Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Mulberry Leaf Powder on the Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism Parameters, Immunity Indicators, and Gut Microbiota of Dogs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. MLP Preparation
2.2. Animals, Experimental Design, and Diets
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Measurement of Lipid Metabolism Parameters
2.5. Fecal Microbiota Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Immunity Indicators
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
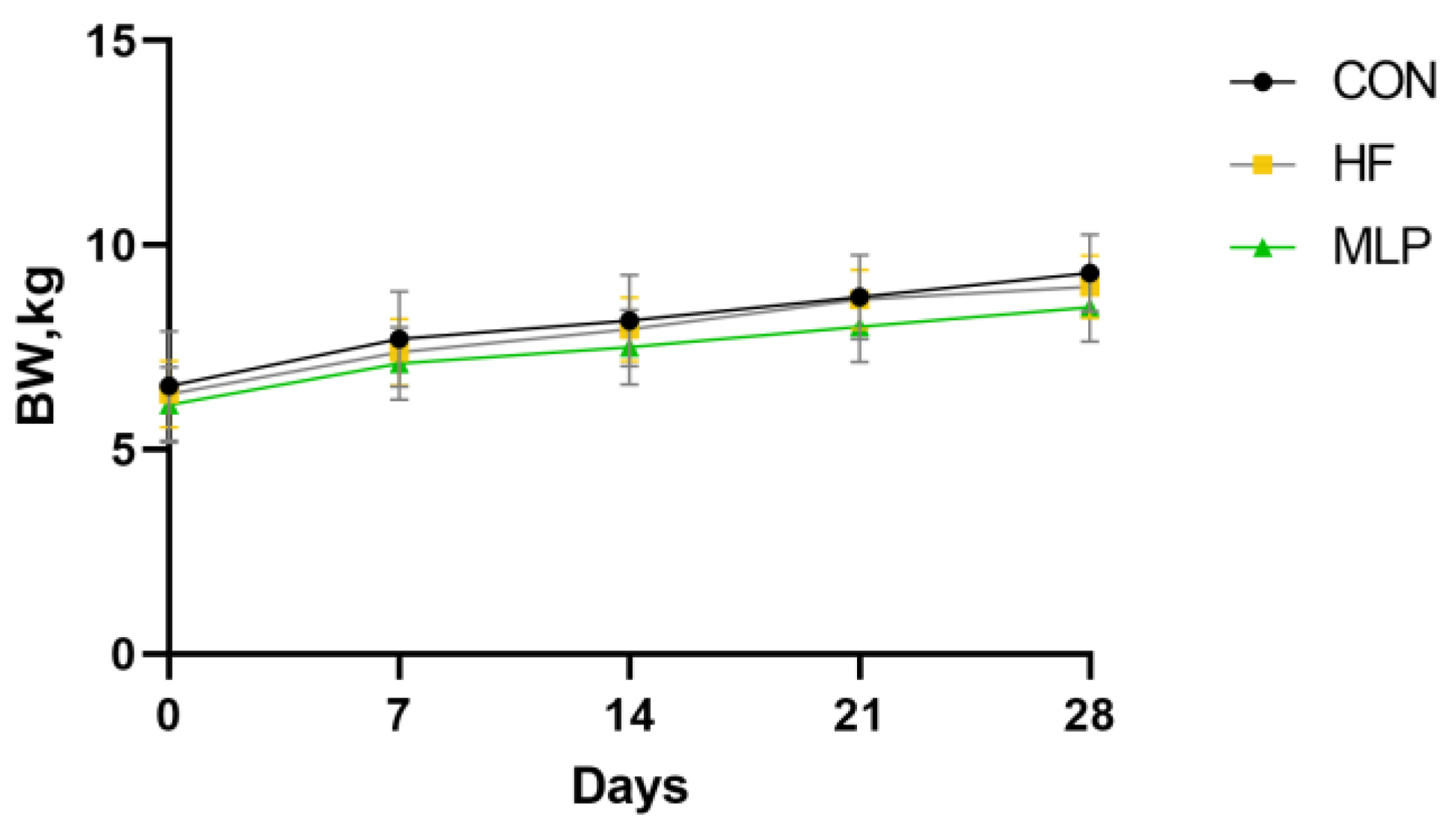
3.1. Growth Performance
3.2. Lipid Metabolism Parameters
3.3. Immunity Indicators
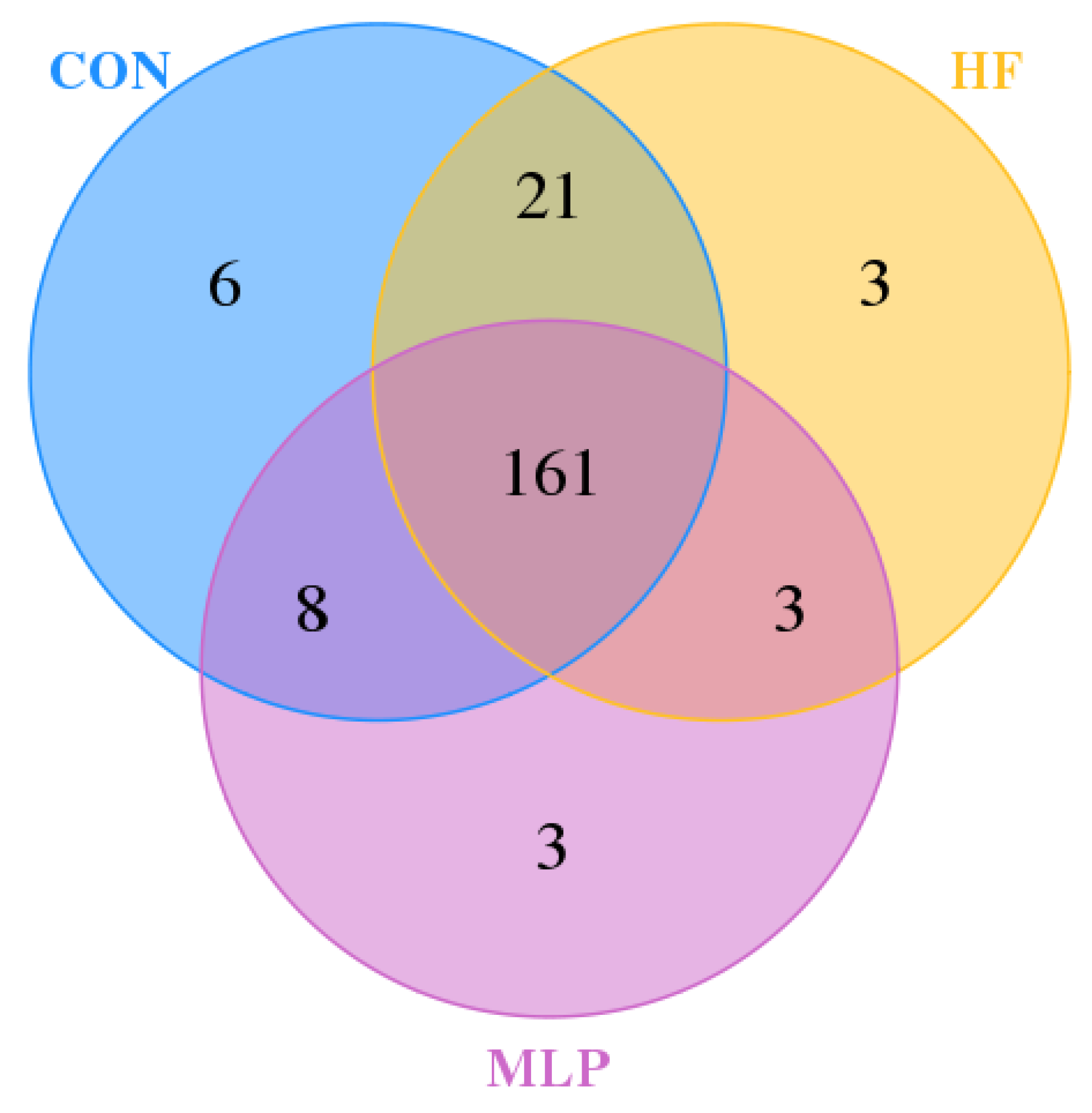
3.4. Gut Microbiota Operational Taxonomic Unit (OTU) Analysis
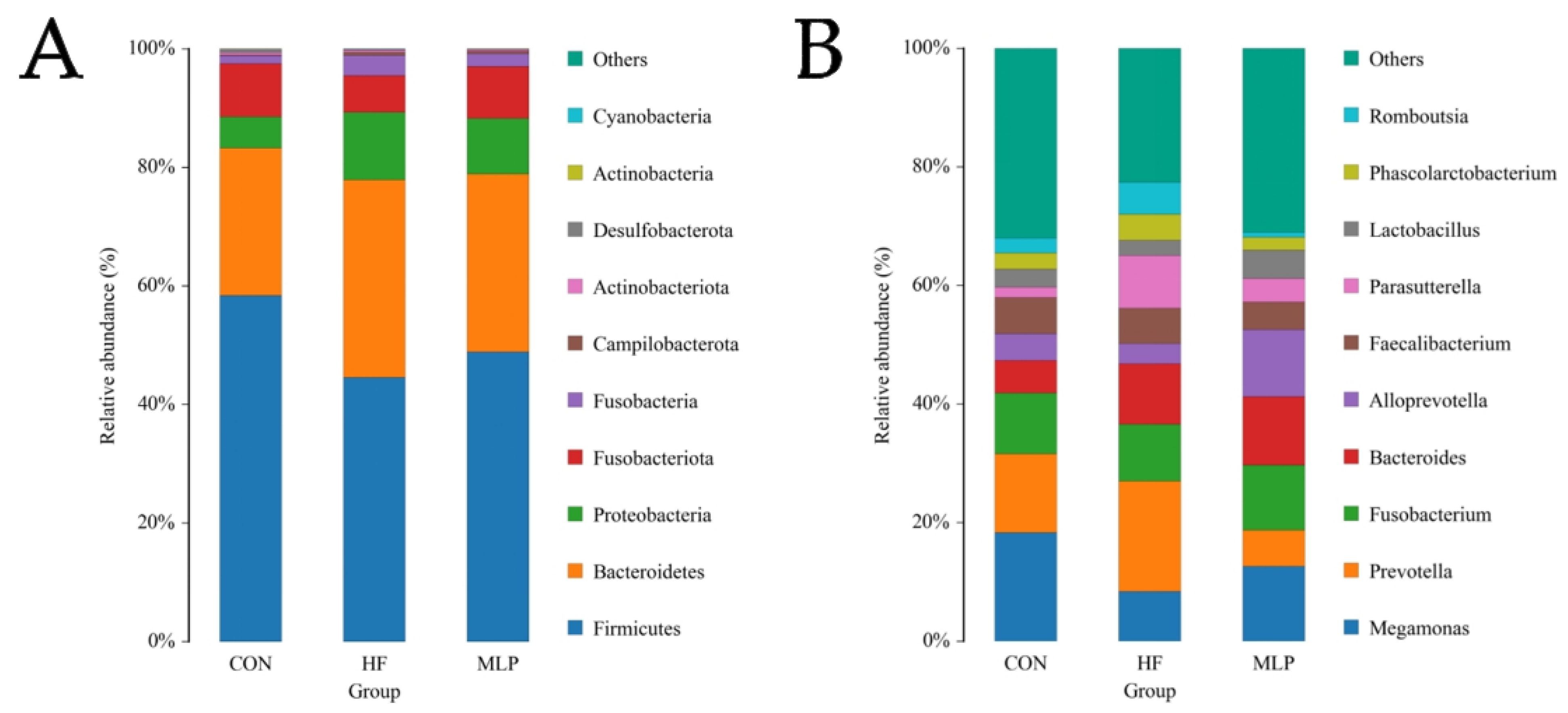
3.5. Species Annotation, Taxonomic Analysis, and Alpha Diversity Analysis
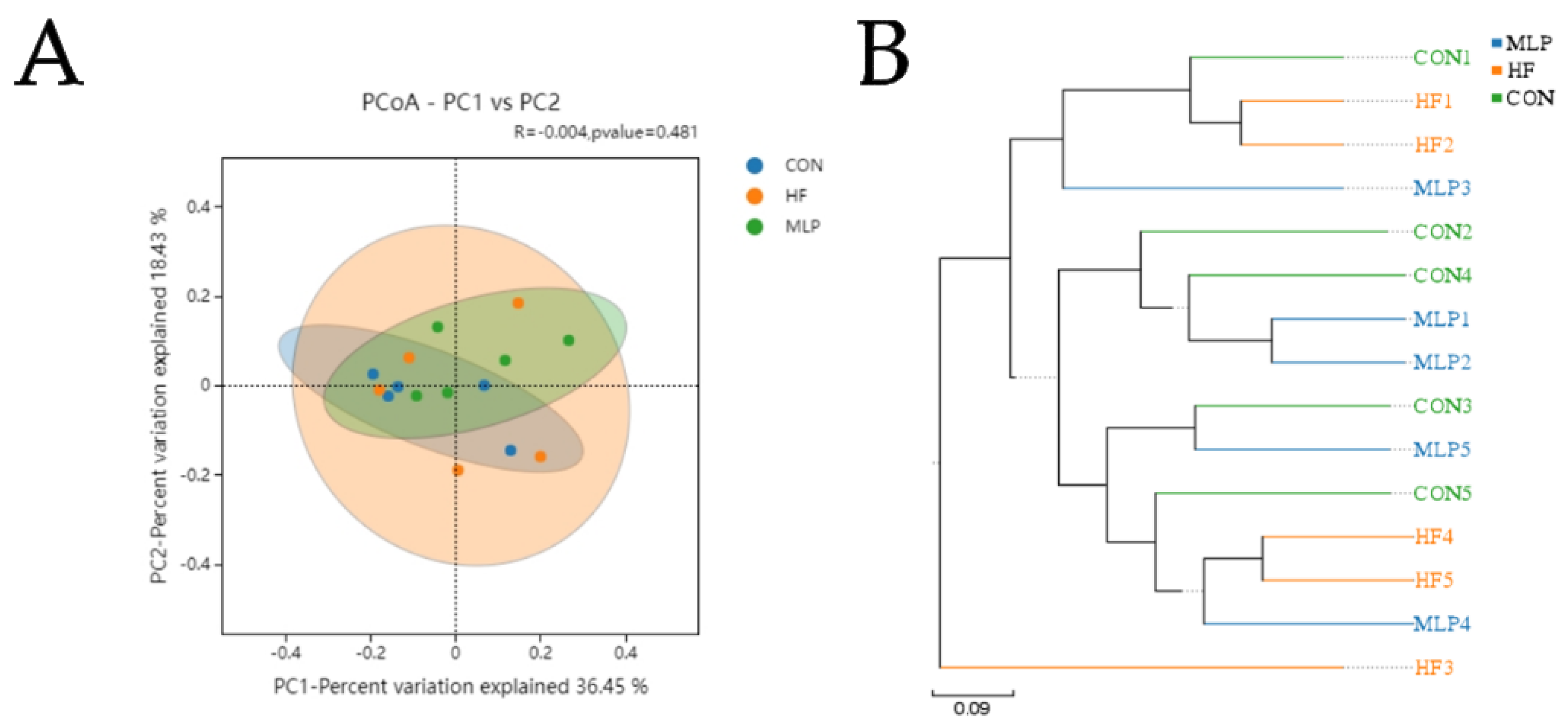
3.6. Beta Diversity Analysis
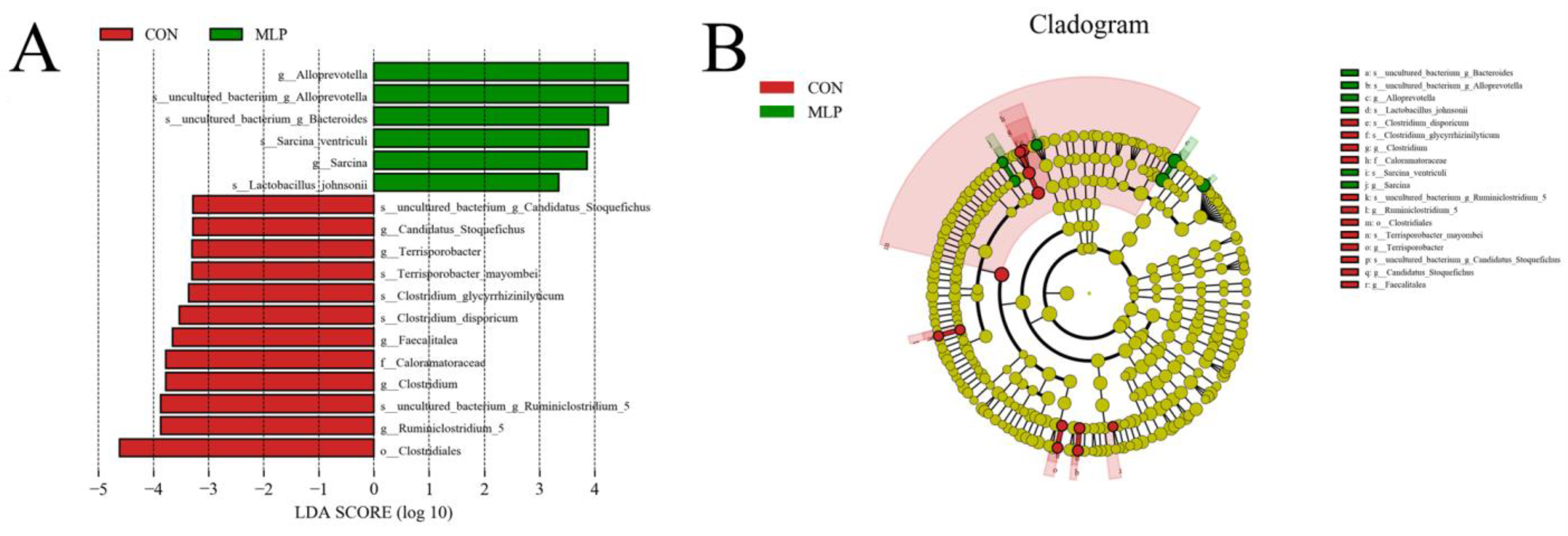
3.7. LEFSe Difference Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deering, S. Clinical public health, climate change, and aging. Can. Fam. Physician 2023, 69, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpell, J.A. In the Company of Animals: A Study of Human-Animal Relationships; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, A.; Towell, T. Cat and Dog Companionship and Well-being: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Appl. Psychol. 2013, 2013, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virués-Ortega, J.; Pastor-Barriuso, R.; Castellote, J.M.; Población, A.; de Pedro-Cuesta, J. Effect of animal-assisted therapy on the psychological and functional status of elderly populations and patients with psychiatric disorders: A meta-analysis. Health Psychol. Rev. 2012, 6, 197–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.M.; Soliman, W.S.; Khalifa, A.A. Benefits of pets’ ownership, a review based on health perspectives. J. Intern. Med. Emerg.Res. 2021, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McConnell, A.R.; Brown, C.M.; Shoda, T.M.; Stayton, L.E.; Martin, C.E. Friends with benefits: On the positive consequences of pet ownership. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 2011, 101, 1239–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, M.J.; Verreynne, M.L.; Harpur, P.; Pachana, N.A. Companion Animals and Health in Older Populations: A Systematic Review. Clin. Gerontol. 2020, 43, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mein, G.; Grant, R. A cross-sectional exploratory analysis between pet ownership, sleep, exercise, health and neighbourhood perceptions: The Whitehall II cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kramer, C.K.; Mehmood, S.; Suen, R.S. Dog Ownership and Survival: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12, e005554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubanga, M.; Byberg, L.; Nowak, C.; Egenvall, A.; Magnusson, P.K.; Ingelsson, E.; Fall, T. Dog ownership and the risk of cardiovascular disease and death—A nationwide cohort study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- German, A.J. The growing problem of obesity in dogs and cats. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 1940s–1946s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marshall, W.G.; Hazewinkel, H.A.; Mullen, D.; de Meyer, G.; Baert, K.; Carmichael, S. The effect of weight loss on lameness in obese dogs with osteoarthritis. Vet. Res. Commun. 2010, 34, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montoya, M.; Morrison, J.A.; Arrignon, F.; Spofford, N.; Charles, H.; Hours, M.-A.; Biourge, V. Life expectancy tables for dogs and cats derived from clinical data. Front Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1082102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, M.; Cunningham, S.; Lund, E.M.; Khanna, C.; Naramore, R.; Patel, A.; Day, M.J. Obesity and Associated Comorbidities in People and Companion Animals: A One Health Perspective. J. Comp. Pathol. 2017, 156, 296–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Courcier, E.A.; Thomson, R.M.; Mellor, D.J.; Yam, P.S. An epidemiological study of environmental factors associated with canine obesity. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 51, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oba, P.M.; Kelly, J.; Kostiuk, D.; Swanson, K.S. Effects of weight loss and feeding specially formulated diets on the body composition, blood metabolite profiles, voluntary physical activity, and fecal metabolites and microbiota of obese dogs. J. Anim. Sci. 2023, 101, skad073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.T.; Tang, C.M.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Z.J.; Meng, F.M.; Luo, G.Q.; Xin, H.Y.; Zhong, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.H.; et al. The Effects of Dietary Inclusion of Mulberry Leaf Powder on Growth Performance, Carcass Traits and Meat Quality of Tibetan Pigs. Animals 2022, 12, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Peng, Y.; He, J.; Chen, C.; Xiao, D.; Yin, Y.; Li, F. Mulberry leaf powder regulates antioxidative capacity and lipid metabolism in finishing pigs. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.; Huang, C.; Wang, D.; Chang, D.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H. Positive effects of Mulberry leaf extract on egg quality, lipid metabolism, serum biochemistry, and antioxidant indices of laying hens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1005643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, T.; Su, S.L.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, J.M.; Qian, D.W.; Tang, Y.P.; Duan, J.A. The mechanism of mulberry leaves against renal tubular interstitial fibrosis through ERK1/2 signaling pathway was predicted by network pharmacology and validated in human tubular epithelial cells. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2044–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Wang, C.; Guo, X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Flavonoid Levels and Antioxidant Capacity of Mulberry Leaves: Effects of Growth Period and Drying Methods. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 684974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Luo, H. Effects of mulberry leaf silage on antioxidant and immunomodulatory activity and rumen bacterial community of lambs. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumkoon, T.; Srisaisap, M.; Boonserm, P. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Morus alba (White Mulberry) Leaf Extract as Potential Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents. Molecules 2023, 28, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, F.; Liu, J.; Liao, S.; Zou, Y. Mulberry Leaf Polyphenols and Fiber Induce Synergistic Antiobesity and Display a Modulation Effect on Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahboubi, M. Morus alba (mulberry), a natural potent compound in management of obesity. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 146, 104341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Jaiswal, V.; Kim, K.; Chun, J.; Lee, M.J.; Shin, J.H.; Lee, H.J. Mulberry Leaf Supplements Effecting Anti-Inflammatory Genes and Improving Obesity in Elderly Overweight Dogs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Gan, T.; Huang, Y.; Bao, L.; Liu, S.; Cui, X.; Wang, H.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, M.; Su, C.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Mulberry Leaf Flavonoids In Vitro and In Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.W.; Yang, T.Y.; Teng, C.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Yu, M.H.; Lee, H.J.; Hsu, L.S.; Wang, C.J. Mulberry leaves extract ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damages through reduction of acetaldehyde toxicity and inhibition of apoptosis caused by oxidative stress signals. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kang, K.H. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Bacterial Potential of Mulberry Leaf Extract on Oral Microorganisms. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Han, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Cho, H.S.; Kang, J.S.; Myung, C.S. Effects of unaltered and bioconverted mulberry leaf extracts on cellular glucose uptake and antidiabetic action in animals. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2019, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, C.; Bao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Qi, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, L.; Tong, X. Clinical potential and mechanistic insights of mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaves in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus: Focusing on gut microbiota, inflammation, and metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 306, 116143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Dai, H.; Jiang, J.; Ye, N.; Zhu, S.; Wei, Q.; Lv, Z.; Shi, F. Dietary mulberry-leaf flavonoids improve the eggshell quality of aged breeder hens. Theriogenology 2022, 179, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Lv, Z.; Dai, H.; Li, S.; Jiang, J.; Ye, N.; Zhu, S.; Wei, Q.; Shi, F. Dietary mulberry-leaf flavonoids supplementation improves liver lipid metabolism and ovarian function of aged breeder hens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 106, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liao, S.; Pang, D.; Li, E.; Liu, T.; Liu, F.; Zou, Y. The transported active mulberry leaf phenolics inhibited adipogenesis through PPAR-γ and Leptin signaling pathway. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Peng, Y.; Wu, D.; Hu, J.; Shi, X.; Yang, G.; Li, X. Dietary supplementation of Morus nigra L. leaves decrease fat mass partially through elevating leptin-stimulated lipolysis in pig model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 249, 112416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kaneko, T.; Qin, L.-Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sato, A. Long-term effects of high dietary fiber intake on glucose tolerance and lipid metabolism in GK rats: Comparison among barley, rice, and cornstarch. Metabolism 2003, 52, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myhrstad, M.C.W.; Tunsjø, H.; Charnock, C.; Telle-Hansen, V.H. Dietary Fiber, Gut Microbiota, and Metabolic Regulation—Current Status in Human Randomized Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.N.; Liu, X.T.; Liang, Z.H.; Wang, J.H. Gut microbiota in obesity. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 3837–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-F.; Villaverde, C.; Chang, W.-C.; Fascetti, A.J.; Larsen, J.A. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Disease Associations of Overweight and Obesity in Dogs that Visited the Veterinary Medical Teaching Hospital at the University of California, Davis from January 2006 to December 2015. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2022, 48, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshourbagy, N.A.; Meyers, H.V.; Abdel-Meguid, S.S. Cholesterol: The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly—Therapeutic Targets for the Treatment of Dyslipidemia. Med. Princ. Pract. 2013, 23, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiu, J.H.C.; Chan, K.-S.; Cheung, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fung, W.W.L.; Cai, J.; Cheung, S.W.M.; Dorweiler, B.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Associated Activation of TLR5 Induces Apolipoprotein A1 Production in the Liver. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1236–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meksawan, K.; Pendergast, D.R.; Leddy, J.J.; Mason, M.; Horvath, P.J.; Awad, A.B. Effect of Low and High Fat Diets on Nutrient Intakes and Selected Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Sedentary Men and Women. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2004, 23, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz-Aliabadi, F.; Noruzi, H.; Hassanabadi, A. Effect of different levels of green tea (Camellia sinensis) and mulberry (Morus alba) leaves powder on performance, carcass characteristics, immune response and intestinal morphology of broiler chickens. Vet. Med. Sci. 2023, 9, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Zhong, G.; Peng, Y.; Zhu, Z. Mulberry leaf and konjac compound powder improves the metabolic capacity of old mice on a high-protein diet by regulating the structure of the intestinal microbiota. J. Sci. Food Agric 2023, 103, 5949–5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Jiao, F.; Bao, L.; Lin, Z.; Wei, X.; Qian, W.; et al. Transcriptomics and metabolomics analysis reveal the anti-oxidation and immune boosting effects of mulberry leaves in growing mutton sheep. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1088850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breedveld, A.; van Egmond, M. IgA and FcαRI: Pathological Roles and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, I.; Kim, M.J. Comparison of Gut Microbiota of 96 Healthy Dogs by Individual Traits: Breed, Age, and Body Condition Score. Animals 2021, 11, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandri, G.; Argentini, C.; Milani, C.; Turroni, F.; Cristina Ossiprandi, M.; van Sinderen, D.; Ventura, M. Catching a glimpse of the bacterial gut community of companion animals: A canine and feline perspective. Microb. Biotechnol. 