Statistical and Radio Analysis of Exoplanets and Their Host Stars
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Parameter Distribution Statistics of Planets and Host Stars
2.1. Selection of Samples
2.2. Host Star System with Extrasolar Planets
2.3. Planetary Related Parameters
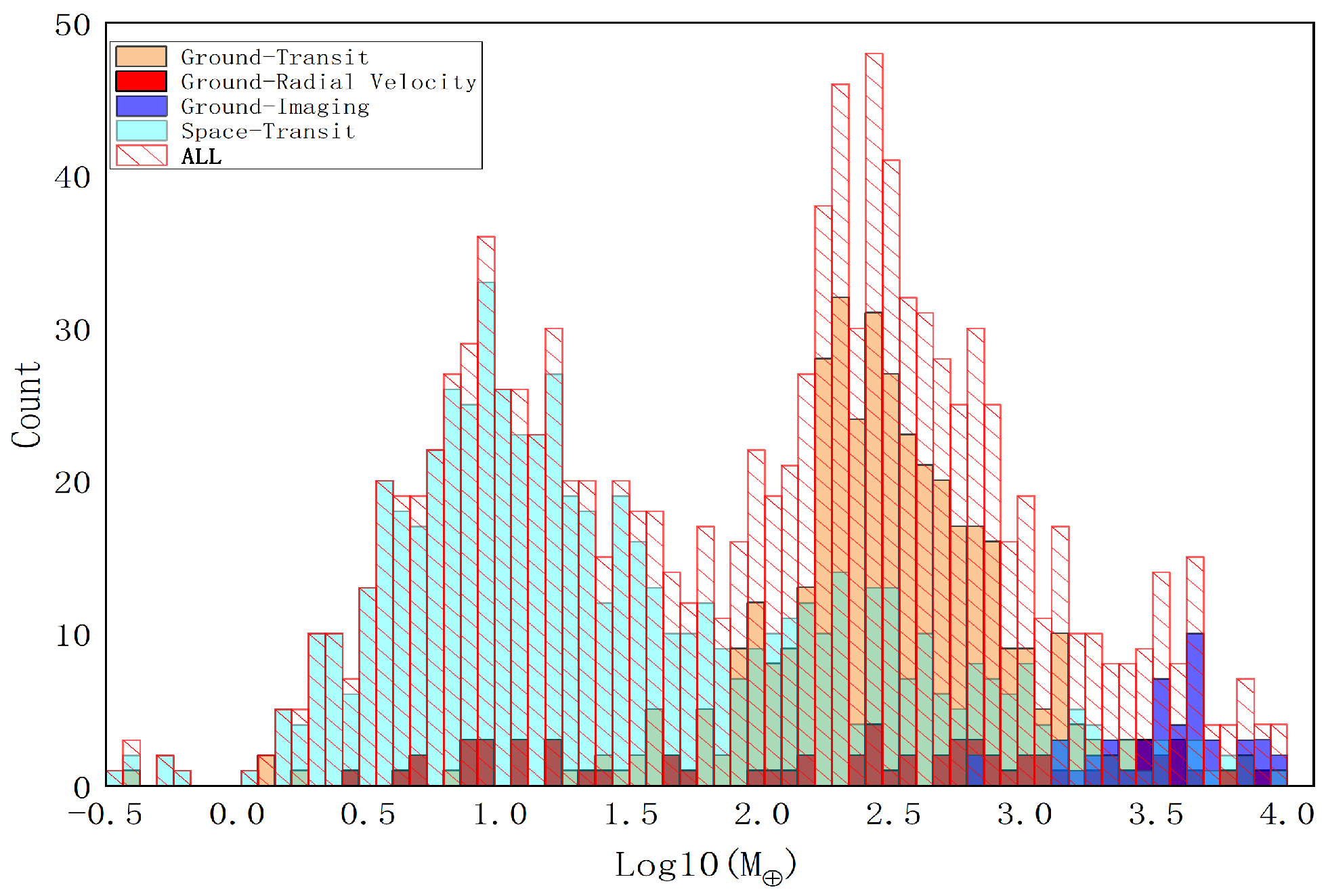
2.3.1. Distribution of True Mass and Radius of Planets
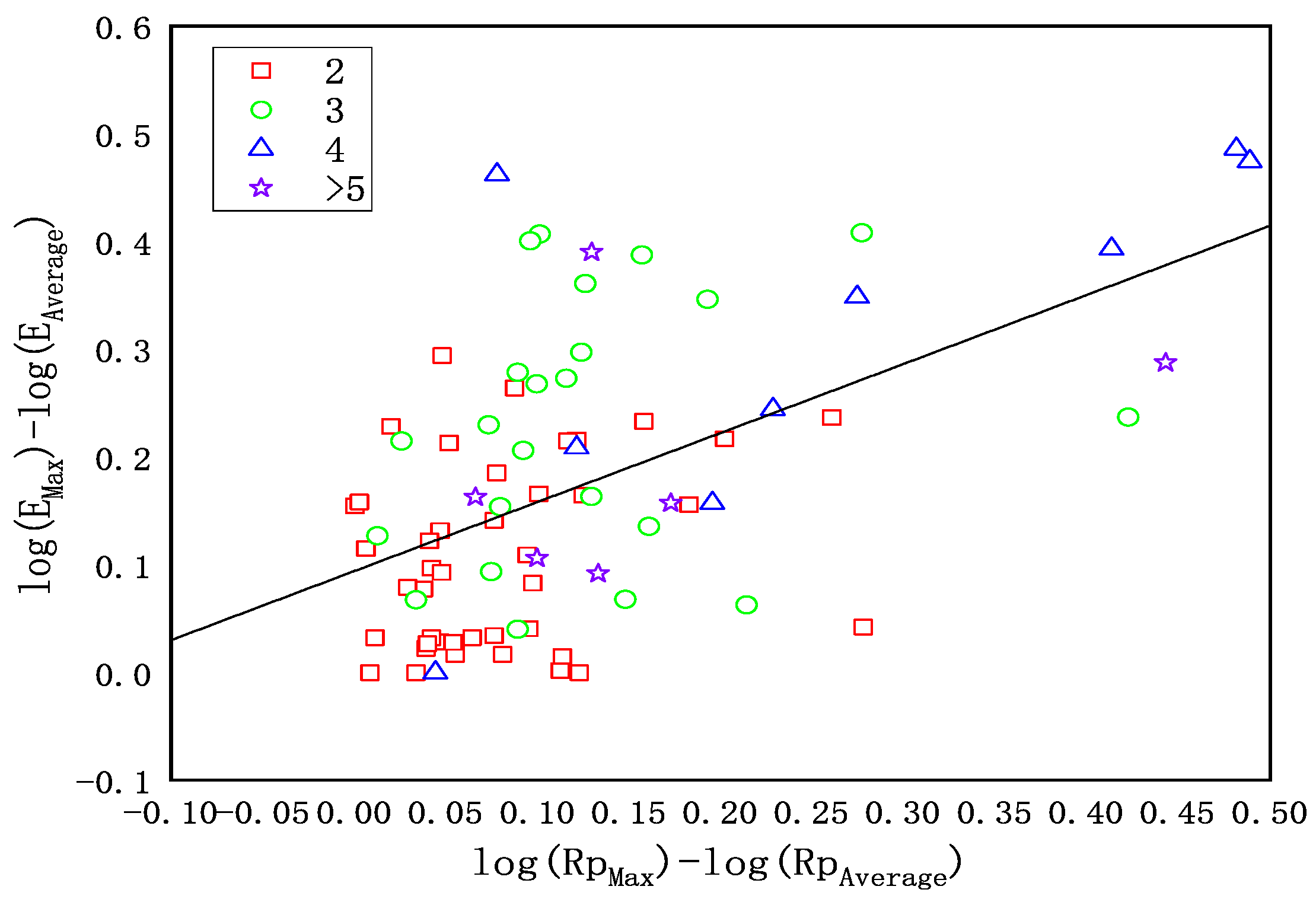
2.3.2. Number of Planets and Eccentricities in the System
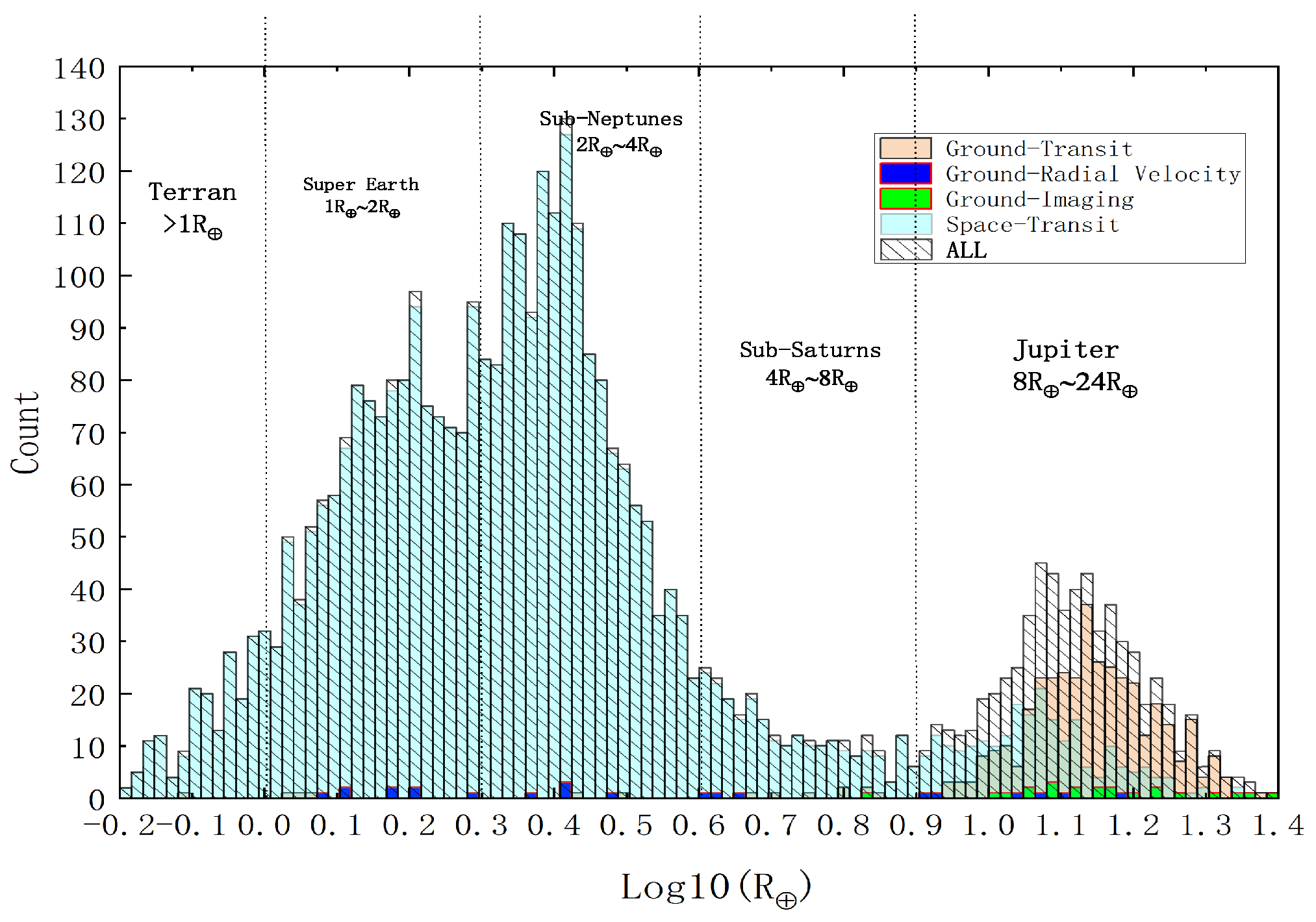
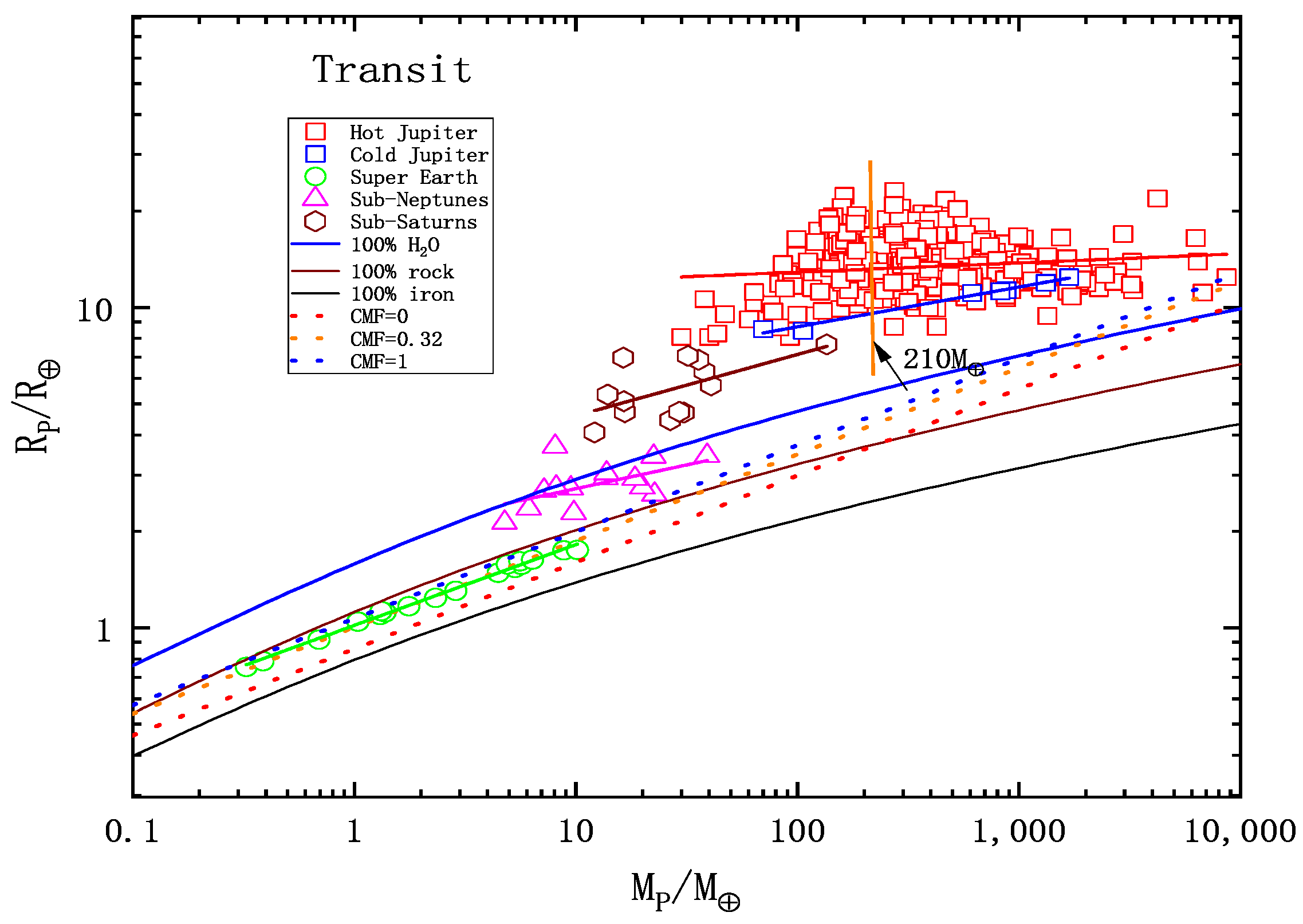
2.3.3. Planet Mass and Planet Radius
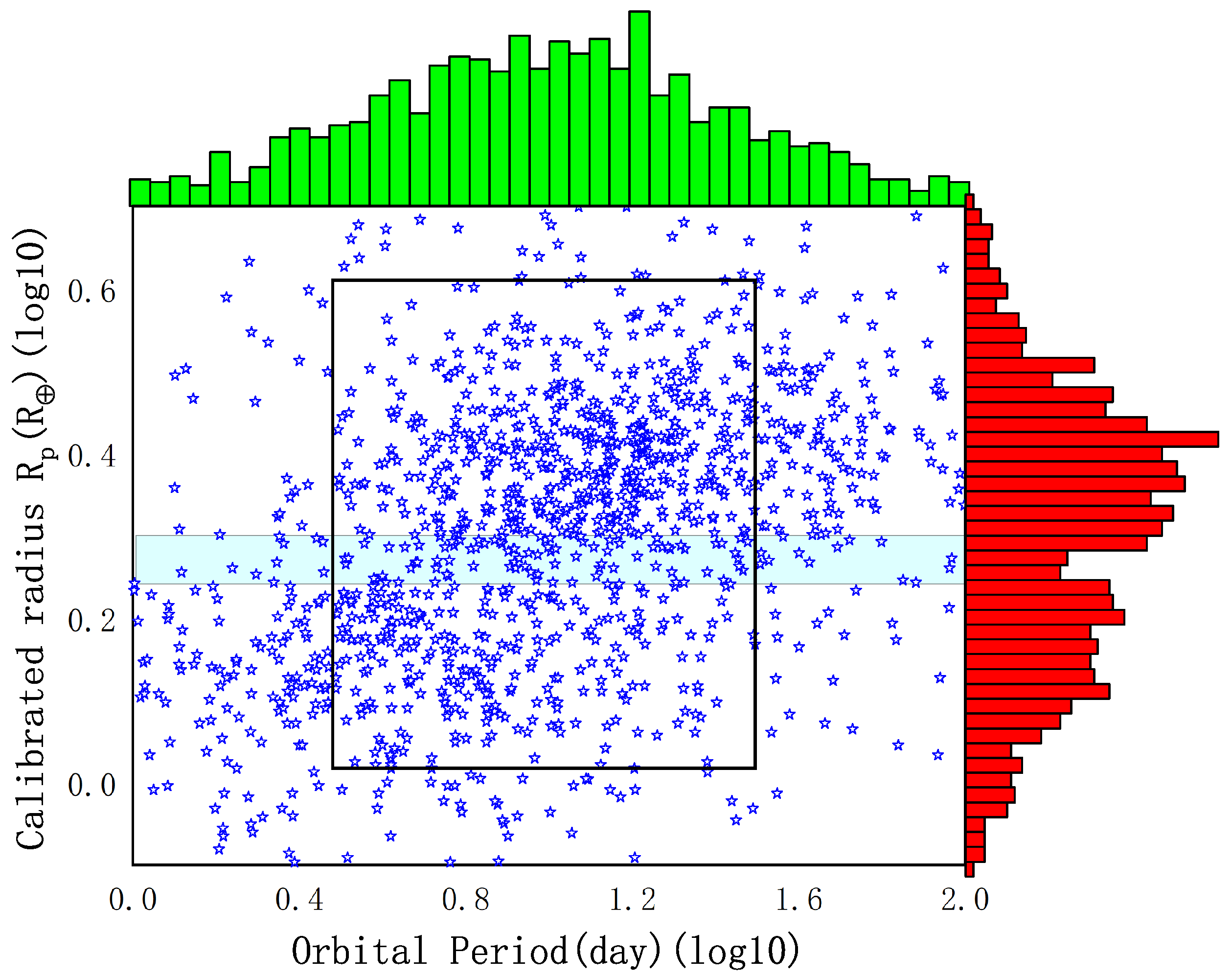
2.3.4. Planetary Radius and Period (Radius Valley)
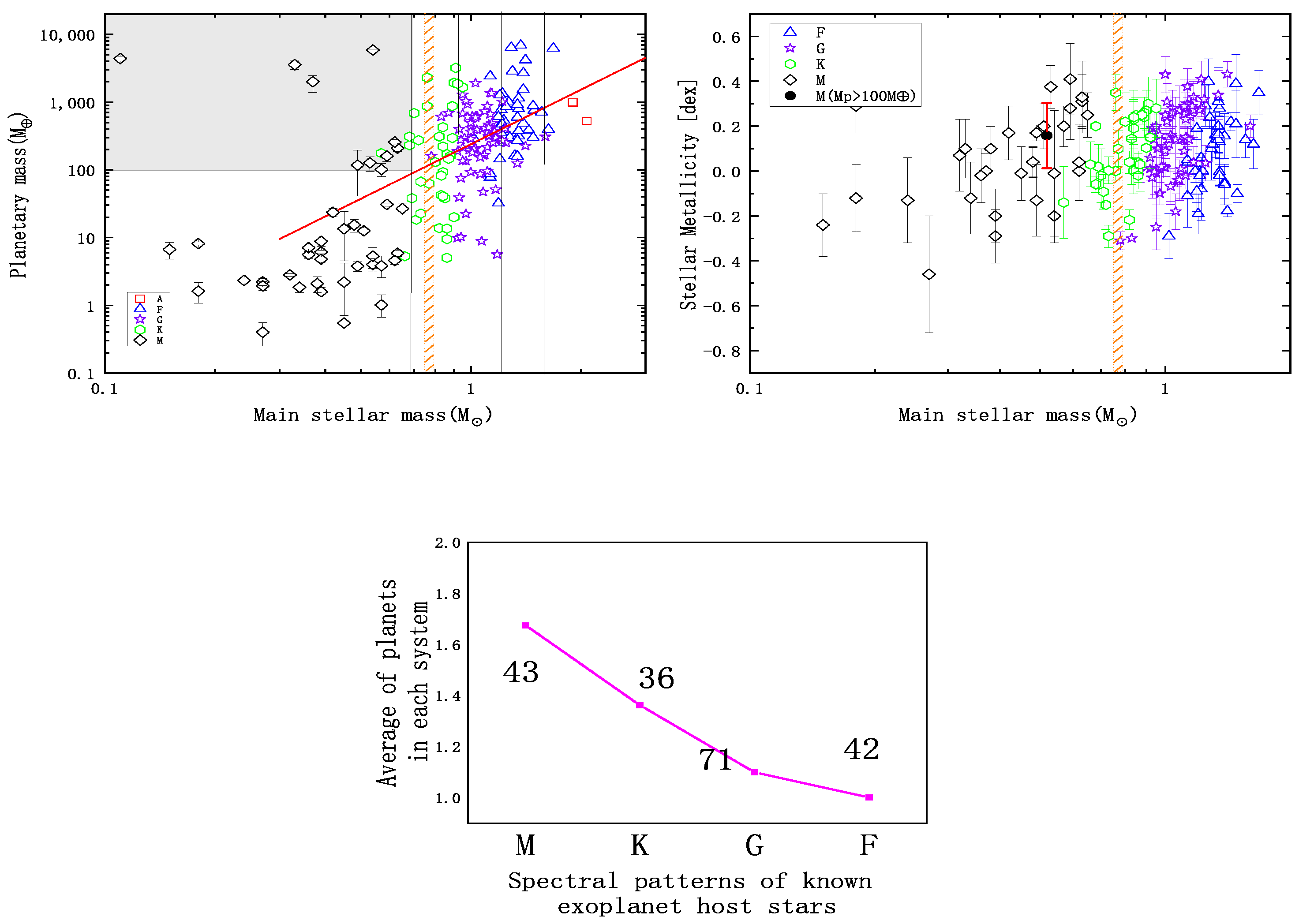
2.4. The Mass of the Host Star and Its Planet
3. Feasibility Analysis of FAST Radio Observation of Extrasolar Planets and Their Host Stars
Radio Flux Estimation of Planets and Their Host Stars
4. Discussion and Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayor, M.; Queloz, D. A Jupiter-mass companion to a solar-type star. Nature 1995, 378, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhao, G. The progress of exploring extra-solar planetary systems. Prog. Astron. 2005, 23, 226–238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Ji, J.H. The detection methods and statistical characteristics of exoplanet. Prog. Astron. 2009, 27, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Udry, S.; Santos, N.C. Statistical Properties of Exoplanets. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2007, 45, 397–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhao, G. A Statistical survey of orbital parameters of extra-solar planets system. Prog. Astron. 2012, 30, 48–63. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, N.C.; Israelian, G.; Mayor, M. Spectroscopic [Fe/H] for 98 extra-solar planet-host stars. Exploring the probability of planet formation. Astron. Astrophys. 2004, 415, 1153–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcy, G.; Butler, R.P.; Fischer, D.; Vogt, S.; Wright, J.T.; Tinney, C.G.; Jones, H.R.A. Observed Properties of Exoplanets: Masses, Orbits, and Metallicities. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, N.C.; Israelian, G.; Mayor, M. The metal-rich nature of stars with planets. Astron. Astrophys. 2001, 373, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulders, G.D.; Pascucci, I.; Apai, D. An Increase in the Mass of Planetary Systems around Lower-mass Stars. Astrophys. J. 2015, 814, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profeta, G.; Continenza, A.; Massidda, S. Phonon and electron-phonon renormalization in Al-doped MgB2. Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 144508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Ford, E.B.; Matsumura, S.; Rasio, F.A. Dynamical Outcomes of Planet-Planet Scattering. Astrophys. J. 2008, 686, 580–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, J.L.; Wang, S. Modeling Planetary System Formation with N-body Simulations: Role of Gas Disk and Statistics Compared to Observations. Astrophys. J. 2011, 732, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolmont, E.; Libert, A.S.; Leconte, J.; Selsis, F. Habitability of planets on eccentric orbits: Limits of the mean flux approximation. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 591, A106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotin, C.; Grasset, O.; Mocquet, A. Mass radius curve for extrasolar Earth-like planets and ocean planets. Icarus 2007, 191, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, B.J.; Petigura, E.A.; Howard, A.W.; Isaacson, H.; Marcy, G.W.; Cargile, P.A.; Hebb, L.; Weiss, L.M.; Johnson, J.A.; Morton, T.D.; et al. The California-Kepler Survey. III. A Gap in the Radius Distribution of Small Planets. Astron. J. 2017, 154, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulton, B.J.; Petigura, E.A. The California-Kepler Survey. VII. Precise Planet Radii Leveraging Gaia DR2 Reveal the Stellar Mass Dependence of the Planet Radius Gap. Astron. J. 2018, 156, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eylen, V.; Agentoft, C.; Lundkvist, M.S.; Kjeldsen, H.; Owen, J.E.; Fulton, B.J.; Petigura, E.; Snellen, I. An asteroseismic view of the radius valley: Stripped cores, not born rocky. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 479, 4786–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Dong, S. Exoplanet Statistics and Theoretical Implications. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys.s 2021, 59, 291–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Murray, N. Planet Migration and Binary Companions: The Case of HD 80606b. Astrophys. J. 2003, 589, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.E. Planet Formation with Migration. Astrophys. J. 2006, 652, L133–L136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strugarek, A. Physics of star-planet magnetic interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2104.05968. [Google Scholar]
- Endl, M.; Cochran, W.D.; Kürster, M.; Paulson, D.B.; Wittenmyer, R.A.; MacQueen, P.J.; Tull, R.G. Exploring the Frequency of Close-in Jovian Planets around M Dwarfs. Astrophys. J. 2006, 649, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ida, S.; Lin, D.N.C. Dependence of Exoplanets on Host Stars’ Metallicity and Mass. Prog. Theor. Phys. Suppl. 2005, 158, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidotto, A.A.; Donati, J.F. Predicting radio emission from the newborn hot Jupiter V830 Tauri b and its host star. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 602, A39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, C.R.; Murphy, T.; Lenc, E.; Kaplan, D.L. The detectability of radio emission from exoplanets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 478, 1763–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Gorman, E.; Coughlan, C.P.; Vlemmings, W.; Varenius, E.; Sirothia, S.; Ray, T.P.; Olofsson, H. A search for radio emission from exoplanets around evolved stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 612, A52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazio, T.; Joseph, W.; Farrell, W.M.; Dietrick, J.; Greenlees, E.; Hogan, E.; Jones, C.; Hennig, L.A. The Radiometric Bode’s Law and Extrasolar Planets. Astrophys. J. 2004, 612, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kipping, D. Probabilistic Forecasting of the Masses and Radii of Other Worlds. Astrophys. J. 2017, 834, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, N.L.; Barragán, O.; Lintott, C.; Aigrain, S.; Nicholson, B.; Boyajian, T.S.; Howell, S.; Johnston, C.; Lakeland, B.; Miller, G.; et al. Planet Hunters TESS II: Findings from the first two years of TESS. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 501, 4669–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietrich, J.; Ginski, C. Archival VLT/NaCo multiplicity investigation of exoplanet host stars. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 620, A102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, E.D.; Fortney, J.J.; Miller, N. How Thermal Evolution and Mass-loss Sculpt Populations of Super-Earths and Sub-Neptunes: Application to the Kepler-11 System and Beyond. Astrophys. J. 2012, 761, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, E.D.; Fortney, J.J. The Role of Core Mass in Controlling Evaporation: The Kepler Radius Distribution and the Kepler-36 Density Dichotomy. Astrophys. J. 2013, 776, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.E.; Wu, Y. Kepler Planets: A Tale of Evaporation. Astrophys. J. 2013, 775, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.W.; Marcy, G.W.; Johnson, J.A.; Fischer, D.A.; Wright, J.T.; Isaacson, H.; Valenti, J.A.; Anderson, J.; Lin, D.N.C.; Ida, S. The Occurrence and Mass Distribution of Close-in Super-Earths, Neptunes, and Jupiters. Science 2010, 330, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.E.; Wetherill, G.W.; Boss, A.P. The Stability of Multi-Planet Systems. Icarus 1996, 119, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohl, F.; Wagner, F.W.; Rauer, H. Mass-Radius Relationships of Rocky Exoplanets. In Proceedings of the Formation, Detection, and Characterization of Extrasolar Habitable Planets; Haghighipour, N., Ed.; IAU Symp; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014; Volume 293, pp. 