Characterization of Urinary N-Acetyltaurine as a Biomarker of Hyperacetatemia in Mice
Abstract
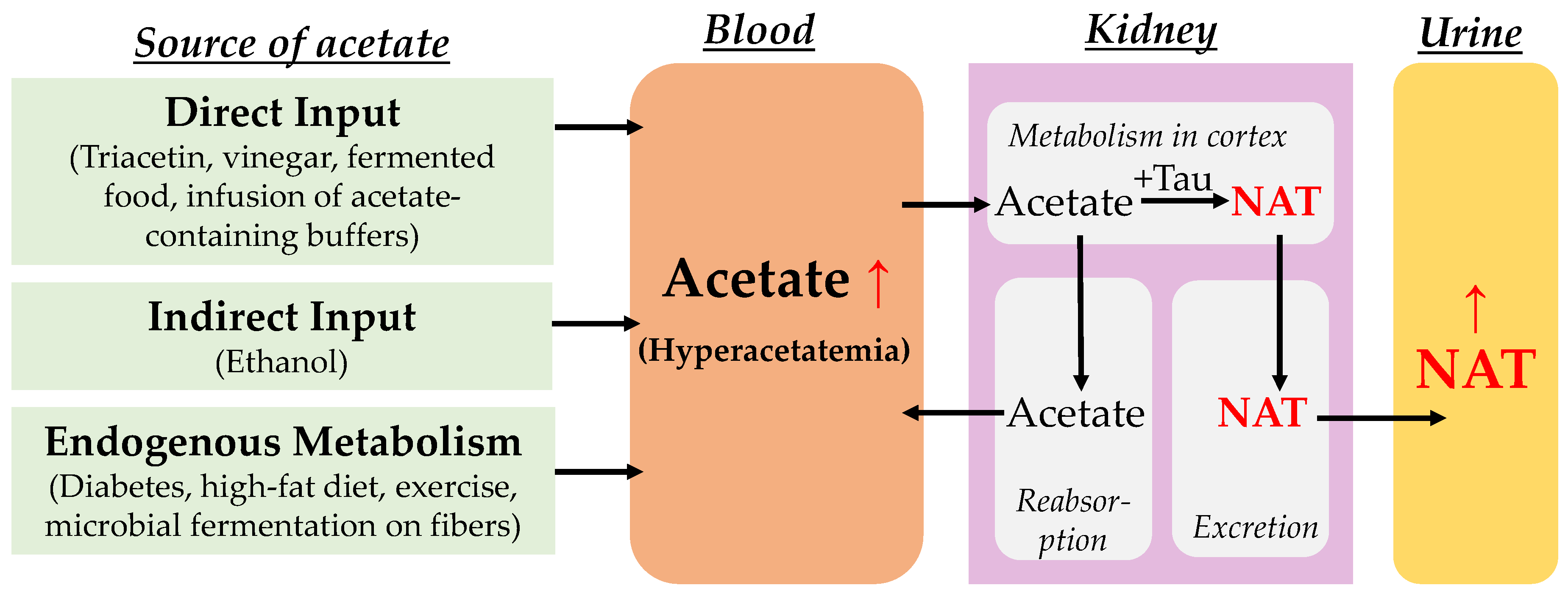
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals, Experimental Design, and Sample Collection
2.3. Sample Preparation and Chemical Derivatization for LC-MS Analysis
2.4. In Vitro Incubation of Renal Tissues for NAT Synthesis
2.5. LC-MS Analysis
2.6. Untargeted Multivariate Data Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
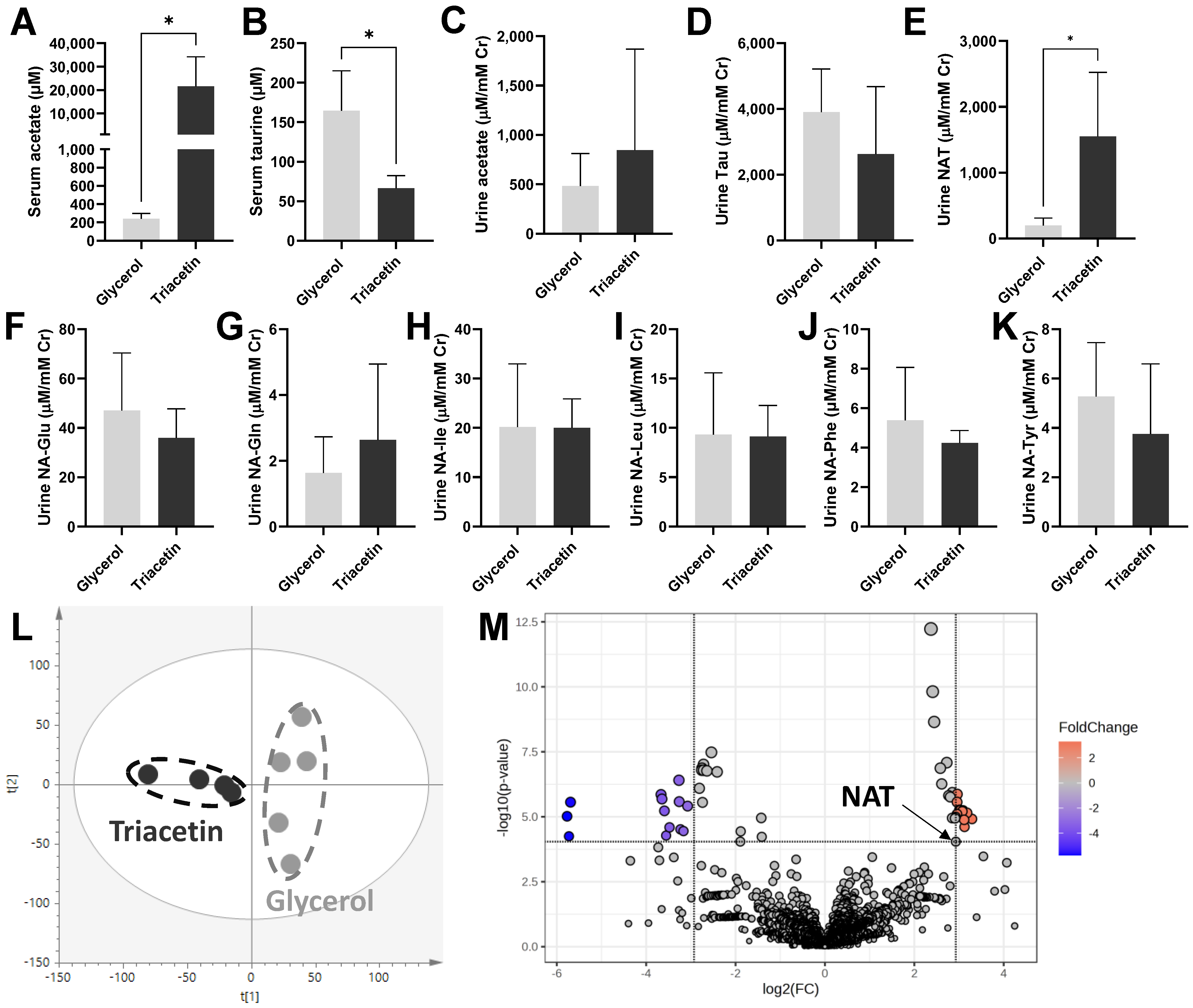
3.1. Influences of Triacetin Dosing on Urinary NAT and Other Urinary Metabolites
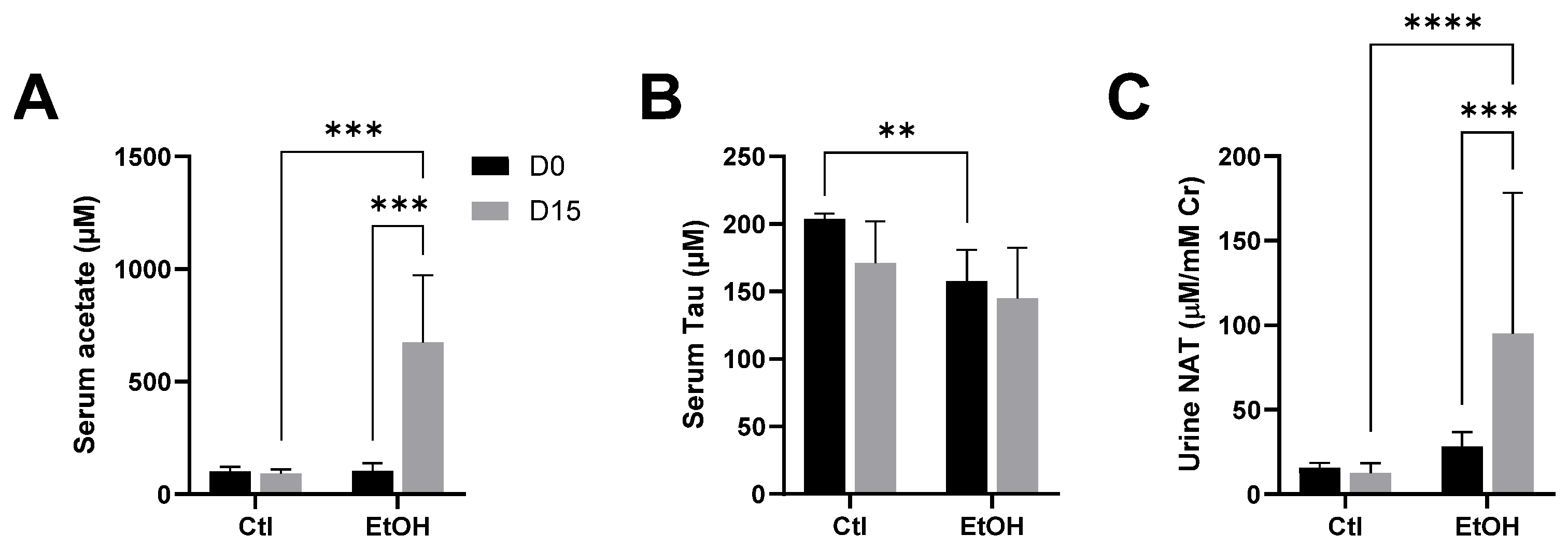
3.2. Influences of Ethanol Dosing on Urinary NAT
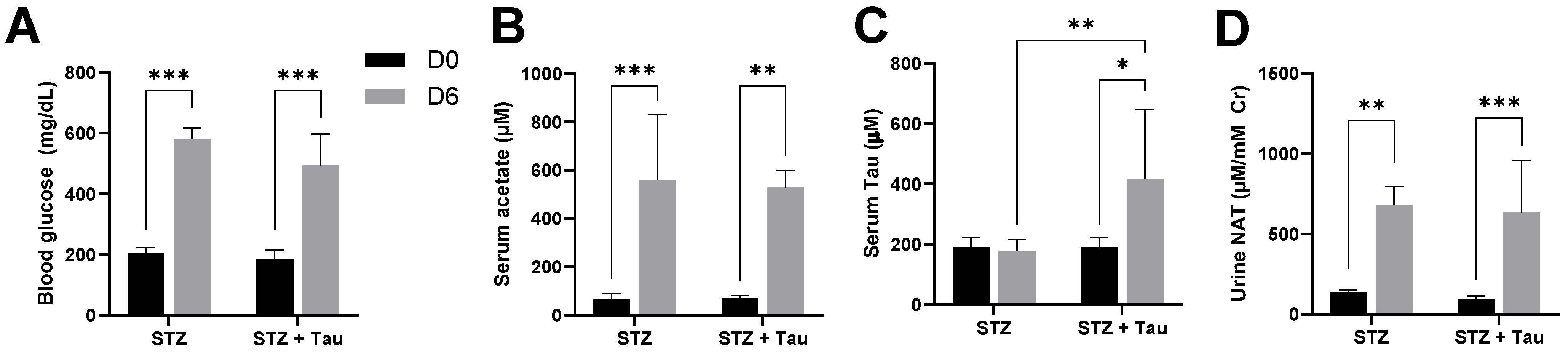
3.3. Influences of STZ-Induced Diabetes and Taurine Supplementation on Urinary NAT
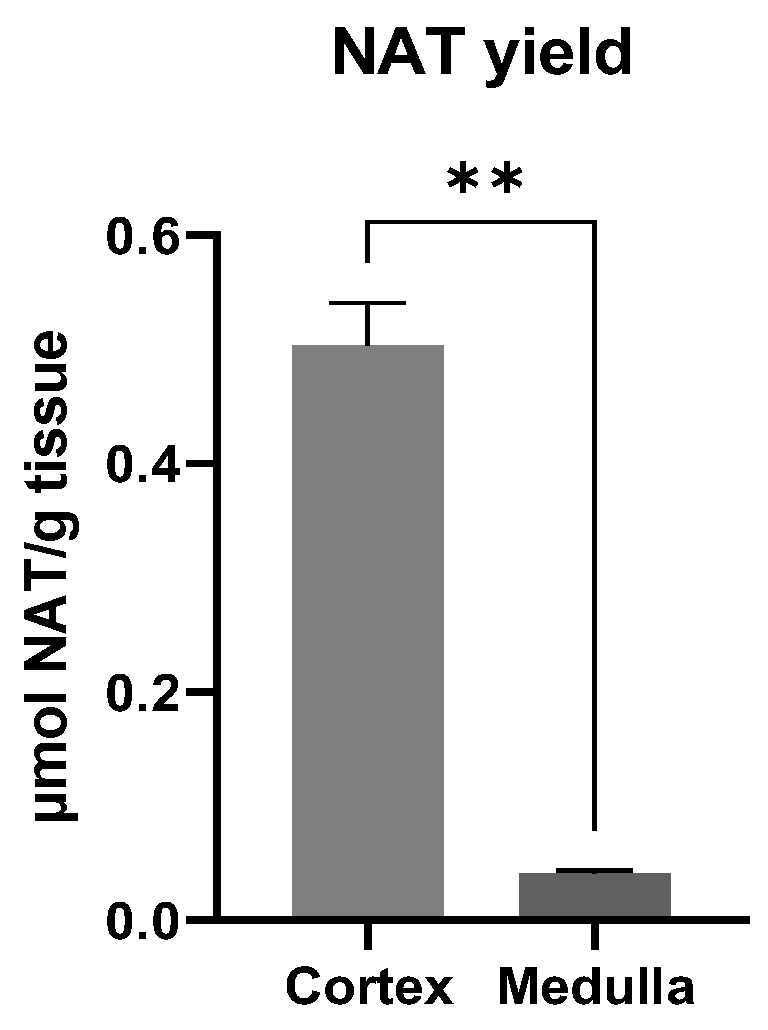
3.4. Site of NAT Synthesis Site in the Kidney
4. Discussion
4.1. Current Knowledge of the Biochemical Properties of NAT Synthesis
4.2. Urinary NAT as a Marker of Hyperacetatemia: A Comparison with Serum and Urinary Acetate
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buckley, B.M.; Williamson, D.H. Origins of Blood Acetate in the Rat. Biochem. J. 1977, 166, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khezri, S.S.; Saidpour, A.; Hosseinzadeh, N.; Amiri, Z. Beneficial effects of Apple Cider Vinegar on Weight Management, Visceral Adiposity Index and Lipid Profile in Overweight or Obese Subjects Receiving Restricted Calorie Diet: A randomized clinical trial. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 43, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.A.; Bogatyrev, A.; Van Zelm, M.C.; Gibson, P.R.; Muir, J.G. Delivery of Acetate to the Peripheral Blood after Consumption of Foods High in Short-Chain Fatty Acids. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2000953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panesar, M.; Shah, N.; Vaqar, S.; Ivaturi, K.; Gudleski, G.; Muscarella, M.; Lambert, J.; Su, W.; Murray, B. Changes in Serum Bicarbonate Levels Caused by Acetate-Containing Bicarbonate-Buffered Hemodialysis Solution: An Observational Prospective Cohort Study. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2017, 21, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederbaum, A.I. Alcohol Metabolism. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horibata, Y.; Ando, H.; Itoh, M.; Sugimoto, H. Enzymatic and Transcriptional Regulation of the Cytoplasmic Acetyl-CoA Hydrolase ACOT12. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2049–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cooper, D.E.; Cluntun, A.A.; Warmoes, M.O.; Zhao, S.; Reid, M.A.; Liu, J.; Lund, P.J.; Lopes, M.; Garcia, B.A.; et al. Acetate Production from Glucose and Coupling to Mitochondrial Metabolism in Mammals. Cell 2018, 175, 502–513.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBrian, M.A.; Behbahan, I.S.; Ferrari, R.; Su, T.; Huang, T.-W.; Li, K.; Hong, C.S.; Christofk, H.R.; Vogelauer, M.; Seligson, D.B. Histone Acetylation Regulates Intracellular pH. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffett, J.R.; Puthillathu, N.; Vengilote, R.; Jaworski, D.M.; Namboodiri, A.M. Acetate Revisited: A Key Biomolecule at the Nexus of Metabolism, Epigenetics, and Oncogenesis—Part 2: Acetate and ACSS2 in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffett, J.R.; Puthillathu, N.; Vengilote, R.; Jaworski, D.M.; Namboodiri, A.M. Acetate Revisited: A Key Biomolecule at the Nexus of Metabolism, Epigenetics and Oncogenesis-Part 1: Acetyl-CoA, Acetogenesis and Acyl-CoA Short-Chain Synthetases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 580167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Lee, M.; Whang, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, A.; Yun, M. Regulation of Acetate Utilization by Monocarboxylate Transporter 1 (MCT1) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, A.; Hannah, V.C.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Molecular Characterization of Human Acetyl-CoA Synthetase, An Enzyme Regulated by Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Proteins. J. Biochem. Chem. 2000, 275, 26458–26466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrocola, F.; Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Madeo, F.; Kroemer, G. Acetyl Coenzyme A: A Central Metabolite and Second Messenger. Cell Metab. 