Combination of Evidence from Bibliometrics and Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies miR-21 as a Potential Therapeutical Target for Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
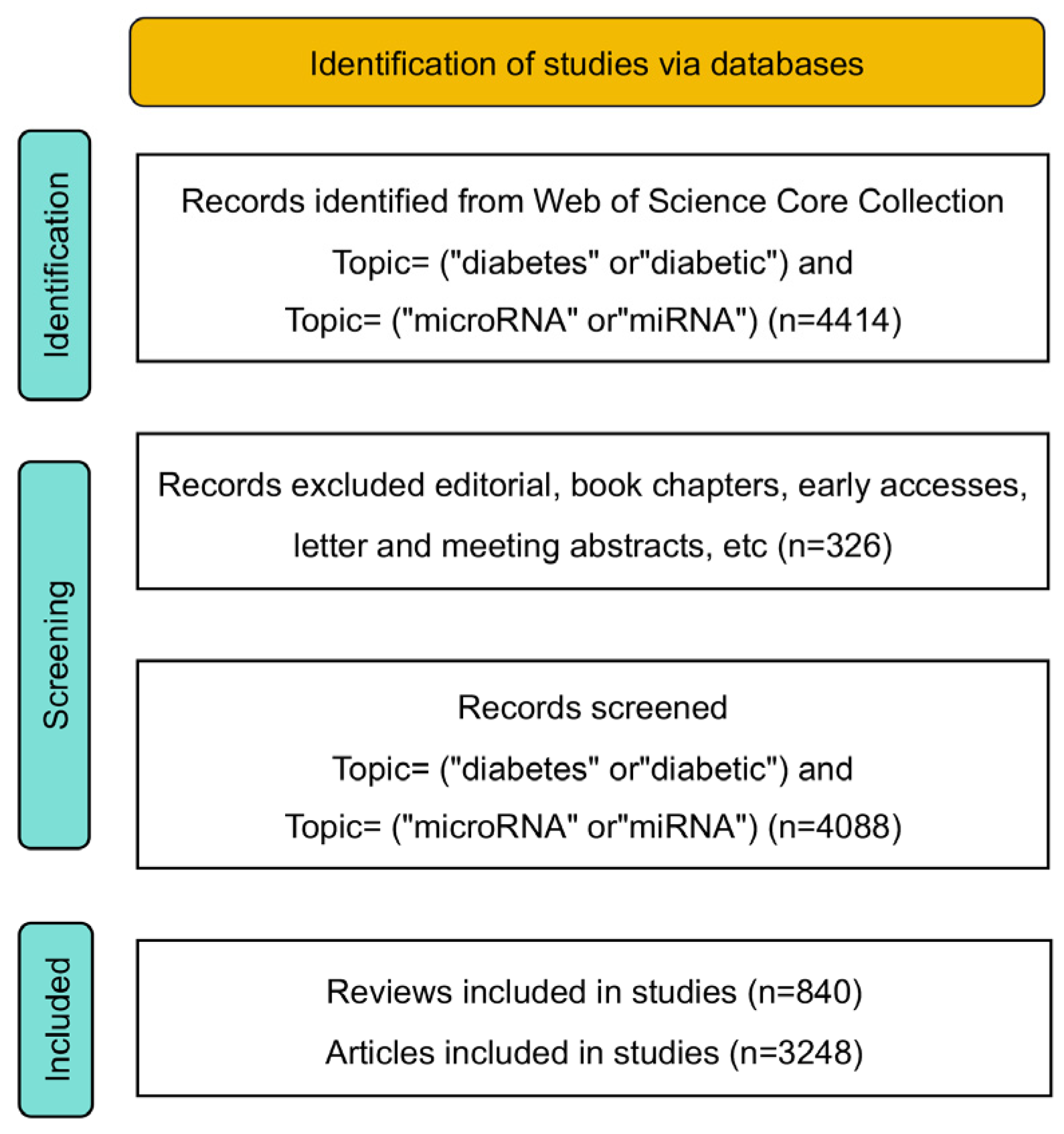
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Collection and Analysis
2.2. Microarray Data Collection and Analysis
2.3. Animals and Treatments
2.4. RNA Isolation and Relative Quantitative Real-Time PCR (Q-PCR)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
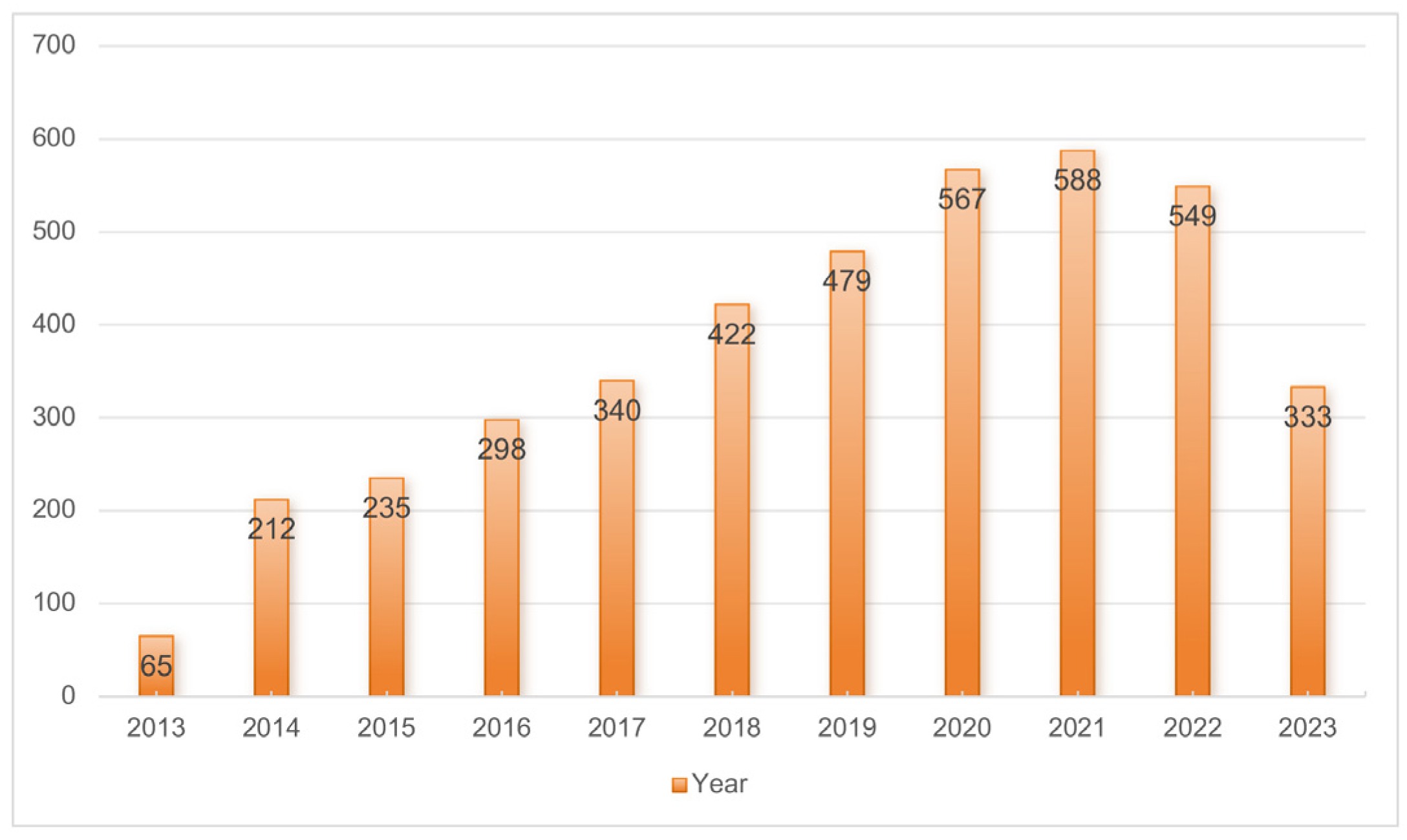
3.1. Annual Trend of Publications in the Diabetes-Associated miRNA Field
3.2. Distribution of Institutions in the Diabetes-Associated miRNA Field
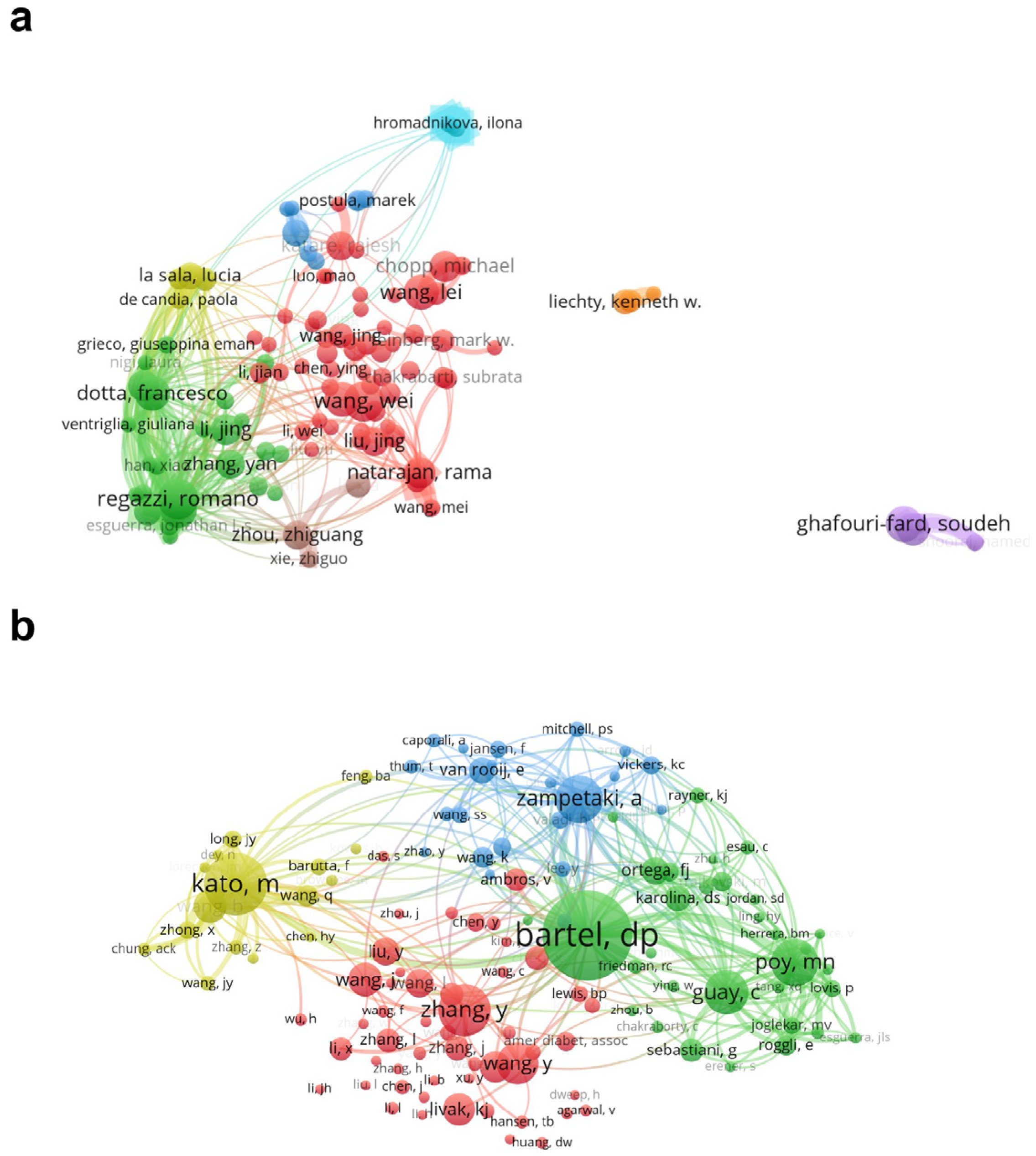
3.3. Authors and Co-Cited Authors in the Diabetes-Associated miRNA Field
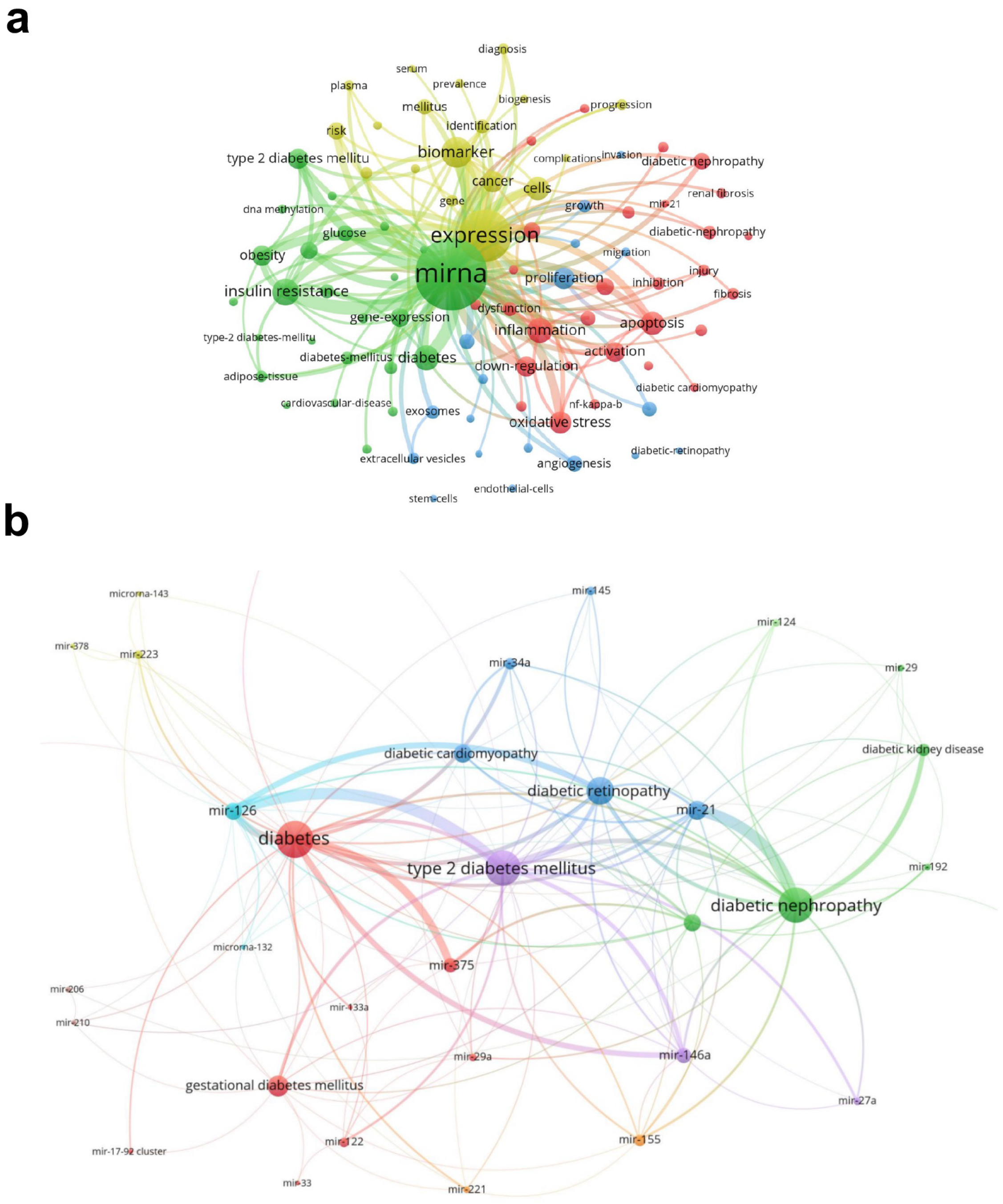
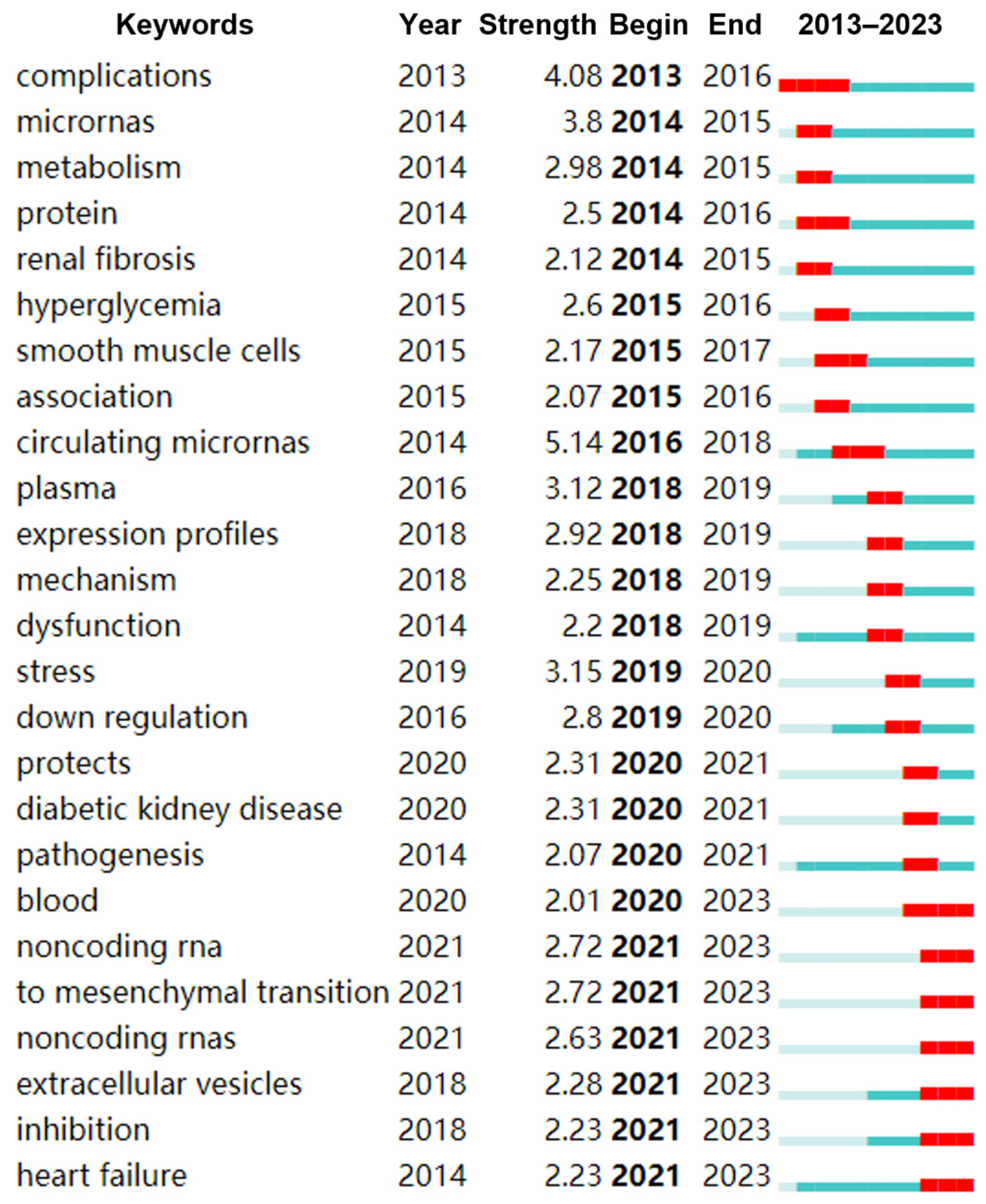
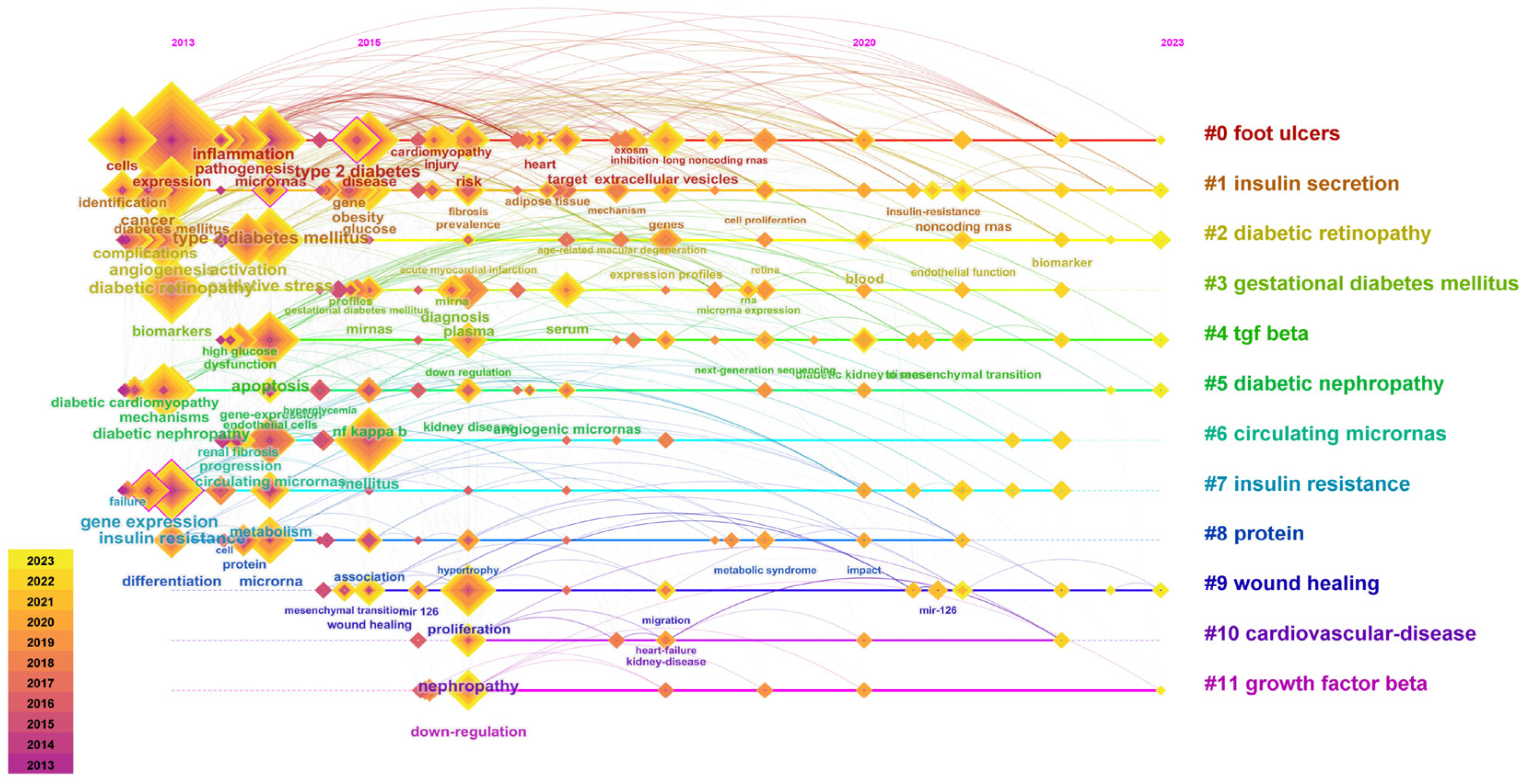
3.4. Keywords in the Diabetes-Associated miRNA Field
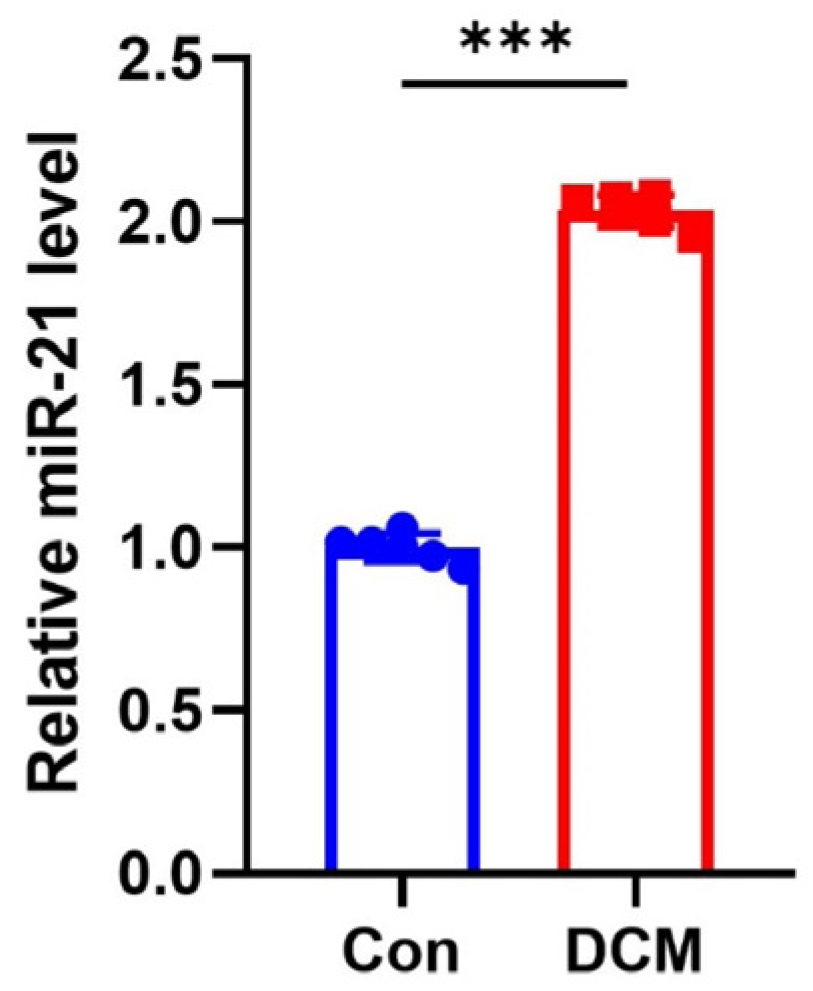
3.5. miR-21 Is a Potential Therapeutical Target for Diabetes
3.6. Hot Topics and Possible Directions in the Field of miRNAs and Diabetes
3.7. Small Molecules with Inhibitory Effects on miR-21
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, Y.; Schultz, R.D.; Li, N.; He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Caron, A.; Zhu, Q.; Sun, K.; Xiong, W.; et al. Partial Leptin Reduction as an Insulin Sensitization and Weight Loss Strategy. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 706–719.e706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, X.F.; Chen, J.; Xia, L.; Cao, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, K.; Guo, K.; et al. Combined lifestyle factors and risk of incident type 2 diabetes and prognosis among individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarp, J.; Luo, M.; Sanchez-Lastra, M.A.; Dalene, K.E.; Cruz, B.D.P.; Ried-Larsen, M.; Thomsen, R.W.; Ekelund, U.; Ding, D. Leisure-time physical activity and all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease in adults with type 2 diabetes: Cross-country comparison of cohort studies. J. Sport Health Sci. 2023, 13, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinajero, M.G.; Malik, V.S. An Update on the Epidemiology of Type 2 Diabetes: A Global Perspective. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 50, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.S.; Ko, S.H. Current trends in epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk management in type 2 diabetes. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2021, 123, 154838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, C.; Keller, A.; Meese, E. Emerging concepts of miRNA therapeutics: From cells to clinic. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotewitsch, M.; Heimer, M.; Schmitz, B.; Mooren, F.C. Non-coding RNAs in exercise immunology: A systematic review. J. Sport Health Sci. 2023, 13, 311–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliminejad, K.; Khorram Khorshid, H.R.; Soleymani Fard, S.; Ghaffari, S.H. An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5451–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miskiewicz, J.; Tomczyk, K.; Mickiewicz, A.; Sarzynska, J.; Szachniuk, M. Bioinformatics Study of Structural Patterns in Plant MicroRNA Precursors. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 6783010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Mei, J.; Ren, G. Plant microRNAs: Biogenesis, Homeostasis, and Degradation. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Hu, B.; Zhang, C. microRNAs and Their Roles in Plant Development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 824240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.; Tran, N. miRNA:miRNA Interactions: A Novel Mode of miRNA Regulation and Its Effect on Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1385, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torma, F.; Gombos, Z.; Jokai, M.; Berkes, I.; Takeda, M.; Mimura, T.; Radak, Z.; Gyori, F. The roles of microRNA in redox metabolism and exercise-mediated adaptation. J. Sport Health Sci. 2020, 9, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasu, S.; Kumano, K.; Darden, C.M.; Rahman, I.; Lawrence, M.C.; Naziruddin, B. MicroRNA Signatures as Future Biomarkers for Diagnosis of Diabetes States. Cells 2019, 8, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampetaki, A.; Kiechl, S.; Drozdov, I.; Willeit, P.; Mayr, U.; Prokopi, M.; Mayr, A.; Weger, S.; Oberhollenzer, F.; Bonora, E.; et al. Plasma microRNA profiling reveals loss of endothelial miR-126 and other microRNAs in type 2 diabetes. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 810–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, M.; Wiklander, O.P.B.; Fritz, T.; Caidahl, K.; El-Andaloussi, S.; Zierath, J.R.; Krook, A. Circulating Exosomal miR-20b-5p Is Elevated in Type 2 Diabetes and Could Impair Insulin Action in Human Skeletal Muscle. Diabetes 2019, 68, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W.; Endo, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, L.; Hu, Y.; Mi, B.; Liu, G. Circulating Exosomal miR-20b-5p Inhibition Restores Wnt9b Signaling and Reverses Diabetes-Associated Impaired Wound Healing. Small 2020, 16, e1904044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chang, T.