Clustering-Based Identification of BMI-Associated Metabolites with Mechanistic Insights from Network Analysis in Korean Men
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Modifiable Behavioral Factors
2.3. Measurement of Serum Metabolites Concentration
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murray, C.J.L.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Zheng, P.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; Abdollahi, M.; Abdollahpour, I.; et al. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitsma, M.B.; Fullman, N.; Ng, M.; Salama, J.S.; Abajobir, A.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; Abraham, B.; Abyu, G.Y. Smoking prevalence and attributable disease burden in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2015: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet 2017, 389, 1885–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.; Collaborators, G.A. Alcohol use and burden for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2018, 392, 1015–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Afshin, A.; Sur, P.J.; Fay, K.A.; Cornaby, L.; Ferrara, G.; Salama, J.S.; Mullany, E.C.; Abate, K.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abebe, Z. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2019, 393, 1958–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Lobelo, F.; Puska, P.; Blair, S.N.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: An analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012, 380, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: The apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floegel, A.; Wientzek, A.; Bachlechner, U.; Jacobs, S.; Drogan, D.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Krumsiek, J.; Schulze, M.; Pischon, T. Linking diet, physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness and obesity to serum metabolite networks: Findings from a population-based study. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacruz, M.E.; Kluttig, A.; Tiller, D.; Medenwald, D.; Giegling, I.; Rujescu, D.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Frantz, S.; Greiser, K.H. Cardiovascular risk factors associated with blood metabolite concentrations and their alterations during a 4-year period in a population-based cohort. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2016, 9, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.J.; Kwak, S.-Y.; Jo, G.; Song, T.-J.; Shin, M.-J. Serum metabolite profile associated with incident type 2 diabetes in Koreans: Findings from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, S.; Takebayashi, T.; Kurihara, A.; Akiyama, M.; Suzuki, A.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Sugiyama, D.; Kuwabara, K.; Takeuchi, A.; Okamura, T. Metabolomic profiling reveals novel biomarkers of alcohol intake and alcohol-induced liver injury in community-dwelling men. Environ. Health Prev. Med. 2016, 21, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, G.; Favero, C.; Savino, D.; Mercadante, R.; Albetti, B.; Dioni, L.; Vigna, L.; Bollati, V.; Pesatori, A.C.; Fustinoni, S. Plasma Metabolomic Profiling in 1391 Subjects with Overweight and Obesity from the SPHERE Study. Metabolites 2021, 11, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borcard, D.; Gillet, F.; Legendre, P. Numerical Ecology with R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 59–61. [Google Scholar]
