Metabolome Profiling and Predictive Modeling of Dark Green Leaf Trait in Bunching Onion Varieties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Optical Property Measurements
2.3. Powdering of Samples
2.4. Pigment Compound Measurement
2.5. Metabolome Analysis
2.6. Statistical Methods
2.7. Classification of Green Color Patterns Using Metabolomics
3. Results
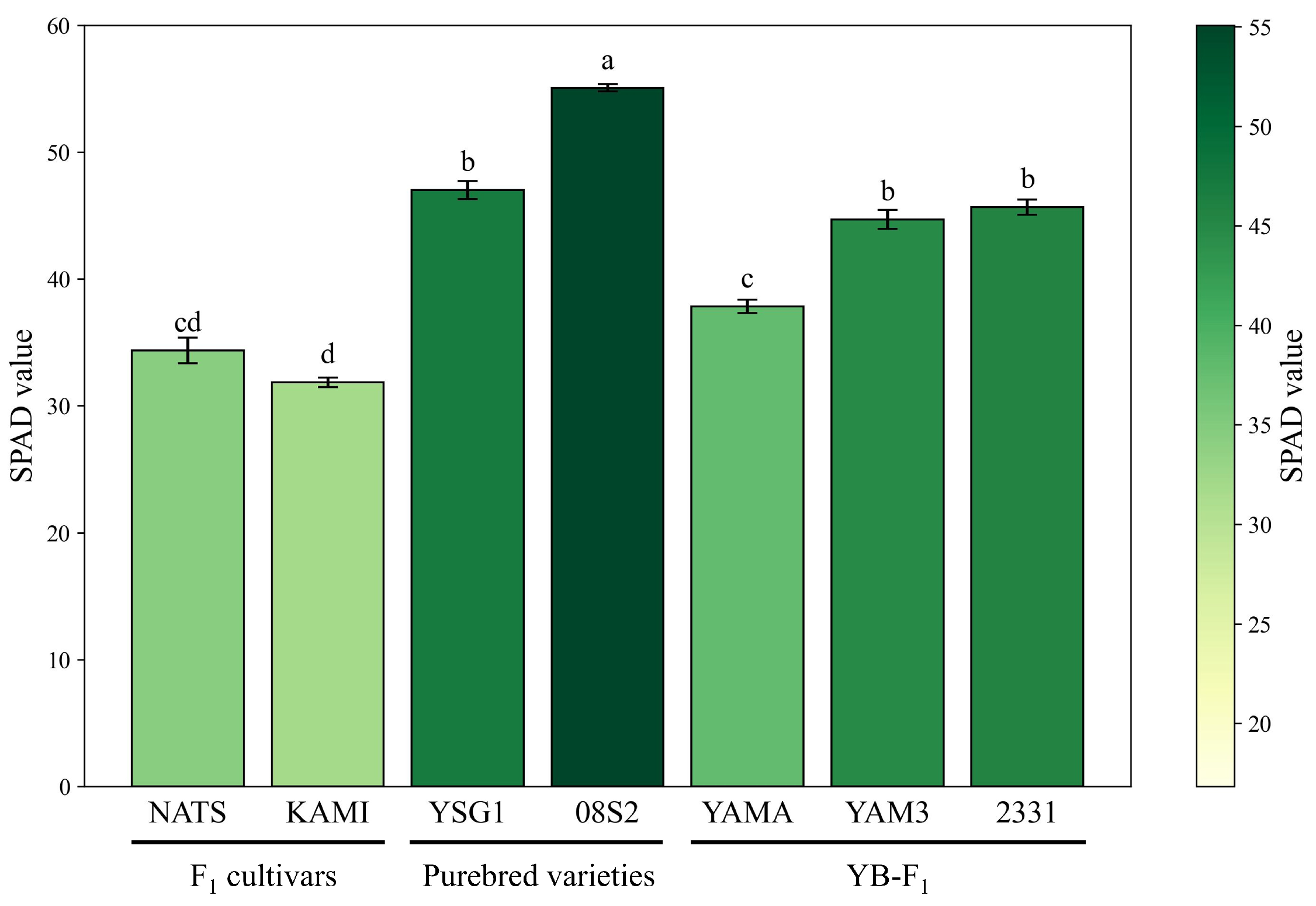
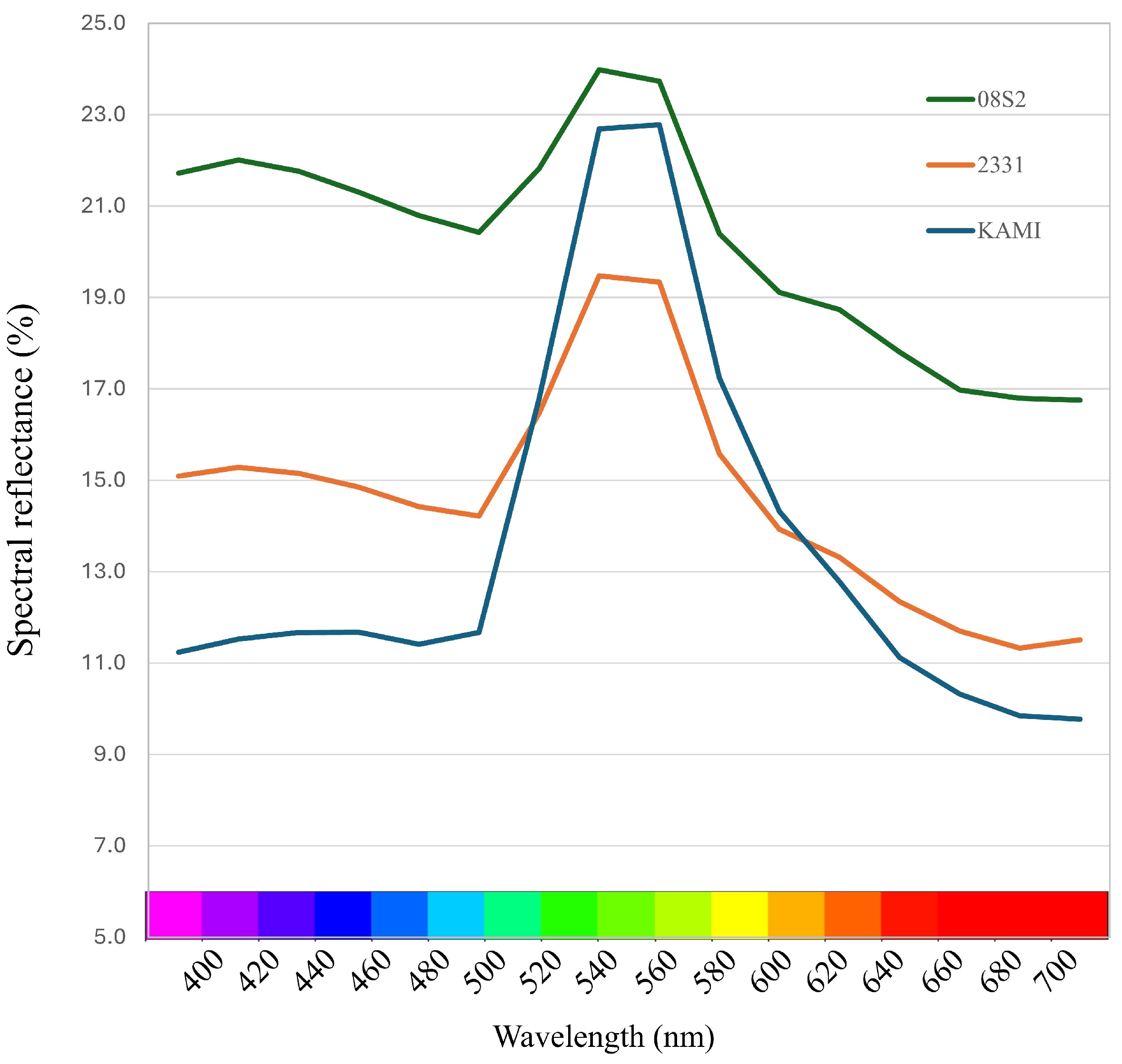
3.1. Optical Property Measurements
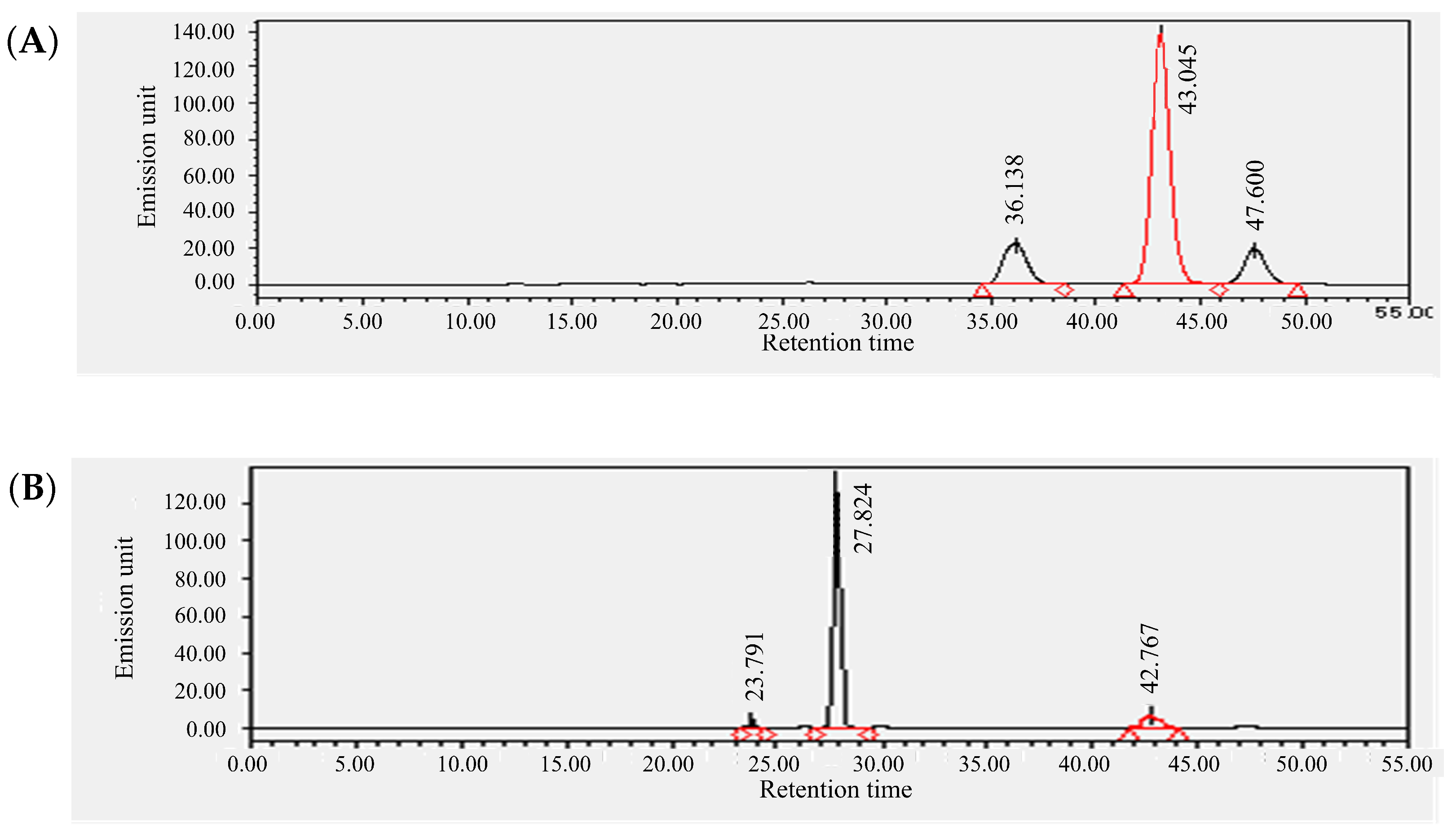
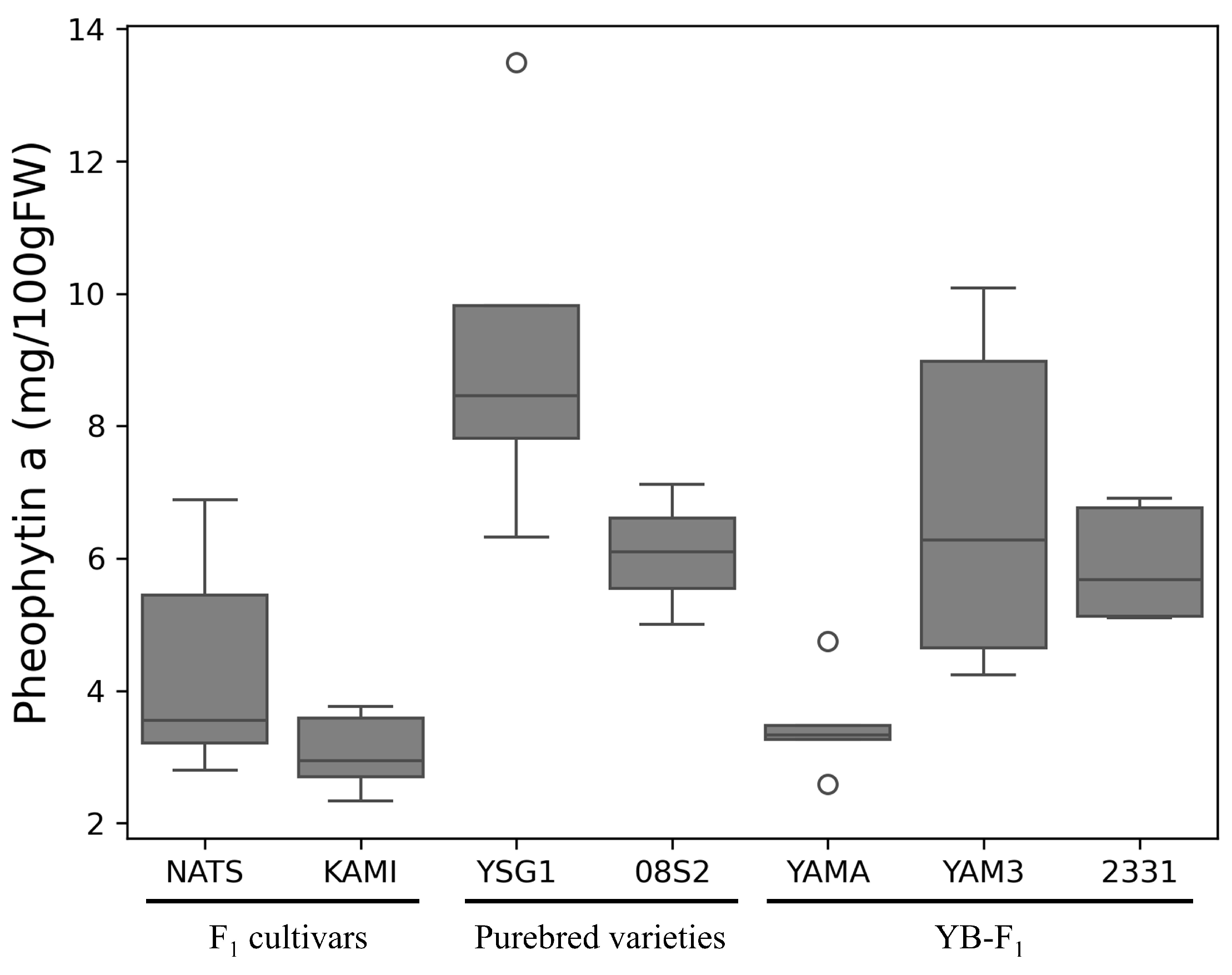
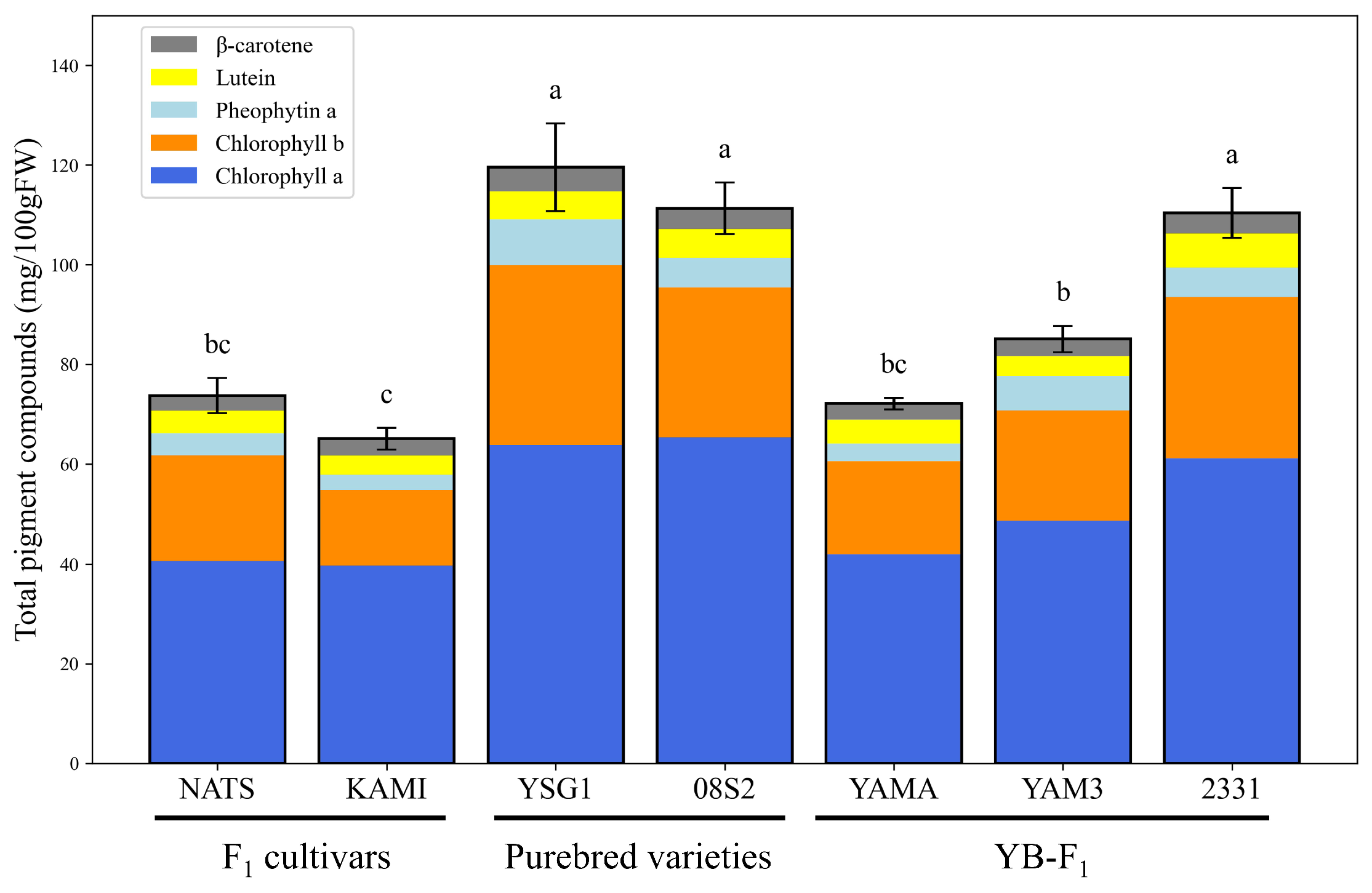
3.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Determination of Pheophytin a and Pigment Compounds
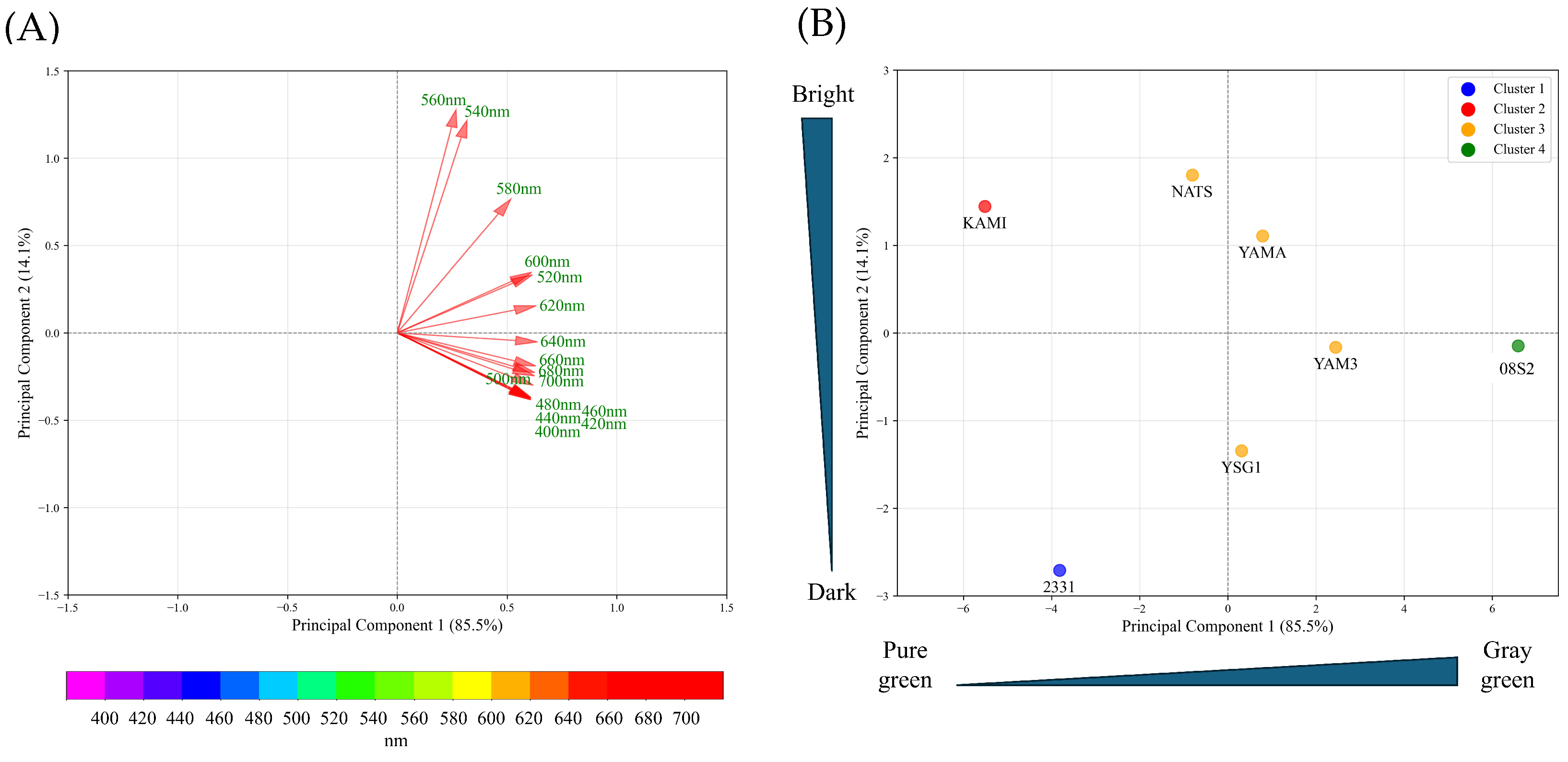
3.3. PCA Analysis Using Spectral Reflectance of Each Variety and Line
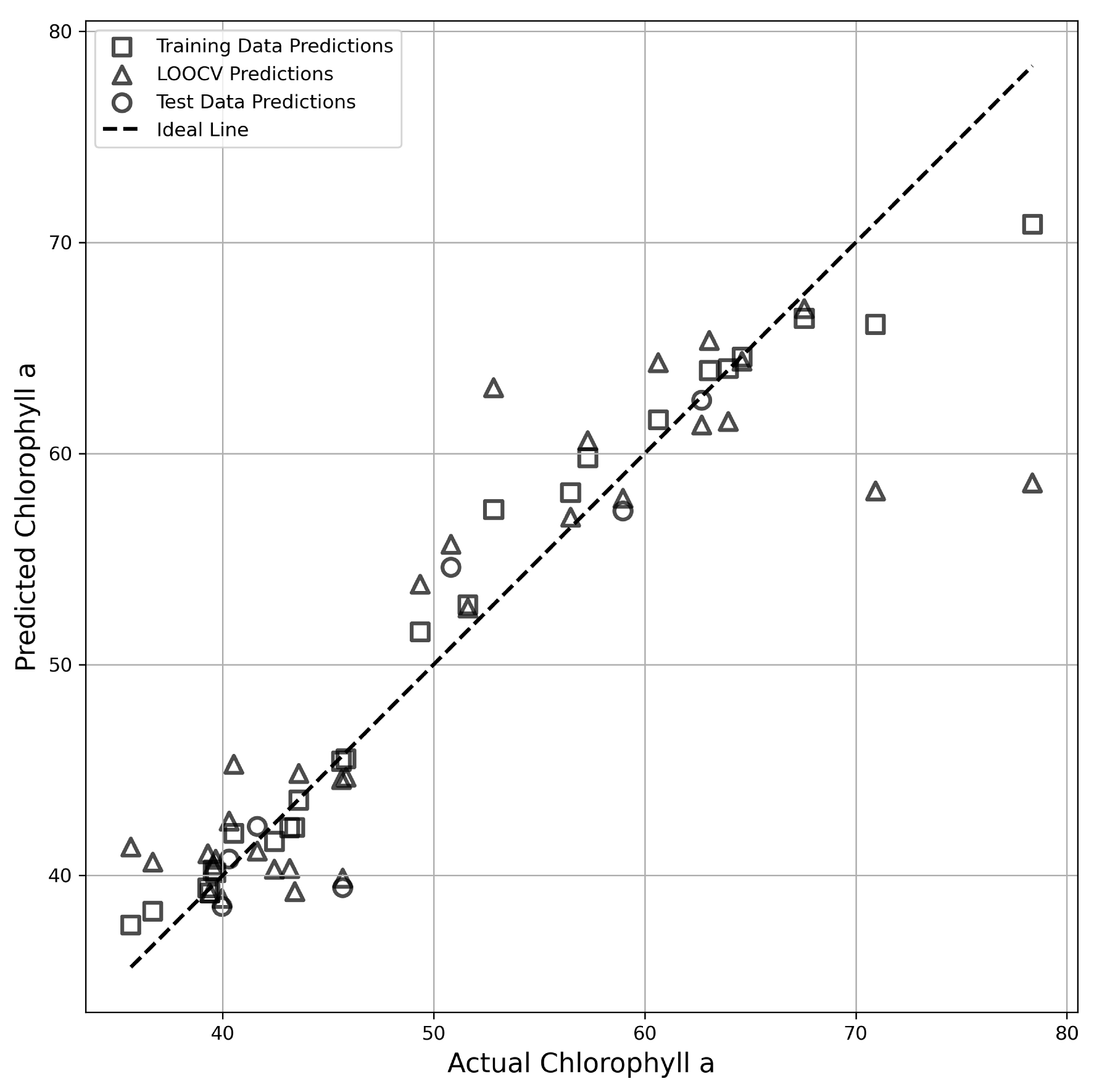
3.4. Development of Prediction Models for Pigment Compounds Using Spectral Reflectance
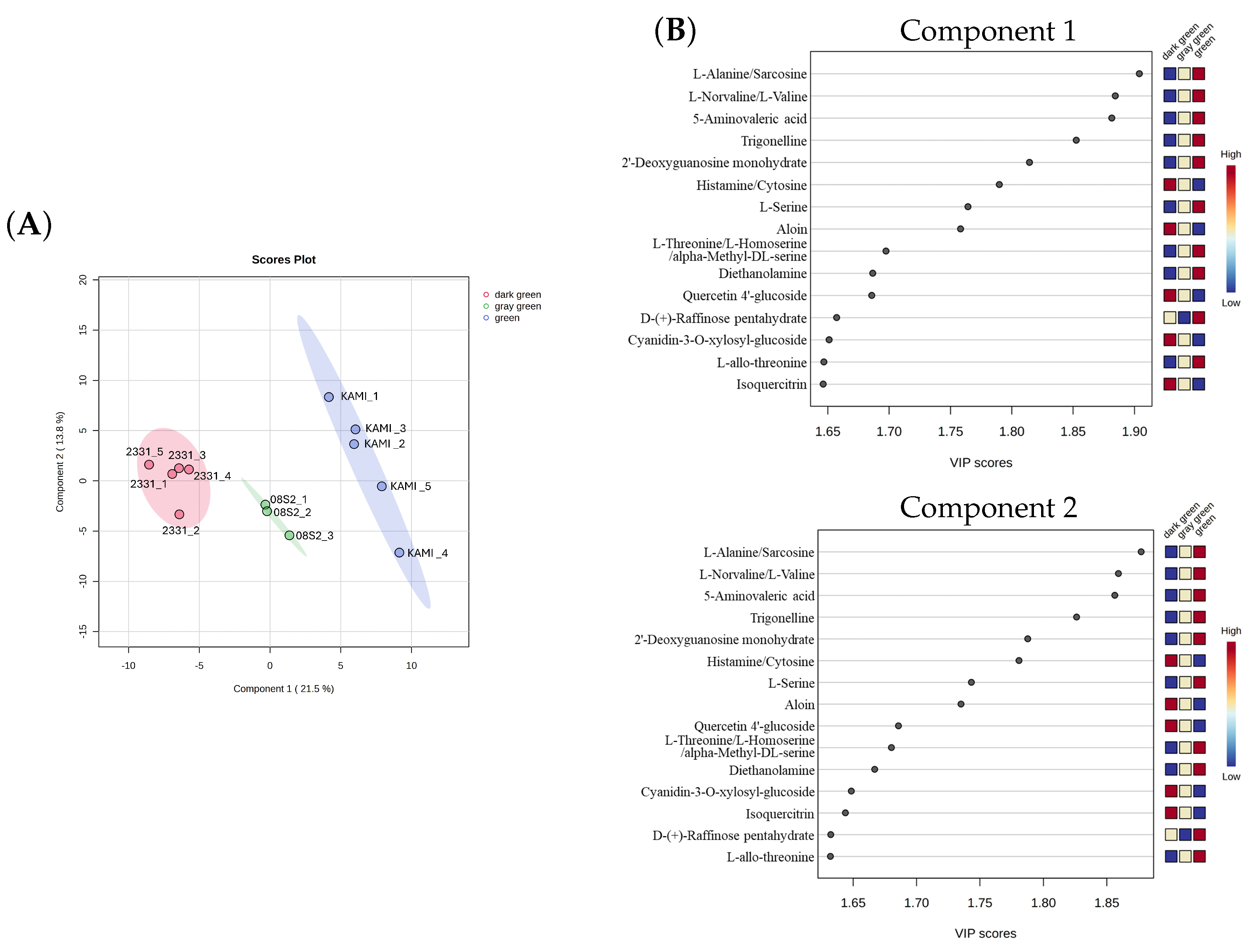
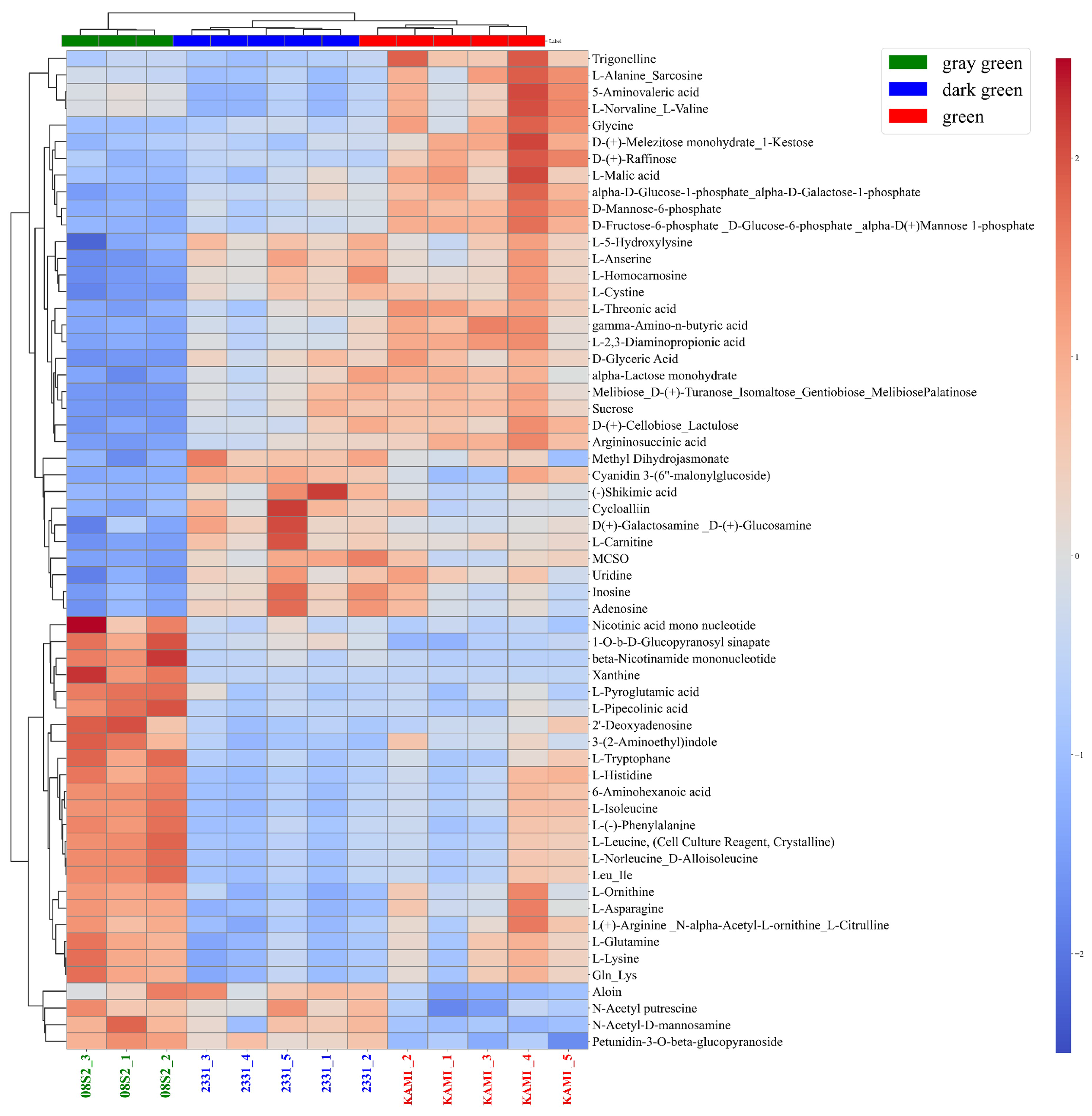
3.5. Metabolomic Analysis of Three Green Color Patterns
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of SPAD Values and Pigment Composition in Dark Green Varieties and Lines
4.2. Classification of Dark Green Varieties and Lines Using Spectral Reflectance
4.3. Metabolic Profiles of the Three Green Color Groups
4.4. Construction of Prediction Models for Pigment Compounds Using Machine Learning
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamasaki, A.; Alliums, E. Botany, Production and Uses; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2022; p. 111. [Google Scholar]
- Kayat, F.; Mohammed, A.; Ibrahim, A. Spring Onion (Allium fistulosum L.) breeding strategies. In Advances in Plant Breeding Strategies: Vegetable Crops; Al-Khayri, J.M., Jain, S.M., Johnson, D.V., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 135–182. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.; Han, J.; Seo, Y.; Kang, B.H.; Lee, J.; Ochar, K. Green Onion (Allium fistulosum): An Aromatic Vegetable Crop Esteemed for Food, Nutritional and Therapeutic Significance. Foods 2023, 12, 4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Ramakrishna, Y. Welsh onion (Allium fistulosum L.): A promising spicing-culinary herb of Mizoram. Indian J. Hill Farming 2017, 30, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Wako, T.; Yamashita, K.i.; Tsukazaki, H.; Ohara, T.; Kojima, A.; Yaguchi, S.; Shimazaki, S.; Midorikawa, N.; Sakai, T.; Yamauchi, N. Screening and incorporation of rust resistance from Allium cepa into bunching onion (Allium fistulosum) via alien chromosome addition. Genome 2015, 58, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padula, G.; Xia, X.; Hołubowicz, R. Welsh Onion (Allium fistulosum L.) Seed Physiology, Breeding, Production and Trade. Plants 2022, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.X.; Li, R.J.; Wang, M.; Huang, L.J.; Khan, A.; Ali, M.; Gong, Z.H. Variation in leaf color and combine effect of pigments on physiology and resistance to whitefly of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Sci. Hortic. 2018, 229, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kołota, E.; Adamczewska-Sowińska, K.; Uklańska-Pusz, C. Yield and nutritional value of Japanese bunching onion (Allium fistulosum L.) depending on the growing season and plant maturation stage. J. Elem. 2012, 17, 587–596. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhou, R.; Xu, K.; Xu, J.; Jin, J.; Fang, H.; He, Y. Rapid Determination of Chlorophyll and Pheophytin in Green Tea Using Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. Molecules 2018, 23, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Sun, D.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Guo, T. Expression of flavonoid biosynthesis genes and accumulation of flavonoid in wheat leaves in response to drought stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 80, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenes-Balbuena, M.; Garcia-Garcia, P.; Garrido-Fernandez, A. Phenolic compounds related to the black color formed during the processing of ripe olives. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuntaş, C.; Demiralay, M.; Muslu, A.S.; Terzi, R. Proline-stimulated signaling primarily targets the chlorophyll degradation pathway and photosynthesis associated processes to cope with short-term water deficit in maize. Photosynth. Res. 2020, 144, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, W.; Wang, G.; Dou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Q.; He, Y.; Tang, Z.; Yu, J. Protective mechanisms of exogenous melatonin on chlorophyll metabolism and photosynthesis in tomato seedlings under heat stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 16, 1519950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Abdallat, A.; Al-Debei, H.; Ayad, J.; Hasan, S. Over-Expression of SlSHN1 Gene Improves Drought Tolerance by Increasing Cuticular Wax Accumulation in Tomato. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19499–19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Hirata, S.; Sawada, Y.; Hirai, M.; Sato, S.; Hirakawa, H.; Mine, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Shigyo, M. Widely targeted metabolome and transcriptome landscapes of Allium fistulosum–A. cepa chromosome addition lines revealed a flavonoid hot spot on chromosome 5A. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, F.; Noceda, C.; Maridueña-Zavala, M.; Cevallos-Cevallos, J. Metabolomics, a Powerful Tool for Understanding Plant Abiotic Stress. Agronomy 2021, 11, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulaev, V.; Cortes, D.; Miller, G.; Mittler, R. Metabolomics for plant stress response. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saviano, G.; Paris, D.; Melck, D.; Fantasma, F.; Motta, A.; Iorizzi, M. Metabolite variation in three edible Italian Allium cepa L. by NMR-based metabolomics: A comparative study in fresh and stored bulbs. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farag, M.; Ali, S.; Hodaya, R.; El-Seedi, H.; Sultani, H.; Laub, A.; Eissa, T.; Abou-Zaid, F.; Wessjohann, L. Phytochemical Profiles and Antimicrobial Activities of Allium cepa Red cv. and A. sativum Subjected to Different Drying Methods: A Comparative MS-Based Metabolomics. Molecules 2017, 22, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Melchor, D.; Zapata-Sarmiento, D.; Becerra-Martínez, E.; Rodríguez-Monroy, M.; Vallejo, L.; Sepúlveda-Jiménez, G. Changes in the metabolomic profiling of Allium cepa L. (onion) plants infected with Stemphylium vesicarium. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2022, 162, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Angel, Y.; Houborg, R.; Ali, S.; McCabe, M. A Random Forest Machine Learning Approach for the Retrieval of Leaf Chlorophyll Content in Wheat. Remote. Sens. 2019, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, G.; Bansod, B.; Mathew, L.; Goswami, J.; Choudhury, B.; Raju, P. Chlorophyll estimation using multi-spectral unmanned aerial system based on machine learning techniques. Remote. Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2019, 15, 100235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Jang, S.; Park, J.; Song, H.; Ryu, C.; Jun, S.; Kim, S. Yield prediction and validation of onion (Allium cepa L.) using key variables in narrowband hyperspectral imagery and effective accumulated temperature. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcone, A.; Impollonia, G.; Croci, M.; Blandinières, H.; Pellegrini, N.; Amaducci, S. Garlic yield monitoring using vegetation indices and texture features derived from UAV multispectral imagery. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 8, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, J.; Osterman, J.; Mitchell, J. Calibration of the Minolta SPAD-502 leaf chlorophyll meter. Photosynth. Res. 1995, 46, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, P.; Yamauchi, N.; Shigyo, M. Chlorophyll degradation and resulting catabolite formation in stored Japanese bunching onion (Allium fistulosum L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2008, 88, 1981–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almela, L.; Fernández-López, J.; Roca, M. High-performance liquid chromatographic screening of chlorophyll derivatives produced during fruit storage. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 870, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, Y.; Tsukaya, H.; Li, Y.; Sato, M.; Kawade, K.; Hirai, M. A novel method for single-grain-based metabolic profiling of Arabidopsis seed. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sawada, Y.; Akiyama, K.; Sakata, A.; Kuwahara, A.; Otsuki, H.; Sakurai, T.; Saito, K.; Hirai, M. Widely targeted metabolomics based on large-scale MS/MS data for elucidating metabolite accumulation patterns in plants. Plant Cell Physiol. 2009, 50, 37–47. [Google Scholar]
- Uchida, K.; Sawada, Y.; Ochiai, K.; Sato, M.; Inaba, J.; Hirai, M. Identification of a Unique Type of Isoflavone O-Methyltransferase, GmIOMT1, Based on Multi-Omics Analysis of Soybean under Biotic Stress. Plant Cell Physiol. 2020, 61, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, S.; Oszmiański, J.; Wiśniewski, R. Determination of triterpenoids, carotenoids, chlorophylls, and antioxidant capacity in Allium ursinum L. at different times of harvesting and anatomical parts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, R.; Wang, K.; Kong, Y.; Lv, Y.; Cao, B.; Gao, S.; Xu, K.; Chen, Z.; Xu, K. Physiological Mechanism of Welsh Onion (Allium fistulosum L.) in Response to High Temperature and Waterlogging Stress. Agronomy 2025, 15, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süß, A.; Danner, M.; Obster, C.; Locherer, M.; Hank, T.; Richter, K.; Consortium, E. Measuring Leaf Chlorophyll Content with the Konica Minolta SPAD-502Plus. 2015. Available online: https://gfzpublic.gfz-potsdam.de/rest/items/item_1388302/component/file_1388303/content (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Madeira, A.; Ferreira, A.; de Varennes, A.; Vieira, M. SPAD Meter Versus Tristimulus Colorimeter to Estimate Chlorophyll Content and Leaf Color in Sweet Pepper. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2003, 34, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, C. A spectrophotometric study of reflection of light from leaf surfaces. Bot. Gaz. 1929, 87, 583–607. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Xin, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, A.; Zhu, J. Ectopic Expression of the Allium cepa 1-SST gene in cotton improves drought tolerance and yield under drought stress in the field. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 783134. [Google Scholar]
