Jittering Jets by Negative Angular Momentum Feedback in Cooling Flows
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Jittering Jets in Cooling Flows
2.1. Uplifting Dense Clumps and Feeding the SMBH
2.2. The Jets Direction
2.3. Conditions for Jittering Jets
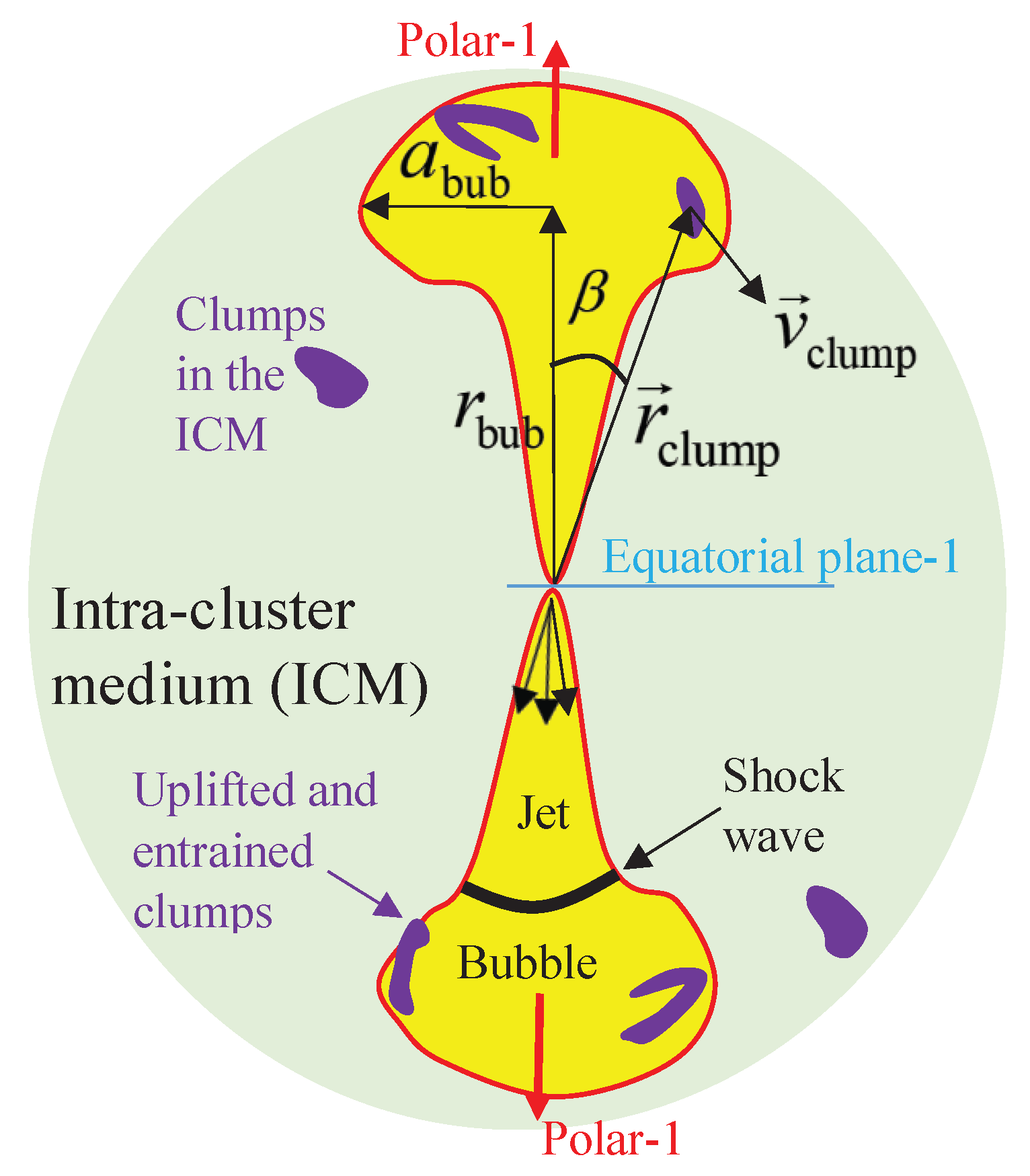
3. The Jets–Clumps Interaction Zone
3.1. The Cluster RBS 797
3.2. The Perseus Cluster
3.3. The MS 0735.6+7421 Cluster
4. Summary
- A group (or few groups) of clumps fall to the center and feed the SMBH of RBS 797 via an accretion disk in size (Equation (9)). Not all clumps reach the center together, and while some clumps reach the center and form the accretion disk that launches the first pair of jets, some clumps still remain further out.
