LC-MS/MS-Based Determination and Optimization of Linoleic Acid Oxides in Baijiu and Their Variation with Storage Time
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Baijiu Samples
2.2. Reagents and Standards
2.3. Instruments and Equipment
2.4. Sample Extraction
2.5. Preparation of Standard Solution
2.6. Instrument Parameters
2.7. Method Validation
2.7.1. Linearity, LOD, and LOQ
2.7.2. Accuracy and Precision
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Detection Conditions
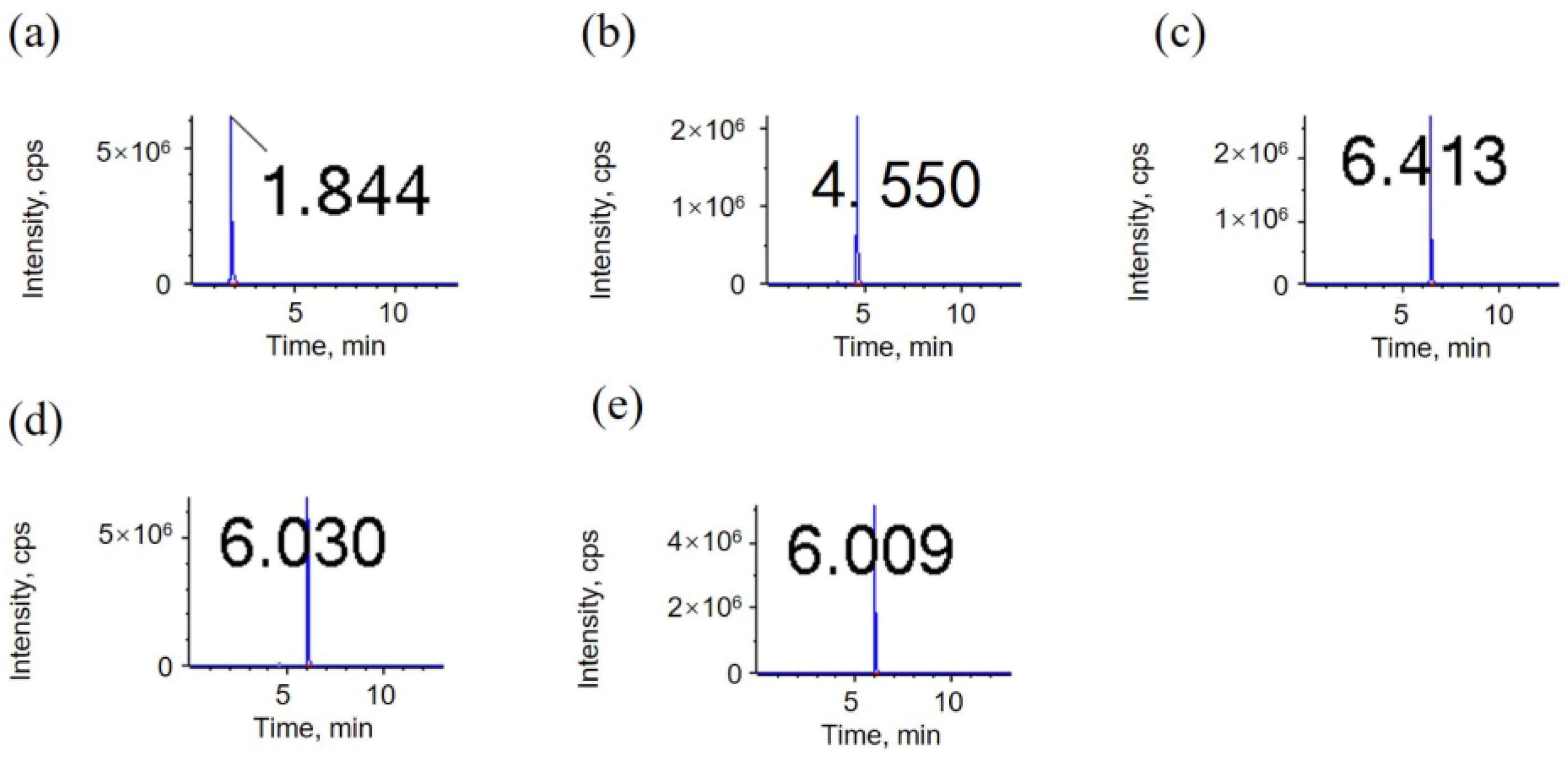
3.1.1. LC Column Selection
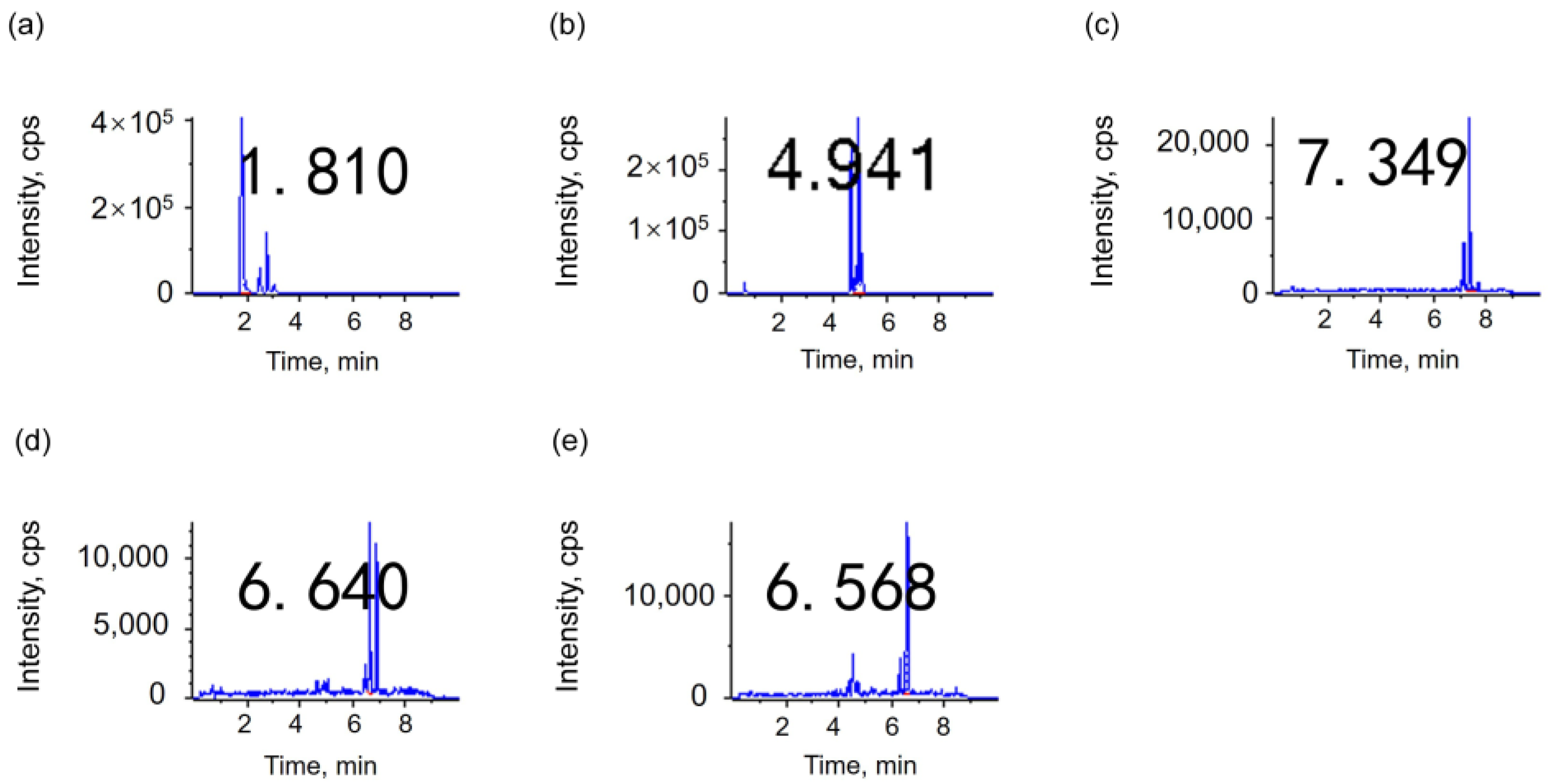
3.1.2. Optimization of Pretreatment Method
3.2. Linear Range, Detection Limit (LOD), and Quantitative Limit (LOQ)
3.3. Recovery and Intra-Day and Inter-Day Precision
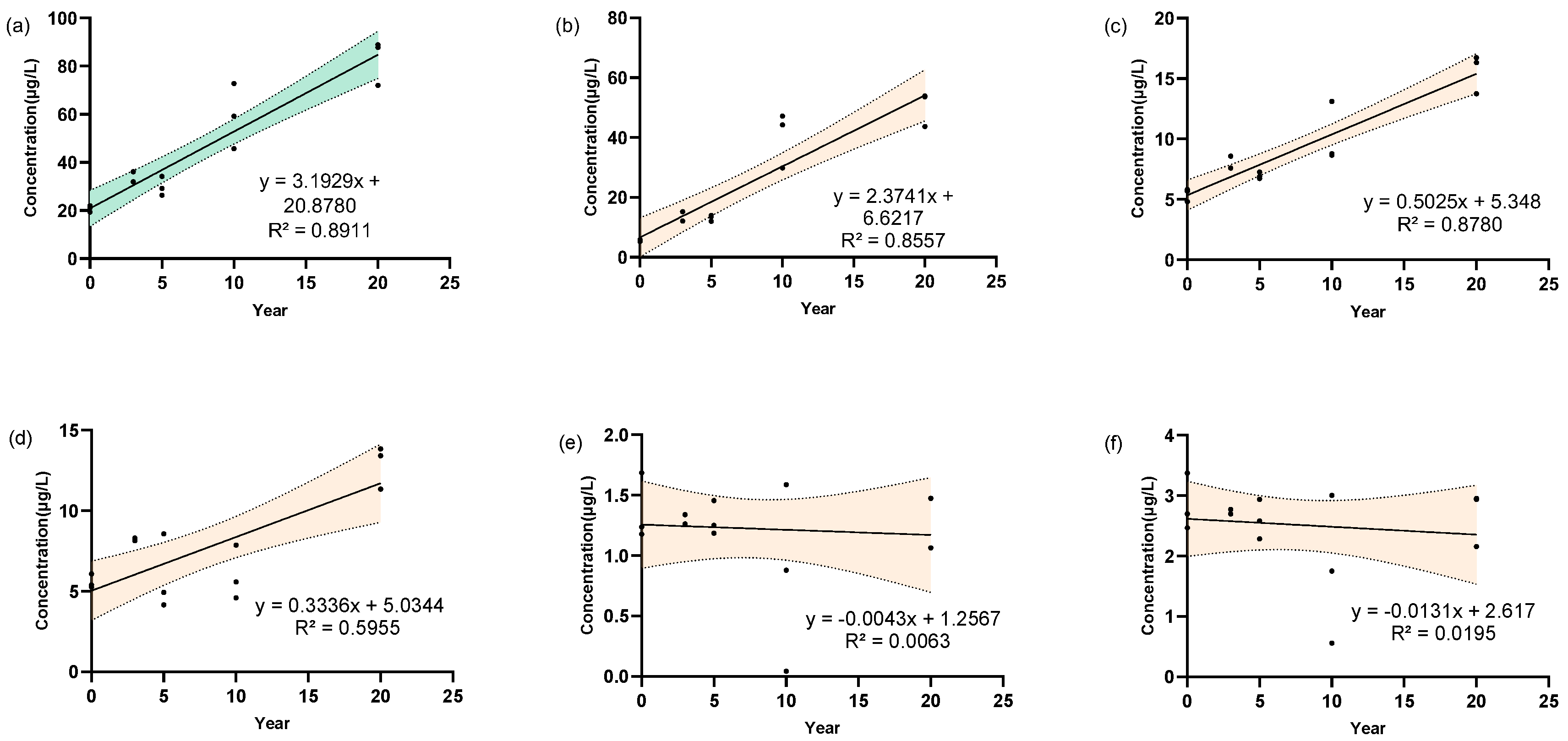
3.4. Determination of 5 Linoleic Acid Oxides in Strong-Aroma Baijiu with Different Storage Time
3.5. Determination of 5 Linoleic Acid Oxides in Light-Aroma Baijiu with Different Storage Time
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LC-MS/MS | Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatograph Mass Spectrometer |
| GC-MS | Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrometry |
| THO | 9,12,13-trihydroxy-10(E)-octadecenoic acid |
| DHO | 9,10-Dihydroxy-12-octadecenoic acid |
| OXO | 9-oxo-(10E,12Z)-octadecadienoic acid |
| 9HO | 9-hydroxy-(10E,12Z)-octadecadienoic acid |
| 13HO | 13-hydroxyoctadeca-(9Z,11E)-octadecadienoic acid |
| MRM | Multi Reaction Monitoring |
| RT | Retention Time |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| R2 | Coefficient of Determination |
| PPARs | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors γ |
| PGI2 | Prostacyclin |
References
- Madrera, R.R.; Gomis, D.B.; Alonso, J.J.M. Influence of distillation system, oak wood type, and aging time on volatile compounds of cider brandy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5709–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollihue, J.; Pook, V.G.; DeBolt, S. Sources of variation in bourbon whiskey barrels: A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2021, 127, 210–223. [Google Scholar]
- Morishima, K.; Nakamura, N.; Matsui, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Masunaga, H.; Mori, S.; Iwashita, T.; Li, X.; Shibayama, M. Formation of Clusters in Whiskies During the Maturation Process. J. Food Sci. 2018, 84, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franitza, L.; Granvogl, M.; Schieberle, P. Influence of the Production Process on the Key Aroma Compounds of Rum: From Molasses to the Spirit. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 9041–9053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Xiong, A.; Hu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, K.; Yu, Y. Elucidating oxidation-based flavour formation mechanism in the aging process of Chinese distilled spirits by electrochemistry and UPLC-Q-Orbitrap-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2021, 355, 129596. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J. Research progress of Moutai-flavor Baijiu aging. China Brew 2021, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Xiong, A.; Zhao, K.; Hu, Y.; Kuang, B.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Q. Mechanisms of the regulation of ester balance between oxidation and esterification in aged Baijiu. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Ma, R.; Hu, L.; Mo, H. Synergy of physicochemical reactions occurred during aging for harmonizing and improving flavor. Food Chem. X 2023, 17, 100554. [Google Scholar]
- Cernîşev, S. Analysis of lignin-derived phenolic compounds and their transformations in aged wine distillates. Food Control 2017, 73, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, F.; Ge, Q.; Li, C.; Gamboa, G.G.; Fang, Y.; Sun, X. Wine aging and artificial simulated wine aging: Technologies, applications, challenges, and perspectives. Food Res. Int. 2022, 153, 110953. [Google Scholar]
- Perestrelo, R.; Silva, C.; Gonçalves, C.; Castillo, M.; Câmara, J.S. An Approach of the Madeira Wine Chemistry. Beverages 2020, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Aquino, F.W.B.; Rodrigues, S.; do Nascimento, R.F.; Casimiro, A.n.R.S. Simultaneous determination of aging markers in sugar cane spirits. Food Chem. 2006, 98, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Duan, C.; Lan, Y. Investigating the Effects of Distillation System, Geographical Origin, and Aging Time on Aroma Characteristics in Brandy Using an Untargeted Metabonomic Approach. Foods 2024, 13, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, Q. 1,1-Diethoxymethane and methanethiol as age markers in Chinese roasted-sesame-like aroma and flavour type liquor. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2016, 242, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, L.; Song, X.; Jing, S.; Zheng, F.; Huang, M.; Feng, S.; La, L. Characterization of terpenoids and norisoprenoids from base and retail Qingke Baijiu by GC × GC-TOFMS and multivariate statistical analysis. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Song, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, H.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F. Evolution of the key odorants and aroma profiles in traditional Laowuzeng baijiu during its one-year ageing. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125898. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Qiao, H.; Wang, W.; Chen, T.; Du, X.; Zhai, X.; Zhang, S. Variations in Physicochemical Properties of Chinese Fenjiu During Storage and High-Gravity Technology of Liquor Aging. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 17, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, S.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Yu, Y. Effect of high pressure treatment and short term storage on changes in main volatile compounds of Chinese liquor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Du, H.; Jia, W.; Xu, Y. Compositional Differences and Similarities between Typical Chinese Baijiu and Western Liquor as Revealed by Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Hu, J.; Pan, C.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, J.; Xi, D.; Chen, M.; Lu, L.; Lu, H.; Hu, F. Effects of different storage containers on the flavor characteristics of Jiangxiangxing baijiu. Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113196. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.-W.; Han, B.-Z. Baijiu (白酒), Chinese liquor: History, classification and manufacture. J. Ethn. Foods 2016, 3, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Zhao, D.; Sun, B. Research Progress on the Profile of Trace Components in Baijiu. Food Rev. Int. 2021, 39, 1666–1693. [Google Scholar]
- Du, P.; Jiao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Dong, J.; Wang, R. Relationship between Representative Trace Components and Health Functions of Chinese Baijiu: A Review. Fermentation 2023, 9, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Cao, X.; Cheng, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, Q.; Xiang, P.; Shen, C.; Li, Q. Chinese Baijiu: The Perfect Works of Microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 919044. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Li, S.; Weiss, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Zheng, Y. Solid-state fermentation of grain sorghum to produce Chinese liquor: Effect of grain properties and fermenting culture. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 114, 103776. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, P.; Geng, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Xu, W. Recombinant Porcine 12-Lipoxygenase Catalytic Domain: Effect of Inhibitors, Selectivity of Substrates and Specificity of Oxidation Products of Linoleic Acid. Foods 2022, 11, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Chen, S.; Li, H.; Xu, Y. Determination of Linoleic Acid Oxylipins in Chinese Baijiu Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Quadruple-Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR). Anal. Lett. 2019, 52, 2165–2179. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, D.; Lopes, F.S.; do Lago, C.L. A sensitive multiresidue method for the determination of pesticides in marijuana by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1603, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Blazics, B.; Alberti, Á.; Béni, S.; Kursinszki, L.; Tölgyesi, L.; Kéry, Á. Identification and LC-MS-MS determination of acteoside, the main antioxidant compound of Euphrasia rostkoviana, using the isolated target analyte as external standard. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2011, 49, 203. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Wu, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhan, B.; Wu, P. A ng/L Level LC-MS Method Using Membrane SPE as Sampling Technology: Determination of Nine Halobenzoquinones in Potable Water. Molecules 2024, 29, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hou, J.; Hu, B.; Shao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, D. Determination of calcium β-hydroxy-β-methyl butyrate content in milk and dairy products by solid-phase extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 132, 106362. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, D. Uncover the flavor code of strong-aroma baijiu: Research progress on the revelation of aroma compounds in strong-aroma baijiu by means of modern separation technology and molecular sensory evaluation. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 109, 104499. [Google Scholar]
- Gowda, S.G.B.; Nath, L.R.; Li, Y.; Jayaprakash, J.; Gowda, D.; Hui, S.-P. Sex-specific effect of ethanol on colonic short-chain fatty acids and derivatives in the mouse model using targeted LC/MS. Med. Mass Spectrom. 2024, 8, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, E.; Wiebel, M.; Hopmann, C.; Kampschulte, N.; Schebb, N.H. Rapid quantification of fatty acids in plant oils and biological samples by LC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 5439–5451. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.; Trinh, M.; Oe, T. Measurement of plasma pristanic, phytanic and very long chain fatty acids by liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry for the diagnosis of peroxisomal disorders. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 798, 159–162. [Google Scholar]
- Takashima, S.; Toyoshi, K.; Shimozawa, N. Analyses of the fatty acid separation principle using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Med. Mass Spectrom. 2018, 2, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Siriwardane, D.A.; Wang, C.; Jiang, W.; Mudalige, T. Quantification of phospholipid degradation products in liposomal pharmaceutical formulations by ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS). Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 578, 119077. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Lee, B.S.; Lee, B.R.; Lee, D.M.; Lee, G.H. A multiresidue method for the determination of 109 pesticides in rice using the Quick Easy Cheap Effective Rugged and Safe (QuEChERS) sample preparation method and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry with temperature control and vacuum concentration. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2007, 21, 3115–3122. [Google Scholar]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.-L.; Tian, D.-W.; Yin, Y.-Y.; Jiang, L.-L.; Li, L.-L.; Zhang, E.-K.; Hu, F.; Cheng, P.-Y. Optimization and Application of Ultra-high Performance Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry for Determination of the Bitter Compound Trihydroxyoctadecenoic Acid in Chinese Baijiu. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 352–359. [Google Scholar]
- Liakh, I.; Pakiet, A.; Sledzinski, T.; Mika, A. Modern Methods of Sample Preparation for the Analysis of Oxylipins in Biological Samples. Molecules 2019, 24, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhong, S.; Shen, X.; Li, Q.; Xu, W.; Tao, Y.; Yin, H. Recent development on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of oxidized lipids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 144, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kusumoto, I.; Kato, S.; Nakagawa, K. Analysis of docosahexaenoic acid hydroperoxide isomers in mackerel using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedel, S.; Osthues, T.; Zimmer, B.; Angioni, C.; Geisslinger, G.; Sisignano, M. Oxidized linoleic acid metabolites maintain mechanical and thermal hypersensitivity during sub-chronic inflammatory pain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2022, 198, 114953. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Hu, P.; Lyu, C.; Tian, J.; Meng, X.; Tan, H.; Dong, W. Targeted Lipidomics Analysis of Oxylipids in Hazelnut Oil during Storage by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.; Yeo, J. Critical overview of mass spectrometry-based lipidomics approach for evaluating lipid oxidation in foods. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 34, 837–849. [Google Scholar]
- Camunas-Alberca, S.M.; Moran-Garrido, M.; Sáiz, J.; Villaseñor, A.; Taha, A.Y.; Barbas, C. The role of oxylipins and their validation as biomarkers in the clinical context. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 164, 117065. [Google Scholar]
