Running Vacuum and H4 Inflation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Vacuum Energy and Cosmological Constant
3. Energy–Momentum Tensor and Effective Action for a Nonminimally Coupled Scalar Field in QFT
3.1. From Classical to Quantum Field Theory
3.2. Vacuum Effective Action and Its Adiabatic Renormalization
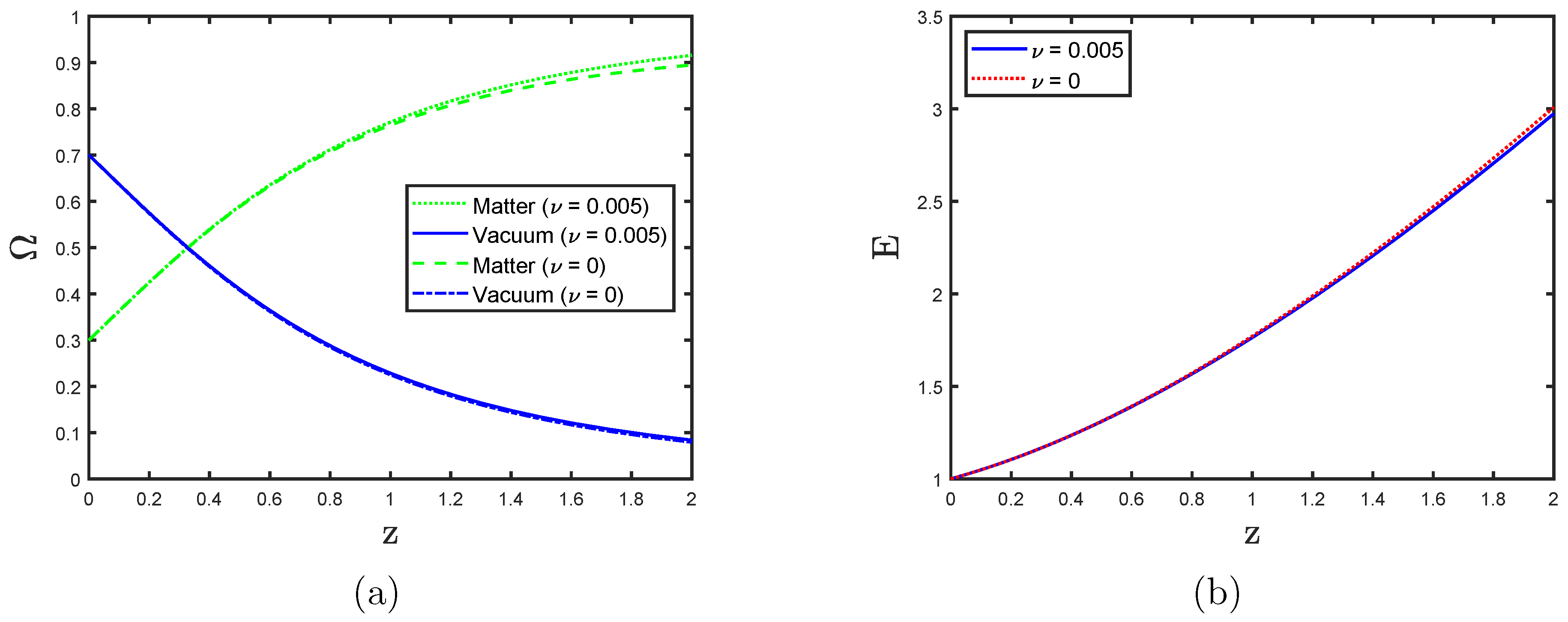
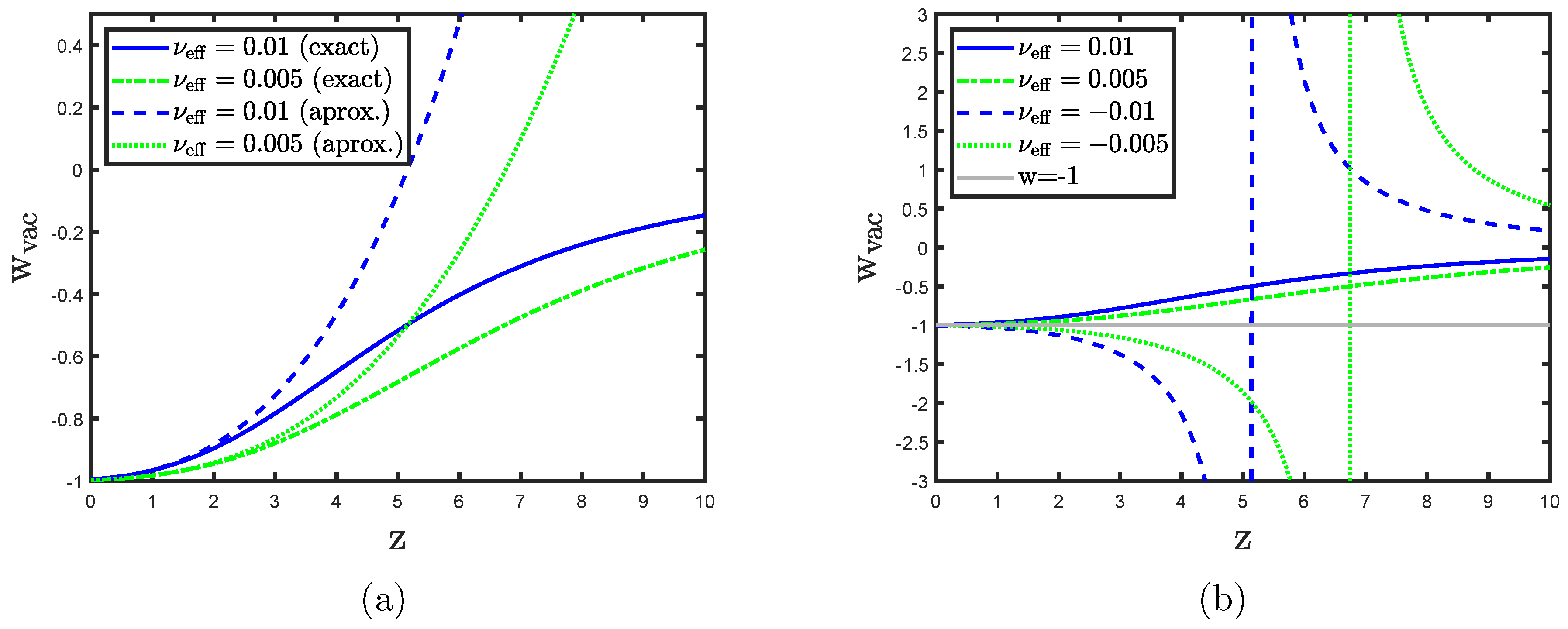
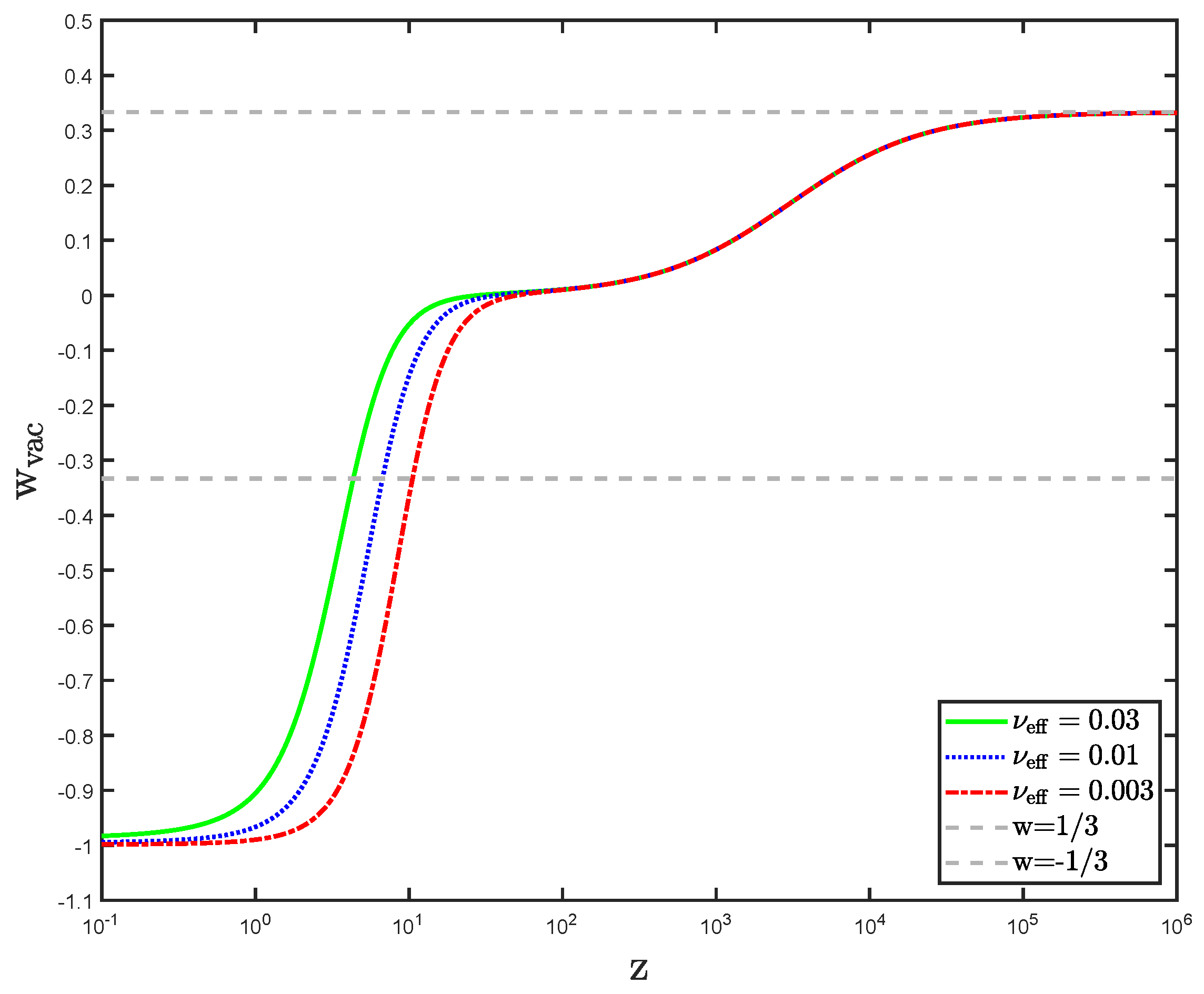
3.3. Running Vacuum and EoS in the Late Universe
4. Inflation from Running Vacuum
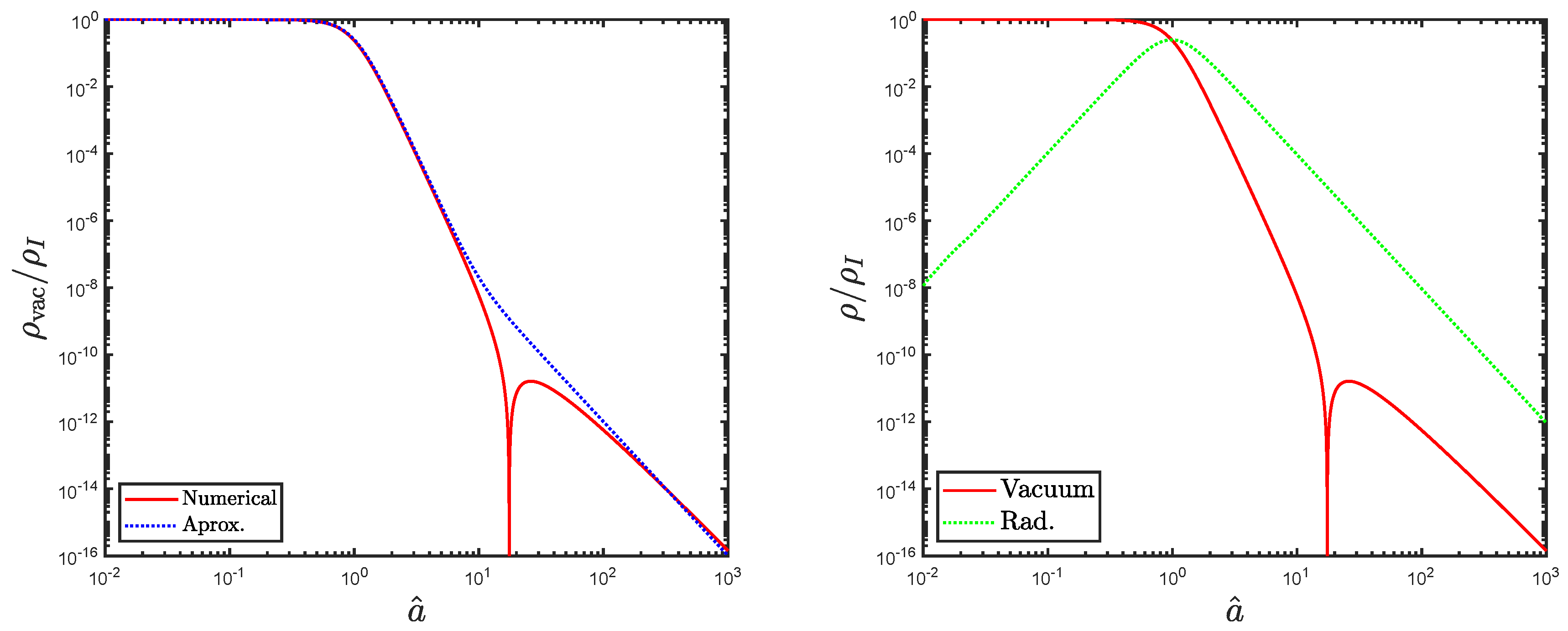
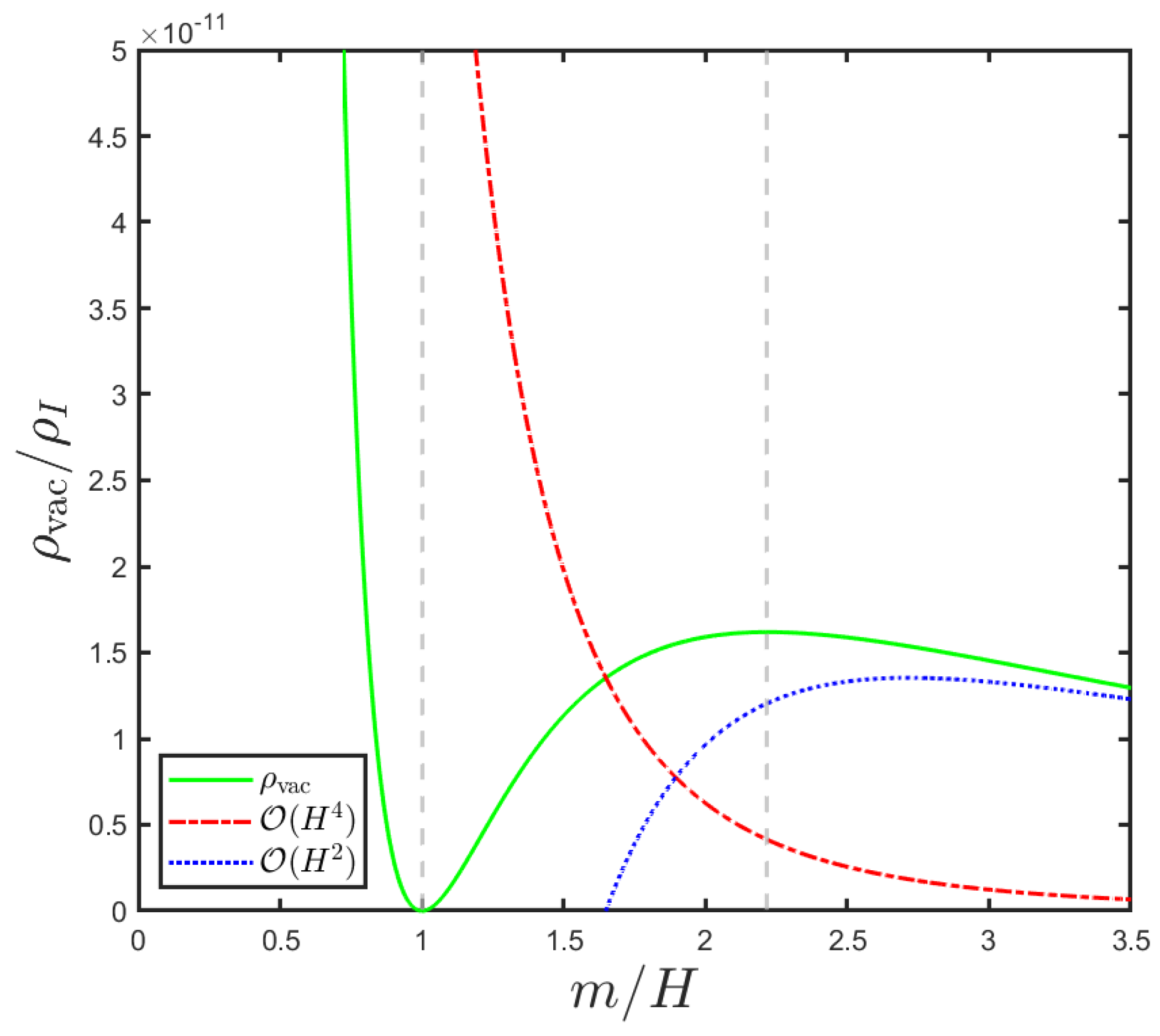
4.1. Analytical and Numerical Solution of the Inflationary Scenario
4.2. Thermodynamic Aspects of Inflation
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | |
| 2 | Despite the notation, the term has no a priori relation with the bare cosmological term of a gravitational action since there is no gravity in this (flat spacetime) context. See, however, the next section. |
| 3 | Our metric and curvature conventions are as in [32], see particularly Appendix A of that reference. |
| 4 | Off-shell renormalization is actually the clue to our approach [31,32], as is also the case in other QFT contexts. For example, the entire QCD theory of strong interactions is renormalized off-shell since the quarks do not participate on-shell in their interactions with gluons. Also, in quantum electrodynamics it allows to discuss the renormalization group running of the fine structure constant, whose confirmation was a major triumph of RG theory. As a matter of fact, off-shell renormalization is completely natural in cosmology if we take into account that the characteristic energy parameter H (in natural units) during most of the cosmological evolution is certainly much smaller than the average mass of any known particle. The exception is during the inflationary period, which we deal in detail in Section 4. |
| 5 | In fact, our final renormalized result depends on M only, not on the auxiliary introduced for DR regularization purposes. In contrast, in the approach of [97], which lacks of our subtraction prescription at M, the final results still carry explicit -dependence and calculations lead to the unwanted ∼ contributions responsible for extreme fine-tuning in the CCP. |
| 6 | The vacuum effective action depends on the renormalization scale M since it is only a part of the full effective action. In fact, in the QFT context the classical part of the action, Equation (17), is also dependent on M through the running couplings. This is how the full renormalized effective action is independent of M, as the bare action itself. |
