The Brightest Point in Accretion Disk and Black Hole Spin: Implication to the Image of Black Hole M87*
Abstract
1. Introduction
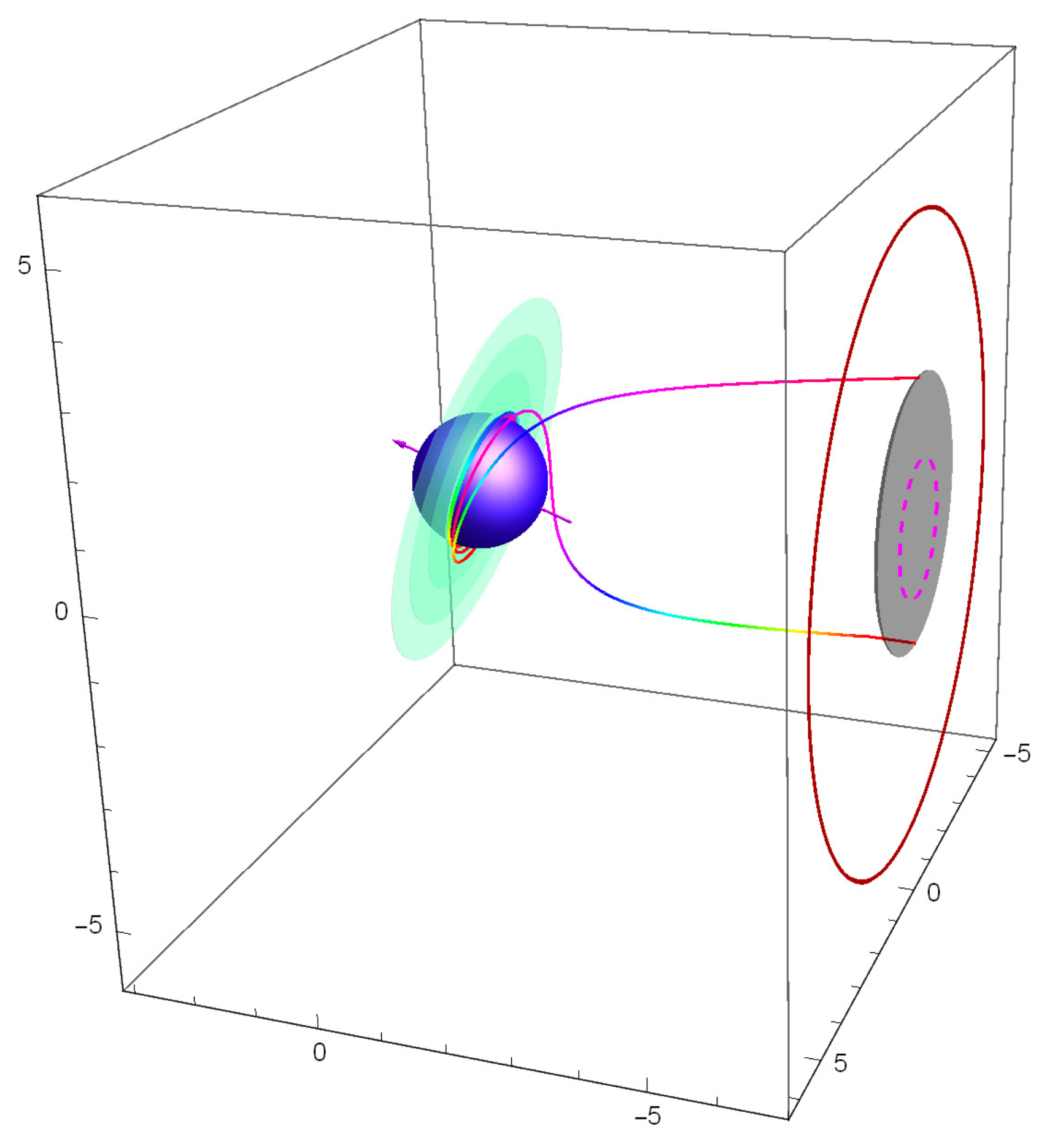
2. Photon Trajectories in the Kerr Metric
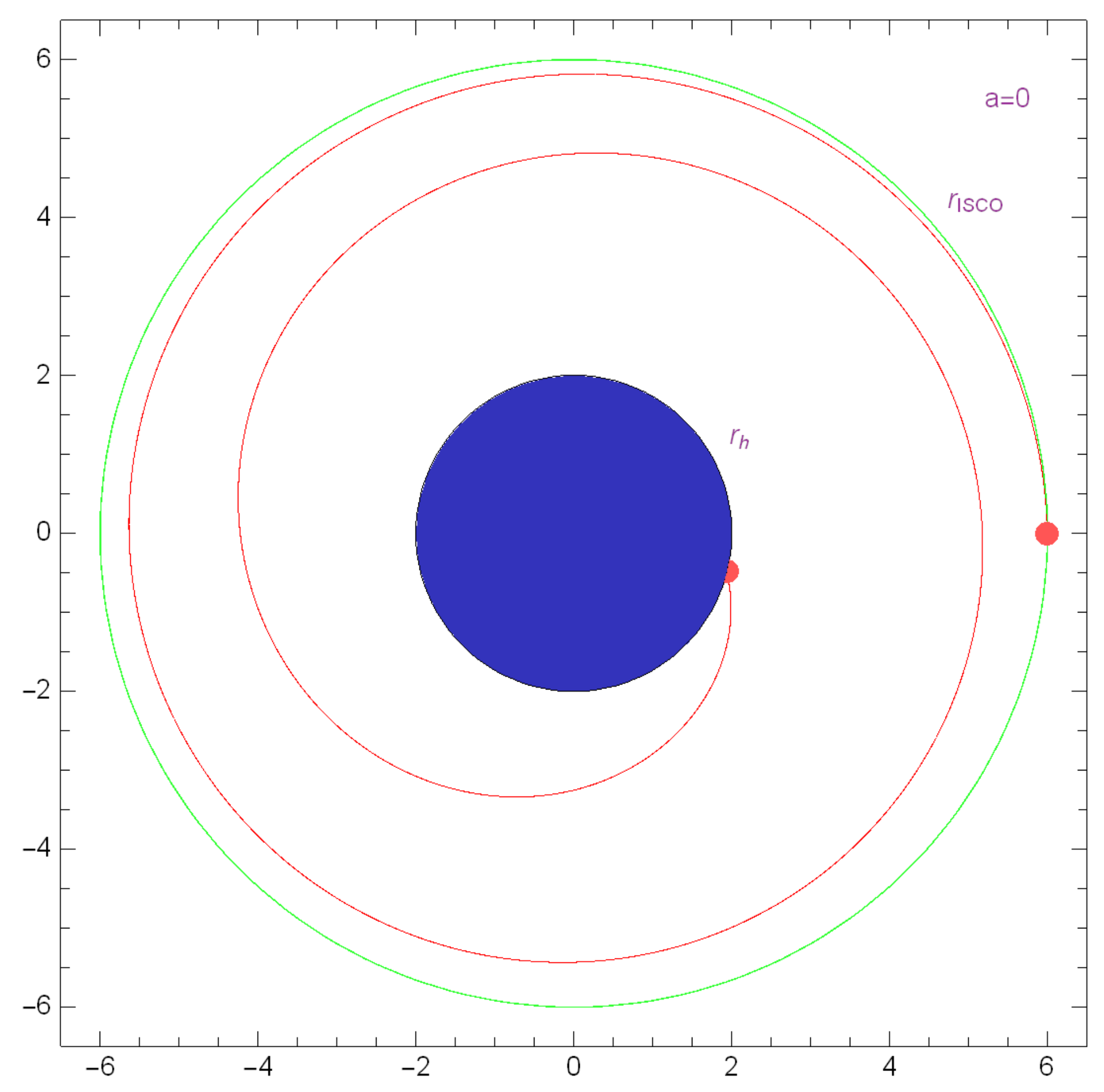
3. Black Hole Shadow
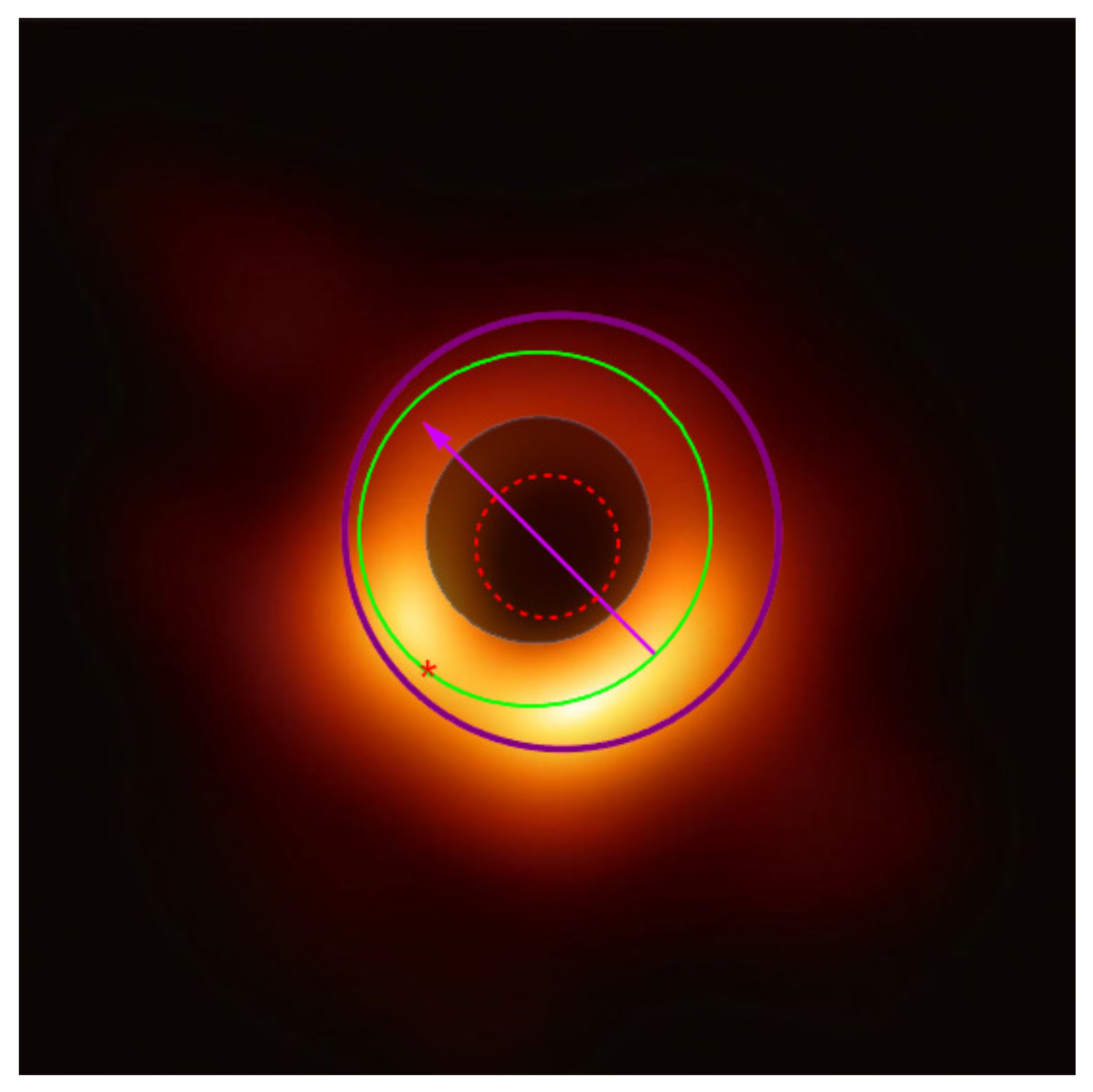
4. Event Horizon Silhouette
5. Spin of the Black Hole M87*
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EHT | Event Horizon Telescope |
| LNRF | Locally Non-Rotating Frames |
| VLBI | Very Long Baseline Interferometry |
References
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.-K.; Ball, D.; Balokovic, M.; Barrett, J.; Bintley, D.; et al. M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L1. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.K.; Ball, D.; Balokovic, M.; Barrett, J.; Bintley, D.; et al. M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. II. Array and Instrumentation. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L2. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.K.; Ball, D.; Balokovic, M.; Barrett, J.; Bintley, D.; et al. M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. III. Data Processing and Calibration. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L3. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.K.; Ball, D.; Balokovic, M.; Barrett, J.; Bintley, D.; et al. M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. IV. Imaging the Central Supermassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L4. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.K.; Ball, D.; Balokovic, M.; Barrett, J.; Bintley, D.; et al. M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. V. Physical Origin of the Asymmetric Ring. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L5. [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.-K.; Ball, D.; Balokovic, M.; Barrett, J.; Bintley, D.; et al. M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. VI. The Shadow and Mass of the Central Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 875, L6. [Google Scholar]
- Bardeen, J.M. Timeline and Null Geodesics in the Kerr Metric. In Black Holes; DeWitt, C., DeWitt, B.S., Eds.; Gordon and Breach: New York, NY, USA, 1973; pp. 217–239. [Google Scholar]
