Metabolic Adaptations in Rapeseed: Hemin-Induced Resilience to NaCl Stress by Enhancing Growth, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Defense Ability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Materials and Salinity Treatment
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
2.3.1. Germination Characteristics
2.3.2. Growth Index Measurement
2.3.3. Determination of Photosynthetic Pigments in Leaves
2.3.4. Determination of Photosynthetic Characteristics of Leaves
2.3.5. Determination of Lipid Peroxidation and Membrane Permeability
2.3.6. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
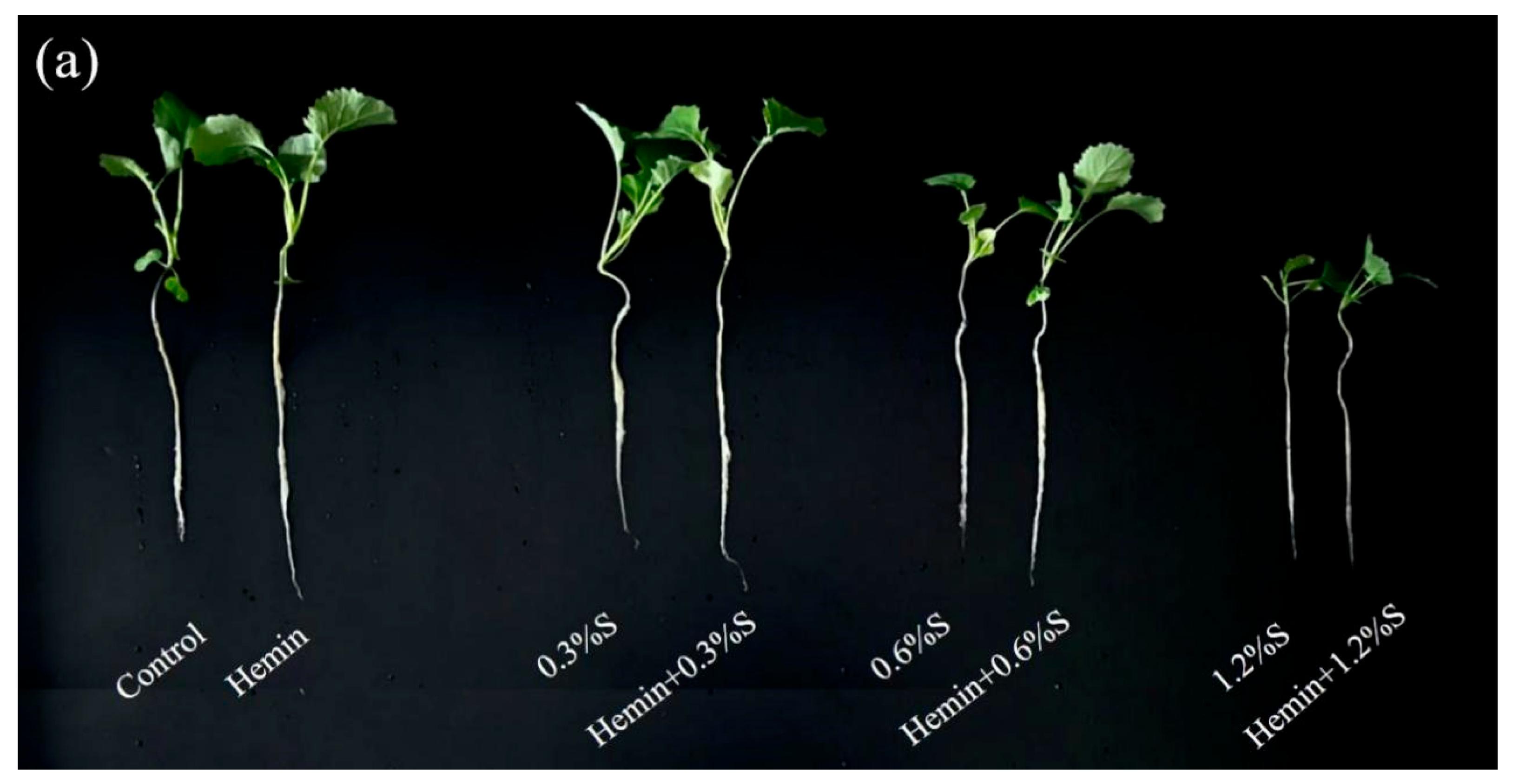
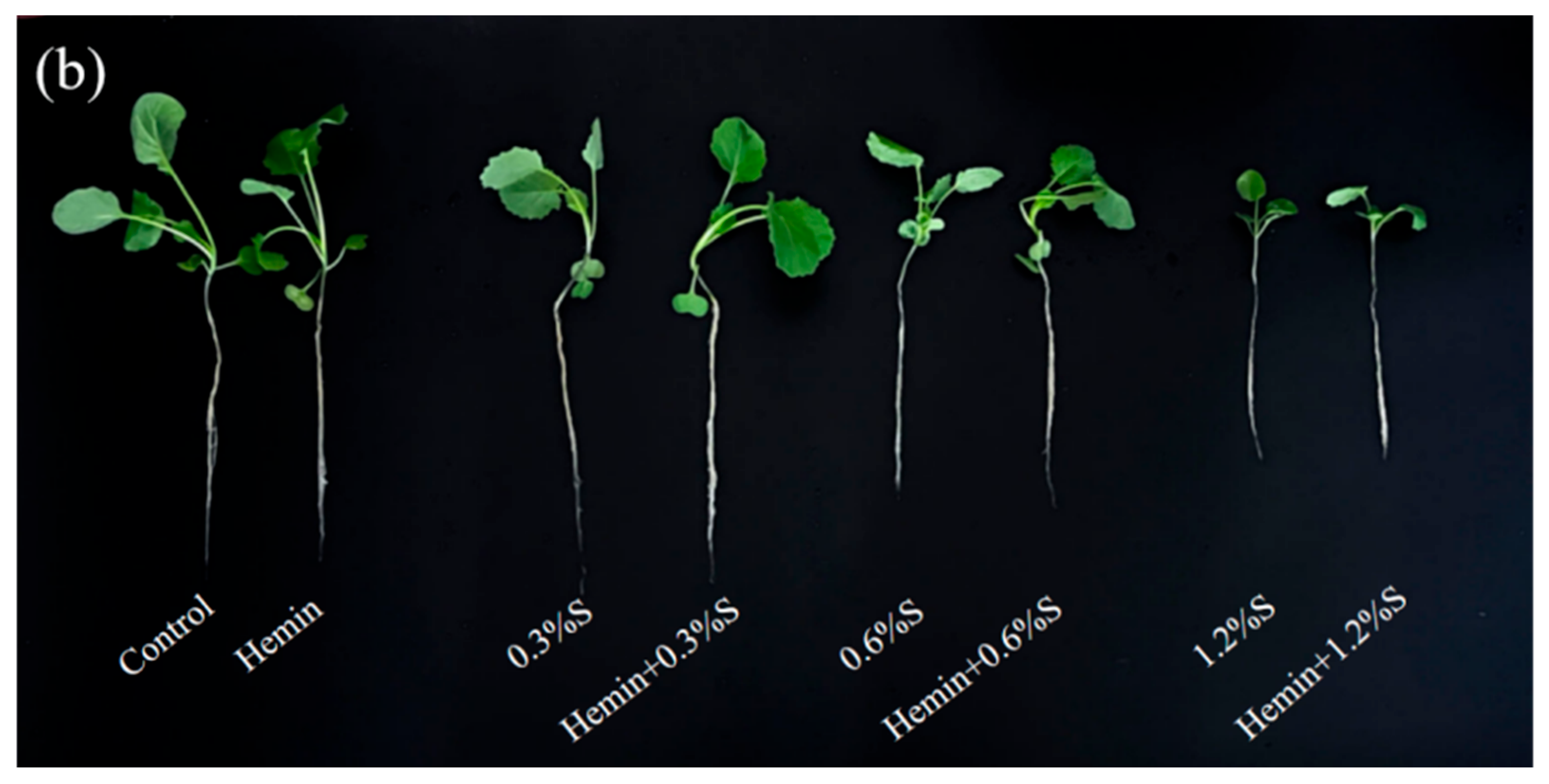
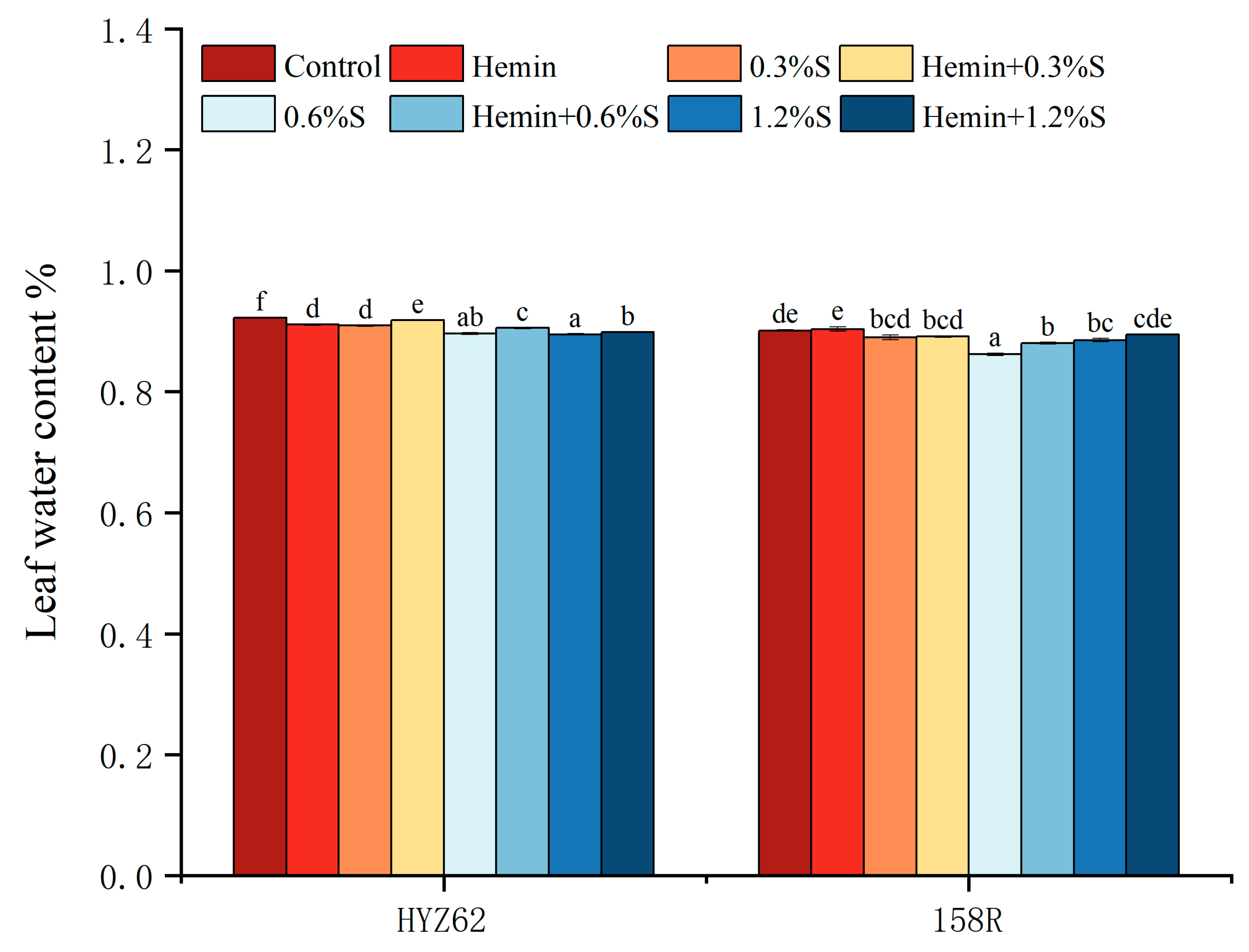
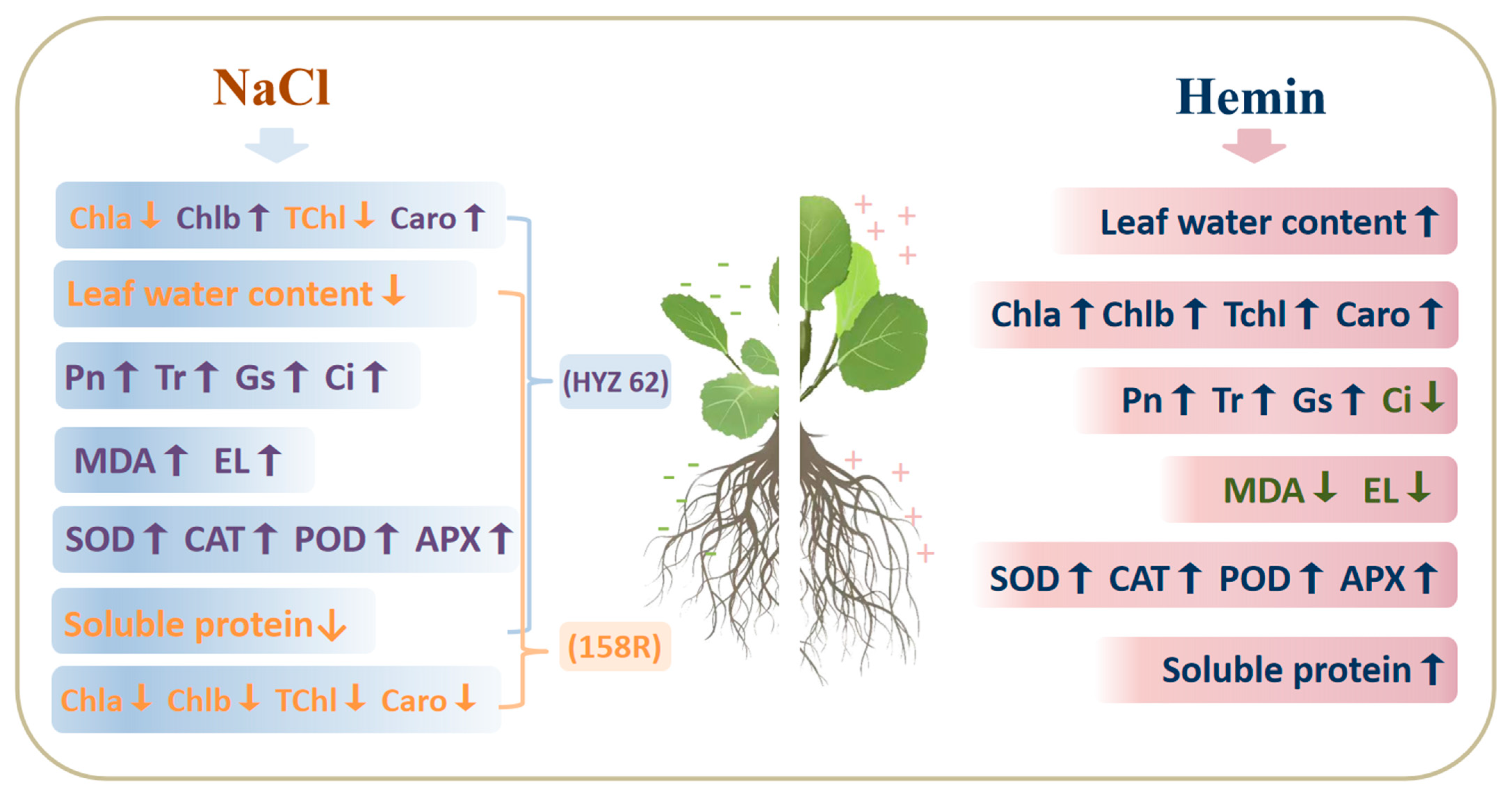
3.1. Effects of Hemin Soaking under NaCl Stress on Seedling Emergence Rate and Leaf Water Content
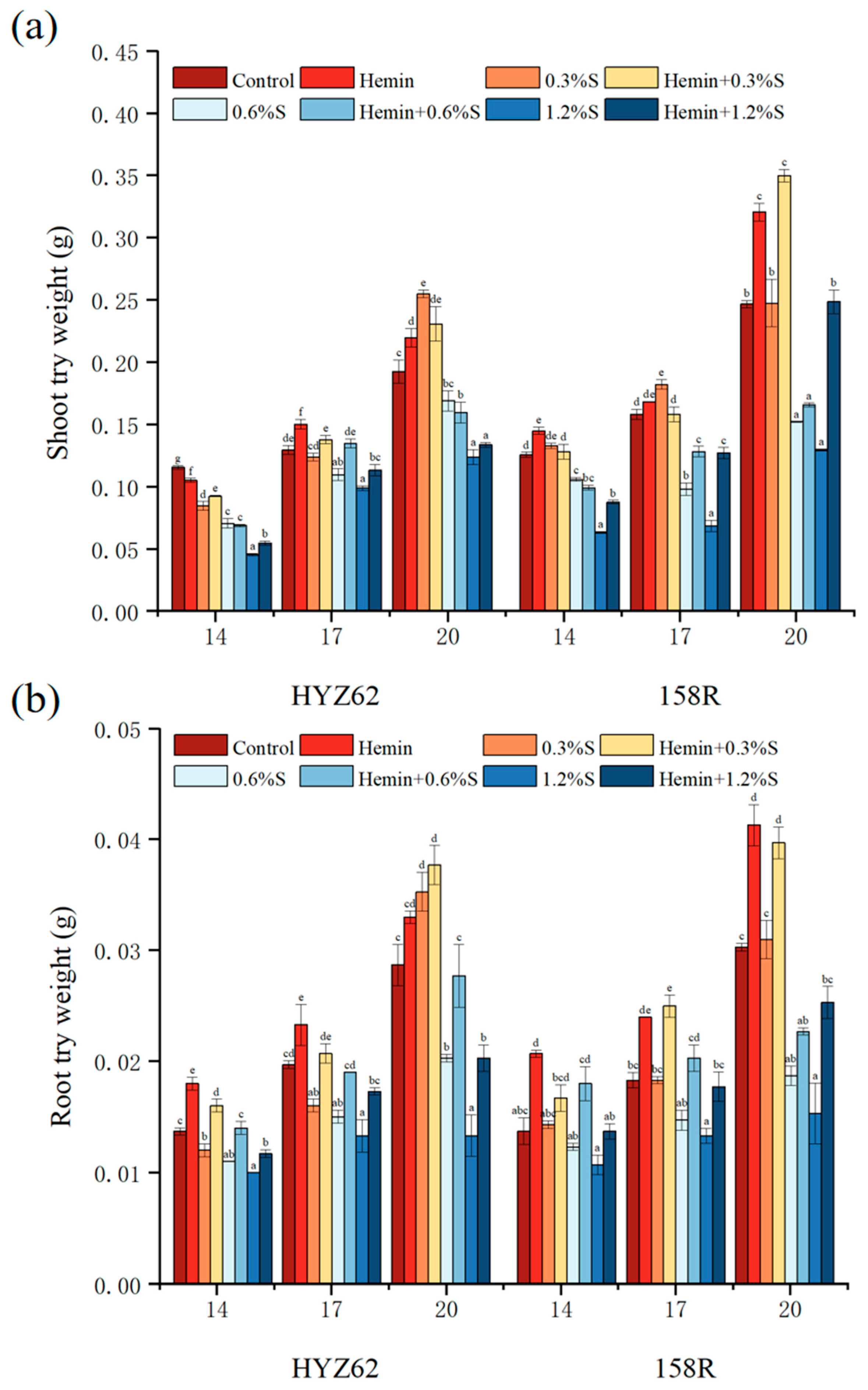
3.2. Effects of Hemin Seed Soaking under NaCl Stress on Growth Performance and Biomass of Rape Plants
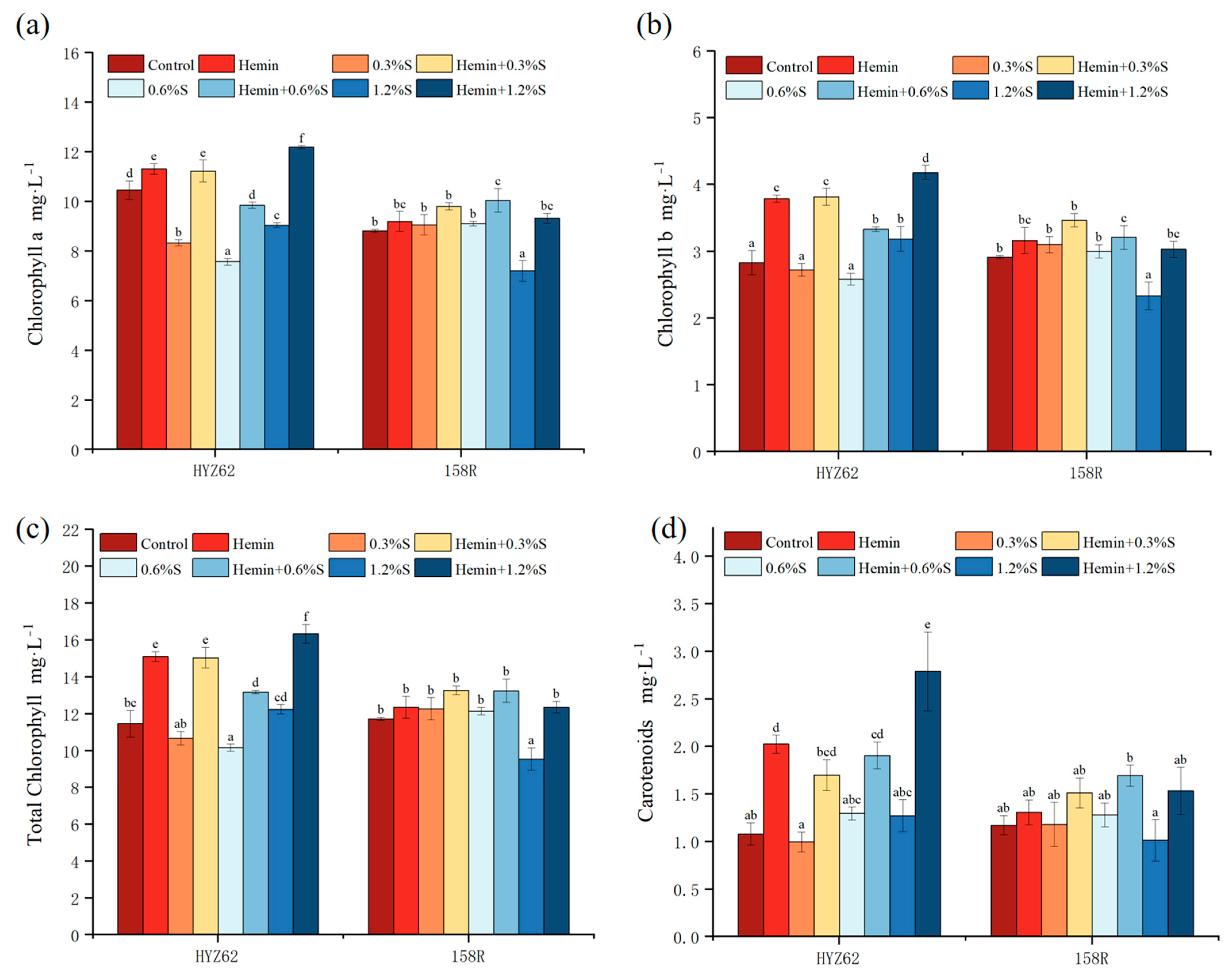
3.3. Effects of Hemin Soaking on Photosynthetic Pigment Content of Rape Seedlings under NaCl Stress
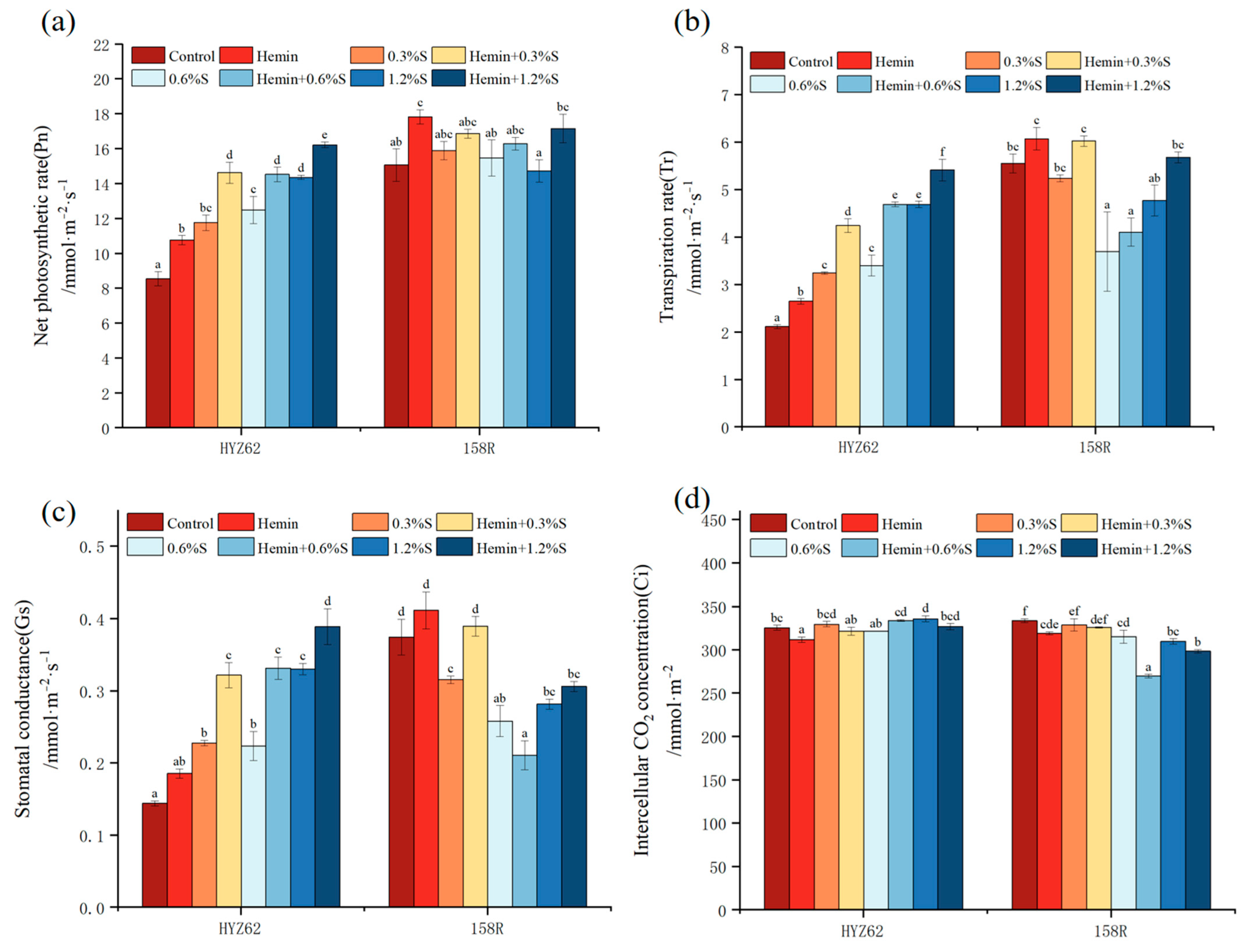
3.4. Effects of Hemin Soaking on Photosynthetic Capacity of Rape Seedlings under NaCl Stress
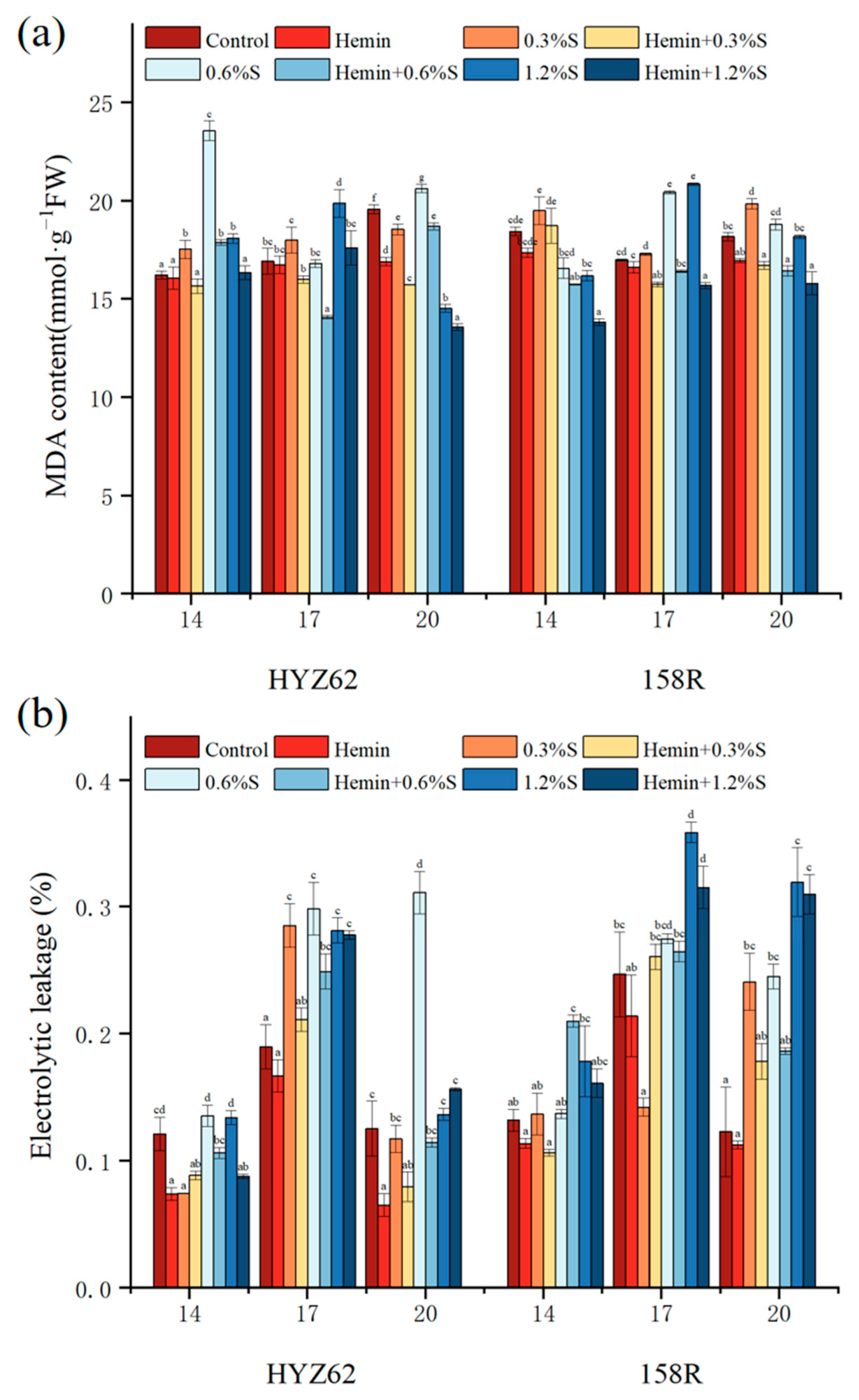
3.5. Hemin Seed Soaking Can Reduce Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Electrolyte Leakage Induced by NaCl
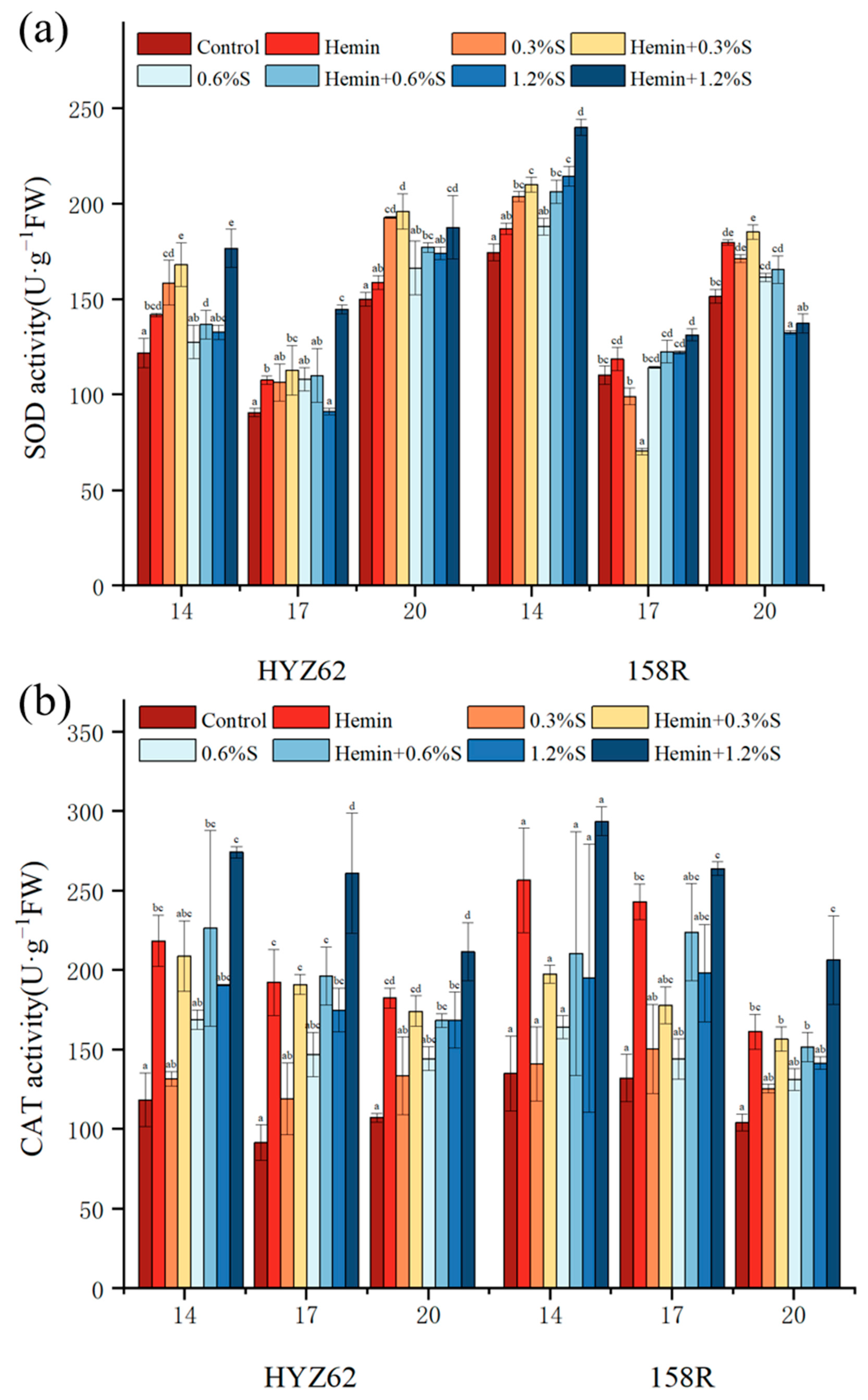
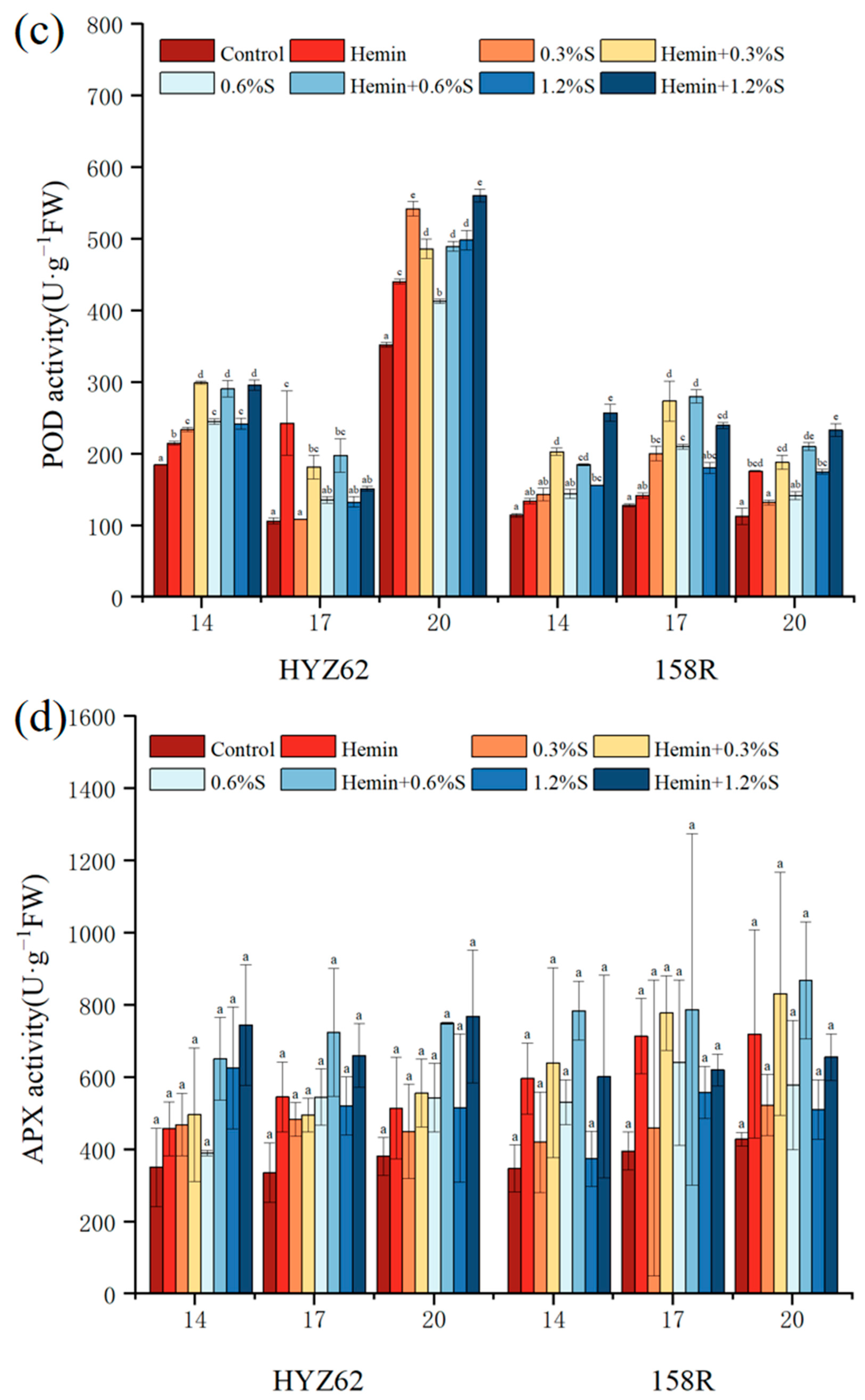
3.6. Effects of Hemin Seed Soaking on Antioxidant Properties of Rape Leaves under NaCl Stress
3.7. Effects of Hemin Seed Soaking on Soluble Protein Content in Rape Leaves under NaCl Stress
4. Discussion
4.1. Hemin Soaking Promotes Early Growth of Plant Seedlings
4.2. Effects of Exogenous Hemin on the Photosynthetic Parameters of Rape Seedlings under NaCl Stress
4.3. Hemin Soaking Induces a Cellular Defense System against Salt Stress
4.4. Effects of Hemin on Soluble Protein in Rapeseed under NaCl Stress
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munns, R. Comparative physiology of salt and water stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorne, S.J.; Stirnberg, P.M.; Hartley, S.E.; Maathuis, F.J. The ability of silicon fertilisation to alleviate salinity stress in rice is critically dependent on cultivar. Rice 2022, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, N. Study on the harm of saline alkali land and its improvement technology in china. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 692, 42053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, S.; Parkin, I.A.P.; Steppuhn, H.; Buchwaldt, M.; Adhikari, B.; Wood, R.; Wall, K.; Buchwaldt, L.; Singh, M.; Bekkaoui, D.; et al. Seedling, early vegetative, and adult plant growth of oilseed rapes (Brassica napus L.) Under saline stress. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2019, 99, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. A review on plant responses to salt stress and their mechanisms of salt resistance. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Oku, H.; Nahar, K.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Mahmud, J.A.; Baluska, F.; Fujita, M. Nitric oxide-induced saltstress tolerance in plants: Ros metabolism, signaling, and molecular interactions. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 12, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilli, C.G.; Balestrasse, K.B.; Yannarelli, G.G.; Polizio, A.H.; Santa-Cruz, D.M.; Tomaro, M.L. Heme oxygenase up-regulation under salt stress protects nitrogen metabolism in nodules of soybean plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2008, 64, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T. Soil Degradation, Land Scarcity and Food Security: Reviewing a Complex Challenge. Sustainability. 2016, 8, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiong, H.; Wei, H.; Yan, Y.; Xuekun, Z.; Lijiang, L.; Jiaqin, S.; Yongguo, Z.; Lu, Q.; Chang, C.; Hanzhong, W. Rapeseed research and production in china. Crop J. 2017, 5, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ashraf, M.; Mcneilly, T. Salinity tolerance in brassica oilseeds. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2004, 23, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orabi, S.A.; El-Shahawy, T.A.; Sharara, F.A. The polyamine spermine in retarding salinity-induced stress in canola. Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 86–100. [Google Scholar]
- Datir, S.; Singh, N.; Joshi, I. Effect of nacl-induced salinity stress on growth, osmolytes and enzyme activities in wheat genotypes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2020, 104, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Badri, A.M.; Batool, M.; A. A. Mohamed, I.; Wang, Z.; Khatab, A.; Sherif, A.; Ahmad, H.; Khan, M.N.; Hassan, H.M.; Elrewainy, I.M. Antioxidative and metabolic contribution to salinity stress responses in two rapeseed cultivars during the early seedling stage. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Wang, D.; Xie, K.; Lu, Y.; Shi, C.; Sabagh, A.E.; Gu, W.; Xu, P. Pre-sowing seed treatment with kinetin and calcium mitigates salt induced inhibition of seed germination and seedling growth of choysum (Brassica rapa var. Parachinensis). Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2021, 227, 112921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.Y.A.; Ibrahim, M.E.H.; Zhou, G.; Nimir, N.E.A.; Elradi, S.B.M. Gibberellic acid and nitrogen efficiently protect early seedlings growth stage from salt stress damage in sorghum. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Zheng, D.; Feng, N.; Huang, A.; Zhang, R.; Meng, F.; Jie, Y.; Mu, B.; Mu, D.; Zhou, H. Effects of prohexadione calcium spraying during the booting stage on panicle traits, yield, and related physiological characteristics of rice under salt stress. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiti, C.; Dan, Z.; Wenbiao, S.; Yudong, M.; Dekun, H.; Yujian, S.; Yong, R.; Wei, S.; Quan, G.; Daokun, X. Hydrogen peroxide is involved in β-cyclodextrin-hemin complex-induced lateral root formation in tomato seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1445. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.J.; Xu, S.; Han, B.; Wu, M.Z.; Shen, W.B. Evidence of arabidopsis salt acclimation induced by up-regulation of hy1 and the regulatory role of rbohd-derived reactive oxygen species synthesis. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 66, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Xuan, W.; Yu, T.; Fang, W.B.; Lou, T.L.; Gao, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Xiao, X.; Shen, W.B. Exogenous hematin alleviates mercury-induced oxidative damage in the roots of medicago sativa. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 1703–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Lou, T.; Zhao, N.; Gao, Y.; Dong, L.; Jiang, D.; Shen, W.; Huang, L.; Wang, R. Presoaking with hemin improves salinity tolerance during wheat seed germination. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2011, 33, 1173–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Ren, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z. Β-cyclodextrin–hemin enhances tolerance against salinity in tobacco seedlings by reestablishment of ion and redox homeostasis. Plant Growth Regul. 2017, 81, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Wei, S.; Gu, W. Exogenous hemin optimized maize leaf photosynthesis, root development, grain filling, and resource utilization on alleviating cadmium stress under field condition. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wang, W.; He, J.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M. Nitric oxide alleviates salt stress in seed germination and early seedling growth of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) By enhancing physiological and biochemical parameters. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 187, 109785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and carotenoids: Pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods Enzymol. 1987, 148C, 350–382. [Google Scholar]
