Characterization of 3-Hydroxyeticyclidine (3-HO-PCE) Metabolism in Human Liver Microsomes and Biological Samples Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
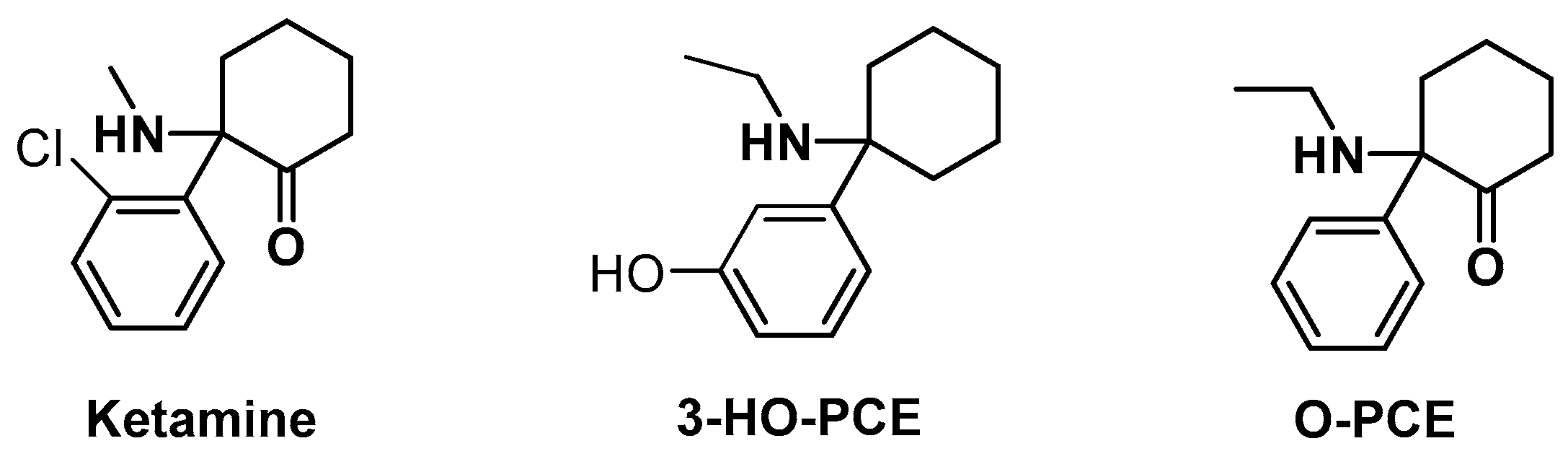
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Study Using Human Liver Microsomes (HLM)
2.1.1. Sample Pretreatment
2.1.2. Instrument Conditions
2.2. Analysis of Biological and Non-Biological Samples from a Drug User
2.2.1. Sample Collection
2.2.2. Urine Pretreatment
2.2.3. Hair Pretreatment
2.2.4. Recovered Material
2.2.5. Instrument Conditions
- Urine
- Hair
- Recovered 3-HO-PCE powder
2.3. Post-Processing of HRAM Data
3. Results
3.1. Identification of 3-HO-PCE by NMR
3.2. Metabolism of 3-HO-PCE
3.2.1. Metabolites Detected in Human Liver Microsomes (HLM)
3.2.2. Metabolites Detected in Biological Samples
- Urine
- Hair
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Drug Report 2021: Trends and Developments. Available online: https://www.emcdda.europa.eu/publications/edr/trends-developments/2021_en (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- World Drug Report 2019: Booklet 4: Stimulants. Available online: https://wdr.unodc.org/wdr2019/prelaunch/WDR19_Booklet_4_STIMULANTS.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Zanos, P.; Moaddel, R.; Morris, P.J.; Riggs, L.M.; Highland, J.N.; Georgiou, P.; Pereira, E.F.R.; Albuquerque, E.X.; Thomas, C.J.; Zarate, C.A.; et al. Ketamine and Ketamine Metabolite Pharmacology: Insights into Therapeutic Mechanisms. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 621–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larabi, I.A.; Fabresse, N.; Etting, I.; Nadour, L.; Pfau, G.; Raphalen, J.H.; Philippe, P.; Edel, Y.; Alvarez, J.C. Prevalence of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS) and Conventional Drugs of Abuse (DOA) in High Risk Populations from Paris (France) and Its Suburbs. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2019, 204, 107508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallach, J.; Brandt, S.D. Phencyclidine-Based New Psychoactive Substances. In New Psychoactive Substances; Maurer, H.H., Brandt, S.D., Eds.; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 252, pp. 261–303. ISBN 978-3-030-10560-0. [Google Scholar]
- Theofel, N.; Möller, P.; Vejmelka, E.; Kastner, K.; Roscher, S.; Scholtis, S.; Tsokos, M. A Fatal Case Involving N-Ethyldeschloroketamine (2-Oxo-PCE) and Venlafaxine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, e2–e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gicquel, T.; Richeval, C.; Mesli, V.; Gish, A.; Hakim, F.; Pelletier, R.; Cornez, R.; Balgairies, A.; Allorge, D.; Gaulier, J. Fatal Intoxication Related to Two New Arylcyclohexylamine Derivatives (2F-DCK and 3-MeO-PCE). Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 324, 110852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameline, A.; Greney, H.; Monassier, L.; Raul, J.-S.; Kintz, P. Metabolites to Parent 3-MeO-PCP Ratio in Human Urine Collected in Two Fatal Cases. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 43, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.V.; Harvey, M.G.; Voss, L.J.; Sleigh, J.W.; Bickerdike, M.J.; Denny, W.A. Structure-Activity Relationships for the Anaesthetic and Analgaesic Properties of Aromatic Ring-Substituted Ketamine Esters. Molecules 2020, 25, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hájková, K.; Jurásek, B.; Čejka, J.; Štefková, K.; Páleníček, T.; Sýkora, D.; Kuchař, M. Synthesis and Identification of Deschloroketamine Metabolites in Rats’ Urine and a Quantification Method for Deschloroketamine and Metabolites in Rats’ Serum and Brain Tissue Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2020, 12, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, R.; Le Daré, B.; Le Bouëdec, D.; Kernalléguen, A.; Ferron, P.-J.; Morel, I.; Gicquel, T. Arylcyclohexylamine Derivatives: Pharmacokinetic, Pharmacodynamic, Clinical and Forensic Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.-C.; Dao, K.