Abstract
Background/Objectives: Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a rare inherited metabolic disorder caused by phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency, resulting in highly elevated blood phenylalanine (Phe) concentrations, leading to neurotoxic effects. Despite advancements in treatment, adult patients with PKU may experience impairments in executive functions (EFs). This study investigates the influence of metabolic control across different life stages on EFs and sociodemographic outcomes in adult PKU. Methods: We conducted a monocentric study with 36 early-diagnosed and treated PKU patients (mean age: 34.8 years). EFs were assessed using the Test Battery for Attentional Performance (TAP) and the Tower of London (TL-D). Metabolic data were extracted from medical records, focusing on childhood and adulthood metabolic control, including Phe fluctuations. Sociodemographic data were collected via questionnaires. Statistical analyses explored relationships between EFs, metabolic control, and sociodemographic data. Results: EFs in the cohort were within the lower average range. Significant negative correlations could be observed between EF performance and dried blood Phe concentrations during childhood (ages 0–10 years) as well as current Phe concentrations and Phe variation. Elevated childhood Phe concentrations were associated with lower educational attainment. Sociodemographic characteristics, such as employment status and living arrangements, aligned with those of the general population. Conclusions: Optimal cognitive development in PKU requires good metabolic control, particularly in early childhood. In adulthood, while dietary restrictions may be relaxed, maintaining low and stable Phe concentrations is crucial for EFs. Consistent monitoring and tailored therapeutic approaches throughout life seem essential for optimizing metabolic and neurocognitive outcome in PKU.
1. Introduction
Phenylketonuria (PKU; ORPHA716) is classified as a rare metabolic disease, affecting the amino acid metabolism. A deficiency of the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), which is responsible for facilitating the conversion of the essential amino acid phenylalanine (Phe) into tyrosine, is causative of this autosomal recessive disorder. Consequently, excess Phe accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to toxic effects on the central nervous system, compounded by a deficiency in tyrosine and the toxic accumulation of phenylketones. If left untreated, PKU causes intellectual disability, along with epileptic seizures and behavioral disturbances characterized by aggression or hyperactivity. Additionally, individuals with untreated PKU often exhibit eczema and a pale complexion, with light skin and hair [1,2,3]. Other causes of hyperphenylalaninemia related to cofactor metabolism are not part of the study population.
With the introduction of newborn screening in the late 1960s, enabling early diagnosis, a Phe-restricted diet can ideally be implemented within the first few weeks of life [4]. This protein-restricted diet must be maintained beyond childhood and, additionally, a supplementation of amino acid mixtures is necessary. Accordingly, the current target Phe levels for children (up to age 12) are 120–360 μmol/L, and for individuals older than 12 years, 120–600 μmol/L. This enables the attainment of almost normal motor and cognitive development [5].
Moreover, newer therapeutic approaches, including the administration of the cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), administered as sapropterin hydrochloride, the injection of the enzyme supplementation therapy pegvaliase, or potentially in the future through sepiapterin (currently at primary endpoint in a pivotal Phase 3 clinical trial), provide relief or even the possibility of discontinuing the dietary restrictions for responsive patients [6,7,8].
PKU thus represents a prime example of a condition for which the development of modern science has provided a treatment that improves the global outcome for patients. When evaluating the success of treatment, the performance in later life is, of course, of particular importance. However, studies involving older adults with PKU have only been conducted in recent years, and the available data remain sparse. Preliminary studies present conflicting findings and indicate the possibility of minor limitations which may still affect the daily living of these patients [9,10,11,12,13]. Several studies have consistently shown that working memory abilities and executive functions in patients with PKU are significantly poorer across studies compared to healthy controls [14,15,16]. In contrast, language abilities, such as verbal fluency, often appear to be well preserved [15,17,18]. These results further emphasize that PKU presents a distinct neurocognitive profile that requires separate consideration, extending beyond the mere assessment of IQ, which aggregates various facets of neurocognitive abilities.
Therefore, we examined a homogeneous group, including some of the oldest patients with PKU, who received early diagnosis and treatment from our research site. Newborn screening, as well as biochemical and genetic testing, was conducted in accordance with the applicable guidelines. In this study, particular emphasis was placed on investigating functions relevant for daily living in relation to cognitive performance, not general intelligence. For this purpose, we assessed certain executive functions (EFs) and sociodemographic data, examining how both current and childhood metabolic control may influence cognitive performance in middle age.
Thus, we aim to explore the significance of sustained good metabolic control across different stages of life in providing optimal care and guidance for adult patients with PKU.
2. Materials and Methods
We conducted a monocentric study in which we assessed EFs using various test batteries, collecting sociodemographic data via questionnaires and data on metabolic control from medical records. Participation was offered to all patients with PKU 18 years or older, who were early-diagnosed, treated, and regularly followed up in the outpatient clinic for inherited metabolic diseases at the University Hospital Leipzig, Germany.
The study received ethical approval from Leipzig University Medical faculty’s ethics committee (registration number: 273/21-ek; date of approval: 5 July 2021) and has been registered with the German Clinical Trial Register (DRKS00032654) at the International Clinical Trials Registry Platform. Informed consent was obtained from all participants. EF tests were conducted after each patient‘s regular appointment for metabolic consultation. The duration of the tests, carried out in a standardized setting, was approximately 45 min.
2.1. Executive Function Testing
2.1.1. Test Battery for Attentional Performance (TAP)
The TAP is a computer-based instrument designed to assess specific attentional functions in participants aged 10 years and older [19]. It comprises simple reaction paradigms where subjects respond to non-verbal, distinguishable stimuli by pressing a designated button. Performance criteria include, depending on the test, response time, error rate, and omissions. The TAP is well validated and includes normative data for various age groups and subtests. We selected the following five subtests, which were adapted based on previous findings in the literature and their relevance to everyday life, for our study: working memory (assessed using the n-back task), flexibility (evaluated through the set shifting task), divided attention (measured by a task requiring simultaneous attention to multiple processes), impulse control (assessed using the Go/NoGo task, which measures the ability to withhold inappropriate responses), and incompatibility (evaluated by tasks assessing interference due to stimulus-response incompatibility).
2.1.2. Tower of London (TL-D—Turm Von London—German Version)
The TL-D assesses complex planning processes that require the identification and evaluation of numerous potential action options to achieve a desired outcome [20]. The task involves moving differently colored balls along rods of various lengths from a starting position to a target position using the fewest possible moves, with only one ball allowed to be moved at a time. The number of moves is recorded as raw data and converted into percentile ranks. A normative dataset is available for the number of problems solved in the age group of 18 to 65 years.
2.2. Metabolic Data
Data on current and long-term therapy (including Phe-restricted diet, BH4, or pegvaliase supplementation) and biochemical parameters were gathered from electronic medical records. With the exception of five patients, we successfully integrated Phe concentrations from childhood and adolescence into our calculations. To assess long-term metabolic control, all available dried blood Phe concentrations until study enrolment were analyzed. This resulted in a median of 272 Phe values per patient. Until 2005, blood values were measured using fluorometry or ion exchange chromatography; afterwards, dried blood analysis was performed by liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry, as previously described [21,22,23,24].
