MetPC: Metabolite Pipeline Consisting of Metabolite Identification and Biomarker Discovery Under the Control of Two-Dimensional FDR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
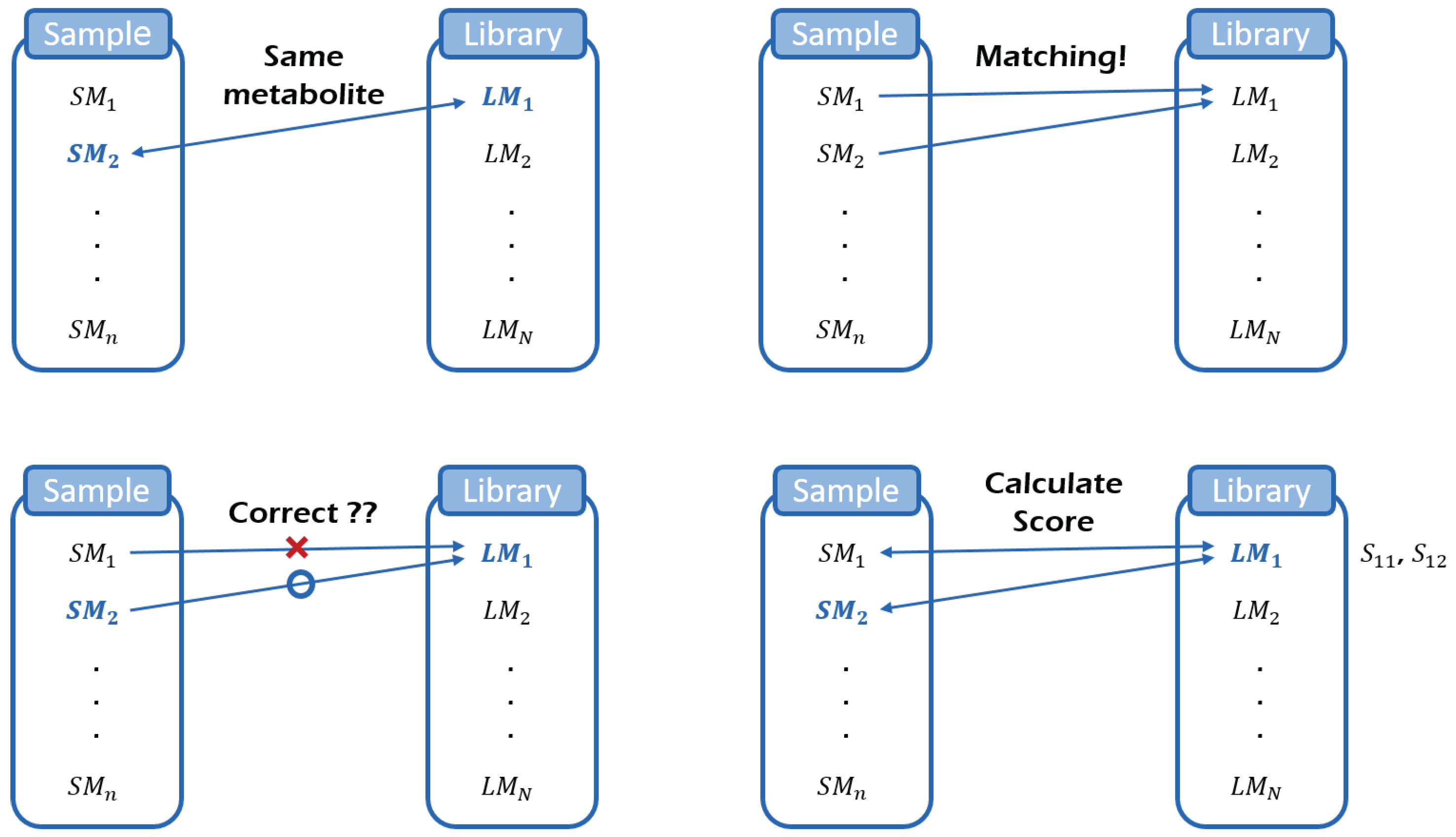
2.1. Metabolite Identification by a Hierarchical Statistical Model
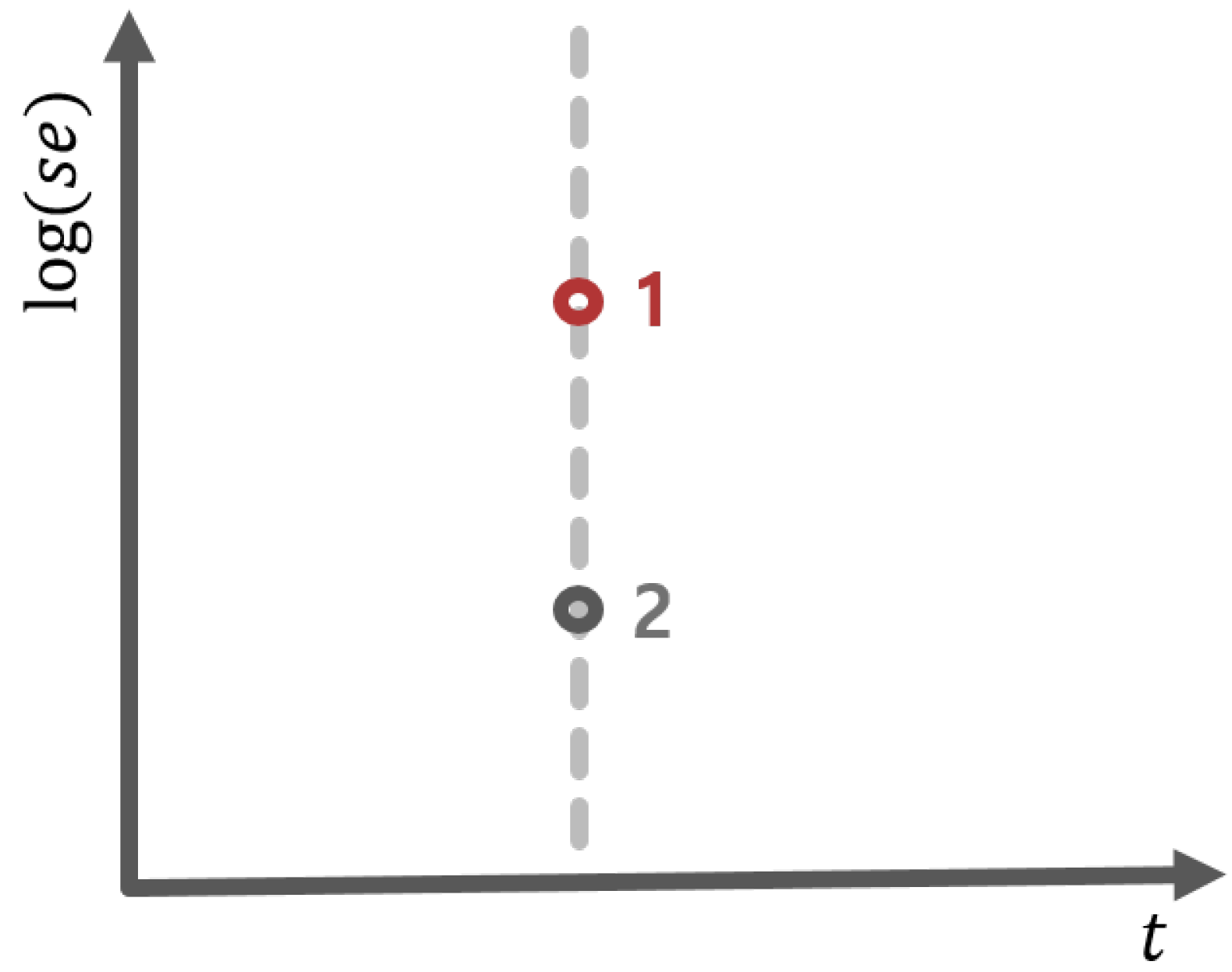
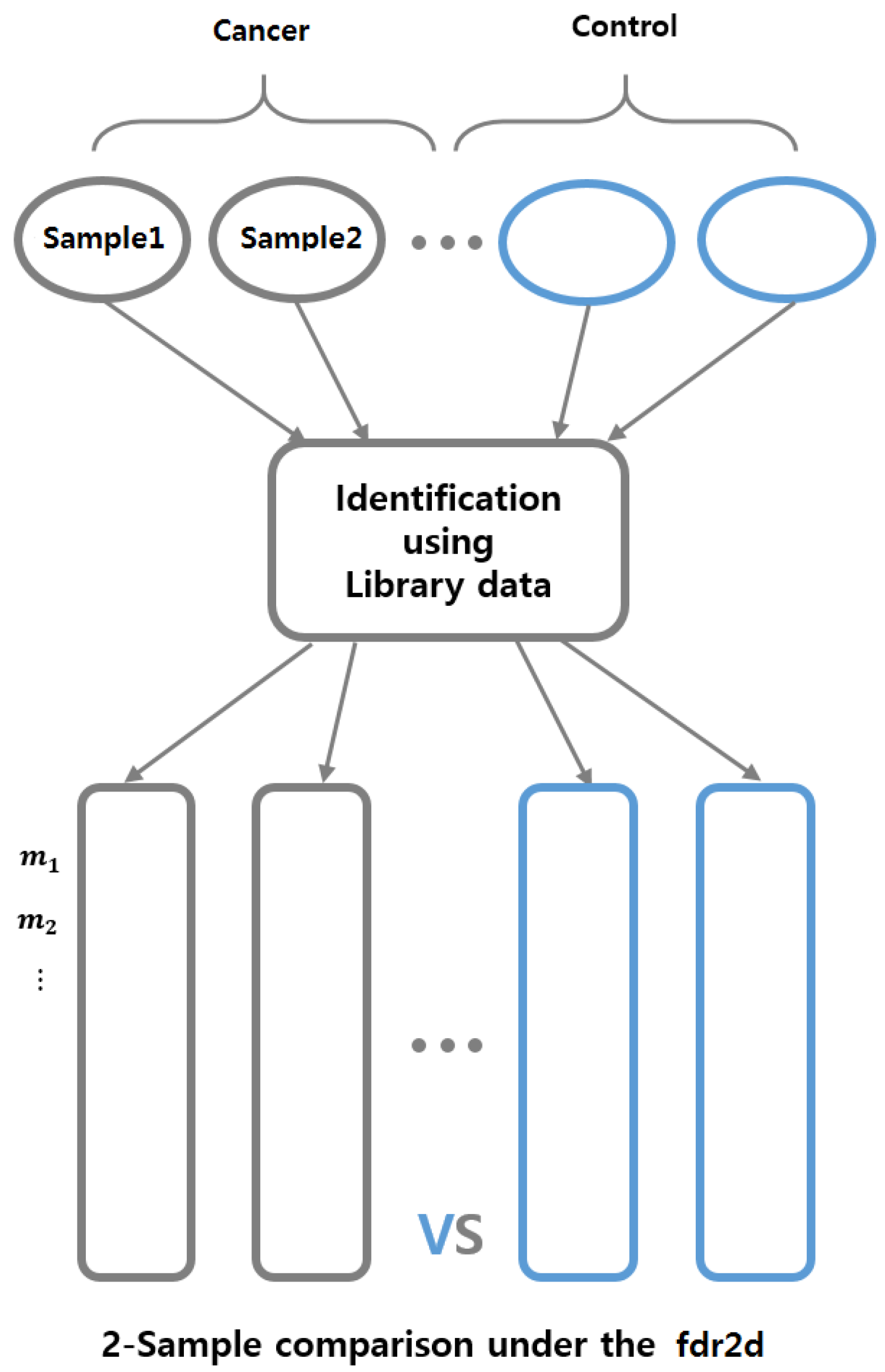
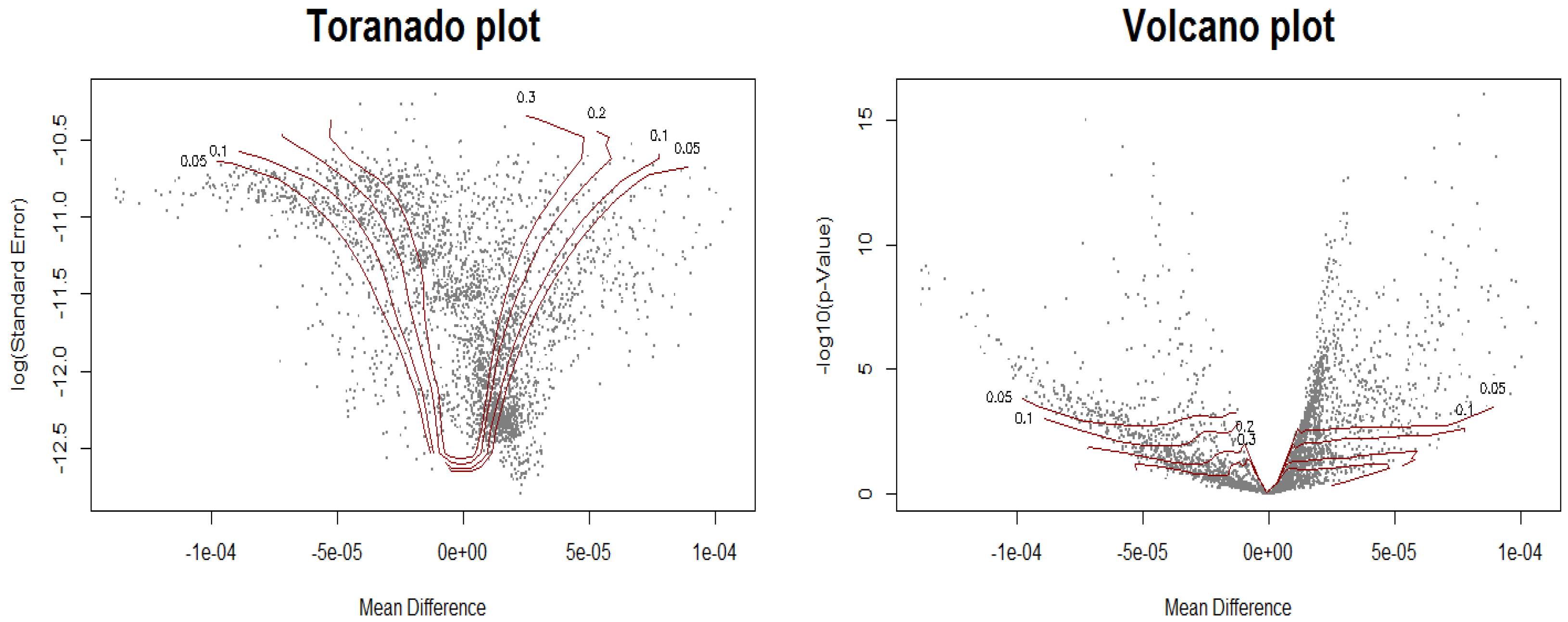
2.2. Biomarker Discovery Under the Control of Two-Dimensional FDR
2.3. Software Implementation
2.3.1. Two Major Goals
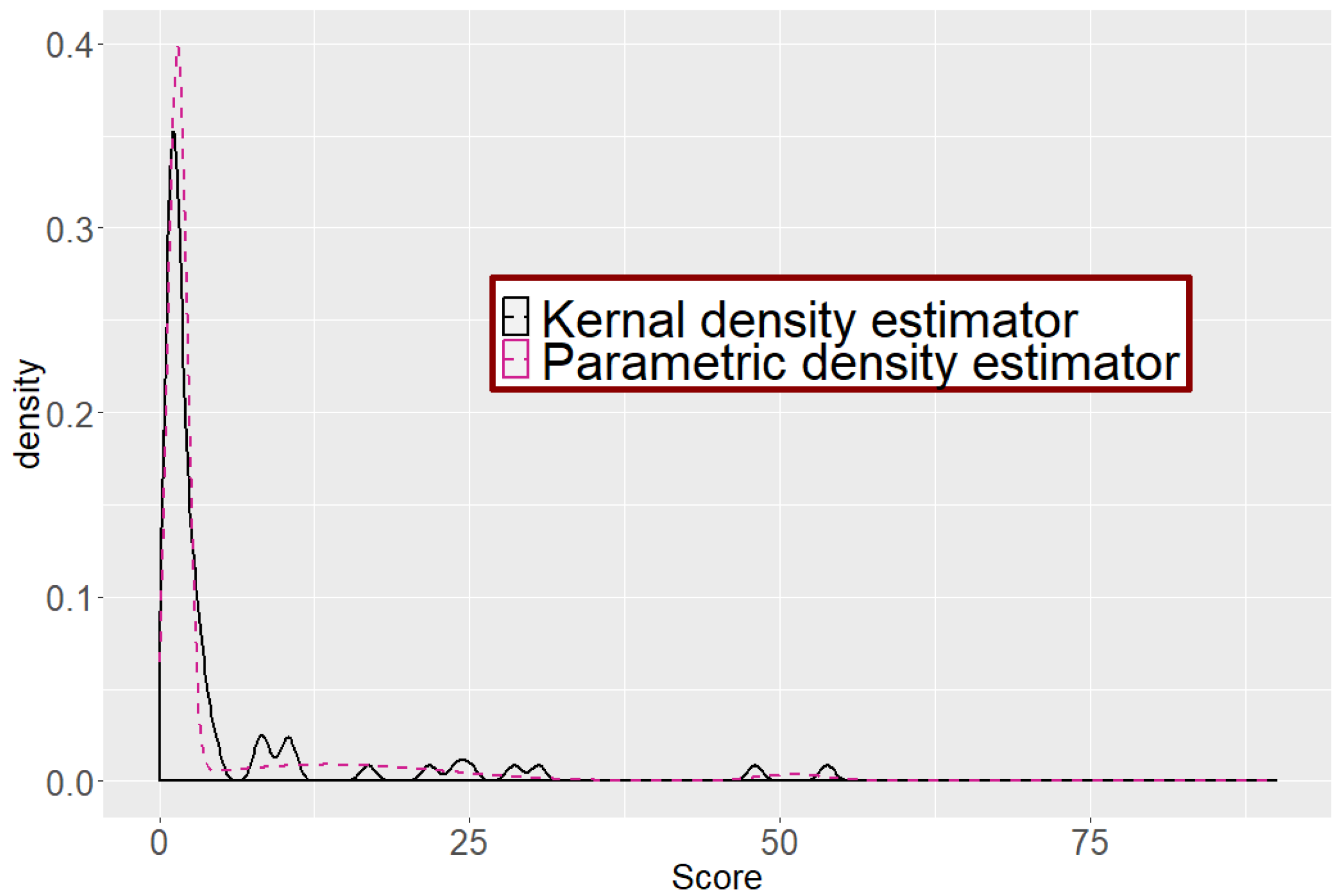
2.3.2. Kernel Density Estimator
3. Results
3.1. Identification
3.1.1. Data
3.1.2. Identification Results
3.2. Real Data Anlaysis
3.2.1. Schisandra Data
3.2.2. Biomarker Discovery
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FDR | false discovery rate |
| fdr2d | two-dimensional local false discovery rate |
| EM | Expectation-Maximization |
References
- Jeong, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Kim, S.; Shen, C. An empirical Bayes model using a competition score for metabolite identification in gas chromatography mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinformat. 