Effects of Cadmium on Liver Function and Its Metabolomics Profile in the Guizhou Black Goat
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Animals, Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Chemicals
2.2. Animal Handing and Sample Collection
2.3. Metabolomics Analysis in the Liver
2.3.1. Liver Preparation for Metabolomics
2.3.2. Metabolomics Data Capture
2.3.3. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
2.3.4. Metabolites Identification and Pathway Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
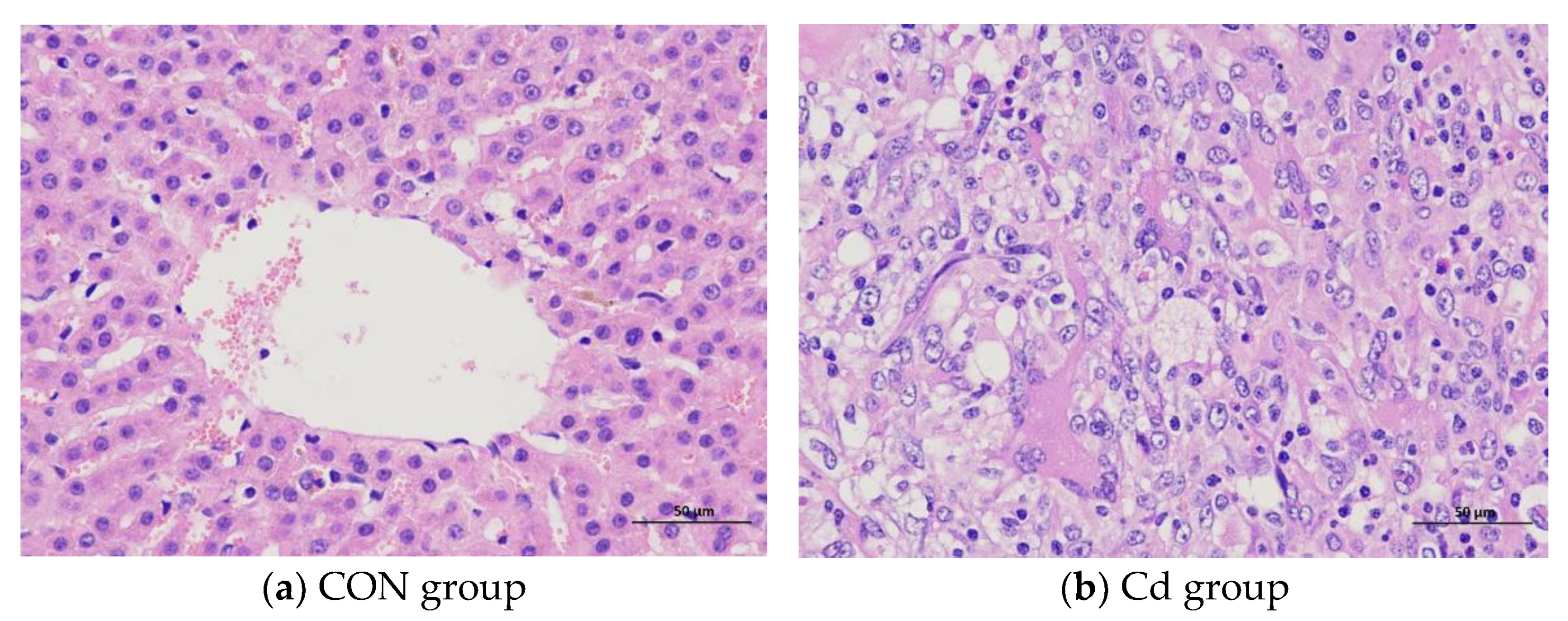
3.1. The Effect of Cd on the Pathological Structure in the Liver of the Guizhou Black Goat
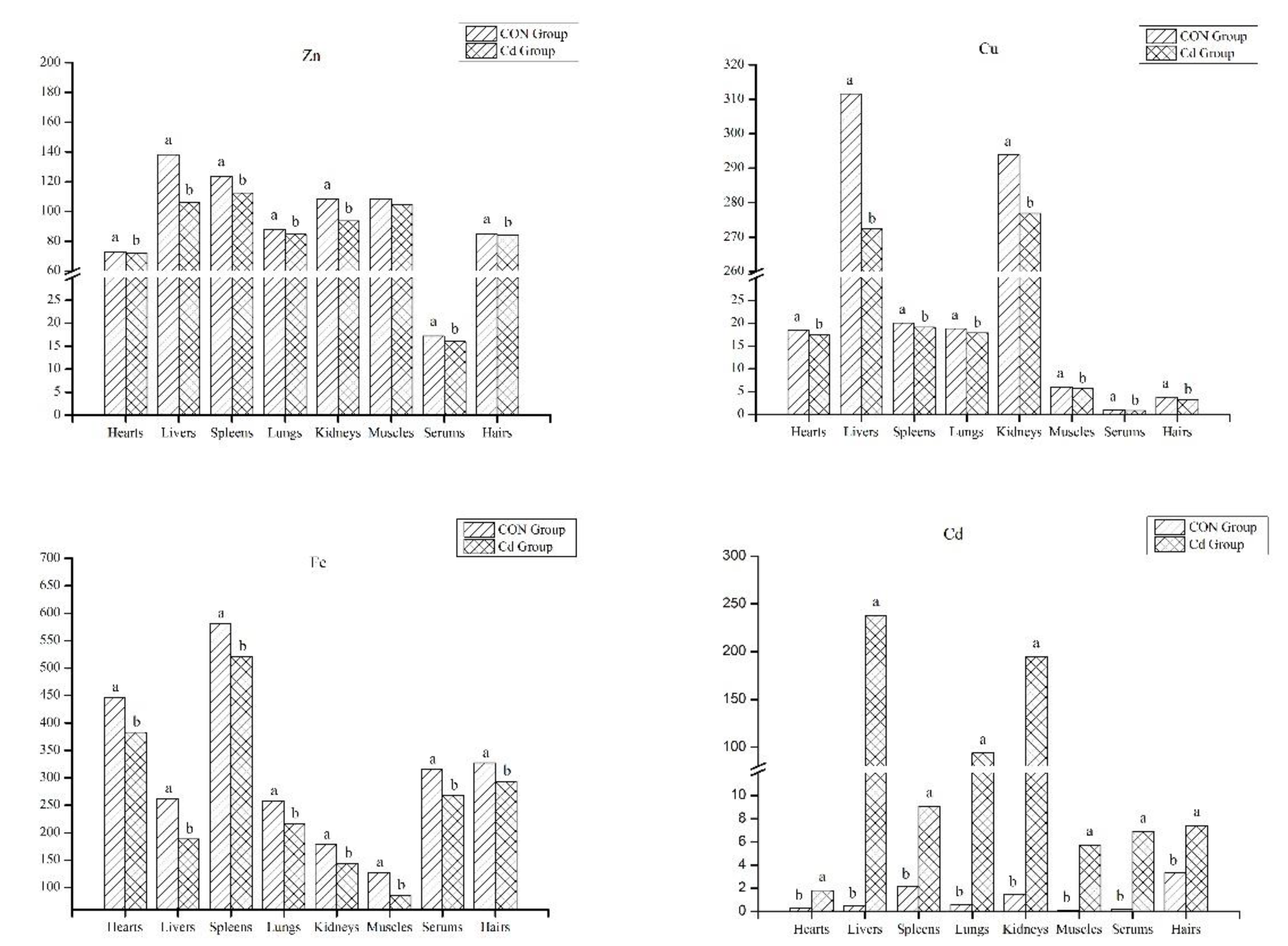
3.2. The Analysis of Mineral Contents in the Organ and Tissue
3.3. The Effect of Cd on the Immune Function of the Goat Serum and Liver
3.4. Liver Metabolic Responses in the Goat to Cd Exposure
4. Discussion
4.1. Mineral Accumulation in the Goat Offal and Tissue and Liver Immune Function
4.2. Alteration of Energy and Lipid Metabolism Associated with Cd Exposures
4.3. Alteration of Amino Acid Metabolism Associated with Cd Exposures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renu, K.; Chakraborty, R.; Myakala, H.; Koti, R.; Famurewa, A.C.; Madhyastha, H.; Vellingiri, B.; George, A.; Gopalakrishnan, A.V. Molecular mechanism of heavy metals (Lead, Chromium, Arsenic, Mercury, Nickel and Cadmium)—Induced hepatotoxicity—A review. Chemosphere 2021, 271, 129735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Niño, W.R.; Pedraza-Chaverrí, J. Protective effect of curcumin against heavy metals-induced liver damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 69, 182–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N.; Yang, Y.J.; Liu, X.W.; Li, S.H.; Qin, Z.; Li, J.Y. Plasma metabonomics and proteomics studies on the anti-thrombosis mechanism of aspirin eugenol ester in rat tail thrombosis model. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, 103631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.X.; Zhu, J.Y.; Li, K.; Gao, X.; Hu, C.; Cheng, J.A.; Ye, G.Y. A proteomic analysis of larval midguts of Boettcherisca peregrina in response to cadmium exposure. Bull. Ins. 2013, 66, 225–229. [Google Scholar]
- Beyoğlu, D.; Idle, J.R. Metabolomic and lipidomic biomarkers for premalignant liver disease diagnosis and therapy. Metabolites 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Jia, S.Q.; Liu, Y.J.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, S.Q.; Bo, L.; Zhao, X.J.; Sun, C.H. Metabonomics analysis of kidneys in rats administered with chronic low-dose cadmium by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2019, 39, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, M.Y.; Bo, L.; Li, S.Q.; Hu, L.Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Sun, C.H. Metabolomic analysis of the toxic effect of chronic exposure of cadmium on rat urine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 3765–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.; Trygg, J.; Wold, S. CV-ANOVA for significance testing of PLS and OPLS® models. J. Chem. 2008, 22, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Liu, H.W.; He, J.; Shen, X.Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, Y.C. The effects of oral administration of molybdenum fertilizers on immune function of Nanjiang brown goat grazing on natural pastures contaminated by mixed heavy metal. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 200, 2750–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.P.; Ma, Z.; Li, W.F.; Cheng, X.F.; Hui, T.C. Toxicological study of cadmium on sheep. Acta Veter. Zoot. Sin. 1996, 27, 546–553. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.Y.; Chi, Y.K.; Xiong, K.N. The effect of heavy metal contamination on humans and animals in the vicinity of a zinc smelting facility. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0207423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Shen, X.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Luo, L.; Wang, Y.C. Molybdenum fertilization improved antioxidant capacity of grazing Nanjiang brown goat on copper-contaminated pasture. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 200, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.Y.; Huo, B.; Li, Y.F.; Song, C.J.; Wu, T.; He, J. Response of the critically endangered Przewalski’s gazelle (Procapra przewalskii) to selenium deprived environment. J. Proteom. 2021, 241, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kippler, M.; Nermell, B.; Hamadani, J.; Tofail, F.; Moore, S.; Vahter, M. Burden of cadmium in early childhood: Longitudinal assessment of urinary cadmium in rural Bangladesh. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 198, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalups, R.K. Evidence for basolateral uptake of cadmium in the kidneys of rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 2000, 164, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoica, A.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Martin, M.B. Activation of estrogen receptor-α by the heavy metal cadmium. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 14, 545–553. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.W.A.; Zhang, S.; Ishfaq, M.; Tang, Y.; Teng, X.H. PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway involvement in autophagy, mediated by miR-99a-3p and energy metabolism in ammonia exposed chicken bursal lymphocytes. Poul. Sci. 2021, 100, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, H.J.; Angiari, S. Metabolite transporters as regulators of immunity. Metabolites 2020, 10, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, R.Z.; Liu, H.W.; Sun, H.X. Effects of dietary Astra-galus polysaccharide and Astragalus membranaceus root supplementation on growth performance, rumen fermentation, immune responses, and antioxidant status of lambs. Anim. Feed Sci. Tech. 2012, 174, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Yu, J.S.; Yu, J.P.; Du, W. Effects of ampelopsis grossedentata flavonoids on serum biochemical indexes and immune function of piglets. China Anim. Husband. Vet. Med. 2016, 43, 1221–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Xie, T.; Yang, S.; Gao, M.; Yao, Y. Effects of subacute ruminal acidosis on plasma cytokine and hormone contents in dairy goats. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 27, 418–425. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.L.; Yang, S.J. Effect of Jiuweibaizhutang on serum levels of interleukin -1β and interleukin-10 in ulcerative colitis rats. China Med. Herald. 2013, 10, 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Michal, K.; Szabo, P.; Barbora, D.; Lukáš, L.; Hans-Joachim, G.; Hynek, S.; Jana, S.; Cestmír, V.; Jan, P.; Martin, C.; et al. Upregulation of IL-6, IL-8 and CXCL-1 production in dermal fibroblasts by normal/malignant epithelial cells in vitro: Immunohistochemical and transcriptomic analyses. Biol. Cell 2012, 104, 738–751. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.Z.; Dai, S.F.; Hua, J.L.; Hu, H.; Wang, S.J.; Wen, A.Y. Influence of dietary copper methionine concentrations on growth performance, digestibility of nutrients, serum lipid profiles, and immune defenses in broilers. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 191, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocquette, J.F.; Bauchart, D. Intestinal absorption, blood transport and hepatic and muscle metabolism of fatty acids in preruminant and ruminant animals. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 1999, 39, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial TCA cycle metabolites control physiology and disease. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, R.; Soni, S.; Houle, S.A. Negative energy balance induced by exercise or diet: Effects on visceral adipose tissue and liver fat. Nutrients 2020, 12, 891. [Google Scholar]