- ElSayed, A.; Rafudeen, M.; Golldack, D. Physiological aspects of raffinose family oligosaccharides in plants: Protection against abiotic stress. Plant Biol. 2014, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, M.; Sawada, Y.; Nakabayashi, R.; Sato, S.; Hirakawa, H.; El-Sayed, M.; Hirai, M.; Saito, K.; Yamauchi, N.; Shigyo, M. Integrating transcriptome and target metabolome variability in doubled haploids of Allium cepa for abiotic stress protection. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, M.; Cui, C.; An, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, G.; Wan, Y.; Bao, W. Overexpression of a Gene Encoding Trigonelline Synthase from Areca catechu L. Promotes Drought Resilience in Transgenic Arabidopsis. Plants 2022, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Alabdallah, N.; Alharbi, B.; Waseem, M.; Yao, G.; Liu, X.D.; Abd El-Gawad, H.; El-Yazied, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Jahan, M.; et al. GABA: A Key Player in Drought Stress Resistance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shahzad, B.; Rehman, A.; Bhardwaj, R.; Landi, M.; Zheng, B. Response of Phenylpropanoid Pathway and the Role of Polyphenols in Plants under Abiotic Stress. Molecules 2019, 24, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharramnejad, S.; Sofalian, O.; Valizadeh, M.; Asghari, A.; Shiri, M.; Ashraf, M. Response of maize to field drought stress: Oxidative defense system, Osmolytes’ accumulation and photosynthetic pigments. Pak. J. Bot. 2019, 51, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte, R.M.; Escudero, A.; Gavilán, R. Metabolic and physiological responses of Mediterranean high-mountain and alpine plants to combined abiotic stresses. Physiol. Plant. 2019, 165, 403–412. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, I. Plant mitochondria and oxidative stress: Electron transport, NADPH turnover, and metabolism of reactive oxygen species. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2001, 52, 561–591. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, J.; Kusaka, R.; Walsh, P.; Allais, F.; Zwier, T. Plant Sunscreens in the UV-B: Ultraviolet Spectroscopy of Jet-Cooled Sinapoyl Malate, Sinapic Acid, and Sinapate Ester Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14780–14795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camarillo-Castillo, F.; Huggins, T.; Mondal, S.; Reynolds, M.; Tilley, M.; Hays, D. High-resolution spectral information enables phenotyping of leaf epicuticular wax in wheat. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, H.; Heilman, J.; McInnes, K.; Rooney, W.; Lewis, K. Epicuticular wax and its effect on canopy temperature and water use of Sorghum. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 284, 107893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Singh, J.; Paul, A.; Sarkar, R.; Khan, Z.; Banerjee, K. Anthocyanin profiling using UV-vis spectroscopy and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Aoac Int. 2020, 103, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, J.; Lv, L.; Zeng, X.; Li, J.; Asghar, S.; Li, Y. Establishment of an efficient regeneration system of ‘ZiKui’ tea with hypocotyl as explants. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naing, A.; Kim, C. Abiotic stress-induced anthocyanins in plants: Their role in tolerance to abiotic stresses. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 172, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victor, P.; Camarena-Bernard, C. Lutein, violaxanthin, and zeaxanthin spectrophotometric quantification: A machine learning approach. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzałka, K.; Kostecka-Gugała, A.; Latowski, D. Carotenoids and Environmental Stress in Plants: Significance of Carotenoid-Mediated Modulation of Membrane Physical Properties. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 50, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pigment Compound | Correlation Coefficient (r) |
