Effect of Methionine Hydroxy Analog on Hu Sheep Digestibility, Rumen Fermentation, and Rumen Microbial Community In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates
2.2. Experimental Design and In Vitro Fermentation
2.3. In Vitro Dry Matter Digestibility, Amino Acid Concentration, and Fermentation Parameters
2.4. DNA Extraction and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Changes in Fermentation Parameters
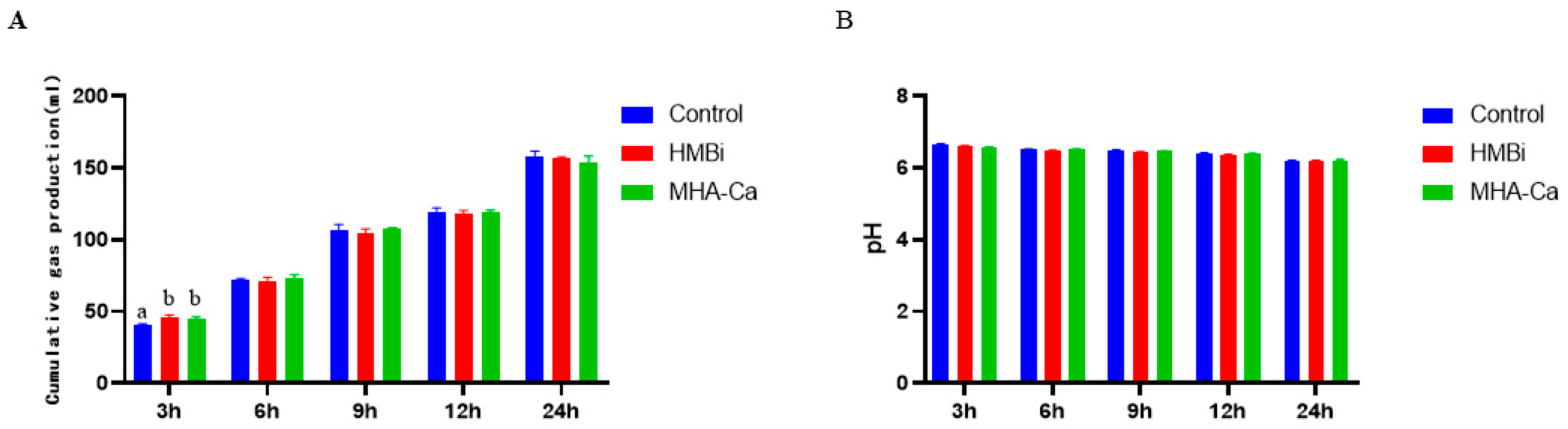
3.2. Effect of Methionine Hydroxy Analog on In Vitro Fermentation Cumulative Gas Production and pH
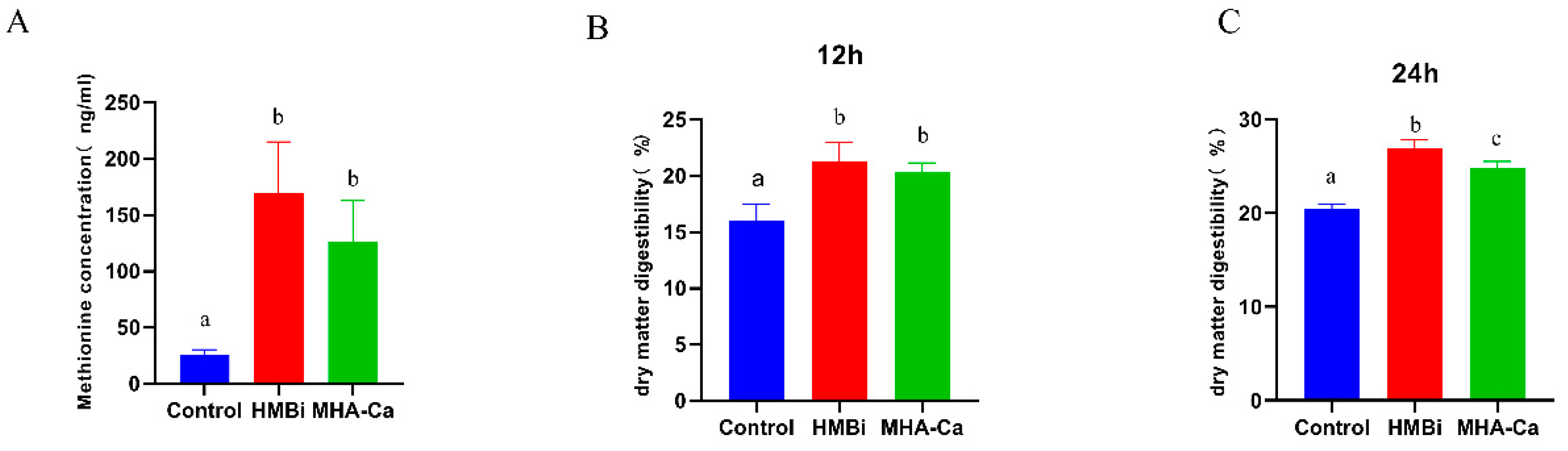
3.3. Changes in Dry Matter Digestibility and Methionine Concentration
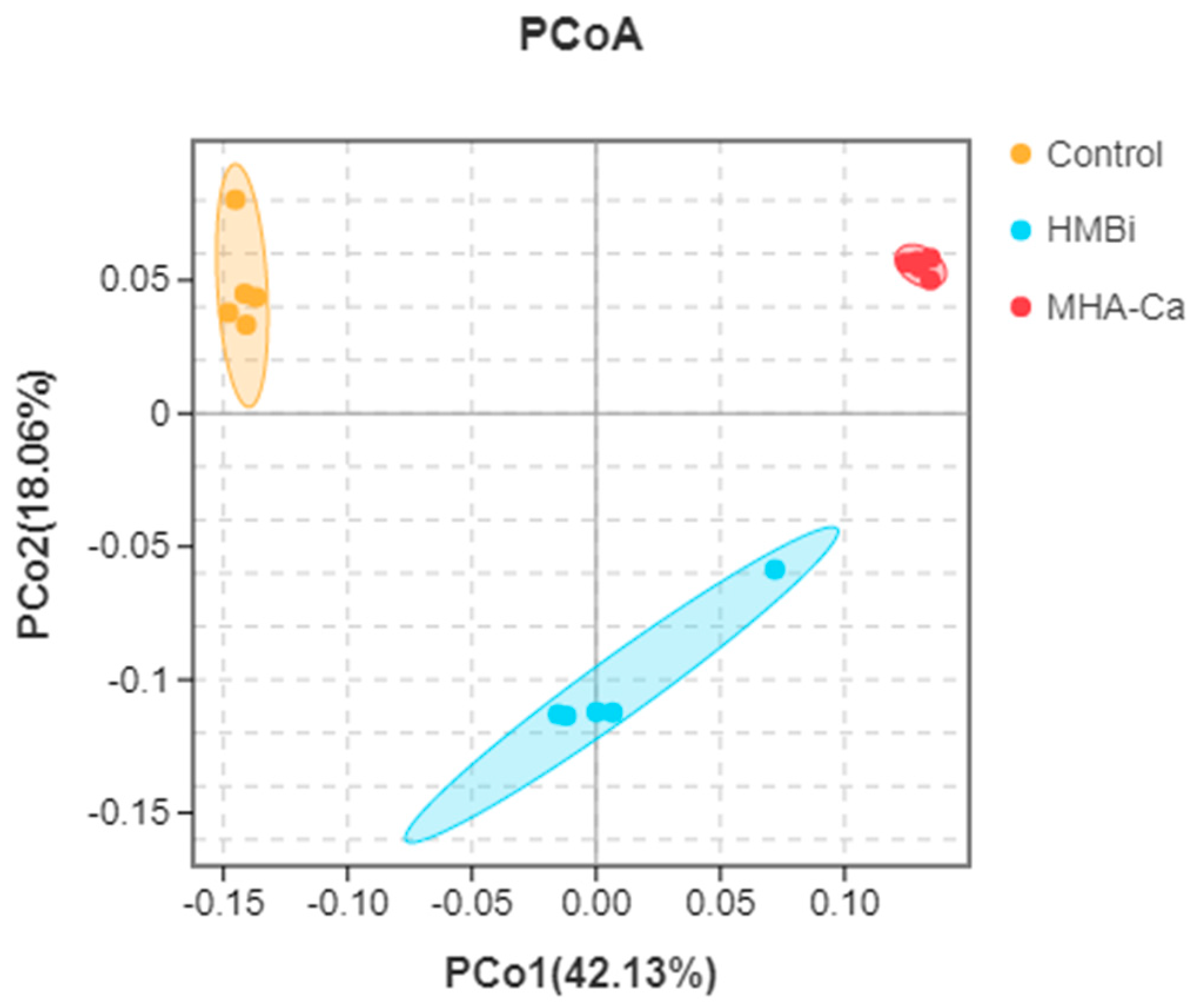
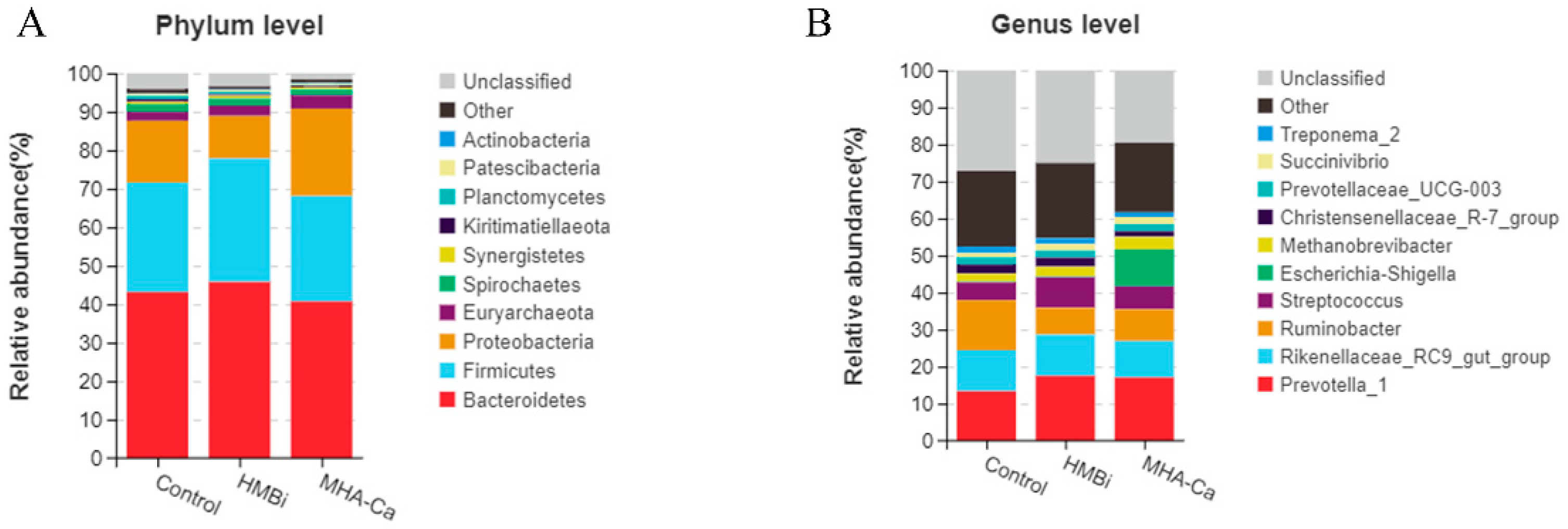
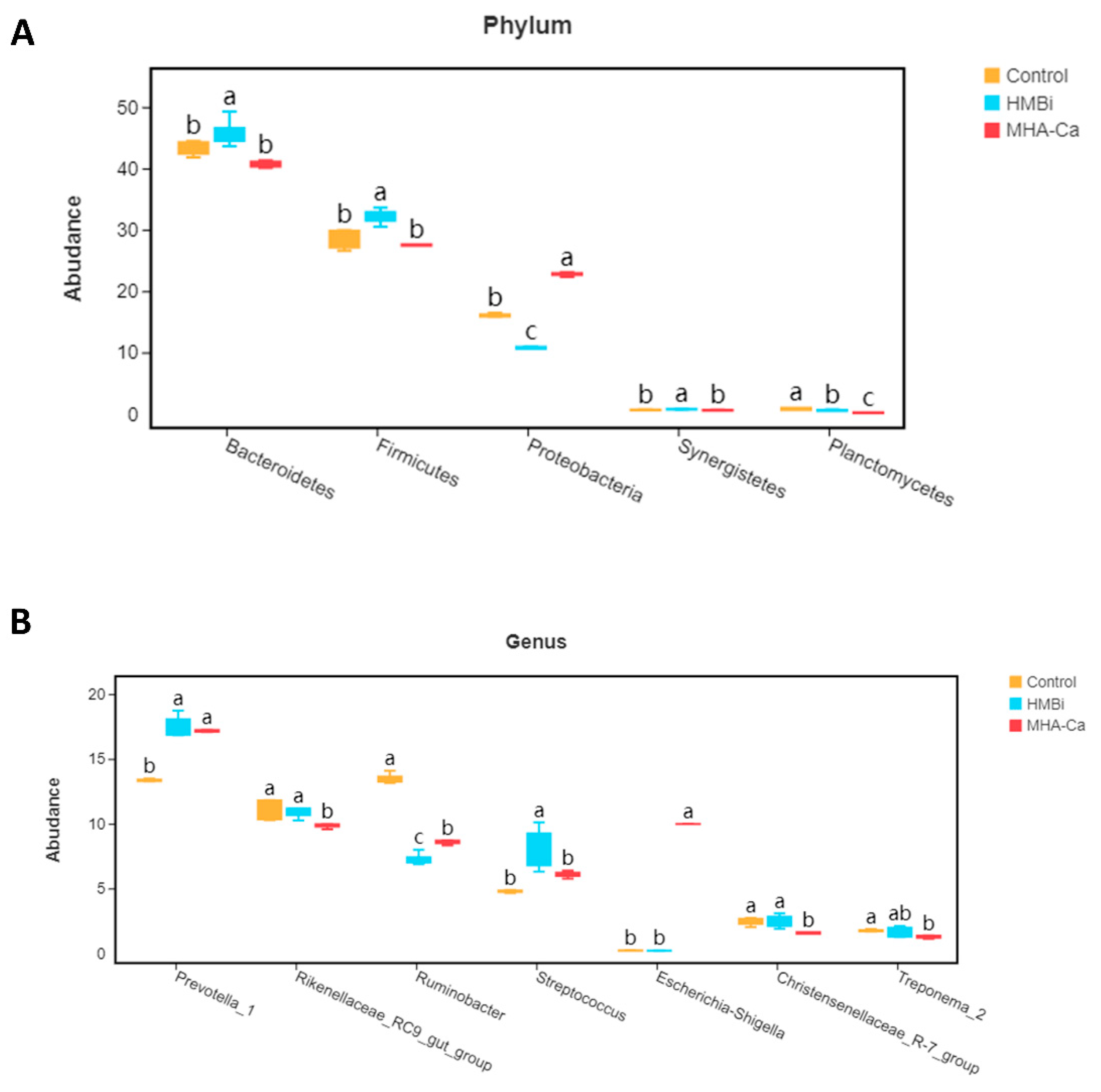
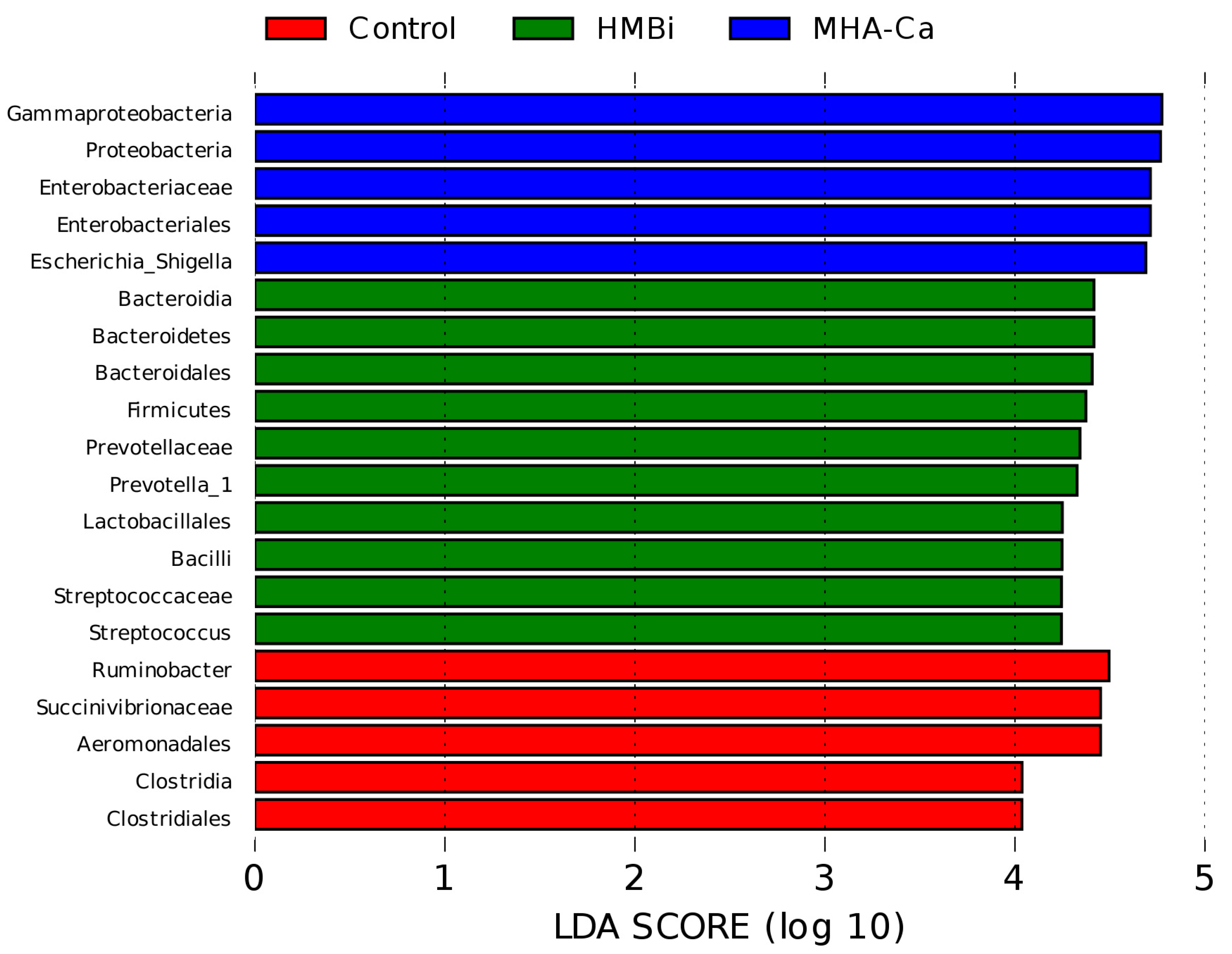
3.4. Alteration in the Composition of Rumen Bacterial Community
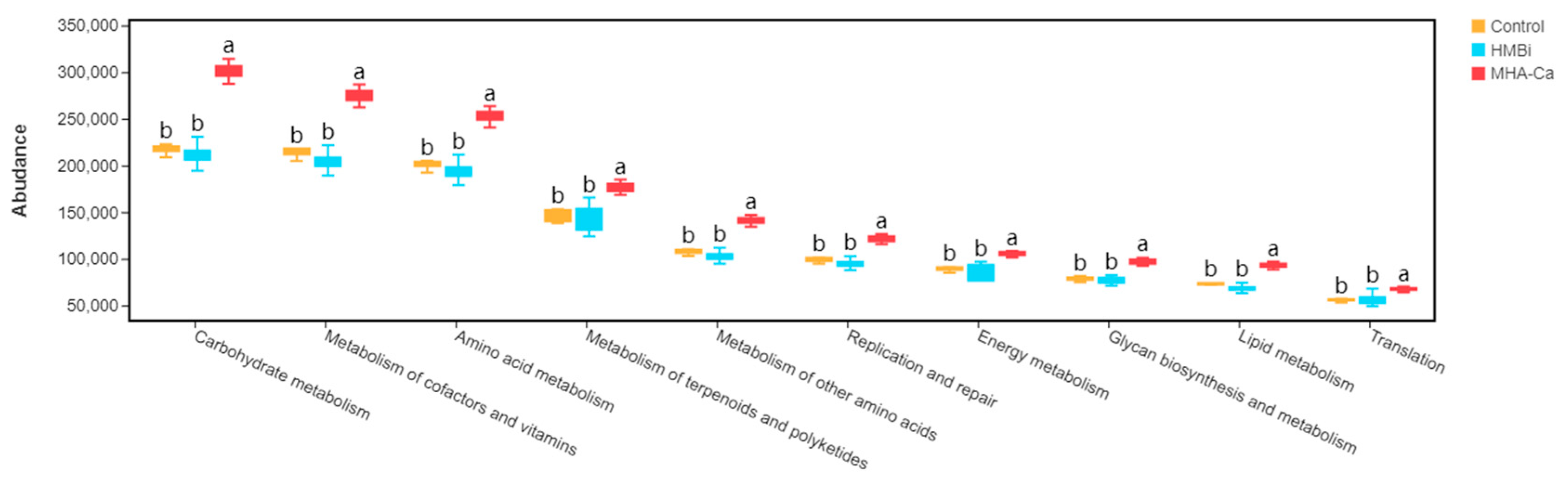
3.5. Predicted Functions of Ruminal Bacterial Microbiota
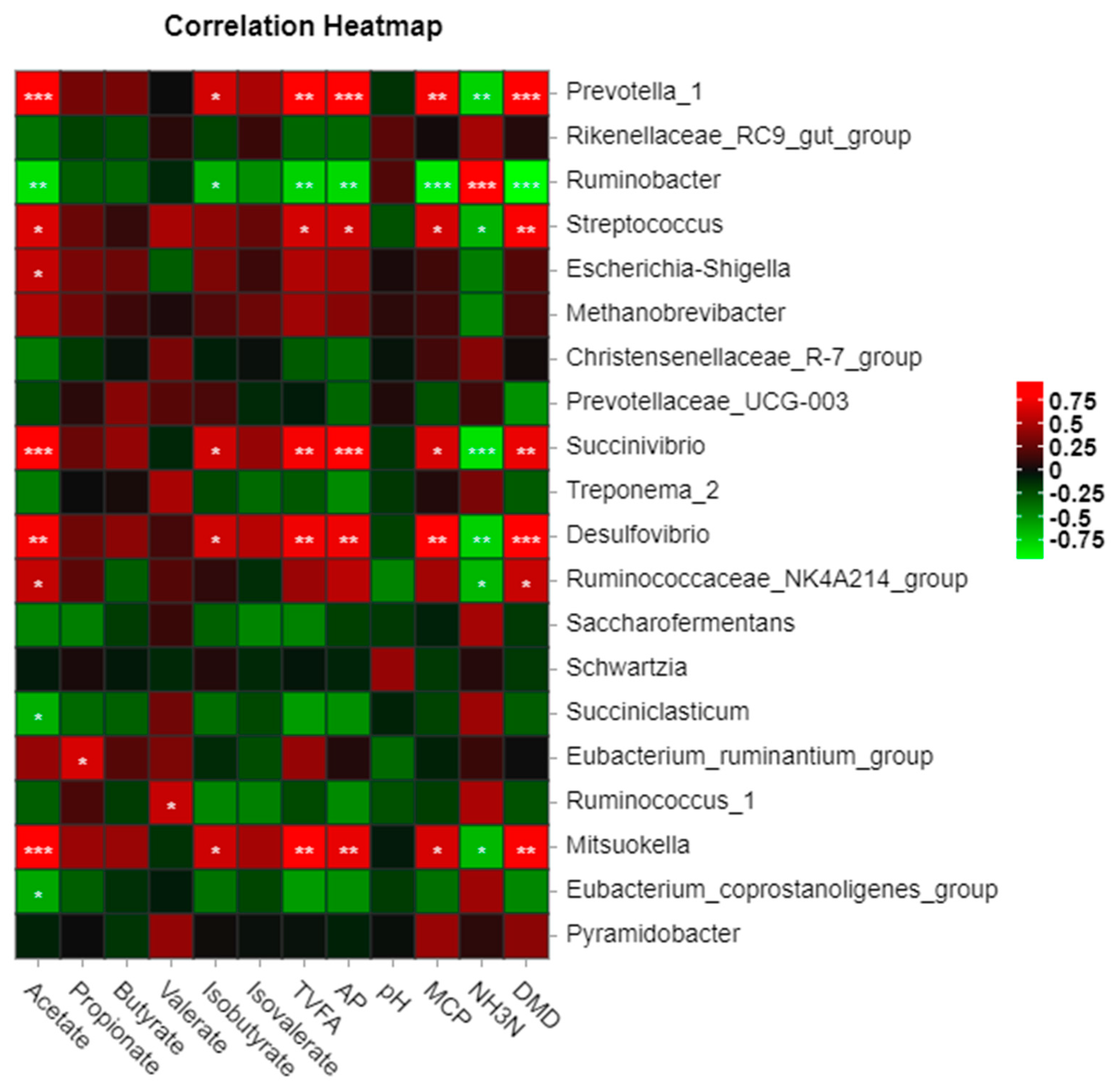
3.6. Interaction of Rumen Microorganisms with In Vitro Fermentation Parameters and Digestibility
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of MHA on Gas Production, Dry Matter Digestibility, and Amino Acid Concentration
4.2. Rumen Fermentation Characteristics
4.3. Rumen Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merchen, N.R.; Titgemeyer, E.C. Manipulation of amino acid supply to the growing ruminant. J. Anim. Sci. 1992, 70, 3238–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atasoglu, C.; Guliye, A.Y.; Wallace, R.J. Use of stable isotopes to measure de novo synthesis and turnover of amino acid-c and -n in mixed micro-organisms from the sheep rumen in vitro. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 91, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kišidayová, S.; Pristaš, P.; Zimovčáková, M.; Blanár Wencelová, M.; Homol’ová, L.; Mihaliková, K.; Čobanová, K.; Grešáková, Ľ.; Váradyová, Z. The effects of high dose of two manganese supplements (organic and inorganic) on the rumen microbial ecosystem. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Awadasseid, A.; Zhou, K.; Wang, X.; Shen, C.