Recurrent Large Sunspot Structures and 27-Day Component of Solar Activity as Proxies to Axis-Nonsymmetry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data
3. Methods
3.1. 27-Day Signal
3.2. A Few Proxies to Axis-Nonsymmetry
3.3. Verification of Significance
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Petrovay, K. Solar cycle prediction. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2020, 17, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruzmaikin, A. Origin of Sunspots. Space Sci. Rev. 2001, 95, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Toma, G.; White, O.R.; Harvey, K.L. A picture of solar minimum and the onset of solar cycle 23. I. Global magnetic field evolution. Astrophys. J. 2000, 529, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castenmiller, M.J.M.; Zwaan, C.; van der Zalm, E.B.J. Sunspot Nests—Manifestations of Sequences in Magnetic Activity. Sol. Phys. 1986, 105, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.X. Activity Complexes and a Prominent Poleward Surge during Solar Cycle 24. Astrophys. J. 2020, 904, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthasar, H.; Schüssler, M. Preferred longitudes of sunspot groups and high-speed solar wind streams: Evidence for a “solar memory”. Sol. Phys. 1983, 87, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, I.G.; Berdyugina, S.; Moss, D.; Sokoloff, D. Long-term persistence of solar active longitudes and its implications for the solar dynamo theory. Adv. Space Res. 2007, 40, 951–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neugebauer, M.; Smith, E.J.; Ruzmaikin, A.; Feynman, J.; Vaughan, A. The solar magnetic field and the solar wind: Existence of preferred longitudes. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 2315–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mursula, K.; Hiltula, T. Systematically asymmetric heliospheric magnetic field: Evidence for a quadrupole mode and non-axisymmetry with polarity flip-flops. Sol. Phys. 2004, 224, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shnirman, M.; Le Mouël, J.L.; Blanter, E. The 27-Day and 22-Year Cycles in Solar and Geomagnetic Activity. Sol. Phys. 2009, 258, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordvinov, A.; Plyusnina, L. Cyclic Changes in Solar Rotation Inferred from Temporal Changes in the Mean Magnetic Field. Sol. Phys. 2000, 197, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, U. Untersuchungen über die Herdbildung der Sonnenflecken. Mit 13 Textabbildungen. Z. Astrophys. 1955, 37, 48–66. [Google Scholar]
- Henwood, R.; Chapman, S.; Willis, D. Increasing lifetime of recurrent sunspot groups within the Greenwich photoheliographic results. Sol. Phys. 2010, 262, 299–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bumba, V.; Howard, R. Solar activity and recurrences in magnetic-field distribution. Sol. Phys. 1969, 7, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, C.S. Sunspot Configurations and Proton Flares. Astrophys. J. 1966, 145, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazev, S. Activity Complexes on the Sun in Solar Cycle 24. Astron. Rep. 2015, 59, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapoval, A.; Le Mouël, J.L.; Shnirman, M.; Courtillot, V. Observational evidence in favor of scale-free evolution of sunspot groups. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 618, A183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagovitsyn, Y.; Ivanov, V.; Skorbezh, N. Refinement of the Gnevyshev-Waldmeier Rule Based on a 140-Year Series of Observations. Astron. Lett. 2019, 45, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charbonneau, P. Dynamo models of the solar cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2020, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazra, G. Recent advances in the 3D kinematic Babcock–Leighton solar dynamo modeling. J. Astrophys. Astron. 2021, 42, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, H.; Sokoloff, D. Meridional circulation and dynamo waves. Astron. Nachrichten Astron. Notes 2008, 329, 766–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiewski, E.V.; Malova, H.V.; Popov, V.Y.; Zelenyi, L.M. Ulysses Flyby in the Heliosphere: Comparison of the Solar Wind Model with Observational Data. Universe 2022, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, A.S.; Miesch, M.S.; Toomre, J. Global-scale turbulent convection and magnetic dynamo action in the solar envelope. Astrophys. J. 2004, 614, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Passos, D.; Charbonneau, P. Characteristics of magnetic solar-like cycles in a 3D MHD simulation of solar convection. Astron. Astrophys. 