Pilot Study on the Use of Untargeted Metabolomic Fingerprinting of Liquid-Cytology Fluids as a Diagnostic Tool of Malignancy for Thyroid Nodules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Sample Collection, Cytological and Histological Diagnoses
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. LC-MS/MS Analyses
2.5. Data Preprocessing and Statistical Analyses
2.6. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
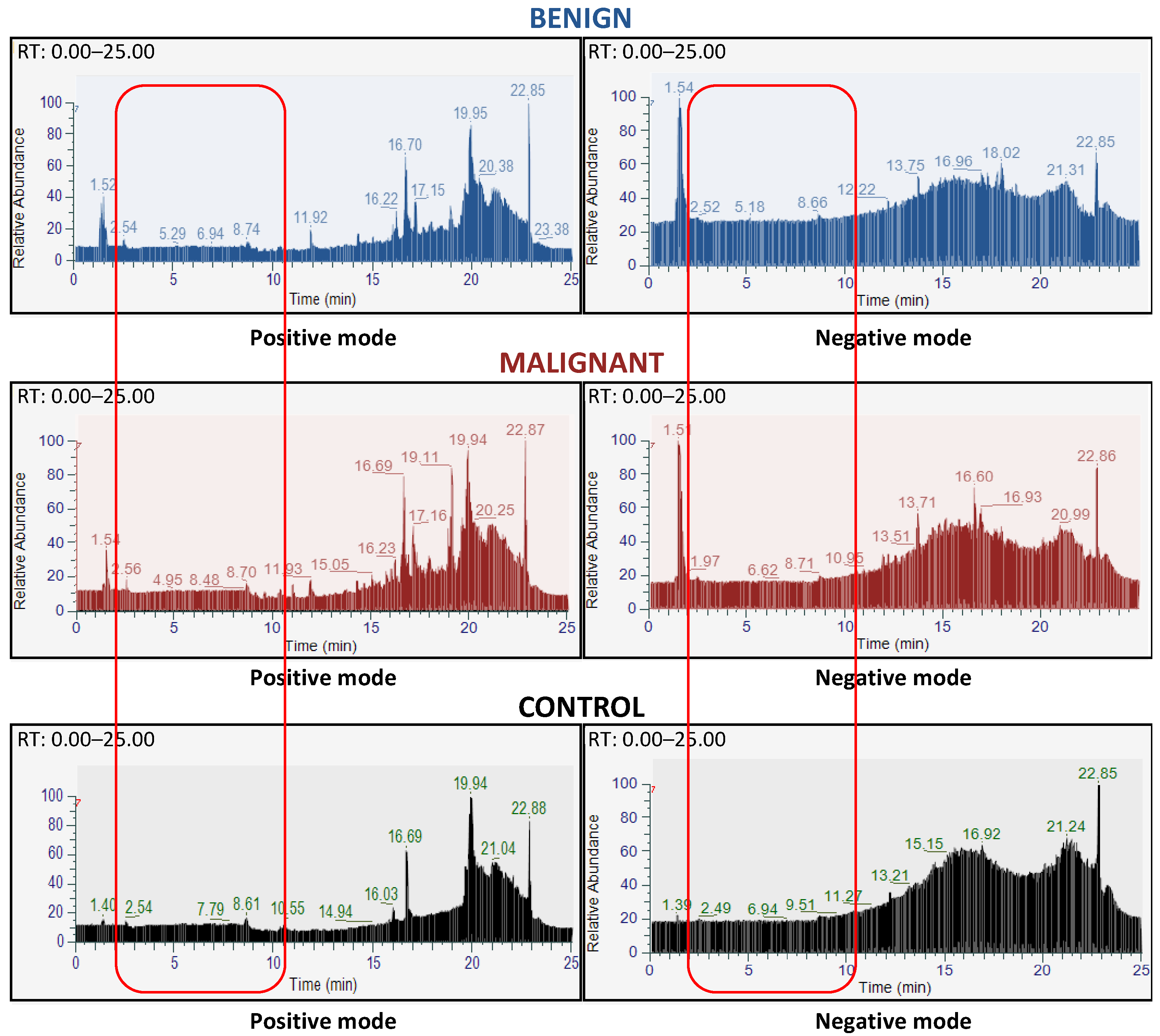
3.1. Database Construction of the FNAC Metabolomic Analyses
3.2. FNAC Metabolomic Analyses Allowed Preoperative Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules
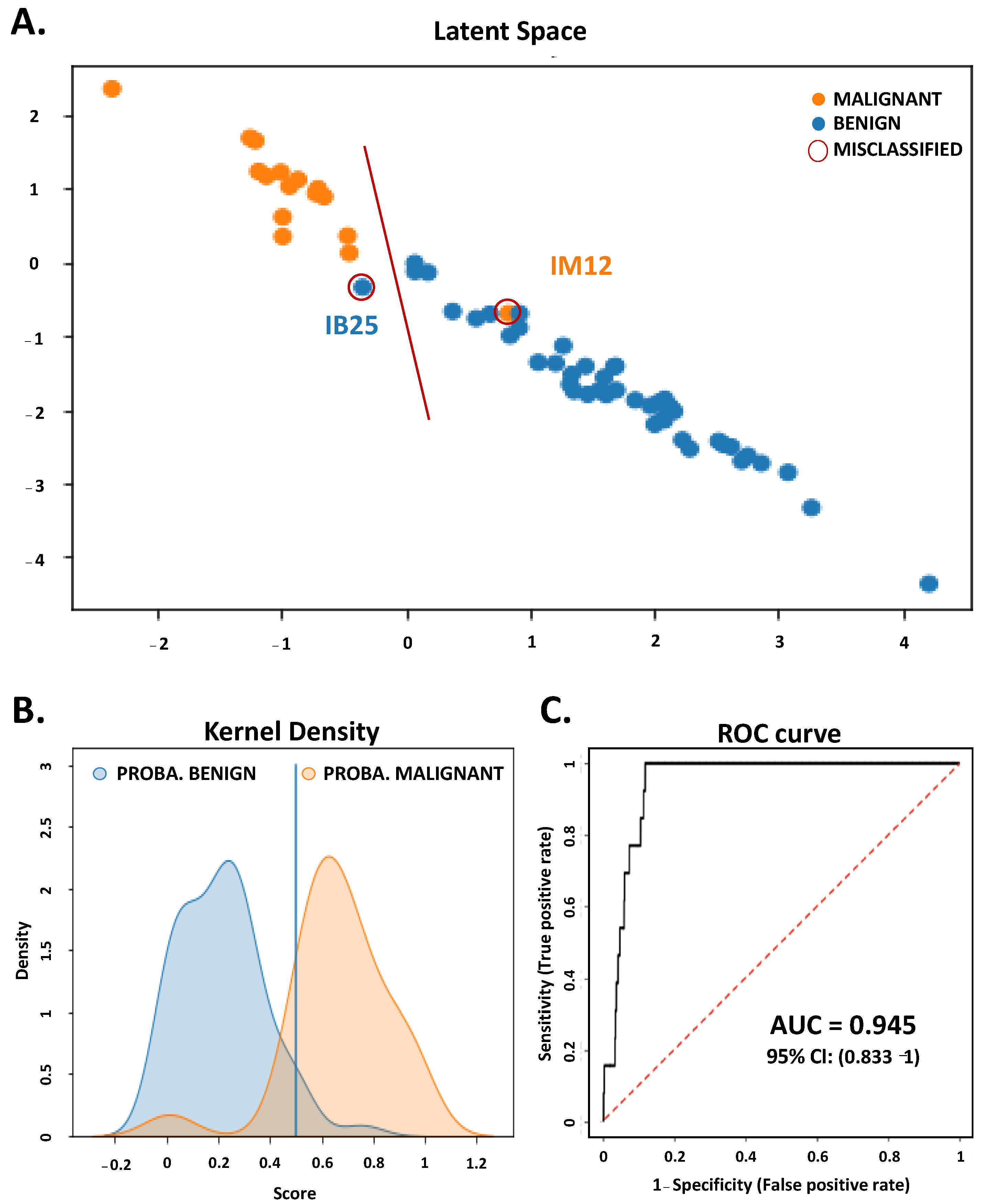
3.3. Metabolomic Profiling with 15 Features from FNAC Samples Allowed Preoperative Diagnosis of Thyroid Nodules
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gharib, H.; Papini, E. Thyroid Nodules: Clinical Importance, Assessment, and Treatment. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 36, 707–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharib, H.; Papini, E.; Garber, J.R.; Duick, D.S.; Harrell, R.M.; Hegedus, L.; Paschke, R.; Valcavi, R.; Vitti, P. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, American College of Endocrinology, and Associazione Medici Endocrinologi Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the Diagnosis and Management of Thyroid Nodules-2016 Update. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22, 622–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabanillas, M.E.; McFadden, D.G.; Durante, C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.D.; Pantanowitz, L.; Hornick, J.L. A worldwide journey of thyroid cancer incidence centred on tumour histology. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cibas, E.S.; Ali, S.Z. The 2017 Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Thyroid 2017, 27, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, T.M.; Zeiger, M.A. Thyroid Nodule Molecular Testing: Is It Ready for Prime Time? Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 590128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, K.; Roberts, M.S.; McCoy, K.L.; Carty, S.E.; Yip, L. Molecular Testing Versus Diagnostic Lobectomy in Bethesda III/IV Thyroid Nodules: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1237–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.D.; Pantanowitz, L.; Faquin, W.C. The Role of Molecular Testing for the Indeterminate Thyroid FNA. Genes 2019, 10, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steward, D.L.; Carty, S.E.; Sippel, R.S.; Yang, S.P.; Sosa, J.A.; Sipos, J.A.; Nikiforov, Y.E. Performance of a Multigene Genomic Classifier in Thyroid Nodules with Indeterminate Cytology: A Prospective Blinded Multicenter Study. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 2014–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, M.; Nabhan, F.; Porter, K.; Roll, K.; Shirley, L.A.; Azaryan, I.; Tonkovich, D.; Perlick, J.; Ryan, L.E.; Khawaja, R.; et al. Afirma Gene Sequencing Classifier Compared with Gene Expression Classifier in Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules. Thyroid 2019, 29, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Layfield, L.; Esebua, M. Performance of Afirma Gene Sequencing Classifier versus Gene Expression Classifier in thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2022, 11, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.G.; Winson, M.K.; Kell, D.B.; Baganz, F. Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckwerth, W.; Fiehn, O. Can we discover novel pathways using metabolomic analysis? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Lum, J.J.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Thompson, C.B. The Biology of Cancer: Metabolic Reprogramming Fuels Cell Growth and Proliferation. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deberardinis, R.J.; Sayed, N.; Ditsworth, D.; Thompson, C.B. Brick by brick: Metabolism and tumor cell growth. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deja, S.; Dawiskiba, T.; Balcerzak, W.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M.; Głód, M.; Pawełka, D.; Młynarz, P. Follicular Adenomas Exhibit a Unique Metabolic Profile. 