Qualitative and Quantitative Mass Spectrometry in Salivary Metabolomics and Proteomics
Abstract
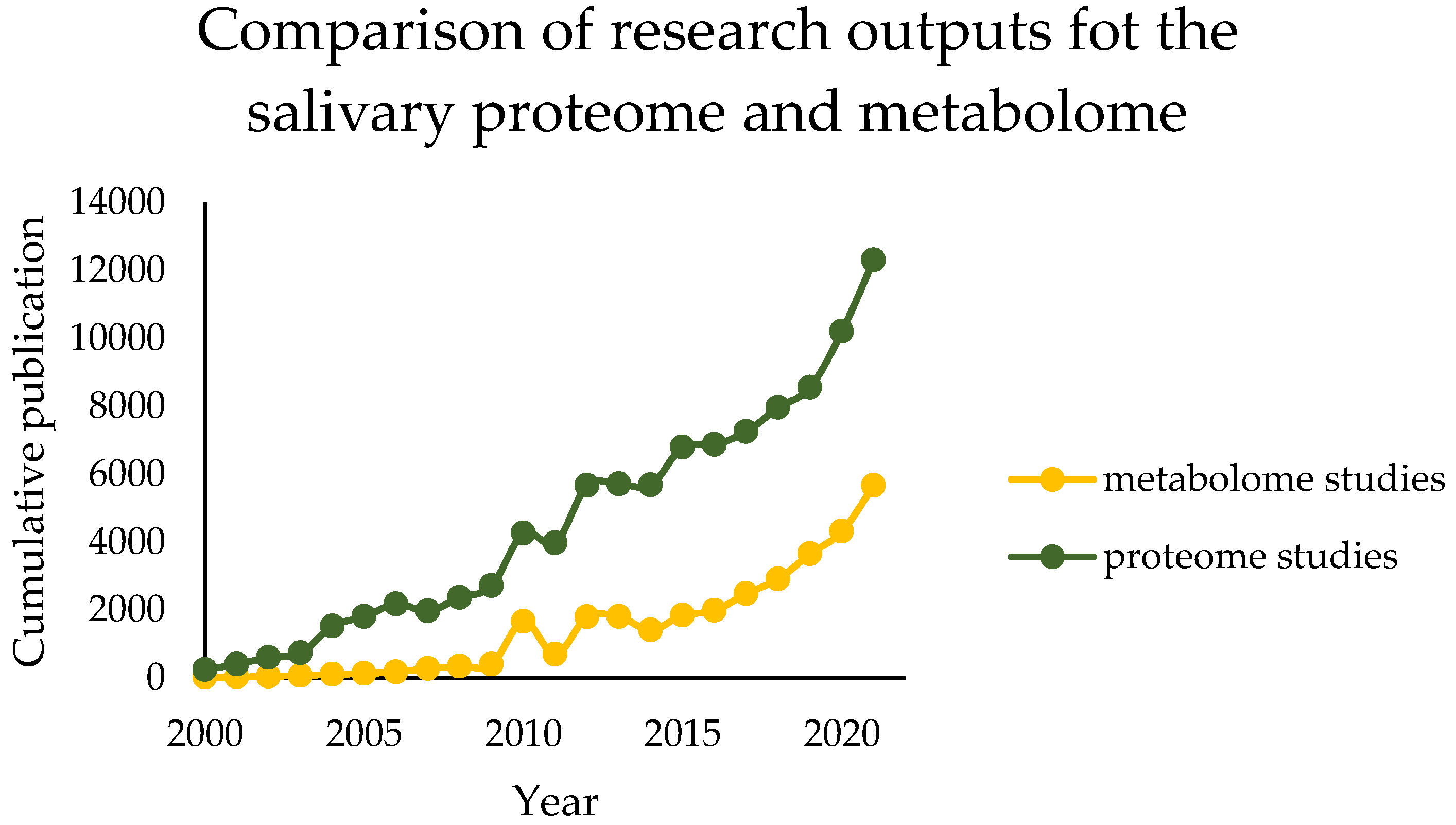
:1. Introduction
1.1. Salivary Metabolomics for Drug, Hormones, and Tissue Metabolites Analysis
1.1.1. Salivary Cortisol Analysis
1.1.2. Salivary p-Cresol Sulphate and Indoxyl Sulphate
1.1.3. Analysis of Steroids
1.1.4. Analysis of Creatinine
1.1.5. Antiepileptic Drugs
Carbamazepine
1.1.6. Soluble Tumour Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (sTRAIL)
1.2. Metabolomics Profiling of the Salivary Microbiome
1.3. Conclusions and Perspectives
2. Salivary Proteome
2.1. Methods of the Salivary Proteome Analysis
2.1.1. General Approaches on Mass Spectrometry Analysis of the Salivary Proteome
2.1.2. Improvement of the Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.2. Salivary Proteome Studies
2.2.1. Characterisation of Salivary Proteome
2.2.2. Studies of the Salivary Proteome for Cancer Detection
2.2.3. Studies of Salivary Proteome in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
2.2.4. Studies of Salivary Proteome during Pregnancy
2.2.5. Studies of Salivary Proteome of Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome
2.2.6. Studies of Salivary Microbiome
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiappin, S.; Antonelli, G.; Gatti, R.; Elio, F. Saliva specimen: A new laboratory tool for diagnostic and basic investigation. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 383, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, E.; Lamster, I.B. The Diagnostic Applications of Saliva—A Review. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2002, 13, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Wong, D.T. Saliva: An emerging biofluid for early detection of diseases. Am. J. Dent. 2009, 22, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagler, R.M. Saliva Analysis for Monitoring Dialysis and Renal Function. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1415–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigler, L.R.; Streckfus, C.F.; Dubinsky, W.P. Salivary Biomarkers for the Detection of Malignant Tumors That Are Remote from the Oral Cavity. Clin. Lab. Med. 2009, 29, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffe, T.; Cooper-White, J.; Beyerlein, P.; Kostner, K.; Punyadeera, C. Diagnostic Potential of Saliva: Current State and Future Applications. Clin. Chem. 2011, 57, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gröschl, M. Current Status of Salivary Hormone Analysis. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Streckfus, C.; Bigler, L. The Use of Soluble, Salivary c-erbB-2 for the Detection and Post-operative Follow-up of Breast Cancer in Women: The Results of a Five-year Translational Research Study. Adv. Dent. Res. 2005, 18, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, A.; Carpenter, G.; So, P.-W. Salivary Metabolomics: From Diagnostic Biomarker Discovery to Investigating Biological Function. Metabolites 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciborowski, M.; Lipska, A.; Godzien, J.; Ferrarini, A.; Korsak, J.; Radziwon, P.; Tomasiak, M.; Barbas, C. Combination of LC–MS- and GC–MS-based Metabolomics to Study the Effect of Ozonated Autohemotherapy on Human Blood. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 6231–6241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-L.; Zheng, P.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Mu, J.; Guo, J.; Huang, T.; Meng, H.-Q.; Xie, P. GC-MS based metabolomics identification of possible novel biomarkers for schizophrenia in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 2398–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raji, M.; Amad, M.; Emwas, A.-H. Dehydrodimerization of pterostilbene during electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, M.; Elmore, C.; Vishwanathan, K. An integrated strategy for in vivo metabolite profiling using high-resolution mass spectrometry based data processing techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 780, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Peng, C.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Z. Discovery of safety biomarkers for realgar in rat urine using UFLC-IT-TOF/MS and 1H NMR based metabolomics. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 4811–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadla, N.C.; Davalagar, V.D.; Sripadi, P. Detection and characterization of N-alkyl diethanolamines and N-2-alkoxyethyl diethanolamines in milk by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Metabolomics 2012, 9, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, E.; Bäckström, D.; Danielsson, R.; Sjöberg, P.J.R.; Bergquist, J. Comparing Capillary Electrophoresis−Mass Spectrometry Fingerprints of Urine Samples Obtained after Intake of Coffee, Tea, or Water. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8946–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, C.-J.; Chen, C.-C. Metabonomic study with a high performance liquid chromatography coupling to a triple quadruple mass spectrometer to identify biomarkers from urine of high-fat fed and streptozotocin treated rats. J. Food Drug Anal. 2009, 17, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-H.; Choi, M.H.; Kwon, O.S.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chung, B.C. Metabolic significance of bisphenol A-induced oxidative stress in rat urine measured by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 29, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.-H.M.; Al-Talla, Z.A.; Kharbatia, N.M. Sample Collection and Preparation of Biofluids and Extracts for Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1277, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.-H.M.; Al-Talla, Z.A.; Yang, Y.; Kharbatia, N.M. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry of Biofluids and Extracts. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1277, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Talla, Z.; Akrawi, S.; Emwas, A.-H.M. Solid state NMR and bioequivalence comparison of the pharmacokinetic parameters of two formulations of clindamycin. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 49, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Talla, Z.; Akrawi, S.; Tolley, L.T.; Sioud, S.H.; Zaater, M.F.; Emwas, A.-H.M. Bioequivalence assessment of two formulations of ibuprofen. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2011, 5, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Shi, W.; Du, X.; Sun, C. The toxicity of 3-chloropropane-1,2-dipalmitate in Wistar rats and a metabonomics analysis of rat urine by ultra-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Chem. Biol. Interactions 2013, 206, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molz, P.; Ellwanger, J.H.; dos Santos, C.E.I.; Dias, J.F.; de Campos, D.; Corbellini, V.A.; Prá, D.; Putzke, M.T.L.; Franke, S.I.R. A metabolomics approach to evaluate the effects of shiitake mushroom (Lentinula edodes) treatment in undernourished young rats. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2014, 318, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szultka, M.; Krzeminski, R.; Walczak, J.; Jackowski, M.; Buszewski, B. Pharmacokinetic study of amoxicillin in human plasma by solid-phase microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2014, 28, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, L. Simple quality assessment approach for herbal extracts using high performance liquid chromatography-UV based metabolomics platform. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 1414–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Dai, W.; Li, H.; Hu, L.; Liu, H.; Su, J.; Zhang, W. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of traditional Chinese medicine Niu Huang Jie Du Pill using ultra performance liquid chromatography coupled with tunable UV detector and rapid resolution liquid chromatography coupled with time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Yu, M.; Lu, X.; Huo, T.; Ge, L.; Yang, J.; Wu, C.; Li, F. Urinary metabonomic study on biochemical changes in chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Ryu, S.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.W.; Lim, M.-S.; Seong, S.J.; Kim, S.; Yoon, Y.-R.; Kim, K.-B. Pattern Recognition Analysis for Hepatotoxicity Induced by Acetaminophen Using Plasma and Urinary 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics in Humans. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11326–11334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Goodpaster, A.M.; Kennedy, M.A. Coefficient of variation, signal-to-noise ratio, and effects of normalization in validation of biomarkers from NMR-based metabonomics studies. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2013, 128, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.-C.; Dai, Y.-Q.; Hui, R.-R.; Hua, J.; Chen, H.-J.; Luo, Q.-Y.; Li, J.-X. NMR-based metabonomic approach on the toxicological effects of a Cimicifuga triterpenoid. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 32, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvani, R.; Miccheli, A.; Capuani, G.; Miccheli, A.T.; Puccetti, C.; Delfini, M.; Iaconelli, A.; Nanni, G.; Mingrone, G. Gut microbiome-derived metabolites characterize a peculiar obese urinary metabotype. Int. J. Obes. 2010, 34, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, R.; Liu, L.; Peng, J.; Xiao, B.; Yang, J.; Miao, Z.; Huang, H. Metabonomics study of urine from Sprague–Dawley rats exposed to Huang-yao-zi using 1H NMR spectroscopy. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Ye, T.; Raftery, D. Advances in NMR-based biofluid analysis and metabolite profiling. Analyst 2010, 135, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wishart, D.S. Quantitative metabolomics using NMR. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gowda, G.N.; Asiago, V.; Shanaiah, N.; Barbas, C.; Raftery, D. Correlative and quantitative 1H NMR-based metabolomics reveals specific metabolic pathway disturbances in diabetic rats. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 383, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emwas, A.H. The strengths and weaknesses of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry with particular focus on metabolomics research. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1277, 161–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emwas, A.-H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Tenori, L.; Saccenti, E.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D.; Alahmari, F.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; et al. NMR Spectroscopy for Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Sengupta, A.; Chandra, K. Quantitative metabolic profiling of NMR spectral signatures of branched chain amino acids in blood serum. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D. Quantitating Metabolites in Protein Precipitated Serum Using NMR Spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 5433–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, A.J.; Tseng, L.-H.; Simpson, M.J.; Spraul, M.; Braumann, U.; Kingery, W.L.; Kelleher, B.P.; Hayes, M.H.B. The application of LC-NMR and LC-SPE-NMR to compositional studies of natural organic matter. Analyst 2004, 129, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.-J.; Capistrano, R.; Dhooghe, L.; Foubert, K.; Lemière, F.; Maregesi, S.; Baldé, A.; Apers, S.; Pieters, L. Herbal Medicines and Infectious Diseases: Characterization by LC-SPE-NMR of Some Medicinal Plant Extracts Used against Malaria. Planta Med. 2011, 77, 1139–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, F.; Fine, D.D.; Wherritt, D.J.; Lei, Z.; Sumner, L.W. PlantMAT: A Metabolomics Tool for Predicting the Specialized Metabolic Potential of a System and for Large-Scale Metabolite Identifications. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11373–11383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellhammer, D.H.; Wüst, S.; Kudielka, B.M. Salivary cortisol as a biomarker in stress research. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieman, L.K.; Biller, B.M.K.; Findling, J.W.; Newell-Price, J.; Savage, M.O.; Stewart, P.M.; Montori, V. The Diagnosis of Cushing’s Syndrome: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1526–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, F.; Stewart, P.M. Cortisol metabolism in hypertension. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 20, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Findling, J.W.; Raff, H. Cushing’s Syndrome: Important Issues in Diagnosis and Management. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitworth, J.A.; Mangos, G.; Kelly, J.J. Cushing, cortisol, and cardiovascular disease. Hypertension 2000, 36, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuerholz, T.; Keil, O.; Wagner, T.; Klinzing, S.; Sümpelmann, R.; Oberle, V.; Marx, G. Hydrocortisone does not affect major platelet receptors in inflammation in vitro. Steroids 2007, 72, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, H.; Kidowaki, T.; Koyama, Y.; Endo, T.; Homma, K.; Kambegawa, A.; Aoki, N. Specificity assessment of immunoassay kits for determination of urinary free cortisol concentrations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 378, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vining, R.F.; McGinley, R.A. The measurement of hormones in saliva: Possibilities and pitfalls. J. Steroid Biochem. 1987, 27, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vining, R.F.; McGinley, R.A.; Symons, R.G. Hormones in saliva: Mode of entry and consequent im-plications for clinical interpretation. Clin. Chem. 1983, 29, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jönsson, B.A.; Malmberg, B.; Åmilon, A.; Garde, A.H.; Ørbaek, P. Determination of cortisol in human saliva using liquid chromatography–electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 784, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruhisa, U.; Ryoji, H.; Taisuke, I.; Tatsuya, S.; Fumihiro, M.; Tatsuo, S. Use of saliva for monitoring unbound free cortisol levels in serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 1981, 110, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perogamvros, I.; Owen, L.J.; Newell-Price, J.; Ray, D.W.; Trainer, P.J.; Keevil, B.G. Simultaneous measurement of cortisol and cortisone in human saliva using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry: Application in basal and stimulated conditions. J. Chromatogr. B 2009, 877, 3771–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Restituto, P.; Galofré, J.; Gil, M.; Mugueta, C.; Santos, S.; Monreal, J.; Varo, N. Advantage of salivary cortisol measurements in the diagnosis of glucocorticoid related disorders. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palo, E.F.; Antonelli, G.; Benetazzo, A.; Prearo, M.; Gatti, R. Human saliva cortisone and cortisol simultaneous analysis using reverse phase HPLC technique. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 405, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Matsuura, E.; Mitani, K. Determination of cortisol in human saliva by automated in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 44, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kwon, S.-H.; Shin, H.-J.; Lim, H.-S.; Singh, R.J.; Lee, K.-R.; Kim, Y.-J. Simultaneous quantitative analysis of salivary cortisol and cortisone in Korean adults using LC-MS/MS. BMB Rep. 2010, 43, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giebułtowicz, J.; Korytowska, N.; Sankowski, B.; Wroczyński, P. Development and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for quantitative analysis of uraemic toxins p-cresol sulphate and indoxyl sulphate in saliva. Talanta 2016, 150, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurgens, E.; Knaven, E.; Hegeman, E.; Van Gemert, M.; Emmen, J.; Mulder, Y.; Ijsselstijn, L.; De Rooij, B.; Noij, T. Quantitative Profiling of Seven Steroids in Saliva using LC-MS/MS. J. Appl. Bioanal. 2019, 5, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Stalder, T.; Kirschbaum, C. Quantitative analysis of estradiol and six other steroid hormones in human saliva using a high throughput liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry assay. Talanta 2015, 143, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabiny, D.L.; Ertingshausen, G. Automated Reaction-Rate Method for Determination of Serum Creatinine with the CentrifiChem. Clin. Chem. 1971, 17, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, A.C.; Hall, J.E. The body fluids and kidneys. In Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th ed.; Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 291–415. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, N. Physiology and Biochemistry of the Mouth, 4th ed.; Blackwell: Kansas City, MO, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Venkatapathy, R.; Govindarajan, V.; Oza, N.; Parameswaran, S.; Dhanasekaran, B.P.; Prashad, K.V. Salivary Creatinine Estimation as an Alternative to Serum Creatinine in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Int. J. Nephrol. 2014, 2014, 742724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davidovich, E.; Davidovits, M.; Peretz, B.; Shapira, J.; Aframian, D.J. The correlation between dental calculus and disturbed mineral metabolism in paediatric patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 2439–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakahari, T.; Yoshida, H.; Imai, Y. Transepithelial fluid shift generated by osmolarity gradients in unstimulated perfused rat submandibular glands. Exp. Physiol. 1996, 81, 767–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
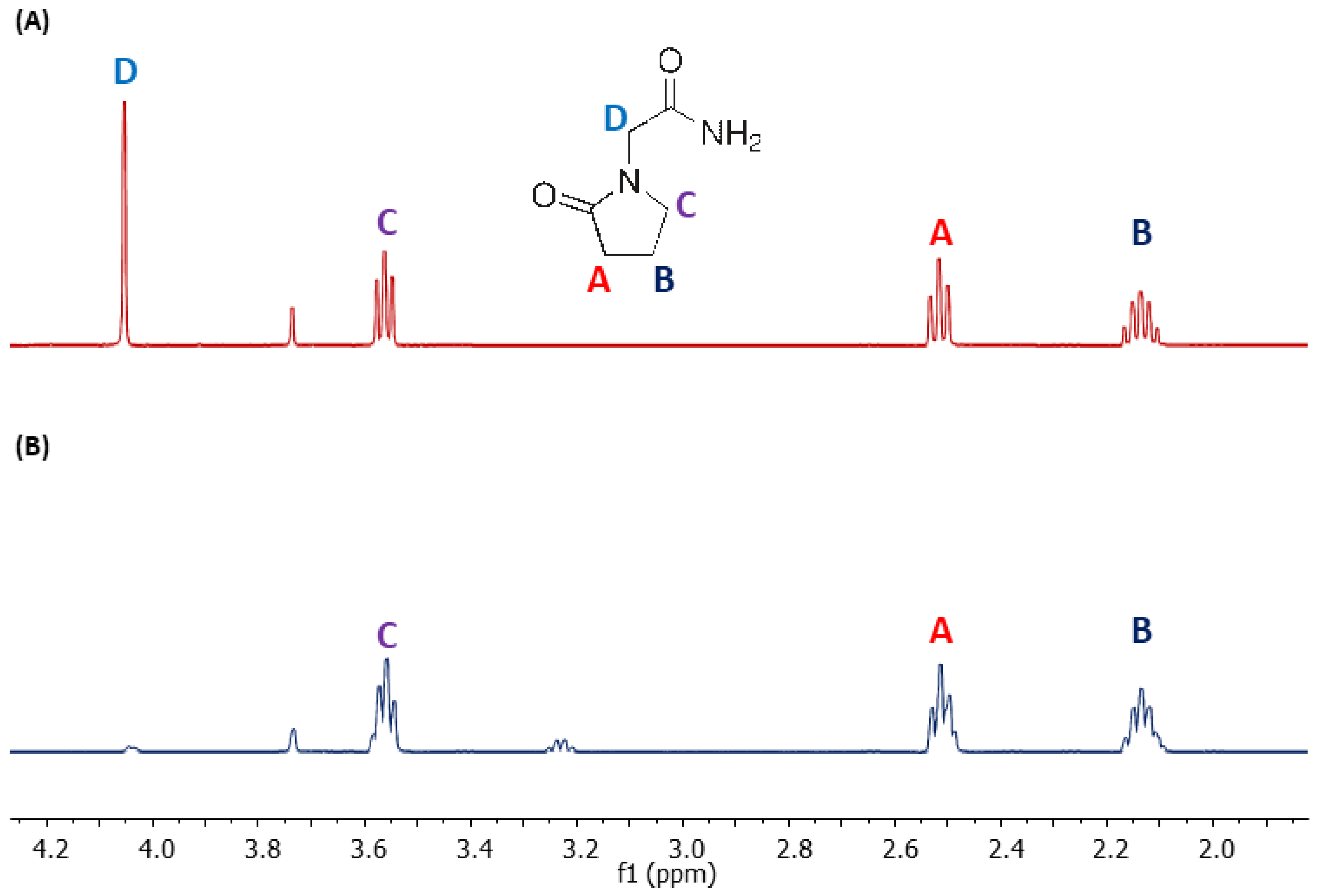