| 7 | We note that the canonical RVM form (45) of the VED, which in our case emerges from off-shell ARP renormalization of the EMT in QFT in curved spacetime, has also been independently highlighted in recent studies of dynamical dark energy in the context of lattice quantum gravity using also the same scale setting [98]. Remarkably enough, these authors obtain numerical lattice calculation estimates for in the ballpark of the fitted values for this parameter from the analyses of cosmological observations [37,38,39,40,41,42,43]. For recent work exploring the running vacuum energy density in cosmology from different perspectives, see e.g., [99]. |
| 8 | In general, we could also have rather than just [32]. However, for the sake of simplicity and aiming to obtain an exact analytical solution of the cosmological equations we shall not consider this possibility here. |
References
- Peebles, P.J.E. Principles of Physical Cosmology; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Einstein, A. Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie. Sitzungsber. Königl. Preuss. Akad. Wiss. Phys. Math. Klasse VI 1917, 8, 142–152. [Google Scholar]
- Zeldovich, Y.B. Cosmological Constant and Elementary Particles. JETP Lett. 1967, 6, 316, Erratum in Pisma Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1967, 6, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeldovich, Y.B. The Cosmological constant and the theory of elementary particles. Sov. Phys. Usp. 1968, 11, 381, Republished in Gen. Rel. Grav. 2008, 40, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. The Cosmological Constant Problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Starobinsky, A.A. The Case for a Positive Cosmological Lambda-term. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2000, 9, 373–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, S.M. The Cosmological Constant. Living Rev. Rel. 2001, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, P.J.E.; Ratra, B. The Cosmological Constant and Dark Energy. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2003, 75, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, T. Cosmological constant: The Weight of the vacuum. Phys. Rep. 2003, 380, 235–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, E.J.; Sami, M.; Tsujikawa, S. Dynamics of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 1753–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitchison, I.J.R. Nothing’s plenty. The vacuum in modern quantum field theory. Contemp. Phys. 2009, 50, 261–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà, J. Cosmological constant and vacuum energy: Old and new ideas. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2013, 453, 012015. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J. Vacuum energy and cosmological evolution. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1606, 19–37. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J.; Gómez-Valent, A. The CDM cosmology: From inflation to dark energy through running Λ. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2015, 24, 1541003. [Google Scholar]