2015, 21, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingitore, A.; Gonzalez-Abuin, N.; Ruz-Maldonado, I.; Huang, G.C.; Frost, G.; Persaud, S.J. Short Chain Fatty Acids Stimulate Insulin Secretion and Reduce Apoptosis in Mouse and Human Islets In Vitro: Role of Free Fatty Acid Receptor 2. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslowski, K.M.; Vieira, A.T.; Ng, A.; Kranich, J.; Sierro, F.; Yu, D.; Schilter, H.C.; Rolph, M.S.; Mackay, F.; Artis, D.; et al. Regulation of Inflammatory Responses by Gut Microbiota and Chemoattractant Receptor GPR43. Nature 2009, 461, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, H.; Fujisawa, K.; Ito, E.; Idei, S.; Kawaguchi, N.; Kimoto, M.; Hiemori, M.; Tsuji, H. Improvement of Obesity and Glucose Tolerance by Acetate in Type 2 Diabetic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty (OLETF) Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2007, 71, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, T.; Kishi, M.; Fushimi, T.; Kaga, T. Acetic Acid Upregulates the Expression of Genes for Fatty Acid Oxidation Enzymes in Liver to Suppress Body Fat Accumulation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 5982–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, A.; Nakatani, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Irie, J.; Ozawa, K.; Tsujimoto, G.; Suganami, T.; Itoh, H.; Kimura, I. The Short Chain Fatty Acid Receptor GPR43 Regulates Inflammatory Signals in Adipose Tissue M2-Type Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheflati, A.; Bashiri, R.; Ghadiri-Anari, A.; Reza, J.Z.; Kord, M.T.; Nadjarzadeh, A. The Effect of Apple Vinegar Consumption On Glycemic Indices, Blood Pressure, Oxidative Stress, and Homocysteine in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Dyslipidemia: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 33, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Peng, L.; Barry, N.A.; Cline, G.W.; Zhang, D.; Cardone, R.L.; Petersen, K.F.; Kibbey, R.G.; Goodman, A.L.; Shulman, G.I. Acetate Mediates a Microbiome–brain–β-cell Axis to Promote Metabolic Syndrome. Nature 2016, 534, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Sun, L.; Jia, Y.; Yang, P.; Guo, D.; Shi, M.; Wang, A.; Chen, G.