Realization of Bounce in a Modified Gravity Framework and Information Theoretic Approach to the Bouncing Point
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Equation of State of Barotropic Fluid
3. Bounce Cosmology with Respect to E-Folding Number
4. Hubble Flow Dynamics
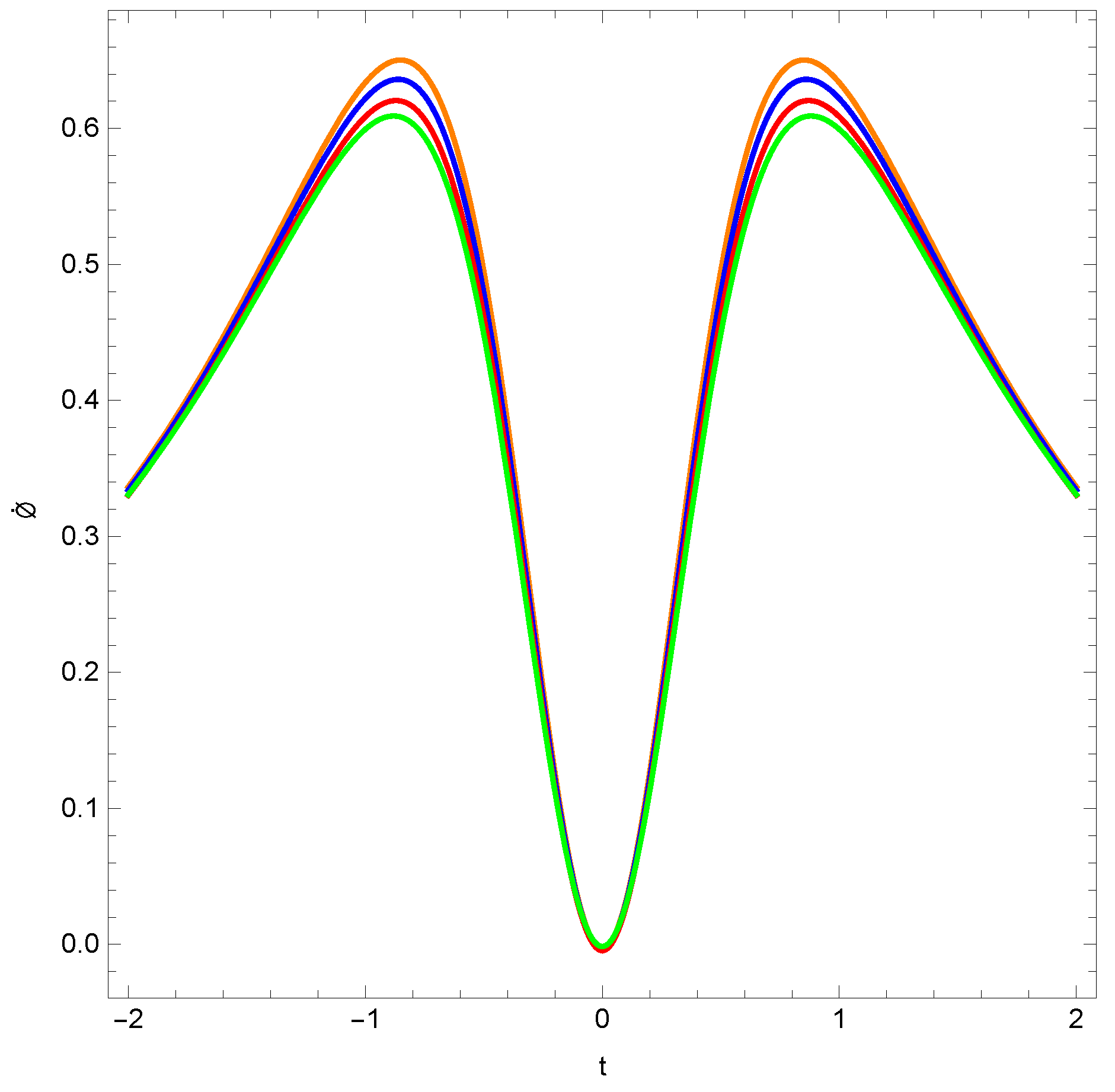
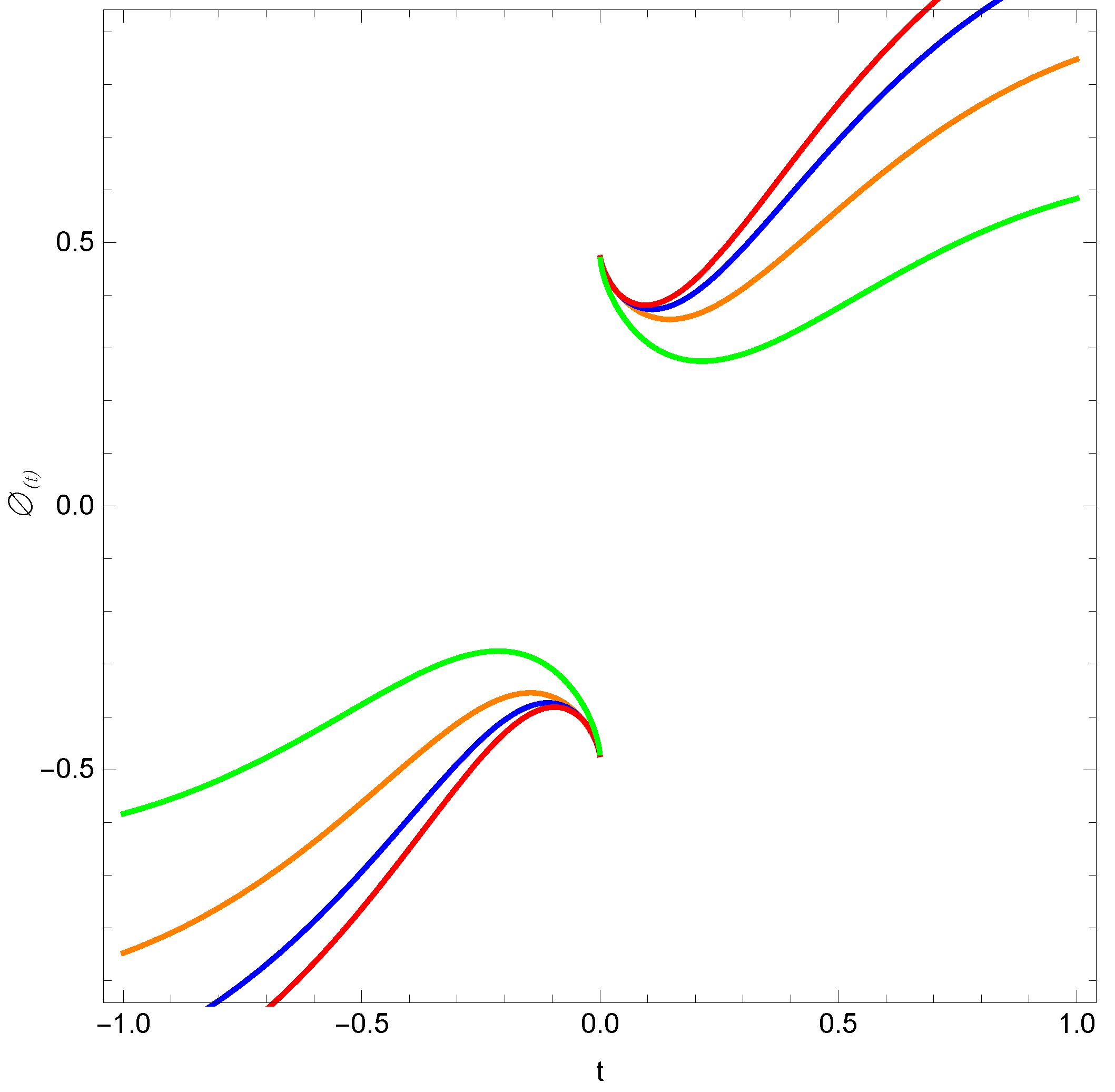
5. Inflation via Scalar Field
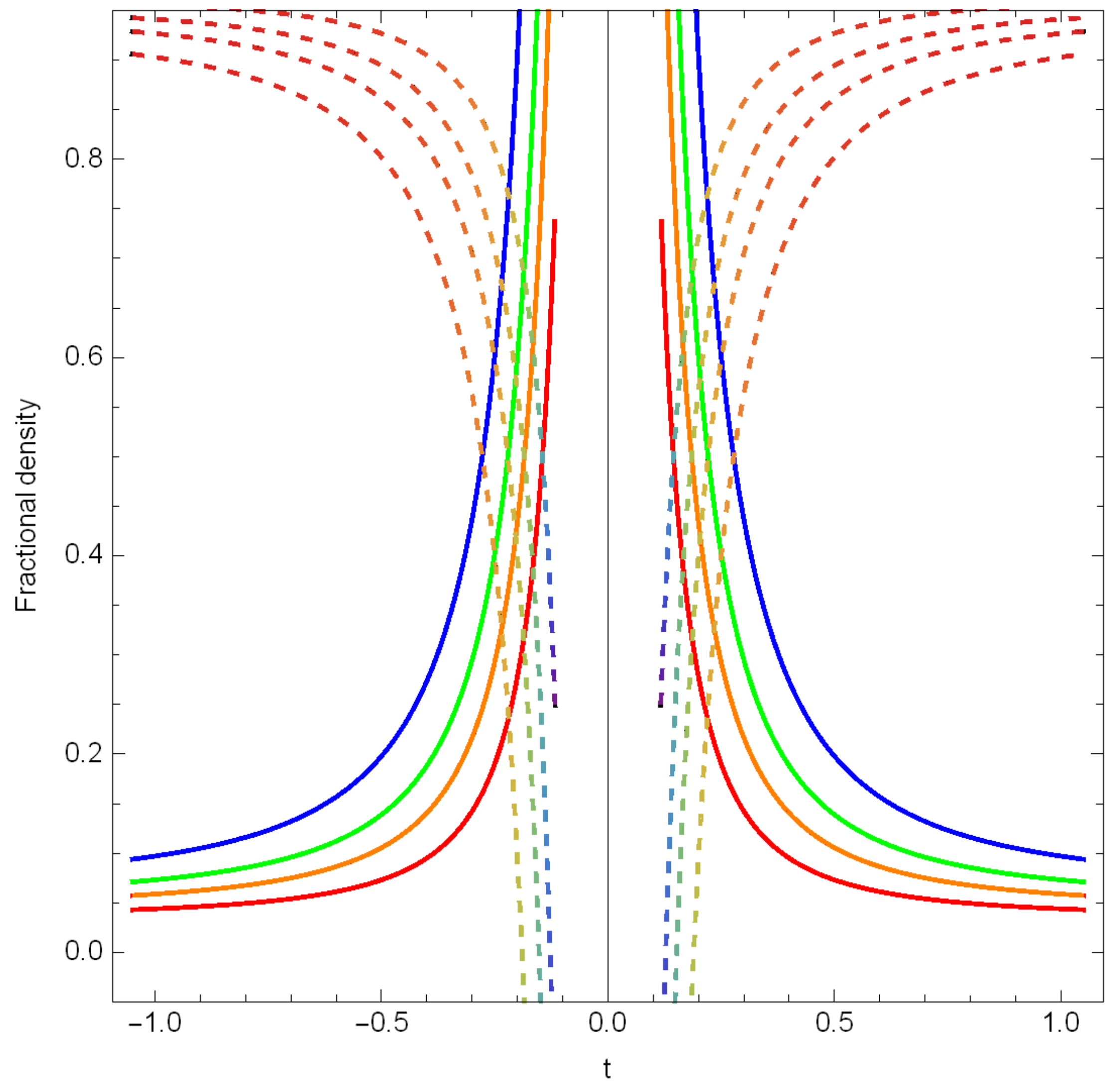
6. Fractional Density
7. MGCG in f(T) Gravity
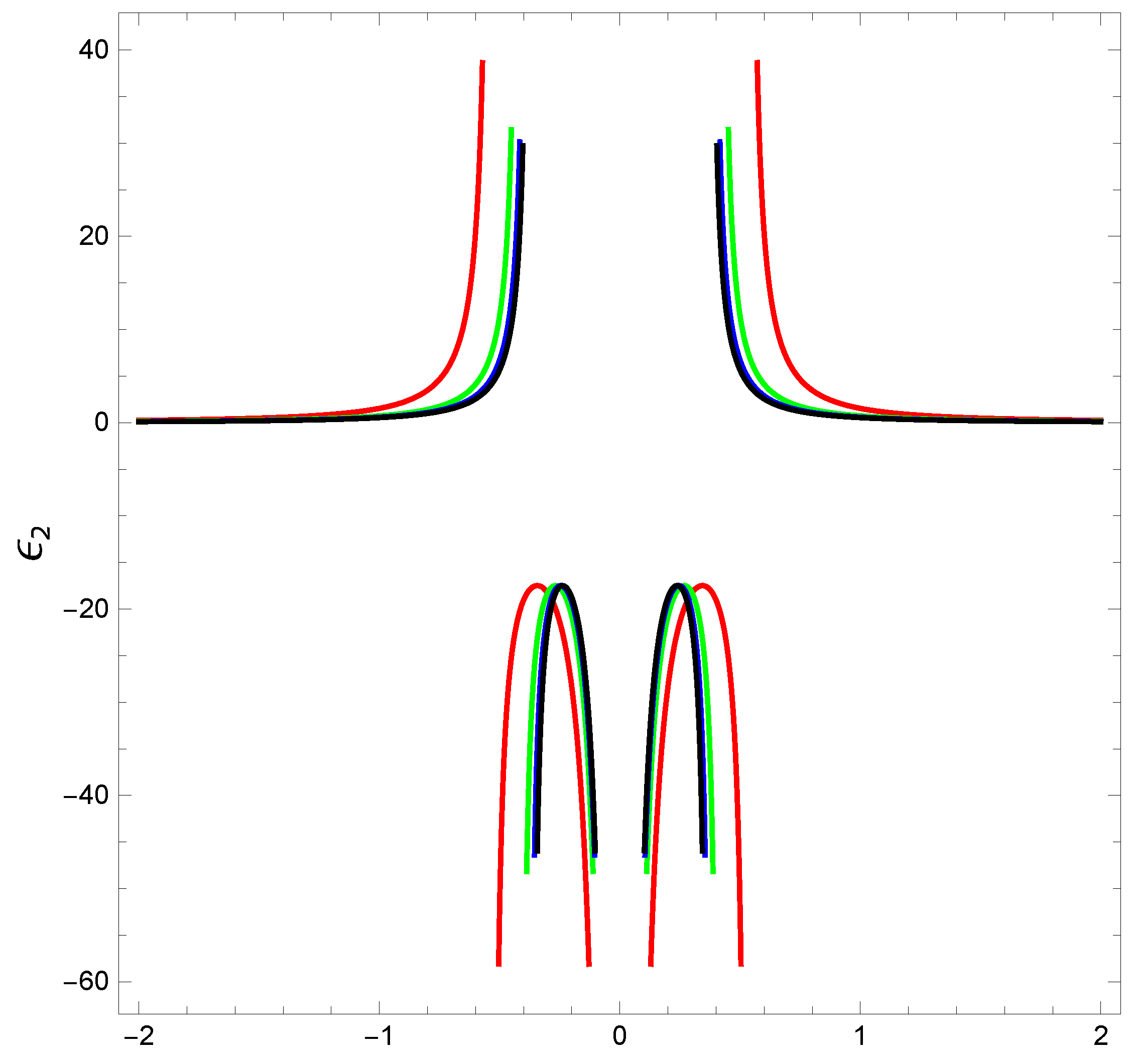
8. Stability Analysis
9. Uncertainty Towards Bouncing Point
10. Discussion and Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Valle, M.D.; Deustua, S.; Ellis, R.S.; Fabbro, S.; Fruchter, A.; Goldhaber, G.; Groom, D.E.; Hook, I.M.; et al. Discovery of a supernova explosion at half the age of the Universe. Nature 1998, 391, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlmutter, S.; Aldering, G.; Goldhaber, G.; Knop, R.A.; Nugent, P.; Castro, G.; Deustua, S.; Fabbro, S.; Goobar, A.; Groom, D.E.; et al. Measurements of Ω and Λ from 42 high-redshift supernovae. Astrophys. J. 1999, 517, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Filippenko, A.V.; Challis, P.; Clocchiatti, A.; Diercks, A.; Garnavich, M.; Gillil, R.L.; Hogan, C.J.; Jha, S.; Kirshner, R.P.; et al. Observational evidence from supernovae for an accelerating universe and a cosmological constant. Astron. J. 1998, 116, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, A.G.; Strolger, L.G.; Tonry, J.; Casertano, S.; Ferguson, H.C.; Mobasher, B.; Challis, P.; Filippenko, A.V.; Jha, S.; Li, W.; et al. Type Ia supernova discoveries at z > 1 from the Hubble Space Telescope: Evidence for past deceleration and constraints on dark energy evolution. Astrophys. J. 2004, 607, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.D.; Caldwell, R.; Devlin, M.J.; Dorwart, W.B.; Herbig, T.; Nolta, M.R.; Page, L.A.; Puchalla, J.; Torbet, E.; Tran, H.T. A Measurement of the Angular Power Spectrum of the Cosmic Microwave Background from l = 100 to 400. Astrophys. J. 1999, 524, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisseau, B.; Esposito-Farese, G.; Polarski, D.; Starobinsky, A.A. Reconstruction of a scalar-tensor theory of gravity in an accelerating universe. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 85, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, C.L.; Larson, D.; Weil, J.L.; Jarosik, N.; Hinshaw, G.; Odegard, N.; Smith, K.M.; Hill, R.S.; Gold, B.; Halpern, M.; et al. Nine-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP) observations: Final maps and results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2013, 208, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.L.; Hill, R.S.; Hinshaw, G.; Larson, D.; Smith, K.M.; Dunkley, J.; Gold, B.; Halpern, M.; Jarosik, N.; Kogut, A.; et al. Seven-year wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP*) observations: Are there cosmic microwave background anomalies? Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 192, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, D.; Dunkley, J.; Hinshaw, G.; Komatsu, E.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Gold, B.; Halpern, M.; Hill, R.S.; Jarosik, N.; et al. Seven-year wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe (WMAP*) observations: Power spectra and WMAP-derived parameters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2011, 192, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridle, S.L.; Lahav, O.; Ostriker, J.P.; Steinhardt, J. Precision cosmology? Not just yet. Science 2013, 299, 1532–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.N.; Verde, L.; Peiris, H.V.; Komatsu, E.; Nolta, M.R.; Bennett, C.L.; Halpern, M.; Hinshaw, G.; Jarosik, N.; Kogut, A.; et al. First-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP)* observations: Determination of cosmological parameters. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2003, 148, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahcall, N.A.; Ostriker, J.P.; Perlmutter, S.; Steinhardt, J. The cosmic triangle: Revealing the state of the universe. Science 1999, 284, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegmark, M.; Strauss, M.A.; Blanton, M.R.; Abazajian, K.; Dodelson, S.; Sandvik, H.; Wang, X.; Weinberg, D.H.; Zehavi, I.; Bahcall, N.A.; et al. Cosmological parameters from SDSS and WMAP. Phys. Rev. D 2004, 69, 103501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Chaubal, P.; Mazumdar, A.; Mohanty, S. Cosmic viscosity as a remedy for tension between PLANCK and LSS data. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2017, 11, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarcelluti, P. Cosmology with mirror dark matter II: Cosmic microwave background and large scale structure. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2005, 14, 223–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.P.; Pacaud, F.; Valtchanov, I.; Pierre, M.; Ponman, T.; Read, A.; Andreon, S.; Altieri, B.; Quintana, H.; Dos Santos, S.; et al. The XMM Large-Scale Structure survey: An initial sample of galaxy groups and clusters to a redshift z < 0.6. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2005, 363, 675–691. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xia, J.Q. Constraints on dark energy parameters from correlations of CMB with LSS. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2010, 4, 026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Tsujikawa, S. Dark Energy: Theory and Observations; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw, G.; Weil, P.J.L.; Hill, R.S.; Odegard, N.; Larson, D.; Bennett, C.L.; Dunkley, J.; Gold, B.; Greason, M.R.; Jarosik, N.; et al. Five-year wilkinson microwave anisotropy probe* observations: Data processing, sky maps and basic results. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 2009, 180, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahaman, F. The General Theory of Relativity: A Mathematical Approach; Cambridge University Press, University Printing House: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.L. General Relativity: Gravitation and Cosmology. Principles and Applications of the General Theory of Relativity. Steven Weinberg. Wiley, New York. Science 1973, 179, 1227–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Cosmological production of baryons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1979, 42, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crispino, L.C.; Kennefick, D.J. A hundred years of the first experimental test of general relativity. Nat. Phys. 2019, 15, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synge, J.L.; Romain, J. Relativity: The general theory. Phys. Today 1961, 14, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colistete, R., Jr.; Fabris, J.C.; Tossa, J.; Zimdahl, W. Bulk viscous cosmology. Phys. Rev. D 2007, 76, 103516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J. Everything you always wanted to know about the cosmological constant problem (but were afraid to ask). C. R. Phys. 2012, 13, 566–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, A. Lectures on the cosmological constant problem. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1502.05296. [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg, S. The cosmological constant problem. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zel’dovich, Y.B. The cosmological constant and the theory of elementary particles. Sov. Phys. USP 1968, 11, 11381–11393. [Google Scholar]
- Sahni, V.; Krasiński, A. Republication of: The cosmological constant and the theory of elementary particles (By Ya. B. Zeldovich). Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2008, 40, 1557–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, T. Cosmological constant—The weight of the vacuum. Phys. Rep. 2003, 380, 235–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.P.; Ma, D.Z.; Ling, Y. Quintessence reconstruction of the new agegraphic dark energy model. Phys. Lett. 2008, 663, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Saridakis, E.N.; Scherrer, R.J. Dark energy from a quintessence (phantom) field rolling near a potential minimum (maximum). Phys. Rev. 2009, 79, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Saridakis, E.N.; Setare, M.R.; Xia, J.Q. Quintom cosmology: Theoretical implications and observations. Phys. Rep. 2010, 493, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, U.