- Sears, D.D.; Hsiao, G.; Hsiao, A.; Yu, J.G.; Courtney, C.H.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Chapman, J.; Subramaniam, S. Mechanisms of human insulin resistance and thiazolidinedione-mediated insulin sensitization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 18745–18750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmad, M.I.; Ijaz, M.U.; Hussain, M.; Khan, I.A.; Mehmood, N.; Siddiqi, S.M.; Liu, C.C.; Zhao, D.; Xu, X.L.; Zhou, G.H.; et al. High fat diet incorporated with meat proteins changes biomarkers of lipid metabolism, antioxidant activities, and the serum metabolomic profile in Glrx1 (-/-) mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente, A.; Fenandez-Rey, E.; Seara, R.; Pérez-Lorenzo, M.; Esquifino, A.I. Alternate cadmium exposure differentially affects amino acid metabolism within the hypothalamus, median eminence, striatum and prefrontal cortex of male rats. Neurochem. Int. 2001, 39, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.M.; Bi, M.Y.; Yang, J.; Cai, J.Z.; Zhang, H.R.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, G.L.; Zhang, Z.W. Cadmium exposure triggers oxidative stress, necroptosis, Th1/Th2 imbalance and promotes inflammation through the TNF-alpha/NF-Kappa B pathway in swine small intestine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 421, 126704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Xu, Y.M.; Han, Q.; Yao, Y.C.; Xing, H.J.; Teng, X.H. Immunosuppression, oxidative stress, and glycometabolism disorder caused by cadmium in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.): Application of transcriptome analysis in risk assessment of environmental contaminant cadmium. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 366, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, M.; Arif, H.; Tabassum, B.; Arif, A.; Rehman, A.A.; Rehman, S.; Khanam, R.; Khan, B.; Hussain, A.; Barnawi, J.; et al. Protective effect of catharanthus roseus extract on cadmium-induced toxicity in albino rats: A putative mechanism of detoxification. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.H.; Li, F.N.; Li, Y.H.; Tang, Y.L.; Kong, X.F.; Feng, Z.M.; Anthony, T.G.; Watford, M.; Hou, Y.Q.; Wu, G.Y.; et al. The role of leucine and its metabolites in protein and energy metabolism. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

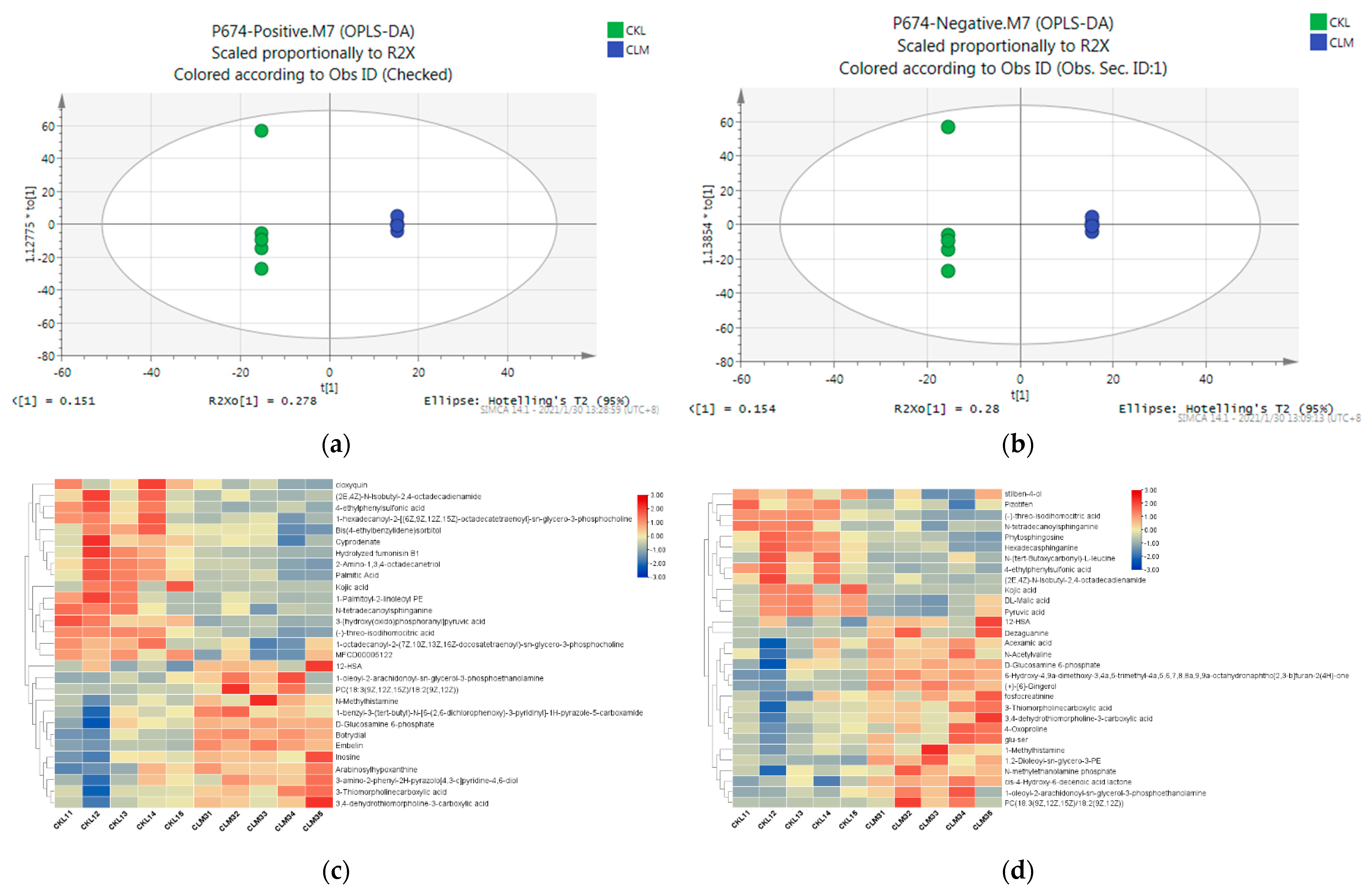

| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | Total | Pop Hit | p-Value_Adjusted |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| oas04931 | Insulin resistance | 12 | 19 | 0.000834 |
| oas00250 | Alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism | 12 | 28 | 0.00139 |
| oas04930 | Type II diabetes mellitus | 12 | 6 | 0.00179 |
| oas04911 | Insulin secretion | 12 | 12 | 0.00583 |
| oas04066 | HIF-1 signaling pathway | 12 | 15 | 0.00739 |
| oas00330 | Arginine and proline metabolism | 12 | 78 | 0.00878 |