- At large distances of , the group (or few groups) of clumps do not fall from the equatorial-1 direction, but rather from a large angle to this plane (see Figure 1). Therefore, the jets interact with many clumps, i.e., they entrain and uplift the clumps. This weakens and terminates the first jet-launching activity (first outburst). Equation (9) gives the lower bound on the jets–clumps interaction zone.
- The jets and the bubbles start to inflate drag and uplift the clumps. The remnants of the clumps fall back and feed the SMBH at a time , as I estimated in Equation (6).
- When the entrained/uplifted remnants of the clumps fall to the center and feed the SMBH, the second jet-launching episode (second outburst) occurs. The new angular momentum direction is highly inclined to that of the first outburst (Equation (1)).
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fabian, A.C.; Ferland, G.J.; Sanders, J.S.; McNamara, B.R.; Pinto, C.; Walker, S.A. Hidden cooling flows in clusters of galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2022, 515, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, A.C. Observational Evidence of Active Galactic Nuclei Feedback. ARA&A 2012, 50, 455–489. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, B.R.; Nulsen, P.E.J. Mechanical feedback from active galactic nuclei in galaxies, groups and clusters. New J. Phys. 2012, 14, 055023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N. The jet feedback mechanism (JFM) in stars, galaxies and clusters. New Astron. Rev. 2016, 75, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, N.; McNamara, B.R.; Churazov, E.; Scannapieco, E. Hot Atmospheres, Cold Gas, AGN Feedback and the Evolution of Early Type Galaxies: A Topical Perspective. Space Sci. Rev. 2019, 215, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baum, S.A.; O’Dea, C.P. Multifrequency VLA observations of PKS 0745-191: The archetypal "cooling flow" radio source? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 1991, 250, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, M.; Brighenti, F.; Temi, P. Chaotic cold accretion on to black holes in rotating atmospheres. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 579, A62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, M.; Ruszkowski, M.; Oh, S.P. Chaotic cold accretion on to black holes. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 432, 3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bryan, G.L.; Ruszkowski, M.; Voit, G.M.; O’Shea, B.W.; Donahue, M. Cooling, AGN Feedback, and Star Formation in Simulated Cool-core Galaxy Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2015, 811, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Sharma, P.; Babul, A. Cool Core Cycles: Cold Gas and AGN Jet Feedback in Cluster Cores. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2015, 811, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzolato, F.; Soker, N. On the Nature of Feedback Heating in Cooling Flow Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2005, 632, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzolato, F.; Soker, N. Solving the angular momentum problem in the cold feedback mechanism of cooling flows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 408, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; McCourt, M.; Quataert, E.; Parrish, I.J. Thermal instability and the feedback regulation of hot haloes in clusters, groups and galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 420, 3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, G.M.; Donahue, M. Cooling Time, Freefall Time, and Precipitation in the Cores of ACCEPT Galaxy Clusters. ApJL 2015, 799, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, G.M.; Donahue, M.; Bryan, G.L.; McDonald, M. Regulation of star formation in giant galaxies by precipitation, feedback and conduction. Nature 2015, 519, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinley, B.; Tingay, S.J.; Gaspari, M.; Kraft, R.P.; Matherne, C.; Offringa, A.R.; McDonald, M.; Calzadilla, M.S.; Veilleux, S.; Shabala, S.S.; et al. Multi-scale feedback and feeding in the closest radio galaxy Centaurus A. Nat. Astron. 2022, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babyk, I.V.; McNamara, B.R.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Russell, H.R.; Vantyghem, A.N.; Hogan, M.T.; Pulido, F.A. A Universal Entropy Profile for the Hot Atmospheres of Galaxies and Clusters within R2500. Astrophys. J. 2018, 862, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, P.P.; Sharma, P.; Quataert, E. Multiphase gas in the circumgalactic medium: Relative role of tcool/tff and density fluctuations. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 3195. [Google Scholar]