2014, 568, A113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Browning, M.K.; Miesch, M.S.; Brun, A.S.; Toomre, J. Dynamo action in the solar convection zone and tachocline: Pumping and organization of toroidal fields. Astrophys. J. 2006, 648, L157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pipin, V.; Kosovichev, A. Effects of large-scale non-axisymmetric perturbations in the mean-field solar dynamo. Astrophys. J. 2015, 813, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shapoval, A.; Le Mouël, J.L.; Shnirman, M.; Courtillot, V. When daily sunspot births become positively correlated. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 2709–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovay, K.; Talafha, M. Optimization of surface flux transport models for the solar polar magnetic field. Astron. Astrophys. 2019, 632, A87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, J.; Hathaway, D.; Cameron, R.; Solanki, S.; Gizon, L.; Upton, L. Magnetic flux transport at the solar surface. Space Sci. Rev. 2014, 186, 491–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.M. Surface flux transport and the evolution of the Sun’s polar fields. Space Sci. Rev. 2017, 210, 351–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovay, K.; Nagy, M.; Yeates, A.R. Towards an algebraic method of solar cycle prediction-I. Calculating the ultimate dipole contributions of individual active regions. J. Space Weather. Space Clim. 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, D. The Solar Cycle. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2015, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obridko, V.; Pipin, V.; Sokoloff, D.; Shibalova, A. Solar large-scale magnetic field and cycle patterns in solar dynamo. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 504, 4990–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broomhall, A.M.; Nakariakov, V.M. A comparison between global proxies of the Sun’s magnetic activity cycle: Inferences from helioseismology. Sol. Phys. 2015, 290, 3095–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernova, E.S.; Tyasto, M.I.; Baranov, D.G.; Danilova, O.A. Nonaxisymmetric Component of Solar Activity: The Vector of the Longitudinal Asymmetry. Sol. Phys. 2020, 295, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, R. Variability in the Periodicity of 27 Days in Solar Indices. Sol. Phys. 2002, 209, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mouël, J.L.; Shnirman, M.; Blanter, E. The 27-Day Signal in Sunspot Number Series and the Solar Dynamo. Sol. Phys. 2007, 246, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanter, E.; Le Mouël, J.L.; Perrier, F.; Shnirman, M. Short-term correlation of solar activity and sunspot: Evidence of lifetime increase. Sol. Phys. 2006, 237, 329–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mouël, J.L.; Lopes, F.; Courtillot, V. Identification of Gleissberg cycles and a rising trend in a 315-year-long series of sunspot numbers. Sol. Phys. 2017, 292, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogart, R. Recurrence of Solar Activity: Evidence for Active Longitudes. Sol. Phys. 1982, 76, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagovitsyn, Y.A.; Kuleshova, A. North–South asymmetry of solar activity on a long timescale. Geomagn. Aeron. 2015, 55, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SILSO World Data Center. The International Sunspot Number. 2021. Available online: https://www.sidc.be/SILSO/home (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- Hathaway, D.; Upton, L. Solar Cycle Science. 2021. Available online: http://solarcyclescience.com/people.html (accessed on 26 May 2023).
- Hathaway, D.; Wilson, R.; Reichmann, E. Group Sunspot Numbers: Sunspot Cycle Characteristics. Sol. Phys. 2002, 211, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapoval, A. The Contribution of Large Recurrent Sunspot Groups to Solar Activity: Empirical Evidence. Universe 2022, 8, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Garzón, P.; Zaliapin, I.; Ben-Zion, Y.; Kwiatek, G.; Bohnhoff, M. Comparative study of earthquake clustering in relation to hydraulic activities at geothermal fields in California. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 4041–4062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoskin, I.G. A history of solar activity over millennia. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2017, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hathaway, D. Available online: http://solarcyclescience.com/activeregions.html (accessed on 26 May 2023).
