Potential of Streptomyces avermitilis: A Review on Avermectin Production and Its Biocidal Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
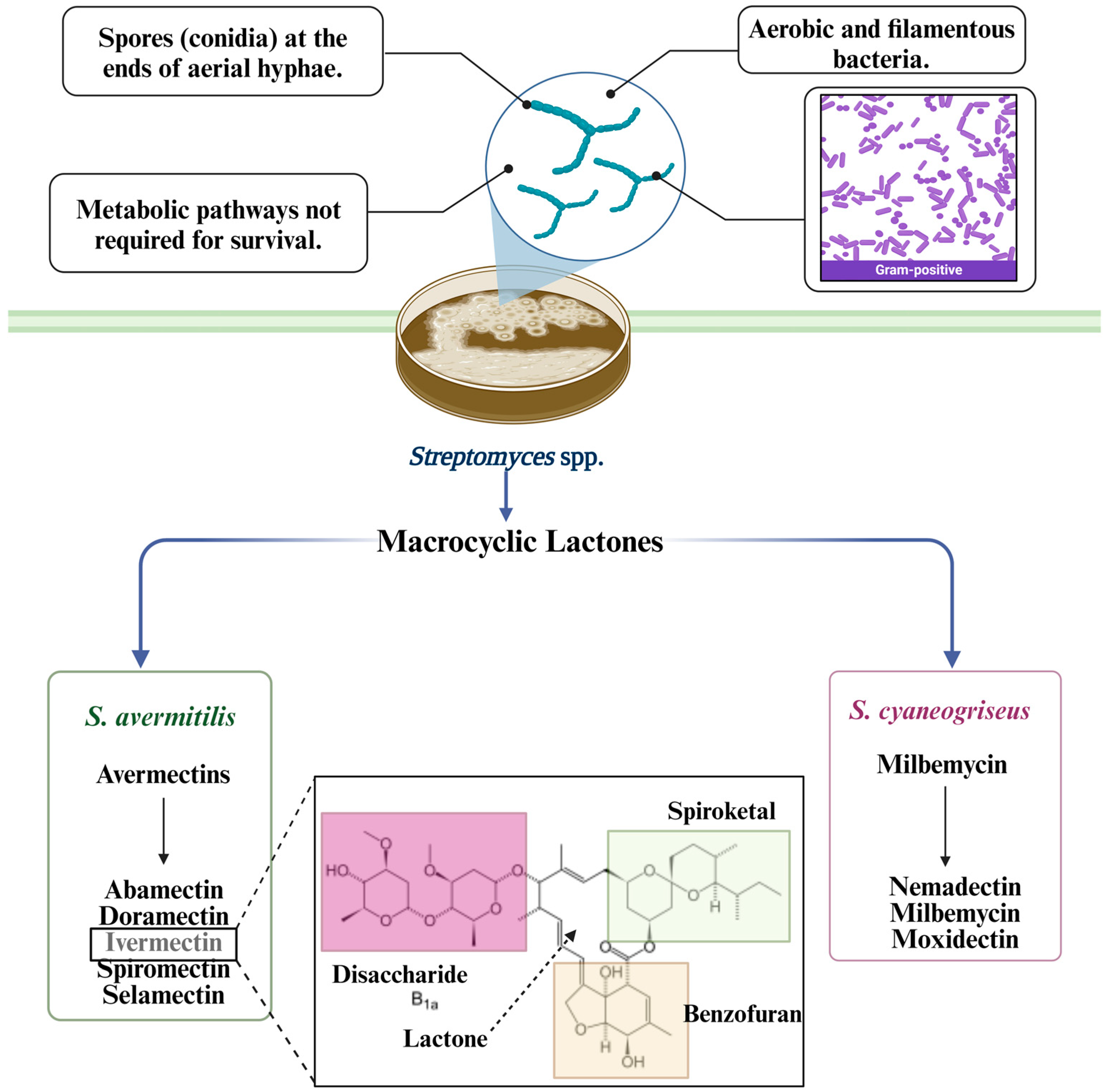
2. Streptomyces avermitillis Origin
3. Streptomyces avermitilis’ Main Secondary Metabolites
3.1. Macrocyclic Lactones
3.1.1. Avermectin
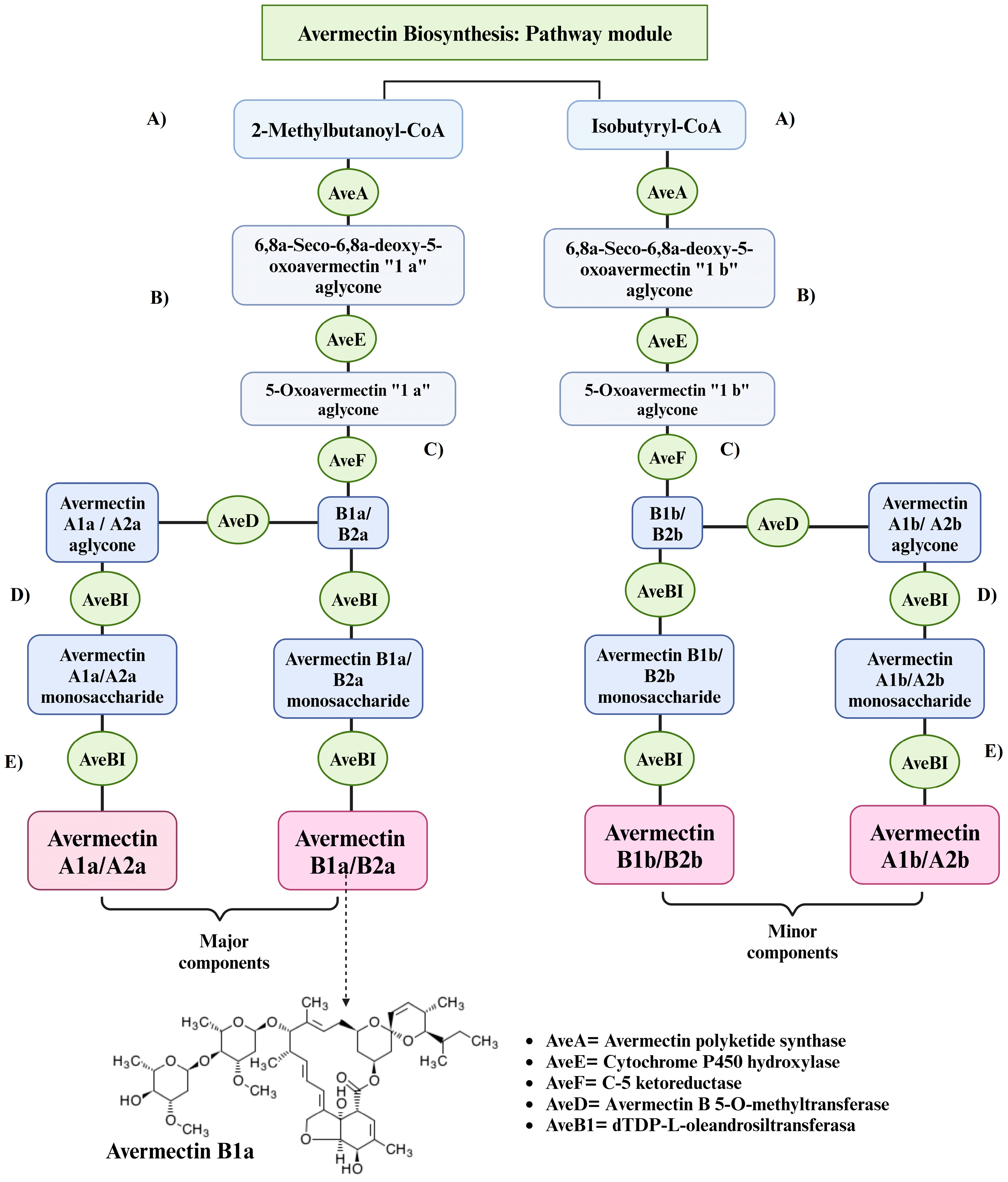
3.1.2. Avermectin Biosyntesis
3.1.3. Avermectin Biocidal Propierties
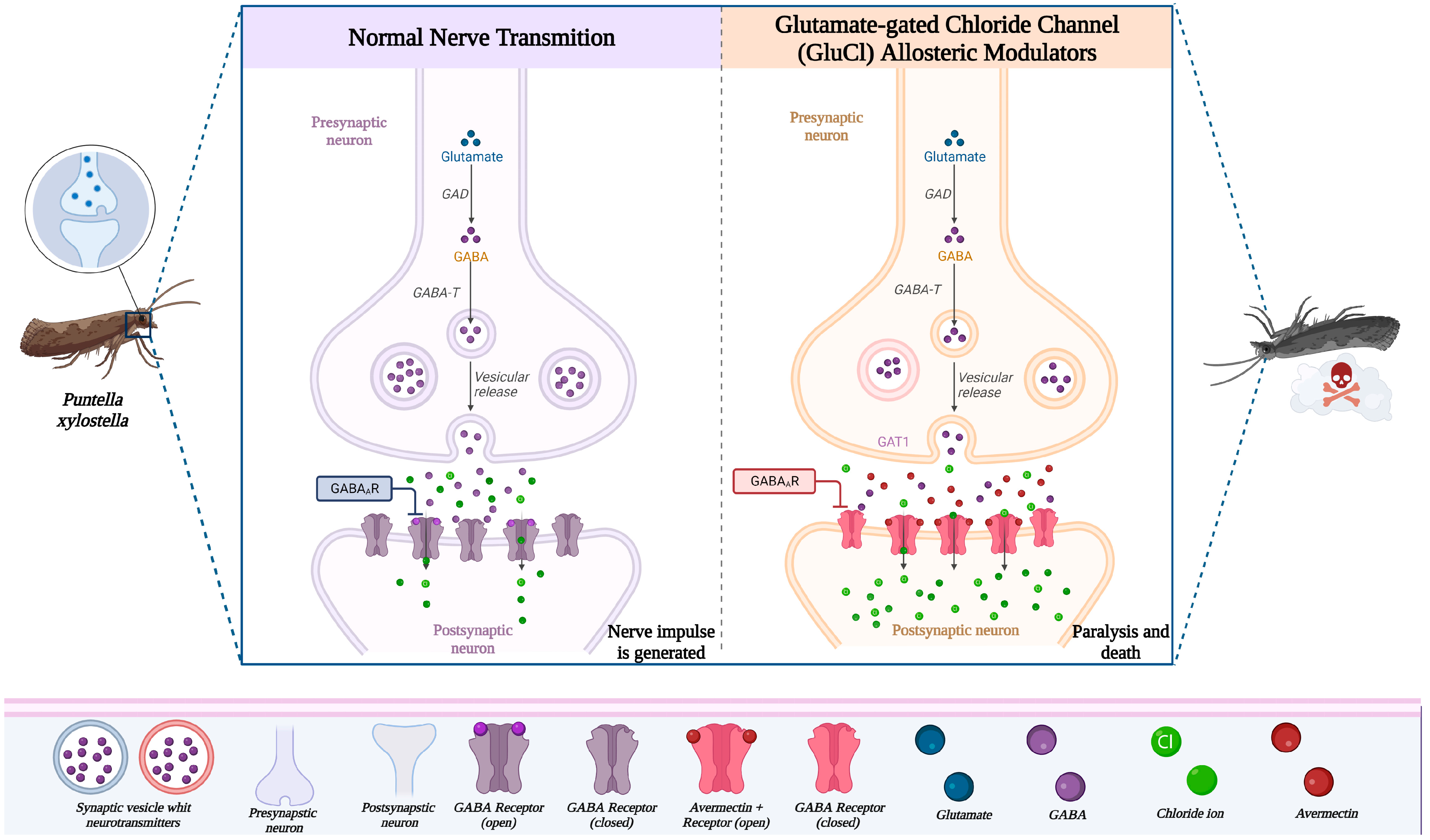
3.1.4. Mode of Action
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burg, R.W.; Miller, B.M.; Baker, E.E.; Birnbaum, J.; Currie, S.A.; Hartman, R.; Kong, Y.L.; Monaghan, R.L.; Olson, G.; Putter, I.; et al. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: Producing organism and fermentation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1979, 15, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.W.; Chaiet, L.; Cole, D.J.; Cole, L.J.; Flor, J.E.; Goegelman, R.T.; Gullo, V.P.; Joshua, H.; Kempf, A.J.; Krellwitz, W.R.; et al. Avermectins, New Family of Potent Anthelmintic Agents: Isolation and Chromatographic Properties. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1979, 15, 368–371. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/aac.15.3.368 (accessed on 18 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Pham, J.V.; Yilma, M.A.; Feliz, A.; Majid, M.T.; Maffetone, N.; Walker, J.R.; Kim, E.; Cho, H.J.; Reynolds, J.M.; Song, M.C.; et al. A review of the microbial production of bioactive natural products and biologics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, N.; Hwang, S.; Kim, W.; Cho, S.; Palsson, B.O.; Cho, B.K. Genome-scale analysis of genetic regulatory elements in Streptomyces avermitilis MA-4680 using transcript boundary information. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentley, S.D.; Chater, K.F.; Cerdeño-Tárraga, A.M.; Challis, G.L.; Thomson, N.R.; James, K.D.; Harris, D.E.; Quail, M.A.; Kieser, H.; Harper, D.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 2002, 417, 141–147. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/417141a (accessed on 18 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Takano, E. γ-Butyrolactones: Streptomyces signalling molecules regulating antibiotic production and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.C.; Allenby, N.E.E. Genome mining for the search and discovery of bioactive compounds: The Streptomyces paradigm. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Mazumder, A.; Sikdar, S.; Zhao, Y.M.; Hao, J.; Song, C.; Wang, Y.; Sarkar, R.; Islam, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Streptomyces: The biofactory of secondary metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 968053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Komatsu, K.; Koiwai, H.; Yamada, Y.; Kozone, I.; Izumikawa, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Takagi, M.; Omura, S.; Shin-ya, K.; et al. Engineered Streptomyces avermitilis host for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene cluster for secondary metabolites. ACS Synth. Biol. 2013, 2, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Rodríguez, A.; Robledo-Casados, I.; Sánchez, S. An overview on transcriptional regulators in Streptomyces. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 1017–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W. Connecting Metabolic Pathways: Sigma Factors in Streptomyces spp. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heul, H.U.; Bilyk, B.L.; McDowall, K.J.; Seipke, R.F.; van Wezel, G.P. Regulation of antibiotic production in Actinobacteria: New perspectives from the post-genomic era. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 575–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nah, H.-J.; Park, J.; Choi, S.; Kim, E.-S. WblA, a global regulator of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 48, kuab007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parte, A.C.; Carbasse, J.S.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Reimer, L.C.; Göker, M. List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature [LPSN] moves to the DSMZ. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razek, A.S.; El-Naggar, M.E.; Allam, A.; Morsy, O.M.; Othman, S.I. Microbial Natural Products in Drug Discovery. Processes 2020, 8, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacios-Michelena, S.; Aguilar-González, C.N.; Alvarez-Perez, O.B.; Rodriguez-Herrera, R.; Chávez-González, M.; Arredondo Valdés, R.