- Eckert, D.; Gaspari, M.; Gastaldello, F.; Le Brun, A.M.C.; O’Sullivan, E. Feedback from Active Galactic Nuclei in Galaxy Groups. Universe 2021, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, M.; McDonald, M.; Hamer, S.L.; Brighenti, F.; Temi, P.; Gendron-Marsolais, M.; Hlavacek-Larrondo, J.; Edge, A.C.; Werner, N.; Tozzi, P.; et al. Shaken Snow Globes: Kinematic Tracers of the Multiphase Condensation Cascade in Massive Galaxies, Groups, and Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2018, 854, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardcastle, M.J.; Croston, J.H. Radio galaxies and feedback from AGN jets. New Astron. Rev. 2020, 88, 101539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iani, E.; Rodighiero, G.; Fritz, J.; Cresci, G.; Mancini, C.; Tozzi, P.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, L.; Rosati, P.; Caminha, G.B.; Zanella, A.; et al. Inquiring into the nature of the Abell 2667 brightest cluster galaxy: Physical properties from MUSE. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 487, 5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Oh, S.P.; McCourt, M. The impact of magnetic fields on thermal instability. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maccagni, F.M.; Serra, P.; Gaspari, M.; Kleiner, D.; Morokuma-Matsui, K.; Oosterloo, T.A.; Onodera, M.; Kamphuis, P.; Loi, F.; Thorat, K.; et al. AGN feeding and feedback in Fornax A. Kinematical analysis of the multi-phase ISM. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 656, A45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martz, C.G.; McNamara, B.R.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Vantyghem, A.N.; Gingras, M.-J.; Babyk, I.V.; Russell, H.R.; Edge, A.C.; McDonald, M.; Tamhane, P.D.; et al. Thermally Unstable Cooling Stimulated by Uplift: The Spoiler Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2020, 897, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, V.; Salome, P.; Hamer, S.L.; Combes, F.; Gaspari, M.; Kolokythas, K.; O’Sullivan, E.; Beckmann, R.S.; Babul, A.; Polles, F.L.; et al. Gas condensation in Brightest Group Galaxies unveiled with MUSE. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.07838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, T.; Finoguenov, A.; Brüggen, M.; Gaspari, M.; de Gasperin, F.; Gozaliasl, G. Radio galaxies in galaxy groups: Kinematics, scaling relations, and AGN feedback. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 505, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Sharma, P.; Babul, A. Cool-core Clusters: The Role of BCG, Star Formation, and AGN-driven Turbulence. Astrophys. J. 2018, 863, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, D.; Voit, G.M.; O’Shea, B.W.; Glines, F. Environmental Dependence of Self-regulating Black Hole Feedback in Massive Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2020, 905, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, F.A.; McNamara, B.R.; Edge, A.C.; Hogan, M.T.; Vantyghem, A.N.; Russell, H.R.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Babyk, I.; Salomé, P. The Origin of Molecular Clouds in Central Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2018, 853, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; McNamara, B.R.; Bogdanovic, T.; Inayoshi, K.; Ho, L.C. On the Mass Loading of AGN-driven Outflows in Elliptical Galaxies and Clusters. Astrophys. J. 2021, 923, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.; Edge, A.C.; Combes, F.; Gaspari, M.; Hamer, S.; Nesvadba, N.; Peck, A.B.; Sarazin, C.; Tremblay, G.R.; Baum, S.A.; et al. Constraining cold accretion on to supermassive black holes: Molecular gas in the cores of eight brightest cluster galaxies revealed by joint CO and CN absorption. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 489, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, H.R.; McNamara, B.R.; Fabian, A.C.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Combes, F.; Edge, A.C.; Madar, M.; Olivares, V.; Salomé, P.; Vantyghem, A.N. Driving massive molecular gas flows in central cluster galaxies with AGN feedback. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 490, 3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, P.; Voit, G.M.; Nath, B.B. Constraints on precipitation-limited hot haloes from massive galaxies to galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 501, 2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, J.; Fielding, D.; Faucher-Giguère, C.-A.; Quataert, E. Cooling flow solutions for the circumgalactic medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 488, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storchi-Bergmann, T.; Schnorr-Müller, A. Observational constraints on the feeding of supermassive black holes. Nat. Astron. 2019, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantyghem, A.N.; McNamara, B.R.; Russell, H.R.; Edge, A.C.