Critical Tests of Leading Gamma Ray Burst Theories
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The GRB Models
2.1. The Cannonball Model
2.2. The Fireball Model
3. The Prompt GRB Emission
3.1. The GRB Polarization (Test 1)
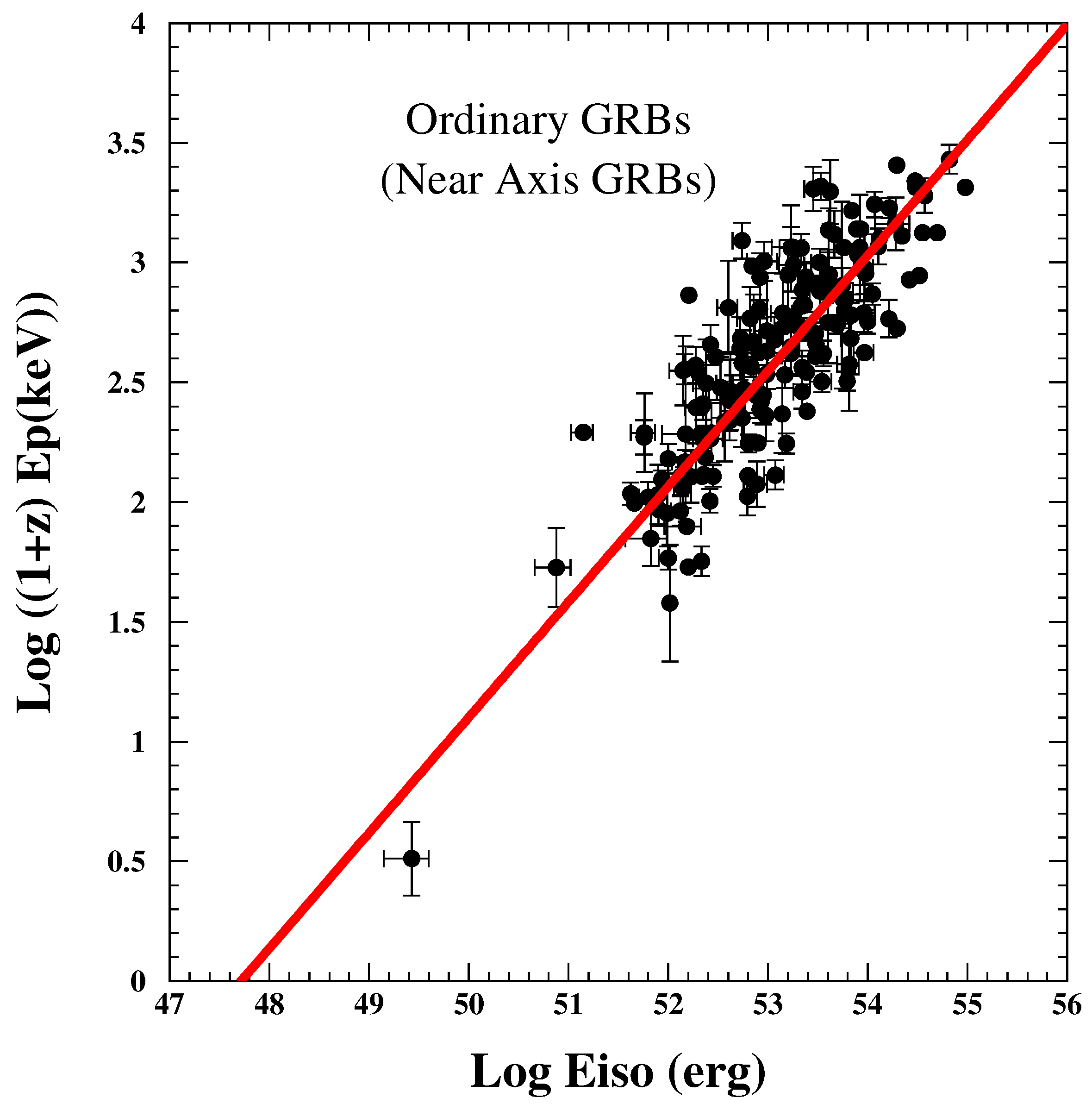
3.2. Prompt-Observable Correlations (Test 2)
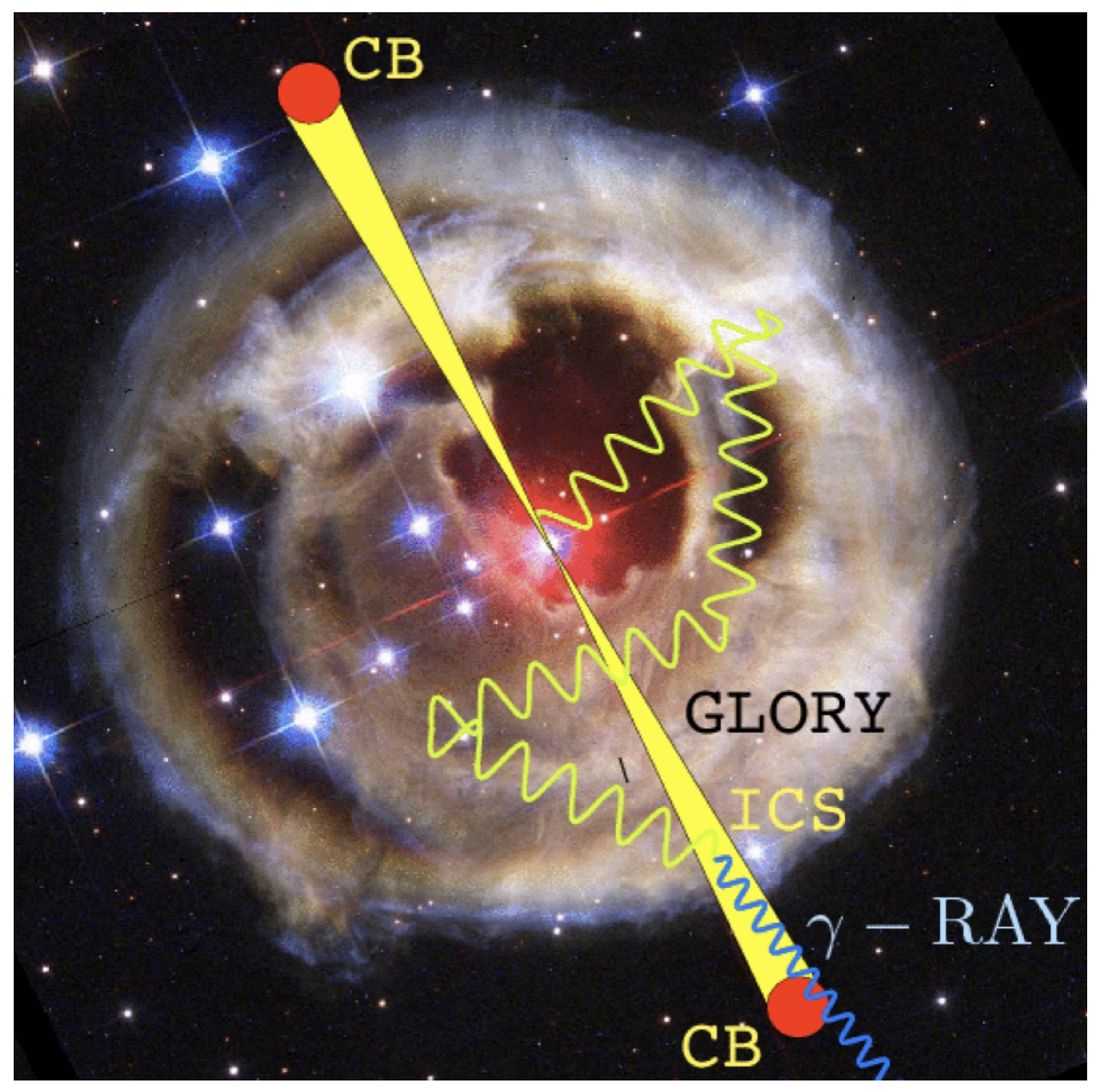
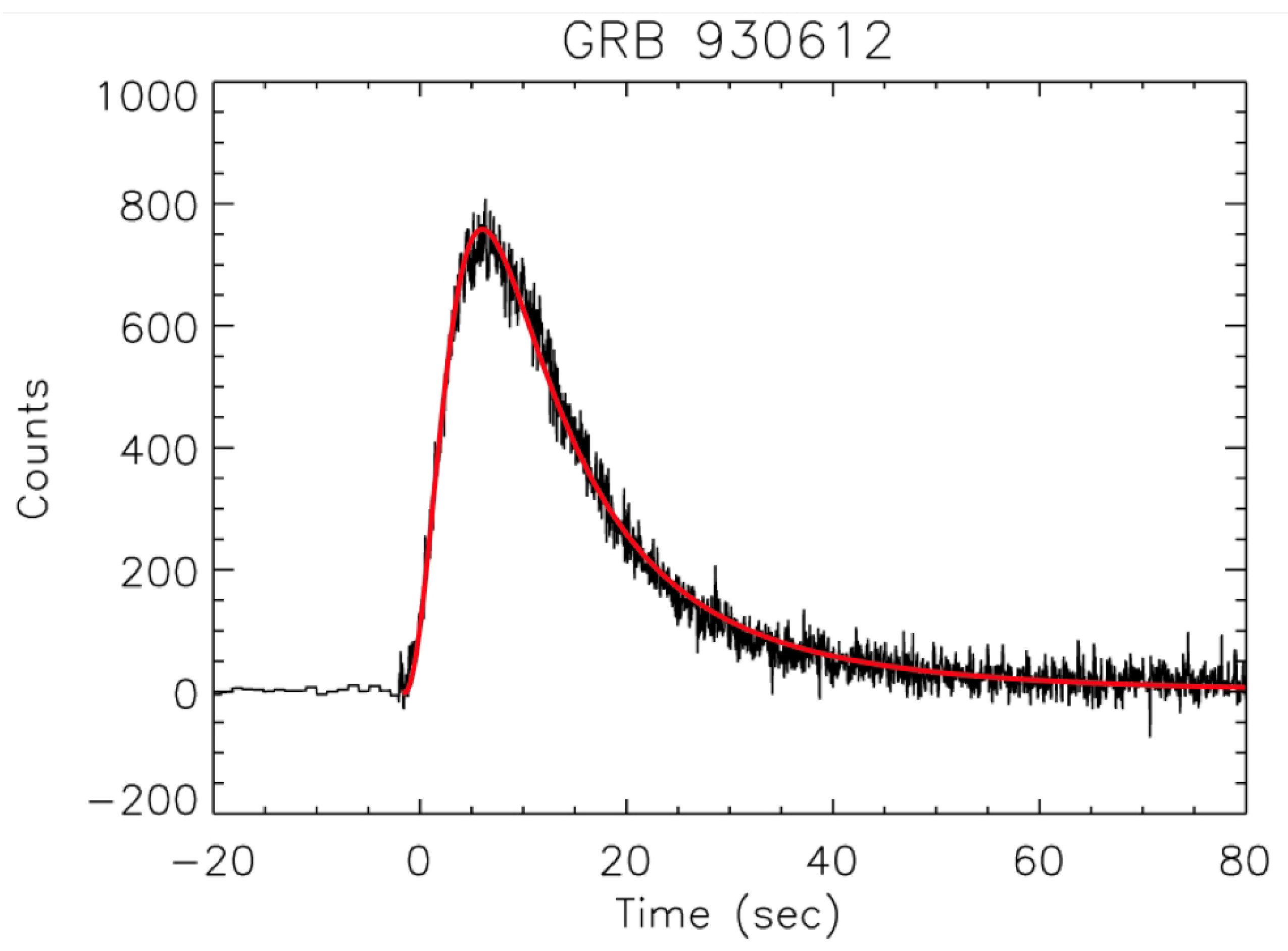
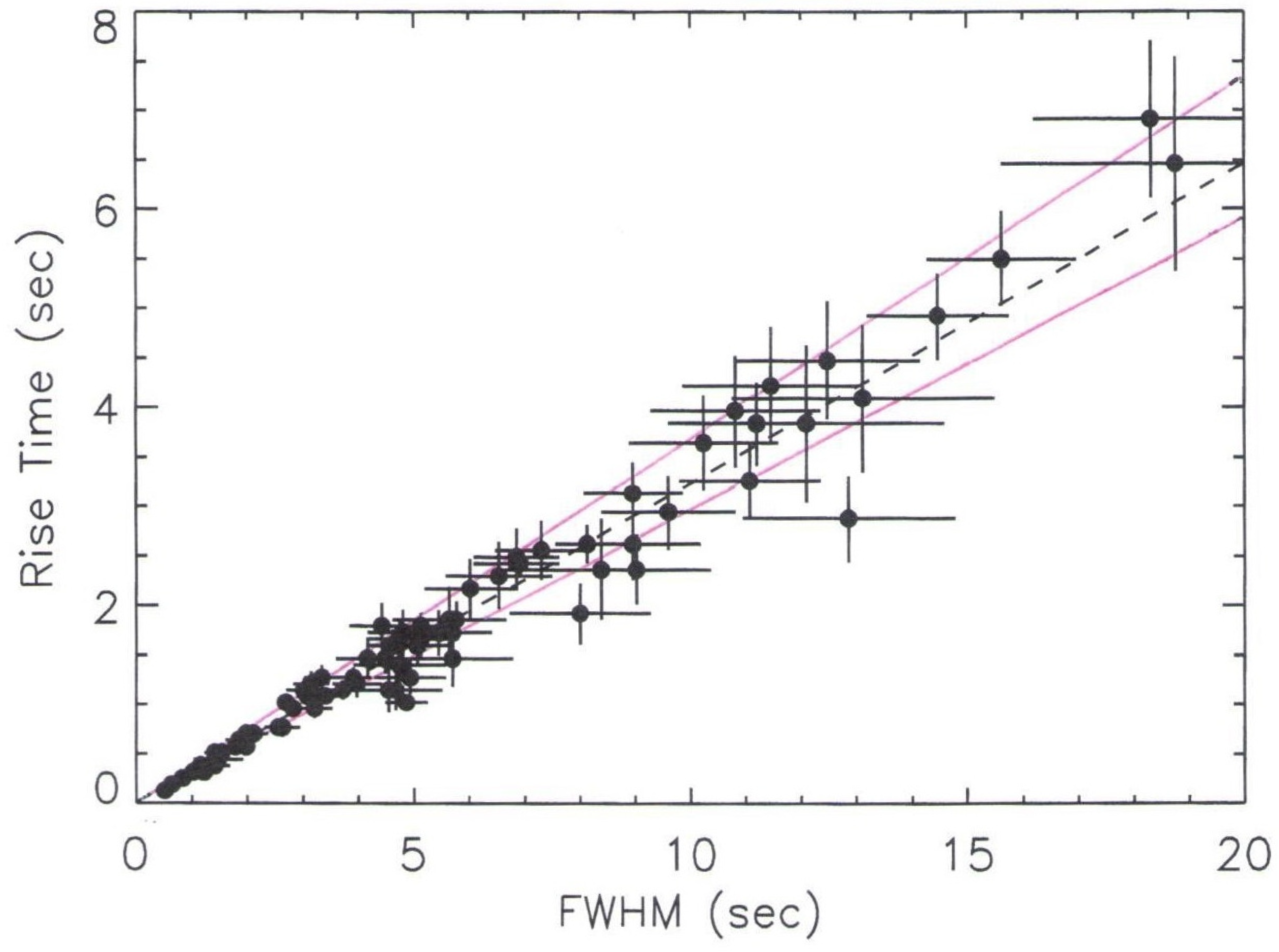
3.3. Temporal Shape of Prompt Pulses (Test 3)
3.3.1. Pulse Shapes in the CB Model
3.3.2. Pulse Shapes in Fireball Models
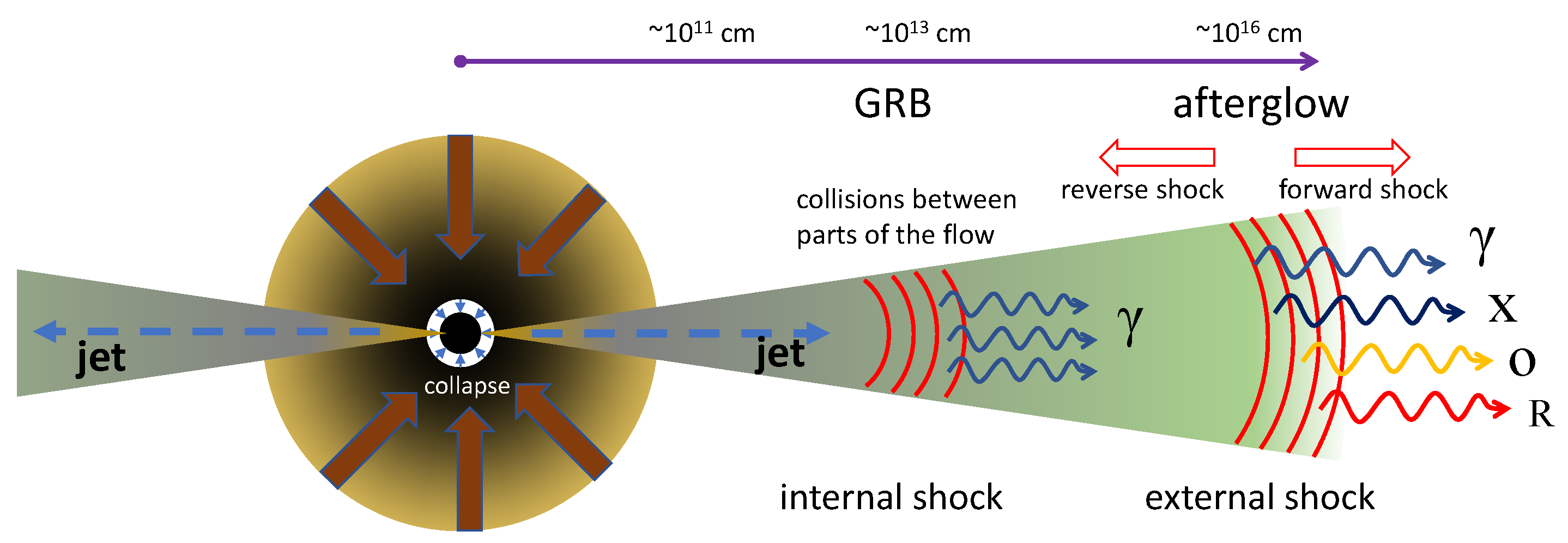
4. The Afterglow of GRBs
4.1. “Canonical” Behavior of the AG of LGRBs (Test 4)
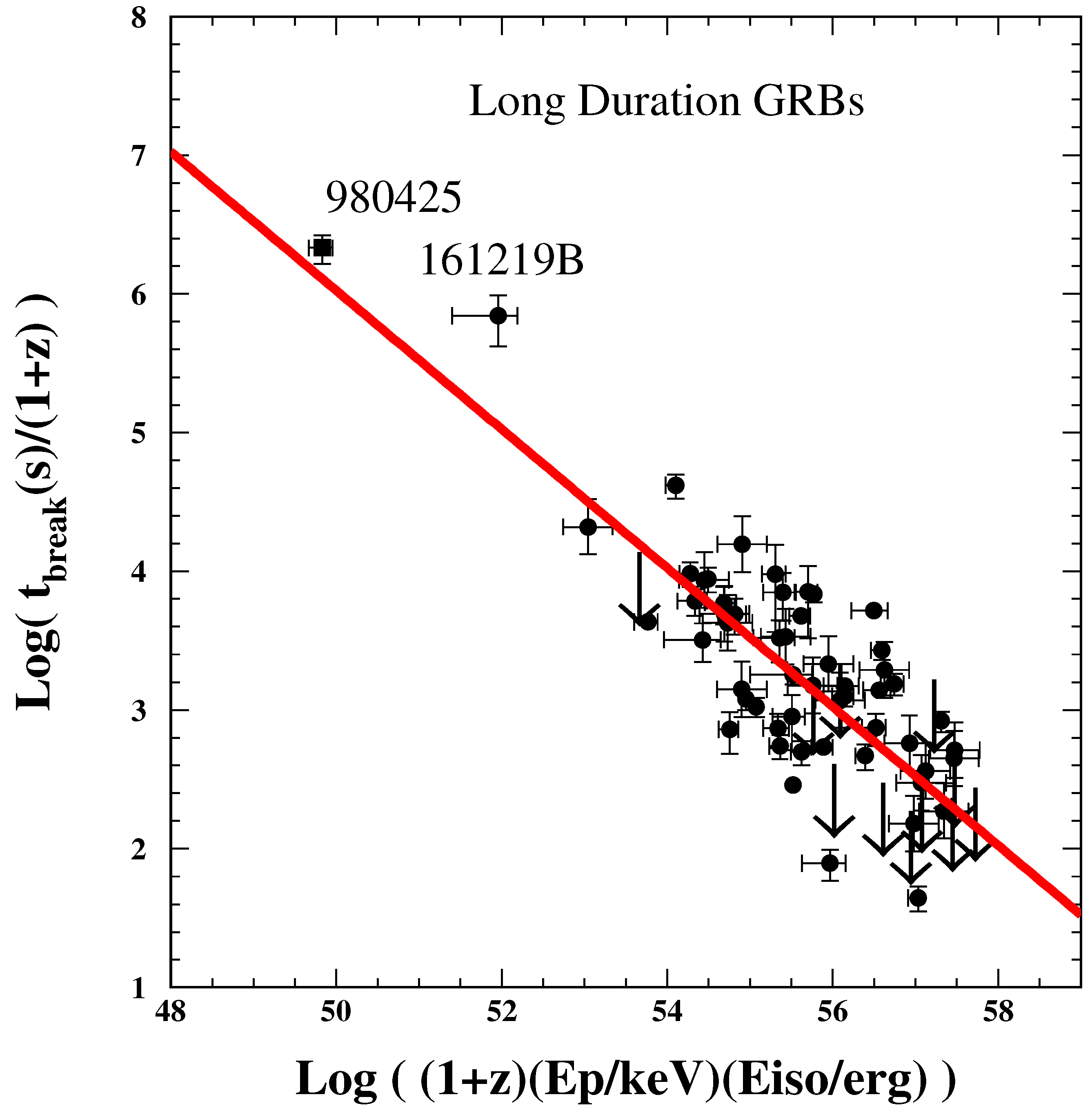
4.2. Break Time Correlations (Test 5)
4.3. Post-Break Closure Relations (Test 6)
4.4. Missing Breaks (Test 7)
5. GRB Afterglows in Fireball Models
5.1. The Canonical AG Shape (Test 4)
5.2. Break-Time Correlations (Test 5)
5.3. Closure Relations (Test 6)
5.4. Missing Breaks (Test 7)
6. Further Afterglow Tests
6.1. Chromatic Jet Breaks (Test 8)
6.2. The Universal Afterglow of SN-Less GRBs (Test 9)
7. The Progenitors of GRBs
8. The Progenitors of SHBs
9. Further Tests
9.1. Redshift Distribution of LGRBs (Test 10)
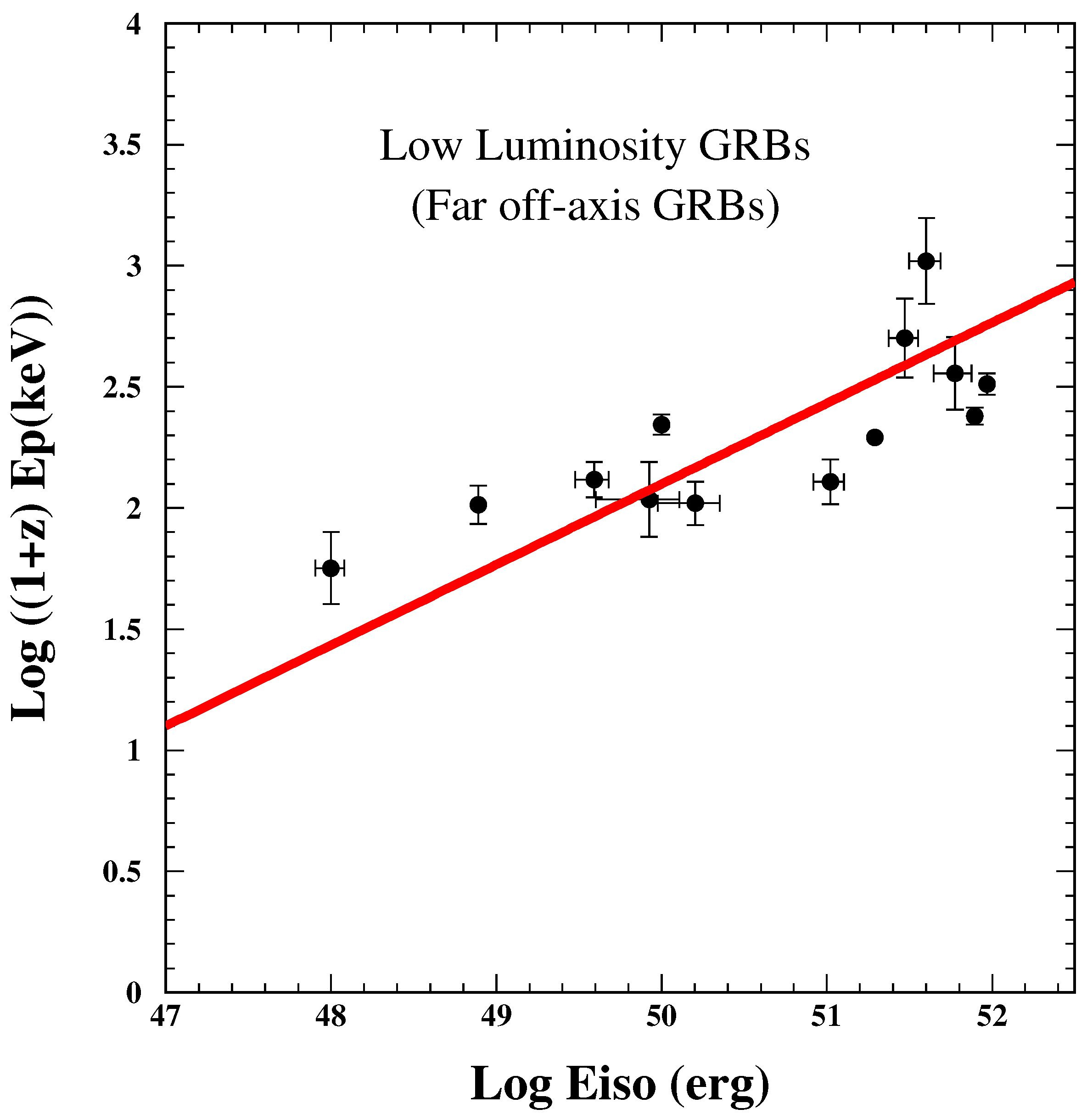
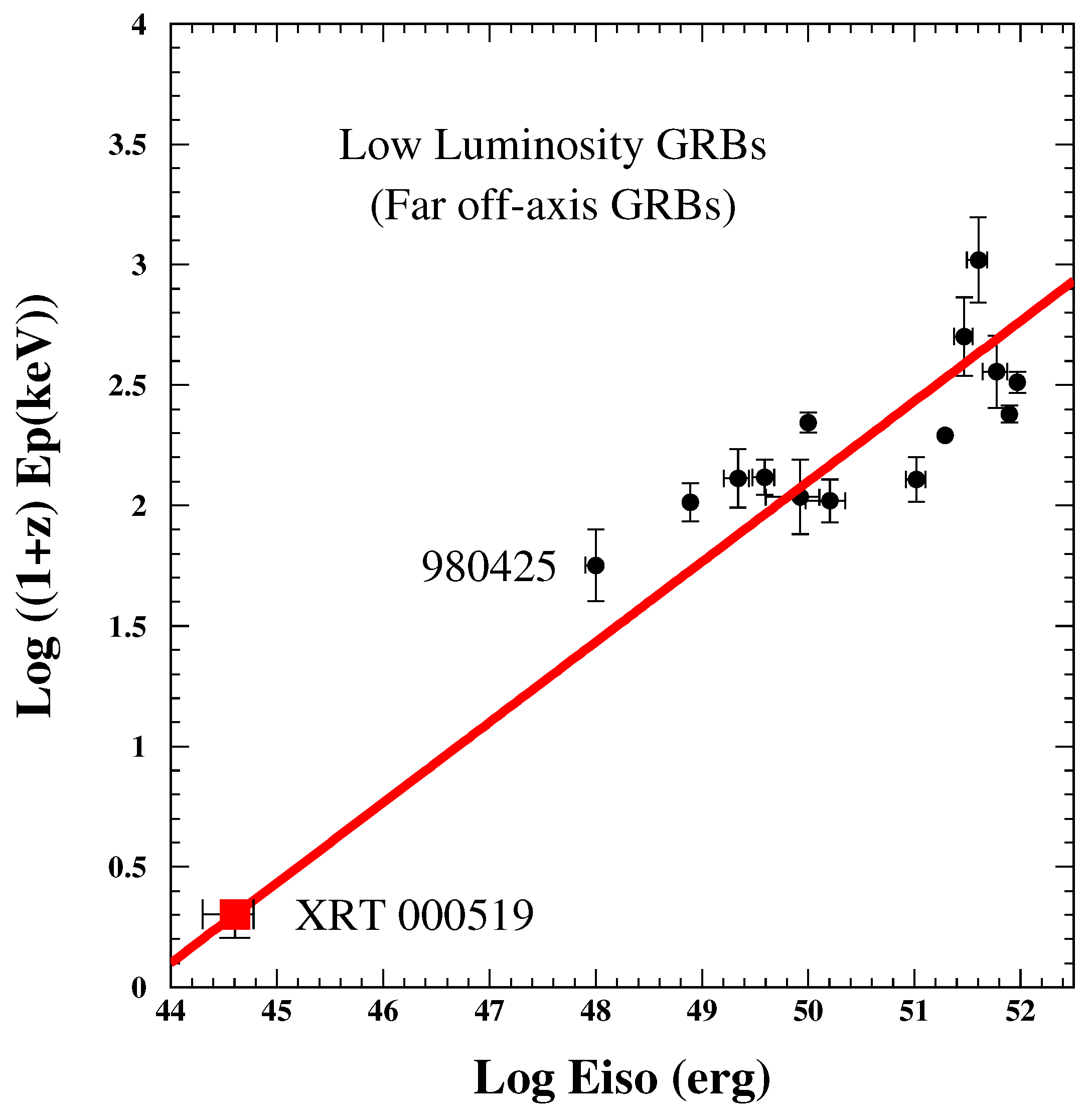
9.2. Low Luminosity GRBs (Test 11)
9.3. The CB’s Superluminal Velocity in SN-GRBs (Test 12)
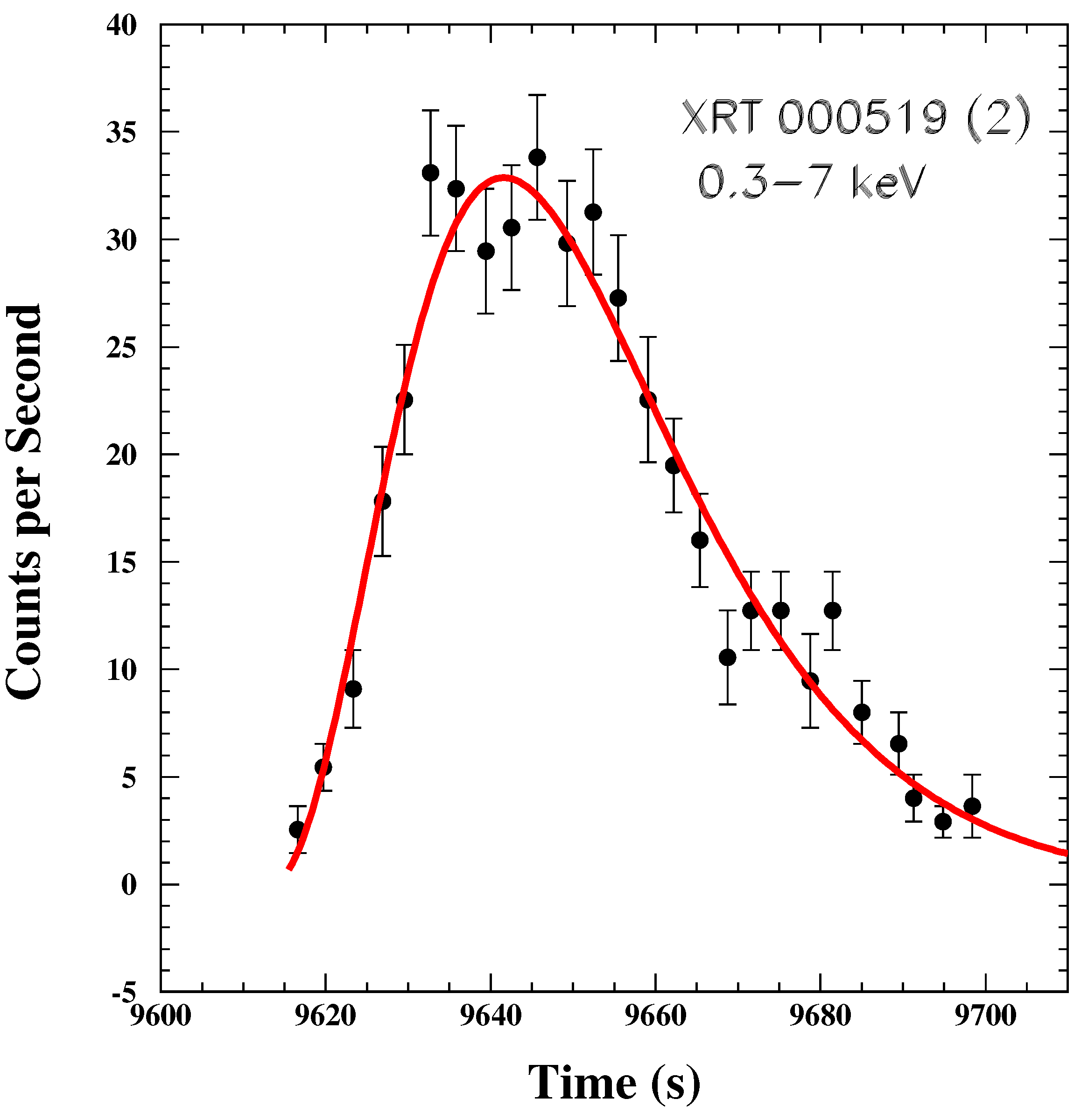
9.3.1. GRB980425
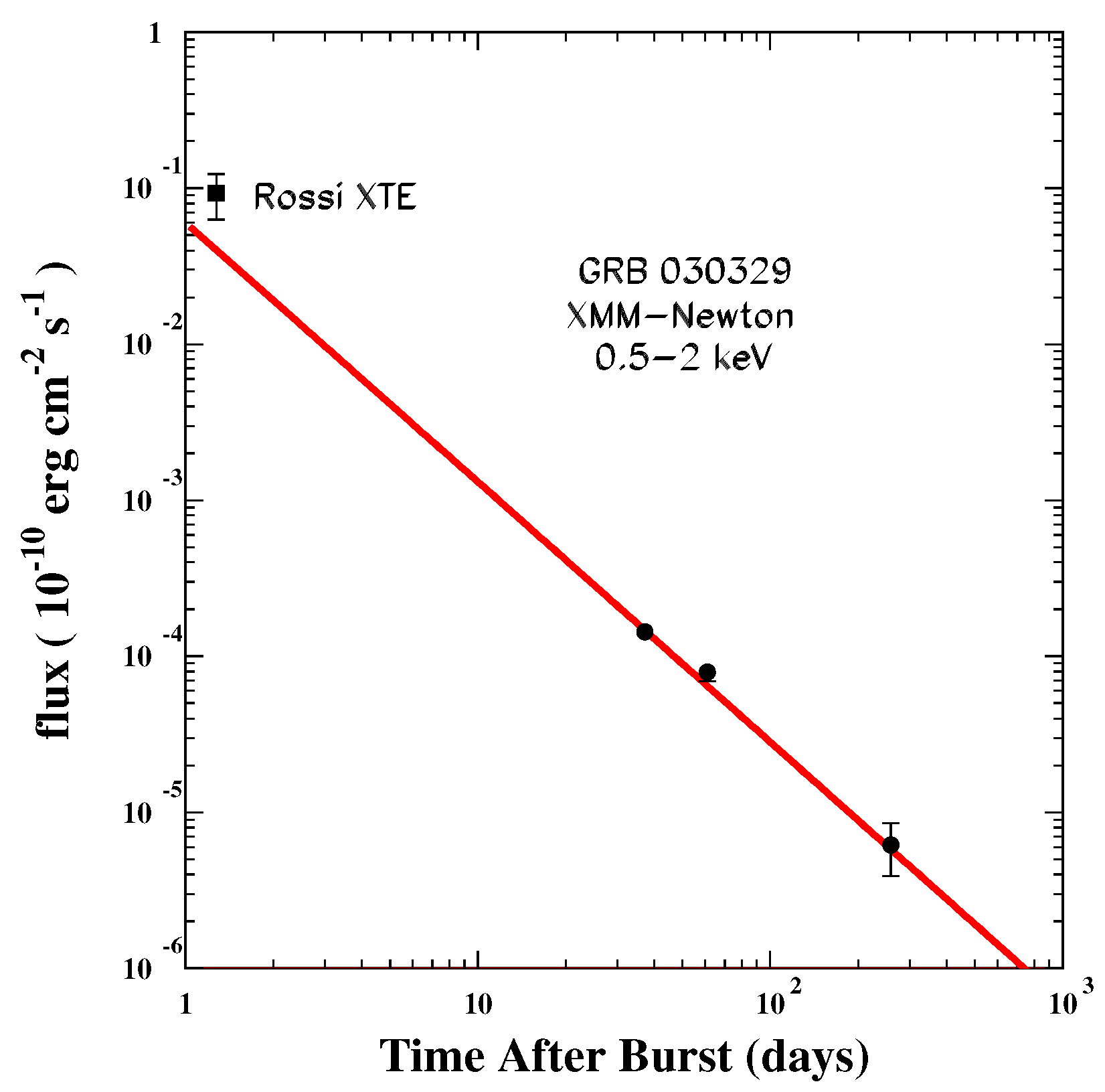
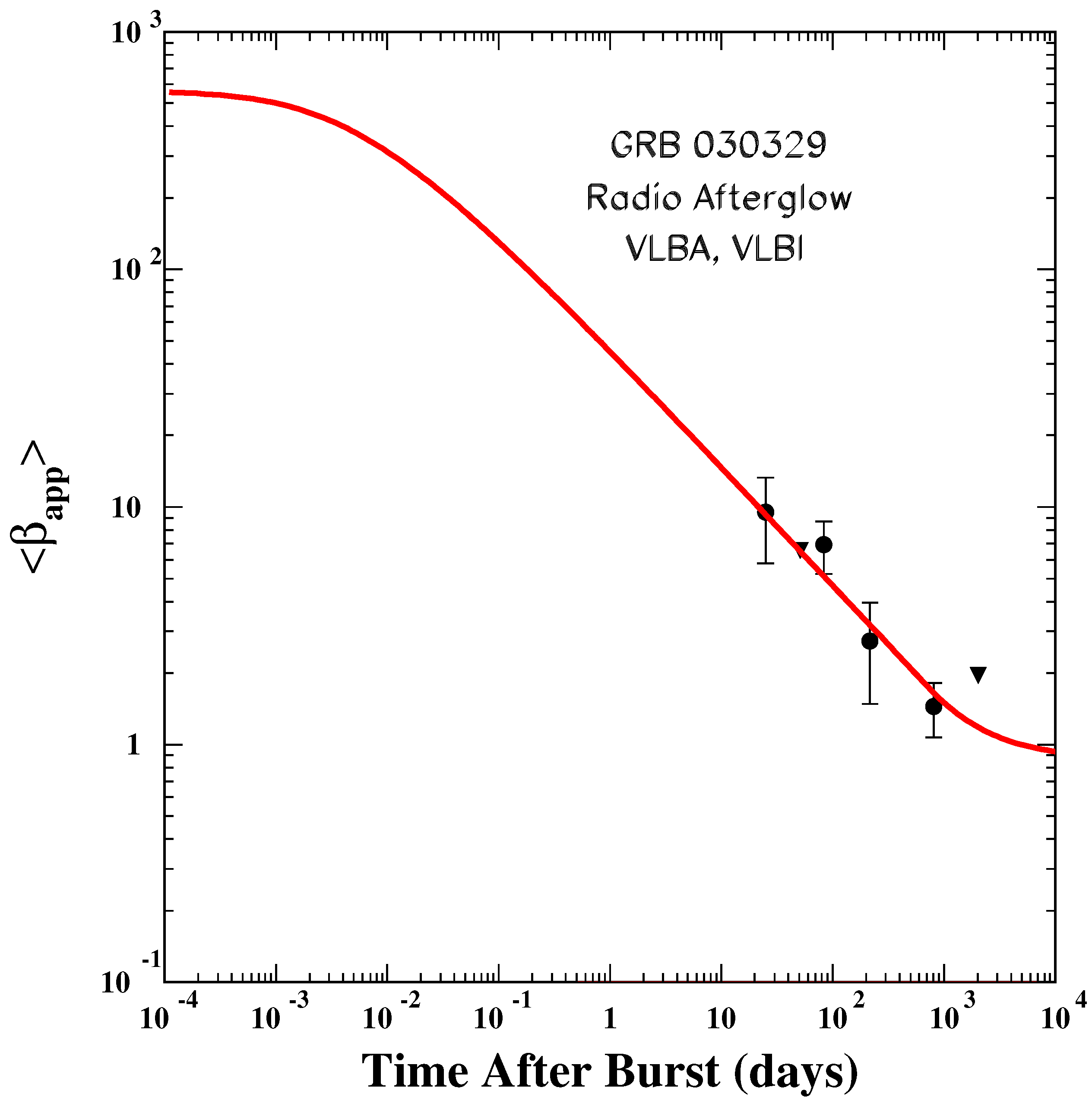
9.3.2. GRB030329
“Since it is only seen at a single frequency, it is remotely possible that this image is an artifact of the calibration.”
10. Fast Extragalactic X-ray Transients, Tests 14 & 15
XRFs in the FB Model
11. GRB Theories Confront SHB170817A (Test 16)
11.1. The Properties of the SHB170817A Ejecta
11.1.1. A Superluminally Moving Source
11.1.2. Superluminal Motion
11.1.3. Initial Lorentz Factor
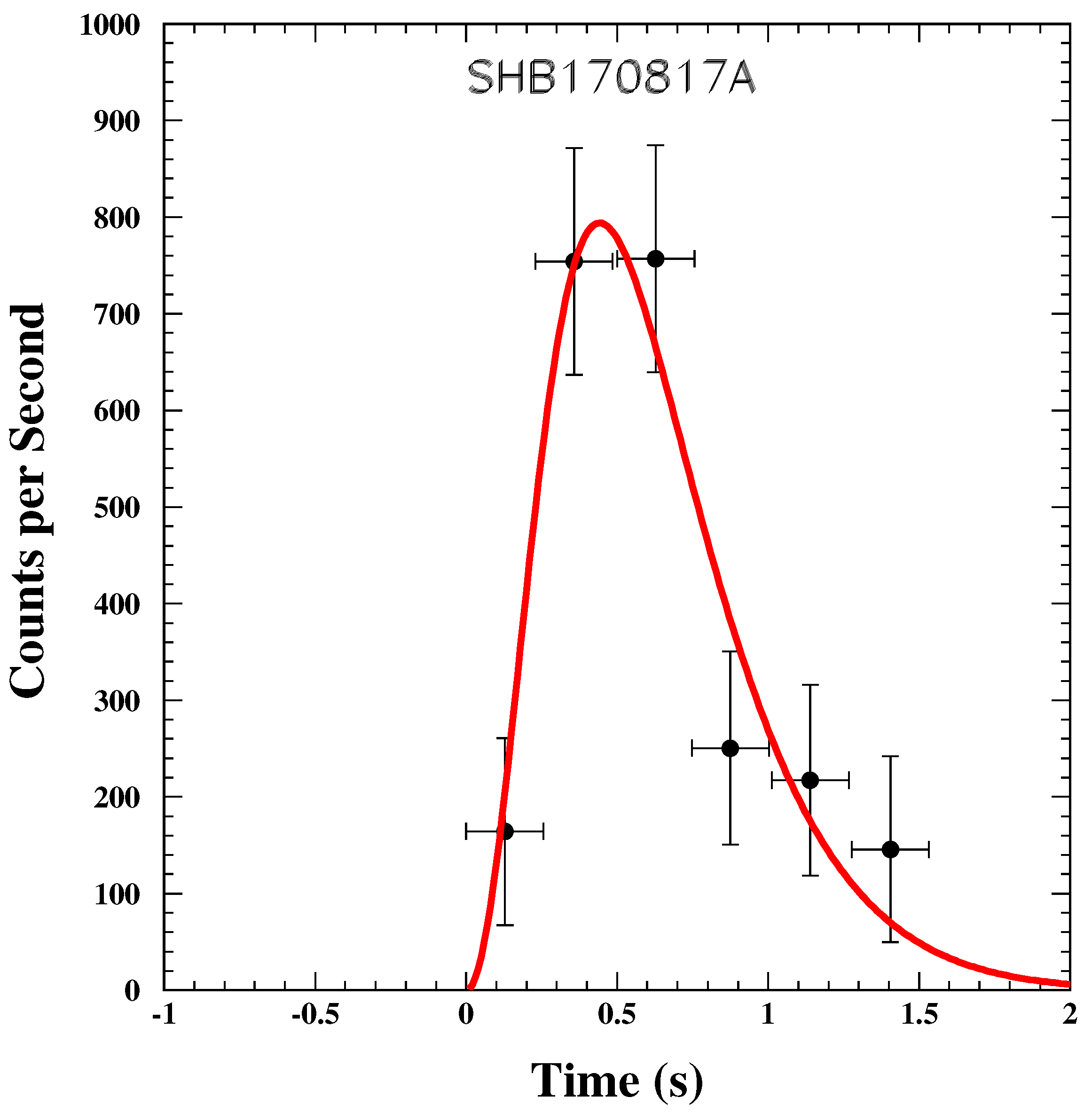
11.1.4. Prompt Emission Observables
11.2. The Single Pulse’s Correlation between Energy and Time
11.2.1. The Early Time Afterglow
11.2.2. The Late-Time Afterglow
12. FB Model Interpretations of SHB170817A
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | The original assumption in the CB model was that the interactions between a CB and the ISM were elastic. It was later realized, in view of the shape of AGs at late times, that a plastic collision—wherein most of the intercepted ISM is engulfed by the CB—was a better approximation in the AG phase. |
| 2 | Quite obviously, the replacements of physical parameters by their means may not be completely reliable, not only because of the spread in their values, but also because of detection thresholds and selection effects. |
References
- Fishman, G.J.; Meegan, C.A. Gamma Ray Bursts. Annual. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 33, 415–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebesadel, R.W.; Strong, I.B.; Olson, R.A. Observations of Gamma-Ray Bursts of Cosmic Origin. Astrophys. J. 1973, 182, L85–L88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemiroff, R.J. A Century of Gamma Ray Burst Models. AIP Conf. Proc. 1994, 307, 730. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, J.P.; Cline, T.L.; Desai, U.D.; Teegarden, B.J. Frequency of fast, narrow γ-ray bursts. Nature 1984, 308, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouveliotou, C.; Meegan, C.A.; Fishman, G.J.; Bhat, N.P.; Briggs, M.S.; Koshut, T.M.; Paciesas, W.S.; Pendleton, G.N. Identification of Two Classes of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 1993, 413, L101–L104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinnikov, S.I.; Novikov, I.D.; Perevodchikova, T.V.; Polnarev, A.G. Exploding Neutron Stars in Close Binaries. Soviet Astron. Lett. 1984, 10, 177–179. [Google Scholar]
- Paczynski, B. On the Cosmological Origin of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 1986, 308, L43–L46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.; Dar, A.; Nussinov, S. Neutrino Annihilation in Type II Supernovae and Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 1987, 314, L7–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J. Are Gamma-ray Bursts Optically Thick? Astrophys. J. 1986, 308, L47–L50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegan, C.A.; Fishman, G.J.; Wilson, R.B.; Paciesas, W.S.; Pendleton, G.N.; Horack, J.M.; Brock, M.N.; Kouveliotou, C. Spatial Distribution of Gamma-ray Bursts Observed by BATSE. Nature 1992, 355, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, P.; Rees, M.J. High-entropy Fireballs and Jets in Gamma-ray Burst Sources. MNRAS 1992, 257, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaviv, N.J.; Dar, A. Gamma Ray Bursts From Minijets. Astrophys. J. 1995, 447, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczynski, B.; Rhoads, J.E. Radio Transients From Gamma-Ray Bursters. Astrophys. J. 1993, 418, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.I. Low Frequency Spectra of Gamma-ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 1998, 432, L107–L109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, P. Rees, M.J. Optical And Long Wavelength Afterglow From Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 1997, 476, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.E.; Frontera, F.; Heise, J.; Feroci, M.A.; Fiore, F.; Cinti, M.N.; Dal Fiume, D.; Nicastro, L.; Orlandini, M.; Palazzi, E.; et al. Discovery of The X-ray Afterglow Of The Gamma-ray Burst of February 28 1997. Nature 1997, 38, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Paradijs, J.; Groot, P.J.; Galama, T.; Kouveliotou, C.; Strom, R.G.; Telting, J.; Rutten, R.G.M.; Fishman, G.J.; Meegan, C.A.; Pettini, M.; et al. Transient Optical Emission From the Error Box of The Gamma-ray Burst of 28 February 1997. Nature 1997, 386, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frail, D.A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Nicastro, L.; Feroci, M.; Taylo, G.B. The radio afterglow from the gamma-ray burst of 8 May 1997. Nature 1997, 389, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, K.C.; Livio, M.; Petro, L.; Macchetto, F.D.; Van Paradijs, J.; Kouveliotou, C.; Fishman, G.J.; Meegan, C.A.; Groot, P.J.; Galama, T. The Optical Counterpart To Gamma-ray Burst GRB970228 Observed Using The Hubble Space Telescope. Nature 1997, 387, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Metzger, M.R.; Djorgovski, S.G.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Steidel, C.C.; Adelberger, K.L.; Frail, D.A.; Costa, E.; Frontera, F. Spectral Constraints on the Redshift of the Optical Counterpart to the Gamma-ray Burst of 8 May 1997. Nature 1997, 387, 878–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, T.J.; Vreeswijk, P.M.; Van Paradijs, J.; Kouveliotou, C.; Augusteijn, T.; Böhnhardt, H.; Brewer, J.P.; Doublier, V.; Gonzalez, J.F.; Leibundgut, B.; et al. Discovery of The Peculiar Supernova 1998bw In The Error Box of GRB980425. Nature 1998, 670, 395. [Google Scholar]