- Solà Peracaula, J. The Cosmological Constant Problem and Running Vacuum in the Expanding Universe. Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 2022, 380, 20210182. [Google Scholar]
- Solà Peracaula, J. Quantum Vacuum: The Cosmological Constant Problem. Available online: https://cosmoversetensions.eu/learn-cosmology/quantum-vacuum-the-cosmological-constant-problem/ (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Birrell, N.D.; Davies, P.C.W. Quantum Fields in Curved Space; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Parker, L.E.; Toms, D.J. Quantum Field Theory in Curved Spacetime: Quantized Fields and Gravity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fulling, S.A. Aspects of Quantum Field Theory in Curved Space-Time; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Overduin, J.M.; Cooperstock, F.I. Evolution of the scale factor with a variable cosmological term. Phys. Rev. D 1998, 58, 043506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgov, A.D. The very Early Universe; Gibbons, G., Hawking, S.W., Tiklos, S.T., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Dolgov, A.D. Mystery of Vacuum Energy or Rise and Fall of Cosmological Constant. arXiv 2002, arXiv:0203245. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, L. A Mechanism for Reducing the Value of the Cosmological Constant. Phys. Lett. B 1985, 150, 427–430. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, T. TCP, Quantum Gravity, the Cosmological Constant and All That…. Nucl. Phys. B 1985, 249, 332–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peccei, R.D.; Solà, J.; Wetterich, C. Adjusting the Cosmological Constant Dynamically: Cosmons and a New Force Weaker Than Gravity. Phys. Lett. B 1987, 195, 183–190. [Google Scholar]
- Barr, S.M. An Attempt at a Classical Cancellation of the Cosmological Constant. Phys. Rev. D 1987, 36, 1691. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, L.H. Cosmological Constant Damping by Scalar Fields. Phys. Rev. D 1987, 35, 2339. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J. The Cosmological Constant and the Fate of the Cosmon in Weyl Conformal Gravity. Phys. Lett. B 1989, 228, 317–324. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J. Scale gauge symmetry and the standard model. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 1990, 5, 4225–4240. [Google Scholar]
- Amendola, L.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark Energy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Pulido, C.; Solà Peracaula, J. Running vacuum in quantum field theory in curved spacetime: Renormalizing ρvac without ∼m4 terms. Eur. Phys. J. C 2020, 80, 692. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Pulido, C.; Solà Peracaula, J. Renormalizing the vacuum energy in cosmological spacetime: Implications for the cosmological constant problem. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 551. [Google Scholar]