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Combes, F.; Fabian, A.C.; McDonald, M.; Salomé, P. An Enormous Molecular Gas Flow in the RX J0821+0752 Galaxy Cluster. Astrophys. J. 2019, 870, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, G.M. A Role for Turbulence in Circumgalactic Precipitation. Astrophys. J. 2018, 868, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voit, G.M. Ambient Column Densities of Highly Ionized Oxygen in Precipitation-limited Circumgalactic Media. Astrophys. J. 2019, 880, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Tozzi, P.; Yu, H.; Lusso, E.; Gaspari, M.; Gilli, R.; Nardini, E.; Risaliti, G. X-Ray Properties of AGN in Brightest Cluster Galaxies. I. A Systematic Study of the Chandra Archive in the 0.2 < z < 0.3 and 0.55 < z < 0.75 Redshift Range. Astrophys. J. 2018, 859, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, F.; Duan, X.; Yuan, Y.-F. Reversing cooling flows with AGN jets: Shock waves, rarefaction waves and trailing outflows. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 473, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, S.W.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Jones, C.; Forman, W.R.; Bulbul, E.; Clarke, T.E.; Kraft, R.; Blanton, E.L.; David, L.; Werner, N.; et al. A Very Deep Chandra Observation of the Galaxy Group NGC 5813: AGN Shocks, Feedback, and Outburst History. Astrophys. J. 2015, 805, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, A.C.; Sanders, J.S.; Taylor, G.B.; Allen, S.W.; Crawford, C.S.; Johnstone, R.M.; Iwasawa, K. A very deep Chandra observation of the Perseus cluster: Shocks, ripples and conduction. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 366, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Churazov, E. Sound wave generation by a spherically symmetric outburst and AGN feedback in galaxy clusters II: Impact of thermal conduction. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 477, 3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Churazov, E.; Schekochihin, A.A. Generation of internal waves by buoyant bubbles in galaxy clusters and heating of intracluster medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, N.; Sharma, P. Turbulence and cooling in galaxy cluster cores. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 443, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Young, D.S. How Does Radio AGN Feedback Feed Back? Astrophys. J. 2010, 710, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspari, M.; Churazov, E.; Nagai, D.; Lau, E.T.; Zhuravleva, I. The relation between gas density and velocity power spectra in galaxy clusters: High-resolution hydrodynamic simulations and the role of conduction. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 569, A67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuravleva, I.; Allen, S.W.; Mantz, A.B.; Werner, N. Gas Perturbations in the Cool Cores of Galaxy Clusters: Effective Equation of State, Velocity Power Spectra, and Turbulent Heating. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 865, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron-Marsolais, M.; Kraft, R.P.; Bogdan, A.; Hlavacek-Larrondo, J.; Forman, W.R.; Jones, C.; Su, Y.; Nulsen, P.; Randall, S.W.; Roediger, E. Uplift, Feedback, and Buoyancy: Radio Lobe Dynamics in NGC 4472. Astrophys. J. 2017, 848, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huško, F.; Lacey, C.G. The complex interplay of AGN jet-inflated bubbles and the intracluster medium. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.09393. [Google Scholar]
- Ehlert, K.; Weinberger, R.; Pfrommer, C.; Pakmor, R.; Springel, V. Simulations of the dynamics of magnetized jets and cosmic rays in galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 481, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Ohira, Y. Radio mini-halo emission from cosmic rays in galaxy clusters and heating of the cool cores. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2013, 428, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempski, P.; Quataert, E. Thermal instability of halo gas heated by streaming cosmic rays. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2020, 493, 1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfrommer, C. Toward a Comprehensive Model for Feedback by Active Galactic Nuclei: New Insights from M87 Observations by LOFAR, Fermi, and H.E.S.S. Astrophys. J. 2013, 779, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruszkowski, M.; Yang, H.-Y.K.; Reynolds, C.S. Powering of Hα Filaments by Cosmic Rays. Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüggen, M.; Kaiser, C.R. Hot bubbles from active galactic nuclei as a heat source in cooling-flow clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 418, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüggen, M.; Scannapieco, E.; Heinz, S. Evolution of X-ray cavities. Astrophys. J. 2009, 395, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkis, A.; Soker, N. Heating the intra-cluster medium perpendicular to the jets axis. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2012, 427, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, S.; Soker, N. Heating cold clumps by jet-inflated bubbles in cooling flow clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 445, 4161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-Y.K.; Reynolds, C.S. How AGN Jets Heat the Intracluster Medium—Insights from Hydrodynamic Simulations. Astrophys. J. 2016, 829, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N. The requirement for mixing-heating to utilize bubble cosmic rays to heat the intracluster medium. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2019, 482, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brienza, M.; Shimwell, T.W.; de Gasperin, F.; Bikmaev, I.; Bonafede, A.; Botteon, A.; Brüggen, M.; Brunetti, G.; Burenin, R.; Capetti, A.; et al. A snapshot of the oldest active galactic nuclei feedback phases. Nat. Astron. 2021, 5, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N.; Hillel, S. Comment on “A snapshot of the oldest AGN feedback phases”. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2110.10608. [Google Scholar]
- Cielo, S.; Babul, A.; Antonuccio-Delogu, V.; Silk, J.; Volonteri, M. Feedback from reorienting AGN jets. I. Jet-ICM coupling, cavity properties and global energetics. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 617, A58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, N. Jittering Jets in Cooling Flow Clusters. Res. Notes Am. Astron. Soc. 2018, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ubertosi, F.; Gitti, M.; Brighenti, F.; Brunetti, G.; McDonald, M.; Nulsen, P.; McNamara, B.; Randall, S.; Forman, W.; Donahue, M.; et al. The Deepest Chandra View of RBS 797: Evidence for Two Pairs of Equidistant X-ray Cavities. ApJL 2021, 923, L25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babul, A.; Sharma, P.; Reynolds, C.S. Isotropic Heating of Galaxy Cluster Cores via Rapidly Reorienting Active Galactic Nucleus Jets. Astrophys. J. 2013, 768, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.K. X-shaped radio galaxies as observational evidence for the interaction of supermassive binary black holes and accretion disc at parsec scale. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2004, 347, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitti, M.; Giroletti, M.; Giovannini, G.; Feretti, L.; Liuzzo, E. A candidate supermassive binary black hole system in the brightest cluster galaxy of RBS 797. Astron. Astrophys. 2013, 557, L14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennett-Thorpe, J.; Scheuer, P.A.G.; Laing, R.A.; Bridle, A.H.; Pooley, G.G.; Reich, W. Jet reorientation in active galactic nuclei: Two winged radio galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2002, 330, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, D.V.; Rao, A.P. Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope observations of X-shaped radio sources. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2007, 374, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natarajan, P.; Pringle, J.E. The Alignment of Disk and Black Hole Spins in Active Galactic Nuclei. ApJL 1998, 506, L97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y. Reverse shock of the Fermi bubbles explains their origin. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.01654. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Leighly, K.M.; Terndrup, D.M.; Dabbieri, C.; Gallagher, S.C.; Richards, G.T. The Physical Properties of Low Redshift FeLoBAL Quasars. I. Spectral Synthesis Analysis of the BAL Outflows using SimBAL. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.11964. [Google Scholar]
- de Kool, M.; Becker, R.H.; Arav, N.; Gregg, M.D.; White, R.L. Keck HIRES Spectroscopy of the Fe II Low-Ionization Broad Absorption Line Quasar FBQS 0840+3633: Evidence for Two Outflows on Different Scales. Astrophys. J. 2002, 570, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.R.; Arav, N.; Xu, X.; Kriss, G.A.; Plesha, R.J. HST/COS Observations of Quasar Outflows in the 500-1050 Å Rest Frame. V. Richness of Physical Diagnostics and Ionization Potential-dependent Velocity Shift in PKS J0352-0711. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2020, 247, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, S.; Soker, N. Uplifted cool gas and heating by mixing in cooling flows. RAA 2018, 18, 081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pope, E.C.D.; Babul, A.; Pavlovski, G.; Bower, R.G.; Dotter, A. Mass transport by buoyant bubbles in galaxy clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2010, 406, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revaz, Y.; Combes, F.; Salomé, P. Formation of cold filaments in cooling flow clusters. Astron. Astrophys. 2008, 477, L33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, B.R.; Russell, H.R.