1H NMR Studies of Thyroid Lesions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miccoli, P.; Torregrossa, L.; Shintu, L.; Magalhaes, A.; Chandran, J.; Tintaru, A.; Ugolini, C.; Minuto, M.N.; Miccoli, M.; Basolo, F.; et al. Metabolomics approach to thyroid nodules: A high-resolution magic-angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance–based study. Surgery 2012, 152, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryoo, I.; Kwon, H.; Kim, S.C.; Jung, S.C.; Yeom, J.A.; Shin, H.S.; Cho, H.R.; Yun, T.J.; Choi, S.H.; Sohn, C.-H.; et al. Metabolomic analysis of percutaneous fine-needle aspiration specimens of thyroid nodules: Potential application for the preoperative diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torregrossa, L.; Shintu, L.; Nambiath Chandran, J.; Tintaru, A.; Ugolini, C.; Magalhães, A.; Basolo, F.; Miccoli, P.; Caldarelli, S. Toward the Reliable Diagnosis of Indeterminate Thyroid Lesions: A HRMAS NMR-Based Metabolomics Case of Study. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 3317–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Shen, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhou, K.; Hu, W.; Xu, B.; Xia, Y.; Tang, W. GC-MS-based metabolomic analysis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma tissue. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, Y.; Jia, W.; Wang, J.; Yin, S. Distinct Metabolomic Profiles of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Benign Thyroid Adenoma. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3315–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russ, G.; Bonnema, S.J.; Erdogan, M.F.; Durante, C.; Ngu, R.; Leenhardt, L. European Thyroid Association Guidelines for Ultrasound Malignancy Risk Stratification of Thyroid Nodules in Adults: The EU-TIRADS. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2017, 6, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lloyd, R.V.; Osamura, R.Y.; Klöppel, G.; Rosai, J. WHO Classification of Tumours of Endocrine Organs; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017.