- Fynbo, J.P.; Malesani, D.; Jakobsson, P. Long Gamma-ray Bursts Host Galaxies And Their Environments. Gamma-Ray Bursts. Camb. Astrophys. Ser. 2012, 51, 269–290. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, W.; Berger, E. The Locations of Short Gamma-ray Bursts As Evidence For Compact Object Binary Progenitors. Astrophy. J. 2013, 776, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E. Short-Duration Gamma-Ray Bursts. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 52, 43–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Kienlin, A.; Meegan, C.; Goldstein, A. GRB 170817A: Fermi GBM Detection. 2017. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017GCN.21520....1V/abstract (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Goldstein, A.; Veres, P.; von Kienlin, A.; GBM-LIGO Group; Blackburn, L.; Briggs, M.S.; Broida, J.; Burns, E.; Camp, J.; Dal Canton, T.; et al. LIGO/Virgo G298048—Update on Fermi/GBM GRB 170817A Analysis. 2017. Available online: https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2017GCN.21528....1G/abstract (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Goldstein, A.; Veres, P.; Burns, E.; Briggs, M.S.; Hamburg, R.; Kocevski, D.; Wilson-Hodge, C.A.; Preece, R.D.; Poolakkil, S.; Roberts, O.J.; et al. An Ordinary Short Gamma-Ray Burst With Extraordinary Implications: Fermi-GBM Detection of GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L14–L28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozanenko, A.S.; Barkov, M.V.; Minaev, P.Y.; Volnova, A.A.; Mazaeva, E.D.; Moskvitin, A.S.; Krugov, M.A.; Samodurov, V.A.; Loznikov, V.M.; Lyutikov, M. GRB170817A Associated with GW170817: Multifrequency Observations and Modeling of Prompt Gamma-ray Emission. Astrophys. J. 2018, 852, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savchenko, V.; Ferrigno, C.; Kuulkers, E.; Bazzano, A.N.G.E.L.A.; Bozzo, E.; Brandt, S.; Chenevez, J.; Courvoisier, T.L.; Diehl, R.; Domingo, A.; et al. INTEGRAL Detection Of The First Prompt Gamma-Ray Signal Coincident with The Gravitational Wave Event GW1708171. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L15–L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligo–Virgo Collaboration. Gravitational-wave Standard Siren Measurement Of The Hubble Constant. Nature 2017, 551, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligo–Virgo Collaboration. Gravitational Waves And Gamma-rays From a Binary Neutron Star Merger: GW170817 And GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L13–L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligo–Virgo Collaboration. GW170817: Observation of Gravitational Waves from a Binary Neutron Star Inspiral. Phys. Rev. Let. 2017, 119, 161101. [Google Scholar]
- Ligo–Virgo Collaboration. Multi-messenger Observations of a Binary Neutron Star Merger. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L12–L71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. Universal Afterglow Of Supernova-Less Gamma Ray Bursts. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 123031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melandri, A.; Pian, E.; D’Elia, V.; D’Avanzo, P.; Della Valle, M.; Mazzali, P.A.; Tagliaferri, G.; Cano, Z.; Levan, A.J.; Møller, P.; et al. Diversity of GRB Energetics vs. SN Homogeneity: Supernova 2013cq Associated with The Gamma-ray Burst 130427A. Astr. Astrophys. 2014, A29, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, Z.; Wang, S.Q.; Dai, Z.G.; Xue-Feng Wu, X.F. The Observer’s Guide To The Gamma-Ray Burst-Supernova Connection. Adv. Astron. 2017, 2017, 8929054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal-Yam, A.; Fox, D.B.; Price, P.A.; Ofek, E.O.; Davis, M.R.; Leonard, D.C.; Soderberg, A.M.; Schmidt, B.P.; Lewis, K.M.; Peterson, B.A.; et al. The Gamma-ray Burst GRB060614 Requires a Novel Explosive Process. Nature 2006, 444, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fynbo, J.P.; Watson, D.; Thöne, C.C.; Sollerman, J.; Bloom, J.S.; Davis, T.M.; Hjorth, J.; Jakobsson, P.; Jørgensen, U.G.; Graham, J.F.; et al. No Supernovae Associated With Two Long-duration Gamma-ray Bursts. Nature 2006, 444, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. The superluminal motion of the jet launched in GW170817, the Hubble constant, and critical tests of gamma ray bursts theory. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.08912. [Google Scholar]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. On The Origin of Supernova-Less Long Gamma Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2018, 855, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T. Gamma-Ray Bursts and the Fireball Model. Phys. Rep. 1999, 314, 575–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T. Gamma-ray Bursts—A Puzzle Being Resolved. Phys. Rep. 2000, 333, 529–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, P. Theories of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Ann. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 40, 137–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piran, T. The Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2004, 76, 1143–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Meszaros, P. Gamma-Ray Bursts: Progress, Problems & Prospects. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2004, 19, 2385–2472. [Google Scholar]
- Meszaros, P. Gamma-Ray Bursts. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2006, 69, 2259–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Making a Short Gamma-Ray Burst from a Long One: Implications for the Nature of GRB 060614. Chin. J. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 7, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakar, E. Short-Hard Gamma-Ray Bursts. Phys. Rep. 2007, 442, 166–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meszaros, P.; Rees, M.J. Gamma-Ray Bursts. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. Centen. Perspect. 2014, 256, 241–251. [Google Scholar]
- Pe’er, A. Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts Prompt Emission. J. Adv. Astron. 2015, 2015, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Zhang, B. The Physics of Gamma-Ray Bursts And Relativistic Jets. Phys. Rep. 2015, 561, 1–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z. Daigne. E, Meszaros, P. The theory of gamma-ray bursts. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 212, 409–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. The Cannonball Model of Gamma Ray Bursts: Spectral and Temporal Properties of the Gamma Rays. arXiv 2000, arXiv:astro-ph/0012227. [Google Scholar]
- Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. Towards a Complete Theory Of Gamma Ray Bursts. Phys. Rep. 2004, 405, 203–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A. Can Fireball or Firecone Models Explain Gamma Ray Bursts? Astrophys. J. 1998, 500, L93–L97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.; Plaga, R. Galactic Gamma-ray Bursters—An Alternative Source of Cosmic Rays at All Energies. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 349, 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. On The Optical And X-ray Afterglows of Gamma Ray Bursts. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 388, 1079D. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E. Hard X-ray and Gamma-ray From Supernovae. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 1993, 97, 205–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Woosley, S.E. Gamma-ray Bursts From Stellar Mass Accretion Disks Around Black Holes. Astrophys. J. 1993, 405, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rújula, A. May a Supernova Bang Twice? Phys. Lett. 1987, B193, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFadyen, A.I.; Woosley, S.E. Collapsars-Gamma-Ray Bursts and Explosions in “Failed Supernovae”. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X.; Paczynski, B. Transient Events from Neutron Star Mergers. Astrophys. J. 1998, 507, L59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covino, S.; Gotz, D. Polarization Of Prompt And Afterglow Emission 0f Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astron. Astrophys. Trans. 2016, 29, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Willis, D.R.; Barlow, E.J.; Bird, A.J.; Clark, D.J.; Dean, A.J.; McConnell, M.L.; Moran, L.; Shaw, S.E.; Sguera, V. Evidence of polarisation in the prompt gamma-ray emission from GRB 930131 and GRB 960924. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 439, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalemci, E.; Boggs, S.E.; Kouveliotou, C.; Finger, M.; Baring, G. Search for polarization from the prompt gamma-ray emission of GRB 041219a with SPI on INTEGRAL. Astrophys. J. Sup. 2017, 169, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coburn, W.; Boggs, S.E. Polarization of the prompt gamma-ray emission from the gamma-ray burst of 6 December 2002. Nature 2003, 423, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonetoku, D.; Murakami, T.; Gunji, S.; Mihara, T.; Toma, K.; Sakashita, T.; Morihara, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Toukairin, N.; Fujimoto, H.; et al. Detection of gamma-ray polarization in prompt emission of GRB 100826A. Astrophys. J. 2011, 743, L30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonetoku, D.; Murakami, T.; Gunji, S.; Mihara, T.; Toma, K.; Morihara, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Wakashima, Y.; Yonemochi, H.; Sakashita, T.; et al. Magnetic Structures in Gamma-Ray Burst Jets Probed by Gamma-Ray Polarization. Astrophys. J. 2012, 758, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotz, D.; Covino, S.; Fernandez-Soto, A.; Laurent, P.; Bosnjak, Z. The polarized Gamma-Ray Burst GRB 061122. MNRAS 2013, 431, 3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götz, D.; Laurent, P.; Antier, S.; Covino, S.; D’Avanzo, P.; d’Elia, V.; Melandri, A. GRB 140206A: The most distant polarized Gamma-Ray Burst. MNRAS 2014, 444, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Iyyani, S.; Bhattacharya, D.; Chattopadhyay, T.; Rao, A.R.; Aarthy, E.; Vadawale, S.V.; Mithun, N.P.S.; Bhalerao, V.B.; Ryde, F. Time-varying Polarized Gamma-Rays from GRB 160821A: Evidence for Ordered Magnetic Fields. Astrophys. J. 2019, 882, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Gupta, S.; Chattopadhyay, T.; Lipunov, V.; Castro-Tirado, A.J.; Bhattacharya, D.P.; Pandey, S.B.; Oates, S.R.; Kumar, A.; Hu, Y.D.; et al. Probing into emission mechanisms of GRB 190530A using time-resolved spectra and polarization studies: Synchrotron Origin? arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.01167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. The Double-Peak Spectral Energy Density of Gamma-ray Bursts and The True Identity of GRB 031203. Astrophys. J. 2005, 627, L109–L112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. On the origin of the correlations between gamma-ray burst observables. Astrophys. J. 2007, 663, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Frontera, F.; Tavani, M.; Antonelli, A.; Costa, E.; Feroci, M.; Guidorzi, C.; Heise, J.; Masetti, N.; Montanari, E.; et al. Intrinsic spectra and energetics of BeppoSAX Gamma-Ray Bursts with known redshifts. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 390, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, A.; Rao, A.R. Pulse-wise Amati correlation in Fermi GRBs. MNRAS 2013, 436, 3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, P.G.; Glennie, A.; Heida, M.; Maccarone, T.; Hodgkin, S.; Nelemans, G.; Miller-Jones, J.C.A.; Torres, M.A.P.; Fender, R. Discovery of a new kind of explosive X-ray transient near M86. Astrophys. J. 2013, 779, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, W.C.; Lada, C.J. Emission From Supernova Remnants. Thermal Bremstrahlung in the Sedov Taylor Phase. Astrophys. J. 1975, 195, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. The diverse broad-band light-curves of Swift LGRBs reproduced with the cannonball model. Astrophys. J. 2009, 696, 994–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocevski, D.; Ryde, F.; Liang, E. Search for Relativistic Curvature Effects in Gamma-Ray Burst Pulses. Astrophys. J. 2003, 596, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenimore, E.E.; Madras, C.D.; Nayakshin, S. Expanding Relativistic Shells and Gamma-Ray Burst Temporal Structure. Astrophys. J. 1996, 473, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Panaitescu, A. Afterglow Emission from Naked Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2000, 541, L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryde, F.; Petrosian, V. Gamma-Ray Burst Spectra and Light Curves as Signatures of a Relativistically Expanding Plasma. Astrophys. J. 2002, 578, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermer, C.D. Curvature Effects in Gamma Ray Burst Colliding Shells. Astrophys. J. 2004, 614, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.W.; Zhang, B.; O’Brien, P.T.; Willingale, R.; Angelini, L.; Burrows, D.N.; Campana, S.; Chincarini, G.; Falcone, A.; Gehrels, N.; et al. Testing the Curvature Effect and Internal Origin of Gamma-Ray Burst Prompt Emissions and X-ray Flares with Swift Data. Astrophys. J. 2006, 646, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaitescu, A. Phases of Swift X-ray Afterglows. Nuovo Cimento 2006, B121, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Norris, J.P.; Bonnell, J.T.; Kazanas, D.; Scargle, J.D.; Hakkila, J.; Giblin, T.W. Long-lag, Wide-Pulse Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2005, 627, 324–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkila, J.; Lien, A.; Sakamoto, T.; Morris, D.; Neff, J.E.; Giblin, T.W. Swift Observations of Gamma-Ray Burst Pulse Shapes: GRB Pulse Spectral Evolution Clarified. Astrophys. J. 2015, 815, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Piran, T.; Sari, R. Can internal shocks produce the variability in GRBs? Astrophys. J. 1997, 490, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederiksen, T.; Hededal, C.B.; Haugble1, T.; Nordlund, A. Magnetic Field Generation in Collisionless Shocks: Pattern Growth and Transport. Astrophys. J. 2004, 608, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. On the canonical behaviour of the X-ray afterglows of the Gamma Ray Bursts observed with Swift’s XRT. Astrophys. J. 2006, 646, L21–L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, S.; Goad, M.R.; Beardmore, A.P.; O’Brien, P.T.; Osborne, J.P.; Page, K.L.; Barthelmy, S.D.; Burrows, D.N.; Campana, S.; Cannizzo, J.K.; et al. Swift observations of the X-ray bright GRB 050315. Astrophys. J. 2006, 638, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cusumano, G.; Mangano, V.; Angelini, L.; Barthelmy, S.; Beardmore, A.P.; Burrows, D.N.; Campana, S.; Cannizzo, J.K.; Capalbi, M.; Chincarini, G.; et al. Swift XRT Observations of the Afterglow of GRB 050319. Astrophys. J. 2006, 639, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. Conical Fireballs, Cannonballs, and Jet-Breaks in the Afterglows of Gamma Ray Burst. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 558, A115. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, P.A.; Beardmore, A.P.; Page, K.L.; Tyler, L.G.; Osborne, J.P.; Goad, M.R.; O’Brien, P.T.; Vetere, L.; Racusin, J.; Morris, D.; et al. Swift-XRT GRB light curve repository, UK Swift Science Data Centre, Univ. of Leicester. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 469, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.A.; Beardmore, A.P.; Page, K.L.; Osborne, J.P.; O’Brien, P.T.; Willingale, R.; Starling, R.L.C.; Burrows, D.N.; Godet, O.; Vetere, L.; et al. Methods and results of an automatic analysis of a complete sample of Swift-XRT observations of GRBs. MNRAS 2009, 397, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, M.; Page, M.J.; Kann, D.A.; Oates, S.R.; Schulze, S.; Zhang, B.; Cano, Z.; Gendre, B.; Malesani, D.; Rossi, A.; et al. The 80 Ms follow-up of the X-ray afterglow of GRB 130427A challenges the standard forward shock model. MNRAS 2016, 462, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, A.; Melandri, A.; Nava, L.; Mundell, C.G.; Kawai, N.; Campana, S.; Covino, S.; Cummings, J.R.; Cusumano, G.; Evans, P.A.; et al. GRB 130427A: A Nearby Ordinary Monster. Science 2014, 343, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. The superluminal motion of Gamma-Ray-Burst sources and the complex afterglow of GRB 030329. arXiv 2004, arXiv:astro-ph/0402374. [Google Scholar]