| oas00020 | Citrate cycle (TCA cycle) | 12 | 20 | 0.00878 |
| oas04152 | AMPK signaling pathway | 12 | 22 | 0.00878 |
| oas00430 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 12 | 22 | 0.00878 |
| oas00290 | Valine, leucine, and isoleucine biosynthesis | 12 | 23 | 0.00878 |
| oas04922 | Glucagon signaling pathway | 12 | 26 | 0.0102 |
| oas00770 | Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 12 | 28 | 0.0106 |
| oas00010 | Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis | 12 | 31 | 0.0106 |
| oas00620 | Pyruvate metabolism | 12 | 31 | 0.0106 |
| oas00730 | Thiamine metabolism | 12 | 31 | 0.0106 |
| oas00030 | Pentose phosphate pathway | 12 | 35 | 0.0127 |
| oas05230 | Central carbon metabolism in cancer | 12 | 37 | 0.0133 |
| oas00650 | Butanoate metabolism | 12 | 42 | 0.0161 |
| oas00900 | Terpenoid backbone biosynthesis | 12 | 45 | 0.0175 |
| oas00340 | Histidine metabolism | 12 | 47 | 0.018 |
| oas00053 | Ascorbate and aldarate metabolism | 12 | 49 | 0.0185 |
| oas00260 | Glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism | 12 | 50 | 0.0185 |
| oas00564 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 12 | 52 | 0.0191 |
| oas00760 | Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism | 12 | 55 | 0.0195 |
| oas00040 | Pentose and glucuronate interconversions | 12 | 55 | 0.0195 |
| oas00440 | Phosphonate and phosphinate metabolism | 12 | 56 | 0.0195 |
| oas00360 | Phenylalanine metabolism | 12 | 60 | 0.0214 |
| oas00630 | Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | 12 | 62 | 0.0219 |
| oas00270 | Cysteine and methionine metabolism | 12 | 63 | 0.0219 |
| oas00350 | Tyrosine metabolism | 12 | 78 | 0.0318 |
| oas05231 | Choline metabolism in cancer | 12 | 11 | 0.0465 |
| oas01200 | Carbon metabolism | 12 | 114 | 0.0602 |
| oas01230 | Biosynthesis of amino acids | 12 | 128 | 0.072 |
| oas01210 | 2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism | 12 | 134 | 0.0759 |
| oas00565 | Ether lipid metabolism | 12 | 25 | 0.0893 |
| oas00600 | Sphingolipid metabolism | 12 | 25 | 0.0893 |
| oas00062 | Fatty acid elongation | 12 | 40 | 0.136 |
| oas00071 | Fatty acid degradation | 12 | 50 | 0.164 |
| oas00061 | Fatty acid biosynthesis | 12 | 58 | 0.183 |
| oas01100 | Metabolic pathways | 12 | 2702 | 0.199 |
| oas01040 | Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 12 | 74 | 0.217 |
| oas00230 | Purine metabolism | 12 | 95 | 0.265 |
| oas00520 | Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism | 12 | 108 | 0.289 |
| oas01212 | Fatty acid metabolism | 12 | 122 | 0.314 |
| oas02010 | ABC transporters ABC | 12 | 137 | 0.338 |