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Hussain, I.; Jamil, M.; Myrzakulov, R. Generalized second law of thermodynamics for FRW cosmology with power-law entropy correction. Eur. Phys. J. 2012, 72, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D.; Tsujikawa, S. Properties of singularities in the (phantom) dark energy universe. Phys. Rev. 2005, 71, 063004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikman, A. Can dark energy evolve to the phantom? Phys. Rev. D 2005, 71, 023515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Quantum de Sitter cosmology and phantom matter. Phys. Lett. 2003, 562, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Late-time cosmology in a (phantom) scalar-tensor theory: Dark energy and the cosmic speed-up. Phys. Rev. 2004, 70, 043539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, M.; Toporensky, A.; Tretjakov, V.; Tsujikawa, S. The fate of (phantom) dark energy universe with string curvature corrections. Phys. Lett. 2005, 619, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Final state and thermodynamics of a dark energy universe. Phys. Rev. 2004, 70, 103522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.K.; Piao, Y.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.Z. Cosmological evolution of a quintom model of dark energy. Phys. Lett. 2005, 608, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Li, M.; Lu, J.X.; Piao, Y.S.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, X. A string-inspired quintom model of dark energy. Phys. Lett. 2007, 651, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.B.; Xia, J.Q.; Li, M.; Feng, B.; Zhang, X. Perturbations of the quintom models of dark energy and the effects on observations. Phys. Rev. 2005, 72, 123515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, B.; Li, M.; Piao, Y.S.; Zhang, X. Oscillating quintom and the recurrent universe. Phys. Lett. 2006, 634, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagla, J.S.; Jassal, H.K.; Padmanabhan, T. Cosmology with tachyon field as dark energy. Phys. Rev. 2003, 67, 063504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setare, M.R.; Sadeghi, J.; Amani, A.R. Interacting tachyon dark energy in non-flat universe. Phys. Lett. 2009, 673, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copel, E.J.; Garousi, M.R.; Sami, M.; Tsujikawa, S. What is needed of a tachyon if it is to be the dark energy? Phys. Rev. 2005, 71, 043003. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Cai, R.G.; Zeng, D.F. Hessence: A new view of quintom dark energy. Class. Quantum Gravity 2005, 22, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohammadi, M.; Sadjadi, H.M. Attractor solutions for general hessence dark energy. Phys. Rev. 2006, 73, 083527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimento, L.P. Extended tachyon field, Chaplygin Gas and solvable k-essence cosmologies. Phys. Rev. 2004, 69, 123517. [Google Scholar]
- Gorini, V.; Kamenshchik, A.; Moschella, U.; Pasquier, V. The Chaplygin Gas as a model for dark energy. In The Tenth Marcel Grossmann Meeting: On Recent Developments in Theoretical and Experimental General Relativity, Gravitation and Relativistic Field Theories (In 3 Volumes); World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2008; pp. 840–859. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, P.; Debnath, U. Study of anisotropic compact stars with quintessence field and modified chaplygin gas in f (T) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2019, 79, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setare, M.R. Holographic Chaplygin DGP cosmologies. Int. J. Mod. Phys. 2009, 18, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avelino, P.; Bolejko, K.; Lewis, G.F. Nonlinear Chaplygin Gas cosmologies. Phys. Rev. 2014, 89, 103004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M. A model of holographic dark energy. Phys. Lett. 2004, 603, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D.; Wang, P. Dark energy: Vacuum fluctuations, the effective phantom phase and holography. Phys. Rev. 2005, 71, 103504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Saridakis, E.N.; Setare, M.R. Holographic dark energy with varying gravitational constant. Phys. Lett. 2009, 679, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Debnath, U. Holographic dark energy scenario and variable modified Chaplygin Gas. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2009, 319, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Dark energy cosmology: The equivalent description via different theoretical models and cosmography tests. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2012, 342, 155–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, U.; Chattopadhyay, S. Statefinder and Om diagnostics for interacting new holographic dark energy model and generalized second law of thermodynamics. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 1250–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Pasqua, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Generalized second law of thermodynamics in the emergent universe for some viable models of f(T) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2013, 128, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saridakis, E.N.; Basilakos, S. The generalized second law of thermodynamics with Barrow entropy. Eur. Phys. J. 2021, 81, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, C.P.; Kumar, A. Viscous Ricci dark energy and generalized second law of thermodynamics in modified f(R,T) gravity. Mod. Phys. Lett. 2018, 33, 1850225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaoum, H. Accelerated universe from modified Chaplygin Gas and tachyonic fluid. Universe 2022, 8, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polarski, D. Dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2013, 22, 1330027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straumann, N. Dark energy: Recent developments. Mod. Phys. Lett. A 2008, 21, 1083–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Watanabe, Y. Theoretical models of dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2021, 21, 1230002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Starobinsky, A. Reconstructing dark energy. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2006, 15, 2105–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Shafieloo, A.; Starobinsky, A.A. Model-independent evidence for dark energy evolution from Baryon acoustic oscillations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2014, 793, L40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spergel, D.N.; Steinhardt, J. Observational evidence for self-interacting cold dark matter. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddle, A.R.; Lyth, D.H. The Cold dark matter density perturbation. Phys. Rep. 1993, 231, 1–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, L.; Finelli, F.; Burigana, C.; Carturan, D. WMAP and the generalized Chaplygin Gas. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2003, 2003, 005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setare, M.R. Interacting holographic generalized Chaplygin gas model. Phys. Lett. B 2007, 654, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, V.; Kamenshchik, A.; Moschella, U. Can the Chaplygin Gas be a plausible model for dark energy? Phys. Rev. 2003, 67, 063509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenshchik, A.; Moschella, U.; Pasquier, V. An alternative to quintessence. Phys. Lett. B 2001, 511, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.C.; Bertolami, O.; Sen, A. Generalized Chaplygin Gas, accelerated expansion and dark Energy-Matter unification. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 043507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bento, M.D.C.; Bertolami, O.; Sen, A.A. Generalized Chaplygin Gas and cosmic microwave background radiation constraints. Phys. Rev. 2003, 67, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.A.; Scherrer, R.J. Generalizing the generalized Chaplygin Gas. Phys. Rev. 2005, 72, 063511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, C.S.J.; Gergely, L.; Mak, M.K.; Kovcs, Z.; Szab, G.M.; Harko, T. Viscous dissipative Chaplygin Gas dominated homogenous and isotropic cosmological models. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 063528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, U.; Banerjee, A.; Chakraborty, S. Role of modified Chaplygin Gas in accelerated universe. Class. Quantum Grav. 2004, 21, 5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourhassan, B. Viscous modified cosmic Chaplygin Gas cosmology. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2013, 22, 1350061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S. Modified Chaplygin Gas equation of state on viscous dissipative extended holographic Ricci dark energy and the cosmological consequences. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2017, 26, 1750042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawad, A.; Ilyas, A.; Rani, S. Dynamics of modified Chaplygin Gas inflation on the Brane with bulk viscous pressure. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2017, 26, 1750031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedran, M.L.; Soares, V.; Araujo, M.E. Temperature evolution of the FRW universe filled with modified Chaplygin Gas. Phys. Lett. 2008, 659, 462–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, D.; Chatterjee, S. Thermodynamics of the variable modified Chaplygin Gas. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 2016, 052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salti, M.; Kangal, E.E.; Aydogdu, O. Variable Polytropic gas cosmology. Ann. Phys. 2019, 407, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamenshchik, A.Y.; Tronconi, A.; Venturi, G. Reconstruction of scalar potentials in induced gravity and cosmology. Phys. Lett. B 2011, 702, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbunov, D.S.; Rubakov, V.A. Introduction to the Theory of the Early Universe; World Scientific: Singapore, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Deformed matter bounce with dark energy epoch. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 064022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified gravity with negative and positive powers of the curvature: Unification of the inflation and of the cosmic acceleration. Phys. Rev. D 2003, 68, 123512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Unified phantom cosmology: Inflation, dark energy and dark matter under the same standard. Phys. Lett. B 2006, 632, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.G.; Li, M. The holographic dark energy in a non-flat universe. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2004, 2004, 013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gong, Y.; Abdalla, E. Transition of the dark energy equation of state in an interacting holographic dark energy model. Phys. Lett. 2005, 624, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F. Exploring bouncing cosmologies with cosmological surveys. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2014, 57, 1414–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhanov, V.F.; Feldman, H.A.; Brandenberger, R.H. Theory of cosmological perturbations. Phys. Rep. 1992, 215, 203–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V. Modified gravity theories on a nutshell: Inflation, bounce and late-time evolution. Phys. Rep. 2017, 692, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Makarenko, A.N.; Myagky, A.N.; Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Bounce cosmology from F (R) gravity and F (R) bigravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2014, 2014, 008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamba, K.; Odintsov, S.D. Inflationary cosmology in modified gravity theories. Symmetry 2015, 7, 220–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D.; Saridakis, E.N. Holographic bounce. Nucl. Phys. 2019, 949, 114790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elizalde, E.