- Grupe, D.; Burrows, D.N.; Wu, X.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, E.W.; Garmire, G.; Nousek, J.A.; Gehrels, N.; Ricker, G.R.; et al. Late-time detections of the X-ray afterglow of GRB 060729 with Chandra-the latest detections ever of an X-ray afterglow. Astrophys. J. 2010, 711, 1008–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. Jet breaks’ and ‘missing breaks’ in the X-ray afterglow of Gamma Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2008, 680, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schady, P.; De Pasquale, M.; Page, M.J.; Vetere, L.; Pandey, S.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Cummings, J.; Zhang, B.; Zane, S.; Breeveld, A.; et al. Extreme Properties Of GRB061007: A Highly Energetic or Highly Collimated Burst? MNRAS 2007, 380, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wijers, R.A.M.; Rees, M.J.; Meszaros, P. Shocked by GRB 970228: The afterglow of a cosmological fireball. MNRAS 1997, 288, L51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fan, Y.Z.; Dyks, J.; Kobayashi, S.; Mészáros, P.; Burrows, D.N.; Nousek, J.A.; Gehrels, N. Physical processes shaping GRB X-ray afterglow lightcurves: Theoretical implications from the Swift XRT observations. Astrophys. J 2006, 642, 354–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, J.E. The Dynamics and Light Curves of Beamed Gamma Ray Burst Afterglows. Astrophys. J. 1999, 525, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.; Piran, T.; Halpern, J.P. Jets in Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 1999, 519, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frail, D.A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Sari, R.; Djorgovski, S.G.; Bloom, J.S.; Galama, T.J.; Reichart, D.E.; Berger, E.; Harrison, F.A.; Price, P.A.; et al. Beaming in Gamma-Ray Bursts: Evidence for a Standard Energy Reservoir. Astrophys. J. 2001, 562, L55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, R.A.; Li, Z.Y. Wind Interaction Models for Gamma-Ray Burst Afterglows: The Case for Two Types of Progenitors. Astrophys. J. 2000, 536, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, J.S.; Frail, D.A.; Kulkarni, S.R. GRB Energetics and the GRB Hubble Diagram: Promises and Limitations. Astrophys. J. 2003, 594, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.W.; Racusin, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, B.B.; Burrows, D.N. A Comprehensive Analysis of Swift/XRT Data: III. Jet Break Candidates in X-ray and Optical Afterglow Lightcurves. Astrophys. J. 2008, 675, L528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racusin, J.L.; Liang, E.W.; Burrows, D.N.; Falcone, A.; Sakamoto, T.; Zhang, B.B.; Zhang, B.; Evans, P.; Osborne, J. Jet breaks and Energetics of Swift GRB X-ray Afterglows. Astrophys. J. 2009, 698, 43–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, E.; Soffitta, P.; Alessi, A.; Amati, L.; Costa, E.; Frontera, F.; Fruchter, A.; Masetti, N.; Palazzi, E.; Panaitescu, A.; et al. BeppoSAX confirmation of beamed afterglow emission from GRB990510. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 372, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, K.Z.; Garnavich, P.M.J.; Kaluzny, J.; Pych, W.; Thompson, I. BVRI Observations of the Optical Afterglow of GRB 990510. Astrophys. J. 1999, 522, L39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, F.A.; Bloom, J.S.; Frail, D.A. Optical and Radio Observations of the Afterglow from GRB990510: Evidence for a Jet. Astrophys. J. 1999, 523, L121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel, G.L.; Marconi, G.; Covino, S.; Lazzati, D.; Ghisellini, G.; Campana, S.; Guzzo, L.; Guerrero, G.; Stella, L. ESO deep observations of the optical afterglow of GRB990510. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 348, L5. [Google Scholar]
- Beuermann, K.; Hessman, F.V.; Reinsch, K.; Nicklas, H.; Vreeswijk, P.M.; Galama, T.J.; Rol, E.; Van Paradijs, J.; Kouveliotou, C.; Frontera, F.; et al. VLT observations of GRB 990510 and its environment. Astron. Astrophys. 1999, 35, L26. [Google Scholar]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. Fast Extragalactic X-ray Transients From Binary Neutron Star Mergers. Phys. Rev. 2019, D101, 063008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drout, M.R.; Piro, A.L.; Shappee, B.J.; Kilpatrick, C.D.; Simon, J.D.; Contreras, C.; Coulter, D.A.; Foley, R.J.; Siebert, M.R.; Morrell, N.; et al. Light Curves of the Neutron Star Merger GW170817/SSS17a: Implications for R-Process Nucleosynthesis. Science 2017, 358, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgate, S.A. Prompt gamma rays and X-rays from supernovae. CaJPS 1968, 46, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colgate, S.A. Early Gamma Rays from Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1974, 187, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczynski, B. Gamma-ray bursters at cosmological distances. Astrophys. J. 1986, 308, L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffitta, P.; Feroci, M.; Piro, L. GRB 98045 IAU Circulars No. 6884.1. 1998. Available online: http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/services/IAUC.html (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Pian, E.; Amati, L.; Antonelli, L.A.; Butler, R.C.; Costa, E.; Cusumano, G.; Danziger, J.; Feroci, M.; Fiore, F.; Frontera, F. et al. BeppoSAX Detection and Follow-up of GRB980425. Astronom. Astrophys. 1999, 138, 463. [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto, K.; Mazzali, P.A.; Nomoto, K.; Umeda, H.; Nakamura, T.; Patat, F.; Danziger, I.J.; Young, T.R.; Suzuki, T.; Shigeyama, T.; et al. A hypernova model for the supernova associated with the gamma-ray burst of 25 April 1998. Nature 1999, 395, 672–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wheeler, J.C. The Supernova Gamma-ray Burst Connection. Astrophys. J. 1998, 504, L87–L90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanderspek, R.; Sakamoto, T.; Barraud, C.; Tamagawa, T.; Graziani, C.; Suzuki, M.; Shirasaki, Y.; Prigozhin, G.; Villasenor, J.; Jernigan, J.G.; et al. HETE Observations of the Gamma-Ray Burst GRB030329: Evidence for an Underlying Soft X-ray Component. Astrophys. J. 2004, 617, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. The Supernova associated with GRB 030329. Astrophys. J. 2003, 594, L89–L92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, J.S.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Harrison, F.; Prince, T.; Phinney, E.S.; Frail, D.A. Expected characteristics of the subclass of Supernova Gamma-ray Bursts. (S-GRBs). Astrophys. J. 1998, 506, L105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woosley, S.E.; Eastman, R.G.; Schmidt, B.P. Gamma-Ray Bursts and Type Ic Supernovae: SN 1998bw. Astrophys. J. 1999, 516, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, K.; Sari, R.; Djorgovski, S.G. Cosmic Gamma-Ray bursts, their afterglows, and their host galaxies. In Compact Stellar X-ray Sources; Lewin, W., van der Klis, M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Patat, F.; Cappellaro, E.; Danziger, J.; Mazzali, P.A.; Sollerman, J.; Augusteijn, T.; Brewer, J.; Doublier, V.; Gonzalez, J.F.; Hainaut, O.; et al. The Metamorphosis of SN 1998bw. Astrophys. J. 2001, 555, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.R.; Frail, D.A.; Wieringa, M.H.; Ekers, R.D.; Sadler, E.M.; Wark, R.M.; Higdon, J.L.; Phinney, E.S.; Bloom, J.S. Radio emission from the unusual supernova 1998bw and its association with the gamma-ray burst of 25 April 1998. Nature 1998, 395, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouveliotou, C.; Woosley, S.E.; Patel, S.K.; Levan, A.; Blandford, R.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Wijers, R.A.M.J.; Weisskopf, M.C.; Tennant, A.; Pian, E.; et al. Chandra Observations of the X-ray Environs of SN 1998bw/GRB 980425. Astrophys. J. 2004, 608, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. The Smoking Guns Of Short Hard Gamma Ray Bursts. arXiv 2007, arXiv:1708.04603. [Google Scholar]
- Wijers, R.A.M.J.; Bloom, J.S.; Bagla, J.S.; Natarajan, P. Gamma-ray bursts from stellar remnants: Probing the Universe at high redshift. MNRAS 1998, 294, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, D.W.; Fruchter, A.S. The faint-galaxy hosts of gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 1999, 520, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A. Long Gamma Ray Bursts Trace The Star Formation History. Astrophys. J. 2014, 785, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabal, N.; Halpern, J.P. GRB 160220B: Swift Detection of a Burst. 2006. Available online: https://gcn.gsfc.nasa.gov/other/160220B.gcn3 (accessed on 31 December 2021).
