Home-Based Exercise in Elderly Patients with Claudication and Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Lower Progressive Renal Function Worsening: A 5-Year Retrospective Study
Abstract
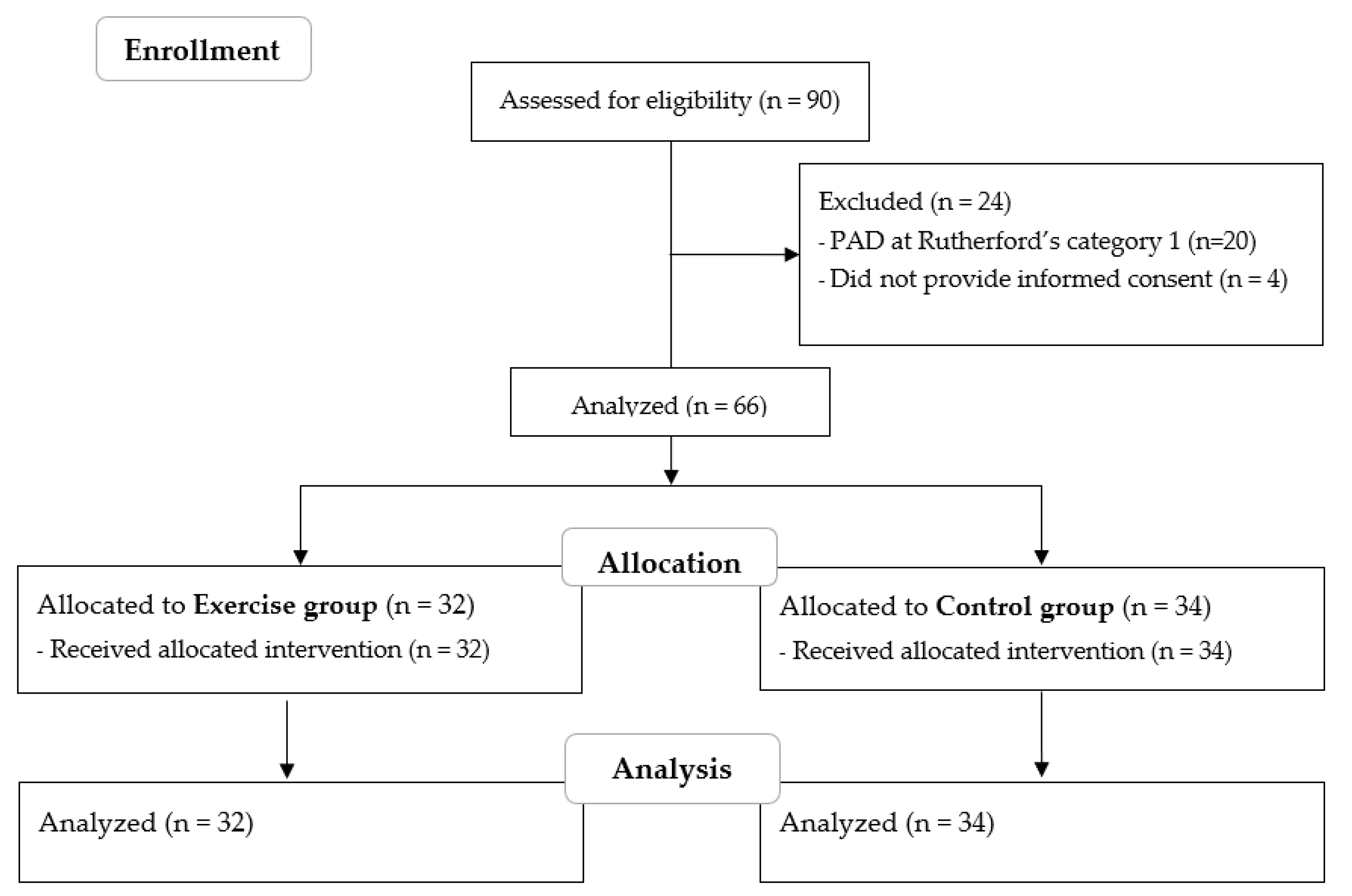
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Exercise Group: Training Program
2.4. Control Group
2.5. Study Outcomes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Long-Term Kidney Function
3.2. Laboratory Parameters
3.3. Revascularizations and All-Cause Hospitalizations
3.4. Predictors of Outcomes Probability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polonsky, T.S.; McDermott, M.M. Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease Without Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia: A Review. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 2188–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowkes, F.G.R.; Aboyans, V.; Fowkes, F.J.I.; McDermott, M.M.; Sampson, U.K.A.; Criqui, M.H. Peripheral Artery Disease: Epidemiology and Global Perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voicehovska, J.G.; Bormane, E.; Grigane, A.; Moisejevs, G.; Moreino, E.; Trumpika, D.; Voicehovskis, V.V. Association of Arterial Stiffness With Chronic Kidney Disease Progression and Mortality. Hear. Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Sung, K.-T.; Tsai, C.-T.; Wu, P.-C.; Lai, Y.-H.; Lo, C.-I.; Yu, F.-C.; Wu, H.-P.; Lan, W.-R.; Kuo, J.-Y.; et al. The Relationship of Renal Function to Segmental Vascular Stiffness, Ankle-Brachial Index, and Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2018, 20, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hobeika, L.; Hunt, K.J.; Neely, B.A.; Arthur, J.M. Comparison of the Rate of Renal Function Decline in NonProteinuric Patients with and without Diabetes. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 350, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al Adas, Z.; Lodewyk, K.; Robinson, D.; Qureshi, S.; Kabbani, L.S.; Sullivan, B.; Shepard, A.D.; Weaver, M.R.; Nypaver, T.J. Contrast-Induced Nephropathy after Peripheral Vascular Intervention: Long-Term Renal Outcome and Risk Factors for Progressive Renal Dysfunction. J. Vasc. Surg. 2019, 69, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Ballew, S.H.; Coresh, J.; Arima, H.; Ärnlöv, J.; Cirillo, M.; Ebert, N.; Hiramoto, J.S.; Kimm, H.; Shlipak, M.G.; et al. Measures of Chronic Kidney Disease and Risk of Incident Peripheral Artery Disease: A Collaborative Meta-Analysis of Individual Participant Data. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourrier, M.; Ferguson, T.W.; Embil, J.M.; Rigatto, C.; Komenda, P.; Tangri, N. Peripheral Artery Disease: Its Adverse Consequences With and Without CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffrin, E.L.; Lipman, M.L.; Mann, J.F.E. Chronic Kidney Disease: Effects on the Cardiovascular System. Circulation 2007, 116, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Owens, C.D.; Ho, K.J.; Kim, S.; Schanzer, A.; Lin, J.; Matros, E.; Belkin, M.; Conte, M.S. Refinement of Survival Prediction in Patients Undergoing Lower Extremity Bypass Surgery: Stratification by Chronic Kidney Disease Classification. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantha-Narayanan, M.; Sheikh, A.B.; Nagpal, S.; Jelani, Q.-U.-A.; Smolderen, K.G.; Regan, C.; Ionescu, C.; Ochoa Chaar, C.I.; Schneider, M.; Llanos-Chea, F.; et al. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes of Lower Extremity Peripheral Arterial Interventions in Patients with and without Chronic Kidney Disease or End-Stage Renal Disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2021, 73, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Matsuzawa, R.; Watanabe, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Imamura, K.; Yoshikoshi, S.; Aoyama, N.; Osada, S.; Yoshida, A.; et al. Physical Function and Physical Activity in Hemodialysis Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease. Hemodial. Int. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ren, Y.; Wang, H.; Bai, Y.; Huang, L. Daily Step Counts in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 842423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamburg, N.M.; Balady, G.J. Exercise Rehabilitation in Peripheral Artery Disease: Functional Impact and Mechanisms of Benefits. Circulation 2011, 123, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Green, D.J.; Hopman, M.T.E.; Padilla, J.; Laughlin, M.H.; Thijssen, D.H.J. Vascular Adaptation to Exercise in Humans: Role of Hemodynamic Stimuli. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 495–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, F.; Rigolin, G.M.; Malagoni, A.M.; Soffritti, S.; Boari, B.; Conconi, F.; Castoldi, G.L.; Catizone, L.; Zamboni, P.; Manfredini, R. Exercise Capacity and Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Hemodialysis Patients. Int. J. Sports Med. 2007, 28, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treat-Jacobson, D.; McDermott, M.M.; Bronas, U.G.; Campia, U.; Collins, T.C.; Criqui, M.H.; Gardner, A.W.; Hiatt, W.R.; Regensteiner, J.G.; Rich, K. Optimal Exercise Programs for Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, E10–E33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, R.; Harwood, A.; Watson, L.; Leng, G.C. Exercise for Intermittent Claudication. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 12, CD000990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gielen, S.; Schuler, G.; Adams, V. Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise Training: Molecular Mechanisms. Circulation 2010, 122, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiwe, S.; Jacobson, S.H. Exercise Training in Adults With CKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014, 64, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, K.; Hoshino, J.; Sugiyama, H.; Hanafusa, N.; Shibagaki, Y.; Komatsu, Y.; Konta, T.; Fujii, N.; Kanda, E.; Sofue, T.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline for Renal Rehabilitation: Systematic Reviews and Recommendations of Exercise Therapies in Patients with Kidney Diseases. Ren. Replace. Ther. 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shlipak, M.G.; Sheshadri, A.; Hsu, F.-C.; Chen, S.-H.; Jotwani, V.; Tranah, G.; Fielding, R.A.; Liu, C.K.; Ix, J.; Coca, S.G. Effect of Structured, Moderate Exercise on Kidney Function Decline in Sedentary Older Adults: An Ancillary Analysis of the LIFE Study Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2022, 182, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson-Cohen, C.; Littman, A.J.; Duncan, G.E.; Weiss, N.S.; Sachs, M.C.; Ruzinski, J.; Kundzins, J.; Rock, D.; de Boer, I.H.; Ikizler, T.A.; et al. Physical Activity and Change in Estimated GFR among Persons with CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, L.; Luo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Yi, B. Exercise Therapy Improves EGFR, and Reduces Blood Pressure and BMI in Non-Dialysis CKD Patients: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamberti, N.; Malagoni, A.M.; Ficarra, V.; Basaglia, N.; Manfredini, R.; Zamboni, P.; Mascoli, F.; Manfredini, F. Structured Home-Based Exercise Versus Invasive Treatment: A Mission Impossible? A Pilot Randomized Study in Elderly Patients with Intermittent Claudication. Angiology 2016, 67, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, F.; Malagoni, A.M.; Mascoli, F.; Mandini, S.; Taddia, M.C.; Basaglia, N.; Manfredini, R.; Conconi, F.; Zamboni, P. Training Rather than Walking—The Test in-Train out Program for Home-Based Rehabilitation in Peripheral Arteriopathy. Circ. J. 2008, 72, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Malagoni, A.M.; Vagnoni, E.; Felisatti, M.; Mandini, S.; Heidari, M.; Mascoli, F.; Basaglia, N.; Manfredini, R.; Zamboni, P.; Manfredini, F. Evaluation of Patient Compliance, Quality of Life Impact and Cost-Effectiveness of a “Test in-Train out” Exercise-Based Rehabilitation Program for Patients with Intermittent Claudication. Circ. J. 2011, 75, 2128–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamberti, N.; Straudi, S.; Manfredini, R.; De Giorgi, A.; Gasbarro, V.; Zamboni, P.; Manfredini, F. Don’t Stop Walking: The in-Home Rehabilitation Program for Peripheral Artery Disease Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 1307–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, N.; López-Soto, P.J.; Guerzoni, F.; Napoli, N.; Gasbarro, V.; Zamboni, P.; Tsolaki, E.; Taddia, M.C.; Rodríguez-Borrego, M.A.; Manfredini, R.; et al. Changes in Exercise Capacity and Risk of All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: A 10-Year Retrospective Cohort Study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2020, 15, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, N.; Tsolaki, E.; Guerzoni, F.; Napoli, N.; Traina, L.; Piva, G.; Gasbarro, V.; Zamboni, P.; Straudi, S.; Manfredini, R.; et al. Survival and Clinical Outcomes of Diabetic Peripheral Artery Disease Patients Following a Pain-Free Home-Based Walking Program. Vessel Plus 2022, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, F.; Mallamaci, F.; D’Arrigo, G.; Baggetta, R.; Bolignano, D.; Torino, C.; Lamberti, N.; Bertoli, S.; Ciurlino, D.; Rocca-Rey, L.; et al. Exercise in Patients on Dialysis: A Multicenter, Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manfredini, F.; D’arrigo, G.; Lamberti, N.; Torino, C.; Tripepi, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. The Legacy Effect of a Home Walking Exercise Program in Kidney Failure Patients on Dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 1974–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallamaci, F.; Arrigo, G.D.; Tripepi, G.; Lamberti, N.; Torino, C.; Manfredini, F.; Zoccali, C. Article Long-Term Effect of Physical Exercise on the Risk for Hospitalization and Death in Dialysis Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2022, 17, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himmelfarb, J.; Vanholder, R.; Mehrotra, R.; Tonelli, M. The Current and Future Landscape of Dialysis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clyne, N.; Anding-Rost, K. Exercise Training in Chronic Kidney Disease-Effects, Expectations and Adherence. Clin. Kidney J. 2021, 14 (Suppl. S2), ii3–ii14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, G.B.; Cupisti, A.; Aucella, F.; Regolisti, G.; Lomonte, C.; Ferraresi, M.; Claudia, D.; Ferraresi, C.; Russo, R.; La Milia, V.; et al. Green Nephrology and Eco-Dialysis: A Position Statement by the Italian Society of Nephrology. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Venkataraman, R.; Sanderson, B.; Bittner, V. Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Undergoing Cardiac Rehabilitation. Am. Heart J. 2005, 150, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaya, Y.; Kumasaka, R.; Arakawa, T.; Ohara, T.; Nakanishi, M.; Noguchi, T.; Yanase, M.; Takaki, H.; Kawano, Y.; Goto, Y. Impact of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Renal Function in Patients with and without Chronic Kidney Disease after Acute Myocardial Infarction. Circ. J. 2014, 78, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hama, T.; Ushijima, A.; Goto, T.; Nagamatsu, H.; Morita, N.; Yoshimachi, F.; Ikari, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Effect of Cardiac Rehabilitation on Glomerular Filtration Rate Using Serum Cystatin C Concentration in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease and Renal Dysfunction. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2022, 42, E15–E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, S.A.; Koufaki, P.; Mercer, T.H.; MacLaughlin, H.L.; Rush, R.; Lindup, H.; O’Connor, E.; Jones, C.; Hendry, B.M.; Macdougall, I.C.; et al. Effect of Exercise Training on Estimated GFR, Vascular Health, and Cardiorespiratory Fitness in Patients with CKD: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 65, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Hu, R.; Wu, Y. Effects of Exercise Training on Proteinuria in Adult Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Kohzuki, M.; Ono, M.; Muto, M.; Osugi, T.; Kawamura, K.; Naganuma, W.; Sato, M.; Tsuchikawa, M.; Shishito, N.; et al. Association between Physical Activity and Changes in Renal Function in Patients after Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Dual-Center Prospective Study. J. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohlke, M.; Barcellos, F.C.; Santos, I.S.; Mielke, G.I.; Vargas, M.d.M.; Hallal, P.C. Effects of a 16-Week Physical Training on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Hypertension and Chronic Kidney Disease: NEPHROS Post-Trial Follow-Up. Cad. Saude Publica 2022, 38, e00061521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, A.W.; Montgomery, P.S.; Wang, M.; Shen, B.; Casanegra, A.I.; Silva-Palacios, F.; Zhang, S.; Pomilla, W.A.; Esponda, O.L.; Kuroki, M. Daily Step Counts in Participants With and Without Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2021, 41, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, F.; Lamberti, N.; Malagoni, A.M.A.M.; Felisatti, M.; Zuccalà, A.; Torino, C.; Tripepi, G.; Catizone, L.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. The Role of Deconditioning in the End-Stage Renal Disease Myopathy: Physical Exercise Improves Altered Resting Muscle Oxygen Consumption on Behalf of the EXCITE Working Group. Am. J. Nephrol. 