| NO | Adduction | RT (min) | m/z | Formula | Metabolite | KEGG Pathway | VIP | Change | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | [M + H]+ | 0.161 | 142.02649 | C6H6O4 | Kojic acid | - | 1.73 | ↓ | 0.034 |
| 2 | [M + H]+ | 6.872 | 405.3448 | C22H47NO5 | Hydrolyzed fumonisin B1 | - | 2.03 | ↓ | 0.007 |
| 3 | [M + H]+ | 10.033 | 715.51426 | C39H74NO8P | 1-Palmitoyl-2-linoleoyl PE | - | 1.66 | ↓ | 0.045 |
| 4 | [M + H]+ | 5.051 | 202.0293 | C8H10O4S | 4-ethylphenylsulfonic acid | - | 2.15 | ↓ | 0.003 |
| 5 | [M + H]+ | 6.84 | 317.29251 | C18H39NO3 | 2-Amino-1,3,4-octadecanetriol | - | 2.16 | ↓ | 0.002 |
| 6 | [M + H]+ | 10.02 | 753.52898 | C42H76NO8P | 1-hexadecanoyl-2-[(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)-octadecatetraenoyl]-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | - | 1.91 | ↓ | 0.015 |
| 7 | [M + H]+ | 10.023 | 837.62212 | C48H88NO8P | 1-octadecanoyl-2-(7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z-docosatetraenoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine | - | 1.68 | ↓ | 0.040 |
| 8 | [M + H]+ | 0.114 | 151.98775 | C3H5O5P | 3-[hydroxyl (oxido) phosphoranyl]pyruvic acid | - | 2.28 | ↓ | 0.001 |
| 9 | [M + H]+ | 0.1 | 179.01454 | C9H6ClNO | cloxyquin | - | 1.79 | ↓ | 0.026 |
| 10 | [M + H]+ | 6.802 | 273.26635 | C16H32O2 | Palmitic Acid | map01100, Metabolic pathways|map00062, Fatty acid elongation|map01212, Fatty acid metabolism|map00061, Fatty acid biosynthesis|map00071, Fatty acid degradation|map01040, Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids | 2.12 | ↓ | 0.004 |
| 11 | [M + H]+ | 0.157 | 220.05786 | C8H12O7 | (-)-threo-isodihomocitric acid | - | 2.35 | ↓ | 0.000 |
| 12 | [M + H]+ | 10.156 | 511.49544 | C32H65NO3 | N-tetradecanoylsphinganine | - | 1.78 | ↓ | 0.027 |
| 13 | [M + H]+ | 7.502 | 414.20355 | C24H30O6 | Bis (4-ethylbenzylidene) sorbitol | - | 1.77 | ↓ | 0.029 |
| 14 | [M + H]+ | 9.484 | 335.31808 | C22H41NO | (2E,4Z)-N-Isobutyl-2,4-octadecadienamide | - | 1.69 | ↓ | 0.039 |
| 15 | [M + H]+ | 6.556 | 227.18827 | C13H25NO2 | Cyprodenate | - | 1.65 | ↓ | 0.046 |
| 16 | [M + H]+ | 7.953 | 196.08868 | C14H12O | MFCD00005122 | - | 1.79 | ↓ | 0.026 |
| 17 | [M + H]+ | 7.251 | 310.17798 | C17H26O5 | Botrydial | - | 2.34 | ↑ | 0.000 |
| 18 | [M + H]+ | 7.19 | 494.1179 | C26H24Cl2N4O2 | 1-benzyl-3-(tert-butyl)-N-[6-(2,6-dichlorophenoxy)-3-pyridinyl]-1H-pyrazole-5-carboxamide | - | 1.71 | ↑ | 0.037 |
| 19 | [M + H]+ | 7.078 | 294.18313 | C17H26O4 | Embelin | - | 2.44 | ↑ | 0.000 |
| 20 | [M + H]+ | 1.004 | 268.08046 | C10H12N4O5 | Inosine | map01100, Metabolic pathways|map02010, ABC transporters|map00230, Purine metabolism | 1.76 | ↑ | 0.030 |
| 21 | [M + H]+ | 1.307 | 268.08064 | C10H12N4O5 | Arabinosylhypoxanthine | - | 1.77 | ↑ | 0.028 |
