Abstract
Background/Objectives: Elevated levels of adiponectin in chronic kidney disease (CKD) have been paradoxically associated with increased mortality. This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the association between circulating adiponectin levels and all-cause mortality in patients with CKD, in total and various subgroups. Methods: We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library from their inception to December 2024 for studies examining baseline adiponectin levels and observed mortality outcomes in patients with CKD. Studies were included if they evaluated CKD stages 2–5 patients, measured baseline circulating adiponectin levels, and reported hazard ratios (HRs) for all-cause mortality. We excluded non-original research, studies of acute conditions, normal kidney function, kidney transplantation, and those using log-transformed or standardized HRs. HRs with a 95% confidence interval (CI) for all-cause mortality risk per 1 µg/mL increase in adiponectin were extracted and analyzed using the Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 4. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale. Results: Twelve studies with 2523 subjects were included. The pooled unadjusted HR was 1.003 (95% CI: 0.981–1.025) using a random-effects model (I2 = 79%). Subgroup analyses demonstrated increased mortality risk with elevated adiponectin levels in non-Asia (HR 1.021 [95% CI: 1.006–1.037], p = 0.006), studies with female proportion <47% (HR 1.021 [95% CI: 1.009–1.033], p < 0.001), and studies with body mass index ≥25 kg/m2 (HR 1.023 [95% CI: 1.008–1.038], p = 0.003). In contrast, higher adiponectin levels were associated with decreased mortality risk in the peritoneal dialysis group (HR 0.956 [95% CI: 0.934–0.979], p < 0.001) and female proportion ≥47% group (HR 0.929 [95% CI: 0.874–0.988], p = 0.019). Discussion/Conclusions: This meta-analysis revealed that elevated adiponectin levels have varying associations with the risk of all-cause mortality across CKD patient subgroups. These findings suggest that the prognostic value of adiponectin levels in CKD may be modulated by demographic and clinical factors. Limitations include poor generalizability with underrepresentation of early-stage CKD. This research received no external funding and was not registered.
1. Introduction
Adiponectin, an adipokine primarily secreted by adipose tissue, plays crucial roles in metabolic signaling and cellular communication [1,2]. It acts through ceramidase-active AdipoR1/R2 receptors, T-cadherin-mediated exosome release, and cross-tissue signaling that collectively enhance insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation [3,4]. Adiponectin has garnered attention for its beneficial effects, including improved glucose metabolism and protection against metabolic and cardiovascular diseases [5,6,7,8].
In the context of chronic kidney disease (CKD), adiponectin levels present a clinical paradox. While plasma adiponectin typically ranges from 2 to 20 µg/mL in healthy individuals, patients with CKD exhibit levels 2–3 times higher than normal. This elevation is attributed primarily to decreased renal clearance, though metabolic disturbances and adiponectin resistance may also contribute [9]. The clinical significance of elevated adiponectin in CKD patients remains unclear as to whether it merely reflects impaired kidney function or serves as a prognostic indicator for clinical outcomes [10,11].
Despite adiponectin’s generally protective effects, several studies have documented an “adiponectin paradox”, where higher levels correlate with increased cardiovascular and all-cause mortality [12,13]. In CKD patients, specifically, the relationship between adiponectin and mortality risk remains controversial, with studies reporting positive [14,15], negative [16], or no association [17] with all-cause mortality. While no direct causal mechanism has been established between adiponectin and mortality, potential pathways linking elevated adiponectin to adverse outcomes in CKD patients include protein-energy wasting syndrome, detrimental cardiovascular effects, and altered immunometabolism in the uremic milieu [18,19].
A previous meta-analysis examining mortality risk factors in hemodialysis (HD) patients reported that adiponectin (per 10.0 µg/mL increment) was associated with increased all-cause mortality risk (relative risk: 1.23, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.08–1.41, p = 0.002) [20]. However, this analysis was limited by the small number of studies specifically investigating adiponectin as a biomarker [21].
Given these conflicting findings and the limited scope of previous analyses, we conducted a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the association between circulating adiponectin levels and all-cause mortality in CKD patients, examining both overall effects and various subgroup analyses
2. Materials and Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines [22] (Supplementary Materials Tables S1 and S2), the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews [23], and Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) reporting guidelines [24].
2.1. Literature Search
We conducted a systematic electronic search of multiple databases including PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library from their inception to December 2024. The search was restricted to English-language publications. We used the following search terms: (adiponectin) and (“chronic kidney/renal disease” or “chronic kidney/renal failure” or “chronic renal insufficiency” or “end stage kidney/renal disease” or “hemodialysis” or “peritoneal dialysis”) and (“death” or “mortality”). References from relevant articles were also reviewed.
2.2. Study Selection
Original articles were included if they met all of the following criteria: (1) evaluated patients with CKD stages 2–5 as defined by the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) guidelines [25], (2) measured baseline circulating total adiponectin levels, and (3) reported a hazard ratio (HR) with a 95% CI for all-cause mortality risk associated with adiponectin levels.
Exclusion criteria were: (1) non-original research formats (reviews, editorials, letters, conference abstracts, or case reports), (2) studies of subjects with acute medical conditions, normal glomerular filtration rate, or history of kidney transplantation, and (3) studies reporting an HR using log-transformed values or standard deviation units. For multiple publications using the same cohort, we included only the report with the largest sample size. Two independent reviewers (HSY and JHR) performed the study selection process. Any disagreements were resolved through consensus discussion or consultation with a third reviewer (SNK).
2.3. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
From each eligible study, we extracted: (1) first author’s last name, (2) publication year, (3) study site, (4) CKD stage or dialysis modality, (5) sample size (total and by sex), (6) mean age, (7) baseline body mass index (BMI), (8) adiponectin measurement methodology, (9) baseline total adiponectin levels, (10) follow-up duration, (11) mortality count, (12) unadjusted and adjusted HR (95% CI) for all-cause mortality, and (13) adjustment variables. No attempts were made to contact study authors for additional information, and no automation tools were used in the data extraction. Study quality was assessed using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Cohort Studies [26], which is specifically designed and widely validated for observational research. Two reviewers (HSY, JHR) independently collected data from reports and evaluated each NOS criterion, with any disagreements resolved through discussion and consultation with a third reviewer (SNK).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
For the meta-analysis, we collected unadjusted HRs and their 95% CI for all-cause mortality risk per 1 µg/mL increase in adiponectin levels. For data from Rhee et al. [17], we standardized the HR from per 10 µg/mL to per 1 µg/mL using the formula: HR (per 1-unit) = exp (ln (HR per 10-units)/10) [27]. Data from Takemoto et al. [28], were stratified by sex and analyzed separately as ‘Takemoto 2009a’ (males) and ‘Takemoto 2009b’ (females), as the original study reported sex-specific analyses without combined data.
We conducted the meta-analysis using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis software (version 4.0) [29]. The pooled mean effect size was calculated using a random-effects model based on unadjusted HRs and a 95% CI from 13 study names (derived from 12 studies) [30]. Statistical significance was assessed using Z-tests with an alpha level of 0.05.