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Hogan, M.T.; Fabian, A.C.; Pulido, F.; Edge, A.C. A Mechanism for Stimulating AGN Feedback by Lifting Gas in Massive Galaxies. Astrophys. J. 2016, 830, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, O.; Liska, M.; Tchekhovskoy, A.; Bromberg, O.; Lalakos, A.; Giannios, D.; Mösta, P. Black Hole to Photosphere: 3D GRMHD Simulations of Collapsars Reveal Wobbling and Hybrid Composition Jets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2022, 933, L9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vantyghem, A.N.; McNamara, B.R.; Russell, H.R.; Main, R.A.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Wise, M.W.; Hoekstra, H.; Gitti, M. Cycling of the powerful AGN in MS 0735.6+7421 and the duty cycle of radio AGN in clusters. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2014, 442, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dullo, B.T.; Gil de Paz, A.; Knapen, J.H. Ultramassive Black Holes in the Most Massive Galaxies: MBH-σ versus MBH-Rb. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bégin, T.; Hlavacek-Larrondo, J.; Rhea, C.L.; Gendron-Marsolais, M.; McNamara, B.; van Weeren, R.J.; Richard-Laferrière, A.; Guité, L.; Prasow-Émond, M.; Haggard, D. Extended radio emission in the galaxy cluster MS 0735.6+7421 detected with the Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2202.01235. [Google Scholar]
- McNamara, B.R.; Rohanizadegan, M.; Nulsen, P.E.J. Are Radio Active Galactic Nuclei Powered by Accretion or Black Hole Spin? Astrophys. J. 2011, 727, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, B.R.; Kazemzadeh, F.; Rafferty, D.A.; Bîrzan, L.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Kirkpatrick, C.C.; Wise, M.W. An Energetic AGN Outburst Powered by a Rapidly Spinning Supermassive Black Hole or an Accreting Ultramassive Black Hole. Astrophys. J. 2009, 698, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternberg, A.; Soker, N. Explaining the energetic AGN outburst of MS0735+7421 with massive slow jets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2009, 398, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, M.W.; McNamara, B.R.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Houck, J.C.; David, L.P. X-Ray Supercavities in the Hydra A Cluster and the Outburst History of the Central Galaxy’s Active Nucleus. Astrophys. J. 2007, 659, 1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kino, M.; Niinuma, K.; Kawakatu, N.; Nagai, H.; Giovannini, G.; Orienti, M.; Wajima, K.; D’Ammando, F.; Hada, K.; Giroletti, M.; et al. Morphological Transition of the Compact Radio Lobe in 3C 84 via the Strong Jet-Cloud Collision. ApJL 2021, 920, L24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, A.; Soker, N. Common Powering Mechanism of Intermediate Luminosity Optical Transients and Luminous Blue Variables. arXiv 2010, arXiv:1011.1222. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, D.; Sharma, P.; Babul, A. AGN jet-driven stochastic cold accretion in cluster cores. Astrophys. J. 2017, 471, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagnolo, K.W.; McNamara, B.R.; Wise, M.W.; Nulsen, P.E.J.; Brüggen, M.; Gitti, M.; Rafferty, D.A. A Powerful AGN Outburst in RBS 797. Astrophys. J. 2011, 732, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, R.J.H.; Fabian, A.C.; Sanders, J.S. Precession of the super-massive black hole in NGC 1275 (3C 84)? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2006, 366, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, E.; Ricci, F.; La Franca, F.; Bianchi, S.; Bongiorno, A.; Brusa, M.; Marconi, A.; Onori, F.; Shankar, F.; Vignali, C. NGC 1275: An outlier of the black hole-host scaling relations. FrASS 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, M.C.H.; Ohyama, Y.; Lim, J. Recent Formation of a Spiral Disk Hosting Progenitor Globular Clusters at the Center of the Perseus Brightest Cluster Galaxy. I. Spiral Disk. Astrophys. J. 2022, 927, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzolato, F.; Soker, N. Binary black holes at the core of galaxy clusters. AdSpR 2005, 36, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biava, N.; Brienza, M.; Bonafede, A.; Gitti, M.; Bonnassieux, E.; Harwood, J.; Edge, A.C.; Riseley, C.J.; Vantyghem, A. Constraining the AGN duty cycle in the cool-core cluster MS 0735.6+7421 with LOFAR data. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 650, A170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soker, N. Jittering Jets by Negative Angular Momentum Feedback in Cooling Flows. Universe 2022, 8, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090483
Soker N. Jittering Jets by Negative Angular Momentum Feedback in Cooling Flows. Universe. 2022; 8(9):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090483
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoker, Noam. 2022. "Jittering Jets by Negative Angular Momentum Feedback in Cooling Flows" Universe 8, no. 9: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090483
APA StyleSoker, N. (2022). Jittering Jets by Negative Angular Momentum Feedback in Cooling Flows. Universe, 8(9), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe8090483