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vázquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chardin, D.; Gille, C.; Pourcher, T.; Humbert, O.; Barlaud, M. Learning a confidence score and the latent space of a new supervised autoencoder for diagnosis and prognosis in clinical metabolomic studies. BMC Bioinform. 2022, 23, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, V.; Light, T.J.; Adil, A.A.; Tao, M.; Chiu, A.S.; Hitchcock, M.; Arroyo, N.; Fernandes-Taylor, S.; Francis, D.O. Complication Rates of Total Thyroidectomy vs Hemithyroidectomy for Treatment of Papillary Thyroid Microcarcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 148, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.D.; Martini, M. New Insight in a New Entity: NIFTPS and Valuable Role of Ancillary Techniques. The Role of PD-L1. Ebiomedicine 2017, 18, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Andréa, G.; Lassalle, S.; Guevara, N.; Mograbi, B.; Hofman, P. From biomarkers to therapeutic targets: The promise of PD-L1 in thyroid autoimmunity and cancer. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1310–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojakowska, A.; Chekan, M.; Widlak, P.; Pietrowska, M. Application of Metabolomics in Thyroid Cancer Research. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 2015, 258763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farrokhi Yekta, R.; Rezaie Tavirani, M.; Arefi Oskouie, A.; Mohajeri-Tehrani, M.R.; Soroush, A.R. The metabolomics and lipidomics window into thyroid cancer research. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, X.; Tian, X.; Wang, S. Diagnosis of papillary thyroid carcinoma by 1H NMR spectroscopy-based metabolomic analysis of whole blood. Drug Discov. Ther. 2020, 14, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Qian, C.; Tian, Y.; Ling, R.; Duan, Y. Diagnostic approach to thyroid cancer based on amino acid metabolomics in saliva by ultra-performance liquid chromatography with high resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 235, 122729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, L.-Y.; Xie, C.; Zhang, M.-L.; Wang, Y.-J.; Liu, G.-H. Metabolomics as a potential method for predicting thyroid malignancy in children and adolescents. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2020, 36, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Zhao, F.; Sun, J.; Lin, B.; Zhao, L.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, S.; Li, A.; Wei, Y. Alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolite profiles of thyroid carcinoma patients. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2728–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezig, L.; Servadio, A.; Torregrossa, L.; Miccoli, P.; Basolo, F.; Shintu, L.; Caldarelli, S. Diagnosis of post-surgical fine-needle aspiration biopsies of thyroid lesions with indeterminate cytology using HRMAS NMR-based metabolomics. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics | All % (nb) | Benign % (nb) | Malignant % (nb) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 78 | 56 | 22 | |||
| Gender | F | 74.4 (58) | 76.8 (43) | 68.2 (15) | |
| Age (mean ±SD) | 52.6 (±15.8) | 56.1 (±14.6) | 43.7 (±15.4) | ||