- Luminet, J.-P. Image of a spherical black hole with thin accretion disk. Astron. Astrophys. 1979, 75, 228–235. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekhar, S. The Mathematical Theory of Black Holes; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Falcke, H.; Melia, F.; Agol, E. Viewing the Shadow of the Black Hole at the Galactic Center. Astrophys. J. 2000, 528, L13–L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, A.F.; De Paolis, F.; Ingrosso, G.; Nucita, A.A. Measuring the black hole parameters in the galactic center with RADIOASTRON. New Astron. 2005, 10, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannsen, T.; Psaltis, D. Testing the No-hair Theorem with Observations in the Electromagnetic Spectrum. II. Black Hole Images. Astrophys. J. 2010, 718, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenzebach, A.; Perlick, V.; Lämmerzahl, C. Photon regions and shadows of Kerr-Newman-NUT black holes with a cosmological constant. Phys. Rev. D 2014, 89, 124004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenzebach, A.; Perlick, V.; Lämmerzahl, C. Photon regions and shadows of accelerated black holes. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2015, 24, 1542024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, P.V.P.; Herdeiro, C.A.R. Shadows and strong gravitational lensing: A brief review. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2018, 50, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, P.V.P.; Herdeiro, C.A.R.; Rodriguez, M.J. Does the black hole shadow probe the event horizon geometry? Phys. Rev. D 2018, 97, 084020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, Y.-P.; Liu, D.-J. Revisiting the shadow of a black hole in the presence of a plasma. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2018, 27, 1850114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S.E.; Porfyriadis, A.P.; Warburton, N. Particle on the innermost stable circular orbit of a rapidly spinning black hole. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 064029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S.E.; Lupsasca, A.; Strominger, A. Near-horizon Kerr magnetosphere. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 93, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S.E.; Zimmerman, A.; Zimmerman, P. Transient instability of rapidly rotating black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 084017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porfyriadis, A.P.; Shi, Y.; Strominger, A. Photon emission near extreme Kerr black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2017, 95, 064009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S.E.; Lupsasca, A.; Strominger, A. Observational signature of high spin at the Event Horizon Telescope. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 475, 3829–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M.; Press, W.H.; Teukolsky, S.A. Rotating Black Holes: Locally Nonrotating Frames, Energy Extraction, and Scalar Synchrotron Radiation. Astrophys. J. 1972, 178, 347–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dexter, J.; Agol, E.; Fragile, P.C. Millimeter Flares and VLBI Visibilities from Relativistic Simulations of Magnetized Accretion onto the Galactic Center Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2009, 703, L142–L146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley, B.C.; Chen, K.; Miller, W.A. Line Emission from an Accretion Disk around a Rotating Black Hole: Toward a Measurement of Frame Dragging. Astrophys. J. 1997, 475, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanton, C.; Calvani, M.; de Felice, F.; Cadez, A. Detecting Accretion Disks in Active Galactic Nuclei. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 1997, 49, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukue, J. Silhouette of a Dressed Black Hole. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 55, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukue, J. Light-Curve Diagnosis of a Hot Spot for Accretion-Disk Models. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 55, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, F.; Thidé, B.; Molina-Terriza, G.; Anzolin, G. Twisting of light around rotating black holes. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 195–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Roelofs, F.; Fish, V.L.; Shiokawa, H.; Doeleman, S.S.; Gammie, C.F.; Falcke, H.; Krichbaum, T.P.; Zensus, J.A. Imaging an Event Horizon: Mitigation of Source Variability of Sagittarius A*. Astrophys. J. 2016, 817, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luminet, J.-P. An Illustrated History of Black Hole Imaging: Personal Recollections (1972–2002). arXiv, 2019; arXiv:1902.11196. [Google Scholar]
