Rapid Orbit-to-Orbit Transfer to Asteroid 4660 Nereus Using Solar Electric Propulsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mission Schematization and Mathematical Model Description
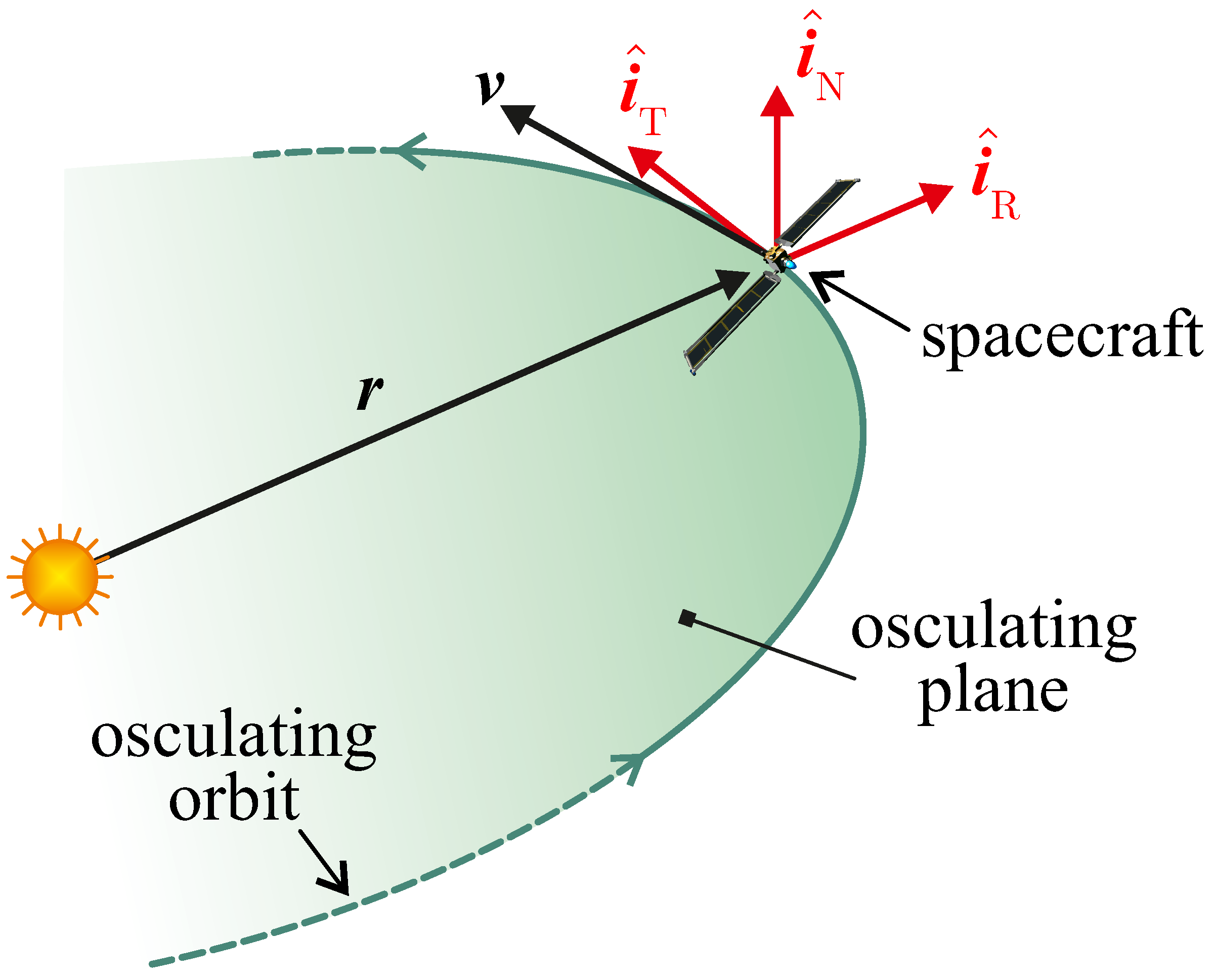
2.1. Spacecraft Dynamics in the Interplanetary Space
2.2. Propulsive Characteristics and Thrust Vector Schematization
2.3. Optimal Trajectory Design
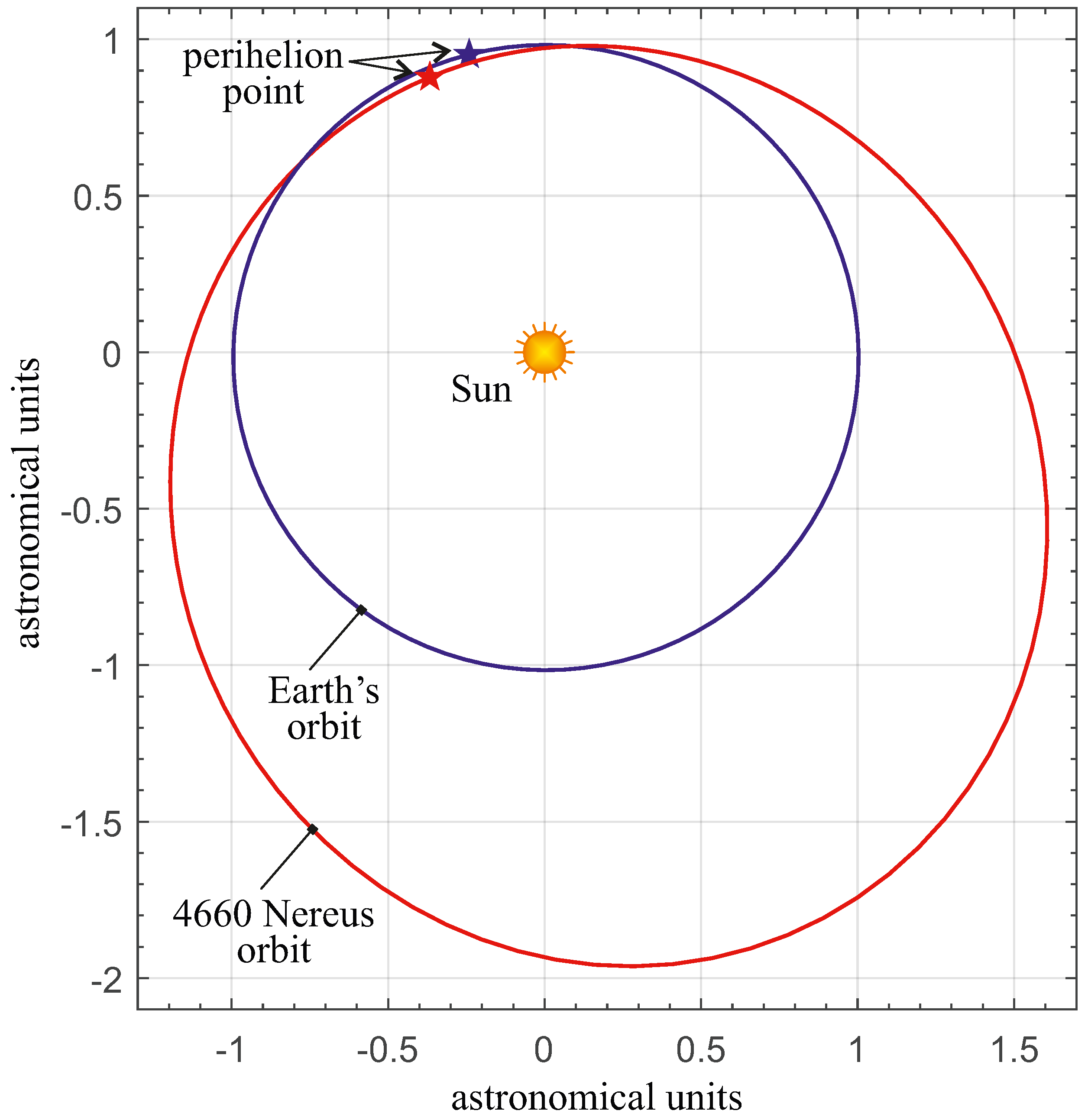
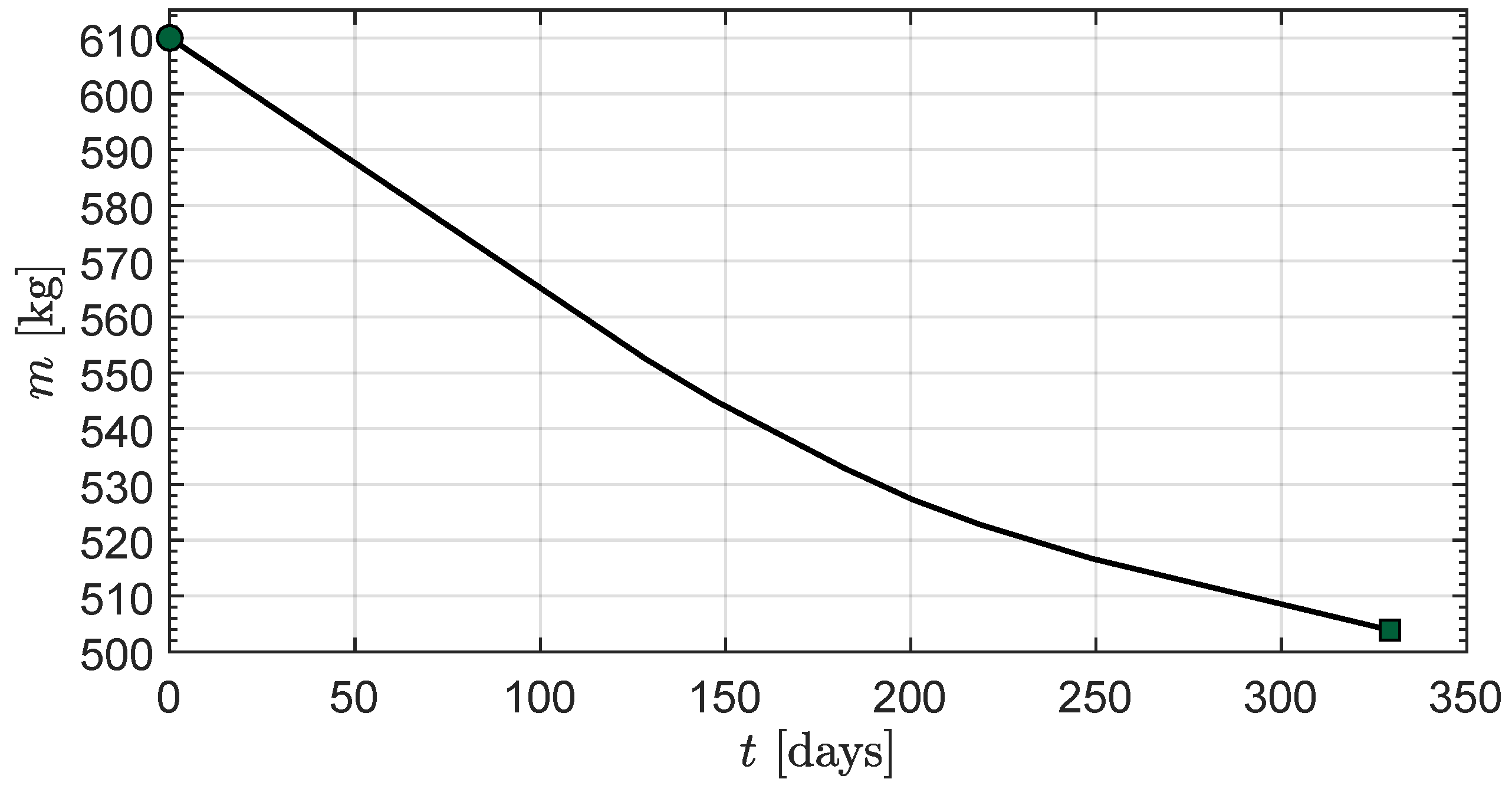
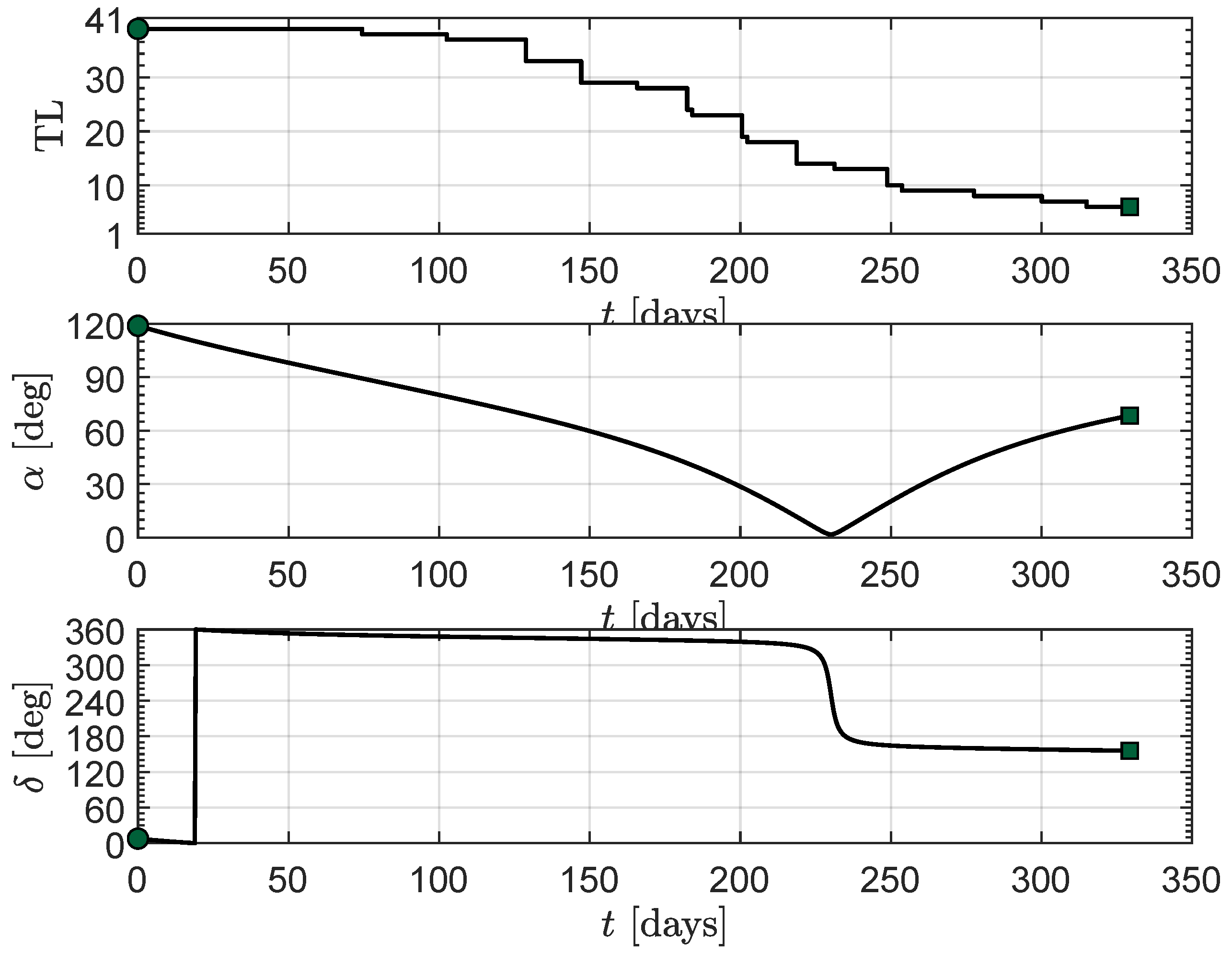
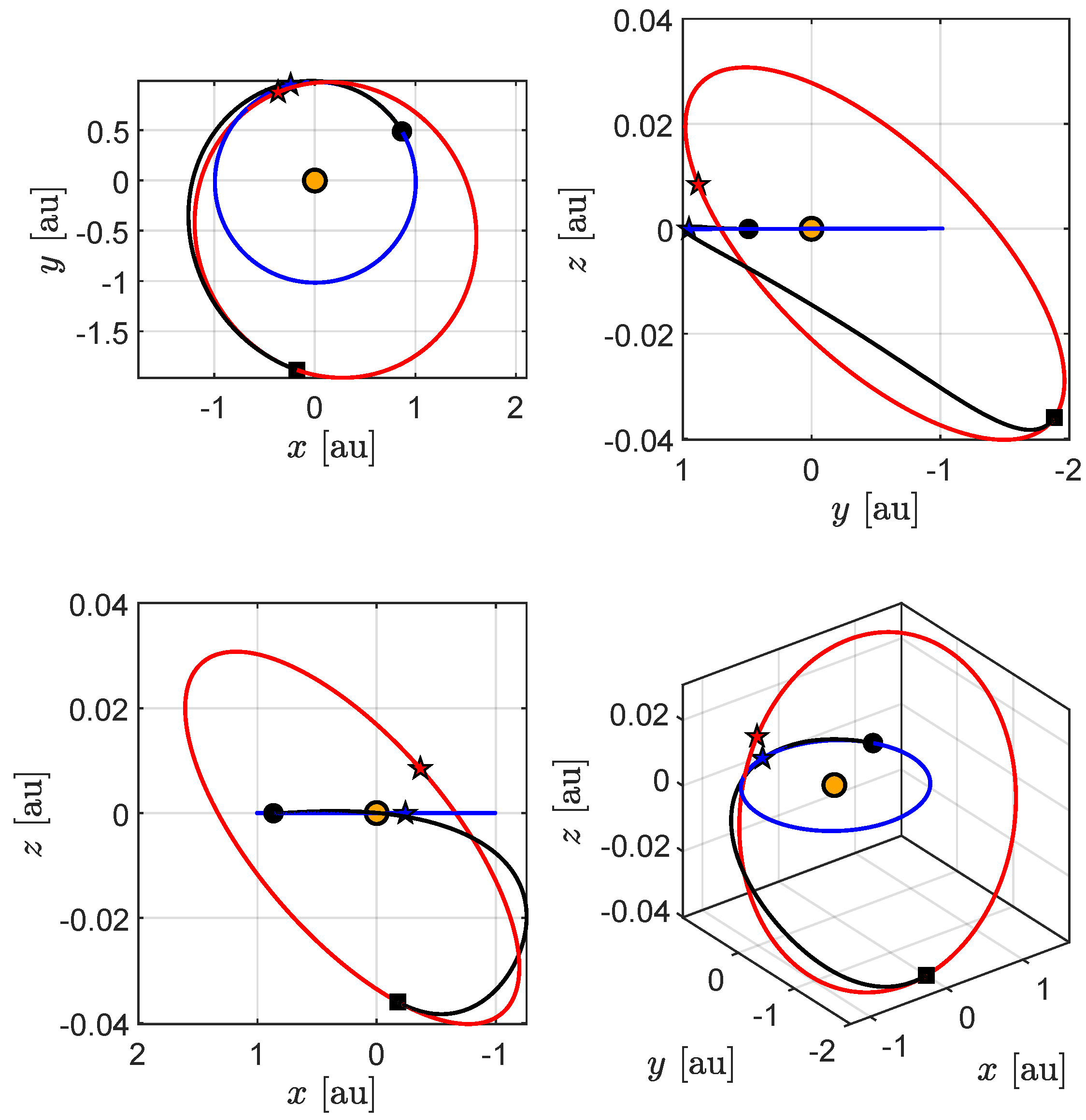
3. Simulations and Numerical Results
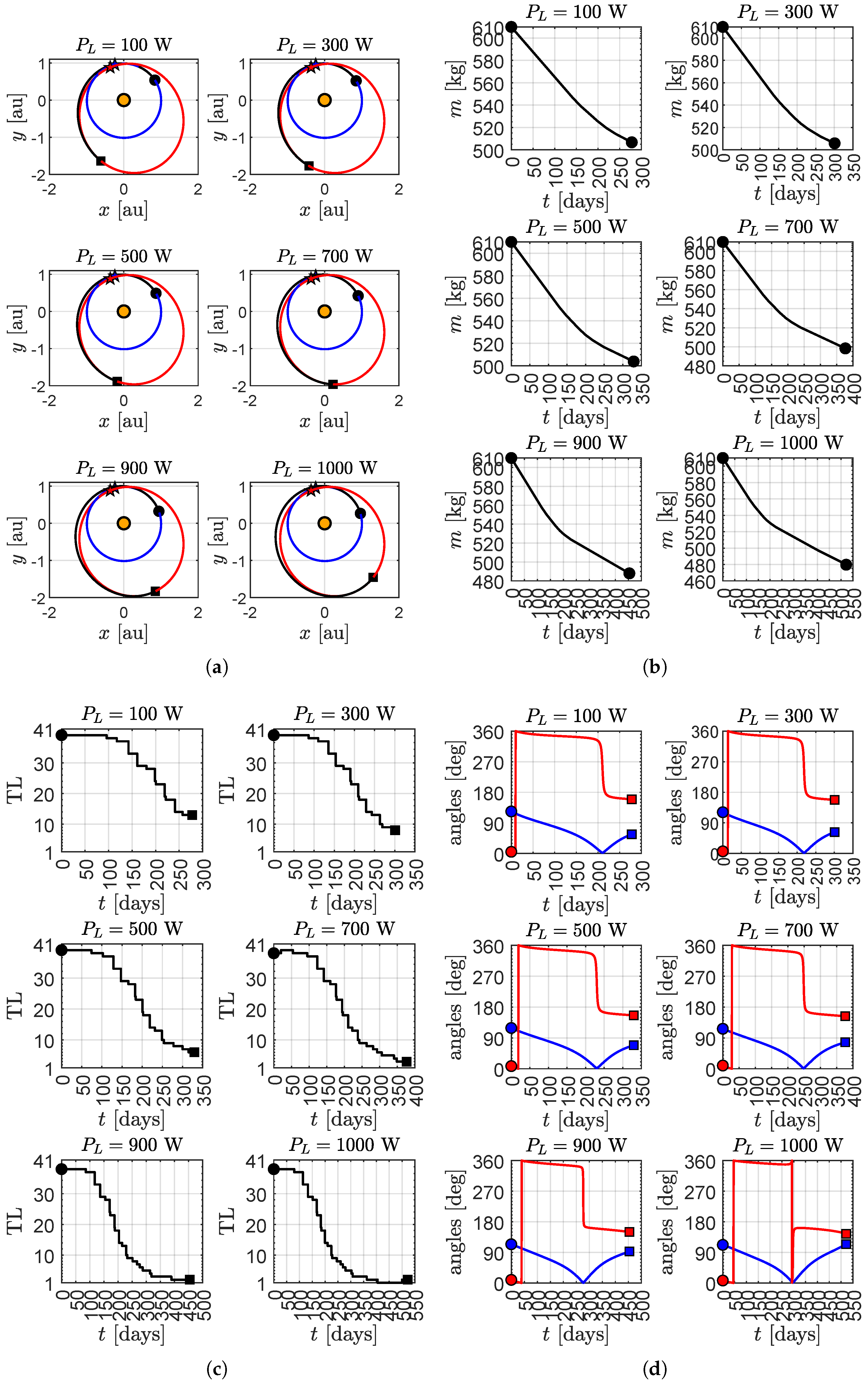
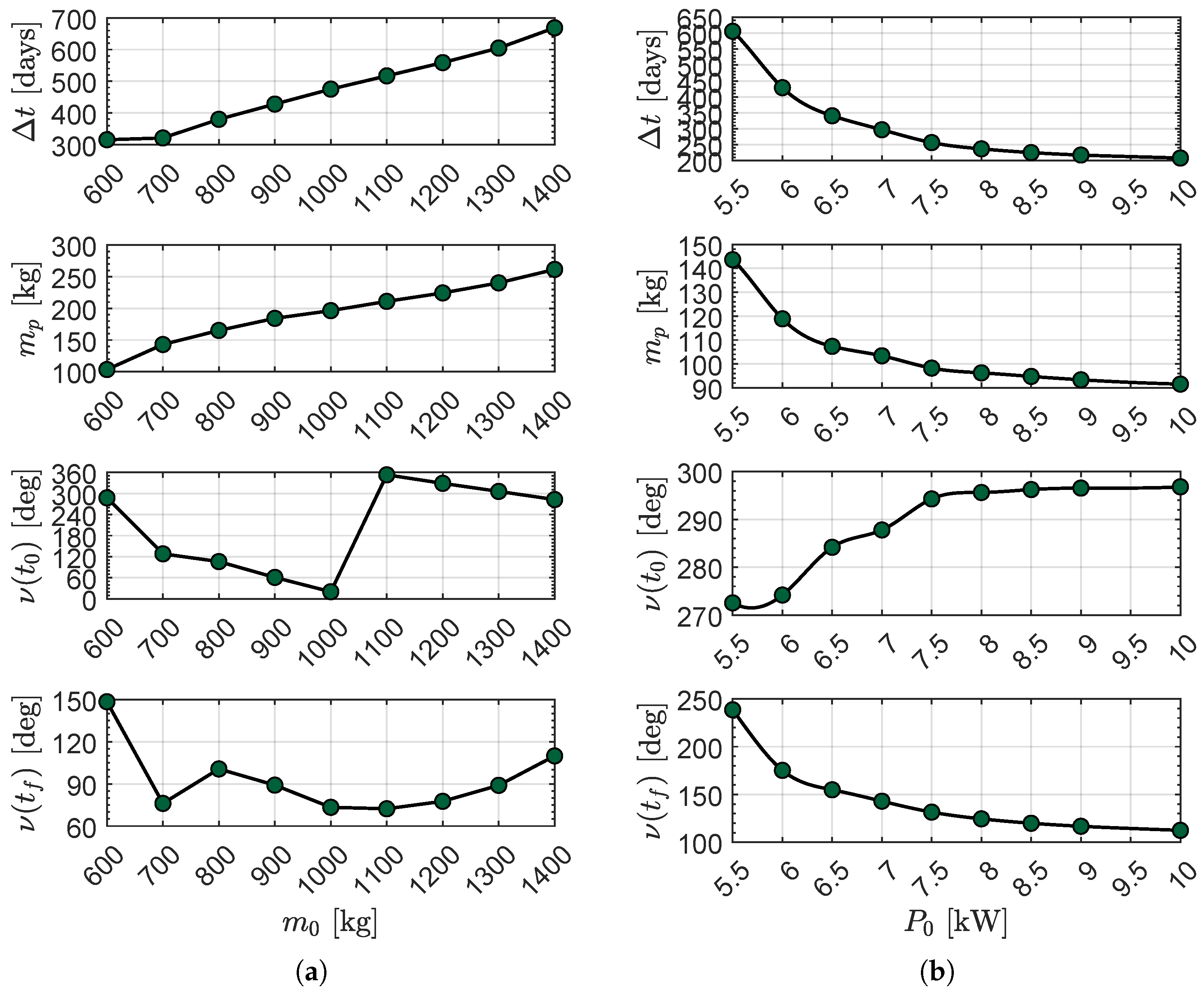
Transfer Performance Sensitivity
4. Final Remarks and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DART | Double Asteroid Redirection Test |
| MEOE | Modified Equinoctial Orbit Elements |
| NEXT-C | NASA’s Evolutionary Xenon Thruster - Commercial |
| PPU | Power Processing Unit |
| RTN | Radial-Tangential-Normal |
| SEP | Solar Electric Propulsion |
| TPBVP | Two-Point Boundary Value Problem |
| a | semimajor axis [au] |
| propulsive acceleration vector [mm/s2] | |
| propulsive acceleration unit vector | |
| matrix, see Equation (8) | |
| vector, see Equation (9) | |
| e | orbital eccentricity |
| Hamiltonian function | |
| i | orbital inclination [deg] |
| radial unit vector | |
| transverse unit vector | |
| normal unit vector | |
| J | performance index [days] |
| m | spacecraft mass [kg] |
| propellant mass flow rate [kg/s] | |
| nominal propellant mass flow rate [kg/s] | |
| P | electric thruster input power [W] |
| solar array output power [W] | |
| available power [W] | |
| load power [W] | |
| MEOEs | |
| r | radial distance [au] |
| spacecraft position vector | |
| reference distance [] | |
| t | time [days] |
| T | thrust magnitude [N] |
| TL | throttle level |
| spacecraft velocity vector | |
| spacecraft state vector | |
| thrust pitch angle [rad] | |
| flight time [days] | |