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A.; Govea-Salas, M.; Ilyina, A. Application of Streptomyces Antimicrobial Compounds for the Control of Phytopathogens. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 696518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, S.; Ikeda, H.; Ishikawa, J.; Hanamoto, A.; Takahashi, C.; Shinose, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Horikawa, H.; Nakazawa, H.; Osonoe, T.; et al. Genome sequence of an industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis: Deducing the ability of producing secondary metabolites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12215–12220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassler, B.L.; Losick, R. Bacterially speaking. Cell 2006, 125, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, G.; Wang, H.H.; Davies, J. Antibiotics as signalling molecules. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 1195–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Ishikawa, J.; Hanamoto, A.; Shinose, M.; Kikuchi, H.; Shiba, T.; Sakaki, Y.; Hattori, M.; Omura, S. Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnishi, Y.; Ishikawa, J.; Hara, H.; Suzuki, H.; Ikenoya, M.; Ikeda, H.; Yamashita, A.; Hattori, M.; Horinouchi, S. Genome Sequence of the Streptomycin-Producing Microorganism Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 4050–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, A.; Omura, S. Ivermectin, ‘Wonder drug’ from Japan: The human use perspective. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2011, 87, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltz, R.H. Renaissance in antibacterial discovery from actinomycetes. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donald, L.; Pipite, A.; Subramani, R.; Owen, J.; Keyzers, R.A.; Taufa, T. Streptomyces: Still the Biggest Producer of New Natural Secondary Metabolites, a Current Perspective. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 13, 418–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokbel, A.A.; Obad, I.M.; Ibrahim, I.K.A. The role of antagonistic metabolites in controlling root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne arenaria on tomato. Alex. J. Agric. Res. 2009, 54, 199–205. [Google Scholar]
- Omura, S.; Crump, A. Ivermectin: Panacea for resource-poor communities? Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Publishes List of Bacteria for Which New Antibiotics Are Urgently Needed. 2017. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/27-02-2017-who-publishes-list-of-bacteria-for-which-new-antibiotics-are-urgently-needed (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Ceylan, Ö.; Ökmen, G.; Uğur, A. Isolation of soil Streptomyces as source antibiotics active against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Eur. Asian J. Biosci. 2008, 2, 73–82. Available online: http://acikerisim.mu.edu.tr/xmlui/handle/20.500.12809/7761 (accessed on 18 April 2024).
- Sottorff, I.; Wiese, J.; Lipfert, M.; Preußke, N.; Sönnichsen, F.D.; Imhoff, J.F. Different Secondary Metabolite Profiles of Phylogenetically almost Identical Streptomyces griseus Strains Originating from Geographically Remote Locations. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, M.; Uchiyama, T.; Omura, S.; Cane, D.E.; Ikeda, H. Genome-minimized Streptomyces host for the heterologous expression of secondary metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2646–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Kazuo, S.; Omura, S. Genome mining of the Streptomyces avermitilis genome and development of genome-minimized hosts for heterologous expression of biosynthetic gene clusters. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wen, J.; Song, Y.; Wen, Y.; Li, J.L. Enhancement and selective production of avermectin B by recombinants of Streptomyces avermitilis via intraspecific protoplast fusion. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, M.; Tsuda, M.; Omura, S.; Oikawa, H.; Ikeda, H. Identification and functional analysis of genes controlling biosynthesis of 2-methylisoborneol. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 7422–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nett, M.; Ikeda, H.; Moore, B.S. Genomic basis for natural product biosynthetic diversity in the actinomycetes. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 1362–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Tetzlaff, C.N.; Takamatsu, S.; Iwatsuki, M.; Komatsu, M.; Ikeda, H.; Cane, D.E. Genome Mining in Streptomyces avermitilis. A Biochemical Baeyer-Villiger Reaction and Discovery of a New Branch of the Pentalenolactone Family Tree. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6431–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Okada, B.K.; Wu, Y.; Xu, F.; Seyedsayamdost, M.R. Recent advances in activating silent biosynthetic gene clusters in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 45, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genilloud, O. Actinomycetes: Still a source of novel antibiotics. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 1203–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bolla, K.; Ashforth, E.J.; Zhuo, Y.; Gao, H.; Huang, P.; Stanley, S.A.; Hung, D.T.; Zhang, L. Systematics-guided bioprospecting for bioactive microbial natural products. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2012, 101, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, K.; Reynolds, K.A.; Kersten, R.D.; Ryan, K.S.; Gonzalez, D.J.; Nizet, V.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Moore, B.S. Direct cloning and refactoring of a silent lipopeptide biosynthetic gene cluster yields the antibiotic taromycin A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suroto, D.A.; Kitani, S.; Arai, M.; Ikeda, H.; Nihira, T. Characterization of the biosynthetic gene cluster for cryptic phthoxazolin A in Streptomyces avermitilis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Meij, A.; Worsley, S.F.; Hutchings, M.I.; van Wezel, G.P. Chemical ecology of antibiotic production by actinomycetes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 392–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Grkovic, T.; Liu, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Quinn, R.J. A systems approach using OSMAC, Log P and NMR fingerprinting: An approach to novelty. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochi, K. Insights into microbial cryptic gene activation and strain improvement: Principle, application and technical aspects. J. Antibiot. 2016, 70, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarins-Tutt, J.S.; Barberi, T.T.; Gao, H.; Mearns-Spragg, A.; Zhang, L.; Newman, D.J.; Goss, R.J. Prospecting for new bacterial metabolites: A glossary of approaches for inducing, activating and upregulating the biosynthesis of bacterial cryptic or silent natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 33, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyurin, A.P.; Alferova, V.A.; Korshun, V.A. Chemical Elicitors of Antibiotic Biosynthesis in Actinomycetes. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B. A New Golden Age of Natural Products Drug Discovery. Cell 2015, 163, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, R.S.; Wuest, W.M. Twelve-membered macrolactones: Privileged scaffolds for the development of new therapeutics. Chem Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, Y.N.; Kumari, T.N.; Thota, P.; Jyothi, P.; Gupta, A.K. Chemoenzymatic total synthesis of cryptocaryalactone natural products. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, S.K.; Diaz MA, N.; Diaz-Muñoz, G. Lactones: Classification, synthesis, biological activities, and industrial applications. Tetrahedron 2021, 84, 132001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I.; Arieta-Román, R.J.; Pérez-Cogollo, L.C.; Rosado-Aguilar, J.A.; Ramírez-Cruz, G.T.; Basto-Estrella, G. Uso de lactonas macrocíclicas para el control de la garrapata Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus en el ganado bovino. Arch. Med. Vet. 2010, 42, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.; Kubo, Y. Ivermectin and its target molecules: Shared and unique modulation mechanisms of ion channels and receptors by ivermectin. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lifschitz, A.; Virkel, G.; Imperiale, F.; Pis, A.; Lanussec, C. Fármacos endectocidas: Avermectinas y milbemicinas. In Farmacología y Terapéutica Veterinaria; Botana, L.M., Landoni, F., Matín-Jiménez, T., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: Madrid, Spain, 2002; pp. 545–558. [Google Scholar]