2015, 41, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredini, F.; Rigolin, G.M.; Malagoni, A.M.; Catizone, L.; Mandini, S.; Sofritti, O.; Mauro, E.; Soffritti, S.; Boari, B.; Cuneo, A.; et al. Exercise Training and Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Haemodialysis Patients. J. Int. Med. Res. 2009, 37, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sprick, J.D.; Mammino, K.; Jeong, J.; DaCosta, D.R.; Hu, Y.; Morison, D.G.; Nocera, J.R.; Park, J. Aerobic Exercise Training Improves Endothelial Function and Attenuates Blood Pressure Reactivity during Maximal Exercise in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 132, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, F.; Traina, L.; Gasbarro, V.; Straudi, S.; Caruso, L.; Fabbian, F.; Zamboni, P.; Manfredini, R.; Lamberti, N. Structured Pain-Free Exercise Progressively Improves Ankle-Brachial Index and Walking Ability in Patients with Claudication and Compressible Arteries: An Observational Study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2022, 17, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigterman, T.A.; Bolt, L.J.J.; Krasznai, A.G.; Snoeijs, M.G.; Heijboer, R.; Schurink, G.-W.H.; Bouwman, L.H. Loss of Kidney Function in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia Treated Endovascularly or Surgically. J. Vasc. Surg. 2016, 64, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredini, F.; Lamberti, N.; Guerzoni, F.; Napoli, N.; Gasbarro, V.; Zamboni, P.; Mascoli, F.; Manfredini, R.; Basaglia, N.; Rodríguez-Borrego, M.A.; et al. Rehabilitative Exercise Reduced the Impact of Peripheral Artery Disease on Vascular Outcomes in Elderly Patients with Claudication: A Three-Year Single Center Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Exercise (n = 32) | Control (n = 34) | p | |
| Age, years | 72 ± 10 | 72 ± 9 | 0.82 |
| Male sex, n(%) | 27 (80) | 25 (78) | 0.90 |
| Risk factors and comorbidities | |||
| Smokers | 22 (68) | 21 (62) | 0.54 |
| Hypertension | 27 (84) | 32 (94) | 0.18 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 13 (40) | 14 (40) | 0.78 |
| Diabetes | 19 (59) | 17 (50) | 0.44 |
| Myocardial infarction | 16 (50) | 17 (50) | 1.00 |
| Coronary revascularization | 17 (53) | 17 (50) | 0.89 |
| Heart failure | 4 (13) | 6 (18) | 0.54 |
| Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | 5 (16) | 3 (9) | 0.47 |
| Neoplastic disease | 7 (22) | 6 (18) | 0.77 |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 6 ± 2 | 6 ± 2 | 0.87 |
| Primary nephropathy, n (%) | |||
| Nephroangiosclerosis | 9 (28) | 16 (46) | 0.17 |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 18 (56) | 14 (42) | |
| Single kidney condition | 5 (16) | 2 (6) | |
| Others | 0 (0) | 2 (6) | |
| Medications, n (%) | |||
| ACE-inhibitors | 4 (12) | 3 (9) | 0.63 |
| Diuretics | 23 (72) | 28 (82) | 0.32 |
| Beta-blockers | 14 (44) | 20 (58) | 0.22 |
| Calcium antagonists | 14 (44) | 7 (21) | 0.10 |
| Statins | 14 (44) | 16 (47) | 0.79 |
| Antiplatelets | 20 (62) | 24 (71) | 0.31 |
| Anticoagulants | 14 (44) | 9 (26) | 0.14 |
| Oral antidiabetic drugs | 1 (3) | 1 (3) | 0.97 |
| Insulin | 15 (47) | 14 (41) | 0.55 |
| Laboratory parameters | |||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 11.8 ± 1.9 | 11.7 ± 1.4 | 0.98 |
| Albumin (%) | 52.0 ± 6.0 | 54.0 ± 5.5 | 0.54 |
| Serum creatinine, mg/dL | 2.35 ± 1.2 | 2.30 ± 1.0 | 0.69 |
| eGFR, 6 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 29 ± 2 | 30 ± 2 | 0.66 |
| Peripheral artery disease | |||
| ABI more impaired limb | 0.64 ± 0.14 | 0.63 ± 0.17 | 0.87 |
| Rutherford’s category 2 | 5 (16) | 6 (18) | 0.76 |
| Rutherford’s category 3 | 18 (56) | 20 (59) | |