Heterogeneity was evaluated using the Cochrane Q test and I2 statistics, with significant heterogeneity defined as p < 0.10 or I2 > 50% [31]. To investigate potential sources of heterogeneity in the relationship between adiponectin levels and mortality, we conducted pre-specified subgroup analyses stratifying by: (a) study site (Asia vs. non-Asia), (b) dialysis modality (HD vs. peritoneal dialysis [PD]), (c) age (<55 vs. ≥55 years), (d) sex proportion (<47% vs. ≥47% female), (e) BMI (<25 vs. ≥25 kg/m2), and (f) baseline adiponectin levels (≤20 vs. >20 µg/mL). Clinically relevant cut-off values were established through a comprehensive systematic review of the literature. For each subgroup analysis, we calculated pooled HRs and assessed heterogeneity using I2 statistics to determine which factors might explain the observed between-study variation.
To assess robustness, we conducted leave-one-out sensitivity analyses and cumulative meta-analyses to evaluate individual study impact and temporal evolution of evidence, respectively. Publication bias was assessed using Begg’s and Egger’s tests through funnel plot analysis, with statistical significance set at p < 0.05 (one-tailed).
3. Results
3.1. Results of Literature Search
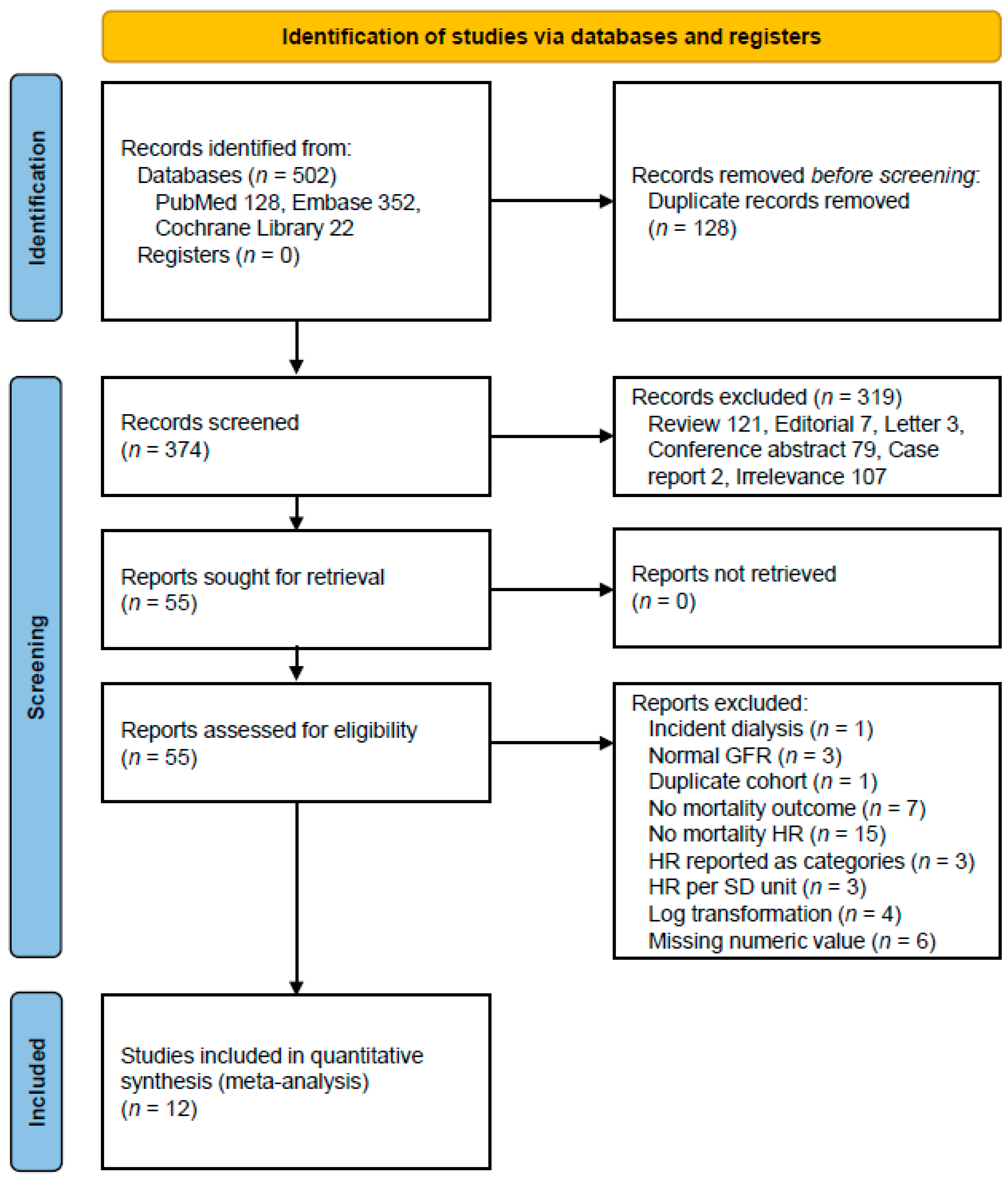
Our systematic database search identified 502 potentially relevant articles across multiple databases: PubMed (n = 128), Embase (n = 352), and Cochrane Library (n = 22). After removing 128 duplicate records, we screened 374 unique abstracts. Following the initial screening, 55 articles were retrieved for full-text assessment. Of these, 12 studies met our inclusion criteria [14,15,16,21,28,32,33,34,35,36,37,38], comprising a total study population of 2523 subjects. The detailed study selection process is illustrated in Figure 1.
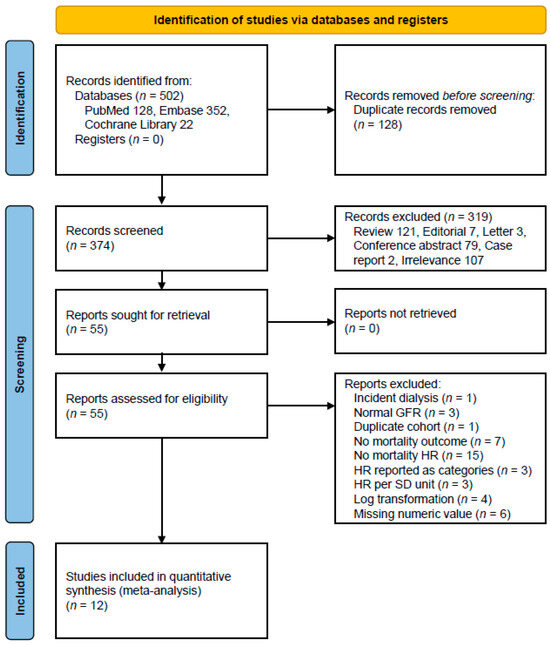
Figure 1.
A flow diagram of the study selection. Abbreviations: GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HR, hazard ratio; SD, standard deviation.