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, M.; Zhang, W. A 1,10-phenanthroline derivative selectively targeting telomeric g-quadruplex induces cytoprotective autophagy, causing apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. Life Sci. 2021, 287, 120095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, R.G.; Stern, M.D.; Otterby, D.E.; Linn, J.G. Influence of methionine hydroxy analog and dl-methionine on rumen protozoa and volatile fatty acids. J. Dairy Sci. 1985, 68, 3055–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molano, R.A.; Saito, A.; Luchini, D.N.; Van Amburgh, M.E. Effects of rumen-protected methionine or methionine analogs in starter on plasma metabolites, growth, and efficiency of holstein calves from 14 to 91 d of age. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10136–10151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, A.; Stern, M.D. Measuring resistance to ruminal degradation and bioavailability of ruminally protected methionine. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2000, 84, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, S.; Liu, C.; Lu, L.; Cui, Y.; Shi, C.; Chen, Z.; et al. 2-hydroxy-4-(methylthio) butanoic acid isopropyl ester supplementation altered ruminal and cecal bacterial composition and improved growth performance of finishing beef cattle. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 833881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.Q.; Huyen, T.T.; Lee, J.W.; Ramos, S.H.; Htoo, J.K.; Kinh, V.; Lindemann, M.D. Bioavailability of the calcium salt of dl-methionine hydroxy analog compared with dl-methionine for nitrogen retention and the preference of nursery pigs for diets based on the 2 forms of methionine. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 98, skaa349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, K.M.; Rode, L.M.; Knight, C.D.; Vázquez-Añón, M. Rumen degradation and availability of various amounts of liquid methionine hydroxy analog in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 930–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salsbury, R.L.; Marvil, D.K.; Woodmansee, C.W.; Haenlein, G.F. Utilization of methionine and methionine hydroxy analog by rumen microorganisms in vitro. J. Dairy Sci. 1971, 54, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fowler, C.M.; Plank, J.E.; Devillard, E.; Bequette, B.J.; Firkins, J.L. Assessing the ruminal action of the isopropyl ester of 2-hydroxy-4-(methylthio) butanoic