- Sammut, C.; Webb, G.I. Encyclopedia of Machine Learning; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Murtagh, F. Ward’s Hierarchical Clustering Method: Clustering Criterion and Agglomerative Algorithm. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1111.6285. [Google Scholar]
- Kohl, M.; Wiese, S.; Warscheid, B. Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. In Data Mining in Proteomics: From Standards to Applications; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 291–303. [Google Scholar]
- Song, M.; Choi, J.-Y.; Yang, J.J.; Sung, H.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.-W.; Kong, S.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kim, H.-H.; Kim, S.G. Obesity at adolescence and gastric cancer risk. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serdar, C.C.; Cihan, M.; Yücel, D.; Serdar, M.A. Sample size, power and effect size revisited: Simplified and practical approaches in pre-clinical, clinical and laboratory studies. Biochem. Medica 2021, 31, 010502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.H.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kim, S.S.; Kang, J.-H.; Kang, J.-H.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, B.-Y.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, E.M. 2018 Korean society for the study of obesity guideline for the management of obesity in Korea. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2019, 28, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.H., Jr. Hierarchical grouping to optimize an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevey, D. Network analysis: A brief overview and tutorial. Health Psychol. Behav. Med. 2018, 6, 301–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulipani, S.; Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Alonso, A.M.; Cardona, F.; Marco-Ramell, A.; Zonja, B.; de Alda, M.L.; Muñoz-Garach, A.; Sanchez-Pla, A.; Tinahones, F.J. Biomarkers of morbid obesity and prediabetes by metabolomic profiling of human discordant phenotypes. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 463, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carayol, M.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Ferrari, P.; Zamora-Ros, R.; Achaintre, D.; Stepien, M.; Schmidt, J.A.; Travis, R.C.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A. Blood metabolic signatures of body mass index: A targeted metabolomics study in the EPIC cohort. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 3137–3146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, M.; Djazayery, A.; Farzadfar, F.; Qi, L.; Yekaninejad, M.S.; Aslibekyan, S.; Chamari, M.; Hassani, H.; Koletzko, B.; Uhl, O. Plasma metabolomic profiling of amino acids and polar lipids in Iranian obese adults. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachlechner, U.; Floegel, A.; Steffen, A.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Pischon, T.; Boeing, H. Associations of anthropometric markers with serum metabolites using a targeted metabolomics approach: Results of the EPIC-potsdam study. Nutr. Diabetes 2016, 6, e215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauschert, S.; Uhl, O.; Koletzko, B.; Kirchberg, F.; Mori, T.A.; Huang, R.-C.; Beilin, L.J.; Hellmuth, C.; Oddy, W.H. Lipidomics reveals associations of phospholipids with obesity and insulin resistance in young adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietiläinen, K.H.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Rissanen, A.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Kaprio, J.; Orešič, M. Acquired obesity is associated with changes in the serum lipidomic profile independent of genetic effects—A monozygotic twin study. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, M.N.; Risis, S.; Yang, C.; Meikle, P.J.; Staples, M.; Febbraio, M.A.; Bruce, C.R. Plasma lysophosphatidylcholine levels are reduced in obesity and type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kougias, P.; Chai, H.; Lin, P.H.; Lumsden, A.B.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Lysophosphatidylcholine and secretory phospholipase A2 in vascular disease: Mediators of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2005, 12, RA5-16. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Allen, T.M.; Umeda, M.; Jewell, L.; Mason, A.; Vance, D.E. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.P. Mitochondrial dysfunction indirectly elevates ROS production by the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 145–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Uña, M.; Varela-Rey, M.; Cano, A.; Fernández-Ares, L.; Beraza, N.; Aurrekoetxea, I.; Martínez-Arranz, I.; García-Rodríguez, J.L.; Buqué, X.; Mestre, D. Excess S-adenosylmethionine reroutes phosphatidylethanolamine towards phosphatidylcholine and triglyceride synthesis. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, K.; Moon, J.; Kang, J.H.; Jang, H.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.; Yu, K.S.; Cho, J.Y. Combined untargeted and targeted metabolomic profiling reveals urinary biomarkers for discriminating obese from normal-weight adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2017, 12, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellot, P.E.N.R.; Moia, M.N.; Reis, B.Z.; Pedrosa, L.F.C.; Tasic, L.; Barbosa, F., Jr.; Sena-Evangelista, K.C.M. Are phosphatidylcholine and lysophosphatidylcholine body levels potentially reliable biomarkers in obesity? A review of human studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 2200568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, L.K.