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, X. Global Trends and Research Hotspots of Exercise for Intervening Diabetes: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 902825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Heikkinen, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.; Wong, G. Trends in the development of miRNA bioinformatics tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1836–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; You, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhai, H.; Hu, Y. A bibliometric analysis of T cell and atherosclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 948314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Gao, J.; Kang, J.; Wang, X.; Niu, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Knowledge Mapping of Exosomes in Autoimmune Diseases: A Bibliometric Analysis (2002–2021). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 939433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Synnestvedt, M.B.; Chen, C.; Holmes, J.H. CiteSpace II: Visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. In AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings; American Medical Informatics Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 2005, pp. 724–728. [Google Scholar]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Tang, M.; Guan, L.; Lee, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, J. Engineering exosomes and their application in cardiovascular field: Bibliometric analysis from 2002 to 2022. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conserva, F.; Barozzino, M.; Pesce, F.; Divella, C.; Oranger, A.; Papale, M.; Sallustio, F.; Simone, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F.; et al. Urinary miRNA-27b-3p and miRNA-1228-3p correlate with the progression of Kidney Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets–Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Meng, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, E.; Yu, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, W. SM2miR: A database of the experimentally validated small molecules’ effects on microRNA expression. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 409–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lew, J.K.; Pearson, J.T.; Saw, E.; Tsuchimochi, H.; Wei, M.; Ghosh, N.; Du, C.K.; Zhan, D.Y.; Jin, M.; Umetani, K.; et al. Exercise Regulates microRNAs to Preserve Coronary and Cardiac Function in the Diabetic Heart. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 1384–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Du, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Ma, M.; Du, W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Pancreatic β cell microRNA-26a alleviates type 2 diabetes by improving peripheral insulin sensitivity and preserving β cell function. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Xu, M.; Tang, Z.; Peng, J. miR-125a-5p ameliorates hepatic glycolipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetes mellitus through targeting of STAT3. Theranostics 2018, 8, 5593–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, D.; Venugopal, B.; Sekar, P.; Ramalingam, K. Role of microRNA 21 in diabetes and associated/related diseases. Gene 2016, 582, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chopp, M.; Szalad, A.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Cepparulo, P.; Lu, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.G. Exosomes Derived from Schwann Cells Ameliorate Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2020, 69, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.X.; Pu, S.D.