Silybin Meglumine Mitigates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis and Bile Acid Metabolism Alterations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. LC-MS/MS
2.3. Histological Analysis of Mouse Liver Tissue
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Integration of Silybin Meglumine–Bile Acid Disorder Targets
2.6. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Network
2.7. Gene Enrichment Analysis
2.8. The qRT-PCR and Western Blot
2.9. Statistical Analysis
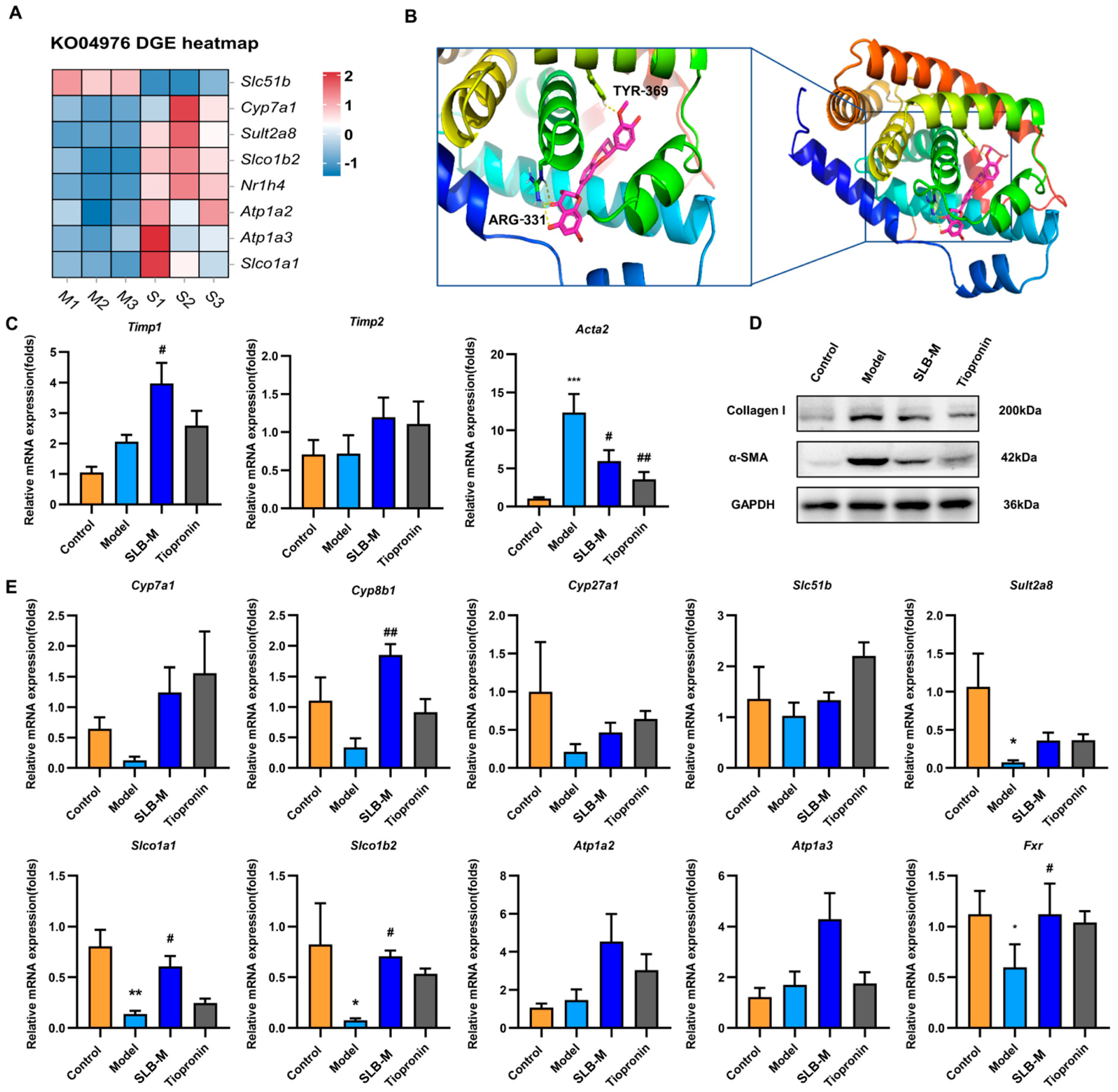
3. Results
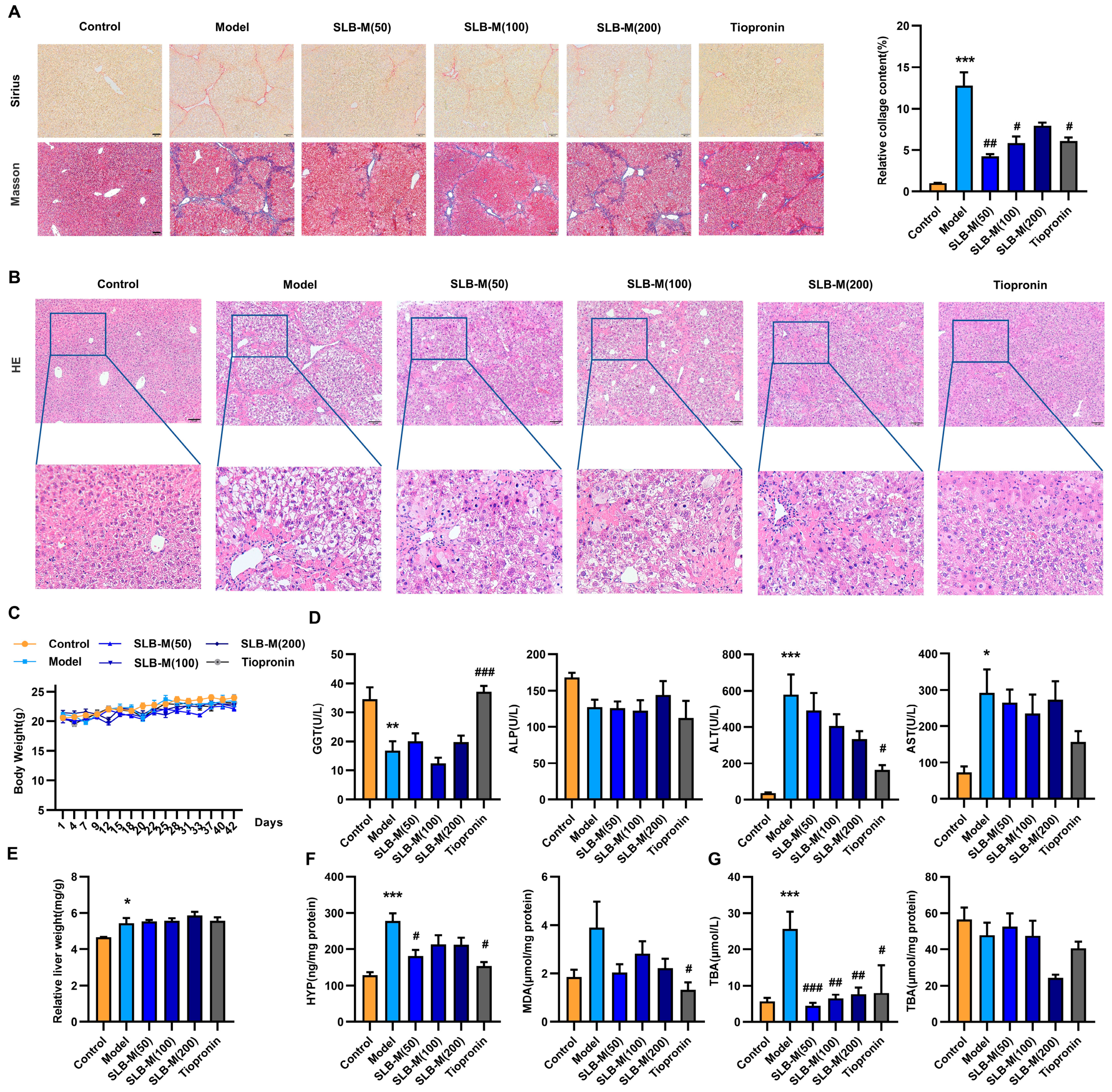
3.1. CCl4 Induces Liver Fibrosis and Bile Acid Profile Alterations in a Mouse Model
3.2. Silybin Meglumine Alleviates Liver Fibrosis in the Murine Model
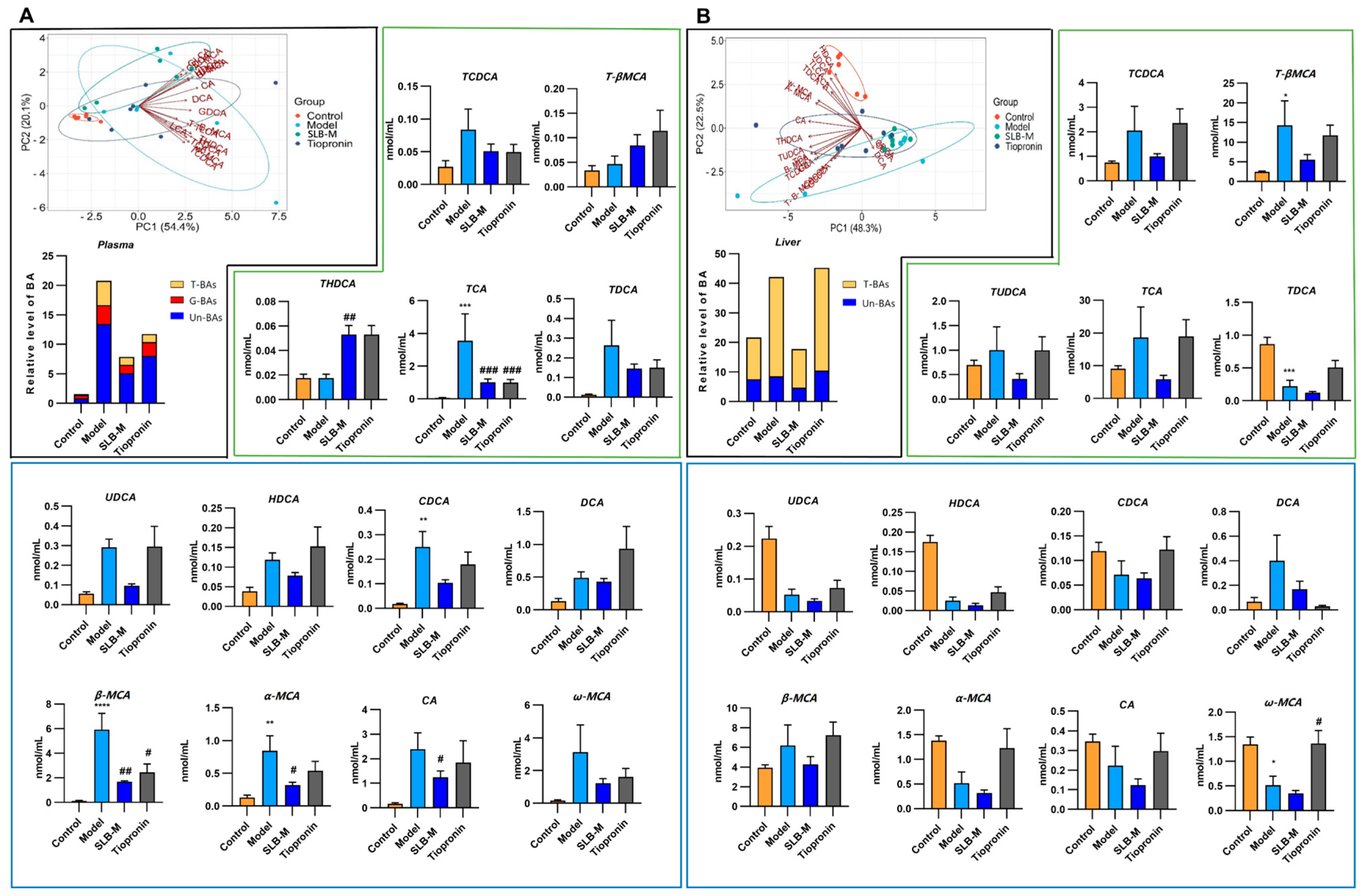
3.3. Silybin Meglumine Modulates BA Composition in CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis Mouse Model
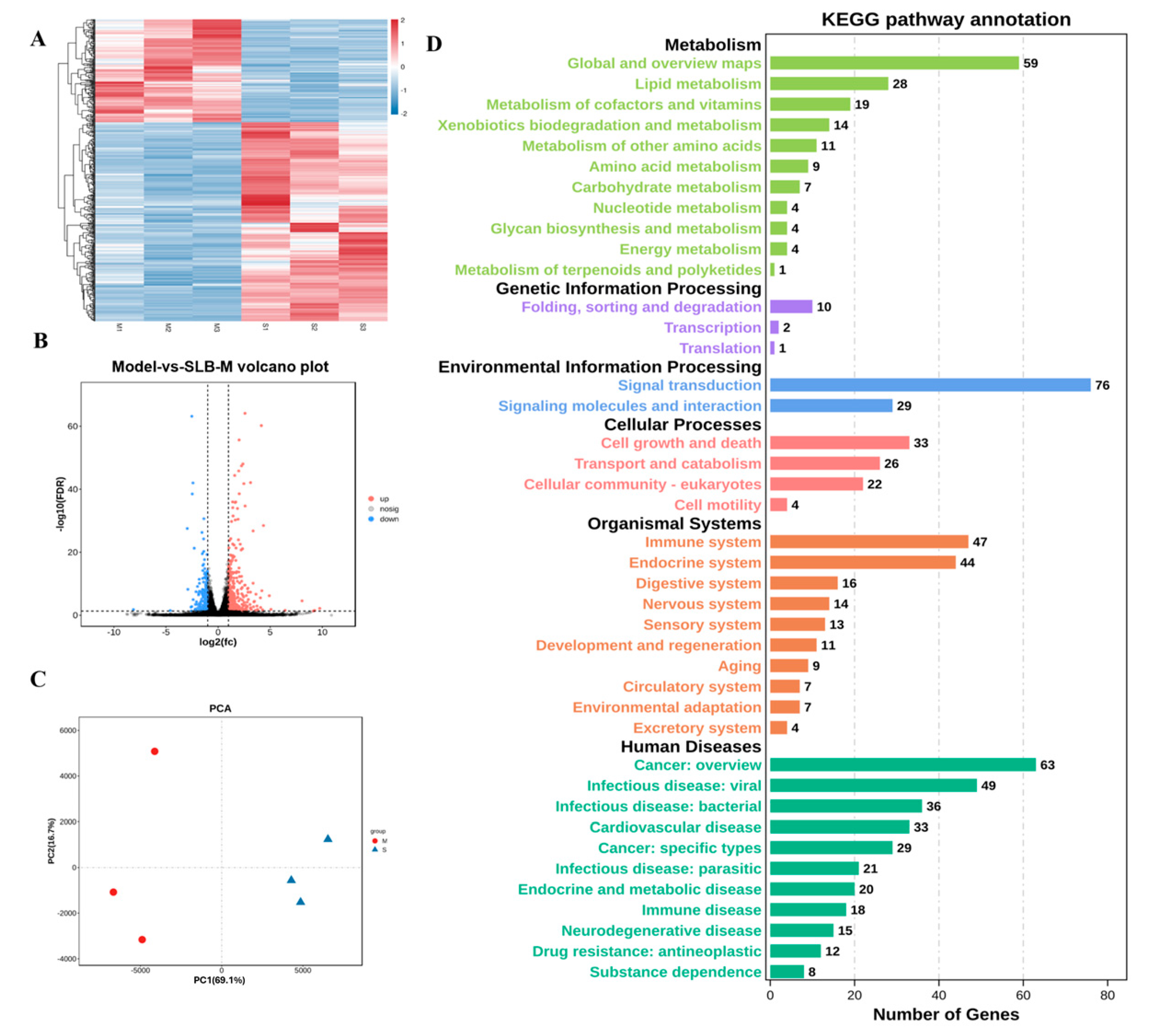
3.4. Identification and Characterization of DEGs in Silybin Meglumine-Treated Liver Fibrosis
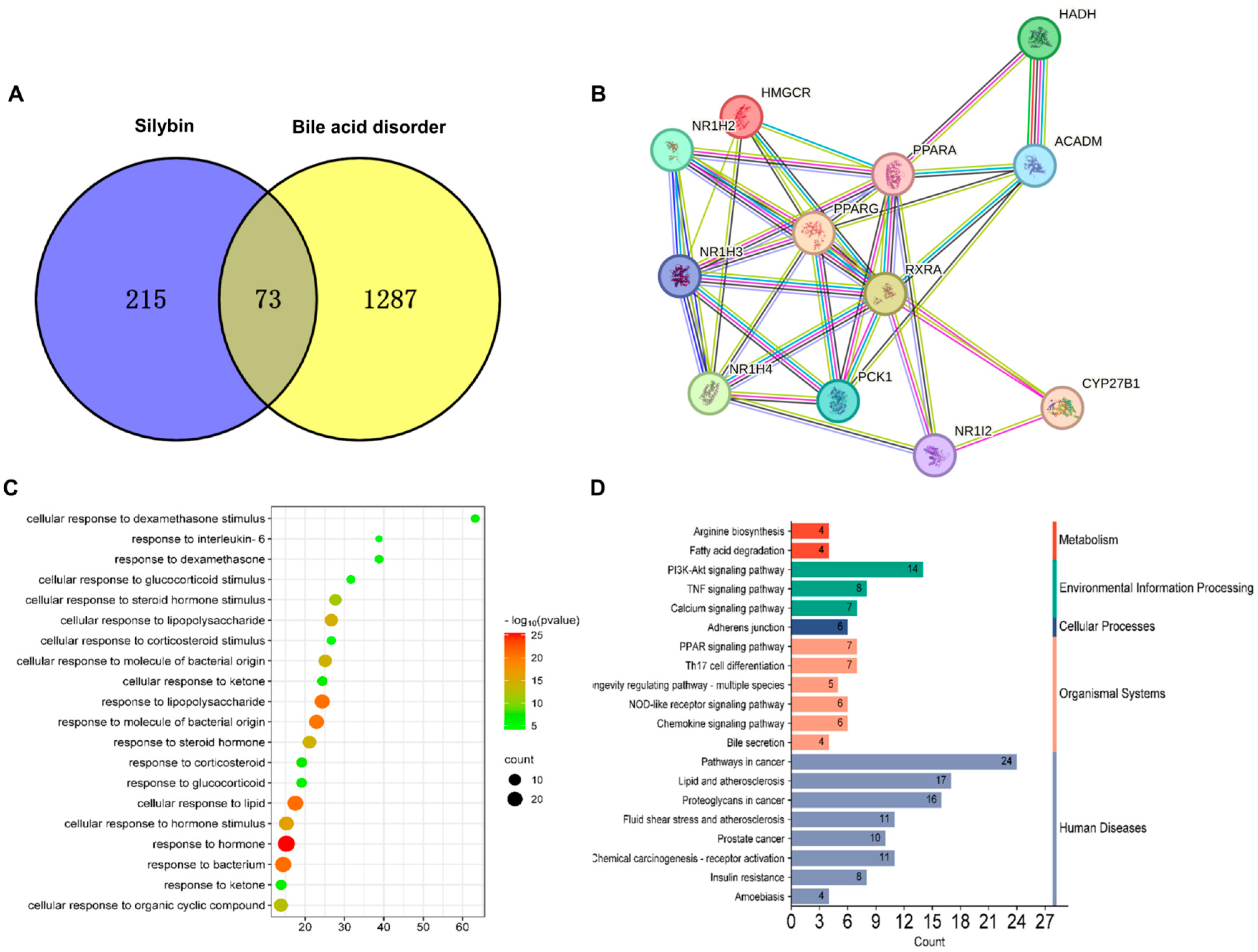
3.5. Network Pharmacology Analysis of Potential Therapeutic Mechanisms of Silybin Meglumine in Liver Fibrosis
3.6. Silybin Meglumine Modulates Bile Secretion Gene Expression through the Activation of Fxr in Liver Fibrosis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dhar, D.; Baglieri, J.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its role in liver cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2020, 245, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, P.; Chouhan, K.; Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 671640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginès, P.; Krag, A.; Abraldes, J.G.; Solà, E.; Fabrellas, N.; Kamath, P.S. Liver cirrhosis. Lancet 2021, 398, 