NMR-Metabolomics Shows That BolA Is an Important Modulator of Salmonella Typhimurium Metabolic Processes under Virulence Conditions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
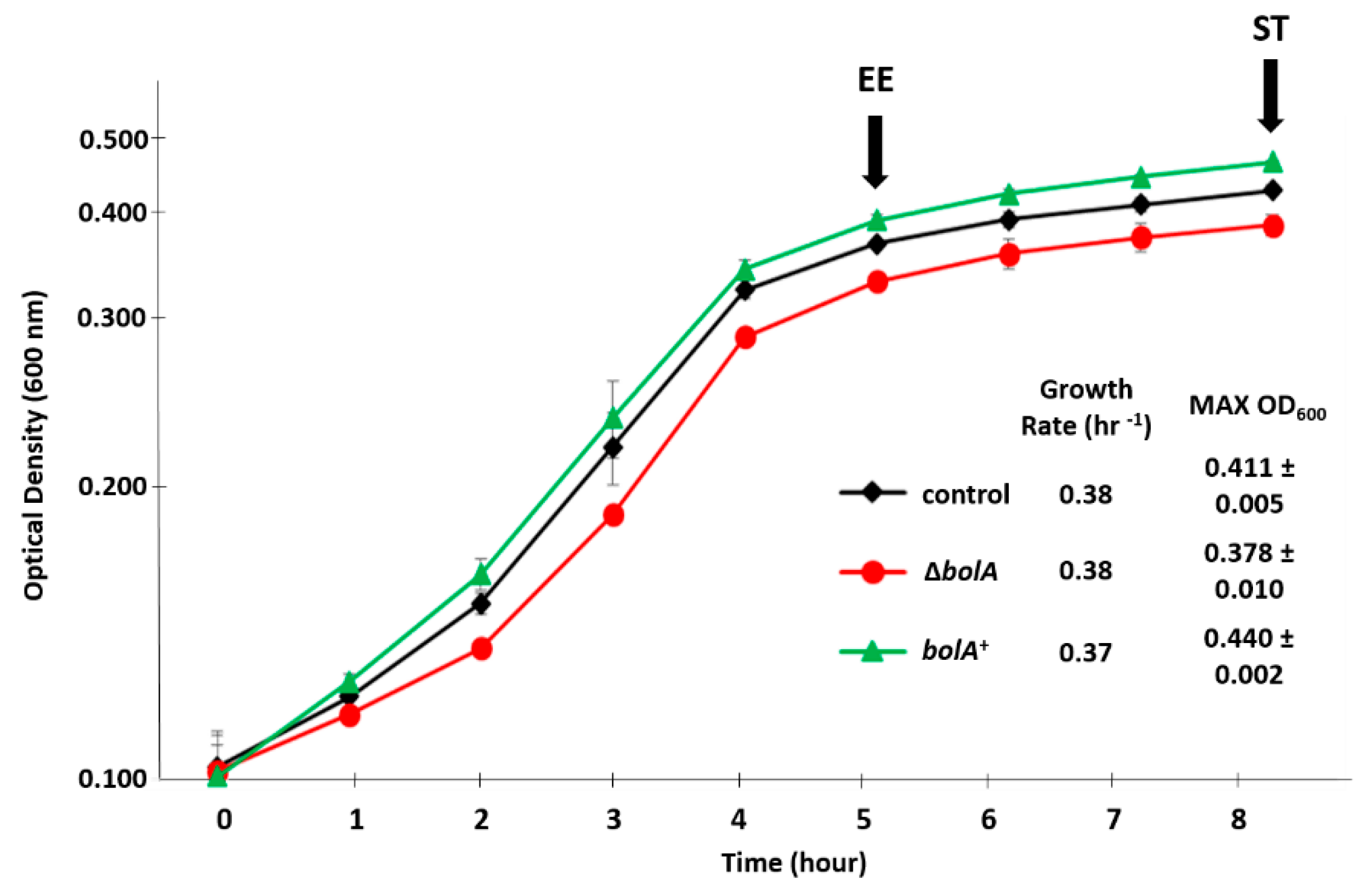
2.1. Influence of BolA on the Growth of Salmonella Typhimurium in a Virulence-Inducing Medium
2.2. 1H-NMR Metabolic Profiles of Salmonella Strains
2.3. Multivariate and Univariate Analysis of 1H-NMR Data
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Plasmids
4.2. Growth Conditions
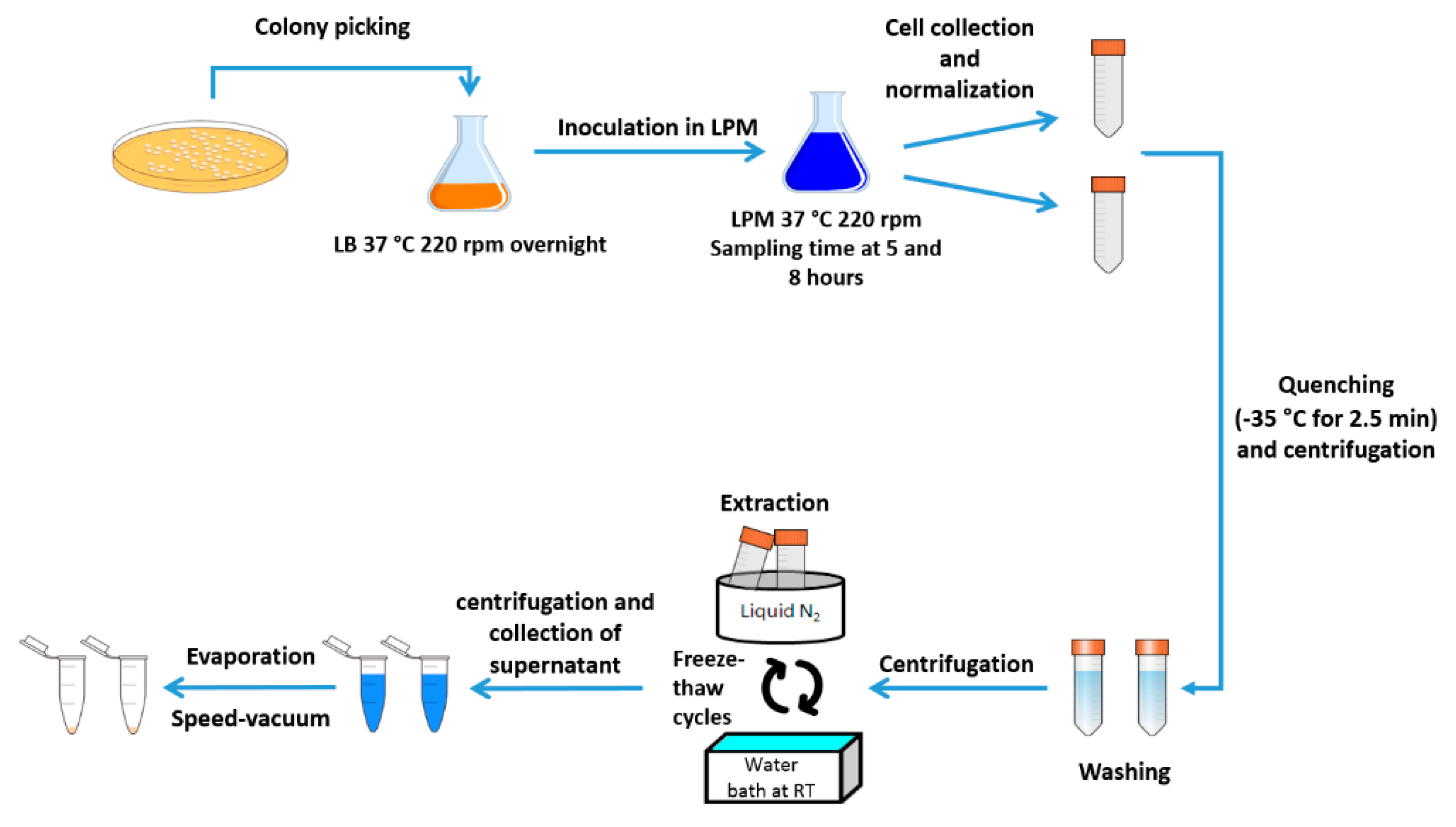
4.3. Sample Preparation for Metabolomics Analysis (NMR)
4.4. NMR Acquisition
4.5. H NMR Data Analysis
4.6. Microscopy Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Data Availability Statement
References
- Gulig, P.A.; Curtiss, R. Plasmid-associated virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Infect. Immun. 1987, 55, 2891–2901. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hendriksen, R.S.; Vieira, A.R.; Karlsmose, S.; Lo Fo Wong, D.M.A.; Jensen, A.B.; Wegener, H.C.; Aarestrup, F.M. Global monitoring of Salmonella serovar distribution from the World Health Organization Global Foodborne Infections Network Country Data Bank: Results of quality assured laboratories from 2001 to 2007. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2011, 8, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, K.Y.; Finlay, B.B. Intracellular replication is essential for the virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11470–11474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele-Mortimer, O.; Brumell, J.H.; Knodler, L.A.; Méresse, S.; Lopez, A.; Finlay, B.B. The invasion-associated type III secretion system of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium is necessary for intracellular proliferation and vacuole biogenesis in epithelial cells. Cell. Microbiol. 2002, 4, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brawn, L.C.; Hayward, R.D.; Koronakis, V. Salmonella SPI1 Effector SipA Persists after Entry and Cooperates with a SPI2 Effector to Regulate Phagosome Maturation and Intracellular Replication. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 1, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, V.; Hwang, C.; Lee, C.A. hilA is a novel ompR/toxR family member that activates the expression of Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes. Mol. Microbiol. 1995, 18, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaniga, K.; Bossio, J.C.; Galán, J.E. The Salmonella typhimurium invasion genes invF and invG encode homologues of the AraC and PulD family of proteins. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmendia, J.; Beuzón, C.R.; Ruiz-Albert, J.; Holden, D.W. The roles of SsrA-SsrB and OmpR-EnvZ in the regulation of genes encoding the Salmonella typhimurium SPI-2 type III secretion system. Microbiology 2003, 149, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, T.; Inoue, M.; Koshiba, S.; Yabuki, T.; Aoki, M.; Nunokawa, E.; Seki, E.; Matsuda, T.; Matsuda, N.; Tomo, Y.; et al. Solution structure of a BolA-like protein from Mus musculus. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynen, M.A.; Spronk, C.A.E.M.; Gabaldón, T.; Snel, B. Combining data from genomes, Y2H and 3D structure indicates that BolA is a reductase interacting with a glutaredoxin. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldea, M.; Hernández-Chico, C.; de la Campa, A.G.; Kushner, S.R.; Vicente, M. Identification, cloning, and expression of bolA, an ftsZ-dependent morphogene of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 5169–5176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aldea, M.; Garrido, T.; Hernández-Chico, C.; Vicente, M.; Kushner, S.R. Induction of a growth-phase-dependent promoter triggers transcription of bolA, an Escherichia coli morphogene. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3923–3931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.M.; Freire, P.; Vicente, M.; Arraiano, C.M. The stationary-phase morphogene bolA from Escherichia coli is induced by stress during early stages of growth. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 32, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Freire, P.; Vieira, H.L.A.; Furtado, A.R.; de Pedro, M.A.; Arraiano, C.M. Effect of the morphogene bolA on the permeability of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 260, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, H.L.A.; Freire, P.; Arraiano, C.M. Effect of Escherichia coli morphogene bolA on biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 5682–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, R.N.; Dressaire, C.; Barahona, S.; Galego, L.; Kaever, V.; Jenal, U.; Arraiano, C.M. BolA Is Required for the Accurate Regulation of c-di-GMP, a Central Player in Biofilm Formation. mBio 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mil-Homens, D.; Barahona, S.; Moreira, R.N.; Silva, I.J.; Pinto, S.N.; Fialho, A.M.; Arraiano, C.M. Stress Response Protein BolA Influences Fitness and Promotes Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Virulence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Outten, C.E. Monothiol CGFS glutaredoxins and BolA-like proteins: [2Fe-2S] binding partners in iron homeostasis. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 4377–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumánovics, A.; Chen, O.S.; Li, L.; Bagley, D.; Adkins, E.M.; Lin, H.; Dingra, N.N.; Outten, C.E.; Keller, G.; Winge, D.; et al. Identification of FRA1 and FRA2 as genes involved in regulating the yeast iron regulon in response to decreased mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 