Exploring Neutrino Mass Orderings through Supernova Neutrino Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Supernova Neutrino Fluxes
Three-Active Scheme: The Two Flavor Approximations
3. Selected Detectors and Interactions Channels
3.1. Interactions in SNO+
3.2. Interactions in HALO
3.3. Interactions in DUNE
4. Combined Signals
- The ratio of 1n and 2n events expected in the HALO detector ().
- The ratio between the pES and IBD events expected in the SNO+ detector ().
- The ratio of CC and NC events on Argon in DUNE ().
- The ratio of and events on Argon in the DUNE detector ().
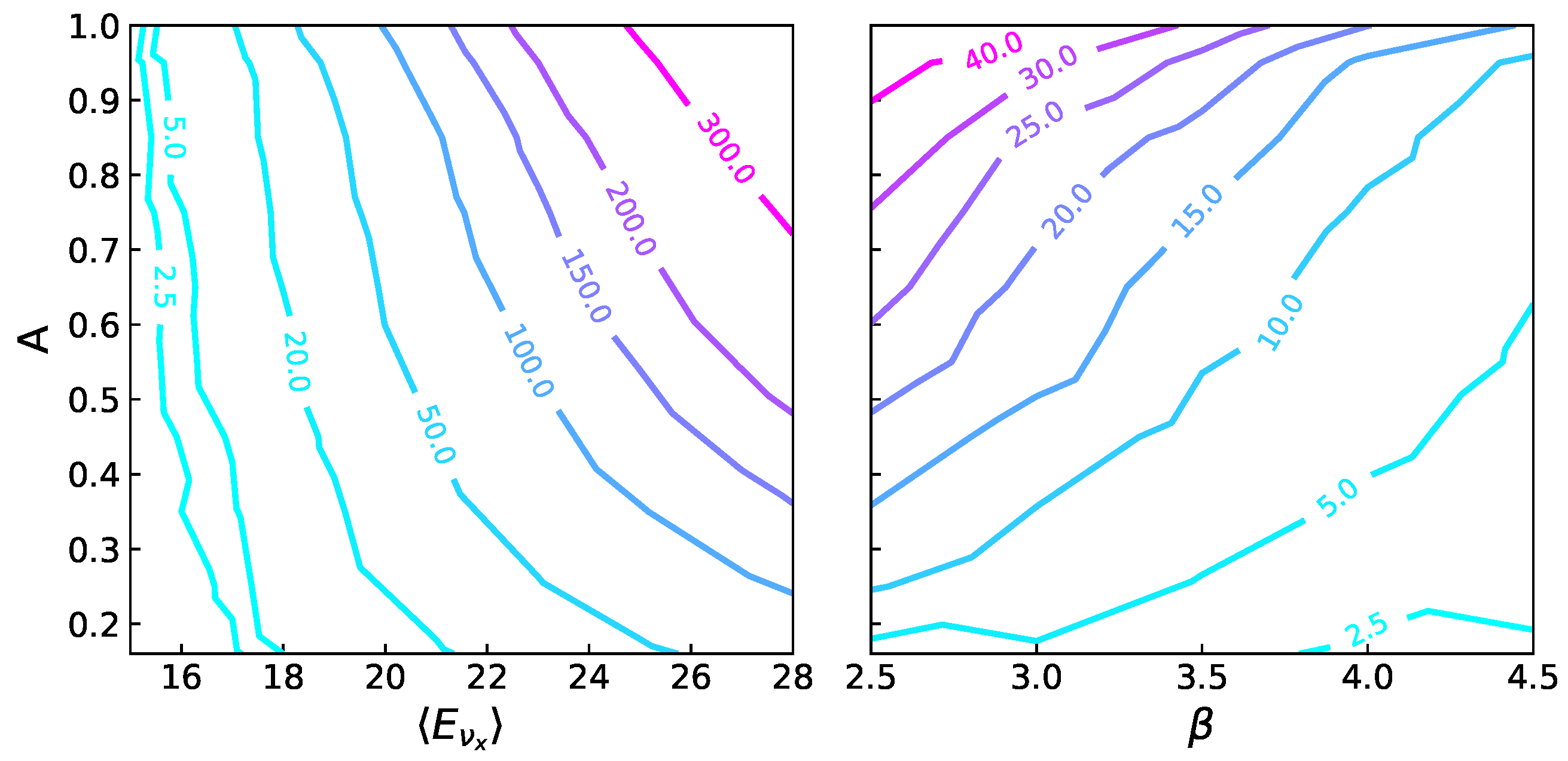
5. Statistical Analysis
5.1. Individual Counts Analysis
5.2. Ratio Analysis
6. Conclusions
- excludes NO, while excludes IO;
- excludes IO;
- excludes NO, while excludes IO;
- , excludes NO, while excludes IO.