| thrust clock angle [rad] | |
| generic adjoint variable to i-th state | |
| adjoint vector | |
| duty cycle | |
| Sun’s gravitational parameter [km3/s2] | |
| argument of periapse [deg] | |
| right ascension of the ascending node [deg] | |
| Subscripts | |
| 0 | initial, parking orbit |
| f | final, target orbit |
| Superscripts | |
| · | derivative with respect to time |
References
- Brophy, J. Advanced ion propulsion systems for affordable deep-space missions. Acta Astronaut. 2003, 52, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.D.; Varghese, P.; Lehman, D.H.; Livesay, L.L. Results from the Deep Space 1 technology validation mission. Acta Astronaut. 2000, 47, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foing, B.; Racca, G.; Marini, A.; Evrard, E.; Stagnaro, L.; Almeida, M.; Koschny, D.; Frew, D.; Zender, J.; Heather, J.; et al. SMART-1 mission to the Moon: Status, first results and goals. Adv. Space Res. 2006, 37, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.D.; Fraschetti, T.C.; Raymond, C.A.; Russell, C.T. Dawn: A mission in development for exploration of main belt asteroids Vesta and Ceres. Acta Astronaut. 2006, 58, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, P.; Tilley, S.; Oh, D.Y.; Goebel, D.; Polanskey, C.; Snyder, S.; Carr, G.; Collins, S.M.; Lantoine, G.; Landau, D.; et al. Psyche: Journey to a metal world. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.N.; Coverstone-Carroll, V. Benefits of Solar Electric Propulsion for the Next Generation of Planetary Exploration Missions. J. Astronaut. Sci. 1997, 45, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaran, K.; Hamming, B.; Grochowski, C.; Hoff, J.; Spaun, M.; Rollins, M. Evaluation of Existing Electric Propulsion Systems for the OSIRIS-REx Mission. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2013, 50, 1292–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutter, B.; Hatten, N.; Getzandanner, K.M.; Hughes, K.M.; Wibben, D.; Williams, K.; Moreau, M.C.; Englander, J.; Mudek, A.J.; Lauretta, D.; et al. OSIRIS-REx Extended Mission Trajectory Design and Target Search. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2022 Forum, San Diego, CA, USA, 3–7 January 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, K.N.; DellaGiustina, D.N.; Bennett, C.A.; Walsh, K.J.; Pajola, M.; Bierhaus, E.B.; Nolan, M.C.; Boynton, W.V.; Brodbeck, J.I.; Connolly, H.C.; et al. Particle Size-Frequency Distributions of the OSIRIS-REx Candidate Sample Sites on Asteroid (101955) Bennu. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, J.; Oleson, S. Spacecraft Conceptual Design for Returning Entire Near-Earth Asteroids. In Proceedings of the 48th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference & Exhibit, Atlanta, GA, USA, 29 July–1 August 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazanek, D.D.; Merrill, R.G.; Brophy, J.R.; Mueller, R.P. Asteroid Redirect Mission concept: A bold approach for utilizing space resources. Acta Astronaut. 2015, 117, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengali, G.; Quarta, A.A. Optimal trade studies of interplanetary electric propulsion missions. Acta Astronaut. 2008, 62, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, E.; Junkins, J.L.; Kolmanovsky, I.; Girard, A. A novel approach for optimal trajectory design with multiple operation modes of propulsion system, part 2. Acta Astronaut. 2020, 172, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurre, N.P.; Taheri, E. Duty-cycle-aware low-thrust trajectory optimization using embedded homotopy. Acta Astronaut. 2023, 212, 630–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, A.A.; Mengali, G. Minimum-Time Space Missions with Solar Electric Propulsion. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2011, 15, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, A.A.; Izzo, D.; Vasile, M. Time-Optimal Trajectories to Circumsolar Space Using Solar Electric Propulsion. Adv. Space Res. 2013, 51, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brozovic, M.; Ostro, S.; Benner, L.; Giorgini, J.; Jurgens, R.; Rose, R.; Nolan, M.; Hine, A.; Magri, C.; Scheeres, D.; et al. Radar observations and a physical model of Asteroid 4660 Nereus, a prime space mission target. Icarus 2009, 201, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, J.; Fujiwara, A.; Sawai, S. Sample and return mission from asteroid Nereus via solar electric propulsion. Acta Astronaut. 1996, 38, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Ferraiuolo, B.; Monheiser, J.; Goodfellow, K.; Hoskins, A.; Myers, R.; Bontempo, J.; McDade, J.; O’malley, T.; Soulas, G.; et al. NEXT-C flight ion system status. In Proceedings of the AIAA Propulsion and Energy 2020 Forum, Virtual Event, 24–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monheiser, J.; Goodfellow, K.; Aubuchon, C.; Wang, J.; Ferraiuolo, B.; Williams, G.; Soulas, G.; Shastry, R.; Arthur, N. A Summary of the NEXT-C Flight Thruster Proto-flight Testing. In Proceedings of the AIAA Propulsin and Energy Forum, Virtual, 11–14 August 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, E.; Oshaughnessy, D.; Reinhart, M.; John, J.; Congdon, E.; Gallagher, D.; Abel, E.; Atchison, J.; Fletcher, Z.; Chen, M.; et al. Double Asteroid Redirection Test: The Earth Strikes Back. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 2–9 March 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, J.; Roufberg, L.; Ottman, G.K.; Adams, E. NEXT-C Lessons Learned on the DART Mission for Future Integration and Test. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, MT, USA, 4–11 March 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coverstone, V.L.; Prussing, J.E. Technique for Escape from Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit Using a Solar Sail. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2003, 26, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechichian, J. Trajectory optimization with a modified set of equinoctial orbit elements. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, Durango, CO, USA, 19–22 August 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Pontani, M. Optimal Space Trajectories with Multiple Coast Arcs Using Modified Equinoctial Elements. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2021, 191, 545–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, M.J.H.; Ireland, B.; Owens, J. A set of modified equinoctial orbit elements. Celest. Mech. 1985, 36, 409–419, Erratum in Celest. Mech. 1986, 38, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, A.A.; Abu Salem, K.; Palaia, G. Solar sail transfer trajectory design for comet 29P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 1 rendezvous. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bate, R.R.; Mueller, D.D.; White, J.E. Fundamentals of Astrodynamics; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1971; Chapter 2; pp. 53–55, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Betts, J.T. Very low-thrust trajectory optimization using a direct SQP method. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2000, 120, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, R.; Soulas, G.; Aulisio, M.; Schmidt, G. Current status of NASA’S NEXT-C ion propulsion system development project. In Proceedings of the 68th International Astronautical Congress, IAC, Adelaide, Australia, 25–29 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Overton, S.; Jackson, J.; Spores, R.; Kelleher, K.; Allen, M.; Hertel, T.; Hoskins, A. GN&C applications using next generation NEXT-C high power ion thruster. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual AAS Rocky Mountain Section Guidance and Control Conference, Breckenridge, CO, USA, 5–10 February 2016; Volume 157, pp. 839–849. [Google Scholar]