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
Our systematic review identified 12 studies, with their key characteristics summarized in Table 1. Six studies [14,16,28,35,36,38] were conducted in Asian countries. Eleven studies included patients with CKD stage 5 or end-stage renal disease on renal replacement therapy [25]: eight [14,21,28,33,34,36,37,38] exclusively on HD, two [16,35] exclusively on PD, and one [15] with both HD and PD patients. Follow-up periods ranged from 1.5 to 10 years, during which all-cause mortality rates varied between 10% and 43%. All studies demonstrated high methodological quality, scoring 8–9 points on the NOS (Supplementary Materials Table S3).

Table 1.
Characteristics of included studies.
The relationship between adiponectin levels and mortality risk was reported using both unadjusted and adjusted HRs per 1 µg/mL increase in adiponectin (Table 2). The unadjusted HRs revealed conflicting results: three studies (Ohashi, 2008 [14], Markaki, 2012 [15], Rhee, 2015 [21]) found higher adiponectin levels were associated with increased mortality risk, while three others (Park, 2013 [16], Tung, 2015 [35], Zhou, 2016 [36]) reported the opposite. In two studies (Menon, 2006 [32], Abdallah, 2012 [33]), the association between adiponectin levels and all-cause mortality became statistically significant only after adjustment.

Table 2.
Unadjusted and adjusted hazard ratios for all-cause mortality per 1 µg/mL increase in adiponectin.
3.3. Association Between Adiponectin Levels and All-Cause Mortality
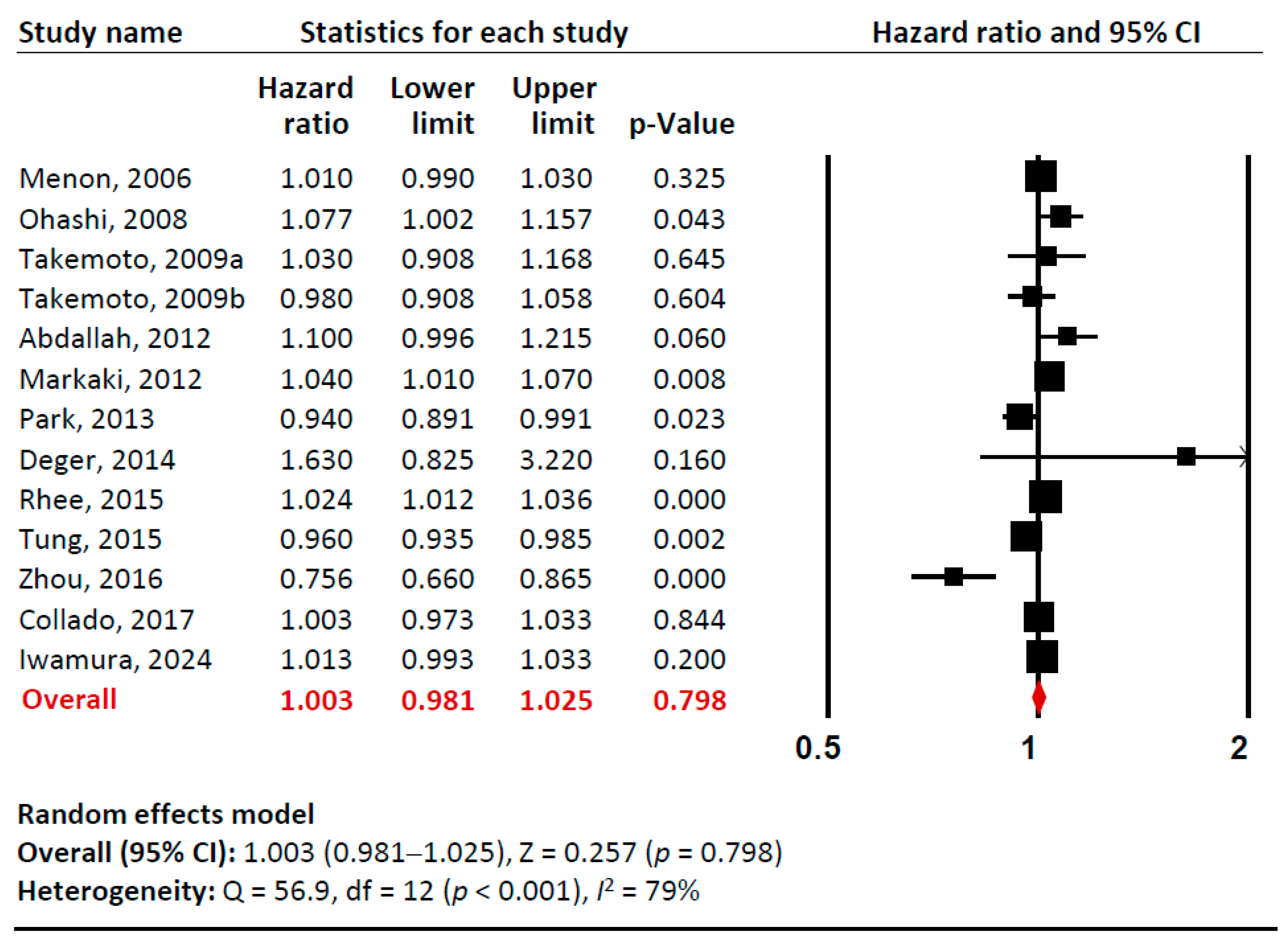
Our meta-analysis examined the relationship between baseline adiponectin levels (per 1 µg/mL) and all-cause mortality risk in total (Figure 2, Supplementary Materials Figures S1 and S2). Sensitivity analysis confirmed that no single study significantly influenced the overall effect estimate, indicating the robustness of our findings. Cumulative analysis demonstrated gradual stabilization of the pooled effect estimate over time as additional studies were incorporated. Overall, we found no significant association between adiponectin levels and all-cause mortality in CKD patients (pooled unadjusted HR 1.003 [95% CI: 0.981–1.025]). However, there was substantial heterogeneity among studies (I2= 79%).
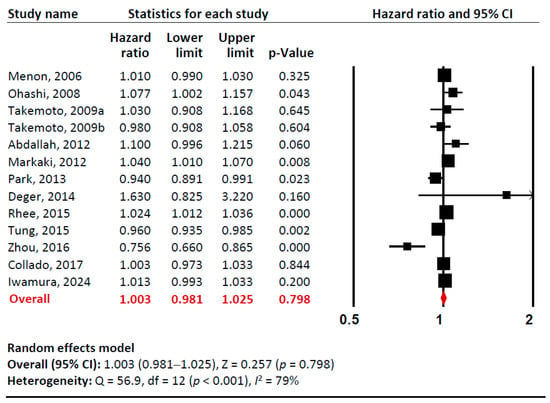
Figure 2.
A forest plot of meta-analysis. Adiponectin (per 1 µg/mL increment) and risk of all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. Studies included: Menon, 2006 [32]; Ohashi, 2008 [14]; Takemoto, 2009a [28]; Takemoto, 2009b [28]; Abdallah, 2012 [33]; Markaki, 2012 [15]; Park, 2013 [16]; Deger, 2014 [34]; Rhee, 2015 [21]; Tung, 2015 [35]; Zhou, 2016 [36]; Collado, 2017 [37]; Iwamura, 2024 [38]. Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom.