- Dokuchaev, V.I. To see invisible: image of the event horizon within the black hole shadow. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2019, 28, 1941005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaev, V.I.; Nazarova, N.O. Event horizon image within black hole shadow. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2019, 128, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokuchaev, V.I.; Nazarova, N.O.; Smirnov, V.P. Event horizon silhouette: Implications to supermassive black holes M87* and SgrA*. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2019, 51, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, R.H.; Lindquist, R.W. Maximal Analytic Extension of the Kerr Metric. J. Math. Phys. 1967, 8, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B. Global Structure of the Kerr Family of Gravitational Fields. Phys. Rev. 1968, 174, 1559–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.T.; Bardeen, J.M. The Optical Appearance of a Star Orbiting an Extreme Kerr Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 1973, 183, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viergutz, S.U. Image generation in Kerr geometry. I. Analytical investigations on the stationary emitter-observer problem. Astron. Astrophys. 1993, 272, 355–377. [Google Scholar]
- Rauch, K.P.; Blandford, R.D. Optical Caustics in a Kerr Spacetime and the Origin of Rapid X-Ray Variability in Active Galactic Nuclei. Astrophys J. 1994, 421, 46–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gralla, S.E.; Holz, D.E.; Wald, R.M. Black Hole Shadows, Photon Rings, and Lensing Rings. arXiv, 2019; arXiv:1906.00873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, R.C.; Hardee, P.E.; Davies, F.B.; Ly, C.; Junor, W. The structure and dynamics of the sub-parsec scale jet in M87 based on 50 VLBA observations over 17 years at 43 GHz. Astrophys. J. 2018, 855, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardeen, J.M. Stability of Circular Orbits in Stationary, Axisymmetric Space-Times. Astrophys. J. 1970, 162, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, K.; Adams, J.; Richstone, D.; Lauer, T.R.; Faber, S.M.; Gltekin, K.; Murphy, J.; Tremaine, S. The black-hole mass in M87 from Gemini/NIFS adaptive optics observations. Astrophys. J. 2011, 729, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broderick, A.E.; Loeb, A. Imaging the Black Hole Silhouette of M87: Implications for Jet Formation and Black Hole Spin. Astrophys J. 2009, 697, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S. Constraining spins of supermassive black holes from TeV variability. II. fully general relativistic calculations. Astrophys. J. 2009, 699, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wu, Q. Constraint on the black hole spin of M87 from the accretion-jet model. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 470, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sob’yanin, D.N. Black hole spin from wobbling and rotation of the M87 jet and a sign of a magnetically arrested disc. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, L65–L69. [Google Scholar]
- Nokhrina, E.E.; Gurvits, L.I.; Beskin, V.S.; Nakamura, M.; Asada, K.; Hada, K. M87 black hole mass and spin estimate through the position of the jet boundary shape break. arXiv, 2019; arXiv:1904.05665. [Google Scholar]
- Tamburini, F.; Thidé, B.; Della Valle, M. Measurement of the spin of the M87 black hole from its observed twisted light. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.07923. [Google Scholar]
- Bambi, C.; Freese, K.; Vagnozzi, S.; Visinelli, L. Testing the rotational nature of the supermassive object M87* from the circularity and size of its first image. arXiv, 2019; arXiv:1904.12983. [Google Scholar]
- Nemmen, R. The Spin of M87*. arXiv, 2019; arXiv:1905.02143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davoudiasl, H.; Denton, P.B. Ultralight Boson Dark Matter and Event Horizon Telescope Observations of M87. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2019, 123, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dokuchaev, V.I.; Nazarova, N.O. The Brightest Point in Accretion Disk and Black Hole Spin: Implication to the Image of Black Hole M87*. Universe 2019, 5, 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5080183
Dokuchaev VI, Nazarova NO. The Brightest Point in Accretion Disk and Black Hole Spin: Implication to the Image of Black Hole M87*. Universe. 2019; 5(8):183. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5080183
Chicago/Turabian StyleDokuchaev, Vyacheslav I., and Natalia O. Nazarova. 2019. "The Brightest Point in Accretion Disk and Black Hole Spin: Implication to the Image of Black Hole M87*" Universe 5, no. 8: 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5080183
APA StyleDokuchaev, V. I., & Nazarova, N. O. (2019). The Brightest Point in Accretion Disk and Black Hole Spin: Implication to the Image of Black Hole M87*. Universe, 5(8), 183. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe5080183