- BioRender. BioRender. 2023. Available online: https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Salazar, B.G.; Moreno, D.H.; Rodríguez, F.S.; Pérez-López, M. Empleo de Ivermectina como parasiticida en ovino: Posibles efectos tóxicos y repercusiones ambientales. An. Vet. Murcia. 2011, 27, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, M.; Abbas, G.; Mughal, M.N. Successful management of ivermectininduced blindness in an African lion [Panthera leo] by intravenous administration of a lipid emulsion. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delayte, E.H.; Otsuka, M.; Larsson, C.E.; Castro, R.C.C. Eficácia das lactonas macrocíclicas sistêmicas [ivermectina e moxidectina] na terapia da demodicidose canina generalizada. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária Zootec. 2006, 58, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Burg, R.W. Trends in the Use of Fermentation Products in Agriculture. In Agricultural Uses of Antibiotics; American Chemical Society: Washington, UT, USA, 1986; Volume 320, pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodruff, H.B. A Soil Microbiologist’s Odyssey. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1981, 35, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egerton, J.R.; Ostlind, D.A.; Blair, L.S.; Eary, C.H.; Suhayda, D.; Cifelli, S.; Riek, R.F.; Campbell, W.C. Avermectins, new family of potent anthelmintic agents: Efficacy of the B1a component. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1979, 15, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cane, D.E.; Liang, T.C.; Kaplan, L.; Nallin, M.K.; Schulman, M.D.; Hensens, O.D.; Douglas, A.W.; Albers-Schoenberg, G. Biosynthetic Origin of the Carbon Skeleton and Oxygen Atoms of the Avermectins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 4110–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Omura, S. Avermectin biosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 2591–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitterna, T. Chloride channel activators/ New natural products (Avermectins and Milbermycins). In Modern Crop Protection Compounds, 3rd ed.; Krämer, W., Schirmer, U., Eds.; Wileyvch: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 1069–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Dai, H.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L. Medium optimization for the production of avermectin B1a by Streptomyces avermitilis 14-12A using response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol. 2009, 100, 4012–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitani, S.; Miyamoto, K.T.; Takamatsu, S.; Herawati, E.; Iguchi, H.; Nishitomi, K.; Uchida, M.; Nagamitsu, T.; Omura, S.; Ikeda, H.; et al. Avenolide, a Streptomyces hormone controlling antibiotic production in Streptomyces avermitilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 16410–16415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrozik, H. Advances in research and development of avermectins. In Natural and Engineered Pest Management Agents, American Chemical Society Symposium Series No 551; Hedin, P.A., Ed.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 54–73. [Google Scholar]
- Shoop, W.; Soll, M. Chemistry, phzarmacology and safety of the macrocyclic lactones: Ivermectin, abamectin and eprinomectin. In Macrocycl Lact Antiparasit Therapy; Vercruysse, J., Rew, R.S., Eds.; CABI; Merck and Co.: Rahway, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 1–29. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, W.C. History of avermectin and ivermectin, with notes on the history of other macrocyclic lactone antiparasitic agents. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitterna, T.; Cassayre, J.; Hüter, O.F.; Jung, P.M.J.; Maienfisch, P.; Kessabi, F.M.; Quaranta, L.; Tobler, H. New ventures in the chemistry of avermectins. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 4085–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, J.A.; Amor, F.; Bengoechea, P.; Budia Marigil, F.; Viñuela Sandoval, E.; Medina, P. Toxicity of emamectin benzoate to adults of “Nesidiocoris tenuis” Reuter, “Macrolophus pygmaeus” [Rambur] [Heteroptera, Miridae] and “Diglyphus isaea” Walker [Hymenoptera, Eulophidae] on tomato plants. Semi-field studies: Short communication. Span. J. Agric. 2011, 9, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, R.K.; Peterson, R.F.; Mookerjee, P.K.; Halliday, W.R.; Argentine, J.A.; Dybas, R.A. Development of a novel soluble granule formulation of emamectin benzoate for control of lepidopterous pests. Florida Entomol. 1997, 80, 425–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, S.; Pozo, V.; Silva, M.T. Evaluación de la efectividad del tratamiento con agua dulce para el control del piojo de mar Caligus rogercresseyi Boxshall & Bravo, 2000. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2015, 43, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, S.; Sevatdal, S.; Horsberg, T.E. Sensitivity assessment of Caligus rogercresseyi to emamectin benzoate in Chile. Aquaculture 2008, 282, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.; Darwesh, D. Avermectins: The promising solution to control plant parasitic nematodes. J. Plant Sci. Phytopathol. 