- Moreno-Pulido, C.; Solà Peracaula, J. Equation of state of the running vacuum. Eur. Phys. J. C 2022, 82, 1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Pulido, C.; Cheraghchi, S.; Solà Peracaula, J. Running vacuum in QFT in FLRW spacetime: The dynamics of ρvac(H) from the quantized matter fields. Eur. Phys. J. C 2023, 83, 637. [Google Scholar]
- Abdalla, E.; Abellán, G.F.; Aboubrahim, A.; Agnello, A.; Akarsu, O.; Akrami, Y.; Alestas, G.; Aloni, D.; Amendola, L.; Anchordoqui, L.A.; et al. Cosmology intertwined: A review of the particle physics, astrophysics, and cosmology associated with the cosmological tensions and anomalies. J. High Energy Astrophys. 2022, 34, 49–211. [Google Scholar]
- Perivolaropoulos, L.; Skara, F. Challenges for ΛCDM: An update. New Astron. Rev. 2022, 95, 101659. [Google Scholar]
- Solà Peracaula, J.; Gómez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Pérez, J.; Moreno-Pulido, C. Running vacuum against the H0 and σ8 tensions. EPL 2021, 134, 19001. [Google Scholar]
- Solà Peracaula, J.; Gómez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Pérez, J.; Moreno-Pulido, C. Running vacuum in the Universe: Phenomenological status in light of the latest observations, and its impact on the σ8 and H0 tensions. Universe 2023, 9, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà, J.; Gómez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Pérez, J. Hints of dynamical vacuum energy in the expanding Universe. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 811, L14. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J.; Gómez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Pérez, J. First evidence of running cosmic vacuum: Challenging the concordance model. Astrophys. J. 2017, 836, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà, J.; Gómez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Pérez, J. The H0 tension in light of vacuum dynamics in the Universe. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 774, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà Peracaula, J.; de Cruz Pérez, J.; Gómez-Valent, A. Dynamical dark energy vs. Λ = const in light of observations. EPL 2018, 121, 39001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà Peracaula, J.; de Cruz Pérez, J.; Gómez-Valent, A. Possible signals of vacuum dynamics in the Universe. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Solà Peracaula, J. Composite Dark Energy and the Cosmological Tensions. Phys. Lett. B 2025, 864, 139391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Solà Peracaula, J. Phantom Matter: A Challenging Solution to the Cosmological Tensions. Astrophys. J. 2024, 975, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà Peracaula, J.; Gómez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Pérez, J.; Moreno-Pulido, C. Brans–Dicke Gravity with a Cosmological Constant Smoothes Out ΛCDM Tensions. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 886, L6. [Google Scholar]