10276–10286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzarska, M.A.; Nasta, V.; Weiler, B.D.; Spantgar, F.; Ciofi-Baffoni, S.; Saviello, M.R.; Gonnelli, L.; Mühlenhoff, U.; Banci, L.; Lill, R. Mitochondrial Bol1 and Bol3 function as assembly factors for specific iron-sulfur proteins. Elife 2016, 5, e16673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banci, L.; Camponeschi, F.; Ciofi-Baffoni, S.; Muzzioli, R. Elucidating the Molecular Function of Human BOLA2 in GRX3-Dependent Anamorsin Maturation Pathway. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 16133–16143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuttle, X.; Giannuzzi, G.; Duyzend, M.H.; Schraiber, J.G.; Narvaiza, I.; Sudmant, P.H.; Penn, O.; Chiatante, G.; Malig, M.; Huddleston, J.; et al. Emergence of a Homo sapiens-specific gene family and chromosome 16p11.2 CNV susceptibility. Nature 2016, 536, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeung, N.; Gold, B.; Liu, N.L.; Prathapam, R.; Sterling, H.J.; Willams, E.R.; Butland, G. The E. coli monothiol glutaredoxin GrxD forms homodimeric and heterodimeric FeS cluster containing complexes. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 8957–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Mapolelo, D.T.; Randeniya, S.; Johnson, M.K.; Outten, C.E. Human glutaredoxin 3 forms [2Fe-2S]-bridged complexes with human BolA2. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, J.; Wu, H.-C.; Dhalleine, T.; Pégeot, H.; Sudre, D.; Gualberto, J.M.; Jacquot, J.-P.; Gaymard, F.; Vignols, F.; Rouhier, N. Monothiol glutaredoxin-BolA interactions: Redox control of Arabidopsis thaliana BolA2 and SufE1. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinote, I.B.; Moreira, R.N.; Freire, P.; Arraiano, C.M. Characterization of the BolA homolog IbaG: A new gene involved in acid resistance. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlouhy, A.C.; Li, H.; Albetel, A.-N.; Zhang, B.; Mapolelo, D.T.; Randeniya, S.; Holland, A.A.; Johnson, M.K.; Outten, C.E. The Escherichia coli BolA Protein IbaG Forms a Histidine-Ligated [2Fe-2S]-Bridged Complex with Grx4. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 6869–6879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J. Microbial Metabolomics. Curr. Genom. 2011, 12, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, A.P.; Weljie, A.M.; Apel, D.; Zhang, P.; Shaykhutdinov, R.; Vogel, H.J.; Surette, M.G. A Global Metabolic Shift Is Linked to Salmonella Multicellular Development. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.S.; Maker, G.L.; Trengove, R.D.; O’Handley, R.M. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium differentiates between biofilm and planktonic phenotypes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Bean, H.D.; Kuo, Y.