Investigation of the Functional Components in Health Beverages Made from Polygonatum cyrtonema Rhizomes Provides Primary Evidence to Support Their Claimed Health Benefits
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection, Pretreatment, and Processing of Plant Materials
2.2. Making “Huangjin” Health Tea and “Huangjin” Health Wine
2.3. Sample Preparation and Extraction for Widely Targeted Metabolomic Analysis
2.4. UPLC Conditions
2.5. ESI-Q TRAP-MS/MS
2.6. Metabolite Annotation
2.7. Multivariate Statistical Analysis
3. Results
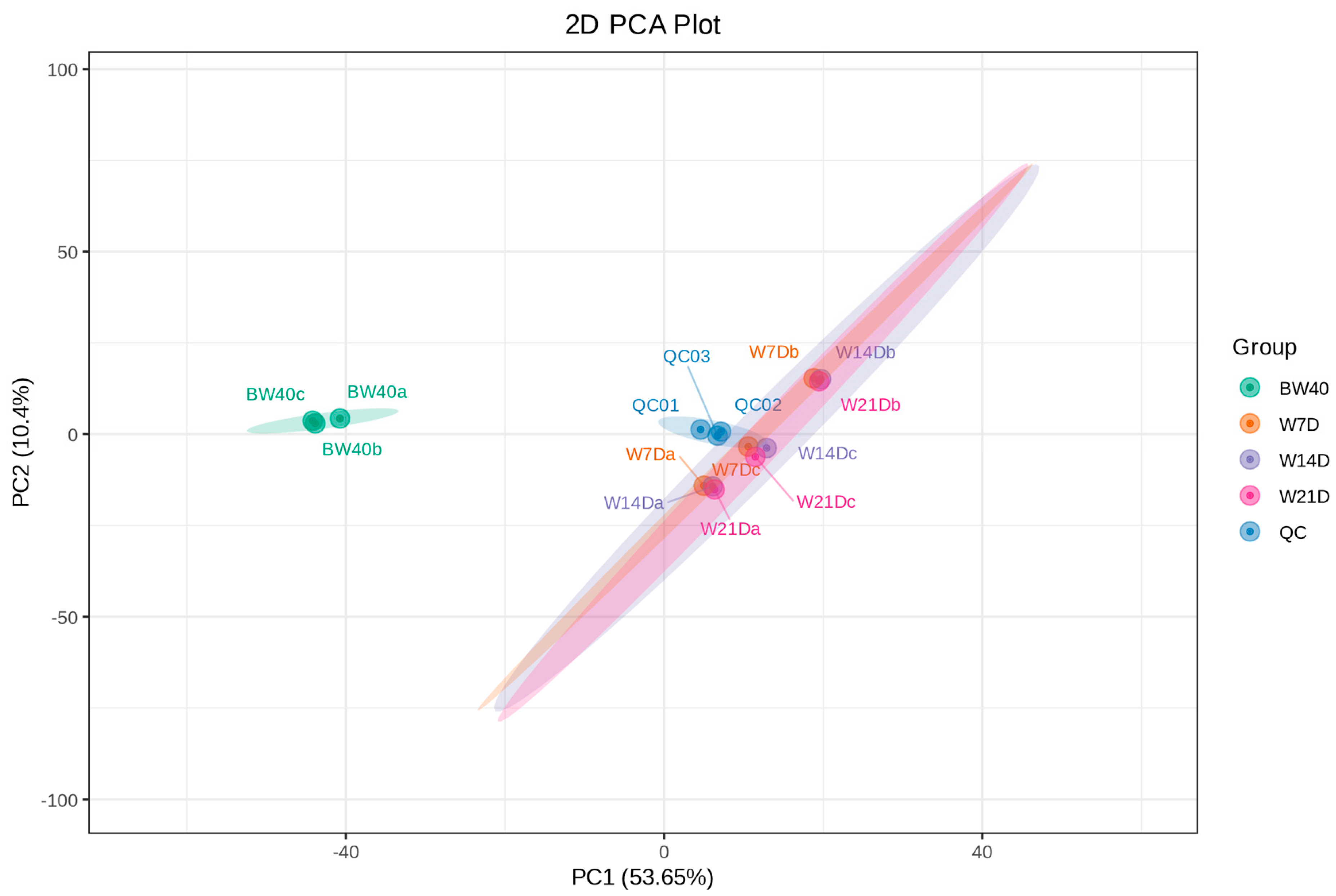
3.1. Metabolomic Profiling of “Huangjin” Tea and “Huangjin” Wine
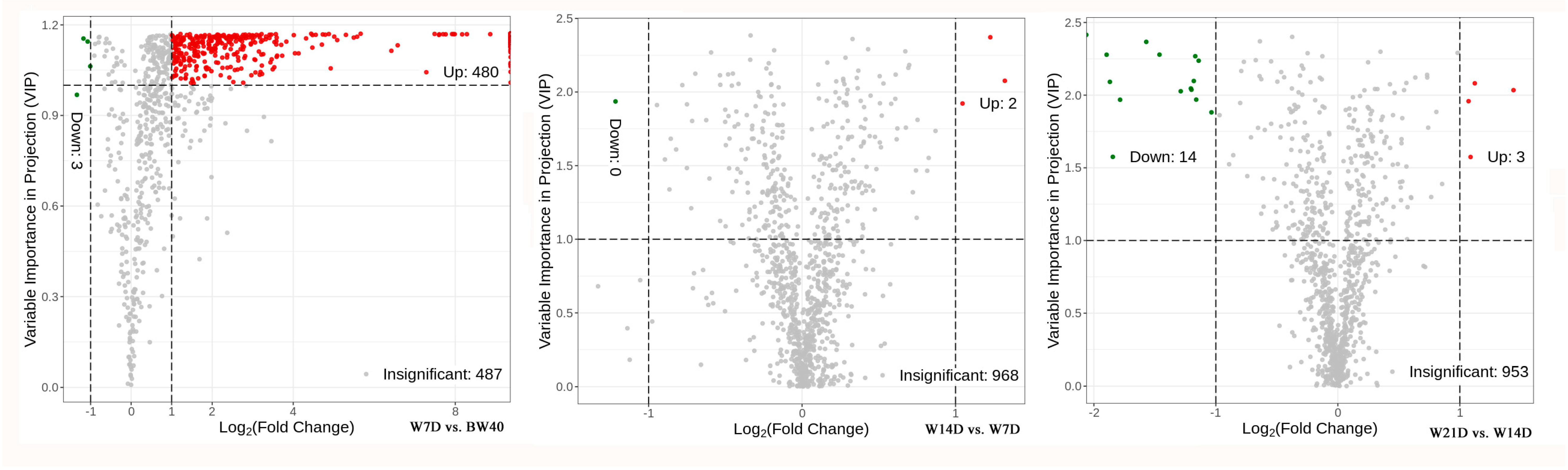
3.2. Profiling of Differentially Extracted Secondary Metabolites between “Huangjin” Tea and “Huangjin” Wine
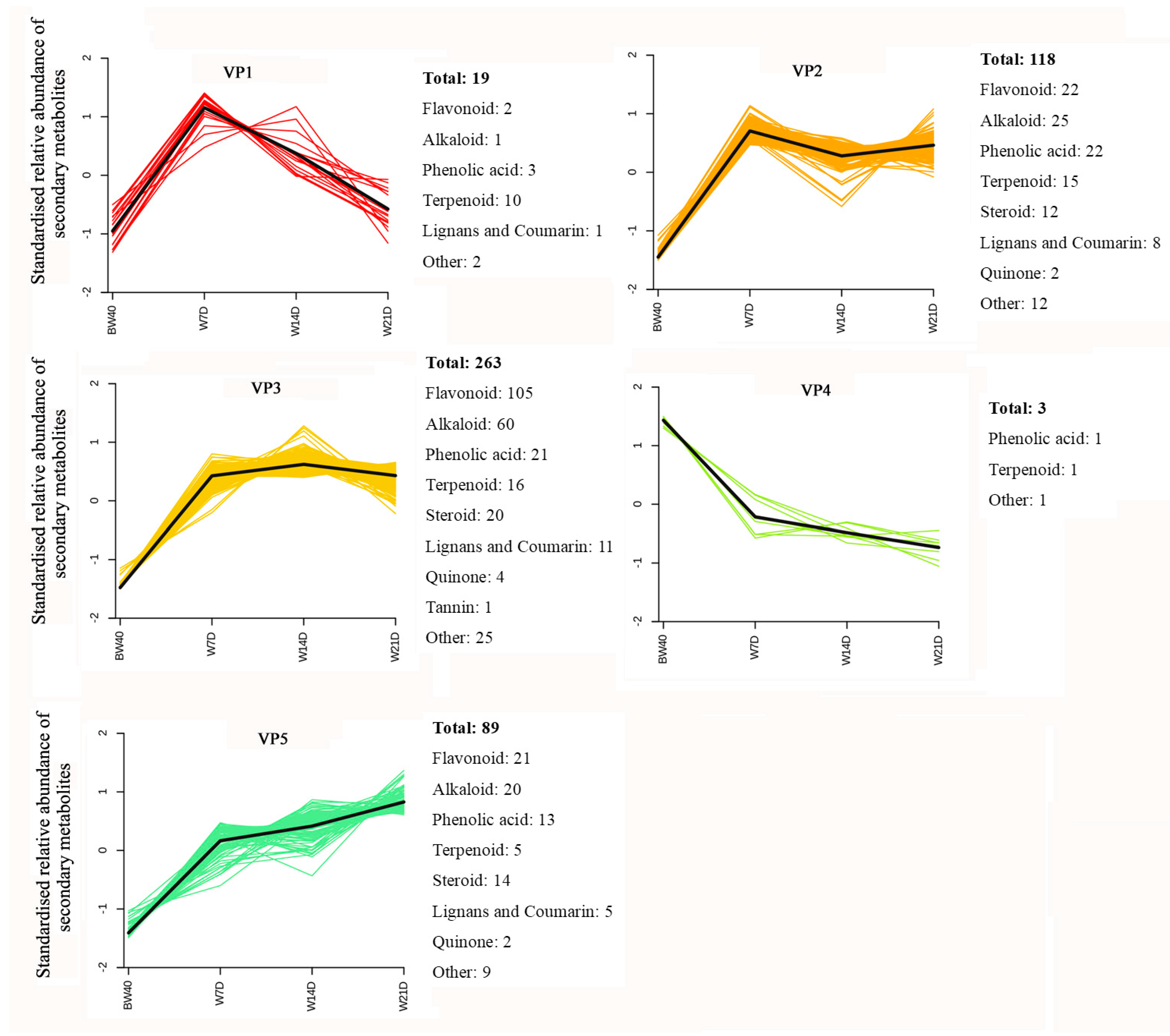
3.3. Variation Pattern in Relative Abundance of Differentially Extracted Secondary Metabolites
3.4. Annotation and Functional Classification of Differentially Extracted Secondary Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, X.; Tamura, M.N. Flora of China; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2000; Volume 24, pp. 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China, One; China Medical Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2020; Volume 4, pp. 387–388. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.J.; Si, J.P. Herbal textual research on Chinese medicine “Huangjing” (Polygonati Rhizoma) and some enlightenments. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2018, 43, 631–636. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Zhao, C.; Li, X.; Gao, Q.; Huang, L.; Xiao, P.; Gao, W. The genus Polygonatum: A review of ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 274–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.D.; Li, X.Y.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zha, X.Q.; Pan, L.H.; Li, Q.M.; Luo, J.P. Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua. polysaccharide exhibits anti-fatigue activity via regulating osteocalcin signaling. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 175, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, C.; Jin, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, L. Research on relationship between processing degree and internal and external quality of Polygonatum cyrtonema processed by “nine-steaming and nine-suncuring” based on color change. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2022, 53, 1719–1729. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Q.; Bao, K.; Jiang, C. Research progress on Polygonatum cyrtonema processed by nine times steaming and nine times shining. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2020, 51, 5631–5637. [Google Scholar]