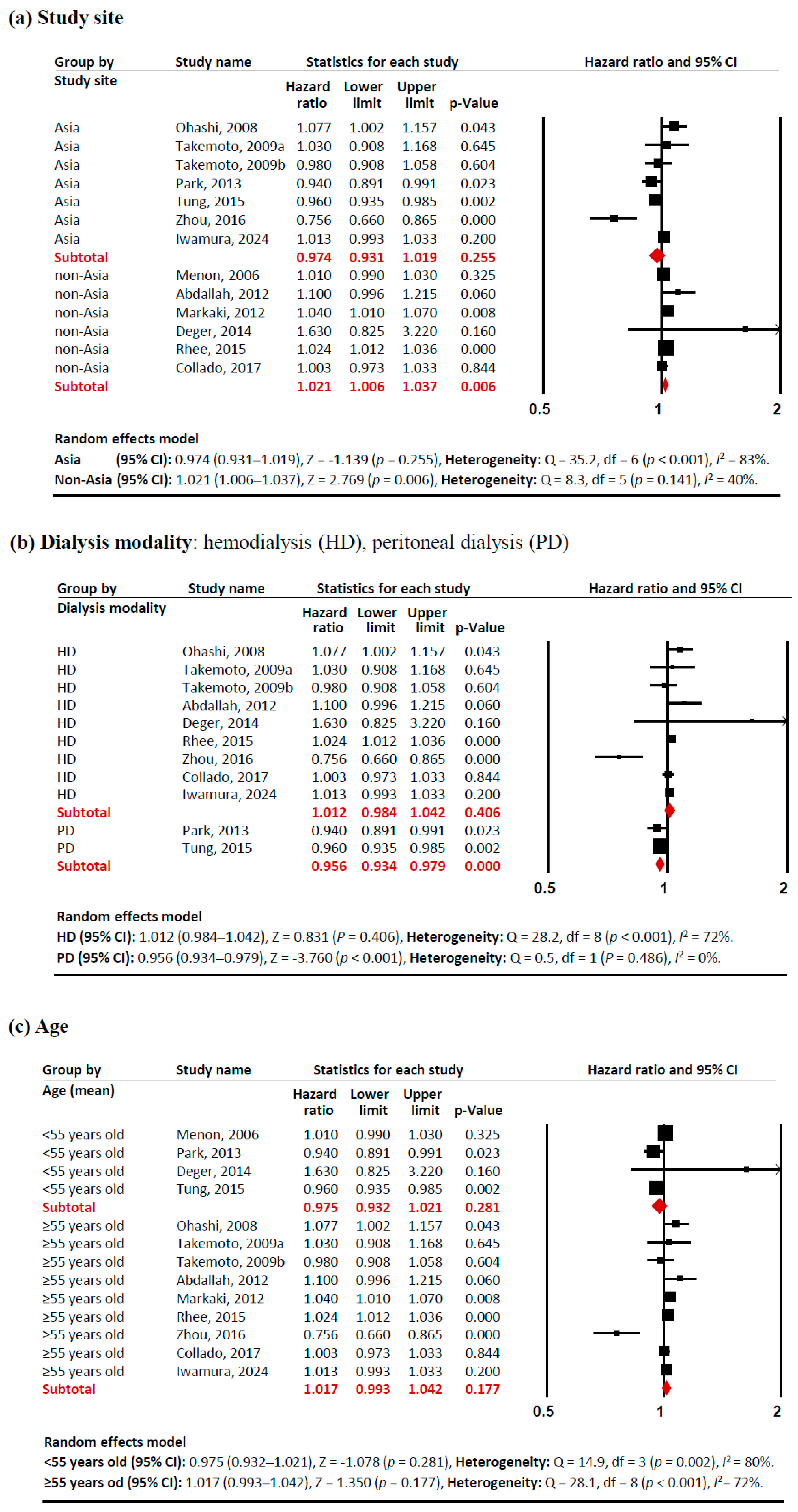
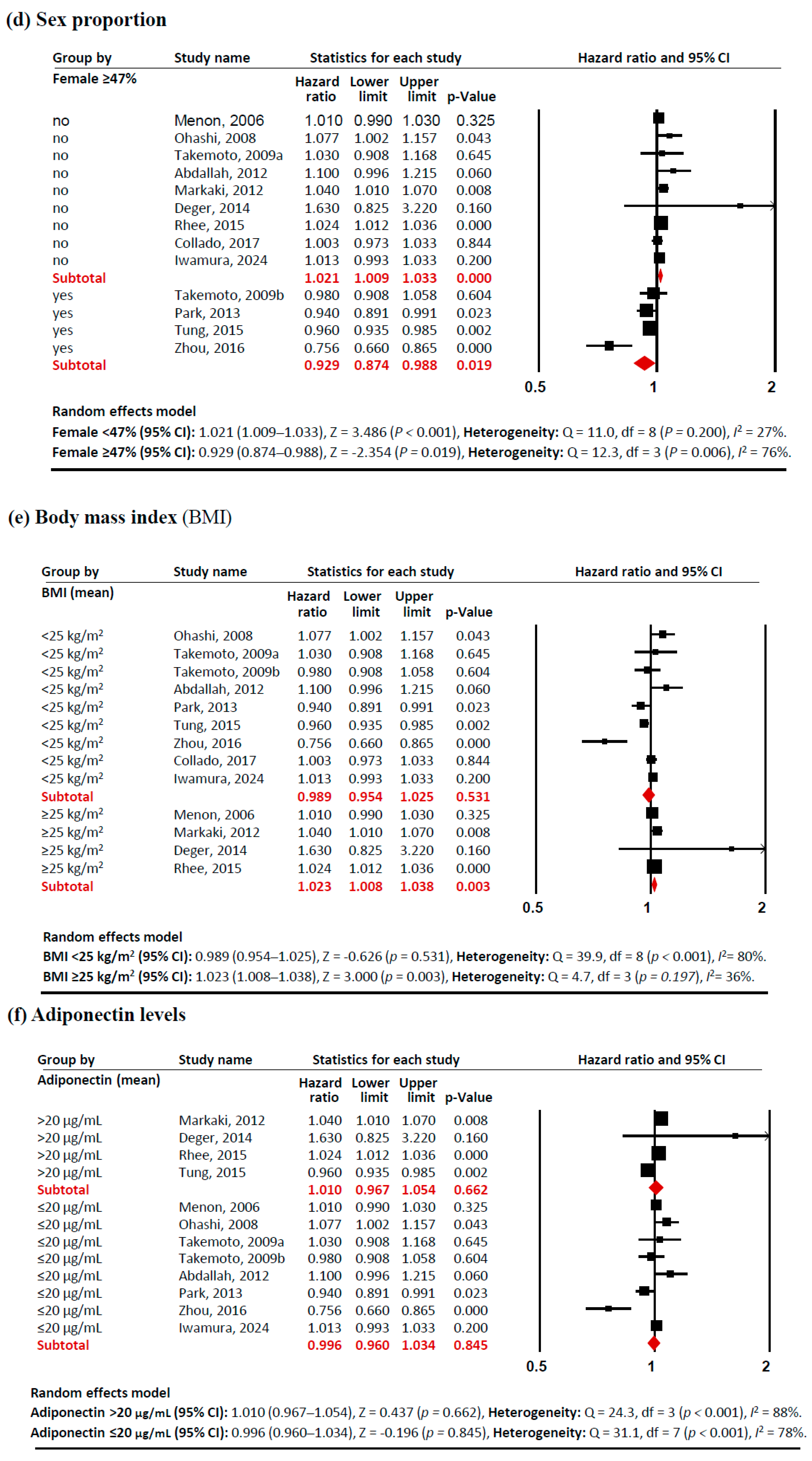
Subgroup analyses revealed several notable patterns that helped explain this heterogeneity (Figure 3). In terms of study sites, studies conducted outside Asia showed a significant positive association between adiponectin levels and mortality risk (HR 1.021 [95% CI: 1.006–1.037]). Similarly, studies with a lower proportion of females (<47%) demonstrated a positive association (HR 1.021 [95% CI: 1.009–1.033]), as did populations with higher BMI (≥25 kg/m2) (HR 1.023 [95% CI: 1.023–1.038]). These associations showed consistent effects across studies, with low heterogeneity (I2 <50%). In contrast, certain subgroups exhibited significant negative associations between adiponectin levels and mortality risk. PD patients showed a protective effect (HR 0.956 [95% CI: 0.934–0.979]) with no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). Studies with a higher proportion of females (≥47%) also demonstrated a negative association (HR 0.929 [95% CI: 0.874–0.988]), although with significant heterogeneity (I2 = 76%). These findings indicate that the relationship between adiponectin and all-cause mortality in CKD patients is significantly modulated by study site, dialysis modality, sex proportion, and BMI, with these factors accounting for much of the observed heterogeneity in the overall analysis.