- Solà Peracaula, J.; Gómez-Valent, A.; de Cruz Pérez, J.; Moreno-Pulido, C. Brans–Dicke cosmology with a Λ-term: A possible solution to ΛCDM tensions. Class. Quant. Grav. 2020, 37, 245003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cruz Pérez, J.; Solà Peracaula, J. Running vacuum in Brans & Dicke theory: A possible cure for the σ8 and H0 tensions. Phys. Dark Univ. 2024, 43, 101406. [Google Scholar]
- Solà Peracaula, J. Composite running vacuum in the Universe: Implications on the cosmological tensions. In Proceedings of the 17th Marcel Grossmann Meeting: On Recent Developments in Theoretical and Experimental General Relativity, Gravitation, and Relativistic Field Theories, Online, 7–12 July 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Akarsu, Ö.; Kumar, S.; Özülker, E.; Vázquez, J.A. Relaxing cosmological tensions with a sign switching cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 123512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarsu, Ö.; Di Valentino, E.; Kumar, S.; Nunes, R.C.; Vazquez, J.A.; Yadav, A. ΛsCDM model: A promising scenario for alleviation of cosmological tensions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.10899. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Favale, A.; Migliaccio, M.; Sen, A.A. Late-time phenomenology required to solve the H0 tension in view of the cosmic ladders and the anisotropic and angular BAO datasets. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 109, 023525. [Google Scholar]
- Giarè, W.; Mahassen, T.; Valentino, E.D. An overview of what current data can (and cannot yet) say about evolving dark energy. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.10264. [Google Scholar]
- Akarsu, Ö.; Perivolaropoulos, L.; Tsikoundoura, A.; Yükselci, A.E.; Zhuk, A. Dynamical dark energy with AdS-to-dS and dS-to-dS transitions: Implications for the H0 tension. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.14667. [Google Scholar]
- Soriano, J.F.; Wohlberg, S.; Anchordoqui, L.A. New insights on a sign-switching Λ. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.19239. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, S.; Högås, M. 2D BAO vs. 3D BAO: Solving the Hubble Tension with Bimetric Cosmology. Universe 2024, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anchordoqui, L.A.; Antoniadis, I.; Lust, D. Anti-de Sitter → de Sitter transition driven by Casimir forces and mitigating tensions in cosmological parameters. Phys. Lett. B 2024, 855, 138775. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Zheng, Z.; Amendola, L.; Pettorino, V.; Wetterich, C. Early dark energy in the pre- and postrecombination epochs. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 083536. [Google Scholar]
- Kamionkowski, M.; Riess, A.G. The Hubble Tension and Early Dark Energy. Ann. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 2023, 73, 153–180. [Google Scholar]