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.W.; Zhang, Y.T.; Tong, X.W.; Shan, Y.Y.; Gao, X.Y. Exosomal ncRNAs: Novel therapeutic target and biomarker for diabetic complications. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Kuang, G.; Wu, Y.; Ou, C. Emerging roles of exosomal miRNAs in diabetes mellitus. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Bi, Y. Extracellular vesicles mediate the communication of adipose tissue with brain and promote cognitive impairment associated with insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1264–1279.e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, F.; Villalobos-Labra, R.; Sobrevia, B.; Toledo, F.; Sobrevia, L. Extracellular vesicles in obesity and diabetes mellitus. Mol. Asp. Med. 2018, 60, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zou, X.; Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhong, T. Extracellular vesicles in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Key roles in pathogenesis, complications, and therapy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1625677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Gao, H.; Dos Reis, F.C.G.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Luo, Z.; Ji, Y.; Jin, Z.; Ly, C.; Olefsky, J.M. miR-690, an exosomal-derived miRNA from M2-polarized macrophages, improves insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 781–790.e785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Kuo, M.C.; Hung, W.W.; Wu, P.H.; Chang, W.A.; Wu, L.Y.; Lee, S.C.; Hsu, Y.L. Proximal tubule-derived exosomes contribute to mesangial cell injury in diabetic nephropathy via miR-92a-1-5p transfer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
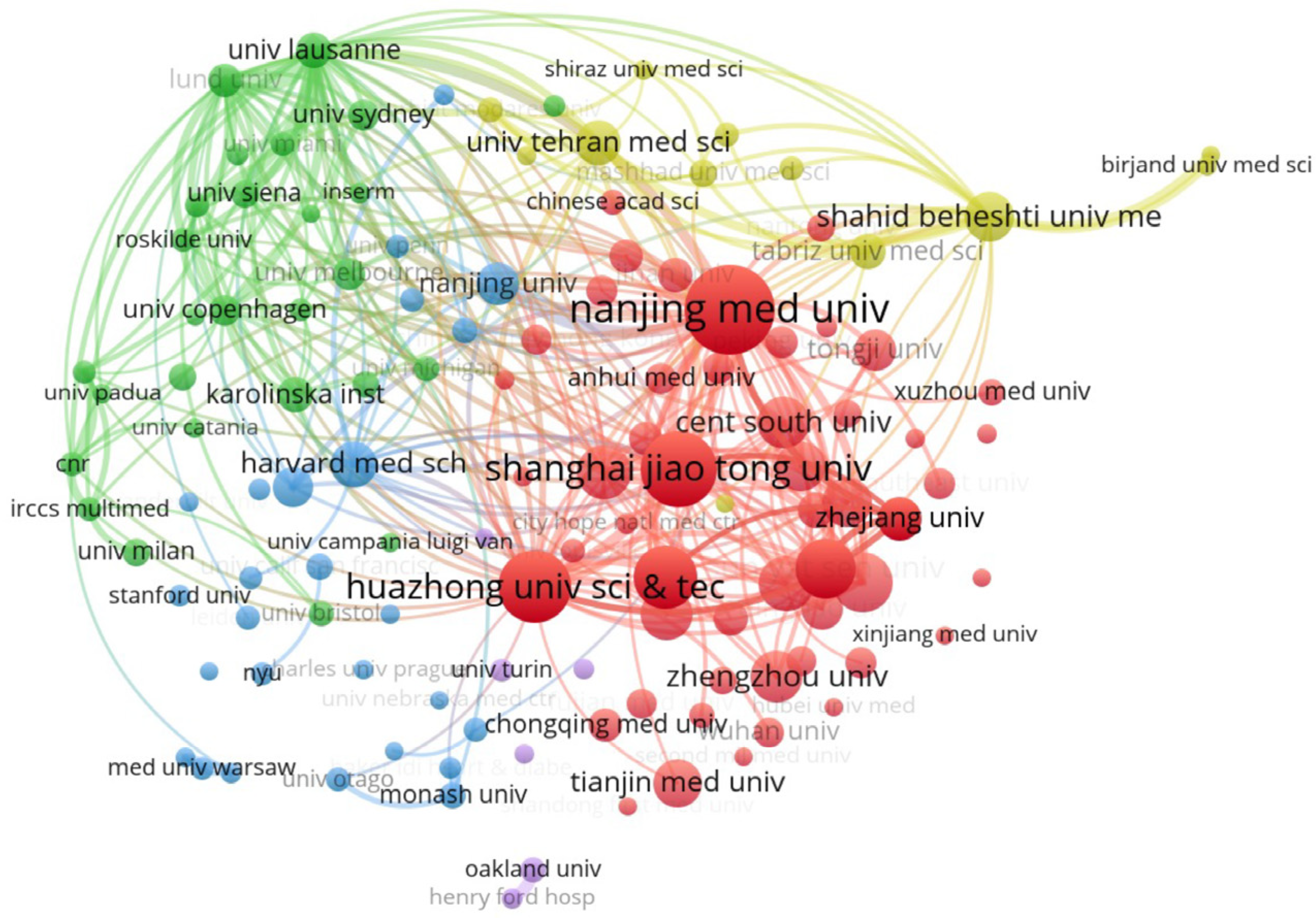

