Targeted Detection of 76 Carnitine Indicators Combined with a Machine Learning Algorithm Based on HPLC-MS/MS in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Blood Preparation
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. HPLC-MS/MS Materials and Equipment
2.5. HPLC-MS/MS Sample Pretreatment
2.6. Mass Spectrum Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
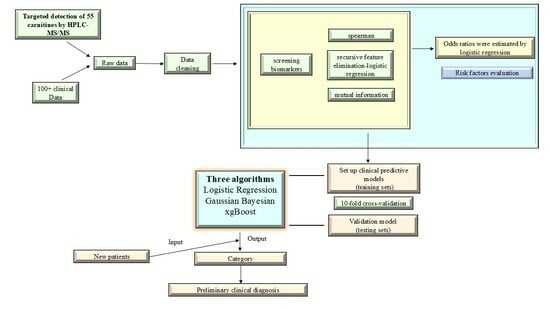
2.8. Establishment of the Diagnostic Models
2.9. SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) Interpretation
3. Results
3.1. Study Participants
3.2. Distribution and Metabolic Pathway of Each Measurement Index
3.3. Metabolic Pathways
3.4. Performance Evaluation of Candidate Indicators for Models Based on Classification Algorithms
3.5. The Role of Carnitine and Its Ratio in RA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tai, W.Y.; Chen, T.L.; Wang, H.M.; Fu, L.M. Rapid Microfluidic Biosensor for Point-of-Care Determination of Rheumatoid Arthritis via Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide Antibody Detection. Biosensors 2024, 14, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Metabolic checkpoints in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2024, 70, 152586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Rasool, M. Genetics, epigenetics and autoimmunity constitute a Bermuda triangle for the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Life Sci. 2024, 357, 123075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, I.; Castellanos-Moreira, R.; Sanmartí, R.; Gómara, M.J. Anti-Modified Peptide Antibodies (AMPAs) in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Study of the Diagnostic Value of Citrullinated, Homocitrullinated, and Acetylated Fibrin/Filaggrin Chimeric Peptides. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichenberger, F.; Popp, F.; Hoffmann, M.; Fischinger, C.; von Wulffen, W.; Kneidinger, N.; Welcker, M. Proposal of a radiation-free screening protocol for early detection of interstitial lung involvement in seropositive and ACPA-positive rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Yang, P.; Hu, J.; Cai, D.; Hu, B.; Rui, G.; Lin, Z. Causal association between plasma metabolites and diverse autoimmune diseases: A two-sample bidirectional mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1437688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, N.; Qiu, D.; Huang, H.; Luo, J.; Xu, A.; Xu, L.; Yu, Z.; et