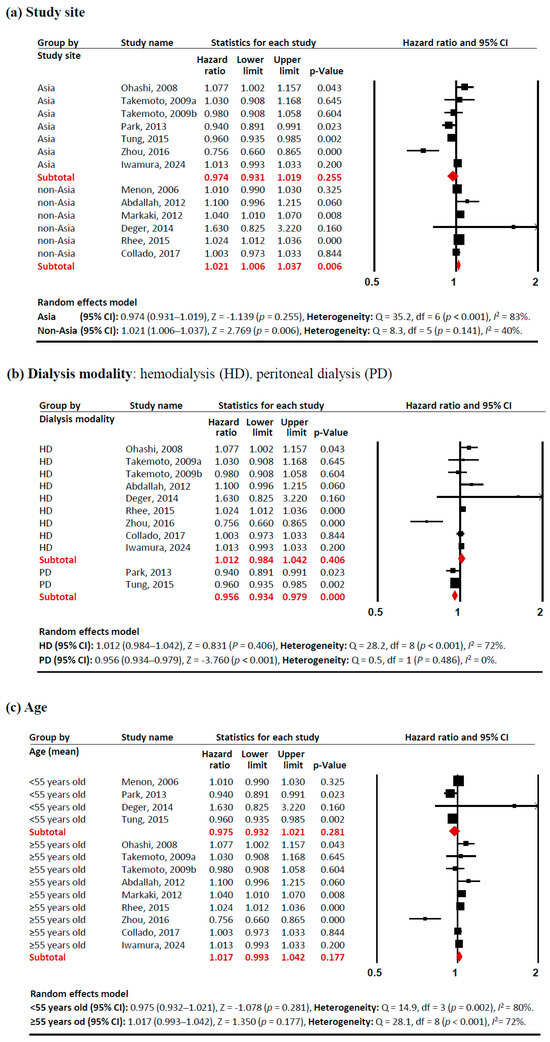
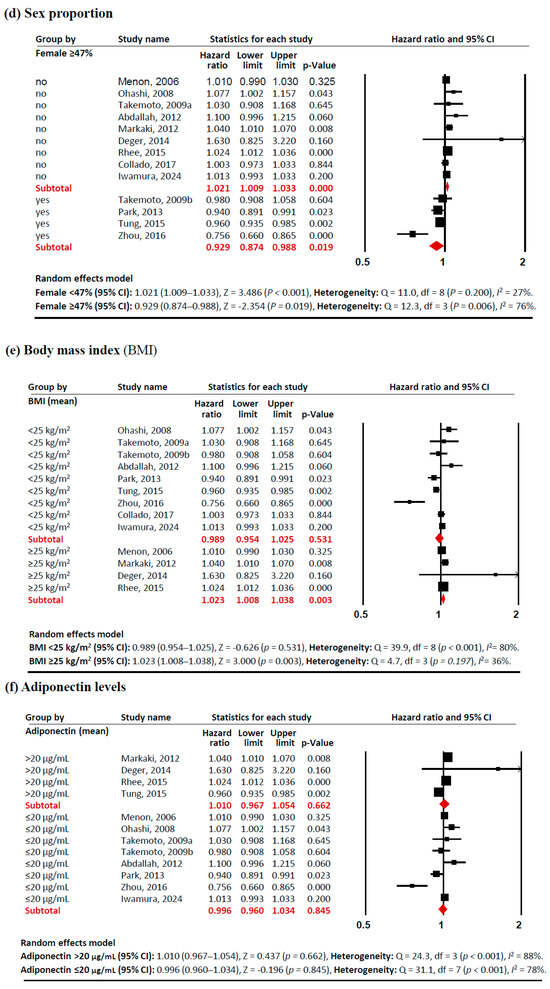
Figure 3.
Forest plots of subgroup meta-analysis. Adiponectin (per 1 µg/mL increment) and risk of all-cause mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. (a) study site (Asia, non-Asia), (b) dialysis modality (HD, PD), (c) age (<55 years old, ≥55 years old), (d)sex proportion (<47% vs. ≥47% female), (e) BMI (<25 kg/m2, ≥25 kg/m2), and (f) adiponectin levels (>20 µg/mL, ≤20 µg/mL). Studies included: Menon, 2006 [32]; Ohashi, 2008 [14]; Takemoto, 2009a [28]; Takemoto, 2009b [28]; Abdallah, 2012 [33]; Markaki, 2012 [15]; Park, 2013 [16]; Deger, 2014 [34]; Rhee, 2015 [21]; Tung, 2015 [35]; Zhou, 2016 [36]; Collado, 2017 [37]; Iwamura, 2024 [38]. Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom.