In our principal research approach, we analyzed two life stages separately: under 18 years of age (Phe childhood) and over 18 years of age (Phe adulthood). These variables are represented by the mean of medians of all Phe values per year of life for each patient (0–18 years and from 18 years onwards, respectively), in analogy to previous studies [25]. Additionally, we illustrated fluctuations through the variable Phe variation (again, for both childhood and adulthood separately). Phe variation is defined as the mean of the standard deviation of all Phe values per year of life for each patient.
Additionally, this approach was employed in presenting the Phe values from different stages of childhood and adolescence (Phe 0–6, 6–10, and 10–18 years, including variation). We selected these age intervals based on the treatment guidelines previously implemented, when the majority of the patients were still underage [9]. To account not only for the blood value on the day of testing (Current Phe) but also for the overall recent metabolic control, we determined the median (Recent Phe) and the standard deviation (Recent Phe SD) of all Phe values from the previous two years (max. 10 values). Additionally, we recorded the duration from birth to start of treatment (Duration) and the first measured Phe value (Newborn screening). For the latter, the measurement method is comparable, whether the value was obtained via mass spectrometry or fluorometry [21]. Therefore, no distinction will be made in what follows.
2.3. Sociodemographic Data
Sociodemographic data, as well as data on dietary management and anthropometric measurements, were collected via questionnaires. This included information on the type of therapy (diet, pegvaliase, and BH4), Body Mass Index (BMI), school-leaving certificate, employment status, form of relationship, living arrangement, and number of children. The reference population was primarily based on data from surveys conducted as part of the micro census of the Federal Statistical Office of Germany [26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. In addition, information on the type of housing and on early retirement are based on data from the Federal Agency for Civic Education (Bundeszentrale für politische Bildung) and the German pension insurance fund (Deutsche Rentenversicherung), respectively [35,36].
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using the statistical software R 22 (R Core Team, 2024), including the following packages: readxl [37], corrplot [38], psych [39], openxlsx [40], rcompanion [41], rstatix [42], and coin [43].
The distribution of patient characteristics and sociodemographic data was analyzed in comparison to the reference population using Chi-square goodness-of-fit tests. We compared the test results for EFs of the complete patient group with the normative sample of the corresponding test (shown in the respective manual) via a one-sided Wilcoxon rank-sum test. For the comparison between genders, the Mann–Whitney U test was employed. The sample was divided into three educational attainment groups (lower secondary school, intermediate secondary school, and higher secondary school), for comparison between groups by using a Kruskal–Wallis test. We calculated Spearman correlations between metabolic control at different stages of life and EFs. Significance was accepted for p < 0.05.
For explorative purposes and to enhance clarity, we summed all twelve correlation coefficients related to EFs for each life stage to provide a clearer understanding of which life periods have a particularly strong impact on EFs.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
A total of 66 patients with PKU were invited to participate in the study. Of these, 21 either could not or did not wish to spend additional time after their regular consultation, particularly given their long travel distances. Another nine patients spontaneously canceled their appointment without providing a reason and did not schedule a new appointment after the recruitment period had ended. In total, 36 patients (20 female) agreed to participate. Five of these were BH4-responsive (and treated for at least 14 years), and four had been successfully treated with pegvaliase (for at least one year), thus not requiring strict dietary treatment. A total of 27 patients received amino acid mixtures as protein substitutes. None of the participating patients in our study could be classified as mild hyperphenylalaninemia (mHPA) (ORPHA79651), thus not requiring any treatment. The average age at participation was 34.8 (SD: 10.9, range 18–53) years (see Table 1).

Table 1.
Characterization of the population.
Anthropometric data did not deviate significantly from the reference population (see Table 2). No significant gender differences were detected, regarding assessments of metabolic control and sociodemographic data. Likewise, no differences in anthropometric data occurred when comparing different treatment groups (diet vs. BH4 or pegvaliase).

Table 2.
Anthropometric description of the sample at the time of investigation.
In terms of sociodemographic data, our sample differed from the normative comparison group. On average, the investigated patients with PKU tended to have higher educational attainment and fewer children compared to a normative sample. However, the frequency of full-time employment, as well as the distribution with regard to living arrangements, was comparable. It is also worth noting that all of our patients have obtained a school-leaving certificate. Additionally, our sample was more frequently in a relationship or married than the reference population (see Table 3).

Table 3.
Selected sociodemographic data.
3.2. Metabolic Control
Regarding metabolic control, median dried blood Phe concentrations during childhood were found to be in accordance with the recommended guidelines. However, Phe concentrations in adulthood, particularly the current Phe level, exceeded the recommended threshold (see Table 4).

Table 4.
Metabolic control.
Age was positively correlated with mean Phe childhood (r = 0.66, p < 0.05), indicating that the older the patient was at the time of testing, the poorer their metabolic control during childhood tended to be. In contrast, no correlation could be found regarding age in relation to mean Phe adulthood (r = −0.15, p = 0.38), recent median (r = −0.00, p = 0.99), or current Phe (r = −0.01, p = 0.95).
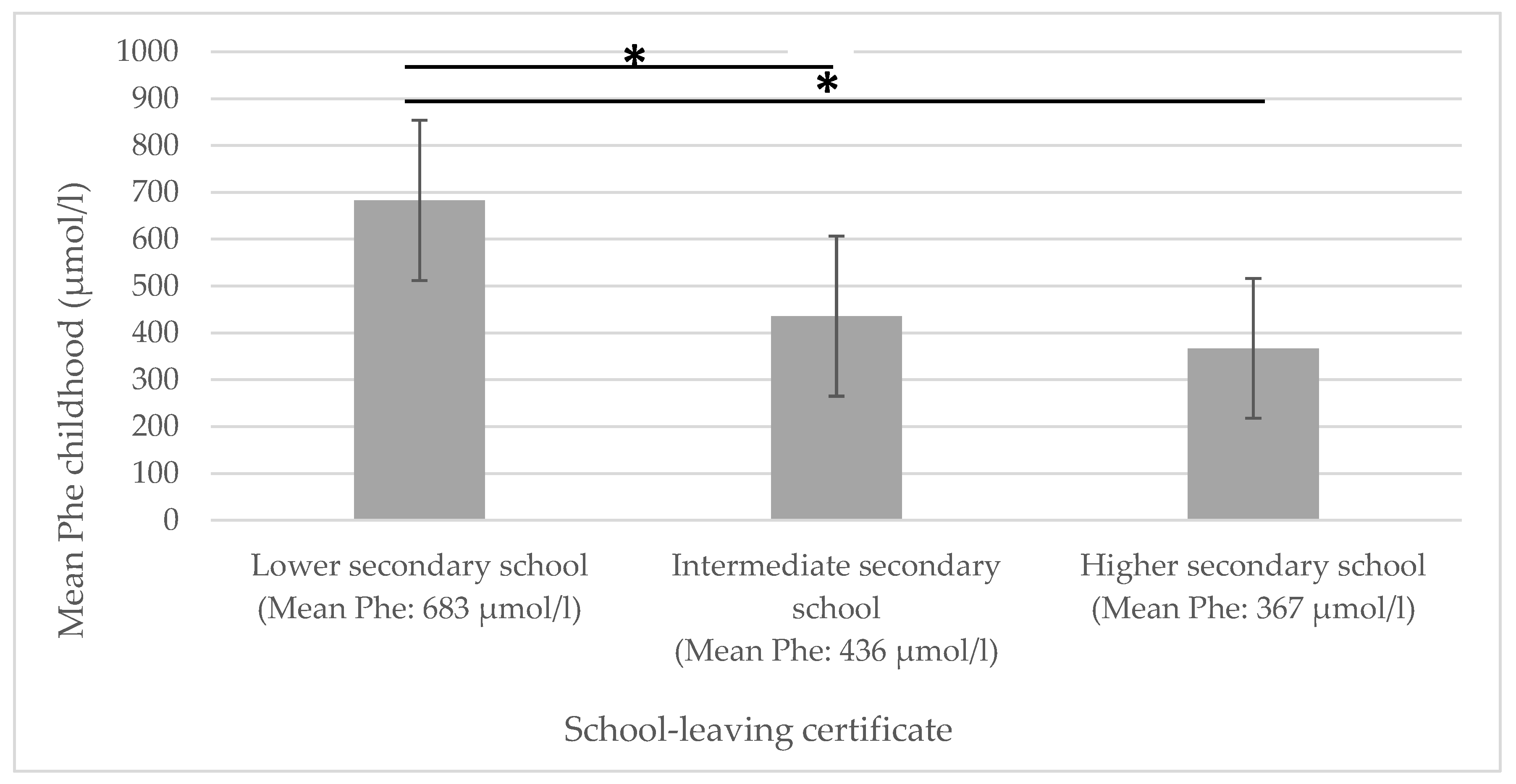
A significant negative correlation could be shown for mean Phe childhood and educational attainment: the higher the mean Phe childhood levels, the lower the educational attainment (see Figure 1).