| Hashimoto | 11.4 (8) | 6.3 (3) | 22.7 (5) | ||
| Thyroid function | Euthyroidism | 83.3 (65) | 82.1 (46) | 86.4 (19) | |
| Hypothyroidism | 7.7 (6) | 7.1 (4) | 9.1 (2) | ||
| Hyperthyroidism | 7.7 (6) | 8.9 (5) | 4.5 (1) | ||
| EU-TIRADS | 3 | 23.1 (18) | 32.1 (18) | 0 | |
| 4 | 46.2 (36) | 48.2 (27) | 36.4 (8) | ||
| 5 | 29.5 (23) | 17.9 (10) | 59.1 (13) | ||
| US size (mm, mean ±SD) | 23.1 (±10.4) | 25.4 (±10.2) | 17.4 (±8.9) | ||
| Cytologic classification (Bethesda) | II | 33.3 (26) | 46.4 (26) | 0 | |
| III | 20.5 (16) | 17.9 (10) | 27.3 (6) | ||
| IV | 32.1 (25) | 35.7 (20) | 22.7 (5) | ||
| V | 6.4 (5) | 0 | 22.7 (5) | ||
| VI | 7.7 (6) | 0 | 27.3 (6) | ||
| Histology | Benign | NNN | 30.4 (17) | 50 (17) | 0 |
| Adenoma | 30.4 (17) | 50 (17) | 0 | ||
| Malignant (PTC) | Classical variant | 15.4 (12) | 0 | 54.5 (12) | |
| Follicular variant | 6.4 (5) | 0 | 22.7 (5) | ||
| Sclerosant variant | 2.6 (2) | 0 | 9.1 (2) | ||
| Oncocytic variant | 1.3 (1) | 0 | 4.5 (1) | ||
| Tall cell variant | 1.3 (1) | 0 | 4.5 (1) | ||
| Solid variant | 1.3 (1) | 0 | 4.5 (1) | ||
| Folds | Global | Benign | Malignant |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 2 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.667 |
| Fold 3 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.875 |
| Fold 4 | 0.842 | 0.727 | 1 |
| Fold 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 6 | 0.95 | 0.933 | 1 |
| Fold 7 | 0.9 | 0.933 | 0.8 |
| Fold 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 11 | 0.95 | 1 | 0.833 |
| Fold 12 | 0.947 | 0.917 | 1 |
| Mean | 0.957 | 0.959 | 0.931 |
| SD | 0.047 | 0.077 | 0.107 |
| Folds | AUC | Precision | Recall | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 2 | 0.833 | 0.972 | 0.833 | 0.886 |
| Fold 3 | 0.938 | 0.962 | 0.938 | 0.947 |
| Fold 4 | 0.864 | 0.864 | 0.864 | 0.842 |
| Fold 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 6 | 0.967 | 0.917 | 0.967 | 0.937 |
| Fold 7 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 | 0.867 |
| Fold 8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Fold 11 | 0.917 | 0.967 | 0.917 | 0.937 |
| Fold 12 | 0.958 | 0.938 | 0.958 | 0.945 |
| Mean | 0.945 | 0.957 | 0.945 | 0.947 |
| SD | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.059 | 0.054 |
| Ion Mode | Row m/z | RT (min) | Main Identity | Row Identity (HMDB) | Molecular Formula | SAE Score | B/M Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neg | 434.872 | 1.41 | - | - | C11H3O13P3 | 0.9726 | 7.002 |
| Pos | 307.083 | 2.56 | (-)-Epigallocatechin | 0038361 | C15H14O7 | 0.7123 | 4.831 |
| Pos | 229.041 | 10.88 | Indolylmethylthiohydroximate | - | C10H10N2OS | 0.3305 | 3.067 |
| Pos | 217.08 | 2.56 | - | - | - | 0.3208 | 3.125 |
| Pos | 229.954 | 2.01 | - | - | - | 0.2623 | 0.554 |
| Pos | 247.965 | 2.02 | - | - | - | 0.1823 | 0.565 |
| Pos | 257.949 | 2 | - | - | - | 0.1790 | 0.573 |
| Pos | 311.9 | 1.78 | - | - | - | 0.1590 | 0.602 |
| Pos | 325.942 | 2 | - | - | - | 0.1495 | 0.590 |
| Pos | 210.933 | 1.7 | - | - | - | 0.1353 | 0.686 |
| Pos | 253.91 | 1.51 | - | - | - | 0.1336 | 0.612 |
| Pos | 162.907 | 1.49 | Phosphoroselenoic acid | 0003840 | H3O3PSe | 0.1329 | 0.682 |