-L. The Emergence of Deschloro-N-Ethyl-Ketamine, a Ketamine Analog, in Drug Seizures and Drug Driving Cases in Hong Kong. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2020, 44, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 3-HO-PCE. Psychonaut Wiki. Available online: https://psychonautwiki.org/wiki/3-HO-PCE (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Madry, M.M.; Rust, K.Y.; Guglielmello, R.; Baumgartner, M.R.; Kraemer, T. Metabolite to Parent Drug Concentration Ratios in Hair for the Differentiation of Tramadol Intake from External Contamination and Passive Exposure. Forensic Sci. Int. 2012, 223, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, F.; Angerer, V.; Hermanns-Clausen, M.; Auwärter, V.; Moosmann, B. Metabolites of Synthetic Cannabinoids in Hair--Proof of Consumption or False Friends for Interpretation? Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 3445–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larabi, I.A.; Zerizer, F.; Ameline, A.; Etting, I.; Joseph, D.; Kintz, P.; Alvarez, J.C. Metabolic Profiling of Deschloro-N-Ethyl-Ketamine and Identification of New Target Metabolites in Urine and Hair Using Human Liver Microsomes and High-Resolution Accurate Mass Spectrometry. Drug Test. Anal. 2021, 13, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, F.T.; Meyer, M.R. In Vitro Approaches to Studying the Metabolism of New Psychoactive Compounds. Drug Test. Anal. 2011, 3, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, M.R.; Bach, M.; Welter, J.; Bovens, M.; Turcant, A.; Maurer, H.H. Ketamine-Derived Designer Drug Methoxetamine: Metabolism Including Isoenzyme Kinetics and Toxicological Detectability Using GC-MS and LC-(HR-)MSn. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 6307–6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzies, E.L.; Hudson, S.C.; Dargan, P.I.; Parkin, M.C.; Wood, D.M.; Kicman, A.T. Characterizing Metabolites and Potential Metabolic Pathways for the Novel Psychoactive Substance Methoxetamine. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 506–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michely, J.A.A.; Manier, S.K.; Caspar, A.T.; Brandt, S.D.; Wallach, J.; Maurer, H.H. New Psychoactive Substances 3-Methoxyphencyclidine (3-MeO-PCP) and 3-Methoxyrolicyclidine (3-MeO-PCPy): Metabolic Fate Elucidated with Rat Urine and Human Liver Preparations and Their Detectability in Urine by GC-MS, “LC-(High Resolution)-MSn” and “LC-(High Resolution)-MS/MS”. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017, 15, 692–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlier, J.; Diao, X.; Scheidweiler, K.B.; Huestis, M.A. Distinguishing Intake of New Synthetic Cannabinoids ADB-PINACA and 5F-ADB-PINACA with Human Hepatocyte Metabolites and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kintz, P.; Richeval, C.; Jamey, C.; Ameline, A.; Allorge, D.; Gaulier, J.-M.; Raul, J.-S. Detection of the Designer Benzodiazepine Metizolam in Urine and Preliminary Data on Its Metabolism: Metizolam Identification in Urine. Drug Test. Anal. 2017, 9, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeval, C.; Gicquel, T.; Hugbart, C.; Le Dare, B.; Allorge, D.; Morel, I.; Gaulier, J.-M. In Vitro Characterization of NPS Metabolites Produced by Human Liver Microsomes and the HepaRG Cell Line Using Liquid Chromatographyhigh Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS) Analysis: Application to Furanyl Fentanyl. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 806–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameline, A.; Richeval, C.; Gaulier, J.-M.; Raul, J.-S.; Kintz, P. Detection of the Designer Benzodiazepine Flunitrazolam in Urine and Preliminary Data on Its Metabolism. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In Vitro Drug Interaction Studies—Cytochrome P450 Enzyme- and Transporter-Mediated Drug Interactions Guidance for Industry. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/in-vitro-drug-interaction-studies-cytochrome-p450-enzyme-and-transporter-mediated-drug-interactions (accessed on 18 February 2023).