- Poulin, V.; Smith, T.L.; Karwal, T. The Ups and Downs of Early Dark Energy solutions to the Hubble tension: A review of models, hints and constraints circa 2023. Phys. Dark Univ. 2023, 42, 101348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Valentino, E.D.; Pan, S.; Shafieloo, A.; Li, X. Generalized emergent dark energy model and the Hubble constant tension. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 063521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Zheng, Z.; Amendola, L.; Wetterich, C.; Pettorino, V. Coupled and uncoupled early dark energy, massive neutrinos, and the cosmological tensions. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 103522. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Abdalla, E.; Atrio-Barandela, F.; Pavón, D. Further understanding the interaction between dark energy and dark matter: Current status and future directions. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2024, 87, 036901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, T.P.; Faraoni, V. f(R) Theories Of Gravity. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. Extended Theories of Gravity. Phys. Rep. 2011, 509, 167–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Capozziello, S.; Laurentis, M.D.; Saridakis, E.N. f(T) teleparallel gravity and cosmology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horndeski, G.W. Second-order scalar-tensor field equations in a four-dimensional space. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 1974, 10, 363–384. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, T. Horndeski theory and beyond: A review. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2019, 82, 086901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.; Ferreira, P.G.; Padilla, A.; Skordis, C. Modified Gravity and Cosmology. Phys. Rep. 2012, 513, 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Brans, C.; Dicke, R. Mach’s principle and a relativistic theory of gravitation. Phys. Rev. 1961, 124, 925. [Google Scholar]
- Basilakos, S.; Lima, J.A.S.; Solà, J. Expansion History with Decaying Vacuum: A Complete Cosmological Scenario. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 431, 923–929. [Google Scholar]
- Basilakos, S.; Lima, J.A.S.; Solà, J. Nonsingular Decaying Vacuum Cosmology and Entropy Production. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2015, 47, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Basilakos, S.; Lima, J.A.S.; Solà, J. Thermodynamical aspects of running vacuum models. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 228. [Google Scholar]
- Perico, E.L.D.; Lima, J.A.S.; Basilakos, S.; Solà, J. Complete Cosmic History with a dynamical Lambda(H) term. Phys. Rev. D 2013, 88, 063531. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J. The cosmological constant and entropy problems: Mysteries of the present with profound roots in the past. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2015, 24, 1544027. [Google Scholar]