- Aulisio, M.; Pinero, L.; White, B.; Hickman, T.; Bontempo, J.; Hertel, T.; Birchenough, A. Status of the development of flight power processing units for the NASA’s evolutionary Xenon Thruster—Commercial (NEXT-C) project. In Proceedings of the 14th International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NASA’s Evolutionary Xenon Thruster (NEXT) Ion Propulsion GFE Component Information Summary for Discovery Missions July 2014. Nasa Discovery Program Announcement of Opportunity Program Library, NASA. 2014. Available online: http://discovery.larc.nasa.gov/discovery/pdf_files/20-NEXT-C_AO_Guidebook_11July14.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- NEXT-C Ion Propulsion System (IPS) Information Summary for New Frontiers Missions. Technical Report, NASA; 2017. Available online: https://newfrontiers.larc.nasa.gov/NF4/PDF_FILES/NEXT-C_New_Frontiers_Guidebook_20161230_REV5.pdf (accessed on 24 October 2023).
- Kerslake, T.; Gustafson, E. On-Orbit Performance Degradation of the International Space Station P6 Photovoltaic Arrays. In Proceedings of the 1st International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference (IECEC), Portsmouth, NH, USA, 15–17 August 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, C.G., Jr.; Bourke, R. The effect of solar array degradation on electric propulsion spacecraft performance. In Proceedings of the 9th Electric Propulsion Conference, Bethesda, MD, USA, 17–19 April 1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, C.G., Jr. Modeling of thruster and solar array characteristics in the JPL low-thrust trajectory analysis. In Proceedings of the 13th International Electric Propulsion Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 27–27 April 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, B.; Coverstone, V.L.; Hartmann, J.W.; Cupples, M. Trajectory and System Analysis For Outer-Planet Solar Electric Propulsion Missions. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2005, 42, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.D.; Williams, S.N. Design of the First Interplanetary Solar Electric Propulsion Mission. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2002, 39, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryson, A.E.J.; Ho, Y.C. Applied Optimal Control; Hemisphere Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Stengel, R.F. Optimal Control and Estimation; Dover Publications: Mineola, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 222–254. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, I.M. A Primer on Pontryagin’s Principle in Optimal Control; Collegiate Publishers: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015; Chapter 2; pp. 127–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mengali, G.; Quarta, A.A. Optimal three-dimensional interplanetary rendezvous using nonideal solar sail. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2005, 28, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengali, G.; Quarta, A.A. Fuel-optimal, power-limited rendezvous with variable thruster efficiency. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 2005, 28, 1194–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Y.; Cao, W.; Kim, J.; Park, K.W.; Park, H.H.; Joung, J.; Ro, J.S.; Hong, C.H.; Im, T. Applied Numerical Methods Using MATLAB®; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Chapters 6–7; pp. 333–336, 376–378. [Google Scholar]
- Shampine, L.F.; Reichelt, M.W. The MATLAB ODE Suite. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 1997, 18, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarli, B.V.; Atchison, J.A.; Ozimek, M.T.; Englander, J.A.; Barbee, B.W. Double Asteroid Redirection Test Mission: Heliocentric Phase Trajectory Analysis. J. Spacecr. Rocket. 2019, 56, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

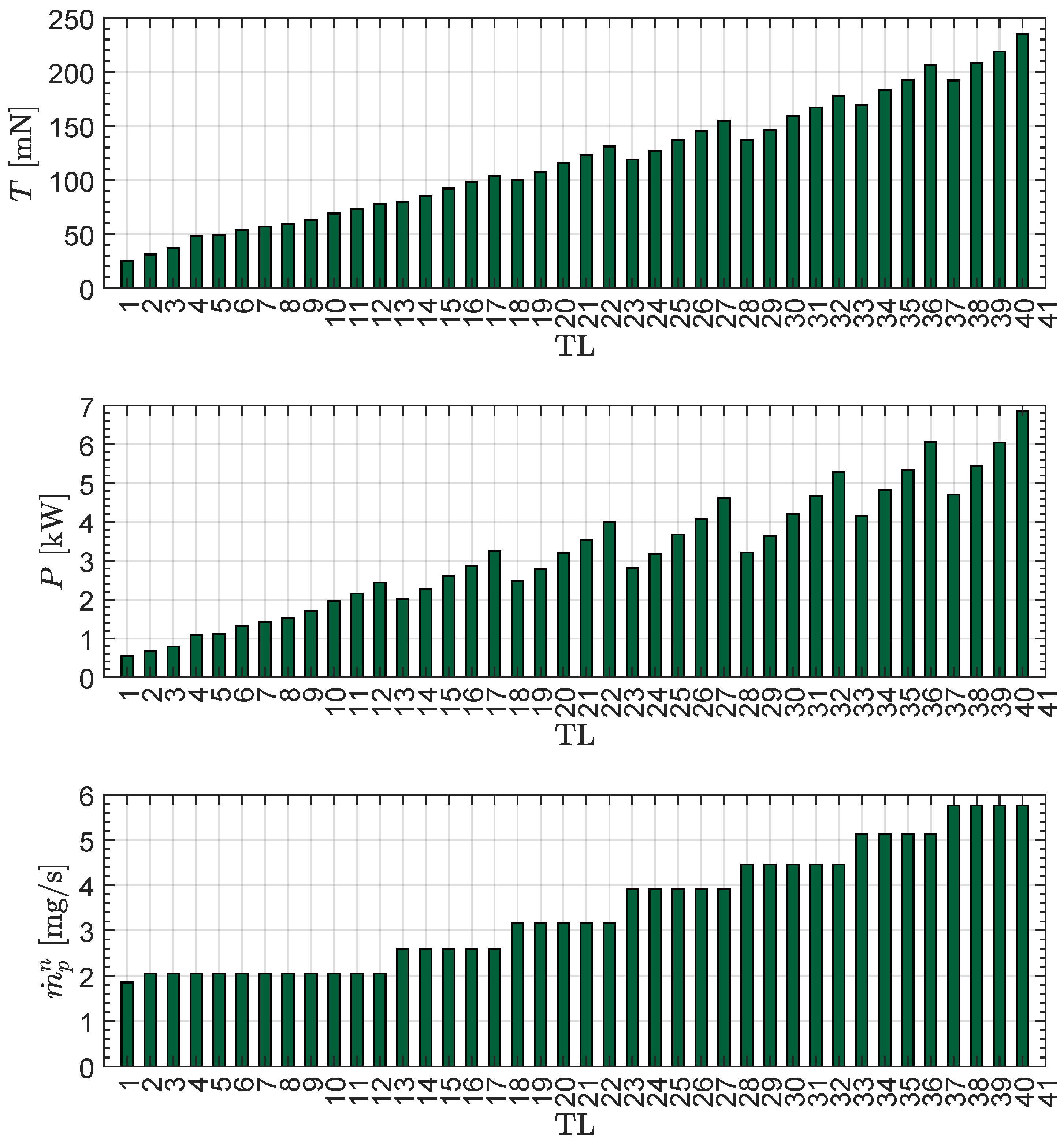




| TL | T | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 0.545 | 1.85 |
| 2 | 31 | 0.668 | 2.05 |
| 3 | 37 | 0.788 | 2.05 |
| 4 | 48 | 1.085 | 2.05 |