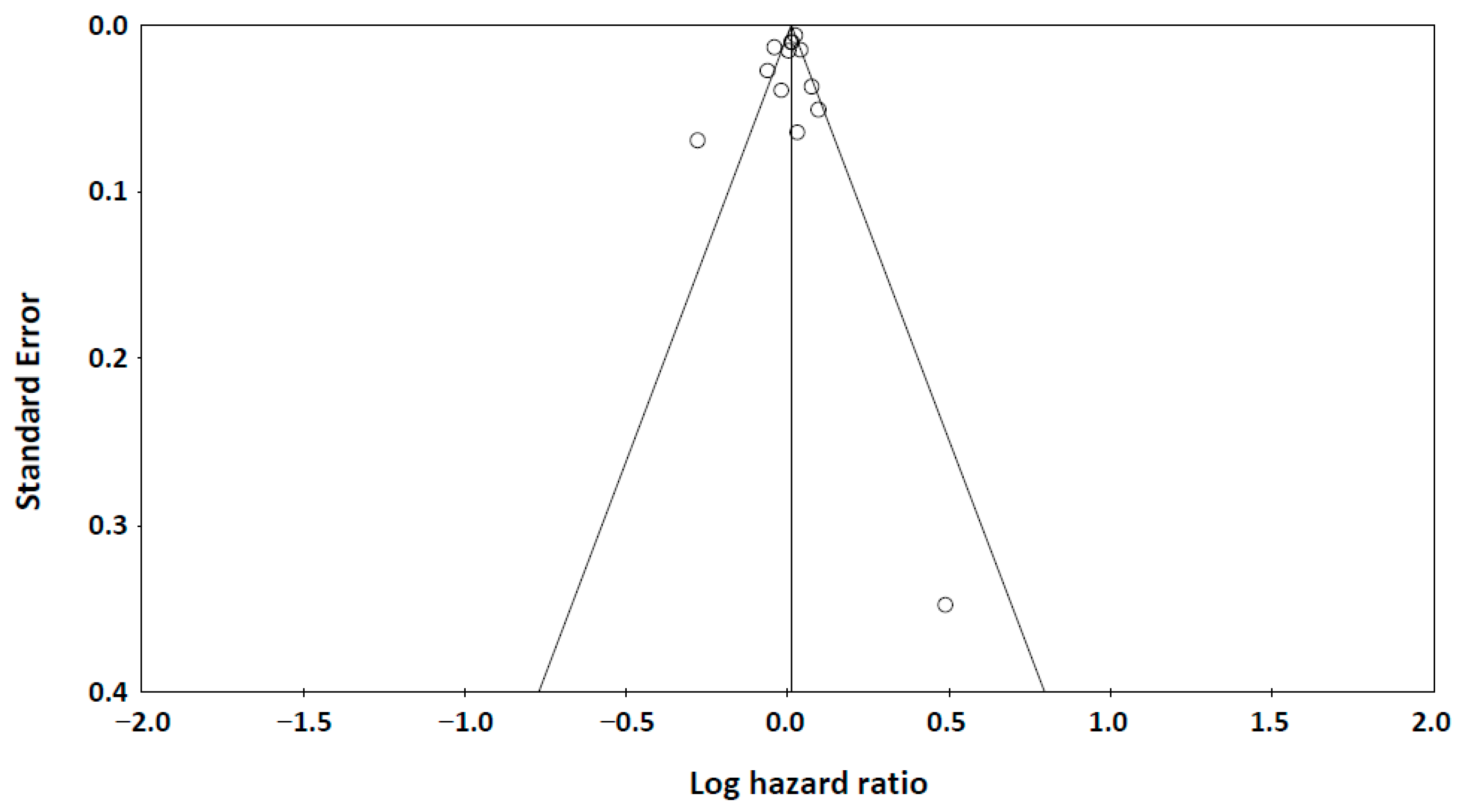
3.4. Publication Bias Analysis
The funnel plot (Figure 4) showed symmetric distribution of studies examining adiponectin levels and all-cause mortality. Both Begg’s test (p = 0.214) and Egger’s test (p = 0.237) confirmed no significant publication bias, supporting the robustness of our findings.
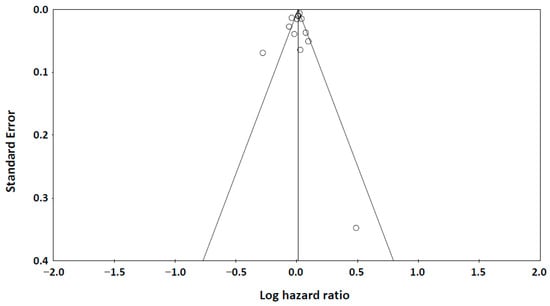
Figure 4.
A funnel plot of publication bias. Begg’s test: Kendall’s tau = −0.167, p = 0.214 (1-tailed). Egger’s test: intercept = −0.723 (95% Confidence Interval: −2.867, 1.421), p = 0.237 (one-tailed).
4. Discussion
This study represents, to our knowledge, the first comprehensive meta-analysis examining the relationship between circulating adiponectin levels and mortality risk in patients with CKD across diverse subgroups. Our analysis revealed that the association between adiponectin levels (per 1 µg/mL increment) and all-cause mortality varies significantly across different patient populations. Specifically, elevated adiponectin levels were associated with increased mortality risk in the non-Asia, higher male proportion, and higher BMI groups. Conversely, higher adiponectin levels correlated with reduced mortality risk in the PD and higher female proportion groups (Figure 3). These findings suggest that elevated adiponectin levels may have a protective effect in specific patient profiles—particularly among young, non-obese, Asian females undergoing PD. However, these interpretations warrant careful consideration, as our analyses were conducted at the aggregate group level rather than the individual patient level, potentially masking important individual variations and interactions.
The elevated adiponectin levels observed in CKD present a complex phenomenon requiring careful interpretation. While Mendelian randomization studies [39,40] suggest adiponectin is unlikely to be a direct causal factor, its elevation may serve as an important biomarker for mortality. Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain this ‘adiponectin paradox’ in CKD patients. Reduced adiponectin clearance corresponding to disease severity appears to be a primary mechanism, while high adiponectin levels may also reflect protein-energy wasting and malnutrition [18] or development of adiponectin resistance [9,41]. Additional proposed mechanisms include broader metabolic dysregulation [42], enhanced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines (particularly IL-6 and TNF-α) [19,43,44], and modification of adiponectin’s protective effects by uremic toxins [19,44]. Our findings suggest an additional perspective regarding the right-arm positioning of the U-shaped mortality risk curve. Our subgroup analysis (Figure 3f) revealed opposing associations with mortality between the low and high adiponectin groups (≤20 µg/mL: HR 0.960; >20 µg/mL: HR 1.010). This pattern suggests a context-dependent relationship: in populations with typically low adiponectin levels (such as healthy individuals), decreased levels are associated with higher mortality risk, while in populations with characteristically high levels (such as CKD patients), further elevation corresponds to increased mortality. This interpretation aligns with previous studies reporting U-shaped associations between adiponectin levels and mortality [41,45,46]. Future research employing non-linear modeling approaches [47] could help identify the optimal adiponectin range and better characterize this U-shaped relationship. Additionally, the ‘adiponectin paradox’ has been observed exclusively in human prospective studies, not in animal models [3], necessitating well-designed clinical trials employing multifactorial analyses or randomized double-blind controls to better understand this species-specific discrepancy.