- Nayeem, M.A. Role of oxylipins in cardiovascular diseases. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, D.; Tang, X.; Johnsson, A.-K.; Dahlén, S.-E.; Hamberg, M.; Wheelock, C.E. Eosinophils synthesize trihydroxyoctadecenoic acids (TriHOMEs) via a 15-lipoxygenase dependent process. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158611. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, H.; Kim, Y.-I.; Hirai, S.; Goto, T.; Ohyane, C.; Tsugane, T.; Konishi, C.; Fujii, T.; Inai, S.; Iijima, Y.; et al. Comparative and Stability Analyses of 9- and 13-Oxo-octadecadienoic Acids in Various Species of Tomato. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar]
- Setty, B.Y.; Berger, M.; Stuart, M.J. 13-Hydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (13-HODE) stimulates prostacyclin production by endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 146, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Geng, Z.; Zhang, M.; Sun, C.; Bian, H.; Wang, D.; Xu, W. Progress in research on hydroxyoctadecaenoic acids as oxidation products of linoleic acid. Food Sci. 2018, 39, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Buchowski, M.; Nieman, D.C.; Scherr, J.; Luo, B.; Meaney, M.P.; Dréau, D.; Sha, W.; Dew, D.A.; Henson, D.A.; Pappan, K.L. Influence of Pistachios on Performance and Exercise-Induced Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, Immune Dysfunction, and Metabolite Shifts in Cyclists: A Randomized, Crossover Trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113725. [Google Scholar]


| Compounds | Abbreviation | Short Abbreviation | CAS Number | Chemical Structure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9,12,13-trihydroxy-10(E)-octadecenoic acid | 9,12,13-TriHOME | THO | 97134-11-7 |  |
| 9,10-Dihydroxy-12-octadecenoic acid | 9,10-DiHOME | DHO | 263399-34-4 |  |
| 9-oxo-(10E,12Z)-octadecadienoic acid | 9-OxoODE | OXO | 54232-59-6 |  |
| 9-hydroxy-(10E,12Z)-octadecadienoic acid | 9-HODE | 9HO | 98524-19-7 | 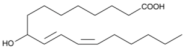 |
| 13-hydroxyoctadeca-(9Z,11E)-octadecadienoic acid | 13-HODE | 13HO | 73804-64-5 | 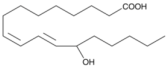 |
| Compounds | Ionization Mode | Q1 a | Q3 b | Ion ratio | Dwell Time | DP c | CE d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THO | Negative | 329.2 | 211 | 1.41 | 1.79 | −120.000 | −31.000 |
| DHO | Negative | 313.2 | 171 | 1.18 | 4.48 | −120.000 | −31.000 |
| OXO | Negative | 293.2 | 185 | 2.81 | 6.36 | −120.000 | −27.000 |
| 9HO | Negative | 295.2 | 171 | 1.71 | 5.97 | −120.000 | −24.000 |
| 13HO | Negative | 295.2 | 195 | 2.08 | 5.95 | −120.000 | −26.000 |
| Columns | THO | DHO | OXO | 9HO | 13HO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8 | 1.84 | 4.63 | 6.50 | 6.01 | 6.01 |
| C18 | 1.81 | 5.04 | 7.35 | 6.64 | 6.57 |
| Pretreatments | THO | DHO | OXO | 9HO | 13HO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Directly dilute | 210.15 | 242.65 | 27.935 | 1.521 | 11.735 |