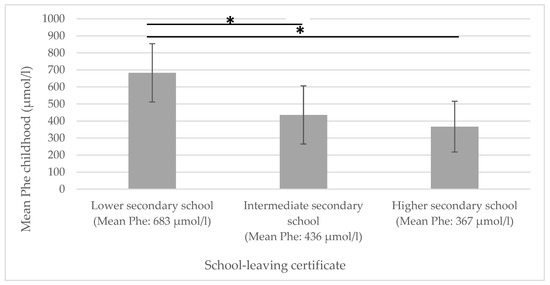
Figure 1.
Mean Phe childhood in relation to educational attainment. Phe = phenylalanine concentrations in dried blood. * significantly different.
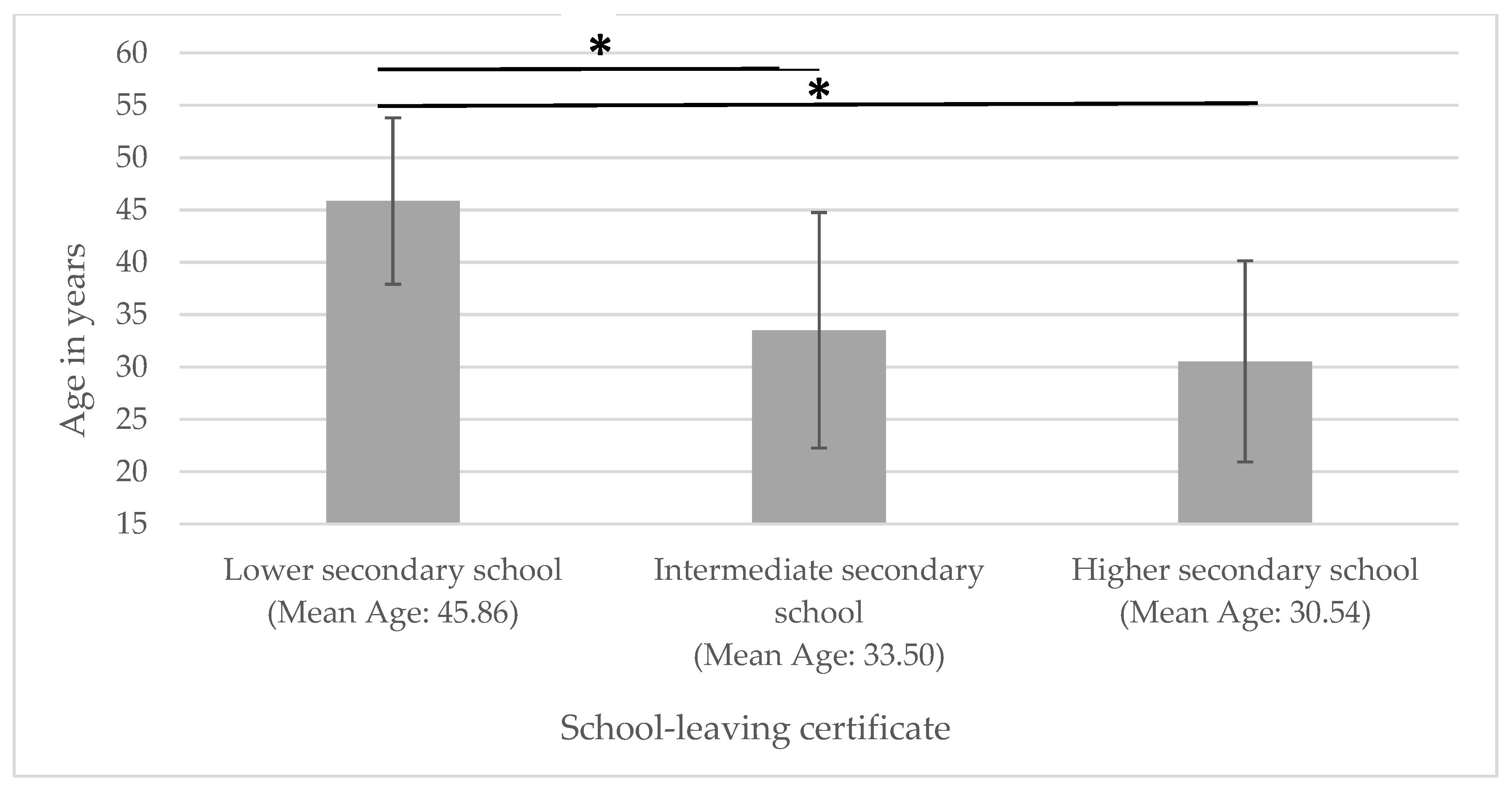
Accordingly, patients with a lower secondary school diploma were significantly older than those with an intermediate secondary school or higher secondary qualifications (see Figure 2).
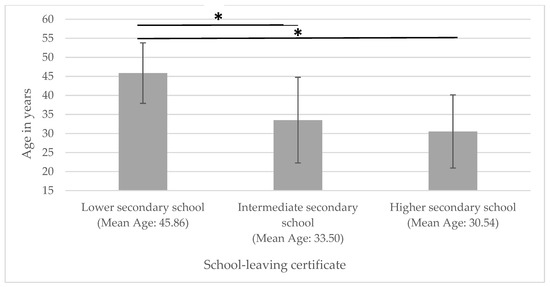
Figure 2.
Age in relation to educational attainment. * significantly different.
