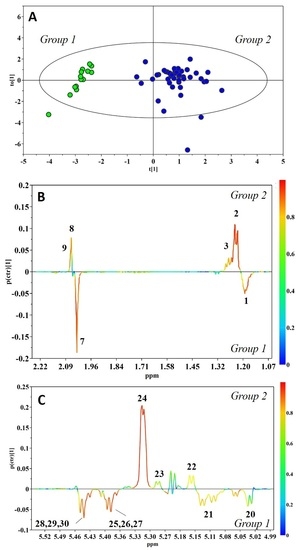
Metabolomics of Breast Milk: The Importance of Phenotypes
Abstract
Share and Cite
Dessì, A.; Briana, D.; Corbu, S.; Gavrili, S.; Cesare Marincola, F.; Georgantzi, S.; Pintus, R.; Fanos, V.; Malamitsi-Puchner, A. Metabolomics of Breast Milk: The Importance of Phenotypes. Metabolites 2018, 8, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040079
Dessì A, Briana D, Corbu S, Gavrili S, Cesare Marincola F, Georgantzi S, Pintus R, Fanos V, Malamitsi-Puchner A. Metabolomics of Breast Milk: The Importance of Phenotypes. Metabolites. 2018; 8(4):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040079
Chicago/Turabian StyleDessì, Angelica, Despina Briana, Sara Corbu, Stavroula Gavrili, Flaminia Cesare Marincola, Sofia Georgantzi, Roberta Pintus, Vassilios Fanos, and Ariadne Malamitsi-Puchner. 2018. "Metabolomics of Breast Milk: The Importance of Phenotypes" Metabolites 8, no. 4: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040079
APA StyleDessì, A., Briana, D., Corbu, S., Gavrili, S., Cesare Marincola, F., Georgantzi, S., Pintus, R., Fanos, V., & Malamitsi-Puchner, A. (2018). Metabolomics of Breast Milk: The Importance of Phenotypes. Metabolites, 8(4), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo8040079