- Rasheed, R.; Ashraf, M.A.; Ahmad, S.J.N.; Parveen, N.; Hussain, I.; Bashir, R. Taurine regulates ros metabolism, osmotic adjustment, and nutrient uptake to lessen the effects of alkaline stress on Trifolium alexandrinum L. plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 148, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar, S.; Bibi, G.; Ahmad, R.; Bilal, M.; Hussain, J. Evaluation of salt tolerance in eruca sativa accessions based on morpho-physiological traits. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Song, L.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, P. Polysaccharides from grateloupia filicina enhance tolerance of rice seeds (Oryza sativa L.) under salt stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 124, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ervin, E.H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, G.; Alpuerto, J. Differential responses of antioxidants, abscisic acid, and auxin to deficit irrigation in two perennial ryegrass cultivars contrasting in drought tolerance. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2015, 140, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, H.; Hu, W.J.; Shen, Z.J.; Qiao, F.; Zhu, C.Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.L. Proteomic analysis reveals the protective role of exogenous hydrogen sulfide against salt stress in rice seedlings. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2021, 111, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.R.; Rashad, M.; Hosny, A.; Shendy, S.; Gad, D.; Saad-Allah, K.M. Enhancement of growth and physiological traits under drought stress in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) Using nanocomposite. J. Plant Interact. 2022, 17, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Cui, W.; Dai, C.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; La, H.; Li, X.; Shen, W. Involvement of hydrogen peroxide and heme oxygenase-1 in hydrogen gas-induced osmotic stress tolerance in alfalfa. Plant Growth Regul. 2016, 80, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, W.; Zhu, F.Y.; Xu, S.; Huang, B.K.; Ling, T.F.; Qi, J.Y.; Ye, M.B.; Shen, W.B. The heme oxygenase/carbon monoxide system is involved in the auxin-induced cucumber adventitious rooting process. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekhawat, G.S.; Verma, K. Haem oxygenase (HO): An overlooked enzyme of plant metabolism and defence. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 2255–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, N.; Niu, M.; Liu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Z.; Zou, J.; Chen, Y.; Cui, J. Hemin-decreased cadmium uptake in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) Seedlings is heme oxygenase-1 dependent and relies on its by-products ferrous iron and carbon monoxide. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 115882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, A.; Pecoraro, V.; Zauli, S.; Ottone, M.; Leonardi, G.; Lauriola, P.; Trenti, T. Use of carboxyhemoglobin as a biomarker of environmental co exposure: Critical evaluation of the literature. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 25798–25809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gong, C.; Ju, X.; Zhu, Z.; Shen, W.; Shen, Z.; Cui, J. Hemin through the heme oxygenase 1/ferrous iron, carbon monoxide system involved in zinc tolerance in oryza sativa L. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 37, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.J.; Cui, W.; Yuan, X.; Shen, W.; Yang, Q. Heme Oxygenase-1 is Associated with Wheat Salinity Acclimation by Modulating Reactive Oxygen Species Homeostasis F. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habbasha, E.S.E. Mitigation salinity stress effects on barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Growth, yield and some physiological aspects by hemin 1,2. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2014, 9, 2411–2421. [Google Scholar]
- Pli, P.C.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, H.M.; Ting PA, N.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Z.F.; Xu, C.W. Metabolic responses to combined water deficit and salt stress in maize primary roots. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 109–119. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Meng, Y.; Wei, S.; Gu, W. Exogenous hemin confers cadmium tolerance by decreasing cadmium accumulation and modulating water status and matter accumulation in maize seedlings. Agronomy 2021, 11, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wei, W.; Chen, C.; Chen, L. Plant root-shoot biomass allocation over diverse biomes: A global synthesis. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2019, 18, e606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, K.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Nahar, K.; Fujita, M. Comparative physiological and biochemical changes in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Under salt stress and recovery: Role of antioxidant defense and glyoxalase systems. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, K.; Seyed Sharifi, R.; Pirzad, A.; Khalilzadeh, R. Effects of bio fertilizer and nano zn-fe oxide on physiological traits, antioxidant enzymes activity and yield of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Under salinity stress. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoufan, P.; Azad, Z.; Rahnama, A.; Kolahi, M. Modification of oxidative stress through changes in some indicators related to phenolic metabolism in malva parviflora exposed to cadmium. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 187, 109811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehdipoor Damiri, G.R.; Motamedzadegan, A.; Safari, R.; Shahidi, S.A.; Ghorbani, A. Evaluation of stability, physicochemical and antioxidant properties of extracted chlorophyll from persian clover (Trifolium resupinatum L.). J. Food Meas. Charact. 