3.3. Executive Functions
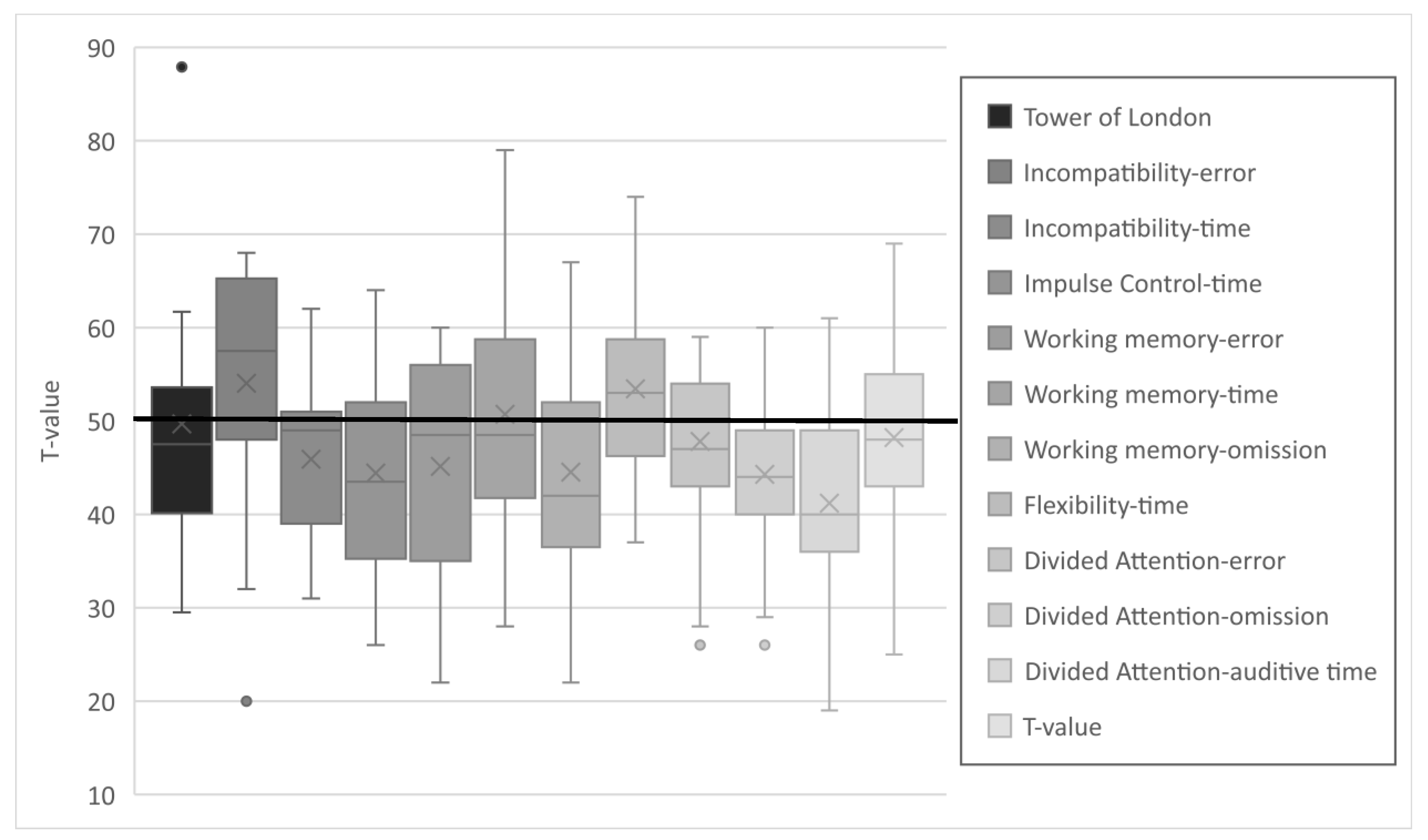
The results of the various subtests of the TAP and TL-D were in the lower average range (see Figure 3). Differences to the reference population were statistically significant in all but 3 of the 12 subtests: working memory (reaction time) and divided attention (errors and visual reaction time). The complete dataset is provided in the Supplementary Materials, Table S2. Due to the test design, it is not possible to compute a composite score for EFs. It appears that particularly the values for auditory reaction time are in the lower average range. This is in contrast to an average performance in visual reaction time and a near-average error rate. A similar trend was observed with respect to incompatibility, where patients made fewer errors but demonstrated reduced response times. An opposite trend was observed in working memory, where patients exhibited average speed but demonstrated a higher omission and error rate.
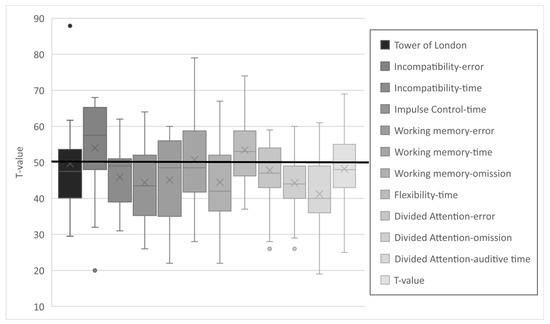
Figure 3.
T-values of the subtests of the executive functions.
Gender differences were identified only in the subtest of divided attention (errors), where male patients made significantly fewer errors (median = 41 vs. 53), z (n1 = 20; n2 = 16) = −2.16; p = 0.03; r = 0.36).
3.4. Relation Between Executive Functions and Metabolic Control (Long Term/Concurrent)
Significant negative correlations were found between specific EFs and metabolic control at different life stages. Errors in the working memory test and the TL-D, as well as performance in tasks requiring divided attention, appeared particularly vulnerable to elevated Phe concentrations (the complete dataset is provided in the Supplementary Materials, Table S1. Most significant correlations found were of medium strength and ranged between −0.35 and −0.44. This applies, among others, to the Phe levels at ages 0–6 years and the TL-D, as well as errors in working memory (−0.44 and −0.41, respectively). Regarding the correlation between Phe variation at age 6–10 years and working memory errors, as well as between recent Phe SD and the omissions at the divided attention test, a strong significant relationship was observed (−0.51 for each).
In line with the average EF values reported above, no consistent correlations with Phe measures in the different life stages were observed regarding (visual) reaction time of divided attention and working memory. For the former, both positive and negative significant correlations were identified, while for the latter, no significant associations were found.