1359–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinter, M.; Trauner, M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Sieghart, W. Cancer and liver cirrhosis: Implications on prognosis and management. ESMO Open 2016, 1, e000042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Moreau, R.; Kamath, P.S.; Jalan, R.; Ginès, P.; Nevens, F.; Fernández, J.; To, U.; García-Tsao, G.; Schnabl, B. Acute-on-chronic liver failure in cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. Treatment of liver fibrosis: Past, current, and future. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Wang, F.; Zhai, D.; Meng, X.; Liu, J.; Lv, X. New drugs for hepatic fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 874408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Gregorio, M.C.; Cautela, J.; Galantini, L. Physiology and physical chemistry of bile acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duszka, K. Versatile Triad Alliance: Bile acid, taurine and microbiota. Cells 2022, 11, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zhong, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H. The Potential of Bile Acids as Biomarkers for Metabolic Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimny, S.; Koob, D.; Li, J.; Wimmer, R.; Schiergens, T.; Nagel, J.; Reiter, F.P.; Denk, G.; Hohenester, S. Hydrophobic bile salts induce pro-fibrogenic proliferation of hepatic stellate cells through PI3K p110 alpha signaling. Cells 2022, 11, 2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Tang, X.; Liang, Z.; Chen, M.; Sun, L. Taurocholic acid promotes hepatic stellate cell activation via S1PR2/p38 MAPK/YAP signaling under cholestatic conditions. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, G.; Jiang, R.; Wang, X.; Liu, P.; Zhao, A.; Wu, Y.; Huang, F.; Liu, Z.; Rajani, C.; Zheng, X. Conjugated secondary 12α-hydroxylated bile acids promote liver fibrogenesis. EBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhail, M.J.; Shawcross, D.L.; Lewis, M.R.; Coltart, I.; Want, E.J.; Antoniades, C.G.; Veselkov, K.; Triantafyllou, E.; Patel, V.; Pop, O. Multivariate metabotyping of plasma predicts survival in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Li, X.; Fan, G.; Liu, R. Targeting bile acid signaling for the treatment of liver diseases: From bench to bed. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Izzo, A.A.; Milić, N.; Cicala, C.; Santini, A.; Capasso, R. Milk thistle (Silybum marianum): A concise overview on its chemistry, pharmacological, and nutraceutical uses in liver diseases. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 2202–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappoliere, M.; Caligiuri, A.; Schmid, M.; Bertolani, C.; Failli, P.; Vizzutti, F.; Novo, E.; di Manzano, C.; Marra, F.; Loguercio, C. Silybin, a component of sylimarin, exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrogenic effects on human hepatic stellate cells. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 1102–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polachi, N.; Bai, G.; Li, T.; Chu, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Gu, N.; Wu, J.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Modulatory effects of silibinin in various cell signaling pathways against liver disorders and cancer—A comprehensive review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 123, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loguercio, C.; Festi, D. Silybin and the liver: From basic research to clinical practice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents in chronic liver diseases: Molecular mechanisms and therapy. World J. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia-chang, S.; Wu-yi, S.; Xin-ran, L.; Wen-ting, P.; Jia-jia, D.; Wei, W. Comparison of hepatic fibrosis model induced by different concentrations of CCl4 in mice. Lab. Anim. Comp. Med. 2018, 38, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Yin, L.; Huang, C.; Fan, S. Mangiferin relieves CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, F.; Li, Y.; Zheng, M.; Xi, X.; Han, C. Silybum marianum seeds oil attenuates CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis via regulation of inflammatory response and oxidative stress. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2018, 14, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yan, T.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, M.; Che, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Cao, L.; Cheng, X.; Xie, Y.; et al. Mechanism-based inhibitory and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha-dependent modulating effects of silybin on principal hepatic drug-metabolizing enzymes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Q.; Zou, Y.H.; Huang, C.; Lu, C.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Y.; Lu, X.W.; Liu, L.P.; Li, J. Protective effects of tiopronin against high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Sun, H.; Xue, T.; Gan, C.; Liu, H.; Xie, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ye, T. Liver fibrosis: Therapeutic targets and advances in drug therapy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 730176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q.; Xie, M.; Lu, Z.M.; Xu, H.y.; Shi, J.S.; Xu, Z.H. Identification of antrodin B from Antrodia camphorata as a new anti-hepatofibrotic compound using a rapid cell screening method and biological evaluation. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, E15–E25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Vlekkert, D.; Machado, E.; d’Azzo, A. Analysis of generalized fibrosis in mouse tissue sections with Masson’s trichrome staining. Bio-Protocol 2020, 10, e3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Han, H. Protective effect of picroside I against hepatic fibrosis in mice via sphingolipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, and PPAR signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, C.; Li, Y.; Nian, C.; Li, J. FGF15 activates Hippo signaling to suppress bile acid metabolism and liver tumorigenesis. Dev. Cell 2019, 48, 460–474.e469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Cai, S.-Y.; Boyer, J.L. The role of the retinoid receptor, RAR/RXR heterodimer, in liver physiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, A.; Dallio, M.; Loguercio, C. Silymarin/Silybin and Chronic Liver Disease: A Marriage of Many Years. Molecules 2017, 22, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lala, V.; Zubair, M.; Minter, D.A. Liver Function Tests. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.W.; Huang, M.S.; Shyu, Y.C.; Chien, R.N. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase elevation is associated with metabolic syndrome, hepatic steatosis, and fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A community-based cross-sectional study. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabr, S.A.; Alghadir, A.H.; Sherif, Y.E.; Ghfar, A.A. Hydroxyproline as a Biomarker in Liver. In Biomarkers in Liver Disease; Springer Science+Business Media: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Fliss-Isakov, N.; Hahn, M.; Webb, M.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R.; Tirosh, O. Serum malondialdehyde is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver and related liver damage differentially in men and women. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Ciaula, A.; Garruti, G.; Baccetto, R.L.; Molina-Molina, E.; Bonfrate, L.; Portincasa, P.; Wang, D.Q. Bile acid physiology. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 16, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, M.; Pinzani, M. Liver fibrosis: Pathophysiology, pathogenetic targets and clinical issues. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauner, M.; Fuchs, C.D. Novel therapeutic targets for cholestatic and fatty liver disease. Gut 2022, 71, 194–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.D.; Trauner, M. Role of bile acids and their receptors in gastrointestinal and hepatic pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 432–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, Y.; Kessoku, T.; Tanaka, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Takahashi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Iwaki, M.; Ozaki, A.; Nogami, A.; Honda, Y. Association of serum and fecal bile acid patterns with liver fibrosis in biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An observational study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, e00503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudoin, J.J.; Brouwer, K.L.; Malinen, M.M. Novel insights into the organic solute transporter alpha/beta, OSTα/β: From the bench to the bedside. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 211, 107542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.; Ferrell, J.M. Up to date on cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) in bile acid synthesis. Liver Res. 2020, 4, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Yuen, Y.-L.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Chan, M.Y.-C.; Wang, K.; Fong, W.-P.; Cheung, W.-T.; Lee, S.S.-T. Identification and characterization of a novel PPARα-regulated and 7α-hydroxyl bile acid-preferring cytosolic sulfotransferase mL-STL (Sult2a8)[S]. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1114–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, E.; Cheema, H.; Waheed, N.; Mushtaq, I.; Erden, N.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Jain, D.; Soroka, C.J.; Boyer, J.L.; Khalil, Y. Organic solute transporter alpha deficiency: A disorder with cholestasis, liver fibrosis, and congenital diarrhea. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1879–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Pathak, P.; Boehme, S.; Chiang, J.L. Cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase protects the liver from inflammation and fibrosis by maintaining cholesterol homeostasis. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 1831–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenoya, F.; Shibato, J.; Yamashita, M.; Kimura, A.; Hirako, S.; Chiba, Y.; Nonaka, N.; Shioda, S.; Rakwal, R. Transcriptomic (DNA Microarray) and Metabolome (LC-TOF-MS) Analyses of the Liver in High-Fat Diet Mice after Intranasal Administration of GALP (Galanin-like Peptide). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, I.; Malkani, N.; Tahir, N.; Khalil, A.; Attar, R.; Mumtaz, S. Silymarin protects the liver from α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis by modulating the expression of genes involved in bile acid homeostasis: Anti-cholestatic effect of silymarin. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2022, 68, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Acta2 | GTACCACCATGTACCCAGGC | GCTGGAAGGTAGACAGCGAA |
| Atp1a2 | ACAGGAACCCTAAGGTGGCAGA | GTGGCTGAACTTGAGGAAACGG |
| Atp1a3 | GGTGTGGGTATCATCTCTGAGG | CGTCAATCTGCTCCGAGGTGAA |
| Cyp27a1 | GGAAGGTGCCCCAGAACAA | GCGCAGGGTCTCCTTAATCA |
| Cyp7a1 | CAGGGAGATGCTCTGTGTTCA | AGGCATACATCCCTTCCGTGA |
| Cyp8b1 | GTACACATGGACCCCGACATC | GGGTGCCATCAGGGTTGAG |