-M.; Hill, J.E. Fast detection of volatile organic compounds from bacterial cultures by secondary electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4426–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gutierrez, E.; Chidlaw, A.C.; Le Gall, G.; Bowden, S.D.; Tedin, K.; Kelly, D.J.; Thompson, A. A Comparison of the ATP Generating Pathways Used by S. Typhimurium to Fuel Replication within Human and Murine Macrophage and Epithelial Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Schmidt, B.J.; Kidwai, A.S.; Jones, M.B.; Deatherage Kaiser, B.L.; Brewer, H.M.; Mitchell, H.D.; Palsson, B.O.; McDermott, J.E.; Heffron, F.; et al. Salmonella modulates metabolism during growth under conditions that induce expression of virulence genes. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vollmer, W.; Blanot, D.; de Pedro, M.A. Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bulmer, D.M.; Kharraz, L.; Grant, A.J.; Dean, P.; Morgan, F.J.E.; Karavolos, M.H.; Doble, A.C.; McGhie, E.J.; Koronakis, V.; Daniel, R.A.; et al. The bacterial cytoskeleton modulates motility, type 3 secretion, and colonization in Salmonella. PLoS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, P.; Moreira, R.N.; Arraiano, C.M. BolA inhibits cell elongation and regulates MreB expression levels. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.; Oh, D.-C.; Cava, F.; Takacs, C.N.; Clardy, J.; de Pedro, M.A.; Waldor, M.K. D-amino acids govern stationary phase cell wall remodeling in bacteria. Science 2009, 325, 1552–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressaire, C.; Moreira, R.N.; Barahona, S.; Alves de Matos, A.P.; Arraiano, C.M. BolA is a transcriptional switch that turns off motility and turns on biofilm development. mBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawhon, S.D.; Maurer, R.; Suyemoto, M.; Altier, C. Intestinal short-chain fatty acids alter Salmonella typhimurium invasion gene expression and virulence through BarA/SirA. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 46, 1451–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausler, N.; Browning, J.; Merritt, M.; Storey, C.; Milde, A.; Jeffrey, F.M.H.; Sherry, A.D.; Malloy, C.R.; Burgess, S.C. Effects of insulin and cytosolic redox state on glucose production pathways in the isolated perfused mouse liver measured by integrated 2H and 13C NMR. Biochem. J. 2006, 394, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLaggan, D.; Logan, T.M.; Lynn, D.G.; Epstein, W. Involvement of gamma-glutamyl peptides in osmoadaptation of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 3631–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Masip, L.; Veeravalli, K.; Georgiou, G. The many faces of glutathione in bacteria. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2006, 8, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorgersen, M.P.; Downs, D.M. Analysis of yggX and gshA Mutants Provides Insights into the Labile Iron Pool in Salmonella enterica. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 7608–7613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iyer, R.; Delcour, A.H. Complex inhibition of OmpF and OmpC bacterial porins by polyamines. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18595–18601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinel, I.C.; Guerra, P.R.; Jelsbak, L. Multiple roles of putrescine and spermidine in stress resistance and virulence of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 95, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mastroeni, P.; Vazquez-Torres, A.; Fang, F.C.; Xu, Y.; Khan, S.; Hormaeche, C.E.; Dougan, G. Antimicrobial actions of the NADPH phagocyte oxidase and inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimental salmonellosis. II. Effects on microbial proliferation and host survival in vivo. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelsbak, L.; Thomsen, L.E.; Wallrodt, I.; Jensen, P.R.; Olsen, J.E. Polyamines are required for virulence in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoiseth, S.K.; Stocker, B.A. Aromatic-dependent Salmonella typhimurium are non-virulent and effective as live vaccines. Nature 1981, 291, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maifiah, M.H.M.; Creek, D.J.; Nation, R.L.; Forrest, A.; Tsuji, B.T.; Velkov, T.; Li, J. Untargeted metabolomics analysis reveals key pathways responsible for the synergistic killing of colistin and doripenem combination against Acinetobacter baumannii. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graça-Lopes, G.; Graça, G.; Barahona, S.; N. Moreira, R.; M. Arraiano, C.; G. Gonçalves, L. NMR-Metabolomics Shows That BolA Is an Important Modulator of Salmonella Typhimurium Metabolic Processes under Virulence Conditions. Metabolites 2019, 9, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110243
Graça-Lopes G, Graça G, Barahona S, N. Moreira R, M. Arraiano C, G. Gonçalves L. NMR-Metabolomics Shows That BolA Is an Important Modulator of Salmonella Typhimurium Metabolic Processes under Virulence Conditions. Metabolites. 2019; 9(11):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110243
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraça-Lopes, Gil, Gonçalo Graça, Susana Barahona, Ricardo N. Moreira, Cecília M. Arraiano, and Luís G. Gonçalves. 2019. "NMR-Metabolomics Shows That BolA Is an Important Modulator of Salmonella Typhimurium Metabolic Processes under Virulence Conditions" Metabolites 9, no. 11: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110243
APA StyleGraça-Lopes, G., Graça, G., Barahona, S., N. Moreira, R., M. Arraiano, C., & G. Gonçalves, L. (2019). NMR-Metabolomics Shows That BolA Is an Important Modulator of Salmonella Typhimurium Metabolic Processes under Virulence Conditions. Metabolites, 9(11), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9110243