| Pos | 225.914 | 1.51 | - | - | - | 0.1154 | 0.634 |
| Neg | 108.901 | 1.65 | - | - | - | 0.0247 | 1.731 |
| Pos | 250.939 | 1.41 | - | - | - | −0.0289 | 5.156 |
| Methods Performance | Fold 1 | Fold 2 | Fold 3 | Fold 4 | Mean | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Support Vector Machines | AUC | 0.833 | 0.771 | 0.938 | 0.958 | 0.875 | 0.088 |
| Accuracy | 0.895 | 0.842 | 0.947 | 0.947 | 0.908 | 0.050 | |
| Precision | 0.833 | 0.771 | 0.938 | 0.958 | 0.875 | 0.088 | |
| Recall | 0.933 | 0.717 | 0.958 | 0.938 | 0.886 | 0.114 | |
| F1 score | 0.864 | 0.737 | 0.945 | 0.945 | 0.873 | 0.098 | |
| Time elapsed | 0.025 | 0.029 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 0.028 | - | |
| Partial Least Squares- Discriminant Analysis | AUC | 0.833 | 0.941 | 1 | 0.944 | 0.930 | 0.070 |
| Accuracy | 0.895 | 0.895 | 1 | 0.947 | 0.934 | 0.050 | |
| Precision | 0.833 | 0.941 | 1 | 0.944 | 0.930 | 0.070 | |
| Recall | 0.933 | 0.750 | 1 | 0.955 | 0.909 | 0.110 | |
| F1 score | 0.864 | 0.802 | 1 | 0.947 | 0.903 | 0.088 | |
| Time elapsed | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | - | |
| sil_plsda | 0.396 | 0.435 | 0.407 | 0.381 | 0.405 | 0.023 | |
| AUC | 1 | 0.969 | 0.887 | 0.958 | 0.953 | 0.048 | |
| Accuracy | 1 | 0.947 | 0.895 | 0.947 | 0.947 | 0.043 | |
| Random | Precision | 1 | 0.969 | 0.887 | 0.958 | 0.953 | 0.048 |
| Forest | Recall | 1 | 0.875 | 0.887 | 0.938 | 0.925 | 0.057 |
| F1 score | 1 | 0.912 | 0.887 | 0.945 | 0.936 | 0.049 | |
| TimeElapsed | 0.362 | 0.343 | 0.344 | 0.342 | 0.348 | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Andréa, G.; Jing, L.; Peyrottes, I.; Guigonis, J.-M.; Graslin, F.; Lindenthal, S.; Sanglier, J.; Gimenez, I.; Haudebourg, J.; Vandersteen, C.; et al. Pilot Study on the Use of Untargeted Metabolomic Fingerprinting of Liquid-Cytology Fluids as a Diagnostic Tool of Malignancy for Thyroid Nodules. Metabolites 2023, 13, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070782
D’Andréa G, Jing L, Peyrottes I, Guigonis J-M, Graslin F, Lindenthal S, Sanglier J, Gimenez I, Haudebourg J, Vandersteen C, et al. Pilot Study on the Use of Untargeted Metabolomic Fingerprinting of Liquid-Cytology Fluids as a Diagnostic Tool of Malignancy for Thyroid Nodules. Metabolites. 2023; 13(7):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070782
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Andréa, Grégoire, Lun Jing, Isabelle Peyrottes, Jean-Marie Guigonis, Fanny Graslin, Sabine Lindenthal, Julie Sanglier, Isabel Gimenez, Juliette Haudebourg, Clair Vandersteen, and et al. 2023. "Pilot Study on the Use of Untargeted Metabolomic Fingerprinting of Liquid-Cytology Fluids as a Diagnostic Tool of Malignancy for Thyroid Nodules" Metabolites 13, no. 7: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070782
APA StyleD’Andréa, G., Jing, L., Peyrottes, I., Guigonis, J.-M., Graslin, F., Lindenthal, S., Sanglier, J., Gimenez, I., Haudebourg, J., Vandersteen, C., Bozec, A., Guevara, N., & Pourcher, T. (2023). Pilot Study on the Use of Untargeted Metabolomic Fingerprinting of Liquid-Cytology Fluids as a Diagnostic Tool of Malignancy for Thyroid Nodules. Metabolites, 13(7), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13070782