2019, 3, 081–085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.M.; Wierman, C.K.; Hutchinson, C.R. Genetic analysis of erythromycin production in Streptomyces erythreus. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 164, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Li, Y.-Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Ye, B.C.; Ge, W.F.; Xia, Y.L. Direct proteomic mapping of Streptomyces avermitilis wild and industrial strain and insights into avermectin production. J. Proteom. 2013, 79, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, F.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W. Spiroketal formation and modification in avermectin biosynthesis involves a dual activity of avec. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1540–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacNeil, D.J. Characterization of a unique methyl-specific restriction system in Streptomyces avermitilis. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 5607–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Peng, M.; Zhou, Z.; Du, X.; Yin, M.; Shen, J.; Yan, S.A. A Star Polyamine-Based Nanocarrier Delivery System for Enhanced Avermectin Contact and Stomach Toxicity against Green Peach Aphids. Nanomater 2022, 12, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KEGG. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Avermectin Biosynthesis. Laboratories, K. 2020. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/module/M00777+C11983 (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Chen, J.; Liu, M.; Lui, X.; Mao, J.; Fu, C.h.; Gao, H.; Müller, R.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. Interrogation of Streptomyces avermitilis for efficient production of avermectins. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2016, 1, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- El-Saber Batiha, G.; Alqahtani, A.; Ilesanmi, O.B.; Saati, A.A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Hetta, H.F. Avermectin Derivatives, Pharmacokinetics, Therapeutic and Toxic Dosages, Mechanism of Action, and Their Biological Effects. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Awadhiya, P.; Patil, S.; Banerjee, T. Avermectin production by solid state fermentation-a novel approach. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm Sci. 2017, 9, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deng, Q.; Xiao, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, C. Streptomyces avermitilis industrial strain as cell factory for Ivermectin B1a production. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2019, 4, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Luo, Z.; Zeng, W.; Xu, S.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, J. Enhanced avermectin production by Streptomyces avermitilis ATCC 31267 using high-throughput screening aided by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; You, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Wen, Y. Avermectin B1a production in Streptomyces avermitilis is enhanced by engineering aveC and precursor supply genes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 2191–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Su, J.; Lu, W. Characterization of a pleiotropic regulator MtrA in Streptomyces avermitilis controlling avermectin production and morphological differentiation. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korystov, Y.N.; Ermakova, N.V.; Kublik, L.N.; Levitman, M.K.; Shaposhnikova, V.V.; Mosin, V.A.; Drinyaev, V.A.; Kruglyak, E.B.; Novik, T.S.; Sterlina, T.S. Avermectins inhibit multidrug resistance of tumor cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 493, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, K.; Shiomi, K.; Sunazuka, T.; Harder, A.; Turberg, A.; Omura, S. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4″-alkoxy avermectin derivatives. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 4135–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Õmura, S.; Crump, A. The life and times of ivermectin-a success story. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.E.; Vilchèze, C.; Ng, C.; Jacobs, W.R.; Ramón-García, S.; Thompson, C.J. Anthelmintic Avermectins Kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Including Multidrug-Resistant Clinical Strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geary, T.G. Ivermectin 20 years on: Maturation of a wonder drug. Trends Parasitol. 