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Sez-Gmez, D.; Faraoni, V. Reconstructing the universe history, from inflation to acceleration, with phantom and canonical scalar fields. Phys. Rev. D 2008, 77, 106005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odintsov, S.D.; Paul, T. Bounce universe with finite-time singularity. Universe 2022, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D.; Paul, T. Towards a smooth unification from an ekpyrotic bounce to the dark energy era. Phys. Dark Universe 2022, 35, 100984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M. Extended theories of gravity. Phys. Rep. 2011, 509, 167–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, J.D.; Graham, A.A. Singular inflation. Phys. Rev. 2015, 91, 083513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Quantitative analysis of singular inflation with scalar-tensor and modified gravity. Phys. Rev. 2015, 91, 084059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D.; Oikonomou, V.K. Singular inflation from generalized equation of state fluids. Phys. Lett. 2015, 747, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrow, J.D. Sudden future singularities. Class. Quantum Gravity 2004, 21, L79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S. Entropy generation and the survival of protogalaxies in an expanding universe. Astrophys. J. 1971, 168, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.; Barrow, J.D. The power of general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 2005, 72, 103005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.B.; Nowakowski, M.; Batic, D. Viscous cosmologies. Class. Quantum Gravity 2019, 36, 215002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, R.L. Casimir effect and the quantum vacuum. Phys. Rev. 2005, 72, 021301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myrzakulov, R.; Sebastiani, L. Bounce solutions in viscous fluid cosmology. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2014, 352, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevik, I.; Timoshkin, A.V. Viscous fluid holographic bounce. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2020, 17, 2050023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, M.; Cruz, N.; Lepe, S. Viscous dark energy and phantom evolution. Phys. Lett. 2005, 619, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.G.; Meng, X.H. Bulk viscous cosmology: Statefinder and entropy. Phys. Lett. 2006, 635, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, T.; Ferreira, G.; Padilla, A.; Skordis, C. Modified gravity and cosmology. Phys. Rep. 2012, 513, 1–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Introduction to modified gravity and gravitational alternative for dark energy. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2007, 4, 115–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujikawa, S. Modified gravity models of dark energy. In Lectures on Cosmology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 99–145. [Google Scholar]
- Josset, T.; Perez, A.; Sudarsky, D. Dark energy from violation of energy conservation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 118, 021102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myrzakulov, R. Accelerating universe from F (T) gravity. Eur. Phys. J. C 2011, 71, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Pasqua, A. Reconstruction of f(T) gravity from the Holographic dark energy. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2012, 344, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, A.; Lombriser, L.; Schmidt, F. Dark energy vs. modified gravity. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1601.06133. [Google Scholar]
- Bertschinger, E.; Zukin, P. Distinguishing modified gravity from dark energy. Phys. Rev. 2008, 78, 024015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Differentiating dark energy and modified gravity with galaxy redshift surveys. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2008, 2008, 021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capozziello, S.; Matsumoto, J.; Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Dark energy from modified gravity with Lagrange multipliers. Phys. Lett. 2010, 693, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Sawicki, I. Parametrized post-Friedmann framework for modified gravity. Phys. Rev. 2007, 76, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Modified gravity and its reconstruction from the universe expansion history. J. Physics Conf. Ser. 2007, 66, 012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, R. VModified gravity without dark matter. In The Invisible Universe: Dark Matter and Dark Energy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 375–402. [Google Scholar]