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Sasselov, D.D.; Jacobsen, S.B. Mass-Radius Relation for Rocky Planets Based on PREM. Astrophys. J. 2016, 819, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortney, J.J.; Marley, M.S.; Barnes, J.W. Planetary Radii across Five Orders of Magnitude in Mass and Stellar Insolation: Application to Transits. Astrophys. J. 2007, 659, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, A.W. Observed Properties of Extrasolar Planets. Science 2013, 340, 572–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.A.; Huber, D.; Gaidos, E.; van Saders, J.L.; Weiss, L.M. The Gaia-Kepler Stellar Properties Catalog. II. Planet Radius Demographics as a Function of Stellar Mass and Age. Astrophys. J. 2020, 160, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginzburg, S.; Schlichting, H.E.; Sari, R. Core-powered mass-loss and the radius distribution of small exoplanets. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2018, 476, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Connors, N.J. Primordial Radius Gap and Potentially Broad Core Mass Distributions of Super-Earths and Sub-Neptunes. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbidelli, A.; Nesvorny, D. Dynamics of pebbles in the vicinity of a growing planetary embryo: Hydro-dynamical simulations. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 546, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, J.E.; Wu, Y. The Evaporation Valley in the Kepler Planets. Astrophys. J. 2017, 847, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, G. Giant Planets around FGK Stars Probably Form through Core Accretion. Astrophys. J. 2018, 860, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, P.; Qian, L.; Krco, M.; Jiang, P.; Yue, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhu, Y.; Pan, Z.; Nan, R.; et al. FAST in Space: Considerations for a Multibeam, Multipurpose Survey Using China’s 500-m Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST). IEEE Microw. Mag. 2018, 19, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Werthimer, D.; Zhang, T.J.; Cobb, J.; Korpela, E.; Anderson, D.; Gajjar, V.; Lee, R.; Li, S.Y.; Pei, X.; et al. First SETI Observations with China’s Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Radio Telescope (FAST). Astrophys. J. 2020, 891, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Gajjar, V.; Wang, P.; Siemion, A.