| Rutherford’s category 4 | 9 (28) | 8 (24) | |
| Previous lower limbs revascularizations | 6 (19) | 8 (24) | 0.56 |
| Ex Group | Baseline | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 |
| S. creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.35 ± 0.32 | 2.43 ± 0.33 | 2.51 ± 0.33 | 2.72 ± 0.36 | 2.79 ± 0.39 * | 2.72 ± 0.39 * |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 29 ± 2 | 29 ± 2 | 27 ± 2 | 26 ± 2 * | 26 ± 3 * | 26 ± 3 * |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.8 ± 1.9 | 11.6 ± 1.6 | 11.8 ± 1.7 | 11.6 ± 1.5 | 12.0 ± 1.5 | 11.6 ± 1.6 |
| Red blood cells (106/μL) | 4.00 ± 0.65 | 4.25 ± 0.57 | 4.06 ± 0.43 | 3.93 ± 0.43 | 4.06 ± 0.56 | 3.87 ± 0.59 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 36 ± 5 | 38 ± 5 | 38 ± 4 | 35 ± 4 | 37 ± 4 | 36 ± 4 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 88 ± 34 | 89 ± 33 | 100 ± 60 * | 114 ± 58 * | 114 ± 53 * | 106 ± 40 * |
| CO Group | Baseline | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 2.30 ± 0.31 | 2.86 ± 0.32 * | 3.37 ± 0.32 * | 3.35 ± 0.33 * | 3.25 ± 0.36 * | 4.22 ± 0.42 * |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 30 ± 2 | 25 ± 2 * | 23 ± 2 * | 24 ± 2 * | 23 ± 2 * | 18 ± 3 * |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 11.7 ± 1.4 | 11.6 ± 1.7 | 11.3 ± 1.5 | 11.4 ± 1.6 | 11.8 ± 1.5 | 11.3 ± 1.5 |
| Red blood cells (106/μL) | 4.01 ± 0.59 | 4.11 ± 0.71 | 3.91 ± 0.63 | 4.02 ± 0.60 | 4.05 ± 0.63 | 3.80 ± 0.53 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 36 ± 5 | 37 ± 6 | 35 ± 4 | 36 ± 4 | 37 ± 4 | 36 ± 7 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 86 ± 38 | 112 ± 53 | 112 ± 66 * | 117 ± 49 * | 114 ± 44 * | 136 ± 71 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piva, G.; Crepaldi, A.; Lamberti, N.; Caruso, L.; Rinaldo, N.; Manfredini, R.; López-Soto, P.J.; Gasbarro, V.; Manfredini, F.; Storari, A. Home-Based Exercise in Elderly Patients with Claudication and Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Lower Progressive Renal Function Worsening: A 5-Year Retrospective Study. Metabolites 2023, 13, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010056
Piva G, Crepaldi A, Lamberti N, Caruso L, Rinaldo N, Manfredini R, López-Soto PJ, Gasbarro V, Manfredini F, Storari A. Home-Based Exercise in Elderly Patients with Claudication and Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Lower Progressive Renal Function Worsening: A 5-Year Retrospective Study. Metabolites. 2023; 13(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010056
Chicago/Turabian StylePiva, Giovanni, Anna Crepaldi, Nicola Lamberti, Lorenzo Caruso, Natascia Rinaldo, Roberto Manfredini, Pablo Jesus López-Soto, Vincenzo Gasbarro, Fabio Manfredini, and Alda Storari. 2023. "Home-Based Exercise in Elderly Patients with Claudication and Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Lower Progressive Renal Function Worsening: A 5-Year Retrospective Study" Metabolites 13, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010056
APA StylePiva, G., Crepaldi, A., Lamberti, N., Caruso, L., Rinaldo, N., Manfredini, R., López-Soto, P. J., Gasbarro, V., Manfredini, F., & Storari, A. (2023). Home-Based Exercise in Elderly Patients with Claudication and Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Lower Progressive Renal Function Worsening: A 5-Year Retrospective Study. Metabolites, 13(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13010056