2020, 13, 1708–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handl, S.; Dowd, S.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Massive parallel 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing reveals highly diverse fecal bacterial and fungal communities in healthy dogs and cats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2011, 76, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alessandri, G.; Milani, C.; Mancabelli, L.; Mangifesta, M.; Lugli, G.A.; Viappiani, A.; Duranti, S.; Turroni, F.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. The impact of human-facilitated selection on the gut microbiota of domesticated mammals. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.-L.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Li, L.; Li, T.-T.; Liu, B.; Lv, X.-C. Ethanol extract of Ganoderma lucidum ameliorates lipid metabolic disorders and modulates the gut microbiota composition in high-fat diet fed rats. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3419–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Zhang, X.; Luo, T.; Wang, D.; Sun, Y.; Dai, J. Effects of Short-Term Dietary Fiber Intervention on Gut Microbiota in Young Healthy People. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 3507–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouzaki, M.; Comelli, E.M.; Arendt, B.M.; Bonengel, J.; Fung, S.K.; Fischer, S.E.; McGilvray, I.D.; Allard, J.P. Intestinal microbiota in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, S.; Bao, L.; Wang, K.; Sun, S.; Liao, M.; Liu, C.; Zhou, N.; Ma, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Activation of a Specific Gut Bacteroides-Folate-Liver Axis Benefits for the Alleviation of Nonalcoholic Hepatic Steatosis. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, F.; Lu, J.; Shi, J.; Guan, J.; Yan, F.; Li, B.; Huo, G. Probiotic Mixture of Lactobacillus plantarum Strains Improves Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota Structure in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Chen, M.; Liu, H.; Ji, H. Two doses of Lactobacillus induced different microbiota profiles and serum immune indices in pigs. J. Funct. Foods 2023, 102, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group | ACE | Chao1 | Simpson | Shannon |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 149.92 ± 15.36 | 149.00 ± 15.72 | 0.85 ± 0.05 | 4.30 ± 0.45 |
| HF | 139.80 ± 7.94 | 136.10 ± 10.04 | 0.84 ± 0.03 | 3.87 ± 0.30 |
| MLP | 129.5 ± 7.38 | 129.2 ± 7.79 | 0.90 ± 0.01 | 4.33 ± 0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, A.; Tang, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Luo, G.; Zhong, J.; Fang, Z.; Wang, Z.; et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Mulberry Leaf Powder on the Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism Parameters, Immunity Indicators, and Gut Microbiota of Dogs. Metabolites 2023, 13, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080918
Yu A, Tang C, Wang S, Wang Y, Chen L, Li Z, Luo G, Zhong J, Fang Z, Wang Z, et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Mulberry Leaf Powder on the Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism Parameters, Immunity Indicators, and Gut Microbiota of Dogs. Metabolites. 2023; 13(8):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080918
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Aiying, Cuiming Tang, Sutian Wang, Yuan Wang, Lian Chen, Zhiyi Li, Guoqing Luo, Jianwu Zhong, Zhengfeng Fang, Zhenjiang Wang, and et al. 2023. "Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Mulberry Leaf Powder on the Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism Parameters, Immunity Indicators, and Gut Microbiota of Dogs" Metabolites 13, no. 8: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080918
APA StyleYu, A., Tang, C., Wang, S., Wang, Y., Chen, L., Li, Z., Luo, G., Zhong, J., Fang, Z., Wang, Z., & Lin, S. (2023). Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Mulberry Leaf Powder on the Growth Performance, Lipid Metabolism Parameters, Immunity Indicators, and Gut Microbiota of Dogs. Metabolites, 13(8), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo13080918