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Neutrino Flavor Evolution Equations
Appendix B. Detection Channels in SNO+
- Inverse beta decay (IBD):
- Neutrino–proton elastic scattering (pES):
- Neutrino–nucleus reactions in 12C:
Appendix C. Some Comments about Collective Effects

| 1 | The relative statistical error has been calculated as . |
| 2 | IMINUIT v2.24.0 maintained by CERN’s ROOT team https://zenodo.org/records/8249703 (accessed on 24 October 2023). |
| 3 | Taking the standard distance of 10 kpc, , , and correspond to luminosities of 1, 25, and 100 foe, respectively. Or, considering a fixed luminosity of 25 foe, the same A values correspond to distances of 5, 10, and 50 kpc, respectively. |
| 4 | The collective flavor oscillations are governed by the neutrino–neutrino forward-scattering rate, . The rate at which these oscillations occur is referred to as slow if it is on the order of ∼ or fast if it is on the order of , where represents the collective synchronized rate. |
References
- Woosley, S.E.; Heger, A.; Weaver, T.A. The evolution and explosion of massive stars. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 1015–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, H.T. Neutrino Emission from Supernovae. In Handbook of Supernovae; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirizzi, A.; Tamborra, I.; Janka, H.-T.; Saviano, N.; Scholberg, K.; Bollig, R.; Hüdepohl, L.; Chakraborty, S. Supernova neutrinos: Production, oscillations and detection. Nuovo C. Riv. Ser. 2016, 39, 1–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, K.; Kajita, T.; Koshiba, M.; Nakahata, M.; Oyama, Y.; Sato, N.; Suzuki, A.; Takita, M.; Totsuka, Y.; Kifune, T. Observation of a neutrino burst from the SN1987A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 1490–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bionta, R.M.; Blewitt, G.; Bratton, C.B.; Casper, D.; Ciocio, A.; Clauss, R.; Cortez, B.; Crouch, M.; Dye, S.T.; Errede, S.; et al. Observation of a neutrino burst in coincidence with supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 58, 1494–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseev, E.N.; Volchenko, V.I. Possible Detection of a Neutrino Signal on 23 February 1987 at the Baksan Underground Scintillation Telescope of the Institute of Nuclear Research. JETP Lett. 1987, 45, 589–592. [Google Scholar]
- Aglietta, M.; Badino, G.; Bologna, G.; Castagnoli, C.; Castellina, A.; Dadykin, V.L.; Fulgione, W.; Galeott, P.; Kalchukov, F.F.; Kortchaguin, B. On the Event Observed in the Mont Blanc Underground Neutrino Observatory. Europhys. Lett. 1987, 3, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüdepohl, L.; Müller, B.; Janka, H.-T.; Marek, A.; Raffelt, G.G. Neutrino Signal of Electron-Capture Supernovae from Core Collapse to Cooling. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 251101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, M.T.; Raffelt, G.G.; Janka, H.-T. Monte Carlo study of supernova neutrino spectra formation. Astrophys. J. 2003, 590, 971–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, E.; Bollig, R.; Burrows, A.; Couch, S.; Fischer, T.; Janka, H.-T.; Kotake, K.; Lentz, E.J.; Liebendörfer, M.; Messer, O.E.B. Global comparison of core-collapse supernova simulations in spherical symmetry. J. Phys. G 2018, 45, 104001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, A.; Vartanyan, D. Core-collapse supernova explosion theory. Nature 2021, 589, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Krosigk, B.; Neumann, L.; Nolte, R.; Röttger, S.; Zuber, K. Measurement of the proton light response of various LAB based scintillators and its implication for supernova neutrino detection via neutrino-proton scattering. Eur. Phys. J. C 2013, 73, 2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.L.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhou, S. Model-independent approach to the reconstruction of multiflavor supernova neutrino energy spectra. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 123009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardini, C.; Smirnov, A.Y. Supernova neutrinos: Earth matter effects and neutrino mass spectrum. Nucl. Phys. D 2001, 616, 307–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunardini, C.; Smirnov, A.Y. Probing the neutrino mass hierarchy and the 13-mixing with supernovae. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 2003, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, F.; Dasgupta, B.; Mirizzi, A. Model-independent diagnostic of self-induced spectral equalization versus ordinary matter effects in supernova neutrinos. Phys. Rev. D 2018, 98, 063013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborra, I.; Raffelt, G.G.; Hüdepohl, L.; Janka, H. Impact of eV-mass sterile neutrinos on neutrino-driven supernova outflows. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giunti, C.; Laveder, M. Neutrino Mixing. arXiv 2003, arXiv:hep-ph/0310238. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban, I.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.C.; Maltoni, M.; Schwetz, T.; Zhou, A. The fate of hints: Updated global analysis of three-flavor neutrino oscillations. Int. J. High Energy Phys. 2020, 2020, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, T. Atmospheric Neutrinos and Discovery of Neutrino Oscillations. Proc. Japan Acad. B 2010, 86, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholberg, K. Supernova signatures of neutrino mass ordering. J. Phys. Nucl. Phys. 2018, 45, 014002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdar, V.; Xu, X.J. Timing and multi-channel: Novel method for determining the neutrino mass ordering from supernovae. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2022, 2022, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesús-Valls, C. Uncovering the neutrino mass ordering with the next galactic core-collapse supernova neutrino burst. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2210.11676. [Google Scholar]
- Balantekin, A.B.; Yüksel, H. Neutrino mixing and nucleosynthesis in core-collapse supernovae. New J. Phys. 2005, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikas, S.; Raffelt, G.G.; Hudepohl, L.; Janka, H.T. Suppression of Self-Induced Flavor Conversion in the Supernova Accretion Phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 061101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Fischer, T.; Mirizzi, A.; Saviano, N.; Tomàs, R. No Collective Neutrino Flavor Conversions during the Supernova Accretion Phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 107, 151101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dighe, A.S.; Smirnov, A.Y. Identifying the neutrino mass spectrum from the neutrino burst from a supernova. Phys. Rev. D 2000, 62, 033007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottingham, W.; Greenwood, D.; Greenwood, D. An Introduction to Nuclear Physics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Zyla, A. et al. [Particle Data Group] Review of Particle Physics. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2020, 2020, 083C01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, B.; Beacom, J.F. Reconstruction of supernova νμ, ντ, anti-νμ, and anti-ντ neutrino spectra at scintillator detectors. Phys. Rev. D 2011, 83, 113006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibley, L. SNO+: Physics program and status update. AIP Conf. Proc. 2015, 1604, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väänänen, D.; Volpe, C. The neutrino signal at HALO: Learning about the primary supernova neutrino fluxes and neutrino properties. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2011, 2011, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, J.; McLaughlin, G.C.; Volpe, C. What can be learned with a lead-based supernova-neutrino detector? Phys. Rev. D 2003, 67, 013005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholberg, K.; Albert, J.B.; Vasel, J. SNOwGLoBES: SuperNova Observatories with GLoBES. Astrophysics Source Code Library, Record ascl:2109.019, 2021. Available online: https://ascl.net/2109.019 (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Abi, B.; Acciarri, R.; Acero, M.A.; Adamov, G.; Adams, D.; Adinolfi, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmed, J.; Alion, T.; Monsalve, S.A. Supernova neutrino burst detection with the deep underground neutrino experiment. Eur. Phys. J. C 2021, 81, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi, B.; Acciarri, R.; Acero, M.A.; Adamov, G.; Adams, D.; Adinolfi, M.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmed, J.; Alion, T.; Monsalve, S.A. Volume I. Introduction to DUNE. J. Instrum. 2020, 15, T08008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi, B. et al. [DUNE Collaboration] Prospects for Beyond the Standard Model Physics Searches at the Deep Underground Neutrino Experiment. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2008.12769. [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner, S. Simulating low-energy neutrino interactions with MARLEY. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2021, 269, 108123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, V.; Marfatia, D.; Wood, B.P. Inverting a supernova: Neutrino mixing, temperatures and binding energy. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 547, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakata, H.; Nunokawa, H.; Tomas, R.; Valle, J.W.F. Probing supernova physics with neutrino oscillations. Phys. Lett. B 2002, 542, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo Rosso, A.; Vissani, F.; Volpe, M.C. What can we learn on supernova neutrino spectra with water Cherenkov detectors? J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2018, 04, 040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stringer, M. Sensitivity of SNO+ to Supernova Neutrinos. Ph.D. Thesis, Sussex University, Sussex, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dembinski, H.; Ongmongkolkul, P.; Deil, C.; Schreiner, H.; Feickert, M.; Burr, C.; Watson, J.; Rost, F.; Pearce, A.; Geiger, L.; et al. Scikit-Hep/Iminuit, v2.24.0; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [CrossRef]
- James, F.; Roos, M. Minuit: A System for Function Minimization and Analysis of the Parameter Errors and Correlations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1975, 10, 343–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenstein, L. Neutrino oscillations in matter. Phys. Rev. D 1978, 17, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strumia, A.; Vissani, F. Precise quasielastic neutrino/nucleon cross-section. Phys. Lett. B 2003, 564, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Effects of a Neutral Intermediate Boson in Semileptonic Processes. Phys. Rev. D 1972, 5, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, L.A.; Aronson, S.H.; Connolly, P.L.; Gibbard, B.G.; Murtagh, M.J.; Murtagh, S.J.; Terada, S.; White, D.H.; Callas, J.L.; Cutts, D.; et al. Measurement of neutrino-proton and antineutrino-proton elastic scattering. Phys. Rev. D 1987, 35, 785–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beringer, J.; Arguin, J.F.; Barnett, R.M.; Copic, K.; Dahl, O.; Groom, D.E.; Lin, C.J.; Lys, J.; Murayama, H.; Wohl, C.G.; et al. Review of Particle Physics. Phys. Rev. D 2012, 86, 010001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, B. et al. [KARMEN Collaboration] Measurement of the weak neutral current excitation 12C(νμνμ′)12C*(1+,1;15.1MeV) at Eνμ=29.8 MeV. Phys. Lett. B 1998, 423, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, T.; Peccei, R. Neutral current effects in nuclei. Phys. Rep. 1979, 50, 1–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Dasgupta, B. Elaborating the ultimate fate of fast collective neutrino flavor oscillations. Phys. Rev. D 2022, 106, 103039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richers, S.; Willcox, D.E.; Ford, N.M.; Myers, A. Particle-in-cell simulation of the neutrino fast flavor instability. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 103, 083013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.R.; George, M.; Lin, C.Y.; Xiong, Z. Collective fast neutrino flavor conversions in a 1D box: Initial conditions and long-term evolution. Phys. Rev. D 2021, 104, 103003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, B.; Mirizzi, A. Temporal instability enables neutrino flavor conversions deep inside supernovae. Phys. Rev. D 2015, 92, 125030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, R.F. Neutrino Cloud Instabilities Just above the Neutrino Sphere of a Supernova. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 081101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, B.; Mirizzi, A.; Sen, M. Fast neutrino flavor conversions near the supernova core with realistic flavor-dependent angular distributions. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 2017, 019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Detector | Location | Tot. Mass (Fid. Mass) | Current | Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SNO+ | SNOLAB | ∼780 t (∼0.45 kt) | CC | |
| NC | ||||
| NC | ||||
| HALO | SNOLAB | ∼79 t | CC | |
| CC | ||||
| NC | ||||
| NC | ||||
| DUNE | Fermilab | ∼70 kt (∼40 kt) | CC | |
| CC | ||||
| NC | ||||
| NC + CC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saez, M.M. Exploring Neutrino Mass Orderings through Supernova Neutrino Detection. Universe 2023, 9, 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110464
Saez MM. Exploring Neutrino Mass Orderings through Supernova Neutrino Detection. Universe. 2023; 9(11):464. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110464
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaez, Maria Manuela. 2023. "Exploring Neutrino Mass Orderings through Supernova Neutrino Detection" Universe 9, no. 11: 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110464
APA StyleSaez, M. M. (2023). Exploring Neutrino Mass Orderings through Supernova Neutrino Detection. Universe, 9(11), 464. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110464