| No. | Institution | Documents | Citations | Average Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nanjing Medical University | 105 | 3746 | 35.68 |
| 2 | Shanghai Jiao Tong University | 83 | 2130 | 25.66 |
| 3 | Huazhong Univ Sci and Technol | 77 | 1485 | 19.29 |
| 4 | Harbin Medical University | 64 | 1533 | 23.95 |
| 5 | Fudan University | 61 | 2369 | 38.84 |
| 6 | Sun Yat-Sen University | 58 | 1609 | 27.74 |
| 7 | Southern med University | 55 | 1510 | 27.45 |
| 8 | China Medical University | 53 | 1030 | 19.43 |
| 9 | Capital Medical University | 51 | 1099 | 21.55 |
| 10 | Cent South University | 50 | 828 | 16.56 |
| No. | Author | Documents | Citations | Total Link Strength | No. | Co-Cited Author | Citations | Total Link Strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Regazzi, Romano | 21 | 1222 | 18,409 | 1 | Bartel, David P | 921 | 7549 |
| 2 | Wang, Wei | 21 | 578 | 4122 | 2 | Kato, Mitsuo | 644 | 7005 |
| 3 | Eliasson, Lena | 19 | 708 | 15,544 | 3 | Zhang, Y | 535 | 4242 |
| 4 | Ghafouri-fard, Soudeh | 19 | 131 | 4844 | 4 | Zampetaki, Anna | 490 | 5580 |
| 5 | Dotta, Francesco | 18 | 725 | 13,981 | 5 | Poy, Matthew N | 486 | 5614 |
| 6 | Li, Yang | 18 | 442 | 2219 | 6 | Guay, Claudiane | 458 | 5073 |
| 7 | Wang, Lei | 18 | 548 | 5069 | 7 | Wang, Y | 427 | 3417 |
| 8 | Taheri, Mohammad | 17 | 116 | 4730 | 8 | Wang, J | 345 | 3119 |
| 9 | Chopp, Michael | 16 | 634 | 5005 | 9 | Wang, B | 343 | 4036 |
| 10 | Li, Jing | 16 | 447 | 4658 | 10 | Livak, Kenneth J | 336 | 1421 |
| 11 | Natarajan, Rama | 16 | 1224 | 9285 | 11 | Li, Y | 319 | 2250 |
| 12 | Sebastiani, Guido | 16 | 684 | 11,995 | 12 | Wang, L | 290 | 2515 |
| No. | Small Molecule | DrugbankID | CID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hydroxychloroquine | DB01611 | 3652 |
| 2 | Prednisone | DB00635 | 5865 |
