Oxidase and Its Inhibitors from Chrysanthemum morifolium Using Computational Simulation and Multispectroscopic Methods. Metabolites 2023, 13, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010113
Wee SP, Loh KE, Lam KW, Ismail IS. A Study of the Interaction between Xanthine Oxidase and Its Inhibitors from Chrysanthemum morifolium Using Computational Simulation and Multispectroscopic Methods. Metabolites. 2023; 13(1):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010113
Chicago/Turabian StyleWee, Sze Ping, Khye Er Loh, Kok Wai Lam, and Intan Safinar Ismail. 2023. "A Study of the Interaction between Xanthine Oxidase and Its Inhibitors from Chrysanthemum morifolium Using Computational Simulation and Multispectroscopic Methods" Metabolites 13, no. 1: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010113
APA StyleWee, S. P., Loh, K. E., Lam, K. W., & Ismail, I. S. (2023). A Study of the Interaction between Xanthine Oxidase and Its Inhibitors from Chrysanthemum morifolium Using Computational Simulation and Multispectroscopic Methods. Metabolites, 13(1), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010113