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yue, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, C.J.; Li, S.Y.; et al. Opportunities to search for extraterrestrial intelligence with the FAST. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 20, 078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarka, P.; Li, D.; Grießmeier, J.M.; Lamy, L.; Girard, J.N.; Hess, S.L.G.; Lazio, T.J.W.; Hallinan, G. Detecting exoplanets with FAST? Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 19, 023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulk, G.A. Radio emission from the sun and stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1985, 23, 169–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitherer, C. Mass Loss from LBVs: Observational Constraints. In Luminous Blue Variables: Massive Stars in Transition; Nota, A., Lamers, H., Eds.; Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series; Astronomical Society of the Pacific: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1997; Volume 120, p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Güdel, M. Stellar Radio Astronomy: Probing Stellar Atmospheres from Protostars to Giants. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2002, 40, 217–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Loeb, A. Nonthermal Emission from the Interaction of Magnetized Exoplanets with the Wind of Their Host Star. Astrophys. J. 2019, 874, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, W.M.; Desch, M.D.; Zarka, P. On the possibility of coherent cyclotron emission from extrasolar planets. J. Geophys. Res. Planets 1999, 104, 14025–14032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazio, J.; Farrell, W.M.; Dietrick, J.; Greenlees, E.; Hogan, E.; Jones, C.; Hennig, L.A. The Radiometric Bode’s Law and Extrasolar Planets. arXiv 