2021, 15, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yang, Z.; Zeng, X.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Yi, B.; Ma, C.; Shen, J.; Tu, J.; Fu, T.; et al. Heme oxygenase 1 defects lead to reduced chlorophyll in brassica napus. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 93, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huaifu, F.; Shirong, G.; Yansheng, J.; Runhua, Z.; Juan, L.I. Effects of exogenous nitric oxide on growth, active oxygen species metabolism, and photosynthetic characteristics in cucumber seedlings under nacl stress. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Marcek, M.C.P.M. Expression of dehydrins, hsp70, cu/zn sod, and rubisco in leaves of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) Dihaploids under salt stress. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biology. Plant J. Tissue Cult. Assoc. 2016, 52, 367–375. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, N.; Koussevitzky, S.; Mittler, R.; Miller, G. Ros and redox signalling in the response of plants to abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.H.Y.M. Abscisic acid primes rice seedlings for enhanced tolerance to alkaline stress by upregulating antioxidant defense and stress tolerance-related genes. Plant Soil 2019, 438, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanger, M.A.R.A. Combined effects of brassinosteroid and kinetin mitigates salinity stress in tomato through the modulation of antioxidant and osmolyte metabolism. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 147, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Badri, A.M.A.; Batool, M.; Mohamed, I.A.A.; Khatab, A.; Sherif, A.; Wang, Z.; Salah, A.; Nishawy, E.; Ayaad, M.; Kuai, J.; et al. Modulation of salinity impact on early seedling stage via nano-priming application of zinc oxide on rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 166, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Q.; Chen, X. Preliminary study on hemin-induced resistance to alkali stress of tobacco. Acta Tabacaria Sin. 2018, 24, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, Z.; Xuan, W.; Xu, S.; Ding, X.; Shen, W. Carbon monoxide alleviates cadmium-induced oxidative damage by modulating glutathione metabolism in the roots of medicago sativa. New Phytol. 2008, 177, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiti Cui, L.L.Z.G. Haem oxygenase-1 is involved in salicylic acid-induced alleviation of oxidative stress due to cadmium stress in medicago sativa. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5521–5534. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L. Melatonin improves the germination rate of cotton seeds under drought stress by opening pores in the seed coat. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alisofi, S.; Einali, A.; Sangtarash, M.H. Jasmonic acid-induced metabolic responses in bitter melon (Momordica charantia) seedlings under salt stress. J. Pomol. Hortic. Sci. 2020, 95, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yang, H. Physiological and biochemical mechanisms of exogenous calcium chloride on alleviating salt stress in two tartary buckwheat (Fagopyrum tataricum) varieties differing in salinity tolerance. Phyton-Int. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 91, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shkliarevskyi, M.A.; Kolupaev, Y.E.; Yastreb, T.O.; Karpets, Y.V.; Dmitriev, A.P. The effect of co donor hemin on the antioxidant and osmoprotective systems state in arabidopsis of a wild-type and mutants defective in jasmonate signaling under salt stress. Ukr. Biochem. J. 2021, 93, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Index | Treatments | HYZ 62 | 158R | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 17 | 20 | 14 | 17 | 20 | ||
| Shoot Length (cm) | Control | 15.23 ± 0.22 e | 15.37 ± 0.03 c | 21.67 ± 0.33 f | 18.57 ± 0.23 e | 20.20 ± 0.36 d | 20.80 ± 0.81 bc |
| Hemin | 14.93 ± 0.07 e | 16.30 ± 0.21 d | 18.83 ± 0.32 cd | 16.93 ± 0.47 d | 20.10 ± 0.26 d | 23.23 ± 0.43 d | |
| 0.3%S | 12.87 ± 0.30 c | 16.33 ± 0.17 d | 20.33 ± 0.33 e | 16.17 ± 0.17 d | 17.77 ± 0.37 c | 22.60 ± 0.31 cd | |
| Hemin + 0.3%S | 14.33 ± 0.09 c | 17.00 ± 0.00 e | 18.17 ± 0.09 c | 14.93 ± 0.07 c | 15.27 ± 0.38 b | 21.33 ± 0.67 bcd | |
| 0.6%S | 10.73 ± 0.12 b | 12.63 ± 0.35 a | 19.77 ± 0.23 de | 12.90 ± 0.06 b | 14.63 ± 0.18 ab | 19.63 ± 0.12 b | |
| Hemin + 0.6%S | 12.47 ± 0.03 c | 14.17 ± 0.09 b | 21.33 ± 0.67 f | 13.70 ± 0.15 b | 17.43 ± 0.22 c | 21.07 ± 0.13 bcd | |
| 1.2%S | 9.83 ± 0.20 a | 13.00 ± 0.40 d | 13.10 ± 0.10 a | 10.33 ± 0.20 a | 13.70 ± 0.30 a | 16.90 ± 0.31 a | |
| Hemin + 1.2%S | 10.60 ± 0.00 b | 14.57 ± 0.15 e | 15.00 ± 0.00 b | 12.67 ± 0.17 b | 15.47 ± 0.23 b | 20.40 ± 0.30 b | |
| Control | 16.97 ± 0.33 d | 19.50 ± 0.26 c | 18.5 ± 0.29 de | 17.33 ± 0.17 b | 17.83 ± 0.41 abc | 18.63 ± 0.43 abc | |
| Hemin | 17.50 ± 0.00 d | 18.83 ± 0.18 c | 19.40 ± 0.44 e | 19.80 ± 0.30 d | 20.03 ± 0.23 c | 17.90 ± 0.38 ab | |
| Root length (cm) | 0.3%S | 15.47 ± 0.47 bc | 16.47 ± 0.34 a | 16.77 ± 0.39 abc | 16.53 ± 0.23 b | 17.77 ± 0.15 abc | 17.97 ± 0.26 ab |
| Hemin + 0.3%S | 15.87 ± 0.13 bc | 17.30 ± 0.31 b | 18.47 ± 0.64 de | 19.93 ± 0.30 d | 18.70 ± 1.05 bc | 20.93 ± 0.56 c | |
| 0.6%S | 15.10 ± 0.06 b | 16.03 ± 0.23 a | 16.27 ± 0.35 ab | 16.83 ± 0.17 b | 16.53 ± 0.23 ab | 16.90 ± 0.47 a | |
| Hemin + 0.6%S | 16.50 ± 0.29 cd | 17.33 ± 0.19 b | 17.43 ± 0.30 bcd | 18.93 ± 0.58 cd | 19.40 ± 0.00 c | 19.93 ± 0.68 bc | |