| 22 | [M + H]+ | 4.912 | 242.08048 | C12H10N4O2 | 3-amino-2-phenyl-2H-pyrazolo [4,3-c]pyridine-4,6-diol | - | 1.63 | ↑ | 0.049 |
| 23 | [M + H]+ | 9.156 | 300.26627 | C18H36O3 | 12-HSA | - | 1.63 | ↑ | 0.050 |
| 24 | [M + H]+ | 0.997 | 147.03538 | C5H9NO2S | 3-Thiomorpholinecarboxylic acid | - | 1.81 | ↑ | 0.024 |
| 25 | [M + H]+ | 0.943 | 259.04518 | C6H14NO8P | D-Glucosamine 6-phosphate | map01100, Metabolic pathways|map00520, Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism|map00250, Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism|map04931, Insulin resistance | 1.84 | ↑ | 0.021 |
| 26 | [M + H]+ | 0.833 | 125.09551 | C6H11N3 | N-Methylhistamine | map01100, Metabolic pathways|map00340, Histidine metabolism | 1.83 | ↑ | 0.021 |
| 27 | [M + H]+ | 1.012 | 145.01971 | C5H7NO2S | 3,4-dehydrothiomorpholine-3-carboxylic acid | - | 1.72 | ↑ | 0.035 |
| 28 | [M + H]+ | 10.5 | 765.5307 | C43H76NO8P | 1-oleoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphoethanolamine | - | 1.74 | ↑ | 0.033 |
| 29 | [M + H]+ | 9.744 | 779.54458 | C44H78NO8P | PC(18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)) | - | 1.64 | ↑ | 0.048 |
| 30 | [M − H]- | 0.175 | 142.02648 | C6H6O4 | Kojic acid | - | 1.70 | ↓ | 0.035 |
| 31 | [M − H]- | 5.08 | 202.0293 | C8H10O4S | 4-ethylphenylsulfonic acid | - | 2.12 | ↓ | 0.003 |
| 32 | [M − H]- | 1.082 | 231.14672 | C11H21NO4 | N-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-L-leucine | - | 1.70 | ↓ | 0.035 |
| 33 | [M − H]- | 6.882 | 317.2925 | C18H39NO3 | Phytosphingosine | map00600, Sphingolipid metabolism|map01100, Metabolic pathways | 2.12 | ↓ | 0.003 |
| 34 | [M − H]- | 6.844 | 273.26635 | C16H35NO2 | Hexadecasphinganine | - | 2.08 | ↓ | 0.004 |
| 35 | [M − H]- | 0.145 | 220.05786 | C8H12O7 | (-)-threo-isodihomocitric acid | - | 2.30 | ↓ | 0.000 |
| 36 | [M − H]- | 10.195 | 511.49544 | C32H65NO3 | N-tetradecanoylsphinganine | - | 1.78 | ↓ | 0.025 |
| 37 | [M − H]- | 1.006 | 134.0203 | C4H6O5 | DL-Malic acid | - | 1.99 | ↓ | 0.008 |
| 38 | [M − H]- | 8.716 | 295.13857 | C19H21NS | Pizotifen | - | 1.66 | ↓ | 0.042 |
| 39 | [M − H]- | 1.001 | 88.01482 | C3H4O3 | Pyruvic acid | - | 1.94 | ↓ | 0.011 |
| 40 | [M − H]- | 9.524 | 335.31808 | C22H41NO | (2E,4Z)-N-Isobutyl-2,4-octadecadienamide | - | 1.66 | ↓ | 0.041 |
| 41 | [M − H]- | 7.997 | 196.08868 | C14H12O | stilben-4-ol | - | 1.65 | ↓ | 0.044 |
| 42 | [M − H]- | 7.294 | 310.17798 | C17H26O5 | 6-Hydroxy-4,9a-dimethoxy-3,4a,5-trimethyl-4a,5,6,7,8,8a,9,9a-octahydronaphtho[2,3-b]furan-2(4H)-one | - | 2.33 | ↑ | 0.000 |
| 43 | [M − H]- | 7.421 | 196.14558 | C12H20O2 | cis-4-Hydroxy-6-decenoic acid lactone | - | 2.22 | ↑ | 0.001 |
| 44 | [M − H]- | 7.121 | 294.18313 | C17H26O4 | (+)-[6]-Gingerol | - | 2.43 | ↑ | 0.000 |