2004, arXiv:astro–ph/0405343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desch, M.D.; Kaiser, M.L. Predictions for Uranus from a radiometric Bode’s law. Nature 1984, 310, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grießmeier, J.M.; Motschmann, U.; Mann, G.; Rucker, H.O. The influence of stellar wind conditions on the detectability of planetary radio emissions. Astron. Astrophys. 2005, 437, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newkirk, G., Jr. Solar variability on time scales of 10 to the 5th years to 10 to the 9.6th years. In The Ancient Sun: Fossil Record in the Earth, Moon and Meteorites; Proceedings of the Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 16–19 October 1979; Pepin, R.O., Eddy, J.A., Merrill, R.B., Eds.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 293–320. [Google Scholar]
- Kudritzki, R.P.; Puls, J. Winds from Hot Stars. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 2000, 38, 613–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, B.; Loeb, A. The Detectability of Radio Auroral Emission from Proxima b. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.D.; Zarka, P.; Grießmeier, J.M.; Lazio, J.; Cecconi, B.; Emilio Enriquez, J.; Girard, J.N.; Jayawardhana, R.; Lamy, L.; Nichols, J.D.; et al. The search for radio emission from the exoplanetary systems 55 Cancri, υ Andromedae, and τ Boötis using LOFAR beam-formed observations. Astron. Astrophys. 2021, 645, A59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Single Planet | Double Planets | Multi-Planet | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single star | 2618 | 496 | 248 |
| Double star | 233 | 36 | 30 |
| Multi-star | 36 | 5 | 2 |
| Percentage | 77.94% | 14.50% | 7.56% |
| Total | 3704 | ||
| Type | Average Semi-Major Axis (Au) | Number of Planets | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Super Earth (0.6–2) | 0.03422889 ± 0.000668125 | 0.00769 ± 0.00277 | 0.2522 ± 0.0048 | 0.99389 | 20 |
| Sub-Neptunes (2–4) | 0.07134143 ± 0.0014143 | 0.28608 ± 0.07047 | 0.14827 ± 0.06305 | 0.31543 | 14 |