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E. Phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and lipoprotein metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2012, 1821, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Ito, M.; Oka, S.; Tanikawa, T.; Waku, K.; Sugiura, T. Acyltransferases and transacylases that determine the fatty acid composition of glycerolipids and the metabolism of bioactive lipid mediators in mammalian cells and model organisms. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 53, 18–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirulli, E.T.; Guo, L.; Swisher, C.L.; Shah, N.; Huang, L.; Napier, L.A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Spector, T.D.; Caskey, C.T.; Thorens, B. Profound perturbation of the metabolome in obesity is associated with health risk. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 488–500.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Likhodii, S.; Sun, G.; Zhai, G.; Fan, Z.; Xuan, C.; Zhang, W. Differential metabolomics analysis allows characterization of diversity of metabolite networks between males and females. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Total | Cluster 1 (N = 41, 64.1%) | Cluster 2 (N = 23, 35.9%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | (%) | N | (%) | N | (%) | p-Value | |
| Age (year), mean ± SD | 40.2 ± 7.01 | 40.0 ± 6.25 | 40.6 ± 8.33 | 0.7696 a | |||
| <40 | 29 | (45.3) | 20 | (48.8) | 9 | (39.1) | 0.6478 b |
| 40–50 | 29 | (45.3) | 18 | (43.9) | 11 | (47.8) | |
| ≥50 | 6 | (9.4) | 3 | (7.3) | 3 | (13.0) | |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean ± SD | 24.1 ± 2.62 | 24.7 ± 2.56 | 23.0 ± 2.46 | 0.0152 a | |||
| <25 | 40 | (62.5) | 23 | (56.1) | 19 | (82.6) | 0.0321 b |
| ≥25 | 22 | (34.4) | 18 | (43.9) | 4 | (17.4) | |
| Regular exercise | |||||||
| No | 25 | (39.1) | 15 | (36.6) | 10 | (43.5) | 0.5876 b |
| Yes | 39 | (60.9) | 26 | (63.4) | 13 | (56.5) | |
| Smoking | |||||||
| Never | 17 | (26.6) | 11 | (26.8) | 6 | (26.1) | 0.8932 b |
| Former | 27 | (42.2) | 18 | (43.9) | 9 | (39.1) | |
| Current | 20 | (31.3) | 12 | (29.3) | 8 | (34.8) | |
| Drinking | |||||||
| No | 5 | (7.8) | 3 | (7.3) | 2 | (8.7) | 0.8437 b |
| Yes | 59 | (92.2) | 38 | (92.7) | 21 | (91.3) | |
| Cluster 2 vs. 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude Model | Adjusted Model | |||
| OR | (95% CI) | OR a | (95% CI) | |
| Age | 1.01 | (0.94–1.09) | 1.00 | (0.92–1.09) |
| BMI | 0.76 | (0.60–0.96) | 0.76 | (0.60–0.96) |
| Regular exercise | ||||
| Yes | 0.75 | (0.27–2.12) | 0.79 | (0.26–2.40) |
| Smoking | ||||
| Former | 0.92 | (0.26–3.29) | 0.97 | (0.24–3.89) |
| Current | 1.22 | (0.32–4.66) | 1.48 | (0.35–6.30) |
| Drinking | ||||
| Yes | 0.83 | (0.13–5.36) | 0.92 | (0.10–8.20) |
| # | Metabolites | β-Coefficient | Standard Error | p Value | FDR-p | Bonferroni-p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | lysoPC a C28:0 | 0.1741 | 0.0426 | 0.0001 | 0.0165 | 0.0209 |
| 2 | lysoPC a C26:0 | 0.1711 | 0.0433 | 0.0002 | 0.0165 | 0.0330 |
| 3 | PC aa C24:0 | 0.1585 | 0.0433 | 0.0006 | 0.0278 | 0.0835 |