2005, 21, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabala, J.C.; Mrozik, H.; Tolman, R.L.; Eskola, P.; Lusi, A.; Peterson, L.H.; Campbell, W.C.; Egerton, J.R.; Ostlind, D.A. Ivermectin, a new broad-spectrum antiparasitic agent. J. Med. Chem. 1980, 23, 1134–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.A.; Diop, I.M.; Diallo, S.; Lariviere, M.; Porta, M. Efficacy and tolerance of ivermectin in human onchocerciasis. Lancet 1982, 2, 171–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shikiya, K.; Kinjo, N.; Uehara, T.; Uechi, H.; Ohshiro, J.; Arakaki, T.; Kinjo, F.; Saito, A.; Iju, M.; Kobari, K. Efficacy of ivermectin against Strongyloides stercoralis in humans. Intern. Med. 1992, 31, 310–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ottesen, E.A.; Campbell, W.C. Ivermectin in human medicine. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1994, 34, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ren, B.; Dai, H.; Dai, S.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, B.; Zhang, L. Reversal of meticillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by the anthelmintic avermectin. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 274–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Yao, Q.; Ma, Z.; Ikeda, H.; Fushinobu, S.; Xu, L.H. Hydroxylation of flavanones by cytochrome P450 105D7 from Streptomyces avermitilis. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2016, 132, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havsteen, B.H. The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 67–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ye, L.; Lin, S.-M.; Leung, L.K. Dietary flavnes and flavonones display differential effects on aromatase [CYP19] transcription in the breast cancer cells MCF-7. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 344, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Chan, F.L.; Chen, S.; Leung, L.K. The citrus flavonone hesperetin inhibits growth of aromatase-expressing MCF-7 tumor in ovariectomized athymic mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2012, 23, 1230–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuhr, U.; Klittich, K.; Staib, A. Inhibitory effect of grapefruit juice and its bitter principal, naringenin, on CYP1A2 dependent metabolism of caffeine in man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1993, 35, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, G.; Alvarez, L.; Castells, D.; Correa, O.; Fagiolino, P.; Lanusse, C. Relative bioavailability and comparative clinical efficacy of different ivermectin oral formulations in lambs. BMC Vet. Res. 2013, 9, 27. Available online: https://bmcvetres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1746-6148-9-27 (accessed on 18 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.T.; Hedges, L.; Sampson, K.E.; Lai, Y.; Mahabir, S.; Balogh, L.; Locuson, C.W. Pharmacokinetic interaction of the antiparasitic agents ivermectin and spinosad in dogs. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2011, 39, 789–795. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21321059/ (accessed on 18 April 2024). [CrossRef]
- Derua, Y.A.; Malongo, B.B.; Simonsen, P.E. Effect of ivermectin on the larvae of Anopheles gambiae and Culex quinquefasciatus. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 131. Available online: https://parasitesandvectors.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13071-016-1417-5 (accessed on 18 April 2024). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumaret, J.P.; Martínez, I. El impacto de productos veterinarios sobre insectos coprófagos: Consecuencias sobre la degradación del estiércol en pastizales. Acta Zoológica Mex. 2005, 21, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumaret, J.-P.; Errouissi, F.; Floate, K.; Rombke, J.; Wardhaugh, K. A review on the toxicity and non-target effects of macrocyclic lactones in terrestrial and aquatic environments. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1004–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Cogollo, L.C.; Rodríguez-Vivas, R.I.; Basto-Estrella, G.d.S.; Reyes-Novelo, E.; Martínez-Morales, I.; Ojeda-Chi, M.M.; Favila, M.E. Toxicidad y efectos adversos de las lactonas macrocíclicas sobre los escarabajos estercoleros: Una revisión. Rev. Mex. Biodiver. 2018, 89, 1293–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Jia, L.; Nie, S. Administration of Flumazenil in a Patient with Acute Abamectin Intoxication: Case Report and Review of the Literature. West Indian Med. J. 2015, 64, 162–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; O’Reilly, A.O.; Wu, Y. A point mutation in the glutamate-gated chloride channel of Plutella xylostella is associated with resistance to abamectin. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2016, 25, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faske, T.R.; Starr, J.L. Cotton Root Protection from Plant-Parasitic Nematodes by Abamectin-Treated Seed. J. Nematol. 2007, 39, 27–30. [Google Scholar]
