Effect of Garlic Straw with Silage Corn Stalks on Hu Sheep Rumen Fermentation and Microbial Community In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Determination of Nutritional Composition of Garlic Straw
2.2. Feed Ingredients Collection
2.3. Animal Feeding Management and Rumen Fluid Collection
2.4. In Vitro Fermentation
2.5. Dry Matter Digestibility, Amino Acid Concentration, and Fermentation Parameters
2.6. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.7. Bioinformatic and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Vitro Fermentation Responses to Varying Garlic Straw Proportions
3.2. Effects of Different Proportions of Garlic Straw on VFA In Vitro Fermentation
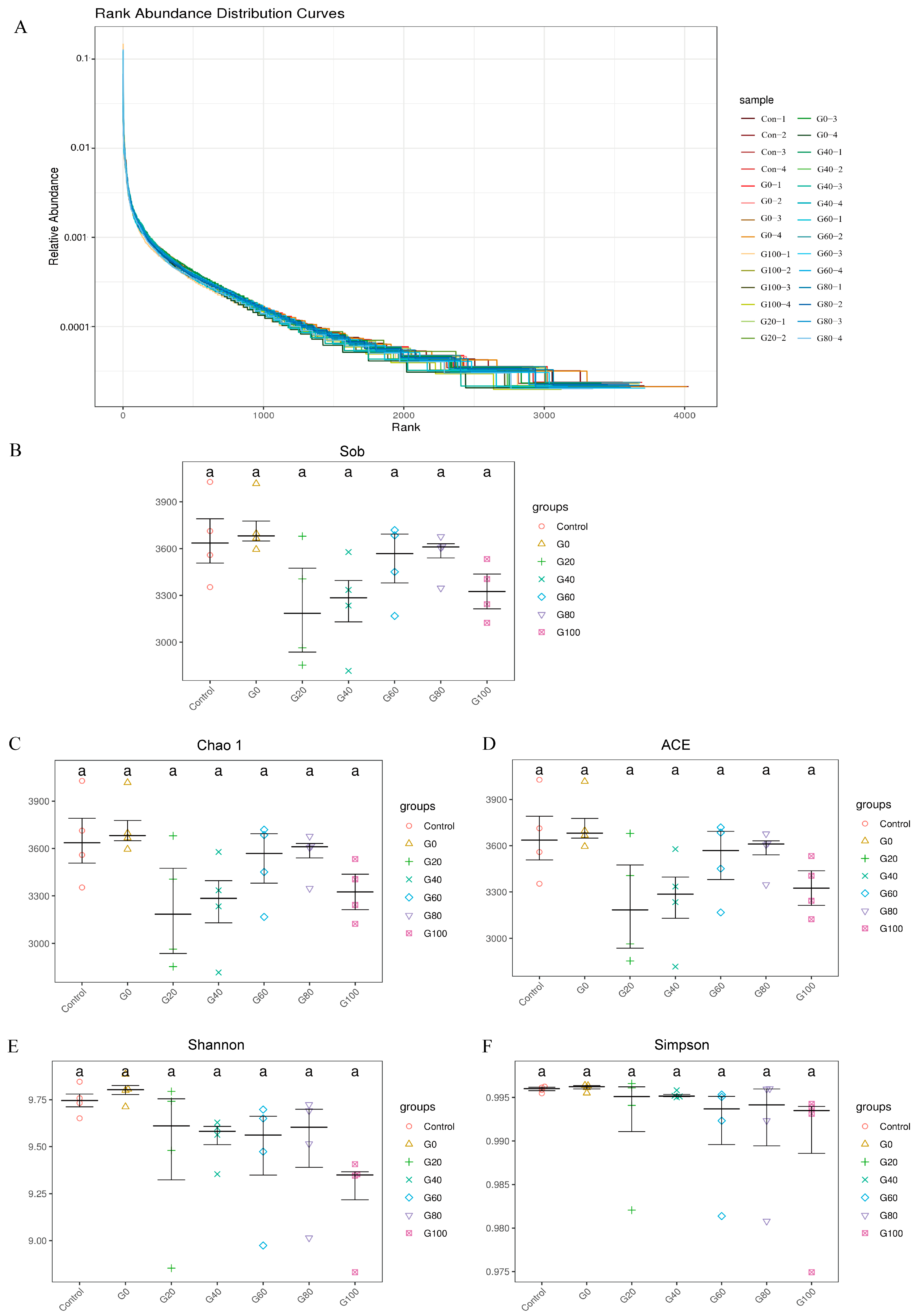
3.3. Analysis of Rumen Flora Composition
3.4. Alpha Diversity
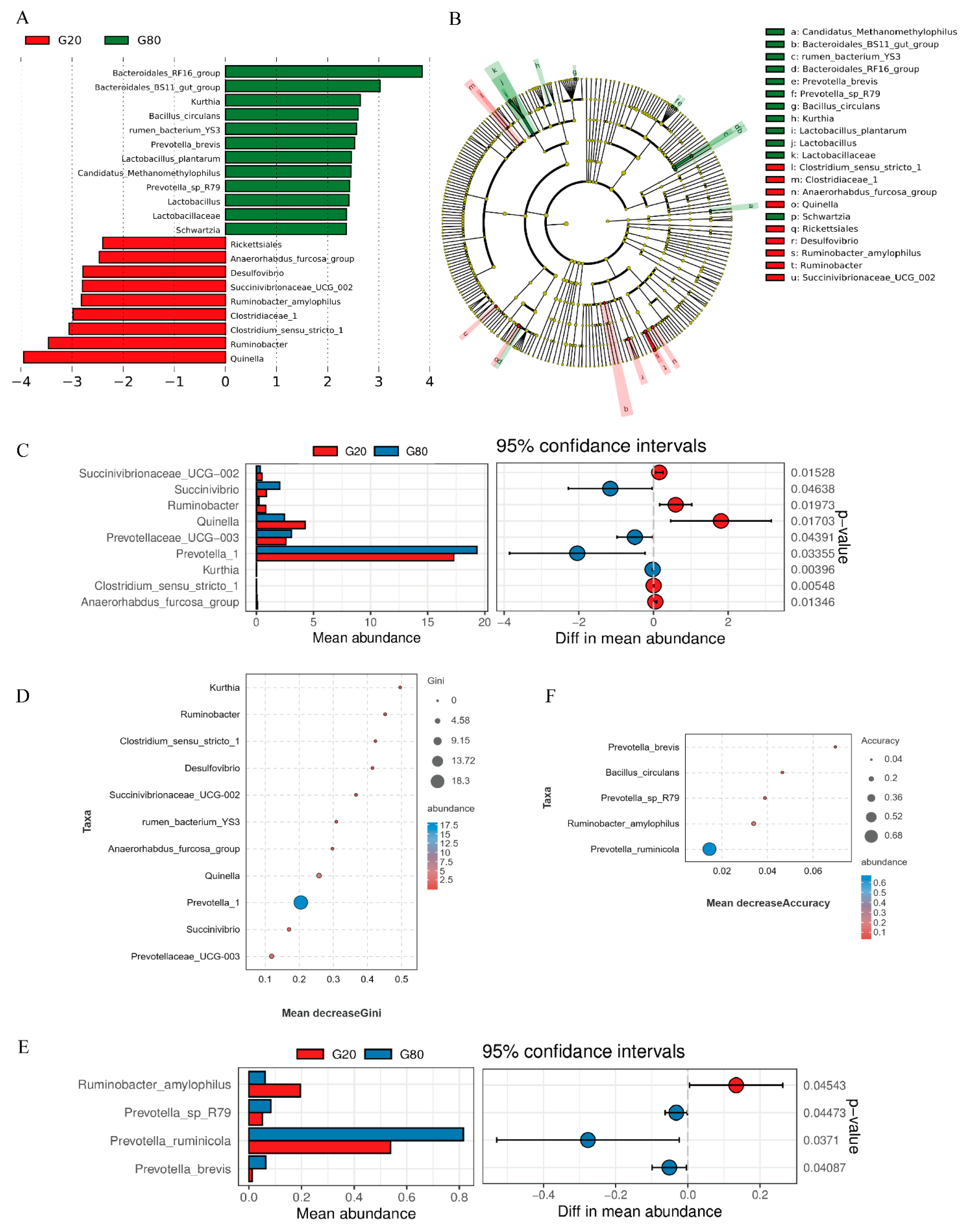
3.5. Microbial Analysis of Rumen Bacterial Flora Differences between Groups
3.6. Effect of Garlic Straw with Silage Corn Stalks on the Functional Pathway of Rumen Bacteria in Hu Sheep
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Addition Ratios on In Vitro Gas Production, pH, and Dry Matter Digestibility
4.2. Effects of Different Addition Ratios on VFA
4.3. Effects of Different Addition Ratios on Microflora
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, W.; Su, Z.; Xu, W.; Sun, H.X.; Gao, J.F.; Tu, D.F.; Ren, C.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Cao, H.G. Garlic skin induces shifts in the rumen microbiome and metabolome of fattening lambs. Animal 2021, 15, 100216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quijada, N.M.; Bodas, R.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Schmitz-Esser, S.; Rodriguez-Lazaro, D.; Hernandez, M. Dietary Supplementation with Sugar Beet Fructooligosaccharides and Garlic Residues Promotes Growth of Beneficial Bacteria and Increases Weight Gain in Neonatal Lambs. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, H. Soil properties, nutrient dynamics, and soil enzyme activities associated with garlic stalk decomposition under various conditions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Vega, A.; Frutos, P.; Gutierrez-Gil, B.; Esteban-Blanco, C.; Toral, P.G.; Arranz, J.J.; Hervas, G. Feed efficiency in dairy sheep: An insight from the milk transcriptome. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1122953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Thiruvengadam, M.; Imran, M.; Olatunde, A.; Shariati, M.A.; Bawazeer, S.; Naz, S.; Shirooie, S.; Sanches-Silva, A.; et al. Garlic (Allium sativum L.): Its Chemistry, Nutritional Composition, Toxicity, and Anticancer Properties. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 957–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Liao, L.; Huang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Wang, X.; Lv, T.; Li, Y.; Fan, Z.; Liu, T.; et al. Effects of Different Levels of Garlic Straw Powder on Growth Performance, Meat Quality, Antioxidant and Intestinal Mucosal Morphology of Yellow-Feathered Broilers. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 902995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthee, A.; Matsuno, A.; Al-Mamun, M.; Sano, H. Effect of feeding garlic leaves on rumen fermentation, methane emission, plasma glucose kinetics, and nitrogen utilization in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, F. Dietary addition of garlic straw improved the intestinal barrier in rabbits. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 97, 4248–4255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, K.; Dey, A.; Dahiya, S.S.; Paul, S.S.; Jerome, A.; Bharadwaj, A.; Kakker, N.K. Abatement of enteric methane production from lactating Murrah buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) with improving production performance and immune status through dietary supplementation of composite feed additive. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 22476–22485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.R.; Solaiman, S. Comparative aspects of plant tannins on digestive physiology, nutrition and microbial community changes in sheep and goats: A review. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 1181–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Morrison, M.; Yu, Z. Status of the phylogenetic diversity census of ruminal microbiomes. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Yao, D.; Li, D.; Lin, Y.; Bureenok, S.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Rumen Fluid and Feces of Dairy Cows on Fermentation Quality, Microbial Community, and in vitro Digestibility of Alfalfa Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, I.; Wallace, R.J.; Morais, S. The rumen microbiome: Balancing food security and environmental impacts. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National, C.N.; National Research, C.; Council, N.R.; National, C.; Council, N.; National, C. Nutrient Requirements of Small Ruminants: Sheep, Goats, Cervids, and New World Camelids; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Menke, K.H.; Raab, L.; Salewski, A.; Steingass, H.; Schneider, W. The estimation of the digestibility and metabolizable energy content of ruminant feedingstuffs from the gas production when they are incubated with rumen liquor in vitro. J. Agric. Sci. 1979, 93, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Chai, S.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, Z. Dynamic Alterations in Yak Rumen Bacteria Community and Metabolome Characteristics in Response to Feed Type. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, T.; Tu, Y.; Ma, S.; Diao, Q. Effects of Circadian Rhythm and Feeding Modes on Rumen Fermentation and Microorganisms in Hu Sheep. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Z.; Benchaar, C.; Ametaj, B.N.; Chaves, A.V.; He, M.L.; McAllister, T.A. Effects of garlic and juniper berry essential oils on ruminal fermentation and on the site and extent of digestion in lactating cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 5671–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, N.F.; Ray, P.; Rymer, C.; Kliem, K.E.; Stergiadis, S. Garlic and Its Bioactive Compounds: Implications for Methane Emissions and Ruminant Nutrition. Animals 2022, 12, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, P. Biogas production: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Fukuma, N.; Hanada, M.; Nishida, T. The Efficacy of Plant-Based Bioactives Supplementation to Different Proportion of Concentrate Diets on Methane Production and Rumen Fermentation Characteristics In Vitro. Animals 2021, 11, 1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, G.; Cox, F.; Ganesh, S.; Jonker, A.; Young, W.; Global Rumen Census, C.; Janssen, P.H. Rumen microbial community composition varies with diet and host, but a core microbiome is found across a wide geographical range. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Guo, L.; Chang, X.; Liu, K.; Tang, W.; Zheng, N.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. Effect of Whole or Ground Flaxseed Supplementation on Fatty Acid Profile, Fermentation, and Bacterial Composition in Rumen of Dairy Cows. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 760528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, F.U.; Arshad, M.A.; Ebeid, H.M.; Rehman, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Shahid, S.; Yang, C. Phytogenic Additives Can Modulate Rumen Microbiome to Mediate Fermentation Kinetics and Methanogenesis through Exploiting Diet-Microbe Interaction. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 575801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Dai, D.; Wu, H.; Chai, S.; Liu, S.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, Z. Dietary Concentrate-to-Forage Ratio Affects Rumen Bacterial Community Composition and Metabolome of Yaks. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 927206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heimesaat, M.M.; Mousavi, S.; Weschka, D.; Bereswill, S. Garlic Essential Oil as Promising Option for the Treatment of Acute Campylobacteriosis-Results from a Preclinical Placebo-Controlled Intervention Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, J.; Tarnonsky, F.; Maderal, A.; Fernandez-Marenchino, I.; Podversich, F.; Cuervo, W.; Gomez-Lopez, C.; Schulmeister, T.; DiLorenzo, N. Effects of