- Guetta, D.; Della Valle, M. On the Rates of Gamma Ray Bursts and Type Ib/c Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2007, 657, L73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigne, F.; Rossi, E.M.; Mochkovitch, R. The redshift distribution of SWIFT Gamma-Ray Bursts: Evidence for evolution. MNRAS 2006, 372, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Dermer, C.D. On the Redshift Distribution of Gamma Ray Bursts in the Swift Era. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, H.; Kistler, M.D. Enhanced Cosmological GRB Rates and Implications for Cosmogenic Neutrinos. Phys. Rev. 2007, D75, 083004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvaterra, R.; Chincarini, C. The Gamma Ray Burst Luminosity Function in the Light of the Swift 2-year Data. Astrophys. J. 2007, 656, L49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.X. Star Formation History up to z = 7.4: Implications for Gamma-Ray Bursts and the Cosmic Metallicity Evolution. MNRAS 2008, 388, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kistler, M.D.; Yuksel, H.; Beacom, J.F.; Stanek, K.Z. An Unexpectedly Swift Rise in the Gamma-ray Burst Rate. Astrophys. J. 2008, 673, L119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel, H.; Kistler, M.D.; Beacom, J.F.; Hopkins, A.M. Revealing the High-Redshift Star Formation Rate with Gamma-Ray Bursts. Astrophys. J. 2008, 683, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvaterra, R.; Guidorzi, C.; Campana, S.; Chincarini, G.; Tagliaferri, G. Evidence for Luminosity Evolution of Long Gamma-ray Bursts in Swift Data. MNRAS 2009, 396, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderberg, A.M.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Berger, E.; Fox, D.W.; Sako, M.; Frail, D.A.; Gal-Yam, A.; Moon, D.S.; Cenko, S.B.; Yost, S.A.; et al. The sub-energetic GRB 031203 as a cosmic analogue to GRB 980425. Nature 2004, 430, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coward, D.M. Simulating a faint gamma-ray burst population. MNRAS 2005, 360, L77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, E.; Mazzali, P.A.; Masetti, N.; Ferrero, P.; Klose, S.; Palazzi, E.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Woosley, S.E.; Kouveliotou, C.; Deng, J.; et al. An optical supernova associated with the X-ray flash XRF 060218. Nature 2006, 442, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, B.E.; Bailyn, C.D.; van Dokkum, P.G.; Natarajan, P. SN 2006aj and the nature of low-luminosity gamma-ray bursts. Astrophys. J. 2006, 645, L113–L116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, E.; Zhang, B.; Virgili, F.; Dai, Z.G. Low Luminosity Gamma-Ray Bursts as a Unique Population: Luminosity Function, Local Rate, and Beaming Factor. Astrophys. J. 2007, 662, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amati, L.; Della Valle, M.; Frontera, F.; Malesani, D.; Guidorzi, C.; Montanari, E.; Pian, E. On the consistency of the peculiar GRBs 060218 and 060614 with the Ep,i—Eiso correlation. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 463, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soderberg, A.M.; Nakar, E.; Cenko, S.B.; Cameron, P.B.; Frail, D.A.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Fox, D.B.; Berger, E.; Gal-Yam, A.; Moon, D.S.; et al. A Spectacular Radio Flare from XRF 050416a at 40 days and Implications for the Nature of X-ray Flashes. Astrophys. J. 2007, 661, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virgili, F.; Liang, E.W.; Zhang, B. Low-Luminosity Gamma-Ray Bursts as a Distinct GRB Population: A Firmer Case from Multiple Criteria Constraints. MNRAS 2009, 392, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Z.; Zhang, B.