-C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Association between Human Blood Metabolome and the Risk of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2023, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, Z.T.; Peck, B.; Jones, D.T.; Zhang, Q.; Grosskurth, S.; Alam, I.S.; Goodwin, L.M.; Smethurst, E.; Mason, S.; Blyth, K.; et al. Acetyl-Coa Synthetase 2 Promotes Acetate Utilization and Maintains Cancer Cell Growth under Metabolic Stress. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schug, Z.T.; Vande Voorde, J.; Gottlieb, E. The Metabolic Fate of Acetate in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabutti, L.; Lucchini, B.; Marone, C.; Alberio, L.; Burnier, M. Citrate- Vs. Acetate-Based Dialysate in Bicarbonate Haemodialysis: Consequences on Haemodynamics, Coagulation, Acid-Base Status, and Electrolytes. BMC Nephrol. 2009, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Yao, D.; Chen, C. Identification of N-Acetyltaurine as a Novel Metabolite of Ethanol through Metabolomics-Guided Biochemical Analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 6336–6349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luginbühl, M.; Rutjens, S.; König, S.; Furrer, J.; Weinmann, W. N-Acetyltaurine as a Novel Urinary Ethanol Marker in A Drinking Study. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7529–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Ishikura, K.; Honda, A.; Ra, S.-G.; Komine, S.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ohmori, H.; Matsuzaki, Y. Increased N-Acetyltaurine in Serum and Urine after Endurance Exercise in Human. In Taurine 9; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki, T.; Nakamura-Shinya, Y.; Ebina, K.; Komine, S.; Ra, S.