Processing Methods and Inclusion Levels of Dried Garlic on In Vitro Fermentation and Methane Production in a Corn Silage-Based Substrate. Animals 2023, 13, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Z.Z.; Liu, Q.; Guo, G.; Huo, W.J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Pei, C.X.; et al. Effects of guanidinoacetic acid supplementation on growth performance, nutrient digestion, rumen fermentation and blood metabolites in Angus bulls. Animal 2020, 14, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tingting, G.; Dandan, H.U.; Zilin, F.U.; Na, L.I.; Xiaofeng, X.U. Effects of Mannan Oligosaccharides on Rumen Microflora Structure of Dairy Cows Based on 16S rDNA High-Throughput Sequencing Technology. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 30, 4048–4058. [Google Scholar]
- Aschenbach, J.R.; Penner, G.B.; Stumpff, F.; Gäbel, G. Ruminant Nutrition Symposium: Role of fermentation acid absorption in the regulation of ruminal pH. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1092–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.G.; Wang, C.D.; Tang, Z.H.; Guo, Y.Q.; Zheng, T.C.; Li, Y.Z.; You, Z.Q. The Gut Bacterial Community Composition of Wild Cervus albirostris (White-Lipped Deer) Detected by the 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene Sequencing. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haworth, S.E.; White, K.S.; Cté, S.D.; Shafer, A.B.A. Space, time, and captivity: Quantifying factors influencing the microbiome of an alpine ungulate. 2019, 95, fiz095. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Ingredients | DM | CP | NDF | ADF | EE | Ca | P | RFV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Garlic straw | 53.36 | 7.29 | 41.11 | 34.34 | 2.52 | 2.05 | 0.19 | 140.63 |
| Silage corn stalks | 32.29 | 6.96 | 58.52 | 32.98 | 1.27 | 0.45 | 0.20 | 143.03 |
| Ingredients | Recipe Contents | Nutritional Indicators | Nutritional Levels |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 43.00 | Crude protein (CP) | 17.06 |
| Soybean meal | 9.20 | Crude fiber (CF) | 5.52 |
| Bran | 10.00 | Ether extract (EE) | 3.80 |
| Protein powder | 7.00 | Ash | 10.95 |
| Distiller-dried grains with solubles | 11.48 | Neutral detergent fiber (NDF) | 19.24 |
| Rice oil | 4.96 | Acid detergent fiber (ADF) | 6.33 |
| Germ meal | 4.95 | Ca | 1.87 |
| Peanut vine | 4.96 | P | 0.67 |
| Premix | 4.00 | / | / |
| Lysine | 0.15 | / | / |
| Methionine | 0.05 | / | / |
| Guanidinoacetic acid | 0.04 | / | / |
| Sodium chloride | 0.21 | / | / |
| Total | 100.00 | / | / |
| Items | Composition |
|---|---|
| Liquid A | Mix and dissolve CaCl2·2H2O 13.2 g, MnCl2·4H2O 10.0 g, CoCl2·6H2O 1.0 g, and FeCl3·6H2O 8.0 g in distilled water at constant volume to 100 mL |
| Solution B | Dissolve 4.0 g NH4CO3 and 35 g NaHCO3 in 1000 mL distilled water |