A key strength of this meta-analysis lies in its comprehensive subgroup analyses. While racial and ethnic data were not available across studies, the geographical subgroup meta-analysis (Figure 3a) unveiled distinct mortality risk patterns: studies from Asian countries demonstrated a trend toward lower mortality risk (HR 0.974), while those from non-Asian countries showed slightly elevated risk (HR 1.021). Although we initially planned to analyze pre-dialysis patients, this was not feasible as only one study examining CKD stages 3–4 was available [32], creating an important knowledge gap regarding adiponectin’s prognostic value in earlier CKD stages. Our findings should be applied cautiously to pre-dialysis populations, as adiponectin-mortality relationships likely differ across the CKD spectrum. The dialysis modality subgroup analysis (Figure 3b) revealed a remarkable contrast: elevated adiponectin levels correlated with increased mortality risk in the HD group (HR 1.012) but decreased risk in the PD group (HR 0.956). This pattern aligns with established demographic differences between dialysis populations, as PD patients generally tend to be younger, more physically independent, and demonstrate better cardiovascular stability compared to HD patients [48,49]. Due to its molecular size (30 kDa), adiponectin is poorly cleared by both HD and PD; therefore, neither modality effectively removes adiponectin from circulation [50]. Elevated adiponectin in both HD and PD patients is primarily due to reduced renal clearance rather than increased production [50,51], with no significant differences having been reported in serum adiponectin levels between HD and PD patients [50,51,52]. Additional subgroup analyses showed protective associations between elevated adiponectin levels and mortality in both younger patients (HR 0.975) (Figure 3c) and non-obese patients (HR 0.989) (Figure 3e).
This study addresses an important topic with significant clinical implications, as understanding the prognostic value of adiponectin levels in CKD could contribute to improved risk stratification for affected patients. Currently, there is no established use of adiponectin levels as a prognostic biomarker in clinical practice for CKD patients. However, our findings suggest that adiponectin levels should be interpreted holistically, considering CKD stage or dialysis modality, concurrent metabolic parameters, and comorbidities, rather than focusing solely on absolute adiponectin values. Given this complexity, a multi-marker approach to risk stratification may be essential for optimal patient care in CKD [16,53].
Several limitations of our systematic review and meta-analysis warrant consideration. First, although publication bias was not significant among included studies, we observed notable omissions of specific numerical data during the exclusion process, particularly regarding non-significant results [17,54,55,56]. Second, the included studies did not adequately represent the complete spectrum of CKD, with particular underrepresentation of early-stage disease, potentially limiting generalizability. Third, we acknowledge that our use of unadjusted HRs in the primary analysis is a limitation, as unadjusted estimates may misrepresent true associations due to the complexity of mortality determinants in CKD patients. However, this methodological decision was necessary due to the substantial heterogeneity in adjustment variables across included studies (Table 2), which would have introduced additional clinical heterogeneity if pooled. We addressed potential confounding through comprehensive subgroup analyses that identified important effect modifiers while maintaining analytical consistency. Additionally, most studies measured adipokine levels at single time points, limiting temporal analysis. Future research should focus on developing non-linear prediction models and multi-factor adjustment models to evaluate multiple adipokine-related biomarkers simultaneously with particular emphasis on including patients across the entire CKD spectrum, especially those in earlier stages.
5. Conclusions
This meta-analysis demonstrated that elevated adiponectin levels have varying associations with all-cause mortality across CKD patient subgroups, with protective effects observed in the PD group and the higher female proportion group. These findings suggest that the prognostic value of adiponectin levels in CKD may be significantly modulated by demographic and clinical factors, highlighting the importance of considering patient-specific characteristics when evaluating mortality risk.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/metabo15040230/s1, Table S1: PRISMA 2020 Checklist; Table S2: PRISMA 2020 for Abstracts Checklist; Table S3: Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale for Cohort Studies; Figure S1: Sensitivity Analysis; Figure S2: Cumulative Analysis.
Author Contributions
H.S.Y. conceptualized and designed the study. H.S.Y. and J.-H.R. conducted a systematic database search and collected data. H.S.Y., J.-H.R. and S.-N.K. performed data extraction and statistical analyses. H.S.Y. drafted the manuscript, with significant intellectual input from M.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data described in this study are available within this article or in the Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CKD | Chronic Kidney Disease |
| HD | Hemodialysis |
| PD | Peritoneal Dialysis |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| MOOSE | Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes |
| NOS | The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale |
References
- Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Physiological and pathophysiological roles of adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in the integrated regulation of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32 (Suppl. S7), S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, L.G.; Scherer, P.E. Metabolic Messengers: Adiponectin. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. New advances of adiponectin in regulating obesity and related metabolic syndromes. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianopoulos, I.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Daskalopoulou, S.S. Adiponectin and Adiponectin Receptors in Atherosclerosis. Endocr. Rev. 2025, 46, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tishinsky, J.M.; Robinson, L.E.; Dyck, D.J. Insulin-sensitizing properties of adiponectin. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2131–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.M.; Doss, H.M.; Kim, K.S. Multifaceted Physiological Roles of Adiponectin in Inflammation and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, E.; Ouimet, M.; Sweeney, G. Cardioprotective Effects of Adiponectin-Stimulated Autophagy. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2025, 14, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, S.; Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Li, W. Adiponectin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical animal studies. Lipids Health Dis. 2024, 23, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.L.; Lau, W.B. Cardiovascular Adiponectin Resistance: The Critical Role of Adiponectin Receptor Modification. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Oh, T.R.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Ma, S.K.; Oh, K.H.; Ahn, C.; Kim, S.W.; Bae, E.H. High serum adiponectin as a biomarker of renal dysfunction: Results from the KNOW-CKD study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo El Fotoh, W.M.; El Mashad, G.M. Elevated baseline adiponectin level predicting an increased risk of disease activity in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome and chronic kidney disease in children. Minerva Pediatr. 2023, 75, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzaghi, C.; Trischitta, V. The Adiponectin Paradox for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality. Diabetes 2018, 67, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.Y.; Scherer, P.E.; Kim, J.Y.; Lim, S.; Koh, K.K. Adiponectin and cardiometabolic trait and mortality: Where do we go? Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, N.; Kato, A.; Misaki, T.; Sakakima, M.; Fujigaki, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hishida, A. Association of serum adiponectin levels with all-cause mortality in hemodialysis patients. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markaki, A.; Kyriazis, J.; Stylianou, K.; Fragkiadakis, G.A.; Perakis, K.; Margioris, A.N.; Ganotakis, E.S.; Daphnis, E. The role of serum magnesium and calcium on the association between adiponectin levels and all-cause mortality in end-stage renal disease patients. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.T.; Yoo, T.H.; Kim, J.K.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Yoo, D.E.; Lee, M.J.; Shin, D.H.; Han, S.H.; Han, D.S.; et al. Leptin/adiponectin ratio is an independent predictor of mortality in nondiabetic peritoneal dialysis patients. Perit. Dial. Int. 2013, 33, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Tripepi, G.; Benedetto, F.A.; Cutrupi, S.; Parlongo, S.; Malatino, L.S.; Bonanno, G.; Seminara, G.; Rapisarda, F.; et al. Adiponectin, metabolic risk factors, and cardiovascular events among patients with end-stage renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Carrero, J.J.