- Portalier, F.; Bourdreux, F.; Marrot, J.; Moreau, X.; Coeffard, V.; Greck, C. Merging Oxidative Dearomatization and Aminocatalysis: One-Pot Enantioselective Synthesis of Tricyclic Architectures. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5642–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabresse, N.; Larabi, I.A.; Stratton, T.; Mistrik, R.; Pfau, G.; Lorin de la Grandmaison, G.; Etting, I.; Grassin Delyle, S.; Alvarez, J.-C. Development of a Sensitive Untargeted Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Screening Devoted to Hair Analysis through a Shared MS2 Spectra Database: A Step toward Early Detection of New Psychoactive Substances. Drug Test. Anal. 2019, 11, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintz, P. Hair Analysis in Clinical and Forensic Toxicology, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-0-12-801700-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Metabolism and Metabolomics of Ketamine: A Toxicological Approach. Forensic Sci. Res. 2017, 2, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raccor, B.S.; Teitelbaum, A.M.; Dinh, J.; Totah, R. Principles of Drug Metabolism 3: Enzymes and Tissues. In Reference Module in Chemistry, Molecular Sciences and Chemical Engineering; Elsevier: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-12-409547-2. [Google Scholar]


| ID | Name | Formula | Theoretical m/z | Observed m/z | Mass Error (ppm) | Isomers | Rt (min) | HLMPAR (%) | UrinePAR (%) | HairPAR (%) | Common Product Ions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3-HO-PCE | 3-HO-PCE | C14 H21 NO | 219.16286 | 219.16231 | −2.52 | NA | 7.11 | NA | ND | 1.6 | 81.06994; 107.04918; |
| M1 | 3′,4′-dihydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-ol | C12 H12 O | 172.08936 | 172.08881 | −3.21 | NA | 6.51 | ND | ND | 4.4 | 81.06995; 107.0492; 131.0494; |
| M2 | 2′,3′,4′,5′-tetrahydro-[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-ol | C12 H14 O | 174.10501 | 174.10447 | −3.10 | M2a | 7.11 | 70.2 | ND | <1 | 79.05428; 81.06996; 107.0492; 133.06494; 175.11192 |
| M2b | 7.84 | <1 | 78.8 | ND | |||||||
| M3 | (3′-hydroxyphenyl) cyclohexenol | C12 H14 O2 | 190.09992 | 190.09938 | −2.84 | NA | 6.049 | 5 | ND | ND | 79.05424; 81.06996; 95.04906; 131.04919; 145.06494 |
| M4 | 1-(3′-hydroxyphenyl) cyclohexanamine 3-HO-PCA | C12 H17 NO | 191.13156 | 191.13101 | −2.87 | NA | 11.68 | ND | ND | 8.9 | 67.0544; 94.0652; 119.04933 |
| M5 | 1-(3′-hydroxyphenyl) cyclohexanol | C12 H16 O2 | 192.11557 | 192.11503 | −2.81 | NA | 13.15 | ND | ND | 26.3 | 67.0545; 79.05430; 81.06991; 121.0650 |
| M6 | dihydroxy-[1,1′-bi(cyclohexan)]-1-en-3-one | C12 H18 O3 | 210.12614 | 210.12559 | −2.61 | M6a | 7.85 | ND | ND | 3.4 | 67.0544; 81.07001; 121.06490 |
| M6b | 13.4 | ND | 3.7 | ND | |||||||
| M7 | dehydro-3-HO-PCE | C14 H19 NO | 217.14721 | 217.14666 | −2.53 | NA | 6.97 | <1 | ND | 48 | 67.0544; 131.04941; 145.06480; 173.09644 |
| M8 | 1′-(ethylamino)-[1,1′-bi(cyclohexan)]-3-ol | C14 H27 NO | 225.20981 | 225.20926 | −2.44 | NA | 15.72 | ND | ND | 4.2 | 68.04974; 70.0653; 110.09655 |
| M9 | phenol- or hydroxy-3-HO-PCE = diHO-PCE | C14 H21 N O2 | 235.15777 | 235.15723 | −2.29 | M9a | 2.59 | ND | 4.8 | ND | 67.05441; 81.0698; 95.0492 |
| M9b | 5.95 | 1.2 | ND | < 1 | |||||||