al. Leflunomide-Induced Weight Loss: Involvement of DAHPS Activity and Synthesis of Aromatic Amino Acids. Metabolites 2024, 14, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ren, S.; Cao, Q.; Kong, H.; Xu, Q.; Liu, R. High-fat diet stimulated butyric acid metabolism dysbiosis, altered microbiota, and aggravated inflammatory response in collagen-induced arthritis rats. Nutr. Metab. 2024, 21, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shi, T.; Wen, C.; Xu, J.; Jiao, Y.; Diao, W.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; et al. Cannabidiol regulates L-carnitine and butyric acid metabolism by modulating the gut microbiota to ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 136, 156270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, M.; Zuo, E.; Wu, X.; Wu, L.; Liu, H.; Zhou, X.; Du, Y.; Lv, X.; Chen, C. Diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus using cross-modal specific transfer fusion technology based on infrared spectra and metabolomics. Anal. Chim. Acta 2024, 1330, 343302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Fan, G.; Xie, X.; Fu, X.; Su, J. Abelmoschus manihot (L.) medik. seeds alleviate rheumatoid arthritis by modulating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 325, 117641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takao, M.; Nishii, T.; Sakai, T.; Sugano, N. Postoperative Limb-Offset Discrepancy Notably Affects Soft-Tissue Tension in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. Vol. 2016, 98, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yao, J.; Zhao, H. Biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1455346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.Y.; Yang, H.Y.; Luo, S.F.; Lai, J.H. From Rheumatoid Factor to Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies and Anti-Carbamylated Protein Antibodies for Diagnosis and Prognosis Prediction in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, G.; Toes, R.E.M. Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis—Rheumatoid factor, anticitrullinated protein antibodies and beyond. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2024, 36, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, H. Identification of immune-related genes in diagnosing atherosclerosis with rheumatoid arthritis through bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1126647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cui, J.