| Sub-Saturns (4–8) | 0.0877815 ± 0.00164923 | 0.47008 ± 0.11561 | 0.19154 ± 0.07928 | 0.34666 | 13 |
| Cold Jupiter (824, >0.1AU) | 0.97186 ± 0.0127614 | 0.69102 ± 0.02045 | 0.12424 ± 0.00746 | 0.98228 | 7 |
| Hot Jupiter (824, <0.1AU) | 0.0563939 ± 0.00111049 | 1.05251 ± 0.03032 | 0.02877 ± 0.01169 | 0.01978 | 302 |
| Frequency (MHz) | (K) | (K) | Sensitivity (mJy) | Angular Resolution (arcmin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | 2500 | 100 | 0.5 | 50 |
| 140 | 420 | 80 | 0.1 | 25 |
| 280 | 72 | 40 | 0.02 | 13 |
| 560 | 13 | 10 | 0.004 | 7 |
| 1150 | 5 | 10 | 0.003 | 3 |
| Pl_Name | Pl_Orbper | Pl_Orbsmax | Pl_Radj | Pl_Massj | (MHz) | (Jy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CoRoT-3 b | 4.2567994 | 0.05694 | 0.993 | 21.23 | 376.2700347 | 0.000346904 |
| GPX-1 b | 1.744579 | 0.0338 | 1.47 | 19.7 | 249.8321386 | 0.002437414 |
| TOI-2109 b | 0.67247414 | 0.01791 | 1.347 | 5.02 | 86.27965369 | 0.00521114 |
| hostname | st_teff | st_mass | sy_dist | st_spectype | st_rad | st_age (Gyr) |
| CoRoT-3 | 1.36 | 768.771 | F3 V | 1.54 | 2.2 | |
| GPX-1 | 7000 | 1.68 | 655.013 | F2 | 1.56 | 0.27 |
| TOI-2109 | 6540 | 1.45 | 262.041 | F | 1.7 | 1.77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Su, T.; Han, X.L.; Misra, P.; Long, L. Statistical and Radio Analysis of Exoplanets and Their Host Stars. Universe 2023, 9, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110475
Li B, Zhang L, Su T, Han XL, Misra P, Long L. Statistical and Radio Analysis of Exoplanets and Their Host Stars. Universe. 2023; 9(11):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110475
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Baoda, Liyun Zhang, Tianhao Su, Xianming L. Han, Prabhakar Misra, and Liu Long. 2023. "Statistical and Radio Analysis of Exoplanets and Their Host Stars" Universe 9, no. 11: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110475
APA StyleLi, B., Zhang, L., Su, T., Han, X. L., Misra, P., & Long, L. (2023). Statistical and Radio Analysis of Exoplanets and Their Host Stars. Universe, 9(11), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9110475







