A Systematic Review: Assessment of the Metabolomic Profile and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Cannabis sativa as a Feed Additive for Ruminants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
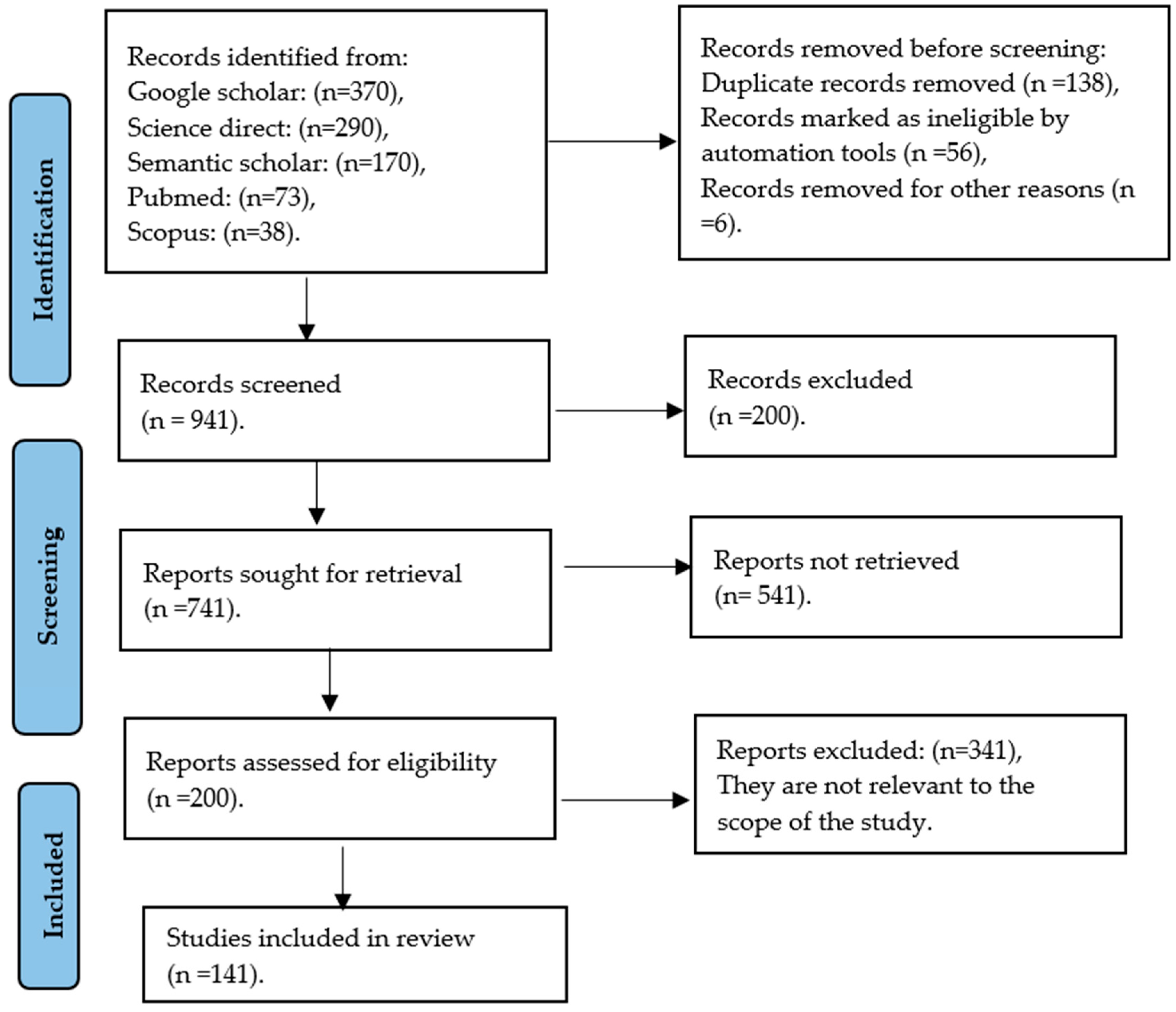
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategies
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Risk of Bias Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
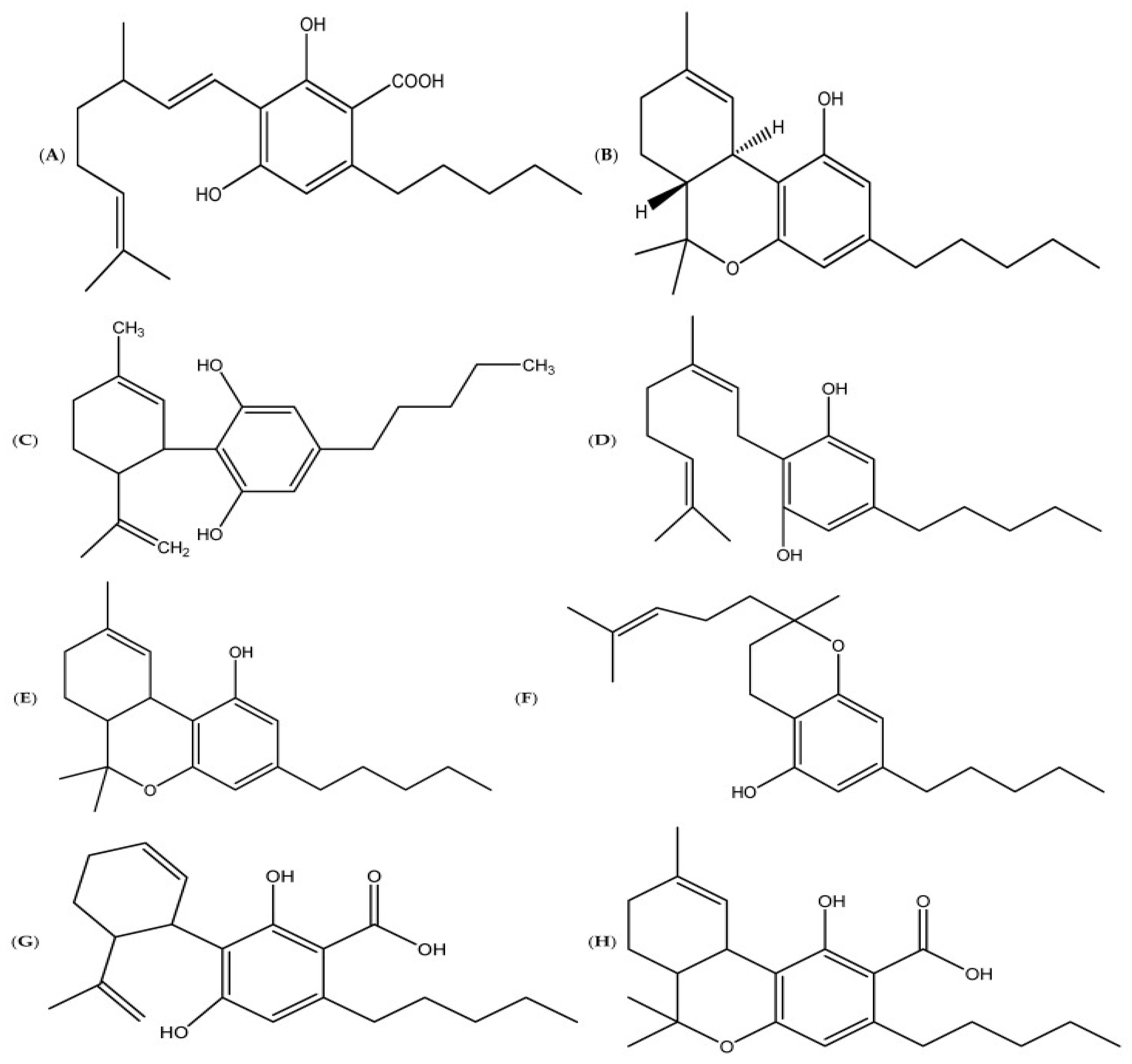
3.1. The Use of Metabolomics to Advance Cannabis Research Subsection
3.2. Nutritional Value of Cannabis
3.3. Anti-Nutritional Factors of Cannabis Sativa
3.4. Fermentation as a Cost-Effective Processing Method to Reduce Anti-Nutritional Factors
3.5. Inclusion of Cannabis Leaf in Ruminants Feed
Inclusion of Cannabis Meal as a Supplement to Sheep Diets
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stringer, C.E. Evaluating hemp (Cannabis sativa) as a forage based on yield, nutritive analysis, and morphological composition. Dissertations. Plant Soil. Sci. 2018, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarjani, M.P.; Young, O.; Kebede, L.; Seyfoddin, A. Processing and extraction methods of medicinal Cannabis: A narrative review. J. Cannabis Res. 2021, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klir, Ž.; Novoselec, J.; Antunović, Z. An overview on the use of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) in animal nutrition. Poljoprivreda 2019, 25, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliferis, K.A.; Bernard-Perron, D. Cannabinomics: Application of metabolomics in Cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.) research and development. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupasinghe, H.V.; Davis, A.; Kumar, S.K.; Murray, B.; Zheljazkov, V.D. Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa subsp. sativa) as an emerging source for value-added functional food ingredients and nutraceuticals. Molecules 2020, 25, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monyela, S.; Kayoka, P.N.; Ngezimana, W.; Nemadodzi, L.E. Evaluating the Metabolomic Profile and Anti-Pathogenic Properties of Cannabis Species. Metabolites 2024, 14, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, J.L. Medical marijuana for cancer. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solimini, R.; Rotolo, M.C.; Pichini, S.; Pacifici, R. Neurological disorders in medical use of Cannabis: An update. CNS Neurol. Disord.-Drug Targets (Former. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord.) 2017, 16, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Coppola, L.; Avilia, G.; Bifulco, M.; Laezza, C. Cannabinoids: Therapeutic use in clinical practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Justice and Correctional Services. Cannabis for Private Purposes Bill; Government Printer: Pretoria, South Africa, 2020; ISBN 978-1-4850-0659-6.