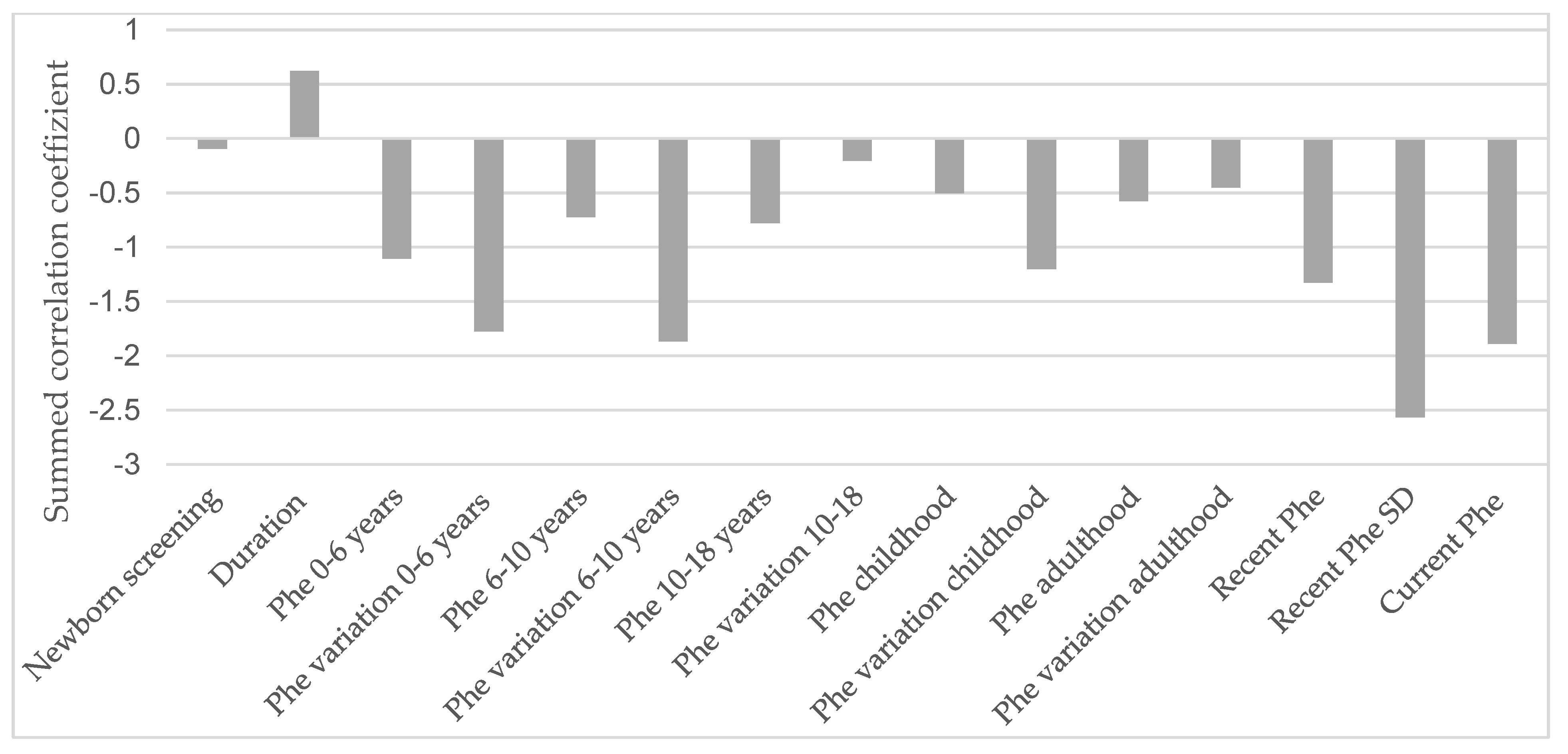
Figure 4 illustrates the influence of various life stages related to metabolic control on all described EFs in an explorative manner.
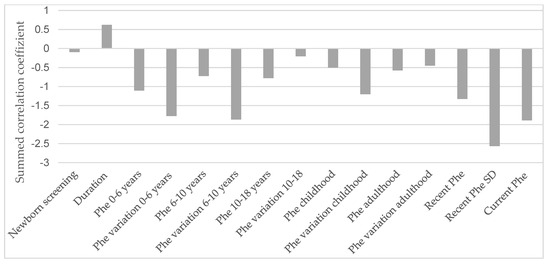
Figure 4.
Influence of metabolic control in each life stage on the correlation sum score of the executive functions. Phe = phenylalanine concentrations in dried blood; SD = standard deviation. The underlying dataset is available in the Supplementary Materials (Table S1).
It is apparent that the current Phe level, recent SD, and Phe concentrations during the first six years of life, as well as variations in Phe levels between the ages of 0 and 10, have the most pronounced impact on current EF performance.
4. Discussion
Advancements in management have led to significant improvements in long-term outcomes for individuals with PKU. However, evidence indicates a close relation to an individual’s metabolic control. Numerous studies have investigated this subject, yielding heterogeneous findings: while some identify impairments in EFs compared to the general population, there remains considerable debate regarding the timing and mechanisms by which Phe concentrations exert their impact. Factors such as Phe concentrations at the time of assessment, long-term metabolic control, and fluctuations in Phe levels are topics of ongoing discussion [9,10,11,12,13].
Given the pivotal role of EFs in daily life, these findings are particularly relevant to understanding the long-term impact of PKU. As EFs facilitate the practical application of intellectual abilities, they should be given due consideration. Furthermore, it is crucial to consider sociodemographic factors, as Phe concentration can influence elements such as education and socioeconomic background and play a significant role in determining the success of therapy. Therefore, we evaluated EFs and sociodemographic factors in a cohort of adult patients with PKU treated in Leipzig, examining the influence of short- and long-term metabolic parameters on these factors. In our study, we found further confirmation of the importance of maintaining low Phe concentrations throughout childhood and demonstrated the correlation with educational success. Furthermore, we found that tasks related to complex planning or working memory are particularly affected as they were completed with either reduced time or increased error rates. This is consistent with findings from several other research groups [12,13,14,44].
In the consideration of potential negative influencing factors on the reduced EFs, elevated current Phe levels appear to be a significant factor. Fluctuations (expressed as variations) in Phe levels, particularly of recent levels, had a negative impact on EFs in our cohort. This confirms findings from other samples [14,25,45,46]. Furthermore, we found that high Phe concentrations at a younger age specifically influenced current performance. Regarding this aspect, the existing data are contradictory. Some study groups have observed a similar relationship: Feldmann et al. [11] showed that cognitive performance correlated significantly with the blood Phe concentrations during childhood and adolescence. Additionally, a meta-analysis by Fonnesbeck et al. [47] demonstrated that Phe levels in the age range of 0–6 years were particularly influential on current cognitive performance. Elevated Phe values beyond this period also had a negative impact on cognitive performance, though the effect was less pronounced. Our data thus constitute a synthesis of the findings from these studies. However, other studies found less influence of childhood blood Phe concentrations. In contrast, Phe levels during adolescence (12–17 years) and adulthood (18+ years) were associated with current cognitive task performance [18,48].
Examining this interdependence in adults is particularly relevant, as it is well established that both the density and volume of white matter, and consequently the capacity for EFs, naturally decline in middle adulthood [49,50]. Considering the inherent cognitive decline in later life, this further underscores the critical importance of monitoring PKU patients in later stages of life, as initial studies provide indications of age-related cognitive deterioration [51]. Optimal metabolic control during adulthood may offer an opportunity to prevent premature dementia. Furthermore, it must, of course, be considered that socioeconomic factors can influence Phe levels at any age. For instance, a negative correlation has been observed between current Phe values in children and parental education, which seems understandable given the complexity of therapy for this condition [52,53]. When the individual treatment goals are determined, this consideration should be actively addressed and integrated into the care of adult patients.
The focus of this study was to investigate the influence of metabolic control during different stages of life on EFs in adulthood. While inclusion was offered to all early treated individuals with PKU, one has to assume that only those interested in good care could be studied. In addition, those with loss of follow-up over time could not be reached. This bias may have influenced our results. While introducing a control group of matched peers would have been valuable, we chose a comparison to the general reference population, which serves as the intended standard in this context. For the tests used, data from large normative samples are available, which cannot be matched numerically by a control group recruited here. Therefore, we consider the data to be highly representative. Additionally, it was not possible to include patients with mild hyperphenylalaninemia (mHPA) in the study, as they are typically not undergoing treatment and therefore often not followed up in an outpatient clinic on a regular basis.