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.B.; Wang, Q. Machine learning and molecular subtype analyses provide insights into PANoptosis-associated genes in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.M.; Gu, W.J.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Lu, L.; Ke, M.Y.; Lu, J.W.; Chen, W.J.; Lan, Z.Z.; Xiao, Y.L.; et al. Serum metabolomic and lipidomic profiling identifies diagnostic biomarkers for seropositive and seronegative rheumatoid arthritis patients. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlik, A.; Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Safranow, K.; Dziedziejko, V.; Dutkiewicz, G.; Slucznowska-Glabowska, S.; Juzyszyn, Z.; Drozdzik, M. SLC22A5 polymorphism associated with risk of extra-articular manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Reumatologia 2019, 57, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Yang, Y.; Lu, H.; Shi, H.; Jiang, L.; Liao, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. Network pharmacology combines machine learning, molecular simulation dynamics and experimental validation to explore the mechanism of acetylbinankadsurin A in the treatment of liver fibrosis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 323, 117682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; Mcshane, D.J.; Fries, J.F.; Cooper, N.S.; Healey, L.A.; Kaplan, S.R.; Liang, M.H.; Luthra, H.S.; et al. The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. J. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; An, G.S.; Li, R.Q.; Hou, Z.J.; Li, J.; Jin, Q.Q.; Du, Q.X.; Sun, J.H. Novel Strategy for Human Deep Vein Thrombosis Diagnosis Based on Metabolomics and Stacking Machine Learning. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 14560–14570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Lu, Y.; Ashrafi, N.; Domingo, I.; Alaei, K.; Pishgar, M. Prediction of sepsis mortality in ICU patients using machine learning methods. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2024, 24, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.R.; Castro, D.C.; Bell, S.E.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Sweedler, J. Single-Cell Classification Using Mass Spectrometry through Interpretable Machine Learning. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9338–9347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tideman, L.E.M.; Migas, L.G.; Djambazova, K.; Patterson, N.H.; Caprioli, R.M.; Spraggins, J.M.; Van de Plas, R. Automated biomarker candidate discovery in imaging mass spectrometry data through spatially localized Shapley additive explanations. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1177, 338522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.I. Explaining a series of models by propagating Shapley values. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.X.; Pi, Z.P.; Kong, K.Y.; Qiao, H.; Jin, M.H.; Chang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.W.; Li, H.W. Analyzing the impact of heavy metal exposure on osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: An approach based on interpretable machine learning. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1422617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.L.; Liu, X.M.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S. Machine learning-based prediction model integrating ultrasound scores and clinical features for the progression to rheumatoid arthritis in patients with undifferentiated arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2025, 44, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yu, Q.; Ma, X.; Lv, D.; Wang, H.; Qiu, W.; Chen, X.F.; Jiao, Y.; Liu, Y. A metabolomics approach reveals metabolic disturbance of human cholangiocarcinoma cells after parthenolide treatment. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 328, 118075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, K.; Lie, S.A.; Bjørndal, B.; Berge, R.K.; Svardal, A.; Brun, J.G.; Bolstad, A.I. Lipid, fatty acid, carnitine- and choline derivative profiles in rheumatoid arthritis outpatients with different degrees of periodontal inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, D.; Kumar, S.; Rawat, A.; Guleria, A.; Kumari, R.; Ahmed, S.; Singh, R.; Misra, R.; Kumar, D. NMR-Based Metabolomics Revealed the Underlying Inflammatory Pathology in Reactive Arthritis Synovial Joints. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 5088–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Guo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ji, W.; Lin, L.; Qian, W.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Lv, X.; Ke, M.; et al. Untargeted lipidomics reveals specific lipid abnormalities in Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2021, 60, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowiec, I.; Ärlestig, L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Trygg, J. Metabolite and Lipid Profiling of Biobank Plasma Samples Collected Prior to Onset of Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D.; McInnes, I.B. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2016, 388, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, T.; Zhang, Y.; Vasileiadis, G.; Rawshani, A.; Van Vollenhoven, R.; Lampa, J.; Gudbjornsson, B.; Haavardsholm, E.; Nordstrom, D.; Grndal, G.; et al. Biomarkers for Disease Activity and Response to Treatment in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: Metabolomics and Machine Learning Analyses in NORD-STAR Cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024, 76, 978–981. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, S.H.; Cui, J.; Sparks, J.A.; Lu, B.; Tedeschi, S.K.; Speyer, C.B.; Moss, L.; Feser, M.L.; Kelmenson, L.B.; Mewshaw, E.A.; et al. Circulating plasma metabolites and risk of rheumatoid arthritis in the Nurses’ Health Study. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3369–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwan, S.M.; Alqulaly, M.; Elsaeed, M.Y.; Elshora, S.Z.; Atwa, A.H.; Wasfey, E.F. L-carnitine reverses methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in experimental rat model: Insight on SIRT1/PGC-1α/Nrf2/HO-1 axis. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2023, 43, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, D.; Wei, L.; Chen, Z.; Yang, B. L-carnitine promotes liver regeneration after hepatectomy by enhancing lipid metabolism. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoen, V.; Vander Stichele, R.; Campens, L.; De Bacquer, D.; Van Bortel, L.; de Backer, T.L. Propionyl-L-carnitine for intermittent claudication. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 12, Cd010117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virmani, M.A.; Cirulli, M. The Role of l-Carnitine in Mitochondria, Prevention of Metabolic Inflexibility and Disease Initiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirrafiei, A.; Jayedi, A.; Shab-Bidar, S. The Effects of L-Carnitine Supplementation on Weight Loss, Glycemic Control, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Dose-response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Ther. 2024, 46, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Pan, D.; Liu, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, S. L-Carnitine in the Treatment