- Zhao, H.; Xiong, H.; Chen, J. Regional comparison and strategy recommendations of industrial hemp in China based on a SWOT analysis. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, A. Legal and regulatory issues governing cannabis and cannabis-derived products in the United States. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motshekga, L.M. Productivity and Physiological Responses of Winter Annual Forage Legumes to Planting Date and Short-Term Rotation with Forage Sorghum for Sheep Production Under No-Till System in Limpopo Province. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Limpopo, Sovenga, South Africa, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, G. Genetic Characterization of Smallholder Sheep Flocks in the Western Cape, South Africa. Master’s Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Western Cape, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobsz, J. Pelvimetry and Other Selected Contributing Factors Causing Dystocia in Dorper Ewes. Master’s Thesis, Central University of Technology, Bloemfontein, South Africa, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Molotsi, A.H.; Dube, B.; Cloete, S.W.P. The current status of indigenous ovine genetic resources in southern Africa and future sustainable utilisation to improve livelihoods. Diversity 2019, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Samuels, M.I.; Swarts, M.; Morris, C.; Cupido, C.F.; Engelbrecht, A. Diet selection and preference of small ruminants during drought conditions in a dryland pastoral system in South Africa. Small Rumin. Res. 2019, 176, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Fahad, S.; Du, G.; Cheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Tang, K.; Liu, L.; Liu, F.H.; Deng, G. Evaluation of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as an industrial crop: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 52832–52843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farinon, B.; Molinari, R.; Costantini, L.; Merendino, N. The seed of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): Nutritional quality and potential functionality for human health and nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famii, Z.L.; Oluwafeyikemi, E.U. The effect of feed Supplementation with Cannabis sativa on the Growth rate and Development of Broiler Chicks. Sciences 2024, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, A.A. Ecological, Commercial and Economic Significance of the Tree Lucerne: A Review. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2021, 91, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołodziej, J.; Pudełko, K.; Mańkowski, J. Energy and Biomass Yield of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as Influenced by Seeding Rate and Harvest Time in Polish Agro-Climatic Conditions. J. Nat. Fibers 2023, 20, 2159609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, A.W.; Kent-Dennis, C.; Klotz, J.L.; McLeod, K.R.; Vanzant, E.S.; Harmon, D.L. Utilizing industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) by-products in livestock rations. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2023, 307, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailoni, L.; Bacchin, E.; Trocino, A.; Arango, S. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed and co-products inclusion in diets for dairy ruminants: A review. Animals 2021, 11, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerino, P.; Buonerba, C.; Cannazza, G.; D’Auria, J.; Ottoni, E.; Fulgione, A.; Di Stasio, A.; Pierri, B.; Gallo, A. A review of hemp as food and nutritional supplement. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021, 6, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollica, M.P.; Trinchese, G.; Cimmino, F.; Penna, E.; Cavaliere, G.; Tudisco, R.; Musco, N.; Manca, C.; Catapano, A.; Monda, M.; et al. Milk fatty acid profiles in different animal species: Focus on the potential effect of selected pufas on metabolism and brain functions. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, P.; Amaral, C.; Teixeira, N.; Correia-da-Silva, G. Cannabis sativa: Much more beyond Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 157, 104822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odieka, A.E.; Obuzor, G.U.; Oyedeji, O.O.; Gondwe, M.; Hosu, Y.S.; Oyedeji, A.O. The medicinal natural products of Cannabis sativa Linn.: A review. Molecules 2022, 27, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, H.; Steele, B.; Bryant, J.; Toyang, N.; Ngwa, W. Non-cannabinoid metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. with therapeutic potential. Plants 2021, 10, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M.M.; Chandra, S.; Gul, S.; ElSohly, M.A. Cannabinoids, phenolics, terpenes and alkaloids of cannabis. Molecules 2021, 26, 2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milay, L.; Berman, P.; Shapira, A.; Guberman, O.; Meiri, D. Metabolic profiling of cannabis secondary metabolites for evaluation of optimal postharvest storage conditions. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 583605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemadodzi, L.E.; Vervoort, J.; Prinsloo, G. NMR-based metabolomic analysis and microbial composition of soil supporting Burkea africana growth. Metabolites 2020, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudge, E.M.; Brown, P.N.; Murch, S.J. The terroir of Cannabis: Terpene metabolomics as a tool to understand Cannabis sativa selections. Planta Med. 2019, 85, 781–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, P.S.; Paul, T. Lucerne (alfalfa). In Forage Crops of the World, 2-Volume Set: Volume I: Major Forage Crops; Volume II: Minor Forage Crops; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; p. 231. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Wen, K.S.; Ruan, X.; Zhao, Y.X.; Wei, F.; Wang, Q. Response of plant secondary metabolites to environmental factors. Molecules 2018, 23, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, G.; Storz, M.A.; Calapai, G. The role of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) as a functional food in vegetarian nutrition. Foods 2023, 12, 3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axentii, M.; Codină, G.G. Exploring the Nutritional Potential and Functionality of Hemp and Rapeseed Proteins: A Review on Unveiling Anti-Nutritional Factors, Bi*oactive Compounds, and Functional Attributes. Plants 2024, 13, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adebiyi, J.A.; Kayitesi, E.; Adebo, O.A.; Changwa, R.; Njobeh, P.B. Food fermentation and mycotoxin detoxification: An African perspective. Food Control. 2019, 106, 106731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Cui, L.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Guo, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Wu, G. Fermentation techniques in feed production. In Animal Agriculture; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 407–429. [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. The PRISMA Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-Ocmín, P.G.; Marti, G.; Bonhomme, M.; Mathis, F.; Fournier, S.; Bertani, S.; Maciuk, A. Cannabinoids vs. whole metabolome: Relevance of cannabinomics in analyzing Cannabis varieties. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1184, 339020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebani, A.; Afonso, C.; Bekri, S. Advances in metabolome information retrieval: Turning chemistry into biology. Part I: Analytical chemistry of the metabolome. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2018, 41, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbs, M.; Leng, S.; Devassy, J.G.; Monirujjaman, M.; Aukema, H.M. Advances in our understanding of oxylipins derived from dietary PUFAs. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 513–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Qi, D.; Sun, M.; Hou, Q.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H. Establishment of the circadian metabolic phenotype strategy in spontaneously hypertensive rats: A dynamic metabolomics study. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Shan, Y.; Song, X.; Hu, H.; Ren, X.; Ma, X.; Cui, J.; Ma, Y. Integrated microbiology and metabolomics analysis reveal plastic mulch film residue affects soil microorganisms and their metabolic functions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Lee, Y.H.; Lu, H. Functional metabolomics decipher biochemical functions and associated mechanisms underlie small-molecule metabolism. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2020, 39, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, P.D.; Shim, Y.Y.; Paek, O.J.; Jeon, J.T.; Park, H.J.; Park, I.; Park, E.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Reaney, M.J. A metabolomics and big data approach to Cannabis authenticity (authentomics). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, B.B. New software tools, databases, and resources in metabolomics: Updates from 2020. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourseyed Lazarjani, M.; Torres, S.; Hooker, T.; Fowlie, C.; Young, O.; Seyfoddin, A. Methods for quantification of cannabinoids: A narrative review. J. Cannabis Res. 2020, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, F.A.; Rosati, G.; Moguet, C.; Fuentes, C.; Marrugo-Ramírez, J.; Lefebvre, T.; Volland, H.; Merkoçi, A.; Simon, S.; Fenaille, F.; et al. Metabolomics for personalized medicine: The input of analytical chemistry from biomarker discovery to point-of-care tests. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022, 414, 759–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Wei, X.; Li, X.; Wei, X.; Wu, S.; Huang, W.; Koidis, A.; Xu, Z.; Lei, H. Untargeted metabolomics by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for food authentication: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 21, 2455–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiebert-Giesbrecht, M.; Torres-Calzada, C.; Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics of the Cannabis plant. In Cannabis Use, Neurobiology, Psychology, and Treatment; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Colella, M.F.; Salvino, R.A.; Gaglianò, M.; Litrenta, F.; Oliviero Rossi, C.; Le Pera, A.; De Luca, G. NMR Spectroscopy Applied to the Metabolic Analysis of Natural Extracts of Cannabis sativa. Molecules 2022, 27, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Daza, M.C.; Pulido-Mateos, E.C.; Lupien-Meilleur, J.; Guyonnet, D.; Desjardins, Y.; Roy, D. Polyphenol-mediated gut microbiota modulation: Toward prebiotics and further. Front Nutr. 2021, 8, 689456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iffland, K.; Grotenhermen, F. An update on safety and side effects of cannabidiol: A review of clinical data and relevant animal studies. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, A.D.; Devi, M. Adverse Effects Associated With Cannabis Use For Medical Problems. Cannabis 2020, 5, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, F.U.; Liu, C.; Mehboob, M.; Bilal, R.M.; Arain, M.A.; Siddique, F.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, P.; et al. Potential of dietary hemp and cannabinoids to modulate immune response to enhance health and performance in animals: Opportunities and challenges. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1285052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, F.U. Effects of Industrial Hemp Supplementation (Cannabis sativa) on Estrous Cycle Characteristics and Serum Biochemistry of Angus Cattle. Master’s Thesis, Alabama Agricultural and Mechanical University, Huntsville, AL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Xiao, G.; Cheng, P.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Y. Protective application of Chinese herbal compounds and formulae in intestinal inflammation in humans and animals. Molecules 2023, 28, 6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassolino, L.; Fulvio, F.; Cerrato, A.; Citti, C.; Cannazza, G.; Capriotti, A.L.; Alberti, I.; Terracciano, I.; Pecchioni, N.; Paris, R. Metabolic characterization and transcriptional profiling of polyphenols in Cannabis sativa L. inflorescences with different chemical phenotypes. Planta 2024, 260, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggan, P.J. The chemistry of cannabis and cannabinoids. Aust. J. Chem. 2021, 74, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamle, M.; Mahato, D.K.; Sharma, B.; Gupta, A.; Shah, A.K.; Mahmud, M.C.; Agrawal, S.; Singh, J.; Rasane, P.; Shukla, A.C.; et al. Nutraceutical potential, phytochemistry of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) and its application in food and feed: A review. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, T.; Luo, G.; Yue, Y.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Lei, Z.; Yang, W.; Wu, D. Partially substituting alfalfa hay with hemp forage promotes the health and well-being of goats via altering ruminal and plasma metabolites and metabolic pathways. Anim. Res. One Health 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Daungchana, N.; Sisubalan, N.; Chaiyasut, C. Composition, Bioactivities, Microbiome, Safety Concerns, and Impact of Essential Oils on the Health Status of Domestic Animals. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego-Poyato, S.; Rodrigo-Garcia, M.; Escudero-Feliu, J.; Garcia-Costela, M.; Lima-Cabello, E.; Carazo-Gallego, A.; Morales-Santana, S.; Leon, J.; Jimenez-Lopez, J.C. Current advances research in nutraceutical compounds of legumes, pseudocereals and cereals. In Grain and Seed Proteins Functionality; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kotsampasi, B.; Karatzia, M.A.; Tsiokos, D.; Chadio, S. Nutritional Strategies to Alleviate Stress and Improve Welfare in Dairy Ruminants. Animals 2024, 14, 2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, N.; Sharififar, F.; Pournamdari, M.; Ansari, M. A review on biosynthesis, analytical techniques, and pharmacological activities of trigonelline as a plant alkaloid. J. Diet. Suppl. 2018, 15, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Mi, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Cao, X.; Wan, H.; Yang, W.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; et al. Genome-wide identification of key enzyme-encoding genes and the catalytic roles of two 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase involved in flavonoid biosynthesis in Cannabis sativa L. Microb. Cell Fact. 2022, 21, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomko, A.M.; Whynot, E.G.; Ellis, L.D.; Dupré, D.J. Anti-cancer potential of cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids present in cannabis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micalizzi, G.; Vento, F.; Alibrando, F.; Donnarumma, D.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Cannabis sativa L.: A comprehensive review on the analytical methodologies for cannabinoids and terpenes characterization. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1637, 461864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingol, K. Recent advances in targeted and untargeted metabolomics by NMR and MS/NMR methods. High-Throughput 2018, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndlangamandla, V.V.; Salawu-Rotimi, A.; Bushula-Njah, V.S.; Hlongwane, N.L.; Sibandze, G.F.; Gebashe, F.C.; Mchunu, N.P. Finally Freed—Cannabis in South Africa: A Review Contextualised within Global History, Diversity, and Chemical Profiles. Plants 2024, 13, 2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.D.; Schlegel, A.; Obour, A.K.; Assefa, Y. Dryland cropping system impact on forage accumulation, nutritive value, and rainfall use efficiency. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 3395–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekasha, A.; Min, D.; Bascom, N.; Vipham, J. Seeding rate effects on forage productivity and nutritive value of sorghum. J. Agron. 2022, 114, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Bai, M.; Song, H.; Yang, L.; Zhu, D.; Liu, H. Hemp (Cannabis sativa subsp. sativa) Chemical composition and the application of hempseeds in food formulations. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2022, 77, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audu, B.S.; Ofojekwu, P.C.; Ujah, A.; Ajima, M.N.O. Phytochemical, proximate composition, amino acid profile and characterization of Marijuana (Cannabis sativa L.). J. Phytopharmacol. 2014, 3, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockson, P.; Landis, H.; Smith, T.; Hicks, K.; Whipker, B.E. Characterization of nutrient disorders of Cannabis sativa. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 4432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinhenz, M.D.; Magnin, G.; Ensley, S.M.; Griffin, J.J.; Goeser, J.; Lynch, E.; Coetzee, J.F. Nutrient concentrations, digestibility, and cannabinoid concentrations of industrial hemp plant components. Appl. Anim. 2020, 36, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araiza-Rosales, E.E.; Herrera-Torres, E.; Carrete-Carreón, F.