acid in continuous and batch cultures of mixed ruminal microbes. J. Dairy Sci. 2015, 98, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Mirande, C.; Morgavi, D.P.; Forano, E.; Devillard, E.; Mosoni, P. Methionine analogues hmb and hmbi increase the abundance of cellulolytic bacterial representatives in the rumen of cattle with no direct effects on fibre degradation. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2013, 182, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C.J.R.; Fernando, S.C.; Anderson, C.L.; Aluthge, N.D.; Castillo-Lopez, E.; Zanton, G.I.; Kononoff, P.J. The effects of 2-hydroxy-4-methylthio-butanoic acid supplementation on the rumen microbial population and duodenal flow of microbial nitrogen. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 10161–10174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, K.M.; Rode, L.M.; Knight, C.D.; McCullough, P.R. Ruminal escape, gastrointestinal absorption, and response of serum methionine to supplementation of liquid methionine hydroxy analog in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noftsger, S.; St-Pierre, N.R.; Sylvester, J.T. Determination of rumen degradability and ruminal effects of three sources of methionine in lactating cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 223–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Jia, M.; Fang, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y. Effects of eucalyptus oil and anise oil supplementation on rumen fermentation characteristics, methane emission, and digestibility in sheep. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar]
- Malmuthuge, N.; Griebel, P.J.; Guan, L.L. The gut microbiome and its potential role in the development and function of newborn calf gastrointestinal tract. Front. Vet. Sci. 2015, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.; Yano, R.; Fujimori, M.; Kand, D.; Hanada, M.; Nishida, T.; Fukuma, N. Impacts of mootral on methane production, rumen fermentation, and microbial community in an in vitro study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 623817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.W.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zou, C.; Li, L.; Liang, X.; Wei, S.; Lin, B. Ruminal fermentation and microbial community differently influenced by four typical subtropical forages in vitro. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 4, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Cai, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guan, L.L.; Qi, D. Effects of thymol supplementation on goat rumen fermentation and rumen microbiota in vitro. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liang, G.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; Yuan, Y.; Jiao, P. The gas production, ruminal fermentation parameters, and microbiota in response to clostridium butyricum supplementation on in vitro varying with media ph levels. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 960623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, S.; Huo, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, W. In vitro effects of sodium bicarbonate buffer on rumen fermentation, levels of lipopolysaccharide and biogenic amine, and composition of rumen microbiota. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, K.H. Estimation of the energetic feed value obtained from chemical analysis and in vitro gas production using rumen fluid. Anim. Res. Dev. 1988, 28, 7–55. [Google Scholar]
- Singer, E.; Bushnell, B.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Bowman, B.; Bowers, R.M.; Levy, A.; Gies, E.A.; Cheng, J.F.; Copeland, A.; Klenk, H.P.; et al. High-resolution phylogenetic microbial community profiling. ISME J. 2016, 10, 2020–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one fastq preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. Flash: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. Qiime allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M.S.; Medeiros, M.C.I.; Crampton, L.H.; Reed, F.A. Wild gut microbiomes reveal individuals, species, and location as drivers of variation in two critically endangered hawaiian honeycreepers. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aßhauer, K.P.; Wemheuer, B.; Daniel, R.; Meinicke, P. Tax4fun: Predicting functional profiles from metagenomic 16s rrna data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2882–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16s rrna marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graulet, B.; Richard, C.; Robert, J.C. Methionine availability in plasma of dairy cows supplemented with methionine hydroxy analog isopropyl ester. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 3640–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.B.; Jiang, S.Z.; Yang, W.R.; Yu, L.L.; Lin, G.M. Study on effects of methionine administrated through the rumenon amino acid of microorganism of the steers. Acta Vet. Et Zootech. Sin. 2004, 35, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Baghbanzadeh-Nobari, B.; Taghizadeh, A.; Khorvash, M.; Parnian-Khajehdizaj, F.; Maloney, S.K.; Hashemzadeh-Cigari, F.; Ghaffari, A.H. Digestibility, ruminal fermentation, blood metabolites and antioxidant status in ewes supplemented with dl-methionine or hydroxy-4(methylthio) butanoic acid isopropyl ester. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 101, e266–e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Jiao, T. Effect of oregano oil and cobalt lactate on sheep in vitro digestibility, fermentation characteristics and rumen microbial community. Animals 2022, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, F.M.; Williams, P.; Losa, R.; Wallace, R.J.; Beever, D.A.; Newbold, C.J. Effects of essential oils on ruminal microorganisms and their protein metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 5011–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqiang, Z.; Ning, J.; Zhongsheng, Y.; Lian, N. Effects of protective methionine and slow—Release urea on rumen fermentation parameters and fiber degradation rate in vitro. Heilongjiang Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2018, 21, 15–21+27. [Google Scholar]
- Shuai, Z.; Zhaoyu, H.; Junbiao, L.; Qun, W.A. Influence of 2-hydroxy-4-(methylthio) butanoic acid isopropyl ester on rumen fermentation parameters in vitro. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 24, 1105–1109. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Chen, A.; Zhang, B.; Kong, P.; Liu, C.; Zhao, J. Rumen degradability and post-ruminal digestion of dry matter, nitrogen and amino acids of three protein supplements. Asian-Australas J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 28, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H. Effects of N-hydroxymethyl-DL-methionine-Ca(N-HMM-Ca) on Ruminal Fermentation and Nutrient Digestion and Metabolism in Sheep. Master’s Thesis, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science, Beijing, China, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jianfei, W.; Mengzhi, W.; Feng, C. Effects of rumen protected methionine on in vitro ruminal fermentation and performance of lactating dairy cows. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 27, 2248–2255. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H.; Fan, Z.; Yang, F.; Wright, A.D.; Li, G. Bacteria and methanogens differ along the gastrointestinal tract of chinese roe deer (capreolus pygargus). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. Parallel functional changes in the digestive rnases of ruminants and colobines by divergent amino acid substitutions. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1310–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svartström, O.; Alneberg, J.; Terrapon, N.; Lombard, V.; de Bruijn, I.; Malmsten, J.; Dalin, A.M.; El Muller, E.; Shah, P.; Wilmes, P.; et al. Ninety-nine de novo assembled genomes from the moose (alces alces) rumen microbiome provide new insights into microbial plant biomass degradation. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2538–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Q.F.; Wu, A.Q. Effects of digestion and metabolism of huai goats added dl-methionine in rumen. China Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2007, 34, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, Y.-H. Effects of Free Methionine and Lysine on in vitro Fermentation and in vivo Performance and Ruminal Fermentation of Late Lactation Holstein Cows. Master’s Thesis, Louisiana State University and Agricultural and Mechanical College, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Noftsger, S.M.; St-Pierre, N.R.; Karnati, S.K.; Firkins, J.L. Effects of 2-hydroxy-4-(methylthio) butanoic acid (hmb) on microbial growth in continuous culture. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2629–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, A.K.; Yu, Z. Effects of essential oils on methane production and fermentation by, and abundance and diversity of, rumen microbial populations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 4271–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.X.; Sun, Y.D.; Liu, X.W.; Sun, G.Q. Effects of combined supplementation of rumen-protected methionine cinnamic aldehyde on lactation performance and nitrogen excretion of dairy cows. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 29, 3202–3210. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.X.; Sun, Y.D.; Liu, X.W.; Sun, G.Q. Effects of rumen protected methionine on ruminal microbial protein production, milk performance and nitrogen excretion of dairy cows. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2017, 29, 1759–1766. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.X.; Teng, L.B.; Liu, X.; Sun, G.Q. Effects of rumen-protected methionine and cinnamic aldehyde on ruminal microbial protein production and nutrient digestibility of dairy cows. Chin. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 53, 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H.; Guo, C.; Sun, D.; Seddik, H.E.; Mao, S. The ruminal microbiome and metabolome alterations associated with diet-induced milk fat depression in dairy cows. Metabolites 2019, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Cao, H. Effects of certain amino acids-removal on the rumen mixed microbes and fermentation in vitro. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2008, 41, 2136–2142. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Irving, B.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Plastow, G.; Guan, L.L. Host genetics influence the rumen microbiota and heritable rumen microbial features associate with feed efficiency in cattle. Microbiome 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, P.; Guivernau, M.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X.; Cardona, L. Fast acquisition of a polysaccharide fermenting gut microbiome by juvenile green turtles chelonia mydas after settlement in coastal habitats. Microbiome 2018, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhao, D.; Xu, C.; Sun, H.; Yang, Q.; Wei, Q.; Si, H.; Wang, K.; Zhang, T. Effect of methionine supplementation on serum metabolism and the rumen bacterial community of sika deer (cervus nippon). Animals 2022, 12, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Ingredients | Content (%) | Chemical Composition | Content |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 30.8 | DM(%) | 87.19 |
| Soybean meal | 5.8 | ME/(MJ/kg) | 16.91 |
| Peanut meal | 3.0 | CP(%) | 14.61 |
| Bean straw | 24.0 | NDF(%) | 49.71 |
| Corn germ meal | 15.0 | ADF(%) | 13.04 |
| Rice husk | 5.0 | EE(%) | 4.71 |