| 5 | 49 | 1.120 | 2.05 |
| 6 | 54 | 1.319 | 2.05 |
| 7 | 57 | 1.419 | 2.05 |
| 8 | 59 | 1.517 | 2.05 |
| 9 | 63 | 1.702 | 2.05 |
| 10 | 69 | 1.958 | 2.05 |
| 11 | 73 | 2.160 | 2.05 |
| 12 | 78 | 2.437 | 2.05 |
| 13 | 80 | 2.019 | 2.60 |
| 14 | 85 | 2.265 | 2.60 |
| 15 | 92 | 2.606 | 2.60 |
| 16 | 98 | 2.876 | 2.60 |
| 17 | 104 | 3.244 | 2.60 |
| 18 | 100 | 2.470 | 3.16 |
| 19 | 107 | 2.778 | 3.16 |
| 20 | 116 | 3.204 | 3.16 |
| 21 | 123 | 3.541 | 3.16 |
| 22 | 131 | 4.002 | 3.16 |
| 23 | 119 | 2.814 | 3.92 |
| 24 | 127 | 3.178 | 3.92 |
| 25 | 137 | 3.680 | 3.92 |
| 26 | 145 | 4.075 | 3.92 |
| 27 | 155 | 4.614 | 3.92 |
| 28 | 137 | 3.217 | 4.46 |
| 29 | 146 | 3.636 | 4.46 |
| 30 | 159 | 4.212 | 4.46 |
| 31 | 167 | 4.666 | 4.46 |
| 32 | 178 | 5.285 | 4.46 |
| 33 | 169 | 4.158 | 5.12 |
| 34 | 183 | 4.819 | 5.12 |
| 35 | 193 | 5.341 | 5.12 |
| 36 | 206 | 6.052 | 5.12 |
| 37 | 192 | 4.703 | 5.76 |
| 38 | 208 | 5.454 | 5.76 |
| 39 | 219 | 6.046 | 5.76 |
| 40 | 235 | 6.853 | 5.76 |
| 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quarta, A.A.; Mengali, G.; Bassetto, M. Rapid Orbit-to-Orbit Transfer to Asteroid 4660 Nereus Using Solar Electric Propulsion. Universe 2023, 9, 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110459
Quarta AA, Mengali G, Bassetto M. Rapid Orbit-to-Orbit Transfer to Asteroid 4660 Nereus Using Solar Electric Propulsion. Universe. 2023; 9(11):459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110459
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuarta, Alessandro A., Giovanni Mengali, and Marco Bassetto. 2023. "Rapid Orbit-to-Orbit Transfer to Asteroid 4660 Nereus Using Solar Electric Propulsion" Universe 9, no. 11: 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110459
APA StyleQuarta, A. A., Mengali, G., & Bassetto, M. (2023). Rapid Orbit-to-Orbit Transfer to Asteroid 4660 Nereus Using Solar Electric Propulsion. Universe, 9(11), 459. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110459