| M10 | 1′-amino-trihydroxy-[1,1-bi(cyclohexan)]-3-one | C12H19NO4 | 241.13195 | 241.13141 | −2.23 | NA | 9.25 | ND | 11.2 | 2.62 | 79.05410; 81.06995; 136.07549 |
| M11 | dehydro-triOH-PCE | C14 H19 NO3 | 249.13704 | 249.13649 | −2.20 | NA | 7.48 | <1 | 1.5 | ND | 100.11208; 132.0608; 147.0799; 161.0835; 174.12802; 202.12263 |
| M12 | 1′-(ethylamino)-trihydroxy-[1,1′-bi(cyclohexan)]-3-one | C14 H25 NO4 | 271.17890 | 271.17836 | −1.99 | NA | 6.17 | <1 | ND | ND | 67.0543; 81.06995; |
| M13 | 1′-(ethylamino)-trihydroxy-[1,1′-bi(cyclohexane)]-dione (3′-hydroxyphenyl)cyclohexenol-O-glucuronide | C18 H22 O8 | 366.13201 | 366.13147 | −1.47 | M13a | 5.18 | <1 | ND | ND | 79.05417; 81.06996; 131.04993; 173.09573 |
| M13b | 5.85 | <1 | ND | ND | |||||||
| M13c | 8.20 | <1 | ND | ND | |||||||
| M14 | 3-HO-PCE-O-glucuronide = 3-OGlu-PCE | C20 H29 NO7 | 395.19495 | 395.19440 | −1.39 | NA | 5.97 | 21.6 | ND | ND | 81.0699; 107.04915; 133.0646 175.11226; |
| M15 | diOH-PCE-O-glucuronide | C20 H29 NO8 | 411.18986 | 411.18932 | −1.31 | M22a | 0.58 | <1 | ND | ND | 81.0698; 123.04411 |
| M22b | 3.97 | <1 | ND | ND | |||||||
| M22c | 5.83 | <1 | ND | ND | |||||||
| M22d | 6.87 | <1 | ND | ND |
| m/z | 3-HO-PCE Metabolism (Present Study) | Rt (min) | O-PCE Metabolism (Previous Study) | Rt (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 172.08881 | M1 | 6.51 | M2b | 6.51 |
| 174.10447 | M2a | 7.11 | M3b | 7.06 |
| 191.09938 | 3-OH-PCA (M4) | 11.68 | 2-OH-PCA (M5a) | 11.67 |
| 217.14666 | Dehydro-3-OH-PCE (M7) | 6.5 | O-PCE (Parent drug) | 6.5 |
| 219.16231 | 3-HO-PCE (Parent drug) | 7.11 | M9a (2-OH-PCE) | 7.06 |
| 235.15723 | DIOH-PCE (M9b) | 5.95 | DIOH-PCE (M12a) | 5.82 |
| Biological Sample | Untargeted Screening Metabolites of the Eticyclidine Derivatives | Targeted Metabolite of 3-HO-PCE |
|---|---|---|
| Urine |  m/z 174.10447 |  m/z 241.13141 |
| Hair |  m/z 191.09938 |  m/z 192.11503 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larabi, I.A.; Joseph, D.; Lesueur, C.; Alvarez, J.-C. Characterization of 3-Hydroxyeticyclidine (3-HO-PCE) Metabolism in Human Liver Microsomes and Biological Samples Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2023, 13, 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030432
Larabi IA, Joseph D, Lesueur C, Alvarez J-C. Characterization of 3-Hydroxyeticyclidine (3-HO-PCE) Metabolism in Human Liver Microsomes and Biological Samples Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites. 2023; 13(3):432. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030432
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarabi, Islam Amine, Delphine Joseph, Camille Lesueur, and Jean-Claude Alvarez. 2023. "Characterization of 3-Hydroxyeticyclidine (3-HO-PCE) Metabolism in Human Liver Microsomes and Biological Samples Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry" Metabolites 13, no. 3: 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030432
APA StyleLarabi, I. A., Joseph, D., Lesueur, C., & Alvarez, J.-C. (2023). Characterization of 3-Hydroxyeticyclidine (3-HO-PCE) Metabolism in Human Liver Microsomes and Biological Samples Using High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites, 13(3), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13030432