| Wheat middling | 2.0 | Ash(%) | 10.06 |
| Molasses | 1.0 | Ca(%) | 1.08 |
| Malt root | 6.0 | P(%) | 0.62 |
| NH4Cl | 0.4 | ||
| Limestone | 2.0 | ||
| Premix | 5.0 | ||
| Total | 100 |
| Item | CON | HMBi | MHA-Ca | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH3N (mg/dL) | 10.18 a | 7.99 b | 7.96 b | 0.37 | 0.004 |
| MCP (mg/mL) | 0.46 b | 0.59 a | 0.55 a | 0.01 | 0.002 |
| Total VFA (mmol/L) | 37.61 b | 44.69 a | 45.99 a | 1.34 | 0.006 |
| Acetate | 21.56 b | 26.61 a | 27.86 a | 0.91 | 0.001 |
| Propionate | 9.65 | 10.01 | 10.36 | 0.22 | 0.482 |
| Butyrate | 1.31 | 1.53 | 1.66 | 0.12 | 0.528 |
| Valerate | 2.99 | 3.23 | 2.80 | 0.14 | 0.530 |
| Isobutyrate | 1.50 | 2.54 | 2.57 | 0.23 | 0.083 |
| Isovalerate | 0.58 | 0.77 | 0.73 | 0.05 | 0.265 |
| Acetate/propionate (A:P) | 2.24 b | 2.66 a | 2.69 a | 0.07 | 0.004 |
| Index Type | Control | HMBi | MHA-Ca | SEM | p-Valve |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed OTU | 2173.6 a | 1887.4 b | 1389.8 c | 95.4 | 0.04 |
| Shannon | 7.53 a | 7.31 a | 6.65 b | 0.11 | 0.06 |
| Simpson | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.01 | 0.06 |
| Chao1 | 2232.4 a | 1950.6 b | 1458.8 c | 93.9 | 0.04 |
| ACE | 2309.5 a | 2022.9 b | 1517.6 c | 95.9 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zeng, H.; Wang, C.; Han, Z. Effect of Methionine Hydroxy Analog on Hu Sheep Digestibility, Rumen Fermentation, and Rumen Microbial Community In Vitro. Metabolites 2023, 13, 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020169
Li S, Zeng H, Wang C, Han Z. Effect of Methionine Hydroxy Analog on Hu Sheep Digestibility, Rumen Fermentation, and Rumen Microbial Community In Vitro. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):169. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020169
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shujie, Hanfang Zeng, Changjian Wang, and Zhaoyu Han. 2023. "Effect of Methionine Hydroxy Analog on Hu Sheep Digestibility, Rumen Fermentation, and Rumen Microbial Community In Vitro" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020169
APA StyleLi, S., Zeng, H., Wang, C., & Han, Z. (2023). Effect of Methionine Hydroxy Analog on Hu Sheep Digestibility, Rumen Fermentation, and Rumen Microbial Community In Vitro. Metabolites, 13(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020169