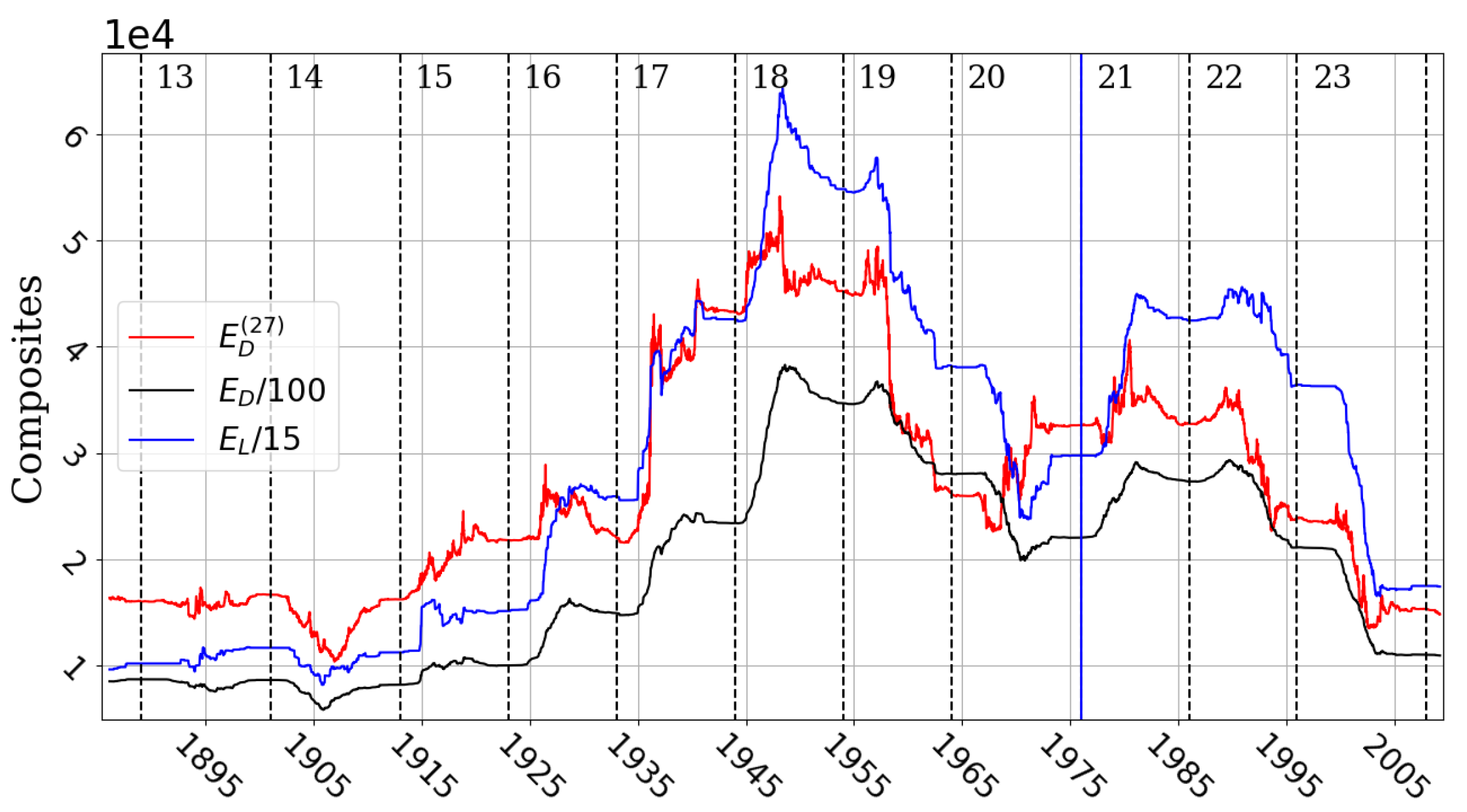

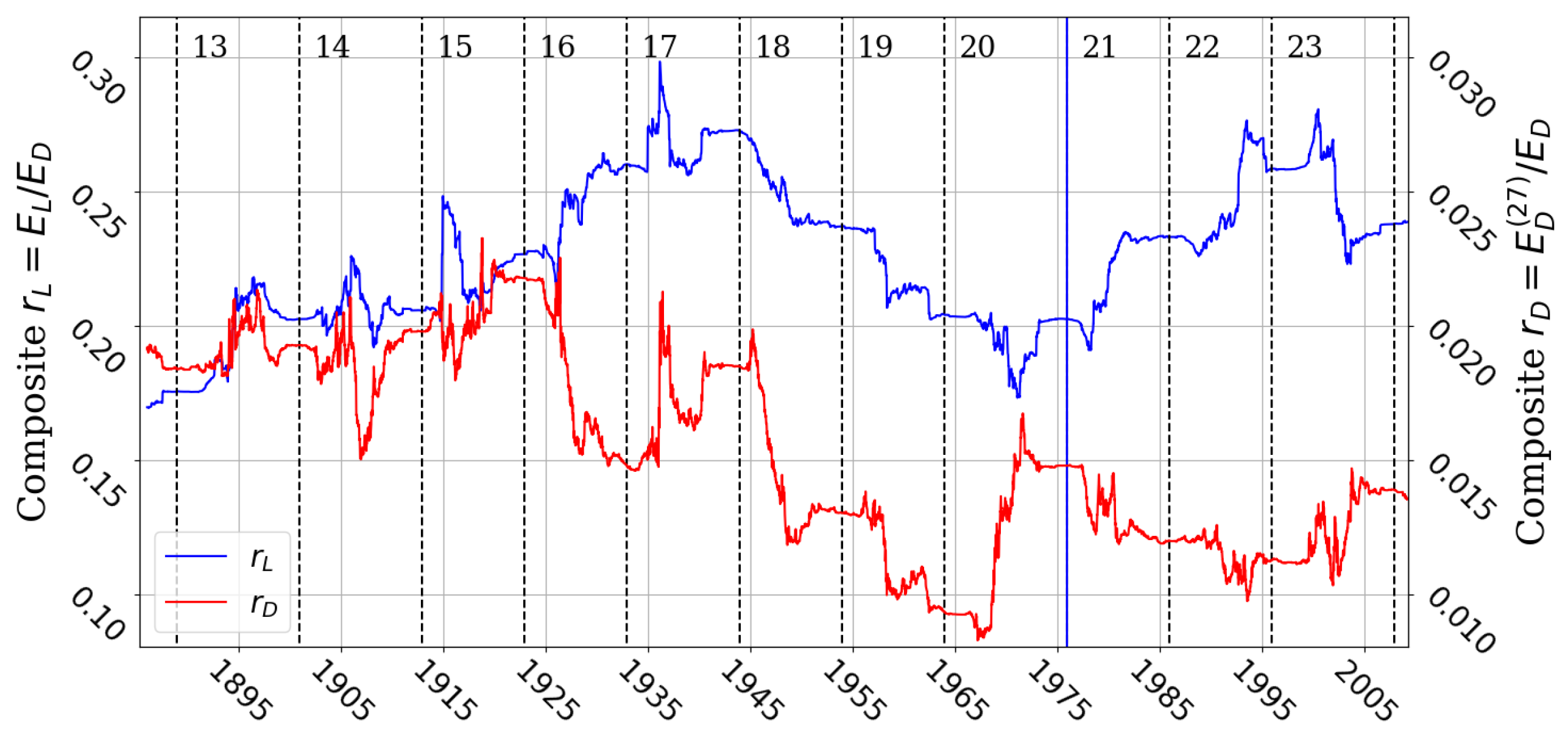
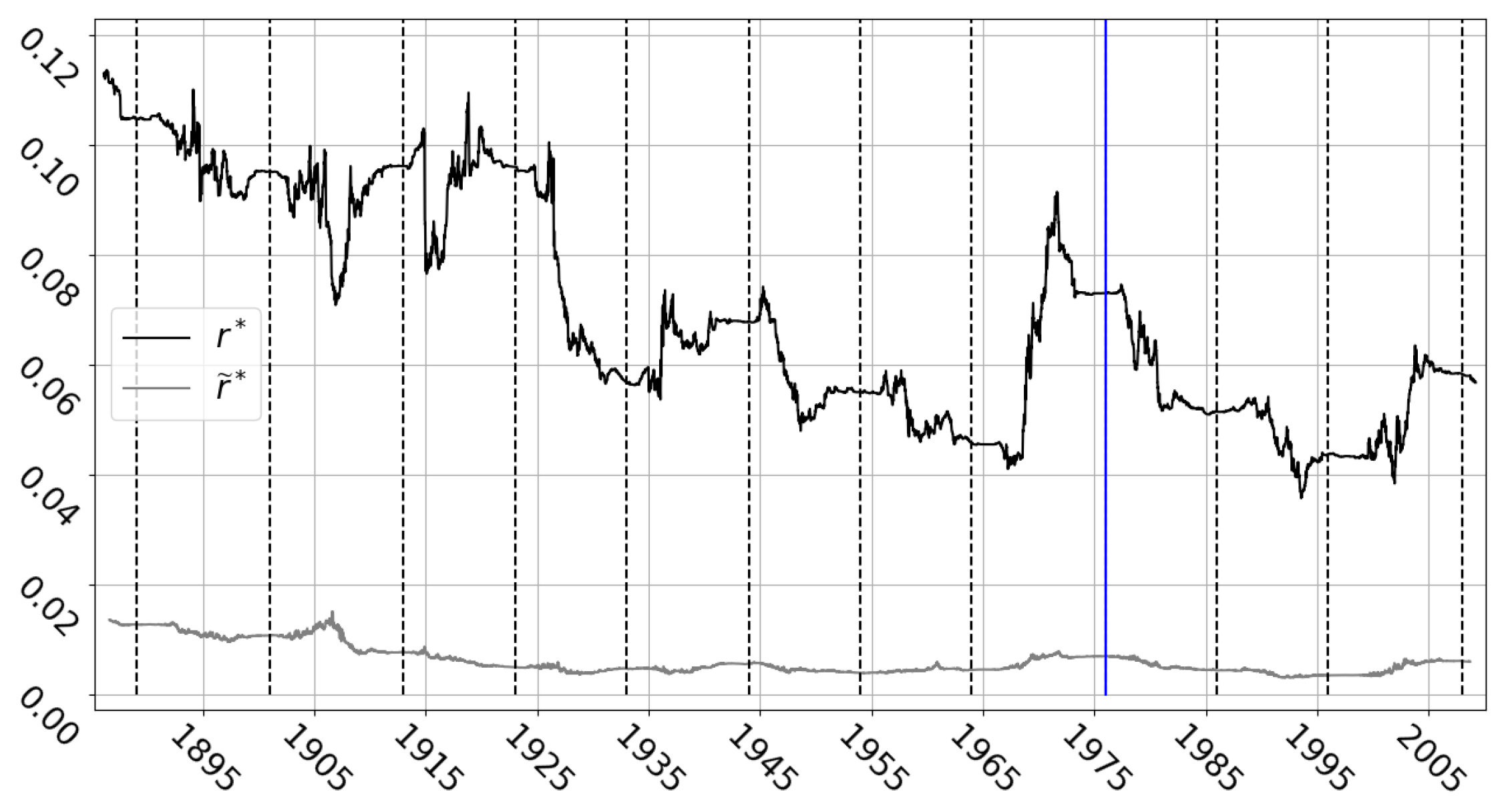
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shapoval, A.; Shnirman, M. Recurrent Large Sunspot Structures and 27-Day Component of Solar Activity as Proxies to Axis-Nonsymmetry. Universe 2023, 9, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060271
Shapoval A, Shnirman M. Recurrent Large Sunspot Structures and 27-Day Component of Solar Activity as Proxies to Axis-Nonsymmetry. Universe. 2023; 9(6):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060271
Chicago/Turabian StyleShapoval, Alexander, and Mikhail Shnirman. 2023. "Recurrent Large Sunspot Structures and 27-Day Component of Solar Activity as Proxies to Axis-Nonsymmetry" Universe 9, no. 6: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060271
APA StyleShapoval, A., & Shnirman, M. (2023). Recurrent Large Sunspot Structures and 27-Day Component of Solar Activity as Proxies to Axis-Nonsymmetry. Universe, 9(6), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/universe9060271