- Solà Peracaula, J.; Yu, H. Particle and entropy production in the Running Vacuum Universe. Gen. Rel. Grav. 2020, 52, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Basilakos, S.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà, J. Starobinsky-like inflation and running vacuum in the context of Supergravity. Universe 2016, 2, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. Stringy-Running-Vacuum-Model Inflation: From primordial Gravitational Waves and stiff Axion Matter to Dynamical Dark Energy. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2021, 230, 2077. [Google Scholar]
- Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. Inflationary physics and transplanckian conjecture in the Stringy Running-Vacuum-Model: From the phantom vacuum to the true vacuum. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2021, 136, 1152. [Google Scholar]
- Basilakos, S.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. Do we Come from a Quantum Anomaly? Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1944002. [Google Scholar]
- Basilakos, S.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. Gravitational and Chiral Anomalies in the Running Vacuum Universe and Matter-Antimatter Asymmetry. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 045001. [Google Scholar]
- Basilakos, S.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. Quantum Anomalies in String-Inspired Running Vacuum Universe: Inflation and Axion Dark Matter. Phys. Lett. B 2020, 803, 135342. [Google Scholar]
- Mavromatos, N.E. Geometrical origins of the Universe dark sector: String-inspired torsion and anomalies as seeds for inflation and dark matter. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 2022, 380, 20210188. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. Stringy running vacuum model and current tensions in cosmology. Class. Quant. Grav. 2024, 41, 015026. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Valent, A.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. String-inspired running-vacuum cosmology, quantum corrections and the current cosmological tensions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.13130. [Google Scholar]
- Dorlis, P.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Vlachos, S.-N. Condensate-induced inflation from primordial gravitational waves in string-inspired Chern-Simons gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2024, 110, 063512. [Google Scholar]
- Dorlis, P.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Vlachos, S.-N. Quantum-Ordering Ambiguities in Weak Chern—Simons 4D Gravity and Metastability of the Condensate-Induced Inflation. Universe 2025, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J. A Running Vacuum Fundamental Approach to Modern Cosmology. in preparation.