Moreover, to better align the assessed functions with practical, everyday applications, future research should investigate fine motor abilities, as deviations in this domain have been documented in prior studies [5,10,13]. This was not feasible in our study due to the extensive number of tests and questionnaires that were administered.
Sociodemographic data, however, seem to increasingly align with those of the general population. Educational attainment and employment status appear to be even above average. Furthermore, a higher proportion of individuals were in a relationship or married compared to the reference population. This is likely due to the young age of our sample, where divorce and widowhood rates are low, and the number of students or apprentices is relatively high. The living arrangements seem comparable. It should be noted, however, that of the six individuals in our sample who lived with their parents, five were under 24 years old. This further underscores the improved independence currently observed in older PKU patients. Consequently, unlike previous research that found significant differences in relationship status, independent living arrangements, and academic achievement, our results indicate a positive trend within our cohort of patients with PKU [54,55]. These findings are consistent with recent studies that show improvements in educational attainment, income, and independence among individuals with PKU [56,57,58]. Nonetheless, the number of children is considerably below the population average, consistent with Klimek et al. (2020) [57]. Again, it is important to consider the relatively young average age of our sample.
We observed a significantly poorer level of educational attainment with increasing age in our cohort. This is attributable, alongside the significantly lower Phe concentrations in the younger cohort, to markedly improved therapy conditions and the continuous advancement and diversification of dietary supplements over the past two decades [59]. Additionally, it should be noted that recent decades have seen a general increase in the prevalence of higher education degrees within the overall population [26].
In relation to anthropometric data, our tested sample did not reveal any significant deviations from the normative population. In addition, no influence of the treatment strategy on anthropometric data could be identified. However, women in our sample showed a tendency to be more likely overweight compared to men. This observation is consistent with earlier research that also found no significant differences between patients with PKU and the reference group, but noted a similar trend concerning women with PKU [60,61,62]. Positive influencing factors in this context include maintaining low Phe concentrations and the intake of amino acid mixtures, both of which are associated with a lower body weight [63,64]. Men in our sample made fewer errors than women in the divided attention subtest of the TAP. This difference was not expected given the normative data of the test battery and study population. However, studies investigating multitasking have shown that men and women employ different strategies when approaching such tasks [65,66,67]. Metabolic control, however, does not appear to be the underlying cause, as it does not differ between the sexes in any life stage.
Taken together, it is of the utmost importance to ensure stable and continuous care for patients with PKU into adulthood, while emphasizing the significance of maintaining good metabolic control. Due to the possibility that patients with PKU do not always perceive fluctuations in their Phe levels, regular monitoring is essential [68]. Moreover, it emphasizes the need for tailored therapeutic approaches to optimize and balance both metabolic and neurocognitive outcomes. Further research is necessary to explore the mechanisms underlying the observed EF variability and to assess long-term effects of emerging treatments.
5. Conclusions
It appears that the foundation for cognitive development is established predominantly during childhood (up to 10 years of age), underscoring the critical importance of maintaining good metabolic control during this period. In adulthood, while dietary restrictions may be relaxed, it remains essential both to avoid general extensive fluctuations in Phe concentrations and to prevent the deterioration of metabolic control, as these directly affect performance in specific executive functions on an everyday basis. Further research in this field in an older PKU population should be performed when these patients have reached advanced age to elucidate possible long-term consequences.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/metabo15030197/s1, Table S1: Spearman correlation of metabolic control and executive functions, Table S2: Comparison of patients’ results with the reference median of 50 (ToL and TAP).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.T. and S.B.; methodology, A.T. and S.B.; formal analysis, A.T.; investigation, A.T., A.G.T. and C.R.; resources, S.B. and W.K.; data curation, A.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.T. and S.B.; writing—review and editing, A.G.T., C.R., H.S. and W.K.; visualization, A.T. and S.B.; supervision, S.B. and W.K.; project administration, A.T., A.G.T., C.R., H.S. and S.B.; funding acquisition, A.T. and S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by an unrestricted research grant from Nutricia Metabolics, Danone Deutschland GmbH (through J. Lahl), to S. Beblo through Leipzig University. Open access publishing was supported by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Leipzig University (BGAAF-2097).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of Leipzig University (registration number: 273/21-ek; date of approval 5 July 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all patients involved in the study. No personal information about patients is displayed.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors express their sincere appreciation to all participating patients for their time and effort. Additionally, we would like to acknowledge our gratitude to Nutricia Metabolics, Danone Deutschland GmbH (via J. Lahl), for their support through an unrestricted research grant.
Conflicts of Interest
Anne Tomm has previously received third-party funding from Biomarin for lecture fees. Skadi Beblo has previously received third-party funding from Sanofi, Immedica, Biomarin, Nutricia, Vitaflo, and MetaX for lecture fees. Alena Thiele has previously received third-party funding from Biomarin and Nutricia for lecture fees. Carmen Rohde has previously received third-party funding from Biomarin, Nutricia, MetaX, and Vitaflo for lecture fees. Haiko Schlögl received third party funding for clinical studies, lecture fees, and travel expenses from Biomarin and lecture fees and travel expenses from MetaX. These funding sources bear no substantive relation to the study, and therefore no conflicts of interest exist in connection with its conduction. Wieland Kiess declares no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Muntau, A.C.; Beblo, S.; Koletzko, B. Phenylketonurie und Hyperphenylalaninämie. In Pädiatrie Upgrade 2002; Koletzko, B., Reinhardt, D., Stöckler-Ipsiroglu, S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Scriver, C.R.; Kaufman, S. Hyperphenylalaninemia: Phenylalanine Hydroxylase Deficiency. In The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease; Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., Valle, D., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Health Professions Division: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 1667–1724. ISBN 0-07-913035-6. [Google Scholar]
- Van Wegberg, A.M.J.; MacDonald, A.; Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Blau, N.; Bosch, A.M.; Burlina, A.; Campistol, J.; Feillet, F.; Giżewska, M.; et al. The complete European guidelines on phenylketonuria: Diagnosis and treatment. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, L.I.; Adams, J. The Early History of PKU. Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietz, J.; Dunckelmann, R.; Rupp, A.; Rating, D.; Meinck, H.M.; Schmidt, H.; Bremer, H.J. Neurological outcome in adult patients with early-treated phenylketonuria. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1998, 157, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blau, N.; Thöny, B.; Cotton, R.; Hyland, K. Disorders of Tetrahydrobiopterin and related Biogenic Amines. In The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease; Scriver, C.R., Beaudet, A.L., Sly, W.S., Valle, D., Eds.; McGraw-Hill Health Professions Division: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 1725–1776. ISBN 0-07-913035-6. [Google Scholar]