- Rathi, V. Herbal Wine: A Review. J. Nutr. Weight Loss 2018, 3, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.G.; Tang, C.; Ye, Y.; Quinn, R.J.; Feng, Y. Traditional Chinese medicine extraction method by ethanol delivers drug-like molecules. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2019, 17, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutchan, T.; Dixon, R.A. Secondary metabolism: Nature’s chemical reservoir under deconvolution. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2005, 8, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, R.A. Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature 2001, 411, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksman-Caldentey, K.M.; Inze, D. Plant cell factories in the post-genomic era: New ways to produce designer secondary metabolites. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seca, A.M.L.; Pinto, D.C.G.A. Biological potential and medical use of secondary metabolites. Medicines 2019, 6, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Fu, Y.; Sussman, M.R.; Wu, H. The effect of developmental and environmental factors on secondary metabolites in medicinal plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Dormann, P.; Altmann, T.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics-the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, R.; Beale, M.; Fiehn, O.; Hardy, N.; Sumner, L.; Bino, R. Plant metabolomics: The missing link in functional genomics strategies. Plant Cell 2022, 14, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bino, R.J.; Hall, R.D.; Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Saito, K.; Draper, J.; Nikolau, B.J.; Mendes, P.; Roessner-Tunali, U.; Beale, M.H.; et al. Potential of metabolomics as a functional genomics tool. Trends Plant Sci. 2004, 9, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sait, K. Phytochemical genomics-A new trend. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2013, 16, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, G.; Hao, X.; Li, X.; Ou, M.; Yang, T. Application of metabolomics in plant research. Bot. Res. 2016, 5, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Wang, R.; Song, Y.; Ye, J.; Jiao, H.; Yu, D.; Chang, H. Chemical components dynamic variation of root of Polygonati rhizoma during a nine-time repeat of the steaming and sundrying process. J. Pharm. Res. 2022, 41, 220–229. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Gong, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.; Xiong, L.; Luo, J. A novel integrated method for large-scale detection, identification, and quantification of widely targeted metabolites: Application in the study of rice metabolomics. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1769–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, C.; Lin, T.; Qin, M.; Peng, M.; Yang, C.; et al. Rewiring of the fruit metabolome in tomato breeding. Cell 2018, 172, 249–261.