-B.; Xu, D.; Liang, E.W.; Zhang, B. XRF 100316D/SN 2010bh: Clue to the diverse origin of nearby supernova-associated GRBs. Astrophys. J. 2011, 726, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, O.; Nakar, E.; Piran, T. Are low luminosity GRBs generated by relativistic jets? Astrophys. J. 2011, 739, L550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guetta, D.; Piran, T. Do long-duration GRBs follow star formation? JCAP 2007, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, B.E.; Ellis, R.S. Connecting the Gamma Ray Burst Rate and the Cosmic Star Formation History: Implications for Reionization and Galaxy Evolution. Astrophys. J. 2012, 744, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.J.; Wu, X.F.; Melia, F.; Wei, D.M.; Feng, L.L. Cosmological Tests Using GRBs, the Star Formation Rate and Possible Abundance Evolution. MNRAS 2014, 439, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pian, E.; Giommi, P.; Amati, L.; Costa, E.; Danziger, J.; Feroci, M.; Fiocchi, M.T.; Frontera, F.; Kouveliotou, C.; Masetti, N.; et al. XMM-Newton Observations of the Field of Gamma-Ray Burst 980425. AdSpR 2004, 34, 2711. [Google Scholar]
- Amati, L. The Ep,i—Eiso correlation in GRBs: Updated observational status, re-analysis and main implications. MNRAS 2006, 372, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooley, K.P.; Deller, A.T.; Gottlieb, O.; Nakar, E.; Hallinan, G.; Bourke, S.; Frail, D.A.; Horesh, A.; Corsi, A.; Hotokezaka, K. Superluminal motion of a relativistic jet in the neutron star merger GW170817. Nature 2018, 561, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooley, K.P.; Frail, D.A.; Dobie, D.; Lenc, E.; Corsi, A.; De, K.; Nayana, A.J.; Makhathini, S.; Heywood, I.; Murphy, T.; et al. A Strong Jet Signature in the Late-Time Lightcurve of GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2018, 868, L11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapteyn, J.C. Über die Bewegung der Nebel in der Umgebung von Nova Persei. Astron. Nachr. 1902, 157, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courdec, P. Les aurles lumineuses des nova. Annales d’Astrophysique 1939, 2, 271. [Google Scholar]
- Rees, M.J. Appearance of relativistically expanding radio sources. Nature 1966, 211, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. A cannonball model of gamma-ray bursts: Superluminal signatures. arXiv 2000, arXiv:astro-ph/0008474. [Google Scholar]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. Hyperluminal Signatures in the Afterglows of Gamma-Ray Bursts 980425 and 030329. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1610.01985. [Google Scholar]
- Soderberg, A.M.; Frail, D.A.; Wieringa, M.H. Constraints on Off-Axis GRB Jets in Type Ibc Supernovae From Late-Time Radio Observations. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; Frail, D.A.; Berger, E.; Kulkarni, S.R. The Angular Size and Proper Motion of the Afterglow of GRB 030329. Astrophys. J. 2004, 609, L1–L4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, P.N.; Briggs, M.S.; Connaughton, V.; Kouveliotou, C.; van der Horst, A.J.; Paciesas, W.; Meegan, C.A.; Bissaldi, E.; Burgess, M.; Chaplin, V.; et al. Temporal Deconvolution study of Long and Short Gamma-Ray Burst Light curves. Astrophys. J. 2012, 744, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.B.; Momjian, E.; Pihlstr, Y.T.; Ghosh, T.; Salte, C. Late-time observations of the afterglow and environment of GRB 030329. Astrophys. J. 2005, 622, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlstrom, T.M.; Taylor, G.B.; Granot, J.; Doeleman, S. Stirring the Embers: High Sensitivity VLBI Observations of GRB030329. Astrophys. J. 2007, 664, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mesler, R.; Pihlstrom, Y.; Taylor, G.; Granot, J. VLBI and Archival VLA and WSRT Observations of the GRB 030329 Radio Afterglow. Astrophys. J. 2012, 759, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesler, R.A.; Pihlstrom, Y.M. Calorimetry of GRB 030329: Simultaneous Fitting to the Broadband Radio Afterglow and the Observed Image Expansion Rate. Astrophys. J. 2013, 774, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiengo, A.; Mereghetti, S.; Ghisellini, G.; Tavecchio, F.; Ghirlanda, G. Late evolution of the X-ray afterglow of GRB 030329. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 423, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granot, J.; Loeb, A. Radio Imaging of Gamma-Ray Burst Jets in Nearby Supernovae. Astrophys. J. 2003, 593, L81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granot, J.; Ramirez-Ruiz, E.; Loeb, A. Implications of the Measured Image Size for the Radio Afterglow of GRB 030329. Astrophys. J. 2004, 2004, 413–425. [Google Scholar]
- Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rujula, A. On the origin of X-ray Flashes. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 422, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glennie, A.; Jonker, P.G.; Fender, R.P.; Nagayama, T.; Pretorius, M.L. Two fast X-ray transients in archival Chandra data. MNRAS 2015, 450, 3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.Q.; Zheng, X.C.; Li, Y.; Brandt, W.N.; Zhang, B.; Luo, B.; Zhang, B.B.; Bauer, F.E.; Sun, H.; Lehmer, B.D.; et al. A magnetar-powered X-ray transient as the aftermath of a binary neutron-star merger. Nature 2019, 568, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjorth, J.; Levan, A.J.; Tanvir, N.R.; Lyman, J.D.; Wojtak, R.; Schrøder, S.L.; Mandel, I.; Gall, C.; Bruun, S.H. The Distance to NGC 4993: The Host Galaxy of the Gravitational-wave Event GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, L31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Macri, L.M.; Hoffmann, S.L.; Scolnic, D.; Casertano, S.; Filippenko, A.V.; Tucker, B.E.; Reid, M.J.; Jones, D.O.; Silverman, J.M.; et al. A 2.4 % Determination of the Local Value of the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2016, 826, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Casertano, S.; Yuan, W.; Macri, L.; Bucciarelli, B.; Lattanzi, M.G.; MacKenty, J.W.; Bowers, J.B.; Zheng, W.; Filippenko, A.V.; et al. Milky Way Cepheid Standards for Measuring Cosmic Distances and Application to Gaia DR2: Implications for the Hubble Constant. Astrophys. J. 2018, 861, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, I. The orbit of GW170817 was inclined by less than 28 degrees to the line of sight. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, L12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissanke, S.; Holz, D.E.; Scott, A.; Hughes, S.A.; Dalal, N.; Sievers, J.L. Exploring short gamma-ray bursts as gravitational-wave standard sirens. Astrophys. J. 2010, 725, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhathini, S.; Mooley, K.P.; Brightman, M.; Hotokezaka, K.; Nayana, A.J.; Intema, H.T.; Dobie, D.; Lenc, E.; Perley, D.A.; Fremling, C.; et al. The Panchromatic Afterglow of GW170817: The full uniform dataset, modeling, comparison with previous results and implications. Astrophys. J. 2021, 922, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mooley, K.P.; Nakar, E.; Hotokezaka, K.; Hallinan, G.; Corsi, A.; Frail, D.A.; Horesh, A.; Murphy, T.; Lenc, E.; Kaplan, D.L.; et al. A mildly relativistic wide-angle outflow in the neutron star merger GW170817. Nature 2018, 554, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobie, D.; Kaplan, D.L.; Murphy, T.; Lenc, E.; Mooley, K.P.; Lynch, C.; Corsi, A.; Frail, D.; Kasliwal, M.; Hallinan, G. A turnover in the radio light curve of GW170817. Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, L15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, R.; Piran, T.; Narayan, R. Spectra and Light Curves of Gamma-Ray Burst Afterglows. Astrophys. J. 1998, 497, L17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzati, D.; Perna, R.; Morsony, B.J.; Lopez-Camara, D.; Cantiello, M.; Ciolfi, R.; Giacomazzo, B.; Workman, J.C. Late time afterglow observations reveal a collimated relativistic jet in the ejecta of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 241103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



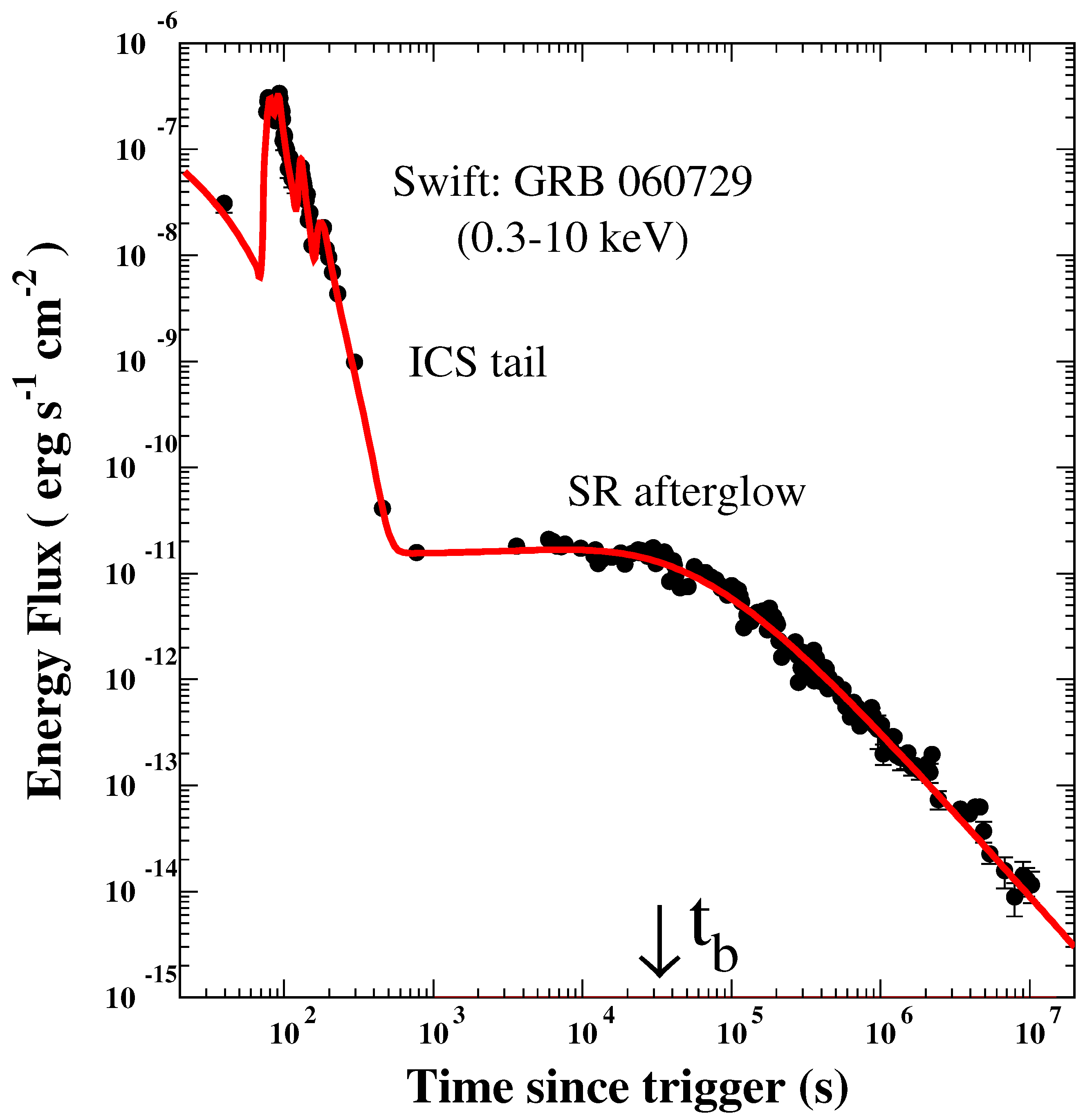
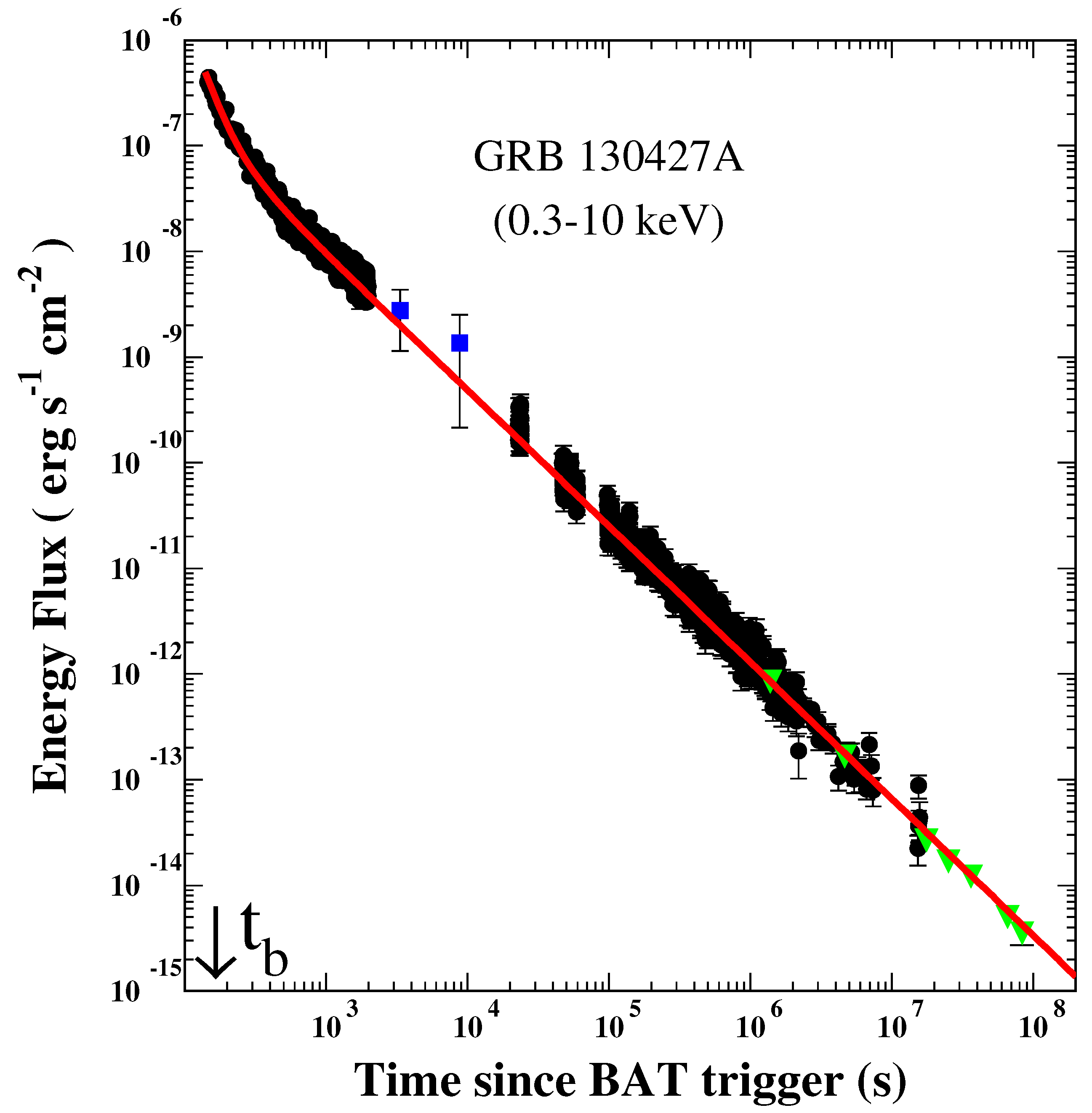

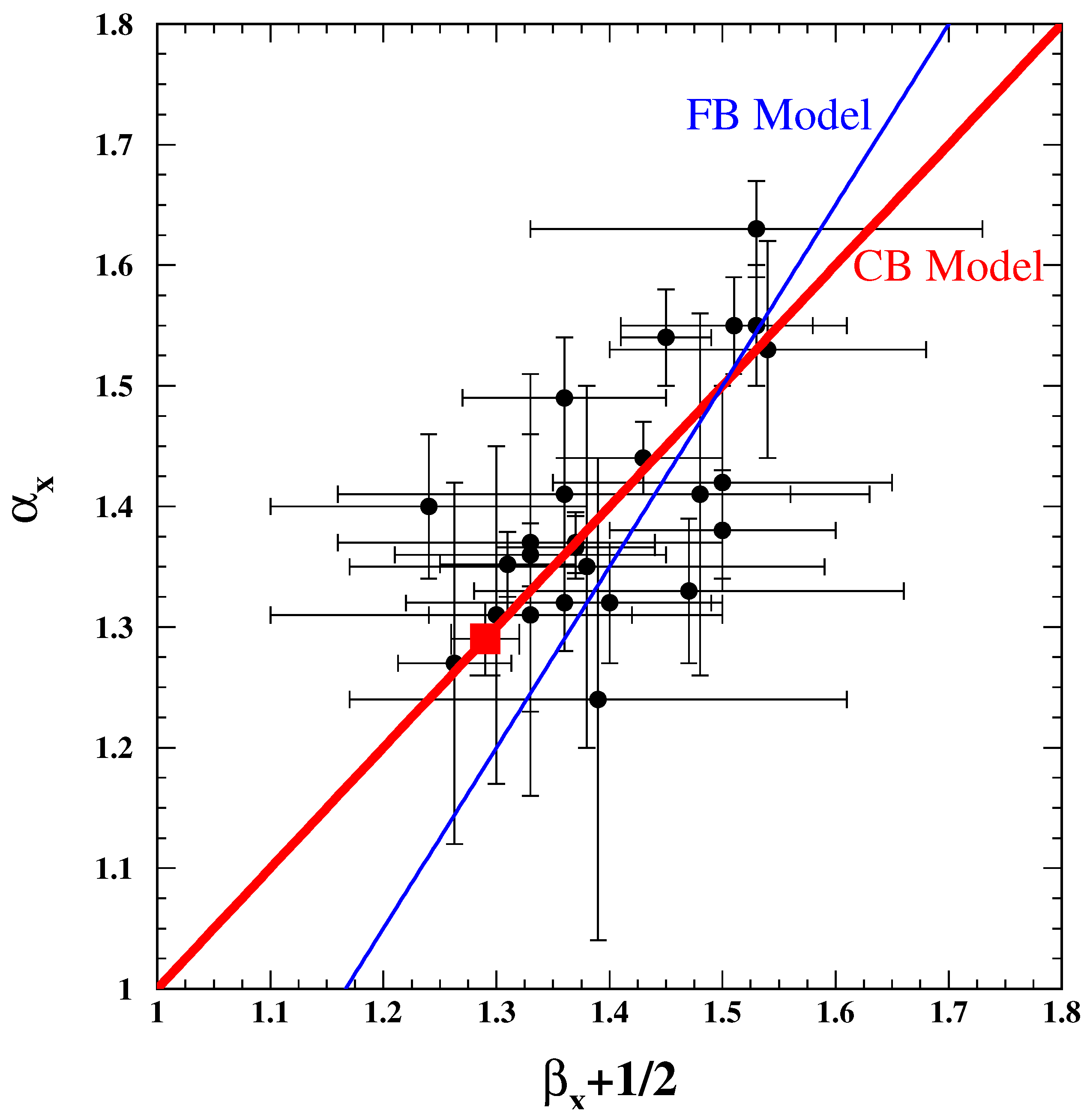

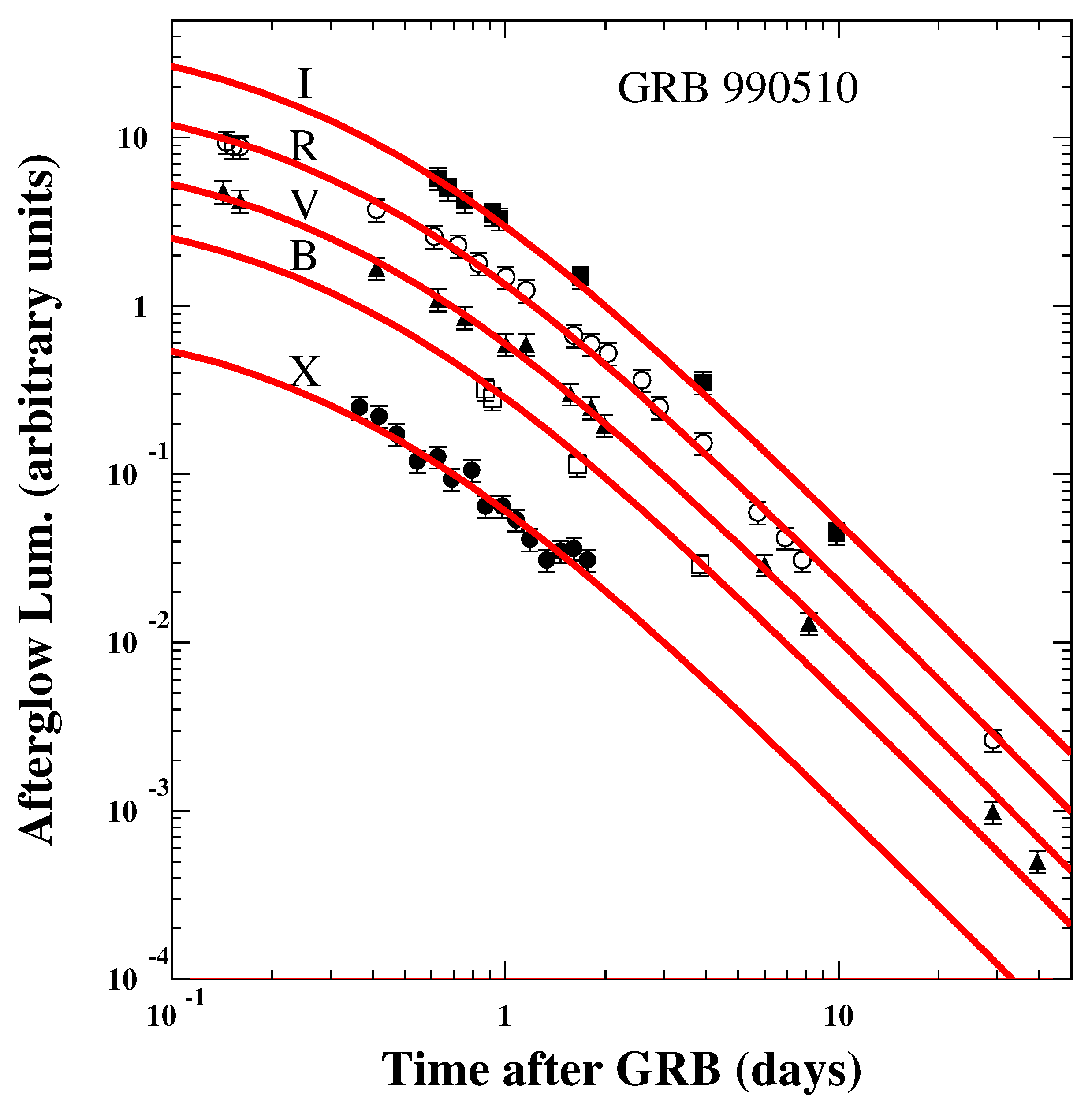
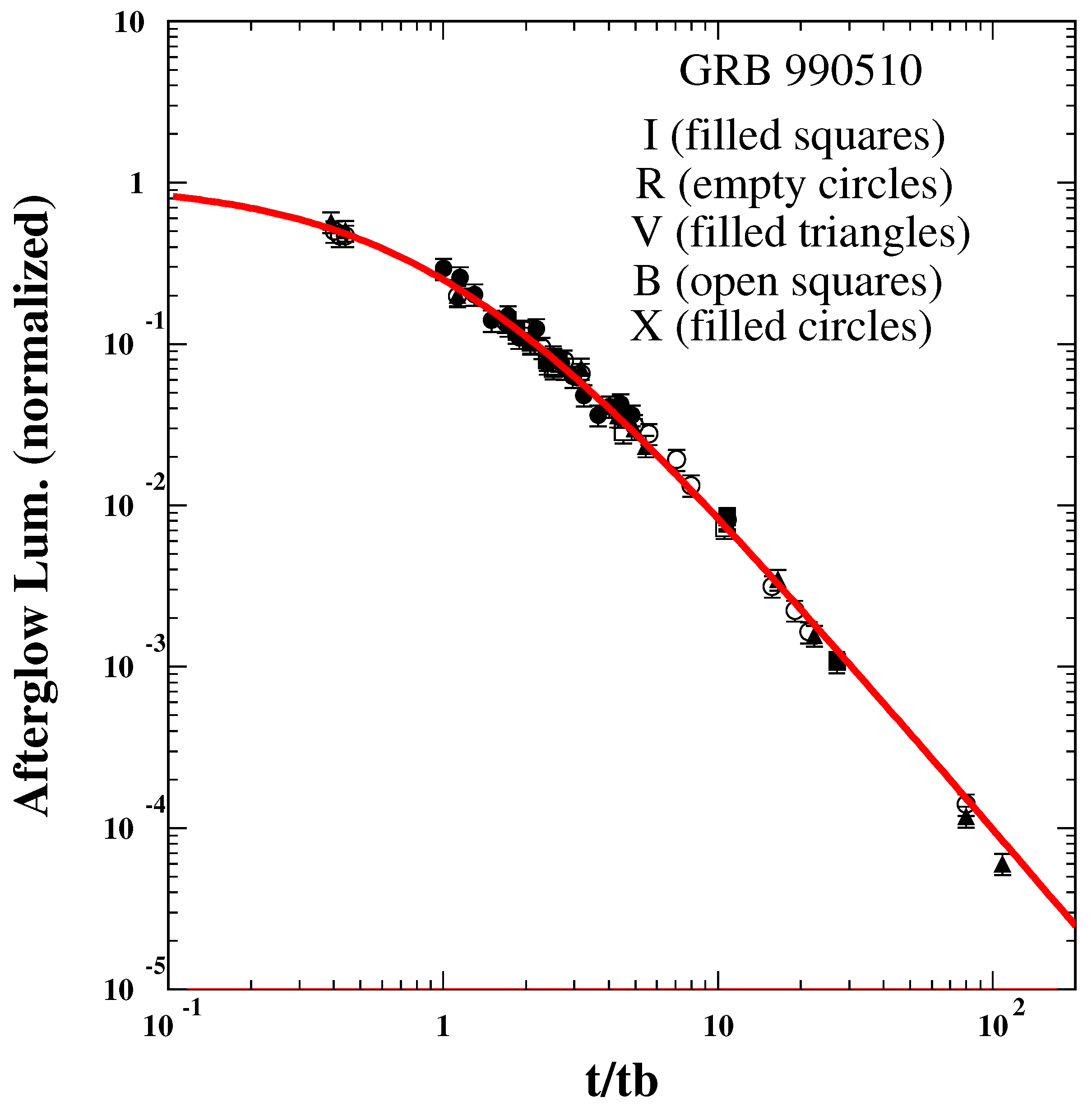

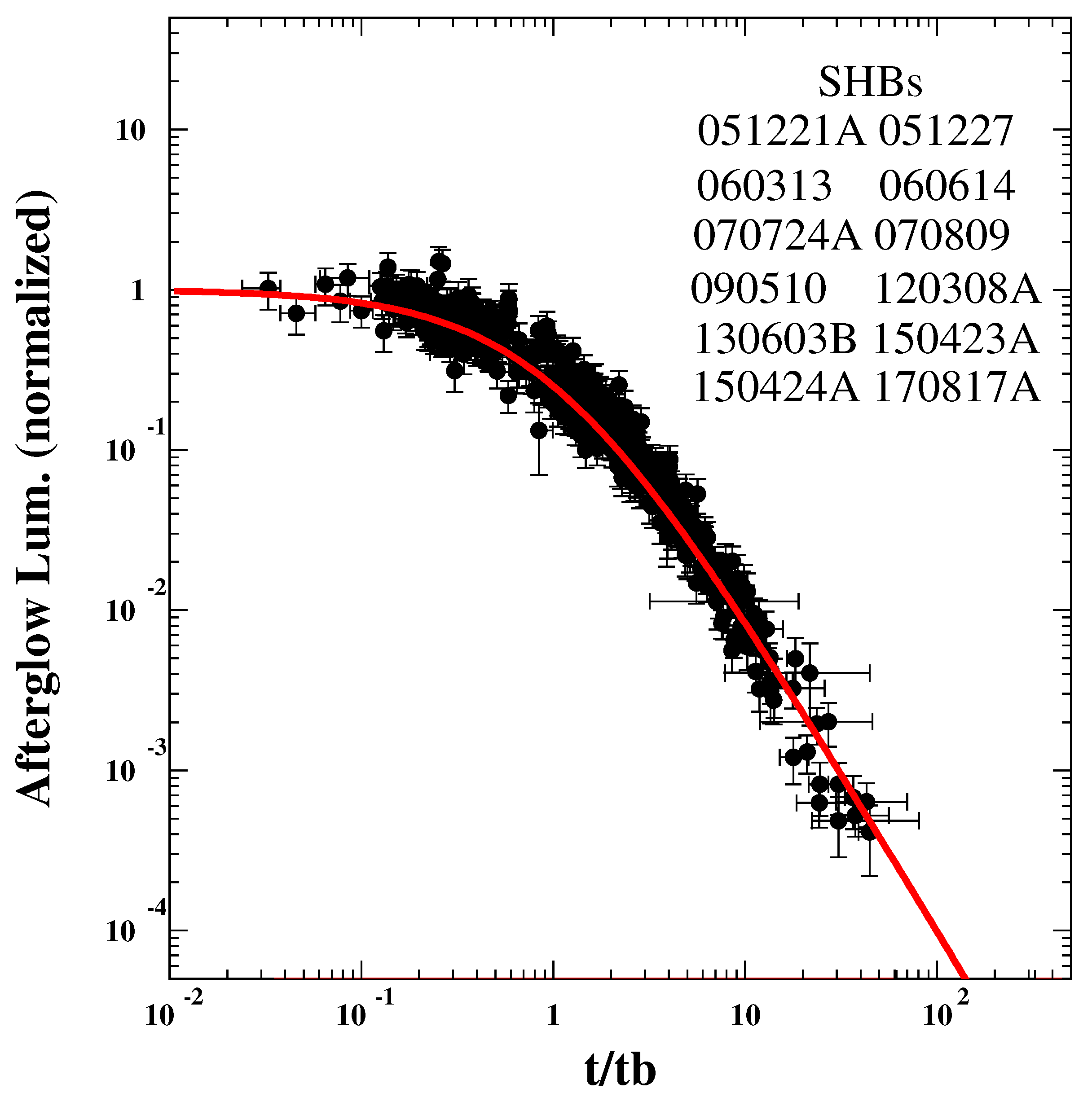
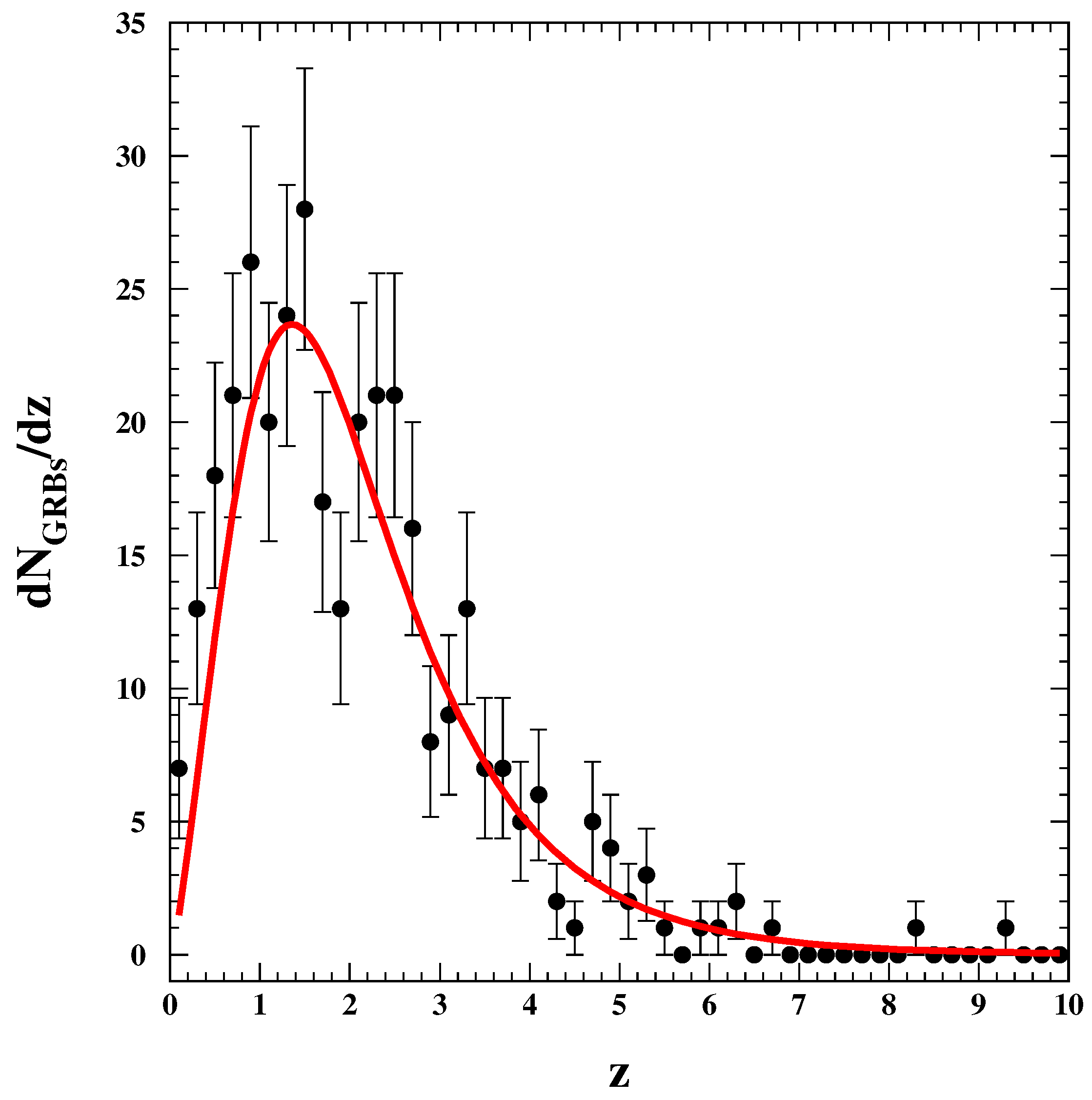

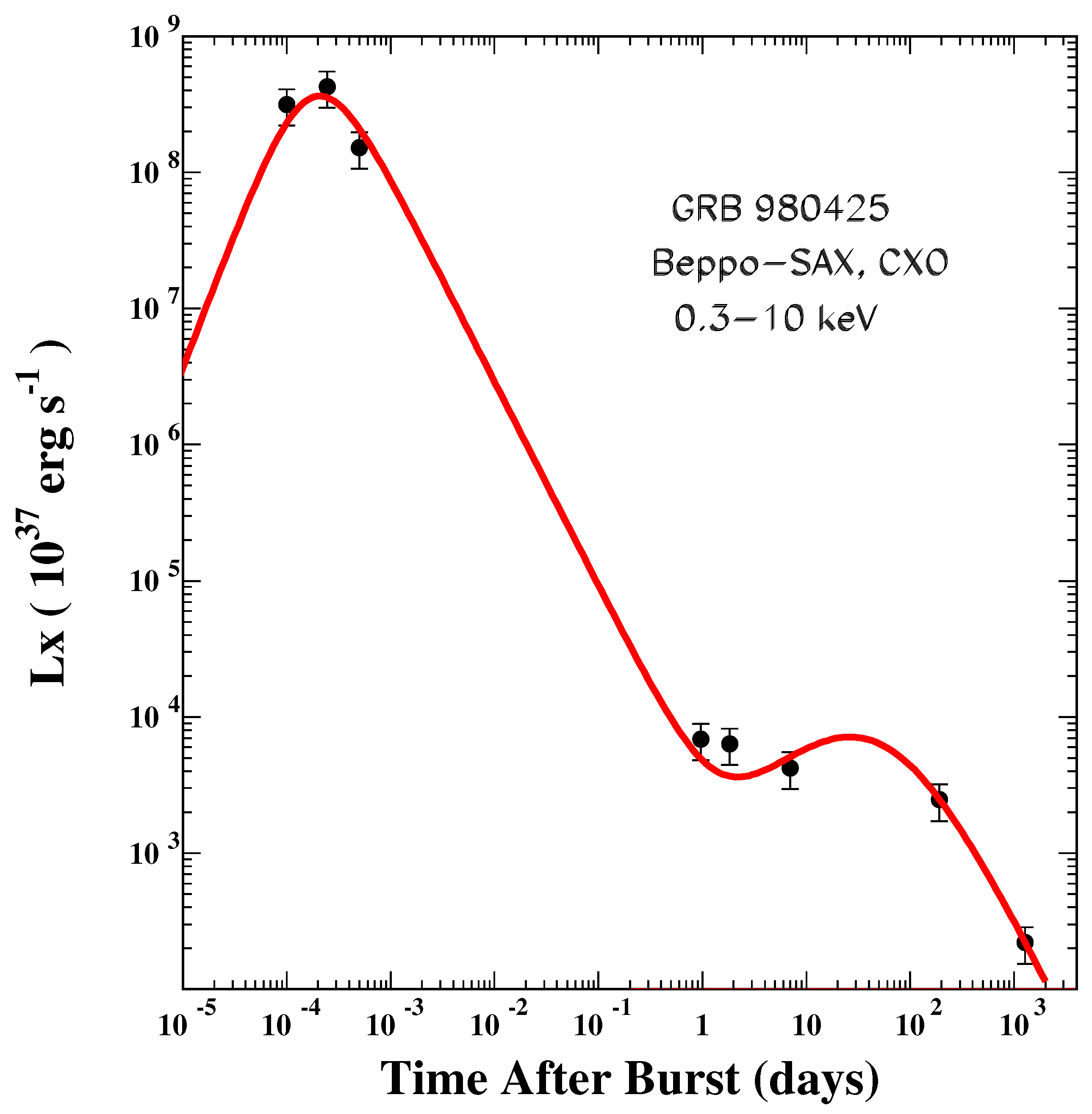

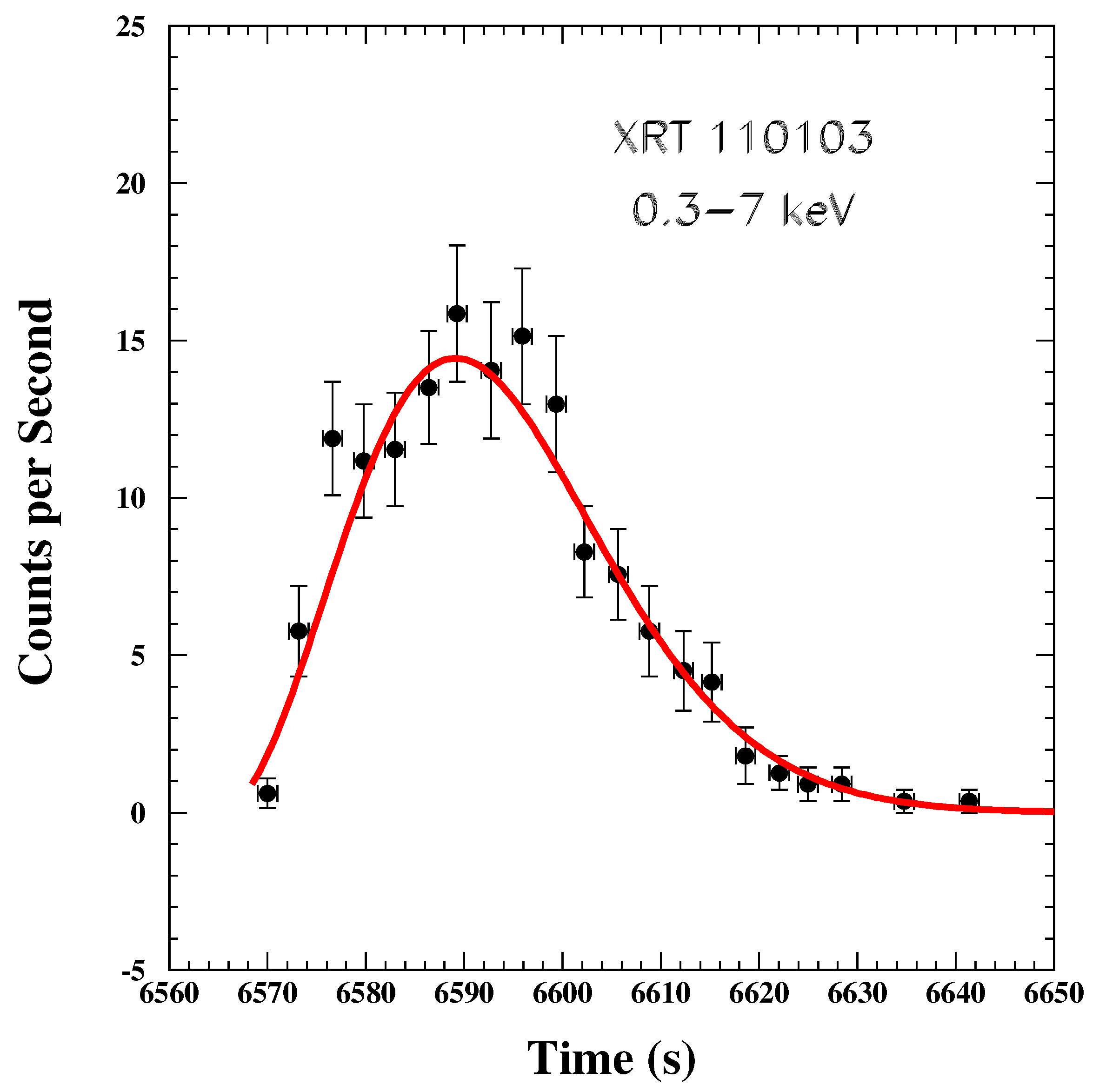

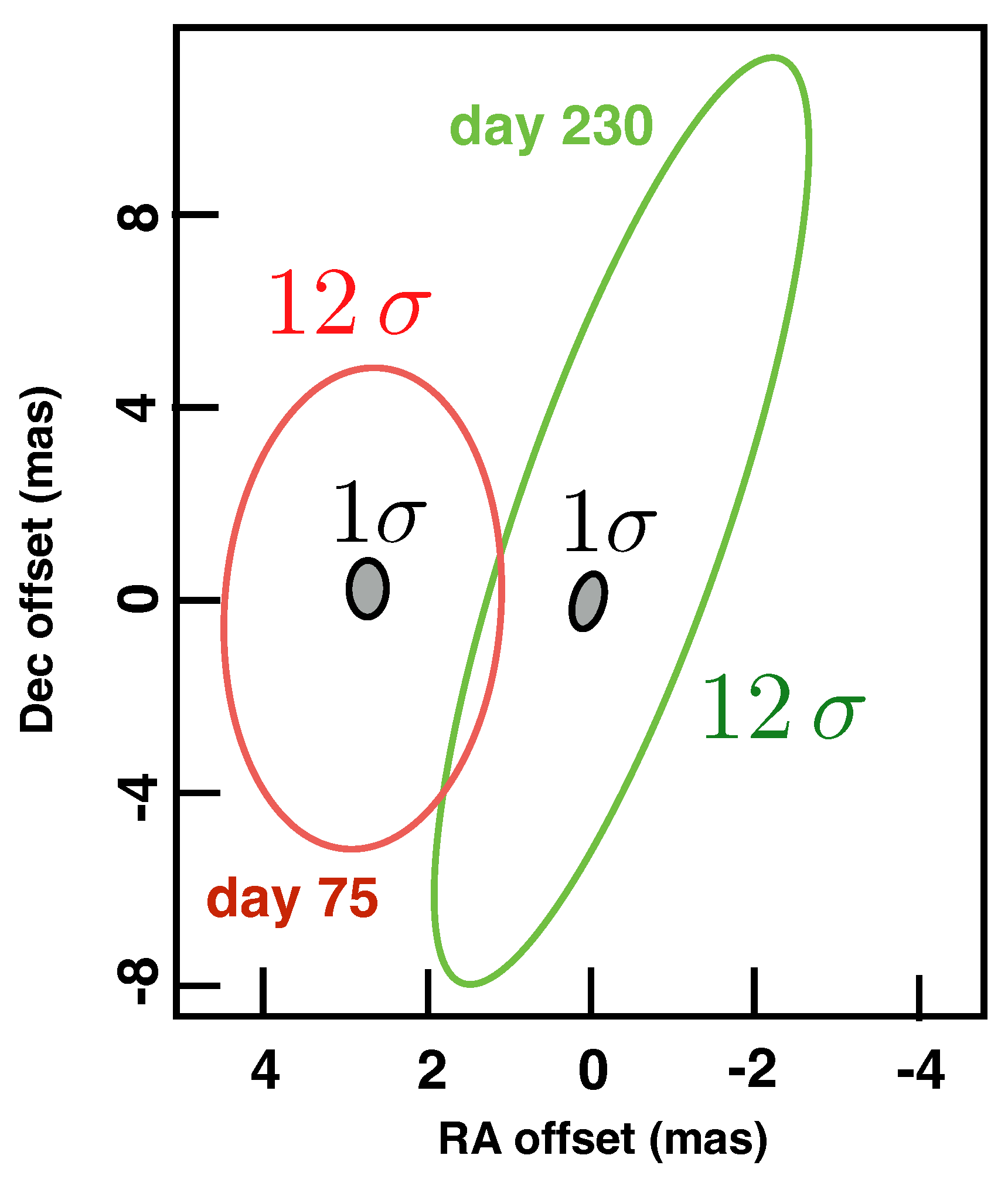

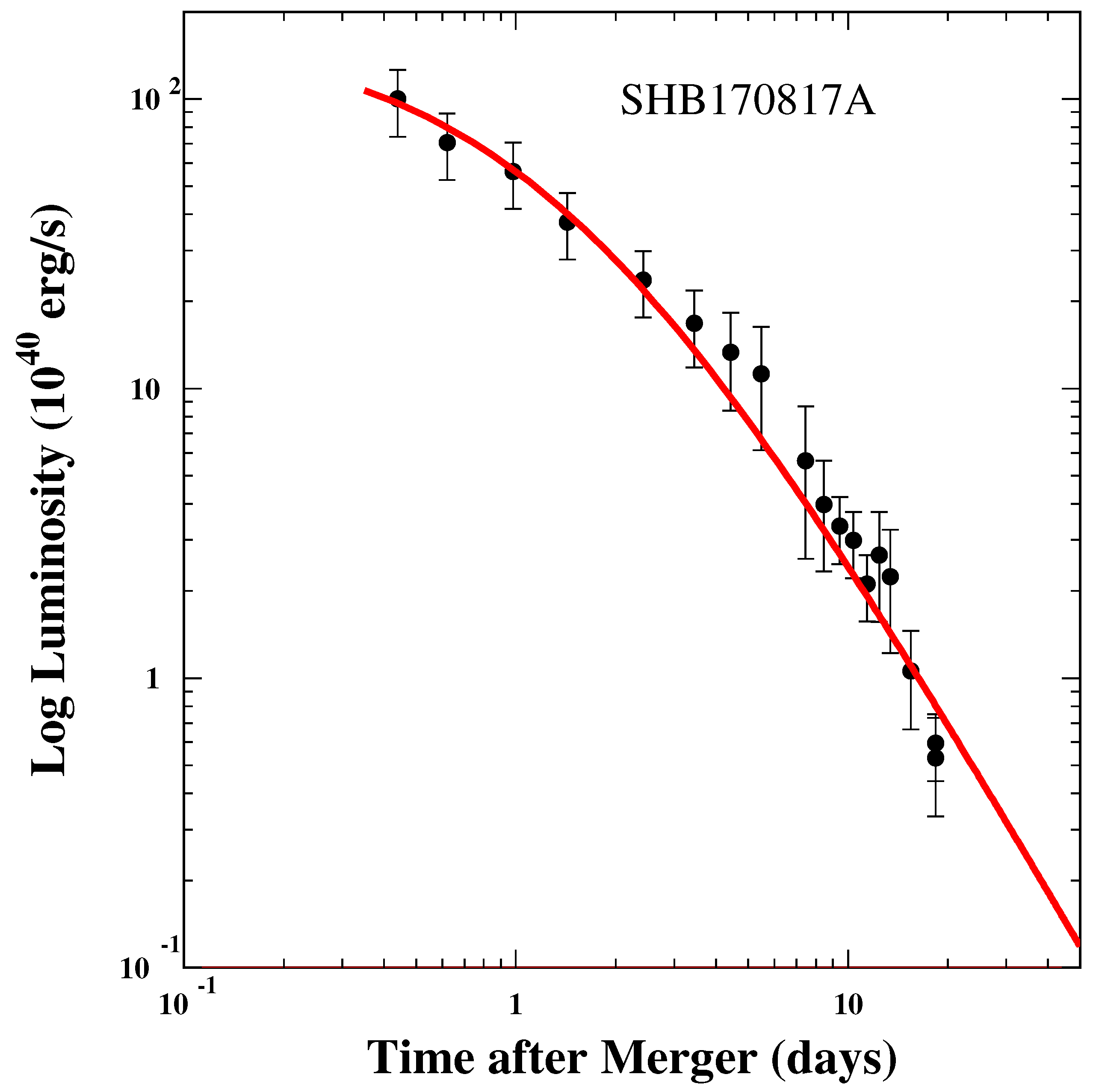
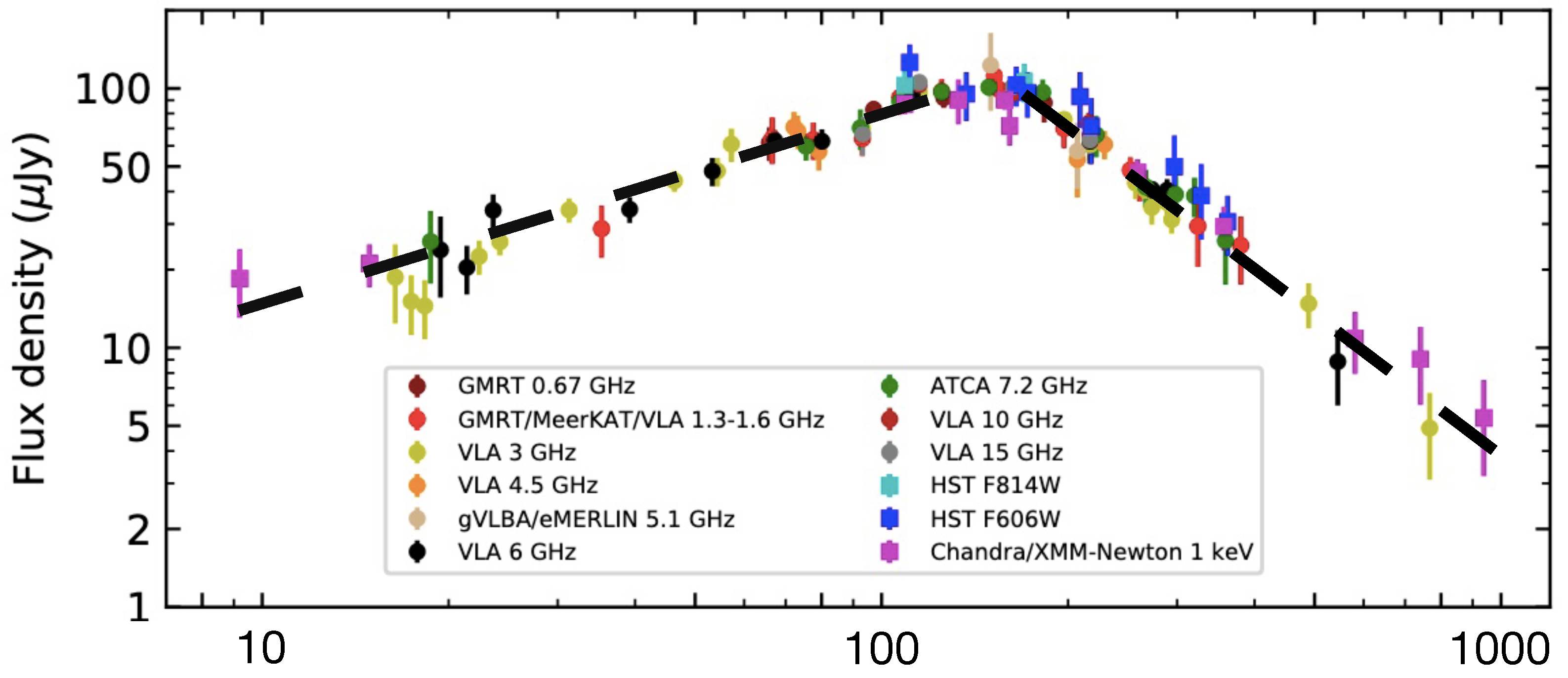
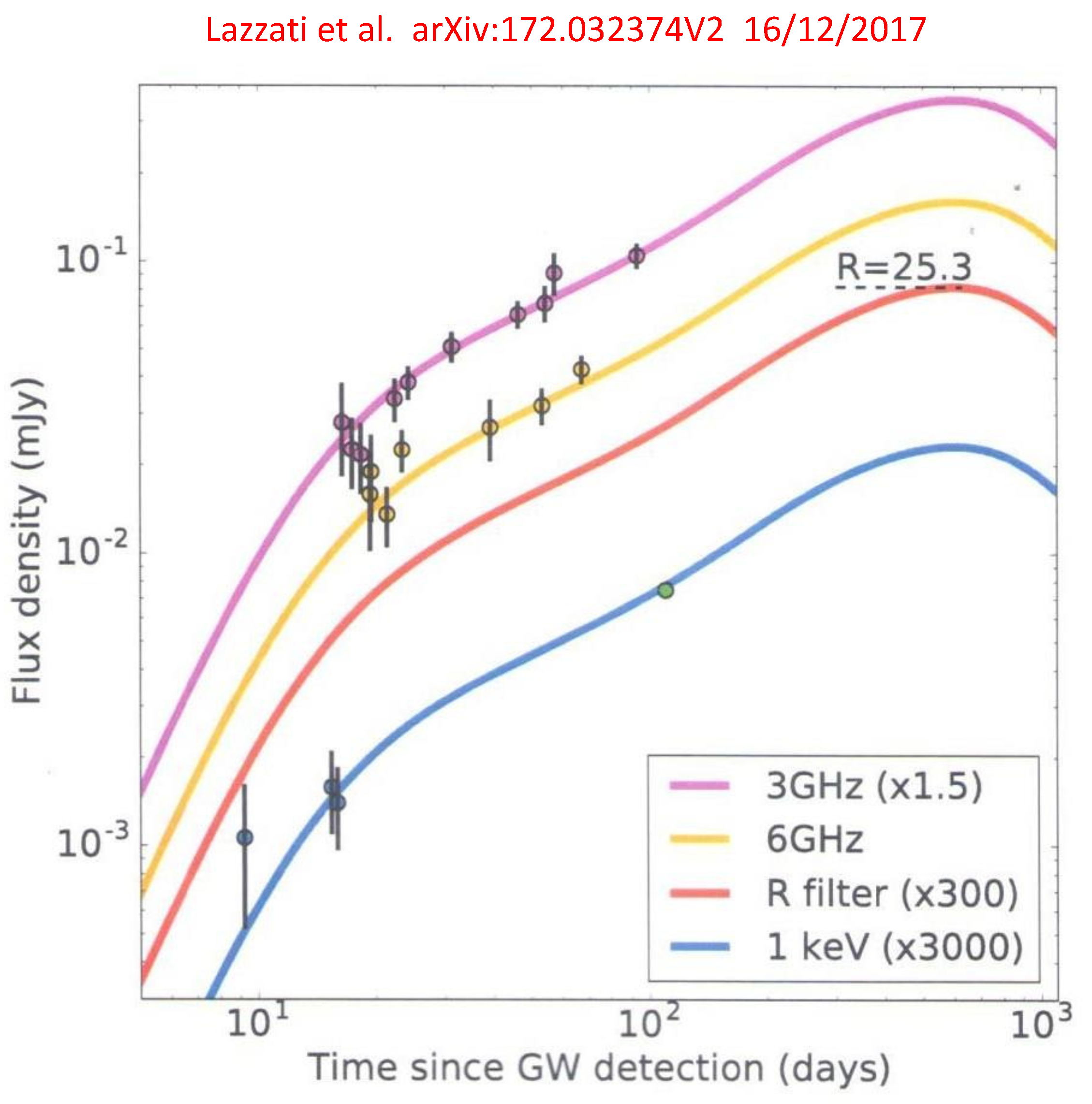
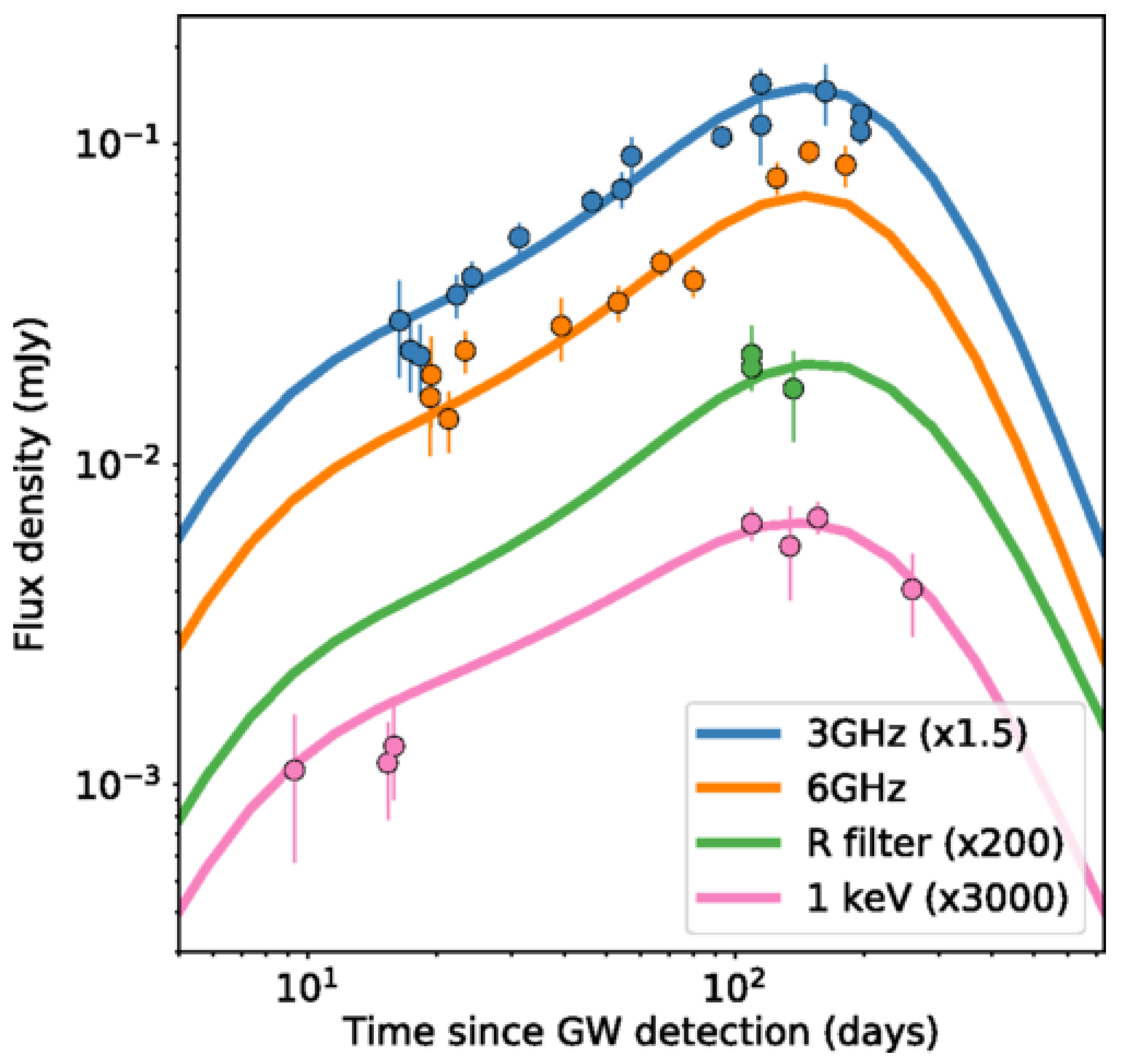