| Liquid C | Dissolve 5.7 g NaH2PO4, 6.2 g KH2PO4, and 0.6 g MgSO4·7H2O in distilled water at constant volume to 1000 mL |
| Azurazine solution | 0.1% (w/v) |
| Reducing agent solution | Mix 95 mL distilled water, 4.0 mL 1N NaOH, and 0.625 g Na2S·9H2O |
| Item/Proportion | CON | G0 | G20 | G40 | G60 | G80 | G100 | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Linear | Quadratic | |||||||||
| Gas/mL | 18.00 c | 49.25 a | 50.25 a | 50.00 a | 52.67 a | 38.67 b | 43.00 ab | 2.58 | <0.001 | 0.207 | 0.441 |
| pH | 6.67 a | 6.46 b | 6.47 b | 6.51 b | 6.57 ab | 6.59 ab | 6.56 ab | 0.02 | <0.001 | 0.022 | 0.313 |
| IVDMD/% | 100.00 c | 37.04 b | 21.07 ab | 44.20 b | 51.14 a | 41.93 a | 31.64 a | 0.05 | <0.001 | 0.692 | 0.414 |
| Proportion (mmol/L) | CON | G0 | G20 | G40 | G60 | G80 | G100 | SEM | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Linear | Quadratic | |||||||||
| Acetic acid | 16.24 c | 23.39 ab | 21.87 ab | 20.64 b | 25.30 a | 21.38 ab | 22.03 ab | 3.40 | <0.001 | 0.853 | 0.996 |
| Propionic acid | 7.72 a | 11.10 c | 10.60 bc | 8.66 ab | 11.58 c | 9.62 abc | 8.31 ab | 1.94 | <0.001 | 0.318 | 0.768 |
| Butyric acid | 4.72 b | 5.59 a | 5.17 ab | 4.82 b | 5.67 a | 4.85 b | 5.17 ab | 0.51 | <0.001 | 0.575 | 0.669 |
| Total VFA | 28.68 | 40.08 | 37.64 | 34.12 | 42.55 | 35.85 | 35.51 | / | / | / | / |
| Acetic acid/ Propionic acid | 2.10 | 2.11 | 2.06 | 2.38 | 2.18 | 2.22 | 2.65 | / | / | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gui, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, S.; Zhong, J.; Qian, Y.; Meng, C. Effect of Garlic Straw with Silage Corn Stalks on Hu Sheep Rumen Fermentation and Microbial Community In Vitro. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13121201
Shen Y, Zhang J, Gui H, Wang H, Li Y, Zhang J, Cao S, Zhong J, Qian Y, Meng C. Effect of Garlic Straw with Silage Corn Stalks on Hu Sheep Rumen Fermentation and Microbial Community In Vitro. Metabolites. 2023; 13(12):1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13121201
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Yangyang, Jianli Zhang, Hongbing Gui, Huili Wang, Yinxia Li, Jun Zhang, Shaoxian Cao, Jifeng Zhong, Yong Qian, and Chunhua Meng. 2023. "Effect of Garlic Straw with Silage Corn Stalks on Hu Sheep Rumen Fermentation and Microbial Community In Vitro" Metabolites 13, no. 12: 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13121201
APA StyleShen, Y., Zhang, J., Gui, H., Wang, H., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Cao, S., Zhong, J., Qian, Y., & Meng, C. (2023). Effect of Garlic Straw with Silage Corn Stalks on Hu Sheep Rumen Fermentation and Microbial Community In Vitro. Metabolites, 13(12), 1201. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13121201