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Adiponectin in chronic kidney disease has an opposite impact on protein-energy wasting and cardiovascular risk: Two sides of the same coin. Clin. Nephrol. 2009, 72, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Zanetti, M.; Bernardi, A.; Guarnieri, G. Inflammation and adipose tissue in uremia. J. Ren. Nutr. 2006, 16, 204–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, S. Risk factors for mortality in patients undergoing hemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 238, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.M.; Nguyen, D.V.; Moradi, H.; Brunelli, S.M.; Dukkipati, R.; Jing, J.; Nakata, T.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Brent, G.A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K. Association of Adiponectin With Body Composition and Mortality in Hemodialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022). Cochrane. 2022. Available online: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Stroup, D.F.; Berlin, J.A.; Morton, S.C.; Olkin, I.; Williamson, G.D.; Rennie, D.; Moher, D.; Becker, B.J.; Sipe, T.A.; Thacker, S.B. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: A proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 2000, 283, 2008–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, S117–S314. [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses; Ottawa Hospital Research Institute: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rothman, K.J.; Greenland, S.; Lash, T.L. Modern Epidemiology, 3rd ed.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto, F.; Katori, H.; Sawa, N.; Hoshino, J.; Suwabe, T.; Nakanishi, S.; Arai, S.; Fukuda, S.; Kodaka, K.; Shimada, M.; et al. Plasma adiponectin: A predictor of coronary heart disease in hemodialysis patients—A Japanese prospective eight-year study. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2009, 111, c12–c20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.E.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Rothstein, H.R. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 4; Biostat Inc.: Englewood, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.; Rothstein, H.R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2010, 1, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Balakrishnan, V.; Madero, M.; Pereira, A.A.; Beck, G.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Collins, A.J.; et al. Adiponectin and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2599–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.; Waked, E.; Nabil, M.; El-Bendary, O. Adiponectin and cardiovascular outcomes among hemodialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2012, 35, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deger, S.M.; Ellis, C.D.; Bian, A.; Shintani, A.; Ikizler, T.A.; Hung, A.M. Obesity, diabetes and survival in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, C.W.; Hsu, Y.C.; Shih, Y.H.; Lin, C.L. Association of Adiponectin with High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein and Clinical Outcomes in Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A 3.5-Year Follow-Up Study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Ni, Z. Association of adiponectin with peripheral arterial disease and mortality in nondiabetic hemodialysis patients: Long-term follow-up data of 7 years. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 21, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collado, S.; Coll, E.; Nicolau, C.; Azqueta, M.; Pons, M.; Cruzado, J.M.; de la Torre, B.; Deulofeu, R.; Mojal, S.; Pascual, J.; et al. Serum osteoprotegerin in prevalent hemodialysis patients: Associations with mortality, atherosclerosis and cardiac function. BMC Nephrol. 2017, 18, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamura, N.; Kidoguchi, S.; Asahi, N.; Takeda, I.; Matsuta, K.; Miyagi, K.; Iwano, M.; Miyazaki, R.; Kimura, H. Superiority of high sensitivity cardiac troponin I over NT-proBNP and adiponectin for 7-year mortality in stable patients receiving haemodialysis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghootkar, H.; Lamina, C.; Scott, R.A.; Dastani, Z.; Hivert, M.F.; Warren, L.L.; Stancáková, A.; Buxbaum, S.G.; Lyytikäinen, L.P.; Henneman, P.; et al. Mendelian randomization studies do not support a causal role for reduced circulating adiponectin levels in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3589–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.C.; Lawlor, D.A.; de Oliveira, C.; White, J.; Horta, B.L.; Barros, A.J. Role of Adiponectin in Coronary Heart Disease Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizer, J.R.; Benkeser, D.; Arnold, A.M.; Mukamal, K.J.; Ix, J.H.; Zieman, S.J.; Siscovick, D.S.; Tracy, R.P.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Defilippi, C.R.; et al. Associations of total and high-molecular-weight adiponectin with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in older persons: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Circulation 2012, 126, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Bernhard, J.; Funahashi, T.; Hadj-Aissa, A.; Fouque, D. Adiponectin in chronic kidney disease is related more to metabolic disturbances than to decline in renal function. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, J.; Heimbürger, O.; Stenvinkel, P. Adipose tissue and inflammation in chronic kidney disease. Contrib. Nephrol. 2006, 151, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Rodríguez, E.; Pizarro-Sánchez, S.; Sanz, A.B.; Ramos, A.M.; Sanchez-Niño, M.D.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Ortiz, A. Inflammatory Cytokines as Uremic Toxins: “Ni Son Todos Los Que Estan, Ni Estan Todos Los Que Son”. Toxins 2017, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Andel, M.; Heijboer, A.C.; Drent, M.L. Adiponectin and Its Isoforms in Pathophysiology. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2018, 85, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spoto, B.; Mattace-Raso, F.; Sijbrands, E.; Pizzini, P.; Cutrupi, S.; D’Arrigo, G.; Tripepi, G.; Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F. Resistin and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: Effect modification by adiponectin in end-stage kidney disease patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28 (Suppl. S4), iv181–iv187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Li, L.; Tighiouart, H.; Jaber, B.L.; Pereira, B.J.; Balakrishnan, V.S. Plasma adiponectin levels and clinical outcomes among haemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 2619–2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuasuwan, A.; Pooripussarakul, S.; Thakkinstian, A.; Ingsathit, A.; Pattanaprateep, O. Comparisons of quality of life between patients underwent peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albakr, R.B.; Bargman, J.M. A Comparison of Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiol. Clin. 2021, 39, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.W.; Yen, C.J.; Chiang, H.W.; Hung, K.Y.; Tsai, T.J.; Wu, K.D. Adiponectin in peritoneal dialysis patients: A comparison with hemodialysis patients and subjects with normal renal function. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2004, 43, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, J.J.; Iglesias, P.; Fernández-Reyes, M.J.; Aguilera, A.; Bajo, M.A.; Alvarez-Fidalgo, P.; Codoceo, R.; Selgas, R. Serum concentrations of leptin, adiponectin and resistin, and their relationship with cardiovascular disease in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 62, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teta, D.; Maillard, M.; Halabi, G.; Burnier, M. The leptin/adiponectin ratio: Potential implications for peritoneal dialysis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2008, 73, S112–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, J.; Takahashi, H.; Kitagawa, F.; Kuno, A.; Okuyama, R.; Kawai, H.; Muramatsu, T.; Naruse, H.; Motoyama, S.; Matsui, S.; et al. Multimarker approach to risk stratification for long-term mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Circ. J. 2015, 79, 656–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Postorino, M.; Marino, C.; Pizzini, P.; Cutrupi, S.; Tripepi, G. Waist circumference modifies the relationship between the adipose tissue cytokines leptin and adiponectin and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in haemodialysis patients. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 269, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, E.M.; Shalan, M. Plasma adiponectin levels for prediction of cardiovascular risk among hemodialysis patients. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2014, 18, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacso, I.M.; Potra, A.R.; Bondor, C.I.; Moldovan, D.; Rusu, C.; Patiu, I.M.; Racasan, S.; Orasan, R.; Vladutiu, D.; Spanu, C.; et al. Adiponectin predicts cardiovascular events in diabetes dialysis patients. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).