of Psychiatric and Neurological Manifestations: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, T.; Hirayama, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Miyazawa, K.; Tamai, I. Mechanism of the regulation of organic cation/carnitine transporter 1 (SLC22A4) by rheumatoid arthritis-associated transcriptional factor RUNX1 and inflammatory cytokines. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katturajan, R.; Prince, S.E. L-carnitine and Zinc supplementation impedes intestinal damage in methotrexate-treated adjuvant-induced arthritis rats: Reinstating enterocyte proliferation and trace elements. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 78, 127188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savvateeva, E.; Smoldovskaya, O.; Feyzkhanova, G.; Rubina, A. Multiple biomarker approach for the diagnosis and therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2021, 58, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Long, W.; Zhang, J.; Jian, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; et al. Integrated multi-omics revealed that dysregulated lipid metabolism played an important role in RA patients with metabolic diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2024, 26, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

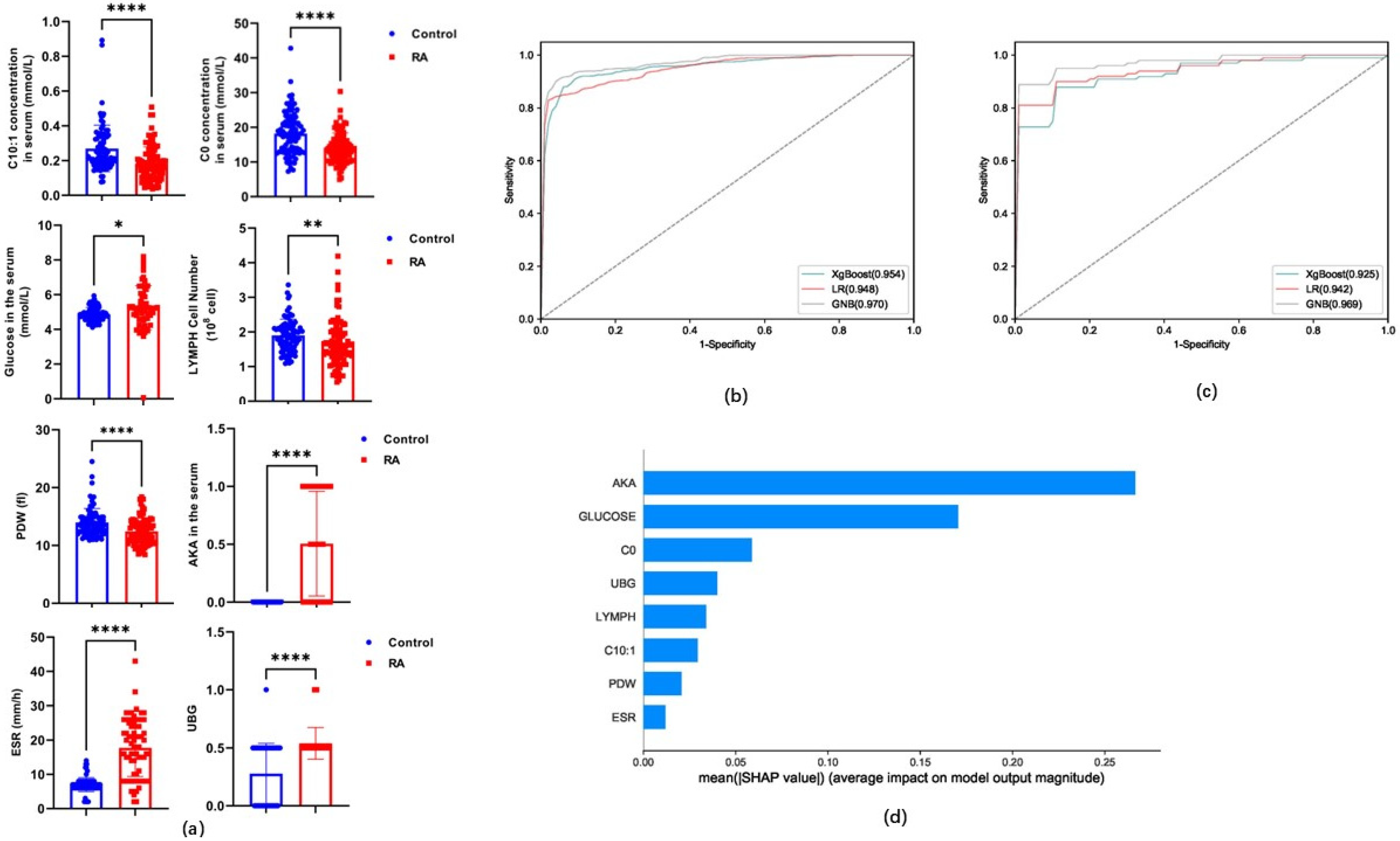
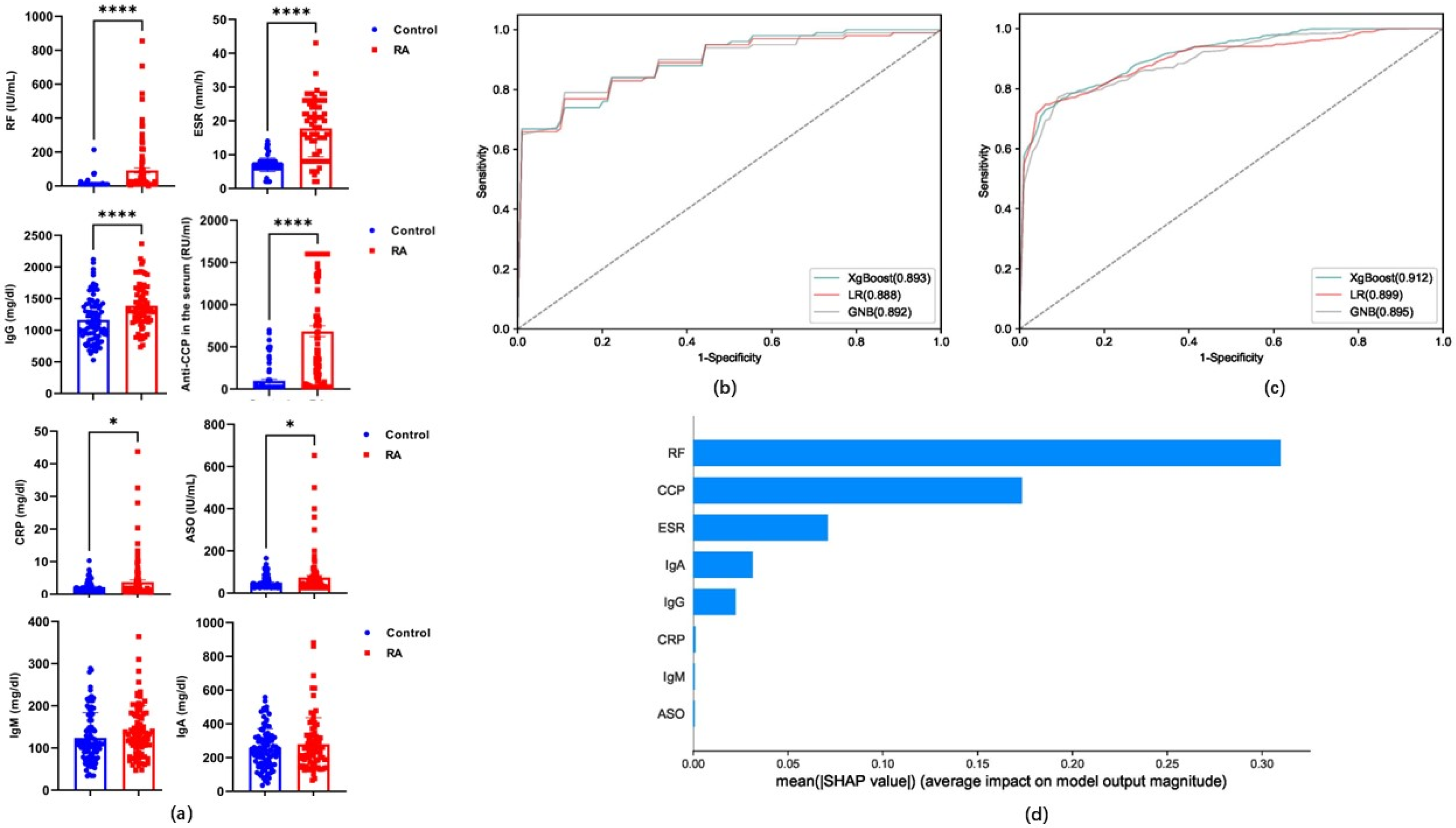
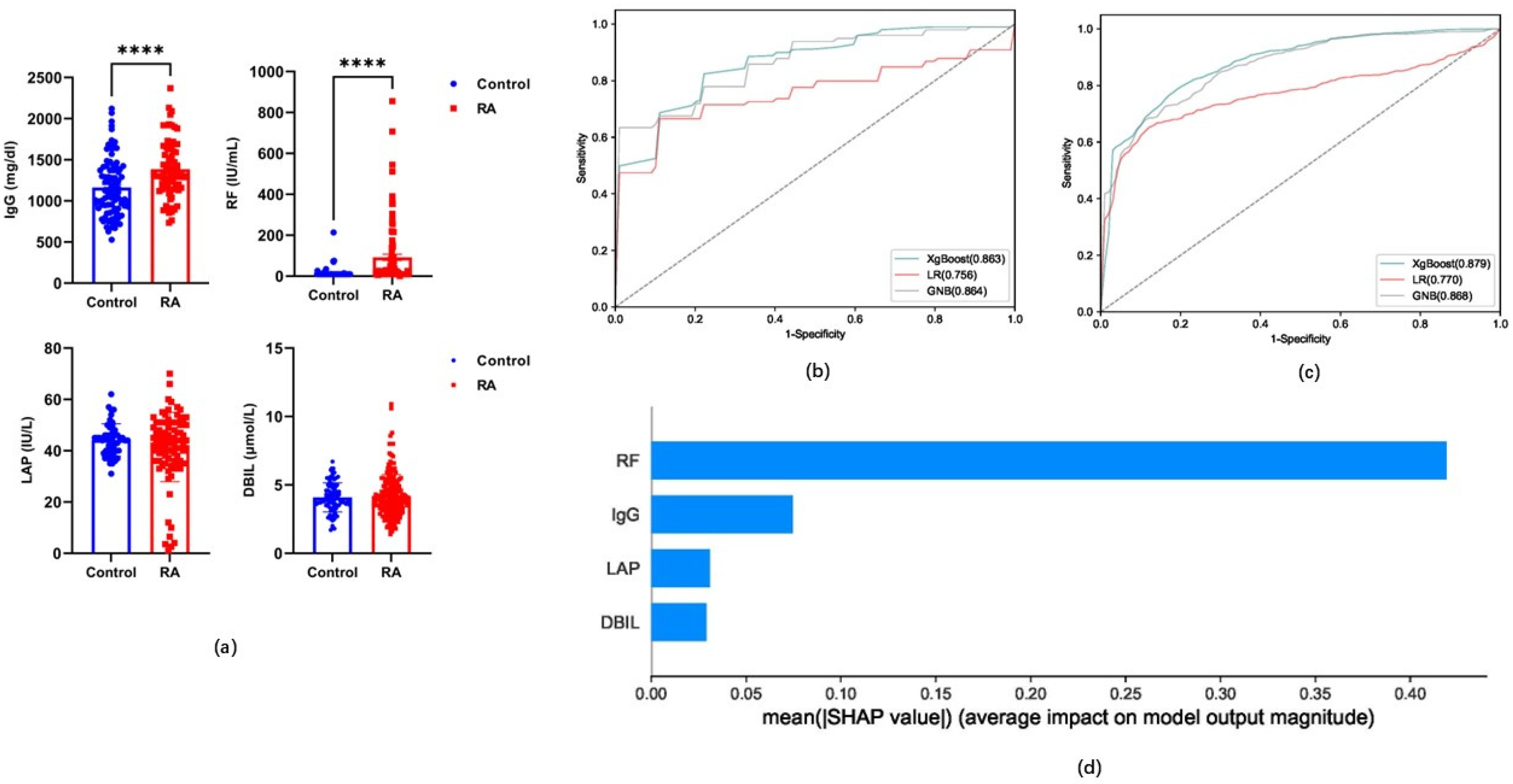

| Algorithms | Sensitivity | Specificity | Accuracy | PPV | NPV | MCC | AUC | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V8 | xgBoost | Training set | 88.10% | 92.99% | 90.46% | 93.14% | 87.95% | 81.09% | 0.954 (0.924–0.984) |
| Test set | 82.89% | 89.22% | 85.87% | 90.14% | 83.92% | 73.06% | 0.925 (0.886–0.964) | ||
| LR | Training set | 84.63% | 95.29% | 89.76% | 95.09% | 85.21% | 80.11% | 0.948 (0.916–0.98) | |
| Test set | 84.00% | 93.33% | 88.47% | 93.96% | 85.28% | 78.27% | 0.942 (0.908–0.976) | ||
| GNB | Training set | 79.46% | 99.64% | 89.18% | 99.59% | 81.87% | 80.27% | 0.970 (0.946–0.994) | |
| Test set | 78.89% | 98.89% | 88.50% | 99.09% | 82.36% | 79.57% | 0.969 (0.944–0.994) | ||
| VR8 | xgBoost | Training set | 79.01% | 85.14% | 81.97% | 85.18% | 79.05% | 64.19% | 0.912 (0.87–0.954) |
| Test set | 75.89% | 82.67% | 79.08% | 82.58% | 76.88% | 59.00% | 0.912 (0.87–0.954) | ||
| LR | Training set | 77.55% | 86.84% | 82.02% | 86.40% | 78.27% | 64.53% | 0.899 (0.854–0.944) | |