Ó.; Jiménez-Ocampo, R.; Gómez-Sánchez, D.; Pámanes-Carrasco, G.A. Nutrient concentrations, in vitro digestibility and rumen fermentation of agro-industrial residues of Cannabis sativa L. as a potential forage source for ruminants. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2023, 14, 366–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samtiya, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Dhewa, T. Plant food anti-nutritional factors and their reduction strategies: An overview. Food Prod. Process. Nutr. 2020, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Dai, K.; Xie, Z.; Chen, J. Secondary metabolites profiled in cannabis inflorescences, leaves, stem barks, and roots for medicinal purposes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Sharma, V.; Thakur, A. An overview of anti-nutritional factors in food. Int. J. Chem. Stud. 2019, 7, 2472–2479. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Jian, C. Sustainable plant-based ingredients as wheat flour substitutes in bread making. NPJ Sci. Food. 2022, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizollahi, E.; Mirmahdi, R.S.; Zoghi, A.; Zijlstra, R.T.; Roopesh, M.S.; Vasanthan, T. Review of the beneficial and anti-nutritional qualities of phytic acid, and procedures for removing it from food products. Int. Food Res. 2021, 143, 110284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Guo, S. Phytic acid and its interactions: Contributions to protein functionality, food processing, and safety. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food. 2021, 20, 2081–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galasso, I.; Russo, R.; Mapelli, S.; Ponzoni, E.; Brambilla, I.M.; Battelli, G.; Reggiani, R. Variability in Seed Traits in a Collection of Cannabis sativa L. Genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Reggiani, R. Evaluation of Protein Concentration, Amino Acid Profile and Anti-nutritional Compounds in Hempseed Meal from Dioecious and Monoecious Varieties. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, P.H.; Pihlava, J.-M.; Hellström, J.; Nurmi, M.; Eurola, M.; Mäkinen, S.; Jalava, T.; Pihlanto, A. Contents of phytochemicals and antinutritional factors in commercial protein-rich plant products. Food Qual. Saf. 2018, 2, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besharati, M.; Maggiolino, A.; Palangi, V.; Kaya, A.; Jabbar, M.; Eseceli, H.; De Palo, P.; Lorenzo, J.M. Tannin in Ruminant Nutrition. Molecules 2022, 27, 8273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelln, B.M.; Penner, G.B.; Acharya, S.N.; McAllister, T.A.; Lardner, H.A. Impact of condensed tannin-containing legumes on ruminal fermentation, nutrition, and performance in ruminants: A review. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 101, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Hoyos-Martínez, P.L.; Merle, J.; Labidi, J.; Charrier–El Bouhtoury, F. Tannins extraction: A key point for their valorization and cleaner production. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 206, 1138–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, S.; Narwal, S.; Gupta, O.P.; Pandey, V.; Singh, G.P. Anti-nutritional factors and bioavailability: Approaches, challenges, and opportunities. Wheat Barley Grain Biofortif. 2020, 101–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, K.; Li, J.; Zhong, C.; He, X. Inactivation of Soybean Trypsin Inhibitor by Dielectric-Barrier Discharge Plasma and Its Safety Evaluation and Application. Foods 2022, 11, 4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Meng, G.; Lu, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhao, P.; Li, Y. Physicochemical Properties and Elimination of the Activity of Anti-Nutritional Serine Protease Inhibitors from Mulberry Leaves. Molecules 2022, 27, 1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulvianti, M.; Zidorn, C. Chemical diversity of plant cyanogenic glycosides: An overview of reported natural products. Molecules 2021, 26, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirenda, K.K. Toxicity potential of cyanogenic glycosides in edible plants. Med. Toxicol. 2020, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Qaderi, M.M.; Martel, A.B.; Strugnell, C.A. Environmental Factors Regulate Plant Secondary Metabolites. Plants 2023, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C. Removal of Cyanogenic Glycosides in Whole Flaxseed via Lactobacillaceae Fermentation. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- El Aziz, M.M.A.; Ashour, A.S.; Melad, A.G. A review on saponins from medicinal plants: Chemistry, isolation, and determination. J. Nanomed. Res. 2019, 8, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Bouzier, A.; Rojas, J.; Ibinga, S.K.K.; Lamarti, A.; Martin, P. The Impact of Saponins on Health-Review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2023, 13, 362. [Google Scholar]
- Anaemene, D.; Fadupin, G. Anti-nutrient reduction and nutrient retention capacity of fermentation, germination and combined germination-fermentation in legume processing. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadele, Y. Important anti-nutritional substances and inherent toxicants of feeds. Food Sci. Qual. Manag. 2015, 36, 40–47. [Google Scholar]