- Krämer, J.; Baerwald, C.; Heimbold, C.; Kamrath, C.; Parhofer, K.G.; Reichert, A.; Rutsch, F.; Stolz, S.; Weinhold, N.; Muntau, A.C. Two years of pegvaliase in Germany: Exsperiences and best practice recommendations. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2023, 139, 107564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntau, A.C.; Longo, N.; Ezgu, F.; Schwartz, I.V.D.; Lah, M.; Bratkovic, D.; Margvelashvili, L.; Kiykim, E.; Zori, R.; Campistol Plana, J.; et al. Effects of oral sepiapterin on blood Phe concentration in a broad range of patients with phenylketonuria (APHENITY): Results of an international, phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2024, 404, 1333–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgard, P.; Bremer, H.J.; Bührdel, P.; Clemens, P.C.; Mönch, E.; Przyrembel, H.; Trefz, F.K.; Ullrich, K. Rationale for the German recommendations for phenylalanine level control in phenylketonuria 1997. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1999, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christ, S.E.; Abbene, E.E.; Clocksin, H.E.; Wegrzyn, A.K. Motor control and learning in individuals with early-treated phenylketonuria. Neuropsychology 2021, 35, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, R.; Osterloh, J.; Onon, S.; Fromm, J.; Rutsch, F.; Weglage, J. Neurocognitive functioning in adults with phenylketonuria: Report of a 10-year follow-up. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2019, 126, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartus, A.; Palasti, F.; Juhasz, E.; Kiss, E.; Simonova, E.; Sumanszki, C.; Reismann, P. The influence of blood phenylalanine levels on neurocognitive function in adult PKU patients. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palermo, L.; Geberhiwot, T.; MacDonald, A.; Limback, E.; Hall, S.K.; Romani, C. Cognitive outcomes in early-treated adults with phenylketonuria (PKU): A comprehensive picture across domains. Neuropsychology 2017, 31, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoen, M.S.; Boland, K.M.; Christ, S.E.; Cui, X.; Ramakrishnan, U.; Ziegler, T.R.; Alvarez, J.A.; Singh, R.H. Total choline intake and working memory performance in adults with phenylketonuria. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2023, 18, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Zipser, C.M.; Leks, E.; Haas, D.; Gramer, G.; Freisinger, P.; Schaeffer, E.; Liepelt-Scarfone, I.; Brockmann, K.; Maetzler, W.; et al. Phenylalanine Effects on Brain Function in Adult Phenylketonuria. Neurology 2021, 96, e399–e411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, C.; Olson, A.; Aitkenhead, L.; Baker, L.; Patel, D.; van Spronsen, F.; MacDonald, A.; van Wegberg, A.; Huijbregts, S. Meta-analyses of cognitive functions in early-treated adults with phenylketonuria. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2022, 143, 104925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, P.M.; López-Paz, J.F.; García, M.; Amayra, I.; Martínez, O.; Pérez, M.; Rodríguez, A.A.; Pérez-Núñez, P.; Ceberio, I.; Mansilla, N.; et al. Cognitive Functioning in Adults with Phenylketonuria in a Cohort of Spanish Patients. Behav. Neurol. 2023, 2023, 9681740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clocksin, H.E.; Hawks, Z.W.; White, D.A.; Christ, S.E. Inter- and intra-tract analysis of white matter abnormalities in individuals with early-treated phenylketonuria (PKU). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2021, 132, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, P.; Fimm, B. Testbatterie zur Aufmerksamkeitsprüfung (TAP); Psytest: Herzogenrath, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tucha, O.; Lange, K.W. TD-L—Turm von London—Deutsche Version; Hogrefe: Göttingen, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ceglarek, U.; Müller, P.; Stach, B.; Bührdel, P.; Thiery, J.; Kiess, W. Validation of the phenylalanine/tyrosine ratio determined by tandem mass spectrometry: Sensitive newborn screening for phenylketonuria. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2002, 40, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, P.M.; Rochfort, K.D.; O’Connor, B.F. Ion-Exchange Chromatography: Basic Principles and Application. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1485, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimova, N.S.; Steklova, I.V.; Tuuminen, T. Fluorometric method for phenylalanine microplate assay adapted for phenylketonuria screening. Clin. Chem. 1989, 35, 2112–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guthrie, R.; Susi, A. A simple phenylalanine method for detecting phenylketonuria in large populations of newborn infants. Pediatrics 1963, 32, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, C.; Manti, F.; Nardecchia, F.; Valentini, F.; Fallarino, N.; Carducci, C.; de Leo, S.; MacDonald, A.; Palermo, L.; Leuzzi, V. Adult cognitive outcomes in phenylketonuria: Explaining causes of variability beyond average Phe levels. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Bevölkerung ab 15 Jahren in Hauptwohnsitzhaushalten: Deutschland, Jahre, Geschlecht, Altersgruppen, Allgemeine Schulausbildung. Available online: https://www-genesis.destatis.de/datenbank/beta/statistic/12211/table/12211-0100 (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Eckzahlen zum Arbeitsmarkt, Deutschland. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Arbeit/Arbeitsmarkt/Erwerbstaetigkeit/Tabellen/eckwerttabelle.html (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Kernerwerbstätige in Unterschiedlichen Erwerbsformen—Atypische Beschäftigung. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Arbeit/Arbeitsmarkt/Erwerbstaetigkeit/Tabellen/atyp-kernerwerb-erwerbsform-zr.html (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Studierende nach Bundesländern. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Gesellschaft-Umwelt/Bildung-Forschung-Kultur/Hochschulen/Tabellen/studierende-insgesamt-bundeslaender.html (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Zahl der Auszubildenden. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Gesellschaft-Umwelt/Bildung-Forschung-Kultur/Bildungsindikatoren/auszubildende-tabelle.html?nn=621104 (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Bevölkerung nach Familienstand 2011 bis 2023 Deutschland. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Gesellschaft-Umwelt/Bevoelkerung/Bevoelkerungsstand/Tabellen/familienstand-jahre-5.html (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Zusammengefasste Geburtenziffern (je Frau): Deutschland, Jahre, Altersgruppen. Available online: https://www-genesis.destatis.de/datenbank/online/statistic/12612/table/12612-0009 (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Durchschnittliche Kinderanzahl nach Lebensformen in Deutschland (2020). Available online: https://www.bib.bund.de/DE/Fakten/Fakt/L42-Lebensformen-Kinderzahl.html (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Statistisches Bundesamt. Körpermaße nach Altersgruppen und Geschlecht. Available online: https://www.destatis.de/DE/Themen/Gesellschaft-Umwelt/Gesundheit/Gesundheitszustand-Relevantes-Verhalten/Tabellen/liste-koerpermasse.html (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Bundeszentrale für Politische Bildung. Lebensformen und Haushalte. Available online: https://www.bpb.de/kurz-knapp/zahlen-und-fakten/soziale-situation-in-deutschland/61568/lebensformen-und-haushalte/ (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Deutsche Rentenversicherung. Anzahl der Renten Wegen Verminderter Erwerbsfähigkeit in Deutschland in den Jahren von 1992 bis 2023 (in 1.000). Available online: https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/616655/umfrage/anzahl-der-renten-wegen-verminderter-erwerbsfaehigkeit-in-deutschland/#:~:text=Anzahl%20der%20Renten%20wegen%20verminderter%20Erwerbsf%C3%A4higkeit%20in%20Deutschland%20bis%202023&text=Zum%20Ende%20des%20Jahres%202023,auf%20rund%201%2C76%20Millionen (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Wickham, H.; Bryan, J. readxl: Read Excel Files (R package version 1.4.0). 