| 4 | lysoPC a C20:4 | 0.1507 | 0.0424 | 0.0008 | 0.0289 | 0.1157 |
| 5 | PC aa C40:2 | 0.1480 | 0.0449 | 0.0017 | 0.0359 | 0.2514 |
| 6 | PC aa C40:3 | 0.1383 | 0.0421 | 0.0018 | 0.0359 | 0.2658 |
| 7 | PC ae C42:1 | 0.1475 | 0.0457 | 0.0021 | 0.0359 | 0.3091 |
| 8 | PC aa C40:4 | 0.1429 | 0.0448 | 0.0023 | 0.0359 | 0.3454 |
| 9 | lysoPC a C26:1 | 0.1457 | 0.0458 | 0.0024 | 0.0359 | 0.3571 |
| 10 | PC aa C40:1 | 0.1404 | 0.0442 | 0.0024 | 0.0359 | 0.3591 |
| 11 | PC aa C36:4 | 0.1321 | 0.0421 | 0.0027 | 0.0370 | 0.4074 |
| 12 | PC aa C38:3 | 0.1365 | 0.0467 | 0.0050 | 0.0623 | 0.7472 |
| 13 | lysoPC a C28:1 | 0.1304 | 0.0457 | 0.0061 | 0.0686 | 0.9112 |
| 14 | PC aa C38:4 | 0.1215 | 0.0429 | 0.0064 | 0.0686 | 0.9598 |
| 15 | lysoPC a C16:0 | 0.1299 | 0.0470 | 0.0077 | 0.0691 | 1.0000 |
| 16 | lysoPC a C20:3 | 0.1283 | 0.0465 | 0.0078 | 0.0691 | 1.0000 |
| 17 | PC ae C42:2 | 0.1217 | 0.0442 | 0.0079 | 0.0691 | 1.0000 |
| 18 | PC aa C42:2 | 0.1137 | 0.0456 | 0.0156 | 0.1293 | 1.0000 |
| 19 | PC aa C36:3 | 0.1129 | 0.0476 | 0.0213 | 0.1606 | 1.0000 |
| 20 | PC aa C38:1 | 0.1080 | 0.0464 | 0.0234 | 0.1606 | 1.0000 |
| 21 | Glutamate | 0.1092 | 0.0473 | 0.0246 | 0.1606 | 1.0000 |
| 22 | C5 | 0.1107 | 0.0482 | 0.0255 | 0.1606 | 1.0000 |
| 23 | PC ae C30:1 | 0.1071 | 0.0468 | 0.0258 | 0.1606 | 1.0000 |
| 24 | SM C24:0 | 0.1083 | 0.0473 | 0.0259 | 0.1606 | 1.0000 |
| 25 | Hexose | 0.0954 | 0.0456 | 0.0410 | 0.2399 | 1.0000 |
| 26 | PC ae C38:4 | 0.0972 | 0.0467 | 0.0419 | 0.2399 | 1.0000 |
| 27 | PC ae C40:2 | 0.0972 | 0.0477 | 0.0462 | 0.2499 | 1.0000 |
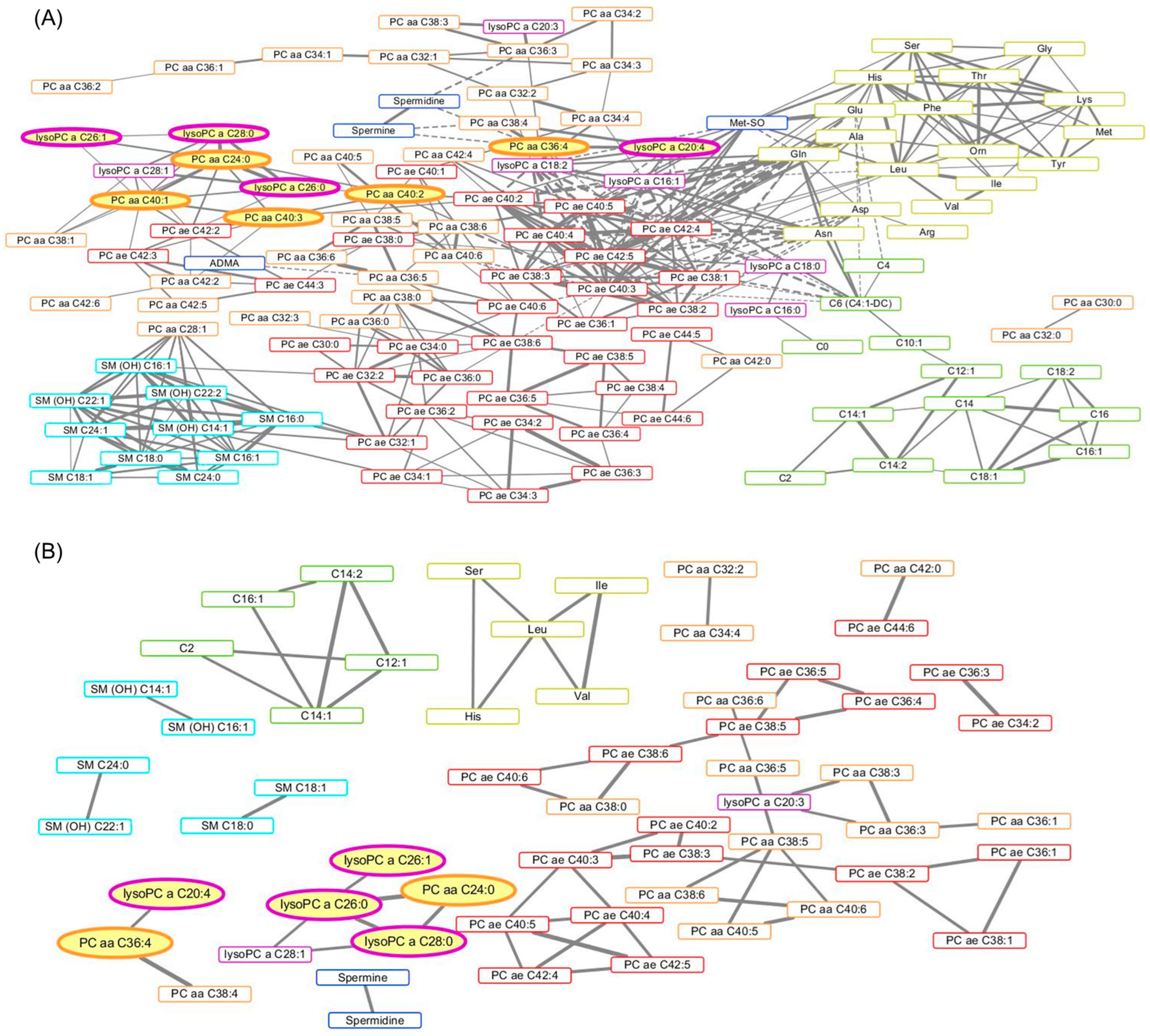
| (A) Parameters of the Network Analysis | Associations with BMI | |||||||
| Rank | Metabolite | Degree | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality | β-Coefficient | Standard Error | p Value | FDR-p |
| 1 | PC ae C40:3 | 23 | 0.4960 | 0.3684 | 0.0746 | 0.0474 | 0.1210 | 0.3539 |
| 2 | PC ae C42:5 | 23 | 0.1111 | 0.3352 | 0.0400 | 0.0472 | 0.4002 | 0.6855 |
| 3 | PC ae C42:4 | 20 | 0.0690 | 0.3306 | 0.0446 | 0.0487 | 0.3636 | 0.6855 |
| 4 | PC ae C40:5 | 17 | 0.0208 | 0.3083 | 0.0407 | 0.0473 | 0.3928 | 0.6855 |
| 5 | Gln | 17 | 0.0107 | 0.3156 | −0.0413 | 0.0502 | 0.4136 | 0.6924 |
| 6 | PC ae C40:2 | 16 | 0.0898 | 0.3140 | 0.0972 | 0.0477 | 0.0462 | 0.2499 |
| 7 | PC ae C38:1 | 15 | 0.0391 | 0.3148 | −0.0116 | 0.0469 | 0.8059 | 0.9455 |
| 8 | Leu | 14 | 0.0910 | 0.3005 | 0.0053 | 0.0496 | 0.9152 | 0.9869 |
| 9 | His | 14 | 0.0280 | 0.2668 | 0.0163 | 0.0503 | 0.7466 | 0.9027 |
| 10 | PC ae C40:4 | 14 | 0.0018 | 0.3028 | 0.0928 | 0.0474 | 0.0550 | 0.2499 |
| 31 | PC aa C24:0 | 9 | 0.0466 | 0.2338 | 0.1585 | 0.0433 | 0.0006 | 0.0278 |
| 32 | PC aa C40:1 | 9 | 0.0071 | 0.2077 | 0.1404 | 0.0442 | 0.0024 | 0.0359 |
| 36 | PC aa C36:4 | 8 | 0.0978 | 0.2680 | 0.1321 | 0.0421 | 0.0027 | 0.0370 |
| 41 | lysoPC a C20:4 | 8 | 0.0110 | 0.2656 | 0.1507 | 0.0424 | 0.0008 | 0.0289 |
| 46 | PC aa C40:3 | 7 | 0.0797 | 0.2527 | 0.1383 | 0.0421 | 0.0018 | 0.0359 |