| 45 | [M − H]- | 0.905 | 193.02524 | C4H8N3O4P | fosfocreatinine | - | 1.63 | ↑ | 0.046 |
| 46 | [M − H]- | 0.937 | 155.03456 | C3H10NO4P | N-methylethanolamine phosphate | map00564, Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 1.68 | ↑ | 0.039 |
| 47 | [M − H]- | 4.526 | 173.10491 | C8H15NO3 | Acexamic acid | - | 1.61 | ↑ | 0.049 |
| 48 | [M − H]- | 9.199 | 300.26627 | C18H36O3 | 12-HSA | - | 1.63 | ↑ | 0.046 |
| 49 | [M − H]- | 1.011 | 129.04142 | C5H7NO3 | 4-Oxoproline | map01100, Metabolic pathways|map00330, Arginine and proline metabolism | 1.68 | ↑ | 0.038 |
| 51 | [M − H]- | 0.956 | 259.04518 | C6H14NO8P | D-Glucosamine 6-phosphate | map01100, Metabolic pathways|map00520, Amino sugar and nucleotide sugar metabolism|map00250, Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism|map04931, Insulin resistance | 1.79 | ↑ | 0.023 |
| 52 | [M − H]- | 3.594 | 159.08951 | C7H13NO3 | N-Acetylvaline | - | 1.73 | ↑ | 0.031 |
| 53 | [M − H]- | 1.023 | 147.03538 | C5H9NO2S | 3-Thiomorpholinecarboxylic acid | - | 1.82 | ↑ | 0.020 |
| 54 | [M − H]- | 0.857 | 125.09551 | C6H11N3 | 1-Methylhistamine | map01100, Metabolic pathways|map00340, Histidine metabolism | 1.77 | ↑ | 0.026 |
| 55 | [M − H]- | 1.04 | 145.01971 | C5H7NO2S | 3,4-dehydrothiomorpholine-3-carboxylic acid | - | 1.71 | ↑ | 0.034 |
| 56 | [M − H]- | 10.536 | 765.53073 | C43H76NO8P | 1-oleoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycerol-3-phosphoethanolamine | - | 1.70 | ↑ | 0.035 |
| 57 | [M − H]- | 10.028 | 743.54515 | C41H78NO8P | 1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-PE | - | 2.26 | ↑ | 0.001 |
| 58 | [M − H]- | 0.985 | 234.08487 | C8H14N2O6 | glu-ser | - | 1.78 | ↑ | 1.782 |
| 59 | [M − H]- | 0.159 | 150.05415 | C6H6N4O | Dezaguanine | - | 1.63 | ↑ | 1.633 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Shen, X. Effects of Cadmium on Liver Function and Its Metabolomics Profile in the Guizhou Black Goat. Metabolites 2023, 13, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020268
Li Y, Shen X. Effects of Cadmium on Liver Function and Its Metabolomics Profile in the Guizhou Black Goat. Metabolites. 2023; 13(2):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020268
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuanfeng, and Xiaoyun Shen. 2023. "Effects of Cadmium on Liver Function and Its Metabolomics Profile in the Guizhou Black Goat" Metabolites 13, no. 2: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020268
APA StyleLi, Y., & Shen, X. (2023). Effects of Cadmium on Liver Function and Its Metabolomics Profile in the Guizhou Black Goat. Metabolites, 13(2), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13020268