- Starobinsky, A.A. A New Type of Isotropic Cosmological Models Without Singularity. Phys. Lett. B 1980, 91, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavromatos, N.E.; Solà Peracaula, J.; Basilakos, S. String-Inspired Running Vacuum—The “Vacuumon”—And the Swampland Criteria. Universe 2020, 6, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.S. Quantum Field Theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Akhmedov, E.K. Vacuum energy and relativistic invariance. arXiv 2002, arXiv:0204048. [Google Scholar]
- Ossola, G.; Sirlin, A. Considerations concerning the contributions of fundamental particles to the vacuum energy density. Eur. Phys. J. C 2003, 31, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J. Renormalization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreiro, A.; Navarro-Salas, J. Running couplings from adiabatic regularization. Phys. Lett. B 2019, 792, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, A.; Navarro-Salas, J. Running gravitational couplings, decoupling, and curved spacetime renormalization. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 102, 045021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohri, K.; Matsui, H. Cosmological Constant Problem and Renormalized Vacuum Energy Density in Curved Background. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 2017, 006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Freeman, W.; Laiho, J.; Schiffer, M.; Unmuth-Yockey, J. Dynamical Dark Energy from Lattice Quantum Gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2025, 111, 034514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montani, G.; Maniccia, G.; Fazzari, E.; Melchiorri, A. Running Einstein Constant and the Vacuum Energy Problem. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2412.14747. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J. Dark energy: A Quantum fossil from the inflationary Universe? J. Phys. A 2008, 41, 164066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimakis, P.; Basilakos, S.; Mavromatos, N.E.; Saridakis, E.N. Big Bang Nucleosynthesis constraints on higher-order modified gravities. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 105, 084010. [Google Scholar]
- Shafieloo, A.; Alam, U.; Sahni, V.; Starobinsky, A.A. Smoothing Supernova Data to Reconstruct the Expansion History of the Universe and its Age. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 366, 1081–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solà, J.; Stefancic, H. Effective equation of state for dark energy: Mimicking quintessence and phantom energy through a variable lambda. Phys. Lett. B 2005, 624, 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Solà, J.; Stefancic, H. Dynamical dark energy or variable cosmological parameters? Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2006, 21, 479–494. [Google Scholar]
- Adame, A.G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Alexander, D.M.; Alvarez, M.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI 2024 VI: Cosmological Constraints from the Measurements of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2025, 2025, 021. [Google Scholar]
- Adame, A.G.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Alexander, D.M.; Prieto, C.A.; Alvarez, M.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; et al. DESI 2024 VII: Cosmological Constraints from the Full-Shape Modeling of Clustering Measurements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.12022. [Google Scholar]
- Karim, M.A.; Aguilar, J.; Ahlen, S.; Alam, S.; Allen, L.; Prieto, C.A.; Alves, O.; Anand, A.; Andrade, U.; Armengaud, E.; et al. DESI DR2 Results II: Measurements of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations and Cosmological Constraints. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2503.14738. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, E.W.; Turner, M.S. The Early Universe; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Boston, MA, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Mathematica, Wolfram Research, Inc. Available online: https://www.wolfram.com/mathematica (accessed on 1 March 2025).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Solà Peracaula, J.; Moreno-Pulido, C.; González-Fuentes, A. Running Vacuum and H4 Inflation. Universe 2025, 11, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040118
Solà Peracaula J, Moreno-Pulido C, González-Fuentes A. Running Vacuum and H4 Inflation. Universe. 2025; 11(4):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040118
Chicago/Turabian StyleSolà Peracaula, Joan, Cristian Moreno-Pulido, and Alex González-Fuentes. 2025. "Running Vacuum and H4 Inflation" Universe 11, no. 4: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040118
APA StyleSolà Peracaula, J., Moreno-Pulido, C., & González-Fuentes, A. (2025). Running Vacuum and H4 Inflation. Universe, 11(4), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe11040118