| GADPH | ATGGAGAAGGCTGGGGCTCACCT | AGCCCTTCCACGATGCCAAAGTTGT |
| FXR | TGGACTCATACAGCAAACAGAGA | GTCTGAAACCCTGGAAGTCTTTT |
| Slc51b | CAAGCATGTTCCTCCTGAGAAGG | CTCTTAGGAAGACCTGGCTGTTG |
| Sult2a8 | AAACAGCAAGGAGGGTCCACGT | CCTGACACAAGAACATCTCTGGG |
| Slco1b2 | GCAATGATCGGACCAATCCTTGG | CCAACGAGCATCCTGAGGAGTT |
| Slco1a1 | GCTGTTCAGTCTTACGAGTGTGC | CAAGGCATACTGGAGGCAAGCT |
| Timp1 | AGATACCATGATGGCCCCCT | CGCTGGTATAAGGTGGTCTCG |
| Timp2 | CTGGGACACGCTTAGCATCA | CCATCCAGAGGCACTCATCC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Xia, N.; Yu, Q.; Jin, M.; Wang, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, A.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Silybin Meglumine Mitigates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis and Bile Acid Metabolism Alterations. Metabolites 2024, 14, 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100556
Liu X, Xia N, Yu Q, Jin M, Wang Z, Fan X, Zhao W, Li A, Jiang Z, Zhang L. Silybin Meglumine Mitigates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis and Bile Acid Metabolism Alterations. Metabolites. 2024; 14(10):556. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100556
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoxin, Ninglin Xia, Qinwei Yu, Ming Jin, Zifan Wang, Xue Fan, Wen Zhao, Anqin Li, Zhenzhou Jiang, and Luyong Zhang. 2024. "Silybin Meglumine Mitigates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis and Bile Acid Metabolism Alterations" Metabolites 14, no. 10: 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100556
APA StyleLiu, X., Xia, N., Yu, Q., Jin, M., Wang, Z., Fan, X., Zhao, W., Li, A., Jiang, Z., & Zhang, L. (2024). Silybin Meglumine Mitigates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis and Bile Acid Metabolism Alterations. Metabolites, 14(10), 556. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14100556