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=readxl (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Wei, T.; Simko, V. R package ‘Corrplot’: Visualizing Correlation Matrices. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=corrplot (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Revelle, W. psych: Procedures for Personality and Psychological Research, (R Package Version 2.2.9); Northwestern University: Evanston, IL, USA, 2024; Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=psych (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Schauberger, P.; Walker, A. openxlsx: Read, Write and Edit Excel Files (R Package Version 4.2.5). 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=openxlsx (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Mangiafico, S.S. rcompanion: Functions to Support Extension Education Programming, (R package version 2.3.2); New Brunswick, NY, USA. 2024. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=rcompanion (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Kassambara, A. rstatix: Pipe-Friendly Framework for Basic Statistical Tests (R Package Version 0.7.0). 2023. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=rstatix (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Hothorn, T.; Hornik, K.; van de Wiel, M.A.; Zeileis, A. A Lego system for conditional inference. Am. Stat. 2006, 60, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bik-Multanowski, M.; Pietrzyk, J.J.; Mozrzymas, R. Routine use of CANTAB system for detection of neuropsychological deficits in patients with PKU. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2011, 102, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Lathan, C.; Vazquez-Agra, N.; Marques-Afonso, A.-T.; Cruces-Sande, A.; Martinez-Olmos, M.-A.; Araujo-Vilar, D.; Hermida-Ameijeiras, A. The role of phenylalanine levels in the neuropsychological and neuroanatomical status of adult patients with phenylketonuria: The impact of fluctuations. J. Investig. Med. 2023, 71, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldmann, R.; Och, U.; Beckmann, L.S.; Weglage, J.; Rutsch, F. Children and Adolescents with Early Treated Phenylketonuria: Cognitive Development and Fluctuations of Blood Phenylalanine Levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2024, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonnesbeck, C.J.; McPheeters, M.L.; Krishnaswami, S.; Lindegren, M.L.; Reimschisel, T. Estimating the probability of IQ impairment from blood phenylalanine for phenylketonuria patients: A hierarchical meta-analysis. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2013, 36, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundermann, B.; Garde, S.; Dehghan Nayyeri, M.; Weglage, J.; Rau, J.; Pfleiderer, B.; Feldmann, R. Approaching altered inhibitory control in phenylketonuria: A functional MRI study with a Go-NoGo task in young female adults. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2020, 52, 3951–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.; Capdevila-Lacasa, C.; Segura, B.; Pané, A.; Montserrat, C.; de Talló Forga-Visa, M.; Moreno, P.J.; Garrabou, G.; Grau-Junyent, J.M.; Junqué, C. Volumetric brain reductions in adult patients with phenylketonuria and their relationship with blood phenylalanine levels. J. Neurodev. Disord. 2024, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, L.; Muri, R.; Wijesinghe, D.; Jann, K.; Maissen-Abgottspon, S.; Radojewski, P.; Pospieszny, K.; Kreis, R.; Kiefer, C.; Hochuli, M.; et al. Cerebral blood flow and white matter alterations in adults with phenylketonuria. Neuroimage Clin. 2024, 41, 103550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Aitkenhead, L.; Stepien, K.M.; Woodall, A.; MacDonald, A.; Romani, C. Cognition and wellbeing in middle-aged early treated people with phenylketonuria: Preliminary results and methodological lessons. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 2024, 41, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomm, A.; Thiele, A.G.; Rohde, C.; Kirmse, S.; Kiess, W.; Beblo, S. Executive functions & metabolic control in phenylketonuria (PKU) and mild hyperphenylalaninemia (mHPA). Mol. Genet. Metab. 2024, 143, 108544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahring, K.; Bélanger-Quintana, A.; Burlina, A.; Giżewska, M.; Maillot, F.; Muntau, A.; Roscher, A.; MacDonald, A. Management of phenylketonuria in European PKU centres remains heterogeneous. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2024, 141, 108120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, E.; Schwarz, M.; Roos, J.; Dragano, N.; Geraedts, M.; Siegrist, J.; Kamp, G.; Wendel, U. Evaluation of quality of life and description of the sociodemographic state in adolescent and young adult patients with phenylketonuria (PKU). Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mütze, U.; Roth, A.; Weigel, J.F.W.; Beblo, S.; Baerwald, C.G.; Bührdel, P.; Kiess, W. Transition of young adults with phenylketonuria from pediatric to adult care. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2011, 34, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mütze, U.; Thiele, A.G.; Baerwald, C.; Ceglarek, U.; Kiess, W.; Beblo, S. Ten years of specialized adult care for phenylketonuria—A single-centre experience. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, A.; Baerwald, C.; Schwarz, M.; Rutsch, F.; Parhofer, K.G.; Plöckinger, U.; Heddrich-Ellerbrok, M.; Vom Dahl, S.; Schöne, K.; Ott, M.; et al. Everyday Life, Dietary Practices, and Health Conditions of Adult PKU Patients: A Multicenter, Cross-Sectional Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 76, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.M.; Goedecke, K.; Meyer, U.; Kanzelmeyer, N.; Koch, S.; Illsinger, S.; Lücke, T.; Hartmann, H.; Lange, K.; Lanfermann, H.; et al. Dietary habits and metabolic control in adolescents and young adults with phenylketonuria: Self-imposed protein restriction may be harmful. JIMD Rep. 2014, 13, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delbreil, P.; Dhondt, S.; Kenaan El Rahbani, R.M.; Banquy, X.; Mitchell, J.J.; Brambilla, D. Current Advances and Material Innovations in the Search for Novel Treatments of Phenylketonuria. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, 13, 2401353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, A.M.; Lima, P.L.; Alves, M.R.A.; Del Soares, R.L.; Kanufre, V.d.C.; Rodrigues, V.d.M.; Starling, A.L.P.; Norton, R.d.C.; de Aguiar, M.J.B. Overweight/obesity in adolescents with phenylketonuria: Protective and predisposing factors. J. Pediatr. 2021, 98, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balci, M.C.; Karaca, M.; Gunes, D.; Korbeyli, H.K.; Selamioglu, A.; Gokcay, G. Evaluation of Body Composition and Biochemical Parameters in Adult Phenylketonuria. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzomo, T.R.; Dias, M.R.M.G.; Pereira, R.M. Adults with early diagnosis of phenylketonuria have higher resting energy expenditure than adults with late diagnosis. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 56, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, A.G.; Gausche, R.; Lindenberg, C.; Beger, C.; Arelin, M.; Rohde, C.; Mütze, U.; Weigel, J.F.; Mohnike, K.; Baerwald, C.; et al. Growth and Final Height Among Children with Phenylketonuria. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20170015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, L.V.; McStravick, N.; Ripley, S.; Weetch, E.; Donald, S.; Adam, S.; Micciche, A.; Boocock, S.; MacDonald, A. Body mass index in adult patients with diet-treated phenylketonuria. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26 (Suppl. S1), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giofrè, D.; Toffalini, E.; Esposito, L.; Cornoldi, C. Sex/gender differences in general cognitive abilities: An investigation using the Leiter-3. Cogn. Process. 2024, 25, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, K.F.; Yip, K.H.; Wong, A.C.-N. Gender differences in multitasking experience and performance. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 2021, 74, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, M.A.; Brewer, N.; Horry, R. Understanding gender bias in face recognition: Effects of divided attention at encoding. Acta Psychol. 2013, 142, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauri, L.; Muri, R.; Everts, R.; Trepp, R. Do early-treated adults with phenylketonuria sense high phenylalanine levels? JIMD Rep. 2024, 65, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).