- Korayem, A.M.; Youssef, M.M.A.; Mohamed, M.M.M. Effect of chitin and abamectin on Meloidogyne incognita infesting rapeseed. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2008, 48, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, J.A.; Kiewnick, S.; Grimm, C.; Dababat, A.A.; Sikora, R.A. Efficacy of abamectin seed treatment on Pratylenchus zeae, Meloidogyne incognita and Heterodera schachtii. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2009, 116, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.K.A.; Basyony, A.B.A.; Handoo ZAChitwood, D.J. Pathogenicity and control of Heterodera schachtii and Meloidogyne spp. on some cruciferous plant cultivars. Int. J. Nematol. 2013, 23, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, M.; Eltanany, M.; El-shahaat, M. Efficacy of three Bio-pesticide products and oxamyl against citrus nematode [Tylenchulus semipenetrans] and on productivity of Washington navel orange trees. Egypt. J. Hortic. 2018, 45, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, R.K.; Rabatin, S. Potential of foliar, dip, and injection applications of avermectins for control of plant-parasitic nematodes. J. Nematol. 1998, 30, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bi, Z.; Gong, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, H.; Bai, L.; Hu, J. Efficacy of Four Nematicides Against the Reproduction and Development of Pinewood Nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. J. Nematol. 2015, 47, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, B.; Xie, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fengshang, Y.; Qingjun, W. Identification and Characterization of the Gene CYP340W1 from Plutella xylostella and Its Possible Involvement in Resistance to Abamectin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Liu, J. Preparation and Characterization of Avermectin B2 Microcapsules and Effective Control of Root-Knot Nematodes. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13038–13047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrón-Bravo, O.G.; Hernández-Marín, J.A.; Gutiérrez-Chávez, A.J.; Franco-Robles, E.; Molina-Ochoa, J.; Cruz-Vázquez, C.R.; Ángel-Sahagún, C. Susceptibility of entomopathogenic nematodes to ivermectin and thiabendazole. Chemosphere 2020, 253, 126658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasanelli, N.; Toderas, I.; Veronico, P.; Iurcu-Straistaru, E.; Rusu, S.; Melillo, M.T.; Caboni, P. Abamectin Efficacy on the Potato Cyst Nematode Globodera pallida. Plants 2020, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Huang, J.M.; Ni, H.; Guo, D.; Yang, F.X.; Wang, X.; Shun, F.W.; Cong-Fen, G. Susceptibility of fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda [J.E. Smith], to eight insecticides in China, with special reference to lambda-cyhalothrin. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2020, 168, 104623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar, J.G.R.; Falconi, R.R.; Gutiérrez, R.C. Efecto de acaricidas sobre Tetranicus sp. En maíz [Zea mays] en el estado de Veracruz / Effect of acaricides on Tetranicus sp. In corn [Zea mays] in the state of Veracruz. Braz. J. Anim. Environ. Res. 2021, 4, 4504–4511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Yu, H.; Li, K.; Li, P. Preparation, Characterization, and Insecticidal Activity of Avermectin-Grafted-Carboxymethyl Chitosan. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 9805675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Nan, X.; Yu, H.T.; Cheng, P.L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.Q.; Zhang, S.Y.; Hu, G.F.; Liu, H.; Chen, A.L. Synthesis, biological activities and structure−activity relationships for new avermectin analogues. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 121, 422–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yan, Y.J.; An, J.; Huang, S.X.; Wang, X.J.; Xiang, W.S. Designed biosynthesis of 25-methyl and 25-ethyl ivermectin with enhanced insecticidal activity by domain swap of avermectin polyketide synthase. Microb. Cell Fact. 2015, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.F.; Tian, M.; Lv, C.; Li, H.Y.; Muhammad, R.H.; Zhong, G.H. Preliminary studies on induction of apoptosis by abamectin in Spodoptera frugiperda [Sf9] cell line. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 100, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, G.H.; McDowell, L.L. Pesticide persistence on foliage. Rev. Environ Contam. Toxicol. 1987, 100, 23–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybas, R.A.; Babu, J.R. 4″-deoxy-4″-methylamino-4″-epiavermectin B1 hydrochloride [MK-243]: A novel avermectin insecticide for crop protection. Proc. BCPC Pests. Dis. 1988, 1, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Ishaaya, I.; Kontsedalov, S.; Horowitz, A.R. Emamectin, a novel insecticide for controlling field crop pests. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Entrocasso, C.; Parra, D.; Vottero, D.; Farias, M.; Uribe, L.F.; Ryan, W.G. Comparison of the persistent activity of ivermectin, abamectin, doramectin and moxidectin in cattle. Vet. Rec. 1996, 138, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumano, H.; Ocampo, L. Farmacología Veterinaria, 3rd ed.; McGraw Hill: Mexico City, Mexico, 2006; p. 482. [Google Scholar]
- IRAC. Plutella Xylostella- Método de Prueba de Susceptibilidad IRAC 018. 2010. Available online: https://irac-online.org/methods/plutella-xylostella-larvae/ (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- Mudd, A.J.; Parker, L.D. Use of the new molecule mixidectin for the control of parasites in sheep. Proc. Sheep Vet. Soc. 1993, 18, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Olsvik, P.A.; Lie, K.K.; Mykkeltvedt, E.; Samuelsen, O.B.; Petersen, K.; Stavrum, A.-K.; Lunestad, B.T. Pharmacokinetics and transcriptional effects of the anti-salmon lice drug emamectin benzoate in Atlantic salmon [Salmo salar L.]. BMC Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. GABAergic Synapse. Laboratories K. 2020. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/pathway/hsa04727 (accessed on 21 June 2023).

| Compound | Application | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avermectin B2 | Microcapsules | Population of RKN = Efficiency 80% | [118] |
| Ivermectin | Ivermectin 1% diluted in DMSO 5% | Susceptibility to EPN (Steinernema y Heterorhabditis) | [119] |
| Abamectin | Abamectin (18 g/L) diluted in N-Methyl-2-Pyrrolidone | Significant Globodera pallida control, soil application | [120] |
| Avermectin B1 | Emamectin benzonate | Susceptibility of Spodoptera fugiperda. | [121] |
| Abamectin | Abamectin 1.8%, per 10 plants 2.5 mL | Efecto acaricida en ninfas de Tetranicus spp. en maíz | [122] |
| Avermectin | N,O-carboxymethylchitosan (NOCC) grafted whit avermectin | Insecticidal activity at 4 mg/L against Spodoptera exigua, Tetranychus cinnabarinus and Aphis fabae. | [123] |
| Avermectin B1a | 40 avermectin derivates | Biological activity against Tetranychus cinnabarinus, Aphis craccivora and Bursaphelenchus xylophilus | [124] |
| Ivermectin B1a | 25-methyl y 25-ethyl ivermectin | Nematicidal activity against Caenorhabditis elegans, and insecticidal activity against Mythimna separata larve. | [125] |
| Abamectin | Abamectin (95%) (avermectin B1a > 80% and avermectin B1b < 20%) | Time and dose dependet cell viability in Spodoptera frugiperda. | [126] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerna-Chávez, E.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J.F.; García-Conde, K.B.; Ochoa-Fuentes, Y.M. Potential of Streptomyces avermitilis: A Review on Avermectin Production and Its Biocidal Effect. Metabolites 2024, 14, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070374
Cerna-Chávez E, Rodríguez-Rodríguez JF, García-Conde KB, Ochoa-Fuentes YM. Potential of Streptomyces avermitilis: A Review on Avermectin Production and Its Biocidal Effect. Metabolites. 2024; 14(7):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070374
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerna-Chávez, Ernesto, José Francisco Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Karen Berenice García-Conde, and Yisa María Ochoa-Fuentes. 2024. "Potential of Streptomyces avermitilis: A Review on Avermectin Production and Its Biocidal Effect" Metabolites 14, no. 7: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070374
APA StyleCerna-Chávez, E., Rodríguez-Rodríguez, J. F., García-Conde, K. B., & Ochoa-Fuentes, Y. M. (2024). Potential of Streptomyces avermitilis: A Review on Avermectin Production and Its Biocidal Effect. Metabolites, 14(7), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070374