| GRB | Polarization(%) | CL | References [64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72] | Polarimetry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 930131 | 90% | Willis et al., 2005 | BATSE (Albedo) | |
| 960924 | 90% | Willis et al., 2005 | BATSE (Albedo) | |
| 021206 | ? | Coburn & Boggs, 2003 | RHESSI | |
| 041219A | 68% | Kalemci et al., 2007 | INTEGRAL-SPI | |
| 100826A | 99% | Yonetoku et al., 2011 | IKARUS-GAP | |
| 110301A | 68% | Yonetoku et al., 2012 | IKARUS-GAP | |
| 110721 | 84 +16/−28 | 68% | Yonetoku et al., 2012 | IKARUS-GAP |
| 061122 | 68% | Gotz et al., 2013 | INTEGRAL-IBIS | |
| 140206A | 68% | Gotz et al., 2014 | INTEGRAL-IBIS | |
| 160821A | 66 +27/−26 | 99% | Sharma et al., 2019 | AstroSat-CZTI |
| 190530A | 99% | Gupta et al., 2022 | AstroSat-CZTI |
| Collision: | Plastic | Plastic | Elastic | Elastic |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Density: | ISM | Wind | ISM | Wind |
| Test | Cannonball Model | Fireball Model | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test 1 | Large GRB linear polarization | √ | Small GRB polarization | X |
| Test 2 | Prompt emission correlations | √ | Frail relation | X |
| Test 3 | Inverse Compton GRB pulses | √ | Curvature-shaped pulses | X |
| Test 4 | SN-GRBs: Canonical afterglow | √ | Canonical AG not expected | X |
| Test 5 | AG’s break correlations | √ | AG’s Break correlations | X |
| Test 6 | Post-break closure relation | √ | Post-break closure relation | X |
| Test 7 | Missing breaks (too early) | √ | Missing breaks (too late) | X |
| Test 8 | Chromatic afterglow | √ | Achromatic afterglow | X |
| Test 9 | MSP-powered AG of SN-less GRB | √ | Magnetar jet re-energization | X |
| Test 10 | GRB rate ∝ SFR | √ | GRB rate not ∝ SFR | X |
| Test 11 | LL GRBs = far off-axis GRBs | √ | LL GRBs = Different GRB class | X |
| Test 12 | Super-luminal CBs | √ | Superluminal fireball | X |
| Test 13 | SHBs optical AG powered by NS | ? | SHBs + macronova | ? |
| Test 14 | XRFs = Far off-axis LGRBs | √ | Different class of LGRBs | X |
| Test 15 | XRTs = NS-powered AGs | √ | AGs of Far-off-axis GRBs | X |
| Test 16 | Radio image of SHB170817A: a CB | √ | A complex structured jet | X |
| Key Property | Majority View | Minority View | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location: | Galactic | X | Extragalactic | √ |
| Produced by | Relativistic fireball | X | Highly relativistic plasmoids | √ |
| Production mechanism | Collisions of shells | X | ICS of light by plasmoids (CBs) | √ |
| Prompt Emission | Synchrotron radiation (SR) | X | Inverse Compton scattering | √ |
| GRB geometry | Isotropic | X | Very narrowly beamed | √ |
| LGRBs origin | Stellar collapse to BH | X | Stripped-envelope SN | √ |
| Afterglows’ origin | SR from shocked ISM | X | Synchrotron from CBs | √ |
| Afterglows’ geometry | Isotropic | X | Narrowly beamed | √ |
| SN1998bw/GRB980425 | Rare SN/Rare GRB | X | SNIc-GRB viewed far off-axis | √ |
| LL GRBs | Different class of GRBs | X | Normal GRBs seen far off-axis | √ |
| SN-Less LGRBs | Stellar Collapse to BH | ? | Phase Transition in HMXRBs | ? |
| AG plateau origin | Jet re-energization | X | Early time jet deceleration | √ |
| AG break origin | Deceleration of conical jet | X | Deceleration of CBs | √ |
| Missing jet breaks | Too late to be seen | X | Too early to be seen | √ |
| Observed rate of GRBs | ∝ SFR + evolution | X | ∝ SFR, modified by beaming | √ |
| Geometry | Spherical → Conical shells | X | Succession of cannonballs | √ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dado, S.; Dar, A.; De Rújula, A. Critical Tests of Leading Gamma Ray Burst Theories. Universe 2022, 8, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070350
Dado S, Dar A, De Rújula A. Critical Tests of Leading Gamma Ray Burst Theories. Universe. 2022; 8(7):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070350
Chicago/Turabian StyleDado, Shlomo, Arnon Dar, and Alvaro De Rújula. 2022. "Critical Tests of Leading Gamma Ray Burst Theories" Universe 8, no. 7: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070350
APA StyleDado, S., Dar, A., & De Rújula, A. (2022). Critical Tests of Leading Gamma Ray Burst Theories. Universe, 8(7), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8070350