2011, 12, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.F.; Zhou, B.; Ressom, H.W. Metabolite identification and quantification in LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Kim, S.; Shen, C. Model-based peak alignment of metabolomic profiling from comprehensive two dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry. BMC Bioinformat. 2012, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Kim, S.; Shen, C. An efficient post-hoc integration method improving peak alignment of metabolomics data from GCxGC/TOF-MS. BMC Bioinformat. 2013, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Fang, A.; Wang, B.; Jeong, J.; Zhang, X. An optimal peak alignment for comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry using mixture similarity measure. Bioinformat. 2011, 27, 1660–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Koo, I.; Fang, A.; Zhang, X. Smith-Waterman peak alignment for comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography mass spectromety. BMC Bioinformat. 2011, 12, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, K.M.; Wood, L.F.; Wright, B.W.; Synovec, R.E. A comprehensive two-dimensional retention time alignment algorithm to enhance chemometric analysis of comprehensive two-dimensional separation data. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 7735–7743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Fang, A.; Heim, J.; Bogdanov, B.; Pugh, S.; Libardoni, M.; Zhang, X. DISCO: Distance and spectrum correlation optimization alignment for two-dimensional gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5069–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R. Empirical Bayes Method and False Discovery Rates for Microarrays. Gene Epidem. 2002, 23, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploner, A.; Calza, S.; Gusnanto, A.; Pawitan, Y. Multidimensional local false discovery rate for micorarray studies. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lim, J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, J. Controlling two-dimensional false discovery rates by combining two univariate multiple testing results with an application to mass spectromety data. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2018, 182, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tautenhahn, R.; Patti, G.; Renehart, D.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS Online: A web-based platform to process untargeted metabolomic data. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5035–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Sun, W.; Shi, X.; Koo, I.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X.; Tang, Y.; Bogdanov, B.; Kim, S.; et al. MetSign: A computational platform for high-resolution mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7668–7675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Tarcea, V.G.; Karnovsky, A.; Mirel, B.; Weymouth, T.E.; Beecher, C.W.; Cavalcoli, J.D.; Athey, B.D.; Omenn, G.S.; Burant, C.F.; et al. Metscape: A cytoscape plug-in for visualizing and interpreting metabolomic data in the context of human metabolic networks. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 971–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamburov, A.; Cavill, R.; Ebbels, T.; Herwig, R.; Keun, H.C.; Notes, A. Integrated pathway-level analysis of transcriptomics and metabolomcs data with IMPaLA. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2917–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottret, L.; Wildridge, D.; Vinson, F.; Barrett, M.; Charles, H.; Sagot, M.; Jourdan, F. MetExplore: A web server to link metabolomic experiments and genome-scale metabolic networks. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Wishart, D.S. MetPA: A web-based metabolomics tool for pathway analysis and visulalization. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2342–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR 2.0: From raw spectra to biological insights. Metabolites 2019, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Catillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Oresic, M. MZmine2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectromety-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinformat. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. Recent trends in the metabolomics. BRIC View 2015, 2015, T09. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B.; Tibshirani, R.; Storey, J.; Tusher, V. Empirical Bayes analysis of a microarray experiment. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2001, 96, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, W.J.; Kim, S.C.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.W. Classification of spectral data using fused lasso logistic regression. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2015, 142, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Sample Availability: All samples used and the current version of the tool are now available at the github website (https://github.com/jjs3098/CNU-Bioinformatics-Lab). |



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Jeong, J. MetPC: Metabolite Pipeline Consisting of Metabolite Identification and Biomarker Discovery Under the Control of Two-Dimensional FDR. Metabolites 2019, 9, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050103
Kim J, Jeong J. MetPC: Metabolite Pipeline Consisting of Metabolite Identification and Biomarker Discovery Under the Control of Two-Dimensional FDR. Metabolites. 2019; 9(5):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050103
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jaehwi, and Jaesik Jeong. 2019. "MetPC: Metabolite Pipeline Consisting of Metabolite Identification and Biomarker Discovery Under the Control of Two-Dimensional FDR" Metabolites 9, no. 5: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050103
APA StyleKim, J., & Jeong, J. (2019). MetPC: Metabolite Pipeline Consisting of Metabolite Identification and Biomarker Discovery Under the Control of Two-Dimensional FDR. Metabolites, 9(5), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo9050103