- Klir, G.J.; Folger, T.A. Fuzzy Sets, Uncertainty and Information; Prentice-Hall Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, E. A mini-introduction to information theory. Riv. Del Nuovo C. 2020, 43, 187–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, V.; Nelson, J.D.; Meder, B.; Cevolani, G.; Tentori, K. Generalized information theory meets human cognition: Introducing a unified framework to model uncertainty and information search. Cogn. Sci. 2018, 42, 1410–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amani, A.R. Pourhassan, B. Viscous generalized Chaplygin gas with arbitrary. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2013, 52, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Exploring of the summer monsoon rainfall around the Himalayas in time domain through maximization of Shannon entropy. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2020, 141, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klir, G.J. Uncertainty and information: Foundations of generalized information theory. Kybernetes 2006, 35, 1297–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-F.; Chen, S.-H.; Dent, J.B.; Dutta, S.; Saridakis, E.N. Matter bounce cosmology with the f(T) gravity. Class. Quantum Grav. 2011, 28, 215011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maartens, R. Dissipative cosmology. Class. Quantum Gravity 1995, 12, 1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, A.; Magueijo, J. Time varying speed of light as a solution to cosmological puzzles. Phys. Rev. 1999, 59, 043516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, T. Emergent perspective of gravity and dark energy. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2012, 12, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coone, D.; Roesta, D.; Venninc, V. The Hubble flow of plateau inflation. J. Cosmol. Astrophys. 2015, 1511, 010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, M.B.; Turner, M.S. Kinematic constraints to the key inflationary observables. Phys. Rev. D 2001, 64, 023506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, W.H. Inflation: Flow, fixed points and observables to arbitrary order in slow roll. Phys. Rev. D 2002, 66, 083508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Unifying phantom inflation with late-time acceleration: Scalar phantom–non-phantom transition model and generalized holographic dark energy. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2006, 38, 1285–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, V.; Saini, T.D.; Starobinsky, A.A.; Alam, U. Statefinder—A new geometrical diagnostic of dark energy. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. Lett. 2003, 77, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, Y.M.P. Perturbation Lagrangian theory for scalar fields-Ward-Takahashi identity and current algebra. Phys. Rev. 1972, 6, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliathanasis, A.; Barrow, J.D.; Leach, P.G.L. Cosmological solutions of f (T) gravity. Phys. Rev. D 2016, 94, 023525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Chakraborty, G. A reconstruction scheme for f (T) gravity: Variable generalized Chaplygin dark energy gas form. Astron. Nachrichten 2021, 342, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.C.B.; Nojiri, S.I.; Odintsov, S.D. Consistent modified gravity: Dark energy, acceleration and the absence of cosmic doomsday. Class. Quantum Gravity 2005, 22, L35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.F.; Capozziello, S.; De Laurentis, M.; Saridakis, E.N. f (T) teleparallel gravity and cosmology. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2016, 79, 106901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capozziello, S.; Nojiri, S.; Odintsov, S.D. Dark energy: The equation of state description versus scalar-tensor or modified gravity. Phys. Lett. 2006, 634, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setare, M.R. Interacting holographic dark energy model in non-flat universe. Phys. Lett. 2006, 642, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannestad, S. Constraints on the sound speed of dark energy. Phys. Rev. 2005, 71, 103519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T.J.; Sun, Y.C. Four new observational H (z) data from luminous red galaxies in the Sloan Digital Sky Survey data release seven. Res. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 14, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Chattopadhyay, G.; Midya, S.K. Shannon entropy maximization supplemented by neurocomputing to study the consequences of a severe weather phenomenon on some surface parameters. Nat. Hazards 2018, 93, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziza, A.; Chakraborty, G.; Chattopadhyay, S. Variable generalized Chaplygin gas in f (Q) gravity and the inflationary cosmology. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 2021, 30, 2150119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamil, M.; Myrzakulov, Y.; Razina, O.; Myrzakulov, R. Modified Chaplygin Gas and solvable F-essence cosmologies. Astrophys. Space Sci. 2011, 336, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, K.; Abdolmaleki, A. Generalized second law of thermodynamics in f(T) gravity. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2012, 2012, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Chang, B.; Gui, Y.; Liu, H. Constraints on modified Chaplygin Gas from recent observations and a comparison of its status with other models. Phys. Lett. 2008, 662, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, K. Chaplygin scalar field reconstruction of the modified ghost dark energy model. Can. J. Phys. 2015, 93, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, J. Concentration in vanishing pressure limit of solutions to the modified Chaplygin Gas equations. J. Math. Phys. 2016, 57, 111504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Viscous generalised Chaplygin Gas under the purview of f(T) gravity and the model assessment through probabilistic information theory. Phys. Scr. 2022, 97, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S. A study on the bouncing behavior of modified Chaplygin Gas in presence of bulk viscosity and its consequences in the modified gravity framework. Int. J. Geom. Methods Mod. Phys. 2017, 14, 1750181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
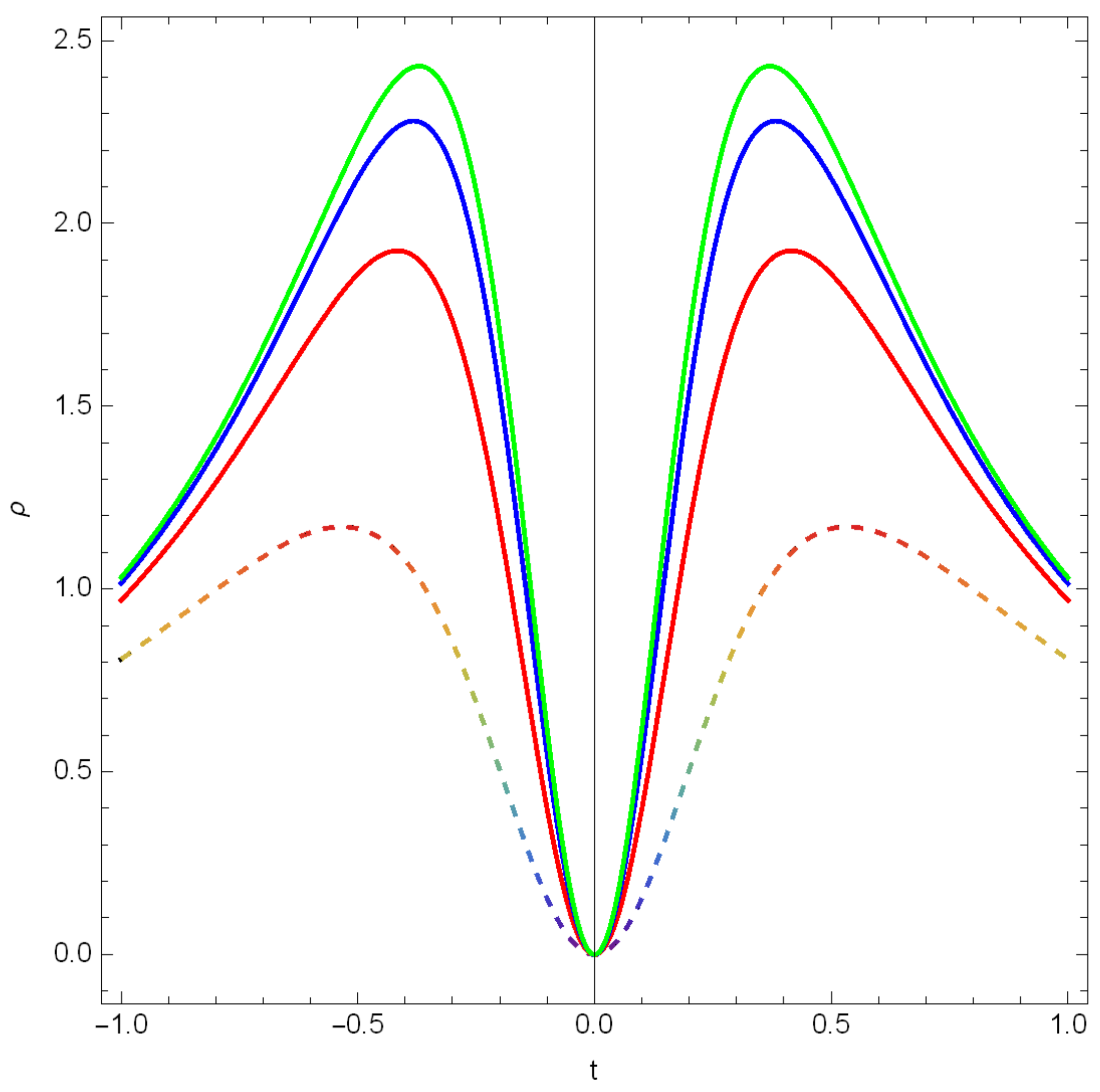
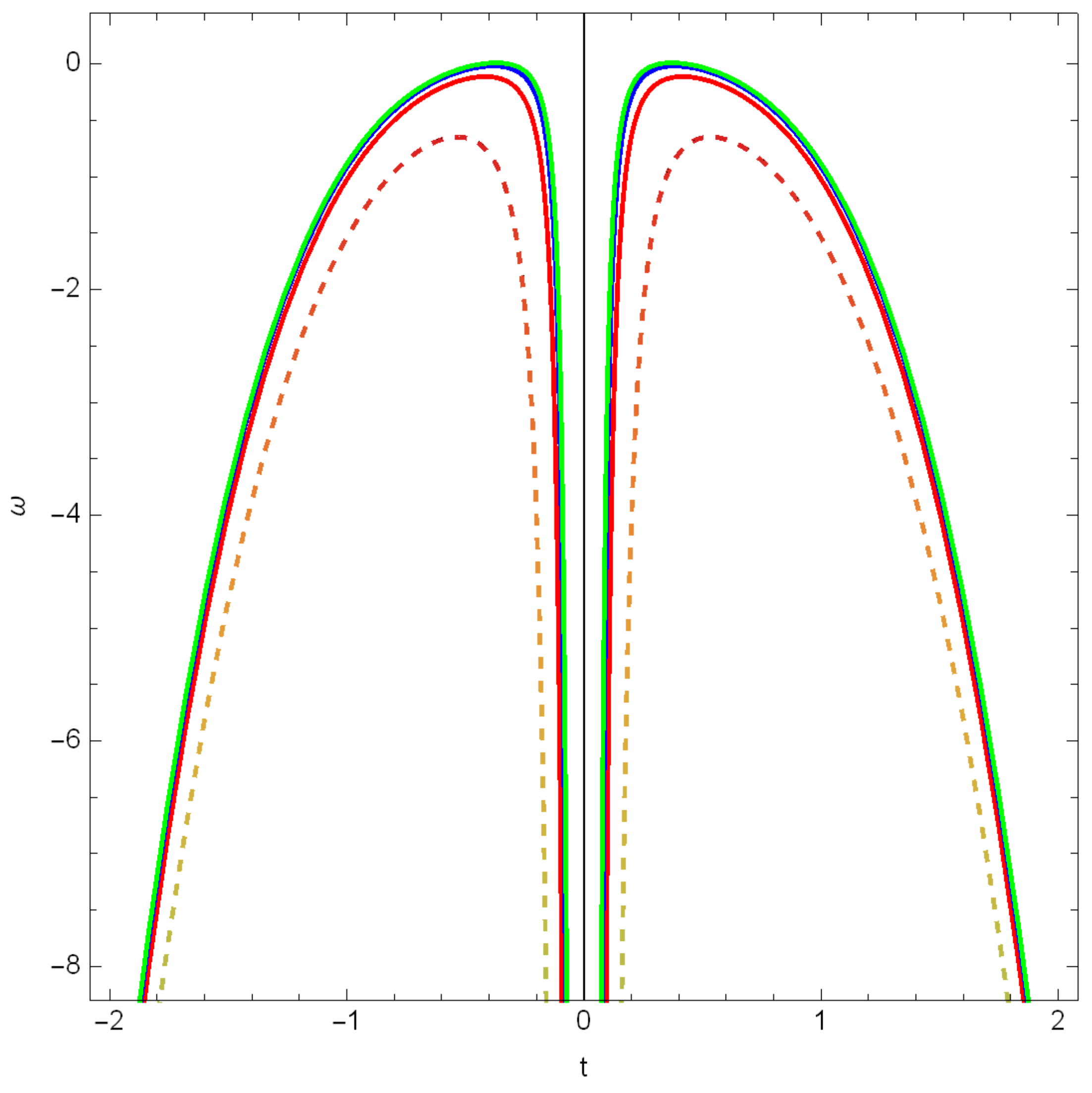
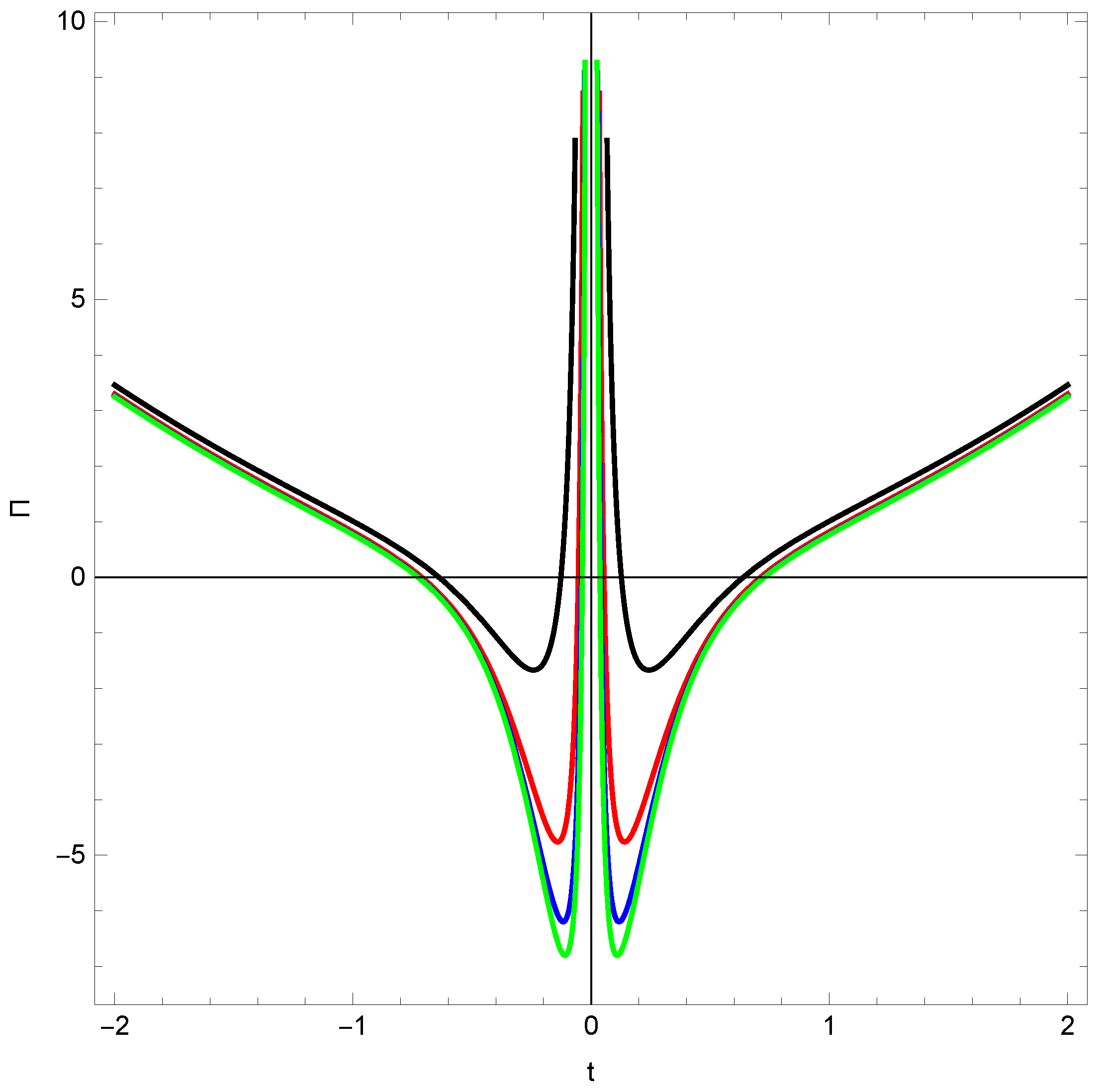
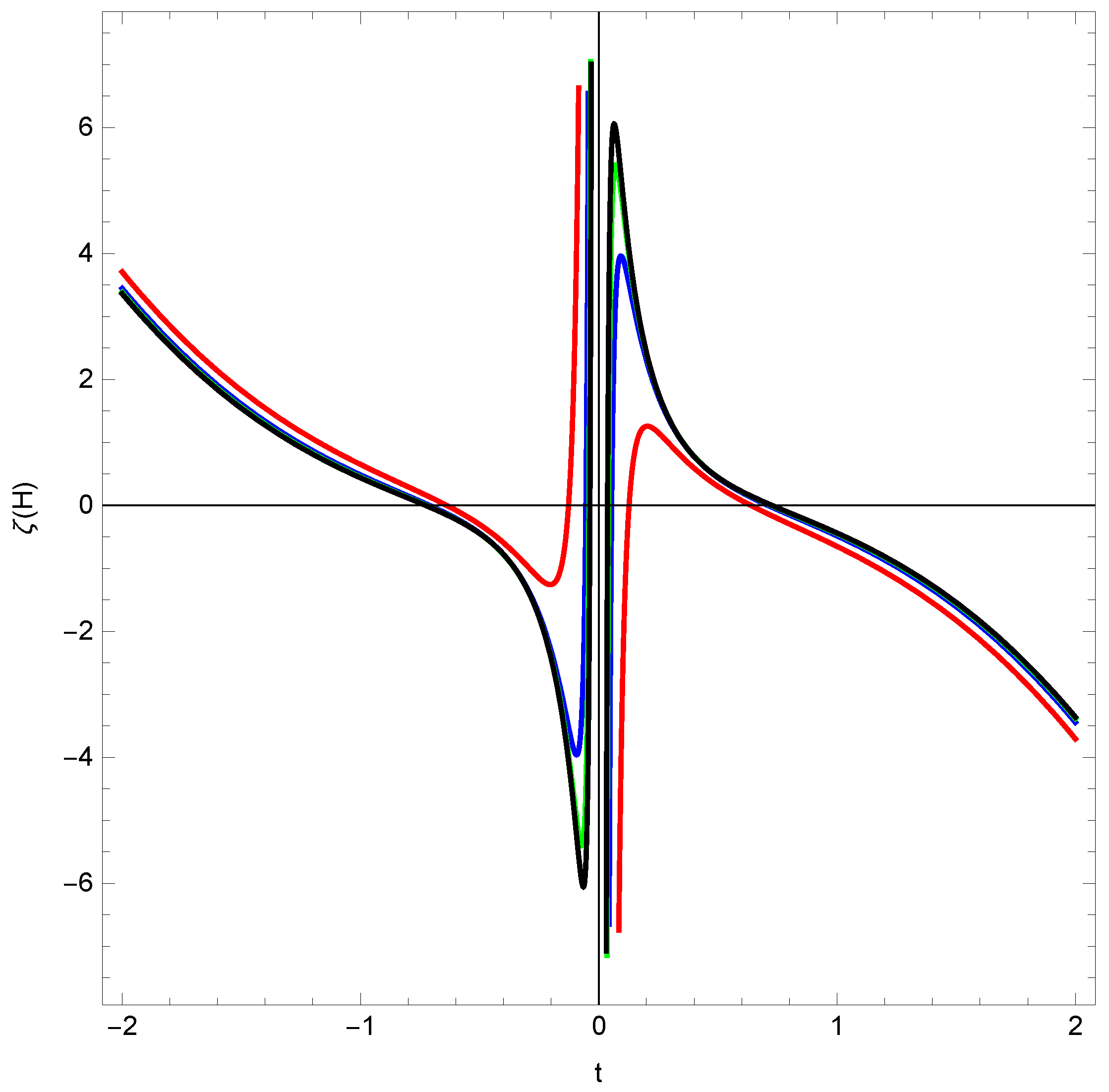
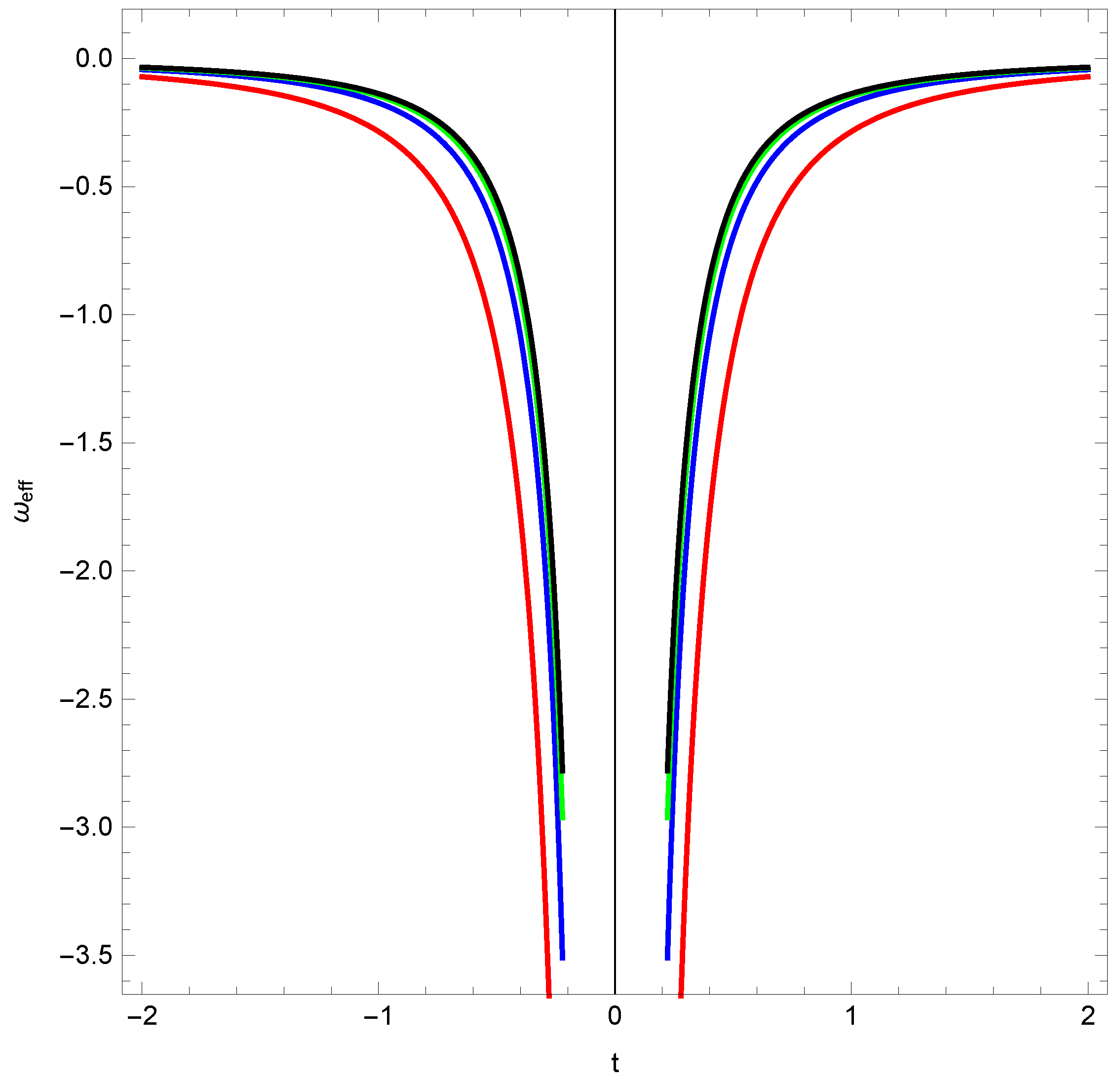
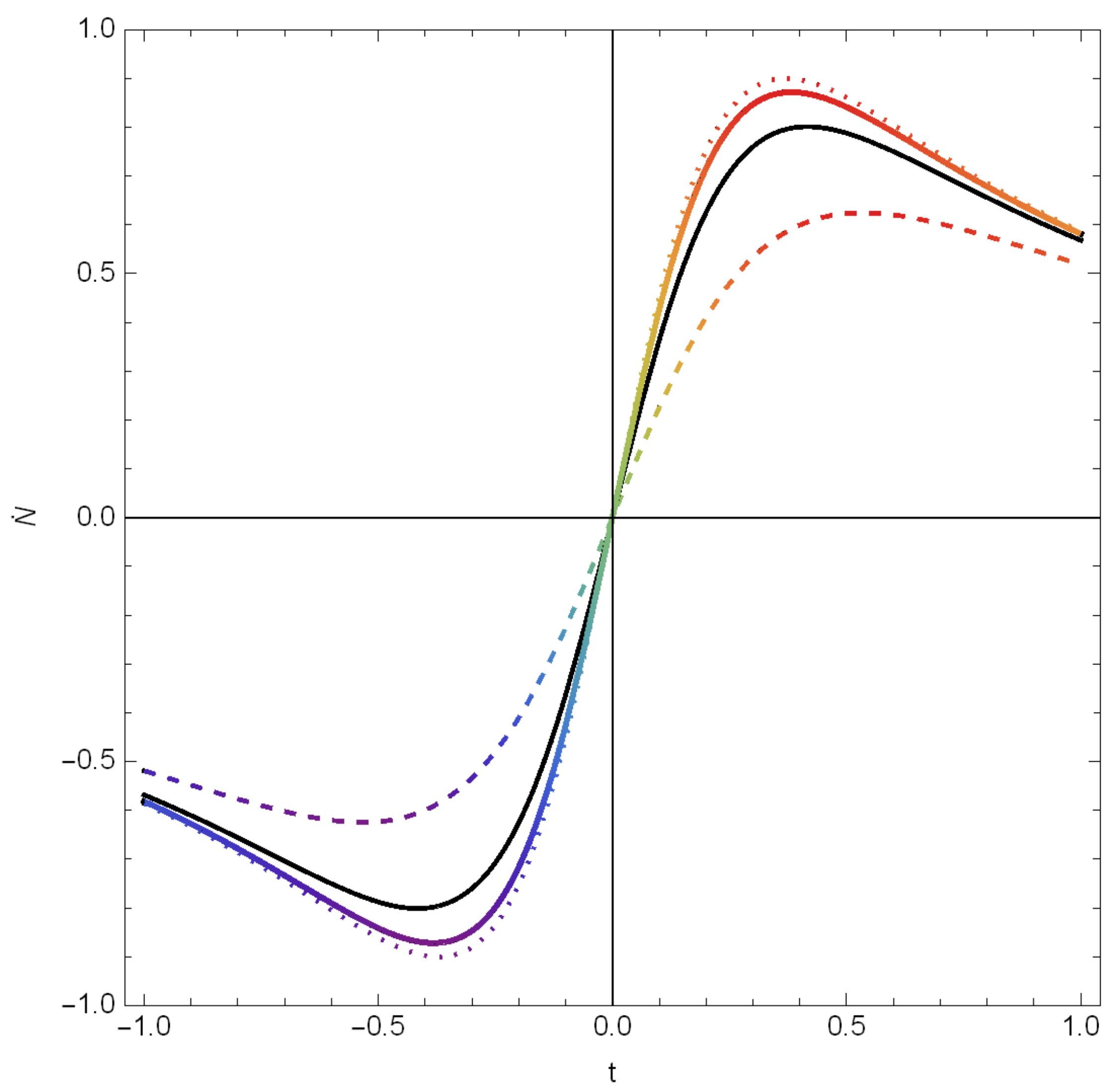
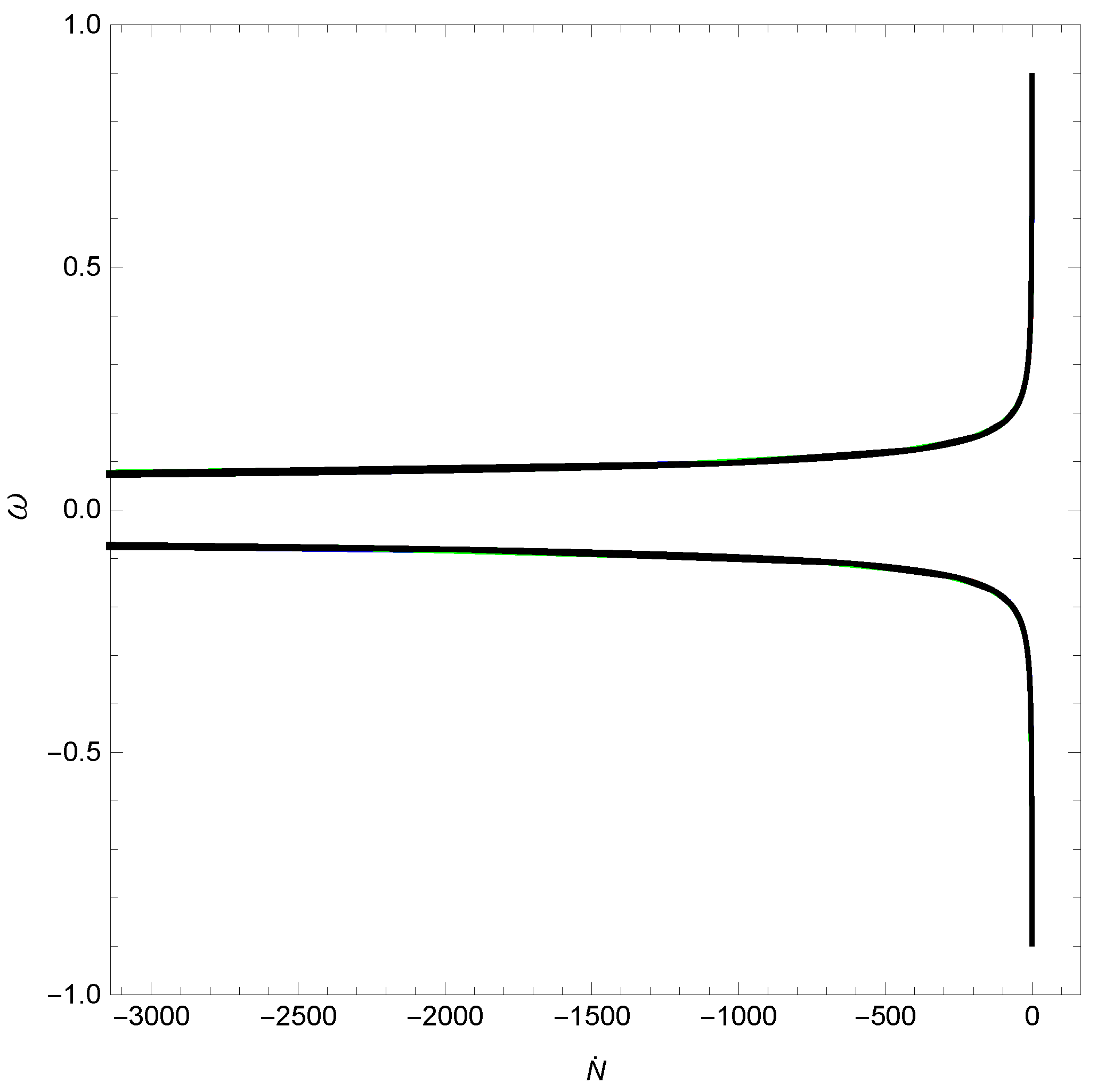

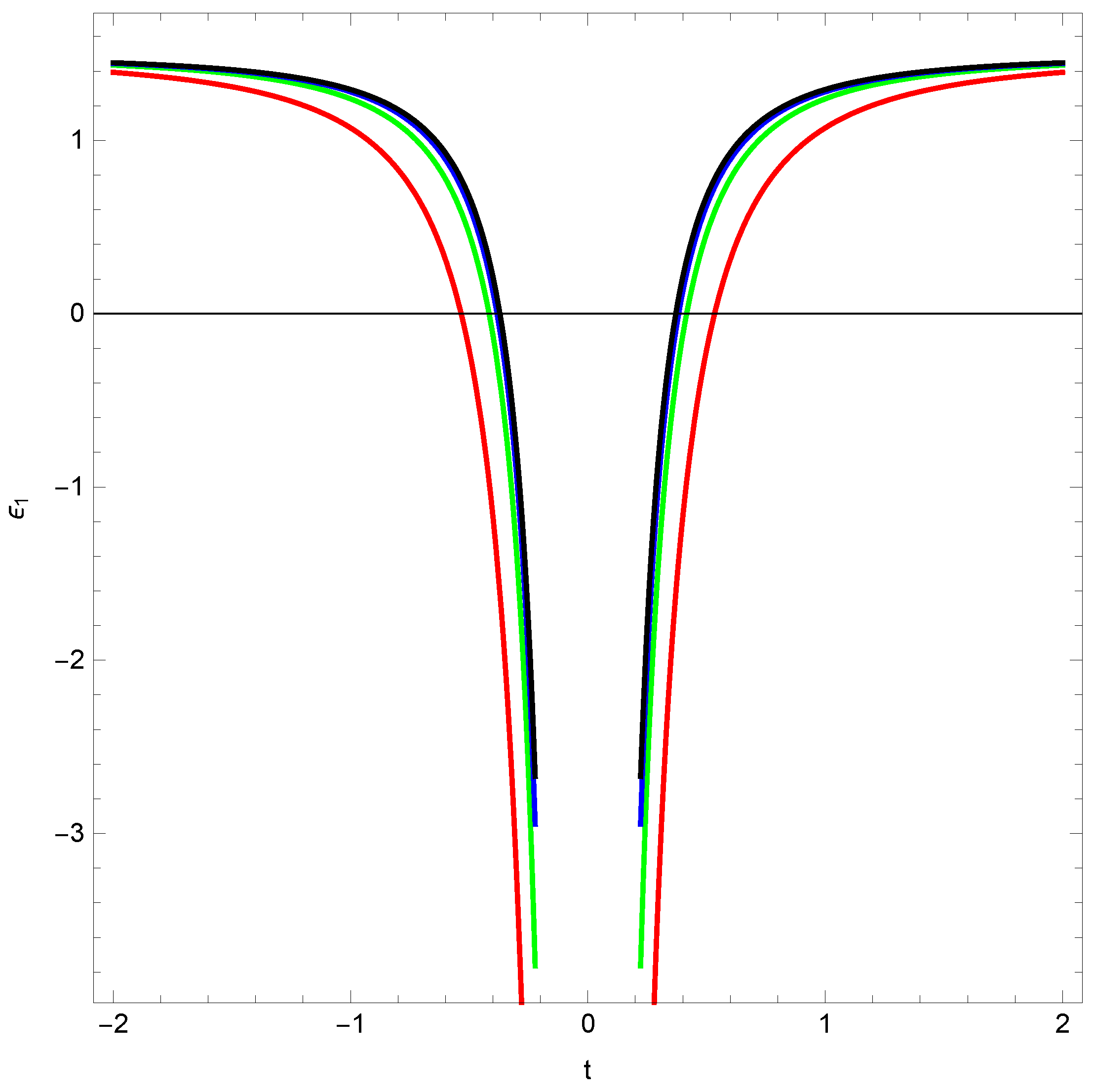


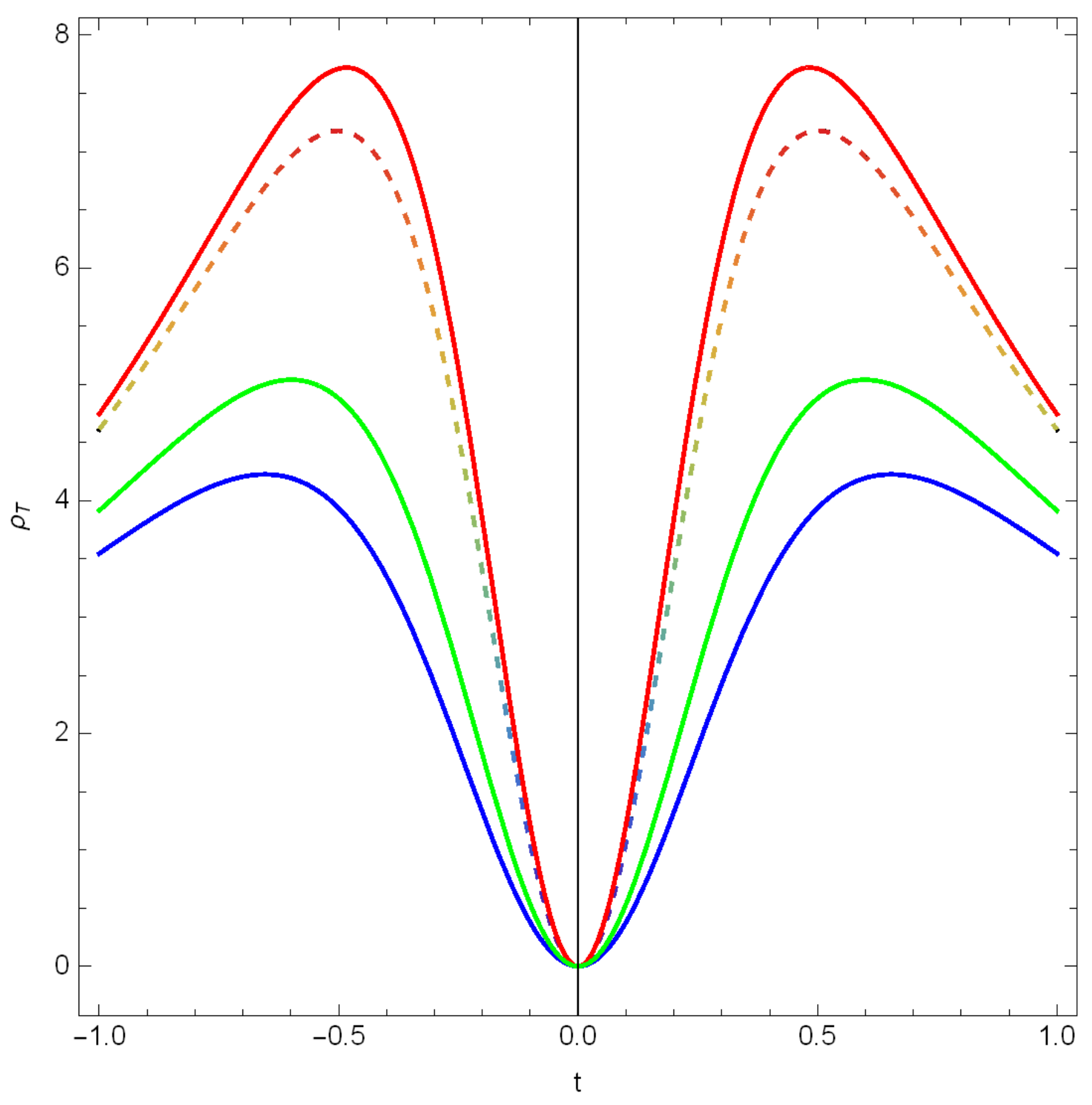
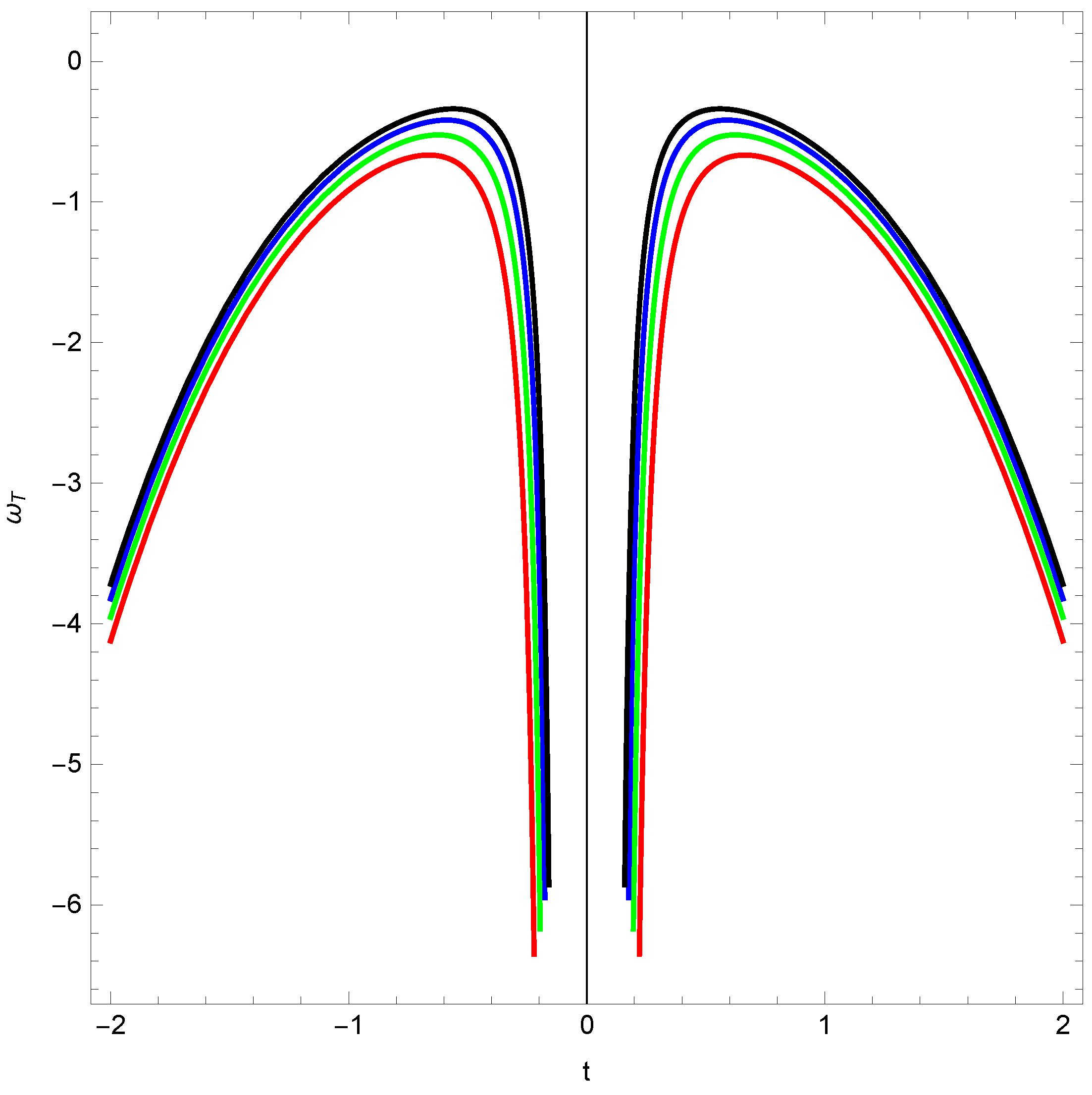
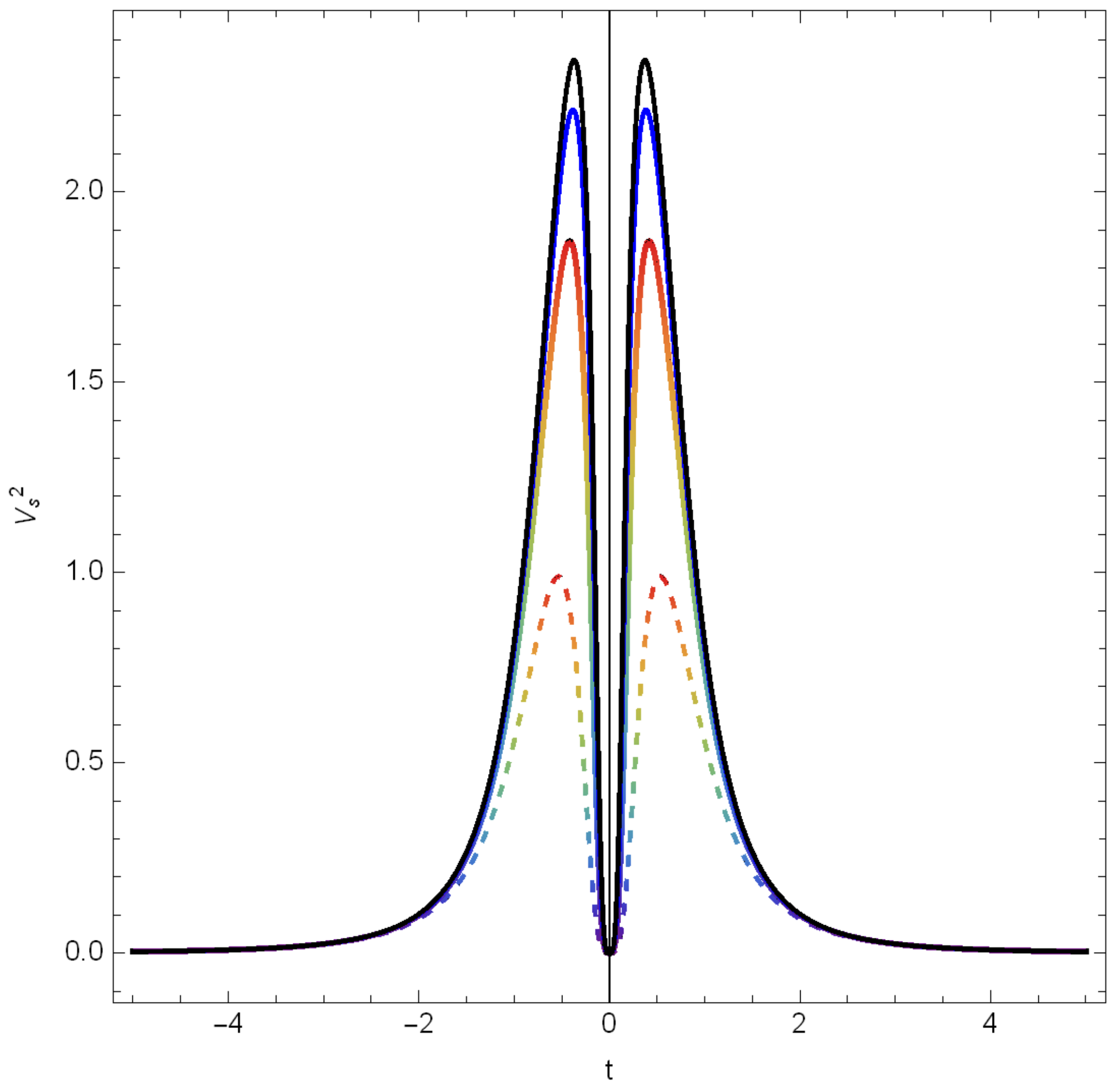
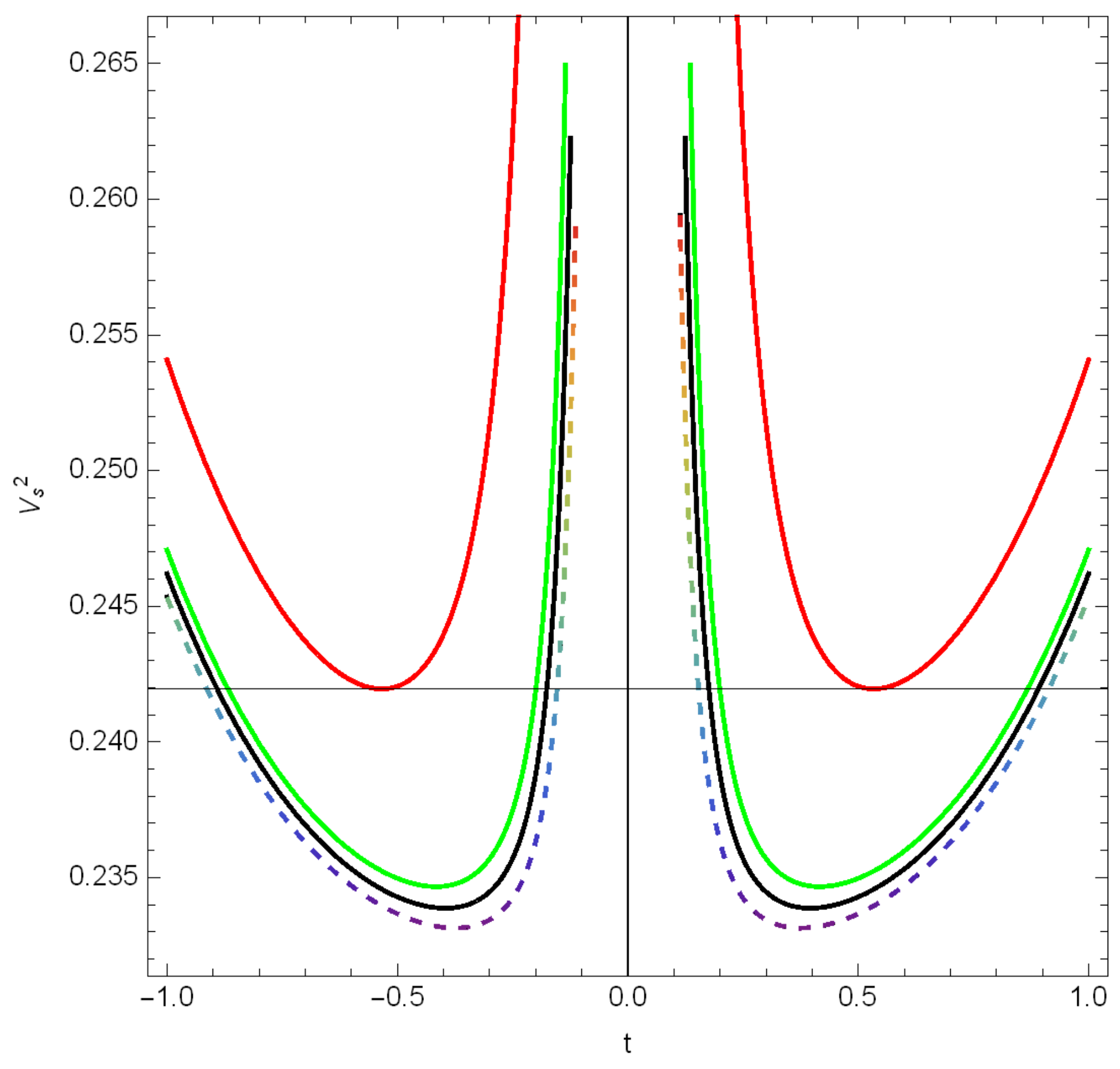

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saha, S.; Chattopadhyay, S. Realization of Bounce in a Modified Gravity Framework and Information Theoretic Approach to the Bouncing Point. Universe 2023, 9, 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9030136
Saha S, Chattopadhyay S. Realization of Bounce in a Modified Gravity Framework and Information Theoretic Approach to the Bouncing Point. Universe. 2023; 9(3):136. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9030136
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaha, Sanghati, and Surajit Chattopadhyay. 2023. "Realization of Bounce in a Modified Gravity Framework and Information Theoretic Approach to the Bouncing Point" Universe 9, no. 3: 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9030136
APA StyleSaha, S., & Chattopadhyay, S. (2023). Realization of Bounce in a Modified Gravity Framework and Information Theoretic Approach to the Bouncing Point. Universe, 9(3), 136. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9030136