|---|---|
| chlorophyll a | 0.850 |
| chlorophyll b | 0.609 |
| Pheophytin a | 0.572 |
| Lutein | 0.405 |
| -Carotene | 0.690 |
| Pigment Compound | Quality Parameter | Calibration | Test | LOOCV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll a | 0.96 | 0.88 | 0.78 | |
| RMSE | 2.28 | 2.91 | 5.28 | |
| Chlorophyll b | 0.79 | −1.07 | 0.38 | |
| RMSE | 4.50 | 6.70 | 7.08 | |
| Pheophytin a | 0.86 | 0.47 | 0.17 | |
| RMSE | 0.96 | 1.58 | 2.26 | |
| Lutein | 0.88 | −0.57 | −0.15 | |
| RMSE | 0.47 | 2.12 | 1.63 | |
| -Carotene | 0.92 | −0.10 | 0.60 | |
| RMSE | 0.19 | 0.38 | 0.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakajima, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Fuji, M.; Fujii, K.; Abdelrahman, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Mano, J.; Sato, M.; Hirai, M.Y.; Yamauchi, N.; et al. Metabolome Profiling and Predictive Modeling of Dark Green Leaf Trait in Bunching Onion Varieties. Metabolites 2025, 15, 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040226
Nakajima T, Kobayashi M, Fuji M, Fujii K, Abdelrahman M, Matsuoka Y, Mano J, Sato M, Hirai MY, Yamauchi N, et al. Metabolome Profiling and Predictive Modeling of Dark Green Leaf Trait in Bunching Onion Varieties. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):226. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040226
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakajima, Tetsuya, Mari Kobayashi, Masato Fuji, Kouei Fujii, Mostafa Abdelrahman, Yasumasa Matsuoka, Jun’ichi Mano, Muneo Sato, Masami Yokota Hirai, Naoki Yamauchi, and et al. 2025. "Metabolome Profiling and Predictive Modeling of Dark Green Leaf Trait in Bunching Onion Varieties" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040226
APA StyleNakajima, T., Kobayashi, M., Fuji, M., Fujii, K., Abdelrahman, M., Matsuoka, Y., Mano, J., Sato, M., Hirai, M. Y., Yamauchi, N., & Shigyo, M. (2025). Metabolome Profiling and Predictive Modeling of Dark Green Leaf Trait in Bunching Onion Varieties. Metabolites, 15(4), 226. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040226