-G.; Ishikura, K.; Ohmori, H.; Honda, A. N-acetyltaurine and Acetylcarnitine Production for the Mitochondrial Acetyl-CoA Regulation in Skeletal Muscles during Endurance Exercises. Metabolites 2021, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, R. Progress toward Acetate Supplementation Therapy for Canavan Disease: Glyceryl Triacetate Administration Increases Acetate, but Not N-Acetylaspartate, Levels in Brain. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 315, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, L.H.; Ørstrup, L.K.H.; Hansen, S.H.; Grunnet, N.; Quistorff, B.; Mortensen, O.H. The Effect of Long-Term Taurine Supplementation and Fructose Feeding on Glucose and Lipid Homeostasis in Wistar Rats. In Taurine 8; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 39–50. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Yao, D.; Chen, C. 2-Hydrazinoquinoline as a Derivatization Agent for LC-MS-Based Metabolomic Investigation of Diabetic Ketoacidosis. Metabolites 2013, 3, 993–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellum, E.; Horn, L.; Thoresen, O.; Kvittingen, E.A.; Stokke, O. Urinary Excretion of N-Acetyl Amino Acids in Patients With Some Inborn Errors of Amino Acid Metabolism. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. Suppl. 1986, 184, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, G.; Coyle, J.T. N-Acetylaspartate in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Prog. Neurobiol. 1995, 46, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronwald, W.; Klein, M.S.; Zeltner, R.; Schulze, B.-D.; Reinhold, S.W.; Deutschmann, M.; Immervoll, A.-K.; Böger, C.A.; Banas, B.; Eckardt, K.-U.; et al. Detection of Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease by NMR Spectroscopic Fingerprinting of Urine. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Bisht, K.S.; Merkler, D.J. The Biosynthesis and Metabolism of the N-Acylated Aromatic Amino Acids: N-Acylphenylalanine, N-Acyltyrosine, N-Acyltryptophan, and N-Acylhistidine. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 8, 801749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, K.C.; Sturman, J.A. Taurine in Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1981, 1, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Budreau, A.M.; Chesney, R.W. Functional Expression of Rat Renal Cortex Taurine Transporter in Xenopus Laevis Oocytes: Adaptive Regulation by Dietary Manipulation. Pediatr. Res. 1997, 41, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesney, R.W.; Friedman, A.L.; Albright, P.W.; Gusowski, N. Fasting Reverses the Renal Adaptation to Altered Dietary Sulfur Amino Acid Intake. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1982, 170, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.-L.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-T.; Huang, C.-Y. Effect of Taurine in Chronic Alcoholic Patients. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtman, H.; Futterweit, S.; Maesaka, J.; Ma, C.; Valderrama, E.; Fuchs, A.; Tarectecan, A.A.; Rao, P.S.; Sturman, J.A.; Boles, T.H.; et al. Taurine Ameliorates Chronic Streptozocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy in Rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 269, F429–F438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, N.T.; Zhang, M.; Juraschek, S.P.; Miller, E.R.; Appel, L.J. Effects of High-Fiber Diets Enriched with Carbohydrate, Protein, or Unsaturated Fat on Circulating Short Chain Fatty Acids: Results from the Omniheart Randomized Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 111, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neavyn, M.J.; Boyer, E.W.; Bird, S.B.; Babu, K.M. Sodium Acetate as a Replacement for Sodium Bicarbonate in Medical Toxicology: A Review. J. Med. Toxicol. 2013, 9, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollinger, C.D.; Vreman, H.J.; Weiner, M.W. Measurement of Acetate in Human Blood by Gas Chromatography: Effects of Sample Preparation, Feeding, and Various Diseases. Clin. Chem. 1979, 25, 1787–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imenez Silva, P.H.; Mohebbi, N. Kidney Metabolism and Acid-base Control: Back to the Basics. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2022, 474, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullrich, K.J.; Rumrich, G.; Klöss, S. Reabsorption of monocarboxylic acids in the proximal tubule of the rat kidney. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1982, 395, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.E.; Kwatra, N.V. Monocarboxylic Acid Transporters. In Drug Transporters; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 143–164. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, R.H.; Vreman, H.J.; Zager, P.; Feldman, C.; Blaschke, T.; Weiner, M.W. Acetate Metabolism in Normal Human Subjects. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1982, 2, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauet, T.; Baumert, H.; Gibelin, H.; Godart, C.; Carretier, M.; Eugene, M. Citrate, Acetate and Renal Medullary Osmolyte Excretion in Urine as Predictor of Renal Changes after Cold Ischaemia and Transplantation. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2000, 38, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sison, R.C.; Collado, A.; Dedeles, J.I.; Reyes, K.J.E.D.; Garcia, C.J.; Manalo, S.M.P.; Nieto, X.A. Diagnostic Significance of Urine Acetic Acid Level among Pregnant Women with Bacterial Urinary Tract Infection. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 144, A216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, Q.; Shi, X.; Ma, Y.; Lu, Y.; Chen, C. Characterization of Urinary N-Acetyltaurine as a Biomarker of Hyperacetatemia in Mice. Metabolites 2024, 14, 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060322
Mao Q, Shi X, Ma Y, Lu Y, Chen C. Characterization of Urinary N-Acetyltaurine as a Biomarker of Hyperacetatemia in Mice. Metabolites. 2024; 14(6):322. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060322
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Qingqing, Xiaolei Shi, Yiwei Ma, Yuwei Lu, and Chi Chen. 2024. "Characterization of Urinary N-Acetyltaurine as a Biomarker of Hyperacetatemia in Mice" Metabolites 14, no. 6: 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060322
APA StyleMao, Q., Shi, X., Ma, Y., Lu, Y., & Chen, C. (2024). Characterization of Urinary N-Acetyltaurine as a Biomarker of Hyperacetatemia in Mice. Metabolites, 14(6), 322. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14060322