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qiu, X.; Tan, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Mei, S. A comparative metabolomics study of flavonoids in Radish with different skin and flesh colors (Raphanus sativus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14463–14470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, S. Identification of medicinal compounds of Fagopyri Dibotryis rhizome from different origins and its varieties using UPLC-MS/MS based metabolomics. Metabolites 2022, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, E.A.; Roux, A.; Xu, Y.; Ezan, E.; Junot, C. Analysis of the human adult urinary metabolome variations with age, body mass index, and gender by implementing a comprehensive workflow for univariate and OPLS statistical analyses. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 3322–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, J.C.; Cunningham, A.B.; Towns, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, J.W.; Yang, X.F. A billion cups: The diversity, traditional uses, safety issues and potential of Chinese herbal teas. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 222, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaskova, A.; Mlcek, J. New insights of the application of water or ethanol-water plant extract rich in active compounds in food. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1118761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L.; Verpoorte, R.; Yen, H.R.; Peng, W.H.; Cheng, Y.C.; Chao, J.; Pao, L.H. Effects of processing adjuvants on traditional Chinese herbs. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, S96–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacobbo, A.; do Prado, J.M.; Meneguzzi, A.; Bernardes, A.M.; de Pinho, M.N. Microfiltration for the recovery of polyphenols from winery effluents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 143, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, L.; Fabiano-Tixier, A.S.; Chemat, F. Water as green solvent: Methods of solubilisation and extraction of natural products-past, present and future solutions. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, O.; Pinho, S.P. Solubility of flavonoids in pure solvents. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 6586–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, V.; Ananga, A.; Tsolova, V. Recent advances and uses of grape flavonoid flavonoidas nutraceuticals. Nutrients 2014, 6, 391–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattila, P.H.; Hellström, J.; Karhu, S.; Pihlava, J.M.; Veteläinen, M. High variability in flavonoid contents and composition between different North European currant (Ribes spp.) varieties. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, F.; Wu, F.; Wu, H.; Huang, X.; Deng, X. Simultaneous determination of 16 flavonoids in the ginkgo dietary supplement tea by high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2015, 33, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeszka-Skowron, M.; Zgoła-Grześkowiak, A.; Frankowski, R. Cistus incanus a promising herbal tea rich in bioactive compounds: LC-MS/MS determination of catechins, flavonols, phenolic acids and alkaloids -a comparison with camellia sinensis, rooibos and hoan ngoc herbal tea. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 74, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, H.; Shen, L. Recent advances in research on vine tea, a potential and functional herbal tea with dihydromyricetin and myricetin as major bioactive compounds. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.C.; Chen, Z.J.; Guo, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, D.H.; Qian, J. Simultaneous determination of 14 kinds of flavones in health-care wine by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 2178–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.J.; Ma, D.J.; Liu, L.S.; Zhao, J.; Peng, L.P.; Yu, T. Qualitative and quantitative studies on the effective monomers of the alcohol extract of Huainiuxi. Clin. J. Chin. Med. 2024, 16, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Castelli, M.V.; López, S.N. Homoisoflavonoids: Occurrence, biosynthesis, and biological activity. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, 1st ed.; eBook; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 54, pp. 315–354. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, A.; Zhang, X.; Du, Z.; Zhao, F.; Xia, C.; Duan, B. Research progress on flavonoids in plants of Polygonatum Mill. and their pharmacological activities. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2018, 49, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar]
- Mottaghipisheh, J.; Stuppner, H. A comprehensive review on chemotaxonomic and phytochemical aspects of homoisoflavonoids, as rare flavonoid derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, H.N.; Fett-Neto, A.G. Plant alkaloids: Main features, toxicity, and mechanisms of action. In Plant Toxins. Toxinology; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Carlini, C., Ligabue-Braun, R., Eds.; Springer Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Huang, Q.; Peng, W.; Wu, C. Processing methods and mechanisms for alkaloid-rich Chinese herbal medicines: A review. J. Integr. Med. 2021, 19, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adibah, K.Z.M.; Azzreena, M.A. Plant toxins: Alkaloids and their toxicities. GSC Biol. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 6, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.J.; Kim, K.; Kim, Y.D.; Lee, S.E. Naturally occurring Piper plant amides potential in agricultural and pharmaceutical industries: Perspectives of piperine and piperlongumine. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2019, 62, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takooree, H.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Venugopala, K.N.; Jeewon, R.; Zengin, G.; Mahomoodally, M.F. A systematic review on black pepper (Piper nigrum L.): From folk uses to pharmacological applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59 (Suppl. S1), S210–S243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhu, C.; Tu, Y.; Lei, J.; Yu, J. The bioactive amide alkaloids from the stems of Piper nigrum. Food Chem. 2023, 405 Pt A, 134736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Santhanam, R.K.; Xue, Z.; Ma, Q.; Guo, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, M.; et al. Effects of N-trans-feruloyltyramine isolated from laba garlic on antioxidant, cytotoxic activities and H2O2-induced oxidative damage in HepG2 and L02 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekara, A.; Shahidi, F. Herbal beverages: Bioactive compounds and their role in disease risk reduction-A review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2018, 8, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, X.; Bao, Q.; Di, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Lian, F.; Tong, X. The interaction between the gut microbiota and herbal medicines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, M.; Wang, Y.; Feng, L.; Xing, H.; Zhang, K. Gut microbiota: A new target for traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of depression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 116038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Comparison Group | DESM | Total Number | Class | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaloids | Phenolic Acids | Flavonoids | Terpenoids | Lignans and Coumarins | Quinones | Steroids | Tannins | Others | |||
| W7D vs. BW40 | Up | 483 | 105 | 58 | 150 | 41 | 25 | 8 | 45 | 47 | |
| Down | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| W14D vs. W7D | Up | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Down | 0 | ||||||||||
| W21D vs. W14D | Up | 3 | 1 | 2 | |||||||
| Down | 14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 1 | |||||
| Class I | Total Number | Class II |
|---|---|---|
| Flavonoids | 75 | Flavones (8); flavanones (8); flavonols (7); chalcones (4); flavanonols (1); other flavonoids (47, including 26 homoisoflavonoids) |
| Alkaloids | 35 | Alkaloids (16); amide (16); isoquinoline alkaloids (1); piperidine alkaloids (1); pyrrole alkaloids (1) |
| Terpenoids | 14 | Ditepenoids (7); sesquiterpenoids (3); triterpene (2); triterpene Saponin (2) |
| Phenolic acids | 8 | Phenolic acids (8) |
| Steroids | 5 | Steroidal saponins (3); steroid (2) |
| Quinones | 4 | Anthraquinone (4) |