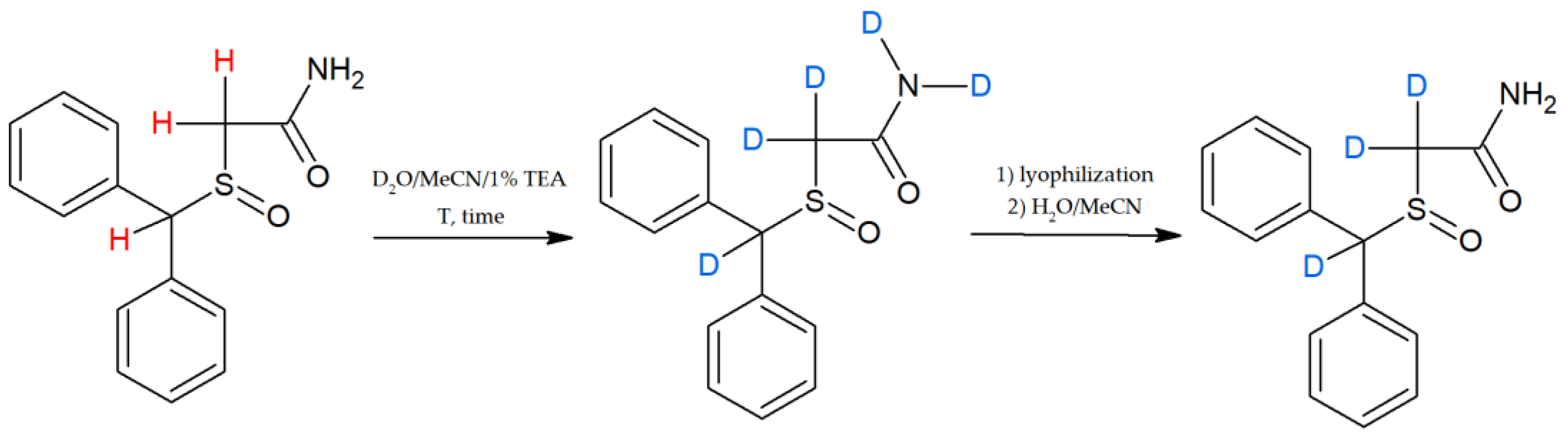
- Bąchor, R.; Konieczny, A.; Szewczuk, Z. Preparation of Isotopically Labelled Standards of Creatinine via H/D Exchange and Their Application in Quantitative Analysis by LC-MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenaway, C.; Ratnaraj, N.; Sander, J.; Patsalos, P.N. Saliva and serum lacosamide concentrations in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsia 2010, 52, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecarelli, O.; Voti, P.L.; Pro, S.; Romolo, F.S.; Rotolo, M.C.; Pulitano, P.; Accornero, N.; Vanacore, N. Saliva and Serum Levetiracetam Concentrations in Patients with Epilepsy. Ther. Drug Monit. 2007, 29, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaś-Ruszczyk, K.; Kuczyńska, J.; Sienkiewicz-Jarosz, H.; Kurkowska-Jastrzębska, I.; Bienkowski, P.; Restel, M.; Samochowiec, J.; Mierzejewski, P. Comparison of Plasma, Saliva, and Hair Levetiracetam Concentrations. Ther. Drug Monit. 2017, 39, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaś, K.; Kuczyńska, J.; Sienkiewicz-Jarosz, H.; Bienkowski, P.; Mierzejewski, P. A Simple Bioanalytical Method for the Quantification of Levetiracetam in Human Plasma and Saliva. J. Chromatogr. Sep. Tech. 2015, 6, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, I.I.; Alsous, M.; Masri, A.T. Chromatographic Characterization and Method Development for Determination of Levetiracetam in Saliva: Application to Correlation with Plasma Levels. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2017, 2017, 7846742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grocholska, P.; Wieczorek, R.; Bąchor, R. Preparation of Deuterium-Labeled Armodafinil by Hydrogen–Deuterium Exchange and Its Application in Quantitative Analysis by LC-MS. Metabolites 2022, 12, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grocholska, P.; Bąchor, R. Trends in the Hydrogen−Deuterium Exchange at the Carbon Centers. Preparation of Internal Standards for Quantitative Analysis by LC-MS. Molecules 2021, 26, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bąchor, R.; Kluczyk, A.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Facile synthesis of deuterium-labeled denatonium cation and its application in the quantitative analysis of Bitrex by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6557–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bąchor, R.; Kluczyk, A.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Preparation of novel deuterated cyclosporin A standards for quantitative LC-MS analysis. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 52, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziurkowska, E.; Wesolowski, M. Deproteinization as a Rapid Method of Saliva Purification for the Determination of Carbamazepine and Carbamazepine-10,11 Epoxide. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilffert, D.; Donzelli, R.; Asselman, A.; Hermans, J.; Govorukhina, N.; Hacken, N.H.T.; Quax, W.J.; van de Merbel, N.C.; Bischoff, R. Quantitative antibody-free LC–MS/MS analysis of sTRAIL in sputum and saliva at the sub-ng/mL level. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1032, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, N.; Grant, M.; Bao, K.; Silbereisen, A.; Hetrodt, F.; Manoil, D.; Belibasakis, G.N. Metaproteome and metabolome of oral microbial communities. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 85, 46–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesan, J.; Morelli, T.; Moss, K.; Barros, S.; Ward, M.; Jenkins, W.; Aspiras, M.; Offenbacher, S. Association of Synergistetes and Cyclodipeptides with Periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bregy, L.; Müggler, A.R.; Sinues, P.; García-Gómez, D.; Suter, Y.; Belibasakis, G.; Kohler, M.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Zenobi, R. Differentiation of oral bacteria in in vitro cultures and human saliva by secondary electrospray ionization—Mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amado, F.M.L.; Vitorino, R.M.P.; Domingues, P.M.D.N.; Lobo, M.J.C.; Duarte, J.A.R. Analysis of the human saliva proteome. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2005, 2, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, W.L.; Dawes, C. The salivary proteome: Challenges and perspectives. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2011, 5, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, A.K.; Kumar, B.; Singh, A.K.; Ranjan, P.; Thiruvengadam, R.; Desiraju, B.K.; Kshetrapal, P.; Wadhwa, N.; Bhatnagar, S.; Rashid, F.; et al. Salivary proteome signatures in the early and middle stages of human pregnancy with term birth outcome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amado, F.M.; Ferreira, R.; Vitorino, R. One decade of salivary proteomics: Current approaches and outstanding challenges. Clin. Biochem. 2013, 46, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Arellano, M.; Boontheung, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Jiang, J.; Elashoff, D.; Wei, R.; Loo, J.A.; Wong, D.T. Salivary Proteomics for Oral Cancer Biomarker Discovery. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 6246–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devic, I.; Shi, M.; Schubert, M.M.; Lloid, M.; Izutsu, K.T.; Pan, C.; Missaghi, M.; Morton, T.H.; Mancl, L.A.; Zhang, J.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Saliva from Patients with Oral Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Castagnola, M.; Scarano, E.; Passali, G.; Messana, I.; Cabras, T.; Iavarone, F.; Di Cintio, G.; Fiorita, A.; De Corso, E.; Paludetti, G. Salivary biomarkers and proteomics: Future diagnostic and clinical utilities. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2017, 37, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanati, A.; Martina, E.; Diotallevi, F.; Radi, G.; Marani, A.; Sartini, D.; Emanuelli, M.; Kontochristopoulos, G.; Rigopoulos, D.; Gregoriou, S.; et al. Saliva Proteomics as Fluid Signature of Inflammatory and Immune-Mediated Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Loo, J.A.; Wong, D.T. Human saliva proteome analysis and disease biomarker discovery. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2007, 4, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griese, M.; Noss, J.; Von Bredow, C. Protein pattern of exhaled breath condensate and saliva. Proteomics 2002, 2, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmarth, P.A.; Riviere, M.A.; Rustvold, D.L.; Lauten, J.D.; Madden, T.E.; David, L.L. Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography Study of the Human Whole Saliva Proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2004, 3, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, A.; Parkes, H.G.; Carpenter, G.H.; So, P.-W. Developing and Standardizing a Protocol for Quantitative Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H NMR) Spectroscopy of Saliva. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duarte, D.; Castro, B.; Pereira, J.; Marques, J.; Costa, A.; Gil, A. Evaluation of Saliva Stability for NMR Metabolomics: Collection and Handling Protocols. Metabolites 2020, 10, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Giulivi, C. Saliva protein profiling for subject identification and potential medical applications. Med. Omics 2021, 3, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xie, Y.; Ramachandran, P.; Loo, R.R.O.; Li, Y.; Loo, J.A.; Wong, D.T. Large-scale identification of proteins in human salivary proteome by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1714–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tarawneh, S.K.; Border, M.B.; Dibble, C.F.; Bencharit, S. Defining Salivary Biomarkers Using Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics: A Systematic Review. OMICS 2011, 15, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fournier, M.L.; Gilmore, J.M.; Martin-Brown, S.A.; Washburn, M.P. Multidimensional Separations-Based Shotgun Proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3654–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherman, A.D.; Skinner, O.S.; Kelleher, N.L. Top Down proteomics: Facts and perspectives. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabe, A.; Salazar, M.G.; Völker, U. Bottom-Up Community Proteome Analysis of Saliva Samples and Tongue Swabs by Data-Dependent Acquisition Nano LC-MS/MS Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2327, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
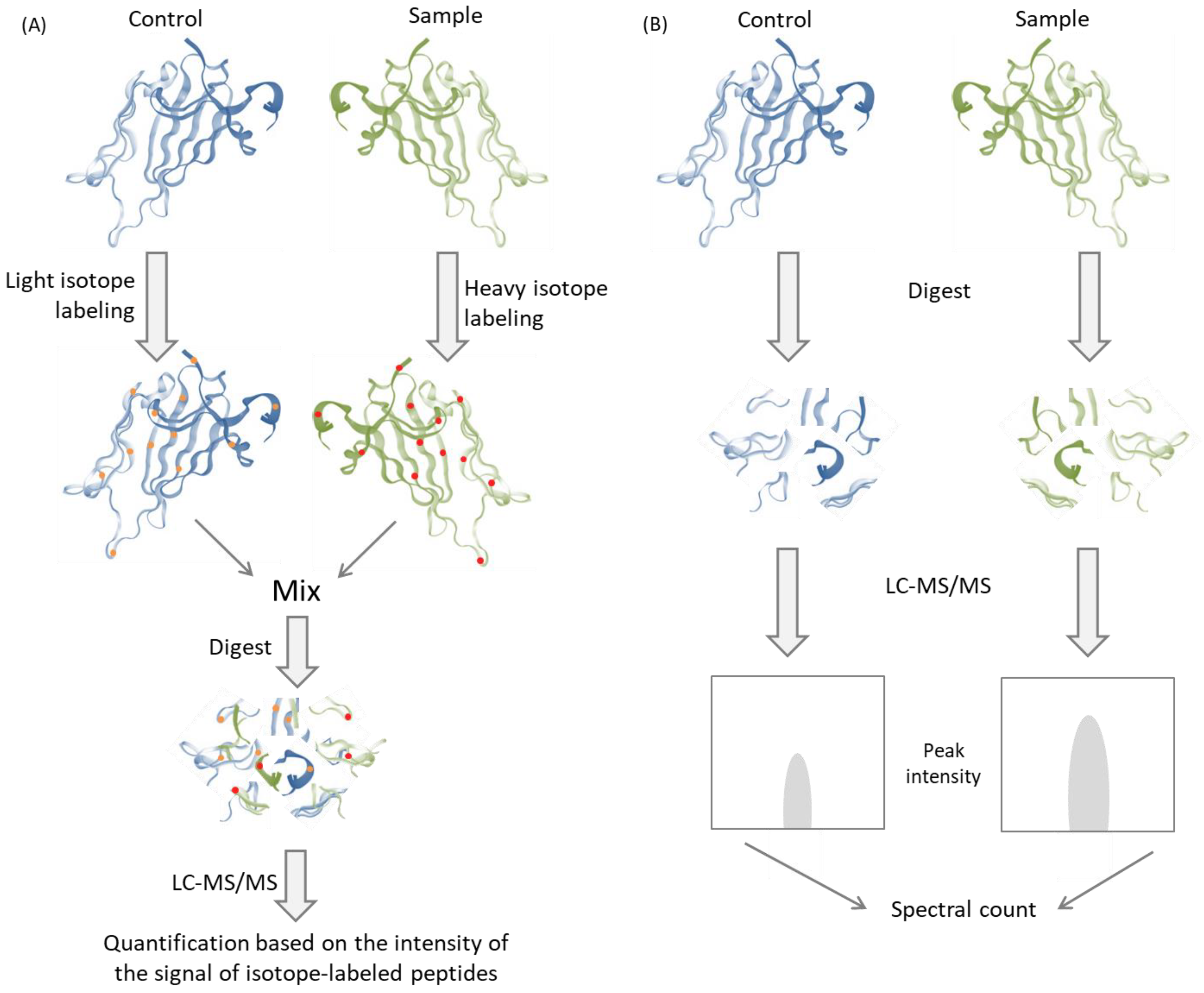
- Zhu, W.; Smith, J.W.; Huang, C.-M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Label-Free Quantitative Proteomics. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 840518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bantscheff, M.; Schirle, M.; Sweetman, G.; Rick, J.; Kuster, B. Quantitative mass spectrometry in proteomics: A critical review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 389, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Licier, R.; Miranda, E.; Serrano, H. A Quantitative Proteomics Approach to Clinical Research with Non-Traditional Samples. Proteomes 2016, 4, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bąchor, R.; Waliczek, M.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Trends in the Design of New Isobaric Labeling Reagents for Quantitative Proteomics. Molecules 2019, 24, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waliczek, M.; Bąchor, R.; Kijewska, M.; Gąszczyk, D.; Panek-Laszczyńska, K.; Konieczny, A.; Dąbrowska, K.; Witkiewicz, W.; Marek-Bukowiec, K.; Tracz, J.; et al. Isobaric duplex based on a combination of 16O/18O enzymatic exchange and labeling with pyrylium salts. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1048, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepankiewicz, B.; Bąchor, R.; Pasławski, R.; Siwińska, N.; Pasławska, U.; Konieczny, A.; Szewczuk, Z. Evaluation of Tryptic Podocin Peptide in Urine Sediment Using LC-MS-MRM Method as a Potential Biomarker of Glomerular Injury in Dogs with Clinical Signs of Renal and Cardiac Disorders. Molecules 2019, 24, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siwińska, N.; Pasławska, U.; Bąchor, R.; Szczepankiewicz, B.; Żak, A.; Grocholska, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Evaluation of podocin in urine in horses using qualitative and quantitative methods. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grocholska, P.; Konieczny, A.; Kaźmierczak, Z.; Dąbrowska, K.; Panek-Laszczyńska, K.; Kłak, M.; Witkiewicz, W.; Szewczuk, Z.; Bąchor, R. Peptide Charge Derivatization as a Tool for Early Detection of Preeclampsia by Mass Spectrometry—A Comparison with the ELISA Test. Molecules 2021, 26, 7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bąchor, R.; Gąszczyk, D.; Panek-Laszczyńska, K.; Konieczny, A.; Witkiewicz, W.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Detection of Podocin in Human Urine Sediment Samples by Charge Derivatization and LC-MS-MRM Method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiktorowicz, J.E.; English, R.D.; Wu, Z.; Kurosky, A. Model Studies on iTRAQ Modification of Peptides: Sequence-dependent Reaction Specificity. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Münchbach, M.; Quadroni, M.; Miotto, G.; James, P. Quantitation and Facilitated de Novo Sequencing of Proteins by Isotopic N-Terminal Labeling of Peptides with a Fragmentation-Directing Moiety. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4047–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, P.L.; Huang, Y.N.; Marchese, J.N.; Williamson, B.; Parker, K.; Hattan, S.; Khainovski, N.; Pillai, S.; Dey, S.; Daniels, S.; et al. Multiplexed Protein Quantitation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Using Amine-reactive Isobaric Tagging Reagents. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 1154–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thompson, A.; Schäfer, J.; Kuhn, K.; Kienle, S.; Schwarz, J.; Schmidt, G.; Neumann, T.; Hamon, C. Tandem Mass Tags: A Novel Quantification Strategy for Comparative Analysis of Complex Protein Mixtures by MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, F.; Ye, H.; Chen, R.; Fu, Q.; Li, L. N,N-Dimethyl Leucines as Novel Isobaric Tandem Mass Tags for Quantitative Proteomics and Peptidomics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 2817–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Setner, B.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Quaternary ammonium isobaric tag for a relative and absolute quantification of peptides. J. Mass Spectrom. 2017, 53, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.A.; Mallis, R.J. Aging and oxidation of reactive protein sulfhydryls. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 1519–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gygi, S.P.; Rist, B.; Gerber, S.; Turecek, F.; Gelb, M.H.; Aebersold, R. Quantitative analysis of complex protein mixtures using isotope-coded affinity tags. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambor, V.; Hunter, C.L.; Seymour, S.L.; Kacerovsky, M.; Stulik, J.; Lenco, J. CysTRAQ—A combination of iTRAQ and enrichment of cysteinyl peptides for uncovering and quantifying hidden proteomes. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Meng, F.; Bomgarden, R.D.; Viner, R.I.; Li, J.; Rogers, J.C.; Cheng, J.; Greenlief, C.M.; Cui, J.; Lubahn, D.B.; et al. Proteomic Quantification and Site-Mapping of S-Nitrosylated Proteins Using Isobaric iodoTMT Reagents. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3200–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmese, A.; De Rosa, C.; Chiappetta, G.; Marino, G.; Amoresano, A. Novel method to investigate protein carbonylation by iTRAQ strategy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 404, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahne, H.; Neubert, P.; Kuhn, K.; Etienne, C.; Bomgarden, R.; Rogers, J.C.; Kuster, B. Carbonyl-Reactive Tandem Mass Tags for the Proteome-Wide Quantification of N-Linked Glycans. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3716–3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frahm, J.L.; Bori, I.D.; Comins, D.L.; Hawkridge, A.M.; Muddiman, D.C. Achieving Augmented Limits of Detection for Peptides with Hydrophobic Alkyl Tags. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3989–3995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, D.; Spiteller, G. Sequencing of Short Peptides Using FAB Mass Spectrometry?Increased Information via Derivatization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1985, 24, 408–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, M.; Hanai, Y.; Awane, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Miyagawa, H. Improving peptide fragmentation by N-terminal derivatization with high proton affinity. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 1130–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stefanowicz, P. Electrospray Mass Spectrometry and Tandem Mass Spectrometry of the Natural Mixture of Cyclic Peptides from Linseed. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 10, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.E.; Roberts, K.D.; Simpson, R.J.; O’Hair, R.A.J. Selective identification and quantitative analysis of methionine containing peptides by charge derivatization and tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 16, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadagopan, N.; Watson, J.T. Investigation of the tris(trimethoxyphenyl)phosphonium acetyl charged derivatives of peptides by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 11, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, K.D.W.; Huang, Z.H.; Sadagopan, N.; Watson, J.T. Charge derivatization of peptides for analysis by mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 1998, 17, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cydzik, M.; Rudowska, M.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. The Competition of Charge Remote and Charge Directed Fragmentation Mechanisms in Quaternary Ammonium Salt Derivatized Peptides—An Isotopic Exchange Study. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 22, 2103–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bąchor, R.; Mielczarek, P.; Rudowska, M.; Silberring, J.; Szewczuk, Z. Sensitive detection of charge derivatized peptides at the attomole level using nano-LC-ESI–MRM analysis. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 362, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudowska, M.; Wojewska, D.; Kluczyk, A.; Bąchor, R.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. The Hydrogen–Deuterium Exchange at α-Carbon Atom in N,N,N-Trialkylglycine Residue: ESI-MS Studies. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 23, 1024–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Waliczek, M.; Kijewska, M.; Rudowska, M.; Setner, B.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. Peptides Labeled with Pyridinium Salts for Sensitive Detection and Sequencing by Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setner, B.; Rudowska, M.; Kluczyk, A.; Stefanowicz, P.; Szewczuk, Z. The 5-azoniaspiro[4.4]nonyl group for improved MS peptide analysis: A novel non-fragmenting ionization tag for mass spectrometric sensitive sequencing of peptides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 986, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska, M.; Bąchor, R. Catch, Modify and Analyze: Methods of Chemoselective Modification of Cysteine-Containing Peptides. Molecules 2022, 27, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, M.; Popiel, D.; Walter, M.; Bąchor, R.; Biernat, M.; Cebrat, M.; Kijewska, M.; Kuczer, M.; Modzel, M.; Kluczyk, A. Veni, Vidi, Vici: Immobilized Peptide-Based Conjugates as Tools for Capture, Analysis, and Transformation. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.F. Thiol/disulfide exchange equilibria and disulfidebond stability. Methods Enzymol. 1995, 251, 8–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.-Q.; Xu, K.; Liu, L.; Raab, H.; Bhakta, S.; Kenrick, M.; Parsons-Reponte, K.L.; Tien, J.; Yu, S.-F.; Mai, E.; et al. Conjugation site modulates the in vivo stability and therapeutic activity of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasicek, L.; Brodbelt, J.S. Enhanced Electron Transfer Dissociation through Fixed Charge Derivatization of Cysteines. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7876–7884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Wang, W.; Luo, L.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Cui, F. Characterization of an aphid-specific, cysteine-rich protein enriched in salivary glands. Biophys. Chem. 2014, 189, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomers, J.; Tabak, L.; Levine, M.; Mandel, I.; Ellison, S. Characterization of Cysteine-containing Phosphoproteins from Human Submandibular-Sublingual Saliva. J. Dent. Res. 1982, 61, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomers, J.; Tabak, L.; Levine, M.; Mandel, I.; Hay, D. Properties of Cysteine-containing Phosphoproteins from Human Submandibular-sublingual Saliva. J. Dent. Res. 1982, 61, 397–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambatipudi, K.S.; Lu, B.; Hagen, F.K.; Melvin, J.E.; Yates, I.J.R. Quantitative Analysis of Age Specific Variation in the Abundance of Human Female Parotid Salivary Proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 5093–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ornoy, A.; Yacobi, S.; Matalon, S.T.; Blank, M.; Blumenfeld, Z.; Miller, R.K.; Shoenfeld, Y. The effects of antiphospholipid antibodies obtained from women with SLE/APS and associated pregnancy loss on rat embryos and placental explants in culture. Lupus 2003, 12, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, E.; Siqueira, W.L.; Helmerhorst, E.J.; Oppenheim, F.G. Large-scale phosphoproteome of human whole saliva using disulfide–thiol interchange covalent chromatography and mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 407, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Brown, J.N.; Tolić, N.; Meng, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, R.; Moore, R.J.; Pevzner, P.; Smith, R.D.; et al. Quantitative analysis of human salivary gland-derived intact proteome using top-down mass spectrometry. Proteomics 2014, 14, 1211–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, T.; Schloss, P.D. Dynamics and associations of microbial community types across the human body. Nature 2014, 509, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grassl, N.; Kulak, N.A.; Pichler, G.; Geyer, P.E.; Jung, J.; Schubert, S.; Sinitcyn, P.; Cox, J.; Mann, M. Ultra-deep and quantitative saliva proteome reveals dynamics of the oral microbiome. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Jong, E.P.; Xie, H.; Onsongo, G.; Stone, M.D.; Chen, X.-B.; Kooren, J.A.; Refsland, E.W.; Griffin, R.J.; Ondrey, F.G.; Wu, B.; et al. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Myosin and Actin as Promising Saliva Biomarkers for Distinguishing Pre-Malignant and Malignant Oral Lesions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kim, J.J.; Kim, K.M.; Yoshizawa, J.; Fan, L.-Y.; Cao, C.; Wong, D.T.W. Differential Proteomic Analysis of Human Saliva using Tandem Mass Tags Quantification for Gastric Cancer Detection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delmonico, L.; Bravo, M.; Silvestre, R.T.; Ornellas, M.H.F.; De Azevedo, C.M.; Alves, G. Proteomic profile of saliva and plasma from women with impalpable breast lesions. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2145–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streckfus, C.F.; Mayorga-Wark, O.; Arreola, D.; Edwards, C.; Bigler, L.; Dubinsky, W.P. Breast Cancer Related Proteins Are Present in Saliva and Are Modulated Secondary to Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast. Cancer Investig. 2008, 26, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streckfus, C.F.; Storthz, K.A.; Bigler, L.; Dubinsky, W.P. A Comparison of the Proteomic Expression in Pooled Saliva Specimens from Individuals Diagnosed with Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast with and without Lymph Node Involvement. J. Oncol. 2009, 2009, 737619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ishikawa, S.; Ishizawa, K.; Tanaka, A.; Kimura, H.; Kitabatake, K.; Sugano, A.; Edamatsu, K.; Ueda, S.; Iino, M. Identification of Salivary Proteomic Biomarkers for Oral Cancer Screening. In Vivo 2021, 35, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostanci, N.; Selevsek, N.; Wolski, W.; Grossmann, J.; Bao, K.; Wahlander, A.; Trachsel, C.; Schlapbach, R.; Öztürk, V.Ö.; Afacan, B.; et al. Targeted Proteomics Guided by Label-free Quantitative Proteome Analysis in Saliva Reveal Transition Signatures from Health to Periodontal Disease. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 1392–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pappa, E.; Vastardis, H.; Mermelekas, G.; Gerasimidi-Vazeou, A.; Zoidakis, J.; Vougas, K. Saliva Proteomics Analysis Offers Insights on Type 1 Diabetes Pathology in a Pediatric Population. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.V.; Reddy, A.P.; Lu, X.; Dasari, S.; Krishnaprasad, A.; Biggs, E.; Roberts, C.; Nagalla, S. Proteomic Identification of Salivary Biomarkers of Type-2 Diabetes. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabras, T.; Pisano, E.; Mastinu, A.; Denotti, G.; Pusceddu, P.P.; Inzitari, R.; Fanali, C.; Nemolato, S.; Castagnola, M.; Messana, I. Alterations of the Salivary Secretory Peptidome Profile in Children Affected by Type 1 Diabetes. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2010, 9, 2099–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bencharit, S.; Baxter, S.S.; Carlson, J.; Byrd, W.C.; Mayo, M.V.; Border, M.B.; Kohltfarber, H.; Urrutia, E.; Howard-Williams, E.L.; Offenbacher, S.; et al. Salivary proteins associated with hyperglycemia in diabetes: A proteomic analysis. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 2785–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, N.; Menon, N.G.; de Almeida, L.G.N.; Woods, P.S.; Heynen, M.L.; Jay, G.D.; Caffery, B.; Jones, L.; Krawetz, R.; Schmidt, T.A.; et al. Proteomics Analysis of Tears and Saliva From Sjogren’s Syndrome Patients. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 787193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczor-Urbanowicz, K.E.; Carreras-Presas, C.M.; Aro, K.; Tu, M.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Wong, D.T. Saliva diagnostics—Current views and directions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 459–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, T.; Rizk, A.M.; Sultan, A.S.; Jabra-Rizk, M.A. The power of saliva: Antimicrobial and beyond. PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1008058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; Sedghi, L.; Ganther, S.; Malone, E.; Kamarajan, P.; Kapila, Y.L. Host-microbe interactions: Profiles in the transcriptome, the proteome, and the metabolome. Periodontol. 2000 2020, 82, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappa, E.; Vastardis, H.; Makridakis, M.; Zoidakis, J.; Vougas, K.; Stamatakis, G.; Samiotaki, M.; Rahiotis, C. Analysis of Human and Microbial Salivary Proteomes in Children Offers Insights on the Molecular Pathogenesis of Molar-Incisor Hypomineralization. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
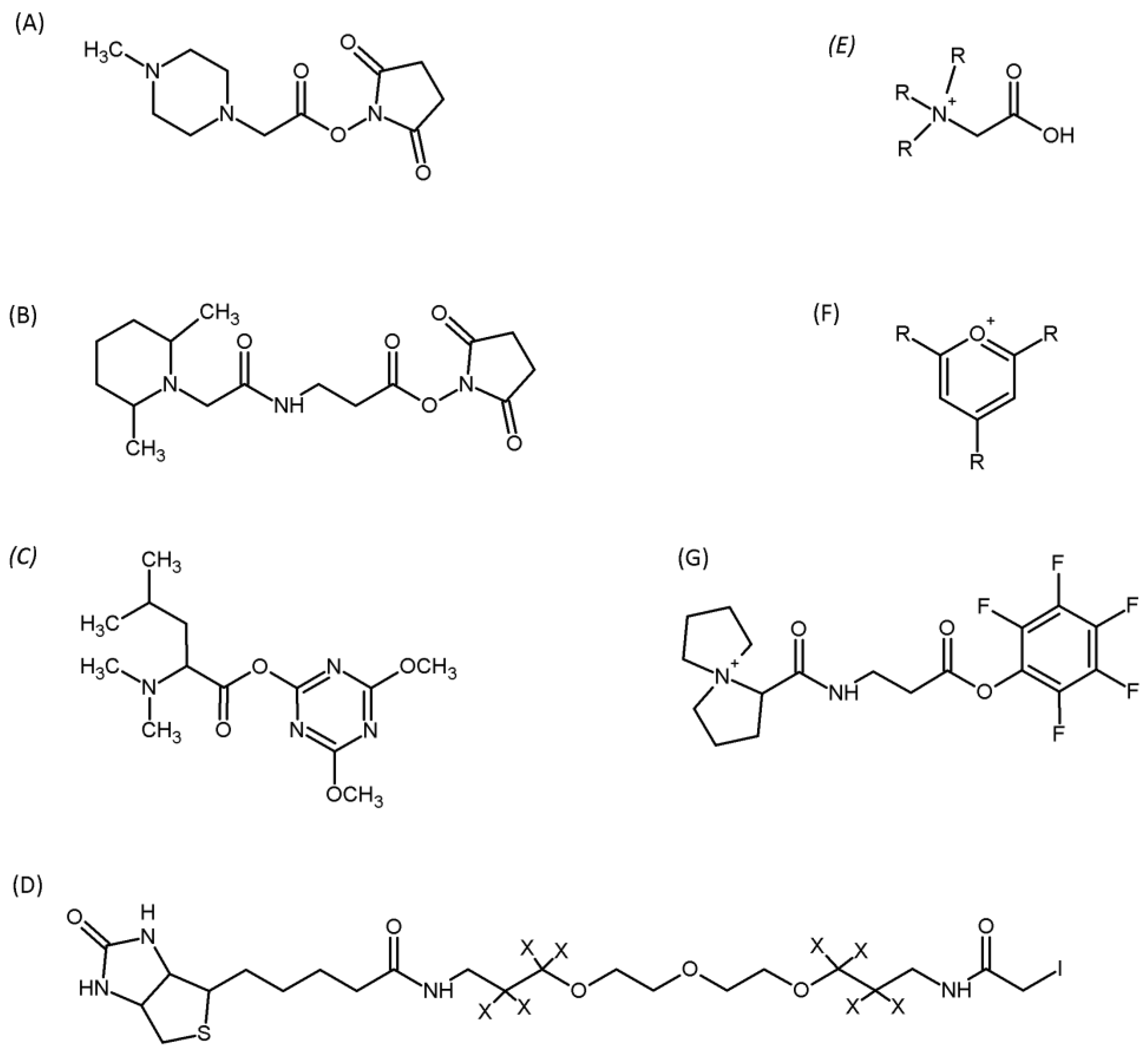
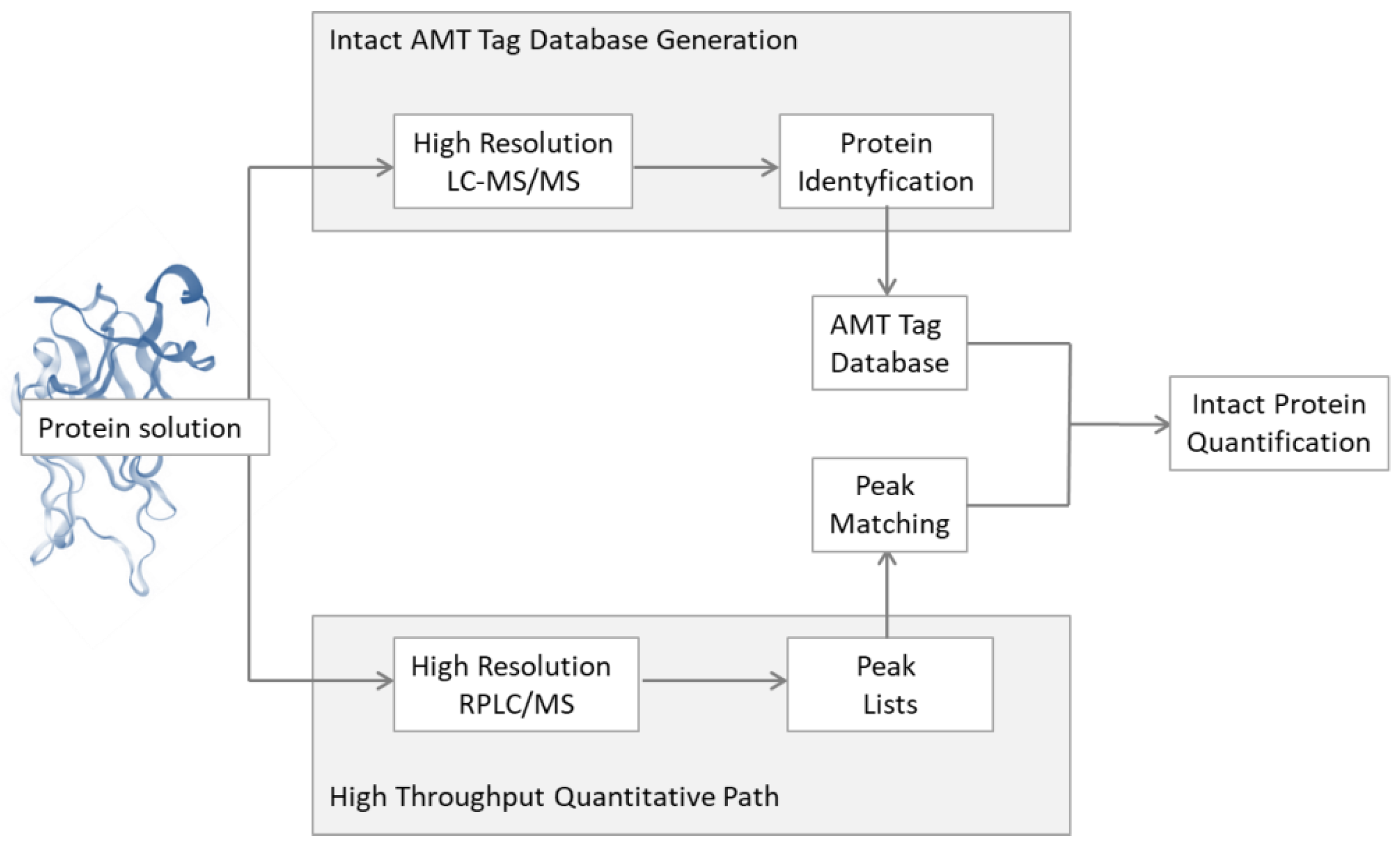
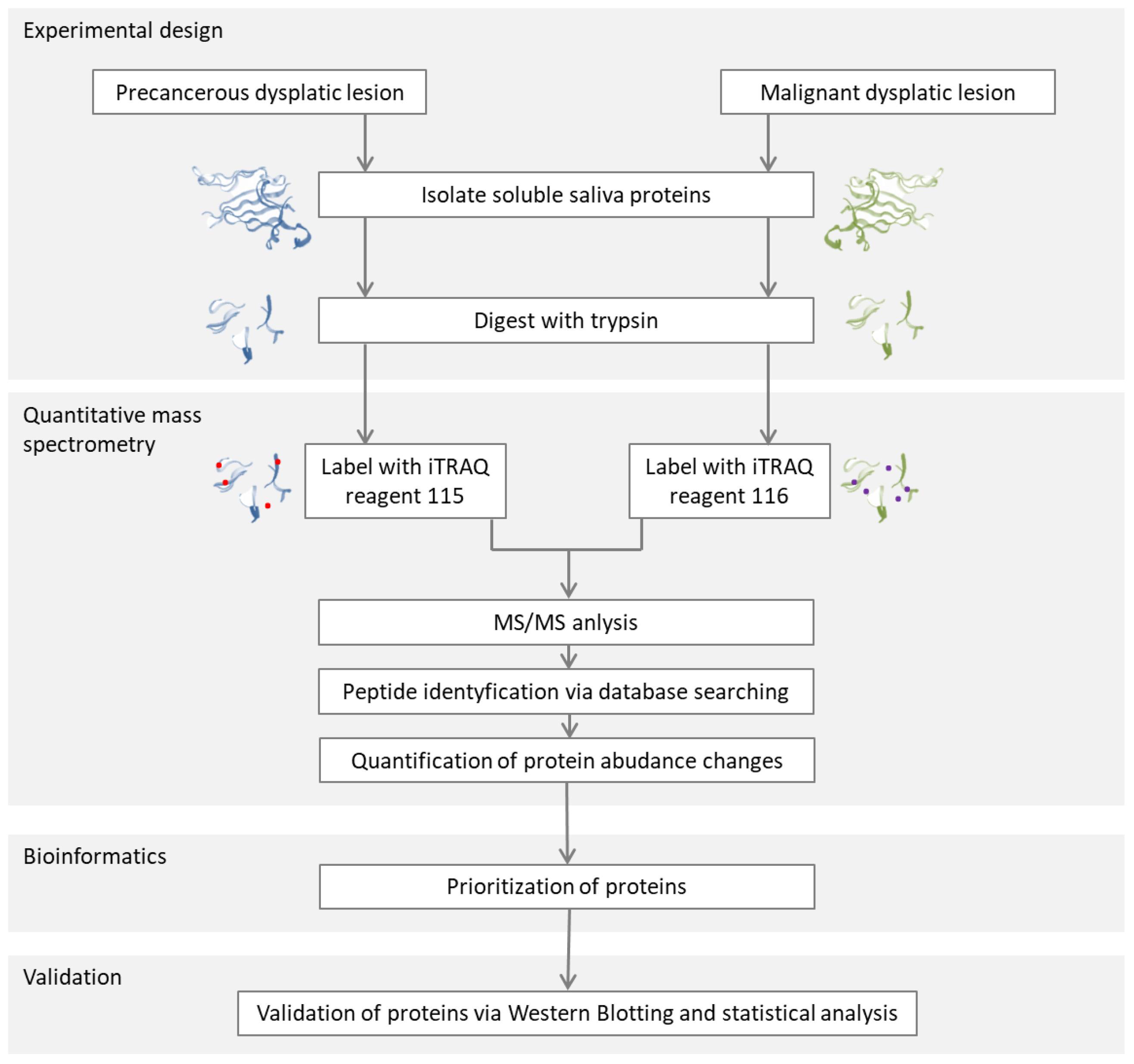
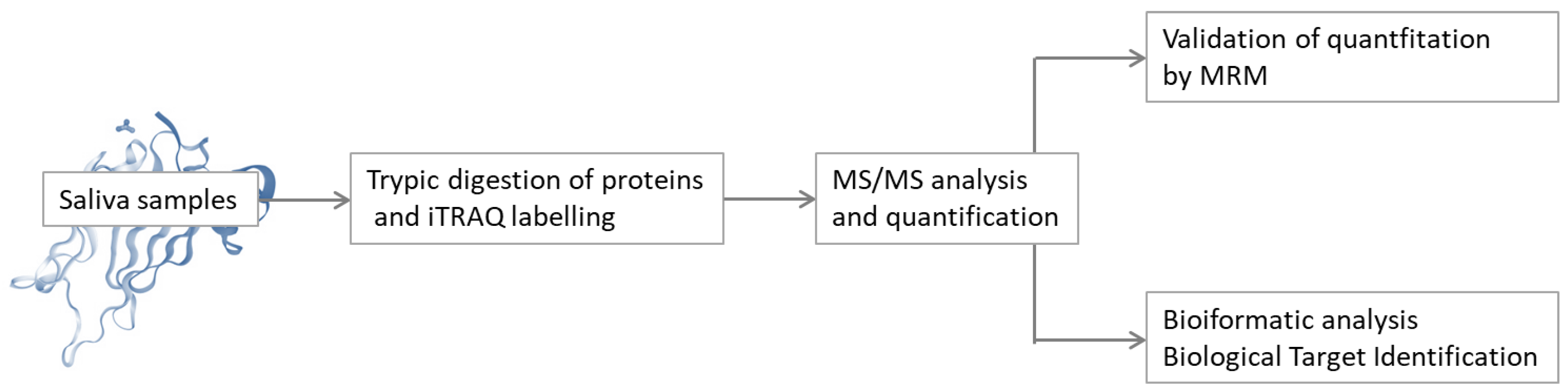
| Metabolite | Analytical Technique | Quantitative Analysis | Literature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cortisol | LC-MS/MS | Internal standard cortisol-d4 | [51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60] |
| p-cresol sulphate and indoxyl sulphate | LC-MS/MS | p-cresol sulphate-d7 and indoxyl sulphate-d4 | [61] |
| Steroids | LC-MS/MS (with multiple reaction monitoring) | Internal standard | [63] |
| Creatinine | LC-MS/MS | Isotope-labelled internal standard creatinine-d3 and creatinine-d5 | [67,68,69,70] |
| Lacosamide | HPLC | internal standard | [71] |
| Levetiracetam | HPLC-MS/MS | Internal standard fluconazole | [72,73,74,75] |
| Armodafinil | LC-MS/MS | Internal standard armodafinil-d3 | [76,77] |
| Cyclosporine A | LC-MS/MS | Internal standard cyclosporine A-d3 | [79] |
| Carbamazepine and its metabolite | UHPLC | Internal standard chlordiazepoxide | [80] |
| sTRAIL | LC-MS/MS | Internal standard 15N-labelled hrTRAIL | [81] |
| Type of Study | Analytical Technique | Proteolysis | Database | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global analysis | Shotgun proteomics, 2D-GE-MS, LC-MS/MS | Trypsin Digestion | MASCOT and Pro ID program | Hu et al. [92] |
| Proteomic profiling of the saliva of women | HCIC MS (MudPIT), Western blot | Trypsin Digestion | EBI International Protein Index | Ambatipudi et al. [144] |
| Phosphoproteins identification | LC-ESI-MS/MS | Trypsin Digestion | Uniprot, Swiss-Prot, TreMBL, PIR | Salih et al. [146] |
| Proteins identification | Top-down LC-MS/MS | - | official_human_TD, UniProt FASTA. | Wu et al. [147] |
| Human and bacteria proteins identification | LC-MS, shotgun | Lysis buffer (1 % sodium dodecyl carbonate (v/v), 10 mM tris (2-carboxyethyl) phosphine, 40 mM 2-chloroacetamide, 100 mM Tris buffer pH 8.5), Trypsin Digestion | UniProt, HMP | Grassl et al. [149] |
| Malignant changes | MS, bioinformatics, Western blotting | Trypsin Digestion | Non-redundant human protein sequence database | de Jong et al. [150] |
| Gastric cancer biomarkers identification | TMT, LC-MS/MS, ELISA | Trypsin Digestion | IPI human database. | Xiao et al. [151] |
| Fibroadenoma or infiltrative ductal carcinoma malignant | LC-MS | Trypsin Digestion | MSDB database | Delmonico et al. [152] |
| Oral cancer biomarkers identification | LC-MS/MS, | Lysis buffer | UniProt, Mascot | Ishikawa et al. [155] |
| Proteome characterisation in periodontitis and gingivitis | nanoLC-1D, shotgun LC-MS, statistical analysis, SRM | Trypsin Digestion | In-house-built database | Bostanci et al. [156] |
| Type 1 diabetes | labelling with iTRAQ, LC-MS, LC-MS/MS, MRM, bioinformatics | Trypsin Digestion | UniProt Fasta | Pappa et al. [157] |
| Type 2 diabetes | 2D-LC-MS/MS | - | Swiss-Prot, TrEmbl | Rao et al. [158] |
| Characterisation of salivary proteome during pregnancy | LC-MS/MS, SWATH-MS, LC-MRM | Trypsin Digestion | UniProt | Dey et al. [86] |
| Sjögren’s syndrome | LC-MS, bioinformatics | Trypsin Digestion | UniProt, PRIDE, STRING | Das et al. [162] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grocholska, P.; Kowalska, M.; Bąchor, R. Qualitative and Quantitative Mass Spectrometry in Salivary Metabolomics and Proteomics. Metabolites 2023, 13, 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020155
Grocholska P, Kowalska M, Bąchor R. Qualitative and Quantitative Mass Spectrometry in Salivary Metabolomics and Proteomics. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):155. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020155
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrocholska, Paulina, Marta Kowalska, and Remigiusz Bąchor. 2023. "Qualitative and Quantitative Mass Spectrometry in Salivary Metabolomics and Proteomics" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020155
APA StyleGrocholska, P., Kowalska, M., & Bąchor, R. (2023). Qualitative and Quantitative Mass Spectrometry in Salivary Metabolomics and Proteomics. Metabolites, 13(2), 155. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020155