| 1.2%S | 13.47 ± 0.55 a | 15.93 ± 0.23 a | 15.73 ± 0.43 a | 14.83 ± 0.17 a | 16.03 ± 0.32 a | 16.53 ± 0.20 a | |
| Hemin + 1.2%S | 15.80 ± 0.42 bc | 17.80 ± 0.06 b | 17.83 ± 0.67 cd | 17.83 ± 0.33 bc | 18.50 ± 0.55 bc | 21.23 ± 1.01 c | |
| Control | 3497.1 ± 146.0 e | 3922.9 ± 70.5 e | 5381.5 ± 59.6 ef | 2634.9 ± 122.6 d | 4636.2 ± 69.5 c | 5086.3 ± 354.2 bc | |
| Hemin | 2772.7 ± 85.1 d | 3388.1 ± 28.9 d | 4948.8 ± 265.2 de | 2462.4 ± 228.5 cd | 4179.3 ± 114.8 bc | 6514.1 ± 61.5 d | |
| Leaf area (cm2) | 0.3%S | 2781.2 ± 111.7 d | 2836.2 ± 81.7 bc | 5823.9 ± 259.1 f | 2581.0 ± 50.2 d | 3782.0 ± 66.2 b | 5973.4 ± 26.4 cd |
| Hemin + 0.3%S | 2449.4 ± 48.7 c | 3463.3 ± 136.5 d | 4167.6 ± 71.5 bc | 2277.8 ± 266.4 bcd | 2832.1 ± 75.1 a | 5309.4 ± 329.6 bc | |
| 0.6%S | 1677.5 ± 16.2 b | 3094.8 ± 179.8 cd | 4577.8 ± 101.9 cd | 1715.8 ± 52.3 abc | 2839.1 ± 29.1 a | 4301.9 ± 102.1 ab | |
| Hemin + 0.6%S | 1756.9 ± 37.6 b | 2670.1 ± 65.6 ab | 3986.9 ± 214.1 b | 1889.0 ± 78.1 abcd | 3630.5 ± 39.7 b | 4881.3 ± 312.9 bc | |
| 1.2%S | 1324.7 ± 12.7 a | 2678.8 ± 203.1 ab | 2786.7 ± 125.3 a | 1222.2 ± 161.3 a | 2698.5 ± 268.7 a | 3518.8 ± 120.1 a | |
| Hemin + 1.2%S | 1130.7 ± 6.3 a | 2338.4 ± 38.1 a | 3281.6 ± 86.8 a | 1616.2 ± 122.0 ab | 2930.6 ± 173.0 a | 5230.5 ± 219.8 bc | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Zheng, D.; Feng, N.; Zhou, G.; Khan, A.; Zhao, H.; Deng, P.; Zhou, H.; Lin, F.; Chen, Z. Metabolic Adaptations in Rapeseed: Hemin-Induced Resilience to NaCl Stress by Enhancing Growth, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Defense Ability. Metabolites 2024, 14, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010057
Lu X, Zheng D, Feng N, Zhou G, Khan A, Zhao H, Deng P, Zhou H, Lin F, Chen Z. Metabolic Adaptations in Rapeseed: Hemin-Induced Resilience to NaCl Stress by Enhancing Growth, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Defense Ability. Metabolites. 2024; 14(1):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010057
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xutong, Dianfeng Zheng, Naijie Feng, Guangsheng Zhou, Aaqil Khan, Huimin Zhao, Peng Deng, Hang Zhou, Feng Lin, and Ziming Chen. 2024. "Metabolic Adaptations in Rapeseed: Hemin-Induced Resilience to NaCl Stress by Enhancing Growth, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Defense Ability" Metabolites 14, no. 1: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010057
APA StyleLu, X., Zheng, D., Feng, N., Zhou, G., Khan, A., Zhao, H., Deng, P., Zhou, H., Lin, F., & Chen, Z. (2024). Metabolic Adaptations in Rapeseed: Hemin-Induced Resilience to NaCl Stress by Enhancing Growth, Photosynthesis, and Cellular Defense Ability. Metabolites, 14(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14010057