| Vacuum concentration | 175.15 | 53.65 | 17.215 | 0.2583 | 1.4785 |
| Compounds | Linear Range (ppb) | Calibration Curve | R2 a | LOD b (ppb) | LOQ c (ppb) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THO | 1–100 | y = 40,411.6x + 13,072.6 | 0.9995 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| DHO | 1–100 | y = 77,417.3x + 15,682.2 | 0.9994 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| OXO | 1–100 | y = 11,560.3x + 7910.8 | 0.9995 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| 9HO | 1–100 | y = 31,758.4x + 25,882.0 | 0.9990 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| 13HO | 1–100 | y = 20,198.3x + 19,326.5 | 0.9993 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| Compounds | Recovery (%) | Average Recovery (%) | Intra-Day RSD d (%) | Inter-Day RSD (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low a | Middle b | High c | Low | Middle | High | Low | Middle | High | Low | Middle | High | |
| THO | 88.13~92.70 | 105.09~108.88 | 105.05~107.86 | 90.12 | 106.91 | 106.71 | 2.01 | 1.42 | 1.01 | 3.60 | 2.47 | 1.04 |
| DHO | 97.93~118.63 | 112.23~117.21 | 109.95~117.85 | 111.91 | 115.03 | 115.14 | 6.66 | 1.42 | 2.72 | 6.96 | 2.13 | 0.50 |
| OXO | 80.51~85.32 | 100.51~107.85 | 107.43~118.14 | 83.19 | 104.49 | 112.89 | 0.55 | 1.24 | 2.95 | 0.63 | 1.71 | 0.90 |
| 9HO | 108.07~119.92 | 106.81~109.73 | 105.02~109.96 | 115.01 | 108.29 | 108.16 | 3.00 | 0.89 | 1.46 | 4.03 | 0.45 | 0.82 |
| 13HO | 94.03~97.93 | 118.29~119.44 | 108.11~112.38 | 95.60 | 118.79 | 110.39 | 1.65 | 0.39 | 1.77 | 6.75 | 0.43 | 4.76 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, C.; Zhuang, X.; Li, Z.; Zou, Y.; Pu, J.; Wang, D.; Xu, Y. LC-MS/MS-Based Determination and Optimization of Linoleic Acid Oxides in Baijiu and Their Variation with Storage Time. Metabolites 2025, 15, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040246
Fang C, Zhuang X, Li Z, Zou Y, Pu J, Wang D, Xu Y. LC-MS/MS-Based Determination and Optimization of Linoleic Acid Oxides in Baijiu and Their Variation with Storage Time. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040246
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Cheng, Xiaotong Zhuang, Zhanguo Li, Yongfang Zou, Jizhou Pu, Dong Wang, and Yan Xu. 2025. "LC-MS/MS-Based Determination and Optimization of Linoleic Acid Oxides in Baijiu and Their Variation with Storage Time" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040246
APA StyleFang, C., Zhuang, X., Li, Z., Zou, Y., Pu, J., Wang, D., & Xu, Y. (2025). LC-MS/MS-Based Determination and Optimization of Linoleic Acid Oxides in Baijiu and Their Variation with Storage Time. Metabolites, 15(4), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040246