- Eze, C.R.; Kwofie, E.M.; Adewale, P.; Lam, E.; Ngadi, M. Advances in legume protein extraction technologies: A review. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 82, 103199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsmann, M.N. Nutritional and Digestive Factors Affecting Health and Performance in Weaned Pigs. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Bologna, Bologna, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, V.K.; Abrol, G.S.; Singh, A.K. Anti-nutritional factors in food and plant crops. Int. J. Food Ferment. Technol. 2020, 10, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, L.P.; Pandey, A.; Carvalho, J.C.; Letti, L.A.; Woiciechowski, A.L.; Karp, S.G.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Martínez-Burgos, W.J.; Penha, R.O.; Herrmann, L.W.; et al. Solid-state fermentation technology and innovation for the production of agricultural and animal feed bioproducts. Syst. Microbiol. Biomanuf. 2021, 1, 142–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.A.; Shukry, M.; Farrag, F.; Soliman, M.M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.M.E. Effect of feeding wet feed or wet feed fermented by Bacillus licheniformis on growth performance, histopathology and growth and lipid metabolism marker genes in broiler chickens. Animals 2021, 11, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilakamarry, C.R.; Sakinah, A.M.; Zularisam, A.W.; Sirohi, R.; Khilji, I.A.; Ahmad, N.; Pandey, A. Advances in solid-state fermentation for bioconversion of agricultural wastes to value-added products: Opportunities and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Uhl, P.; Zhu, Y.; Wijffels, R.H.; Xu, Y.; Rinzema, A. Modeling of industrial-scale anaerobic solid-state fermentation for Chinese liquor production. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 394, 124942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, L.; Lin, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Paper Mulberry Silage. Fermentation 2022, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassa, M.; Filip, M.; Țăranu, I.; Marin, D.; Untea, A.E.; Ropotă, M.; Dragomir, C.; Sărăcilă, M. The Yeast Fermentation Effect on Content of Bioactive, Nutritional and Anti-Nutritional Factors in Rapeseed Meal. Foods 2022, 11, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samtiya, M.; Aluko, R.E.; Puniya, A.K.; Dhewa, T. Enhancing micronutrients bioavailability through fermentation of plant-based foods: A concise review. Fermentation 2021, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Lal, M.K.; Dutt, S.; Raigond, P.; Changan, S.S.; Tiwari, R.K.; Chourasia, K.N.; Mangal, V.; Singh, B. Functional Fermented Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics from Non-Dairy Products: A Perspective from Nutraceutical. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.B.; Mao, S. Influence of yeast on rumen fermentation, growth performance and quality of products in ruminants: A review. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.K.; Choudhury, B. Synthetic dyes degradation using lignolytic enzymes produced from Halopiger aswanensis strain ABC_IITR by Solid State Fermentation. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Pobiega, K.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M. Characteristics of the proteolytic enzymes produced by lactic acid bacteria. Molecules 2021, 26, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhull, S.B.; Kidwai, M.K.; Noor, R.; Chawla, P.; Rose, P.K. A review of nutritional profile and processing of faba bean (Vicia faba L.). Legum. Sci. 2022, 4, e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S.; Kumar, K.; Yadav, A.N.; Ahmed, N.; Thakur, P.; Chauhan, D.; Dhaliwal, H.S. Effect of diverse fermentation treatments on nutritional composition, bioactive components, and anti-nutritional factors of finger millet (Eleusine coracana L.). J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S.; Kumar, K.; Ahmed, N.; Thakur, P.; Chauhan, D.; Rizvi, Q.E.H.; Vyas, P. Beneficial effect of diverse fermentation treatments on nutritional composition, bioactive components, and anti-nutritional factors of foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). J. Postharvest Technol. 2022, 10, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Shiferaw Terefe, N.; Augustin, M.A. Fermentation for tailoring the technological and health-related functionality of food products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2887–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanilas, K.; Kriščiunaite, T. Development of LC-MS-ESI-TOF method for quantification of phytates in food using 13C-labelled maize as internal standard. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1539–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogodo, A.C.; Ugbogu, O.C.; Onyeagba, R.A.; Okereke, H.C. Microbiological quality, proximate composition and in vitro starch/protein digestibility of Sorghum bicolor flour fermented with lactic acid bacteria consortia. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2019, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Qian, J.; Guo, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W.; Cheng, Y. Applicable Strains, Processing Techniques and Health Benefits of Fermented Oat Beverages: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, W.; Griffin, J.; Li, Y.; Bean, S.; Tilley, M.; Wang, D. Hempseed as a nutritious and healthy human food or animal feed source: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, S.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Liu, G.; Beckers, Y.; Cai, H. Improving the Nutritional Value of Plant Protein Sources as Poultry Feed through Solid-State Fermentation with a Special Focus on Peanut Meal—Advances and Perspectives. Fermentation 2023, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginindza, M.M. Lucerne meal in the diet of indigenous chickens: A review. Front. Anim. Sci. 2023, 4, 1274473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Roux, S.; Swanepoel, P.A. Lucerne establishment in dryland conditions: Effects of crop residues and wheat as a nurse crop. Afr. J. Range Forage Sci. 2024, 41, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, S.; Bobak, Ł.; Opaliński, S. Hemp in animal diets—Cannabidiol. Animals 2022, 12, 2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visković, J.; Zheljazkov, V.D.; Sikora, V.; Noller, J.; Latković, D.; Ocamb, C.M.; Koren, A. Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) agronomy and utilization: A review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, L. Hempseed Cake as a Protein Feed for Ruminant; Department of Agricultural Research for Northern Sweden, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences: Uppsala, Sweden, 2010; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Ncogo Nchama, C.N.; Fabro, C.; Baldini, M.; Saccà, E.; Foletto, V.; Piasentier, E.; Sepulcri, A.; Corazzin, M. Hempseed by-product in diets of Italian simmental cull dairy cows and its effects on animal performance and meat quality. Animals 2022, 12, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irawan, A.; Muchiri, R.N.; Parker, N.B.; van Breemen, R.B.; Ates, S.; Bionaz, M. Cannabinoid residuals in tissues of lambs fed spent hemp biomass and consumer’s exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 191, 114848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irawan, A.; Puerto-Hernandez, G.M.; Ford, H.R.; Busato, S.; Ates, S.; Cruickshank, J.; Ranches, J.; Estill, C.T.; Trevisi, E.; Bionaz, M. Feeding spent hemp biomass to lactating dairy cows: Effects on performance, milk components and quality, blood parameters, and nitrogen metabolism. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourencon, R.V.; Patra, A.K.; Puchala, R.; Dawson, L.J.; Ribeiro, L.P.S.; Encinas, F.; Goetsch, A.L. Effects of Nutritional Plane at Breeding on Feed Intake, Body Weight, Condition Score, Mass Indexes, and Chemical Composition, and Reproductive Performance of Hair Sheep. Animals 2023, 13, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, L.; Martinsson, K. Growth performance of lambs fed different protein supplements in barley-based diets. Livest. Sci. 2011, 138, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, K.J.; Kinman, L.A.; Owsley, W.F.; Muir, J.P.; Smith, W.B. Nutritive value variation and in vitro digestibility of hempseed meal. Animals 2021, 11, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Q.; Dai, Z.; Deng, C.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, C.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Integrated metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis revealed the regulation of yields, cannabinoid, and terpene biosynthesis in Cannabis sativa L. under different photoperiods. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 174, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzoni, D.; Skrivanova, E.; Pinotti, L.; Rebucci, R.; Baldi, A.; Giromini, C. Nutritional aspects of hemp-based products and their effects on health and performance of monogastric animals. Animal 2023, 18, 101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, G.L.; De Rosa, D.W.; White, D.M.; Blake, B.L.; Dods, K.C.; May, C.D.; Tai, Z.X.; Clayton, E.H.; Lynch, E.E. Intake, nutrient digestibility, rumen parameters, growth rate, carcase characteristics and cannabinoid residues of sheep fed pelleted rations containing hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) stubble. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2021, 5, txab213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, T.; Xu, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, D.; Wu, D. Partially substituting alfalfa hay with hemp forage in the diet of goats improved feed efficiency, ruminal fermentation pattern and microbial profiles. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 17, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, S.A.; Krebs, G.L.; Scrivener, C.J.; Noble, G.K.; Blake, B.L.; Dods, K.C.; May, C.D.; Tai, Z.X.; Clayton, E.H.; Lynch, E.E.; et al. Nutrient digestibility, rumen parameters, and (cannabinoid) residues in sheep fed a pelleted diet containing green hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) biomass. Transl. Anim. Sci. 2022, 6, txac141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Feed Ingredient | DM (g/kg) | CP | CF | NDF | ADF | ASH | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seed | 912 | 246 | 327 | 297 | 213 | - | [75] |
| Stem | - | 172 | 231 | - | - | 68 | [76] |
| Leaves | 887 | 314 | 152 | 471 | 310 | 305 | [23] |
| Lucerne | 870 | 198 | 16 | 417 | 333 | 119 | [23] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ntsoane, T.; Nemukondeni, N.; Nemadodzi, L.E. A Systematic Review: Assessment of the Metabolomic Profile and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Cannabis sativa as a Feed Additive for Ruminants. Metabolites 2024, 14, 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120712
Ntsoane T, Nemukondeni N, Nemadodzi LE. A Systematic Review: Assessment of the Metabolomic Profile and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Cannabis sativa as a Feed Additive for Ruminants. Metabolites. 2024; 14(12):712. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120712
Chicago/Turabian StyleNtsoane, Tumisho, Ndivho Nemukondeni, and Lufuno Ethel Nemadodzi. 2024. "A Systematic Review: Assessment of the Metabolomic Profile and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Cannabis sativa as a Feed Additive for Ruminants" Metabolites 14, no. 12: 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120712
APA StyleNtsoane, T., Nemukondeni, N., & Nemadodzi, L. E. (2024). A Systematic Review: Assessment of the Metabolomic Profile and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Cannabis sativa as a Feed Additive for Ruminants. Metabolites, 14(12), 712. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14120712