| 53 | lysoPC a C26:0 | 6 | 0.0167 | 0.2324 | 0.1711 | 0.0433 | 0.0002 | 0.0165 |
| 61 | PC aa C40:2 | 5 | 0.1029 | 0.2888 | 0.1480 | 0.0449 | 0.0017 | 0.0359 |
| 73 | lysoPC a C28:0 | 5 | 0.0001 | 0.1916 | 0.1741 | 0.0426 | 0.0001 | 0.0165 |
| 98 | lysoPC a C26:1 | 3 | 0.0000 | 0.1910 | 0.1457 | 0.0458 | 0.0024 | 0.0359 |
| (B) Parameters of the Network Analysis | Associations with BMI | |||||||
| Rank | Metabolite | Degree | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality | β-Coefficient | Standard Error | p Value | FDR-p |
| 1 | Leu | 4 | 0.6667 | 1.0000 | 0.0053 | 0.0496 | 0.9152 | 0.9869 |
| 2 | PC aa C38:5 | 4 | 0.6500 | 0.8333 | 0.0930 | 0.0470 | 0.0530 | 0.2499 |
| 3 | lysoPC a C26:0 | 4 | 0.5833 | 1.0000 | 0.1711 | 0.0433 | 0.0002 | 0.0165 |
| 4 | PC ae C40:3 | 4 | 0.5556 | 0.5625 | 0.0746 | 0.0474 | 0.1210 | 0.3539 |
| 5 | C14:1 | 4 | 0.3333 | 1.0000 | 0.0009 | 0.0490 | 0.9860 | 0.9927 |
| 6 | PC ae C40:4 | 4 | 0.1667 | 0.4737 | 0.0928 | 0.0474 | 0.0550 | 0.2499 |
| 7 | PC ae C40:5 | 4 | 0.1667 | 0.4737 | 0.0407 | 0.0473 | 0.3928 | 0.6855 |
| 8 | PC aa C36:3 | 3 | 0.6667 | 1.0000 | 0.1129 | 0.0476 | 0.0213 | 0.1606 |
| 9 | PC ae C38:5 | 3 | 0.6000 | 0.7143 | 0.0490 | 0.0468 | 0.2993 | 0.5946 |
| 10 | PC ae C38:6 | 3 | 0.6000 | 0.7143 | 0.0316 | 0.0481 | 0.5146 | 0.7619 |
| 15 | lysoPC a C28:0 | 3 | 0.0833 | 0.8000 | 0.1741 | 0.0426 | 0.0001 | 0.0165 |
| 19 | PC aa C36:4 | 2 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.1321 | 0.0421 | 0.0027 | 0.0370 |
| 30 | PC aa C24:0 | 2 | 0.0000 | 0.6667 | 0.1585 | 0.0433 | 0.0006 | 0.0278 |
| 54 | lysoPC a C20:4 | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.6667 | 0.1507 | 0.0424 | 0.0008 | 0.0289 |
| 57 | lysoPC a C26:1 | 1 | 0.0000 | 0.5714 | 0.1457 | 0.0458 | 0.0024 | 0.0359 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Kang, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kang, D.; Cho, J.-Y.; Choi, J.-Y. Clustering-Based Identification of BMI-Associated Metabolites with Mechanistic Insights from Network Analysis in Korean Men. Metabolites 2025, 15, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020088
Park J, Kang J, Lee J-Y, Kang D, Cho J-Y, Choi J-Y. Clustering-Based Identification of BMI-Associated Metabolites with Mechanistic Insights from Network Analysis in Korean Men. Metabolites. 2025; 15(2):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020088
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, JooYong, Jihyun Kang, Ji-Yeoun Lee, Daehee Kang, Joo-Youn Cho, and Ji-Yeob Choi. 2025. "Clustering-Based Identification of BMI-Associated Metabolites with Mechanistic Insights from Network Analysis in Korean Men" Metabolites 15, no. 2: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020088
APA StylePark, J., Kang, J., Lee, J.-Y., Kang, D., Cho, J.-Y., & Choi, J.-Y. (2025). Clustering-Based Identification of BMI-Associated Metabolites with Mechanistic Insights from Network Analysis in Korean Men. Metabolites, 15(2), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15020088