| Test set | 76.00% | 82.89% | 79.00% | 84.21% | 77.46% | 60.23% | 0.888 (0.841–0.935) | ||
| GNB | Training set | 72.73% | 92.63% | 82.31% | 91.39% | 75.95% | 66.34% | 0.895 (0.849–0.941) | |
| Test set | 73.89% | 92.33% | 82.66% | 91.67% | 77.11% | 67.45% | 0.892 (0.845–0.939) | ||
| V4 | XgBoost | Training set | 78.01% | 77.89% | 77.95% | 80.51% | 77.89% | 57.13% | 0.879 (0.83–0.928) |
| Test set | 75.78% | 68.67% | 72.32% | 73.87% | 75.64% | 46.86% | 0.863 (0.811–0.915) | ||
| LR | Training set | 56.90% | 93.12% | 74.34% | 90.15% | 66.74% | 53.34% | 0.770 (0.704–0.836) | |
| Test set | 55.56% | 93.44% | 73.76% | 89.83% | 66.66% | 52.55% | 0.756 (0.688–0.824) | ||
| GNB | Training set | 57.24% | 93.36% | 74.64% | 90.29% | 67.01% | 53.84% | 0.868 (0.817–0.919) | |
| Test set | 57.56% | 91.44% | 73.82% | 88.36% | 66.85% | 51.98% | 0.864 (0.812–0.916) | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhai, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, L.; Hao, X.; Yang, L.; Xing, R.; Hu, J.; Gao, J.; et al. Targeted Detection of 76 Carnitine Indicators Combined with a Machine Learning Algorithm Based on HPLC-MS/MS in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Metabolites 2025, 15, 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030205
Zhang R, Wang J, Zhai X, Guo Y, Zhou L, Hao X, Yang L, Xing R, Hu J, Gao J, et al. Targeted Detection of 76 Carnitine Indicators Combined with a Machine Learning Algorithm Based on HPLC-MS/MS in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Metabolites. 2025; 15(3):205. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030205
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Rui, Juan Wang, Xiaonan Zhai, Yuanbing Guo, Lei Zhou, Xiaoyan Hao, Liu Yang, Ruiqing Xing, Juanjuan Hu, Jiawei Gao, and et al. 2025. "Targeted Detection of 76 Carnitine Indicators Combined with a Machine Learning Algorithm Based on HPLC-MS/MS in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis" Metabolites 15, no. 3: 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030205
APA StyleZhang, R., Wang, J., Zhai, X., Guo, Y., Zhou, L., Hao, X., Yang, L., Xing, R., Hu, J., Gao, J., Wang, F., Yang, J., & Liu, J. (2025). Targeted Detection of 76 Carnitine Indicators Combined with a Machine Learning Algorithm Based on HPLC-MS/MS in the Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Metabolites, 15(3), 205. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15030205