| 3 | Trypaflavine | DB03843 | 712 |
| 4 | 5-fluorouracil | DB00544 | 3385 |
| 5 | Gemcitabine | DB00441 | 60750 |
| 6 | 5-aza-2′-deoxycytidine (5-Aza-CdR) | DB01262 | 451668 |
| 7 | Sulindac sulfide | DB00605 | 5352624 |
| 8 | 17beta-estradiol (E2) | DB00783 | 5757 |
| 9 | Sevoflurane | DB01236 | 5206 |
| 10 | Nicotine | DB00184 | 89594 |
| 11 | Morphine | DB00295 | 5288826 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Ye, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Yao, J. Combination of Evidence from Bibliometrics and Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies miR-21 as a Potential Therapeutical Target for Diabetes. Metabolites 2024, 14, 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080403
Chen Y, Ye X, Zhang X, Guo Z, Chen W, Pan Z, Zhang Z, Li B, Wang H, Yao J. Combination of Evidence from Bibliometrics and Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies miR-21 as a Potential Therapeutical Target for Diabetes. Metabolites. 2024; 14(8):403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080403
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yiqing, Xuan Ye, Xiao Zhang, Zilin Guo, Wei Chen, Zihan Pan, Zengjie Zhang, Bing Li, Hongyun Wang, and Jianhua Yao. 2024. "Combination of Evidence from Bibliometrics and Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies miR-21 as a Potential Therapeutical Target for Diabetes" Metabolites 14, no. 8: 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080403
APA StyleChen, Y., Ye, X., Zhang, X., Guo, Z., Chen, W., Pan, Z., Zhang, Z., Li, B., Wang, H., & Yao, J. (2024). Combination of Evidence from Bibliometrics and Bioinformatics Analysis Identifies miR-21 as a Potential Therapeutical Target for Diabetes. Metabolites, 14(8), 403. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14080403