| Lignans and coumarins | 3 | Coumarins (3) |
| Others | 15 | Others (14); aldehyde compound (1) |
| Pathway | Upregulated DESMs | Number of Upregulated DESMs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Class | Compounds | ||
| ko00941: flavonoid biosynthesis | Flavanones | Naringenin (5,7,4′-Trihydroxyflavanone) | 12 |
| Flavonols | Kaempferol (3,5,7,4′-Tetrahydroxyflavone) | ||
| Flavanones | Sakuranetin | ||
| Flavanonols | 3,5,7-Trihydroxyflavanone (Pinobanksin) | ||
| Flavanones | Butin 7,3′,4′-Trihydroxyflavanone | ||
| Phenolic acids | 5-O-p-Coumaroylquinic acid | ||
| Phenolic acids | Chlorogenic acid (3-O-Caffeoylquinic acid) | ||
| Flavanones | Pinocembrin (Dihydrochrysin) | ||
| Flavanonols | Aromadendrin (Dihydrokaempferol) | ||
| Flavanones | Naringenin-7-O-glucoside (Prunin) | ||
| Chalcones | Naringenin chalcone 2′,4,4′,6′-Tetrahydroxychalcone | ||
| Flavonols | Quercetin | ||
| ko00943: Isoflavonoid biosynthesis | Flavanones | Naringenin (5,7,4′-Trihydroxyflavanone) | 1 |
| ko00944: flavone and flavonol biosynthesis | Flavonols | Kaempferol (3,5,7,4′-Tetrahydroxyflavone) | 6 |
| Flavones | Vitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside | ||
| Flavonols | Quercetin-3-O-rhamnoside (Quercitrin) | ||
| Flavones | Apigenin-7-O-neohesperidoside (Rhoifolin) | ||
| Flavones | Apigenin-6-C-glucoside (Isovitexin) | ||
| Flavonols | Quercetin | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Q.; Chen, Y.; Shao, Y.; Pu, W.; Ye, B.; Shi, X.; Shen, J.; Li, H. Investigation of the Functional Components in Health Beverages Made from Polygonatum cyrtonema Rhizomes Provides Primary Evidence to Support Their Claimed Health Benefits. Metabolites 2024, 14, 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070376
Song Q, Chen Y, Shao Y, Pu W, Ye B, Shi X, Shen J, Li H. Investigation of the Functional Components in Health Beverages Made from Polygonatum cyrtonema Rhizomes Provides Primary Evidence to Support Their Claimed Health Benefits. Metabolites. 2024; 14(7):376. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070376
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Qiyan, Youwu Chen, Ye Shao, Weiting Pu, Bihuan Ye, Xiaoxiao Shi, Jianjun Shen, and Haibo Li. 2024. "Investigation of the Functional Components in Health Beverages Made from Polygonatum cyrtonema Rhizomes Provides Primary Evidence to Support Their Claimed Health Benefits" Metabolites 14, no. 7: 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070376
APA StyleSong, Q., Chen, Y., Shao, Y., Pu, W., Ye, B., Shi, X., Shen, J., & Li, H. (2024). Investigation of the Functional Components in Health Beverages Made from Polygonatum cyrtonema Rhizomes Provides Primary Evidence to Support Their Claimed Health Benefits. Metabolites, 14(7), 376. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14070376







