Cowan Code: 50 Years of Growing Impact on Atomic Physics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
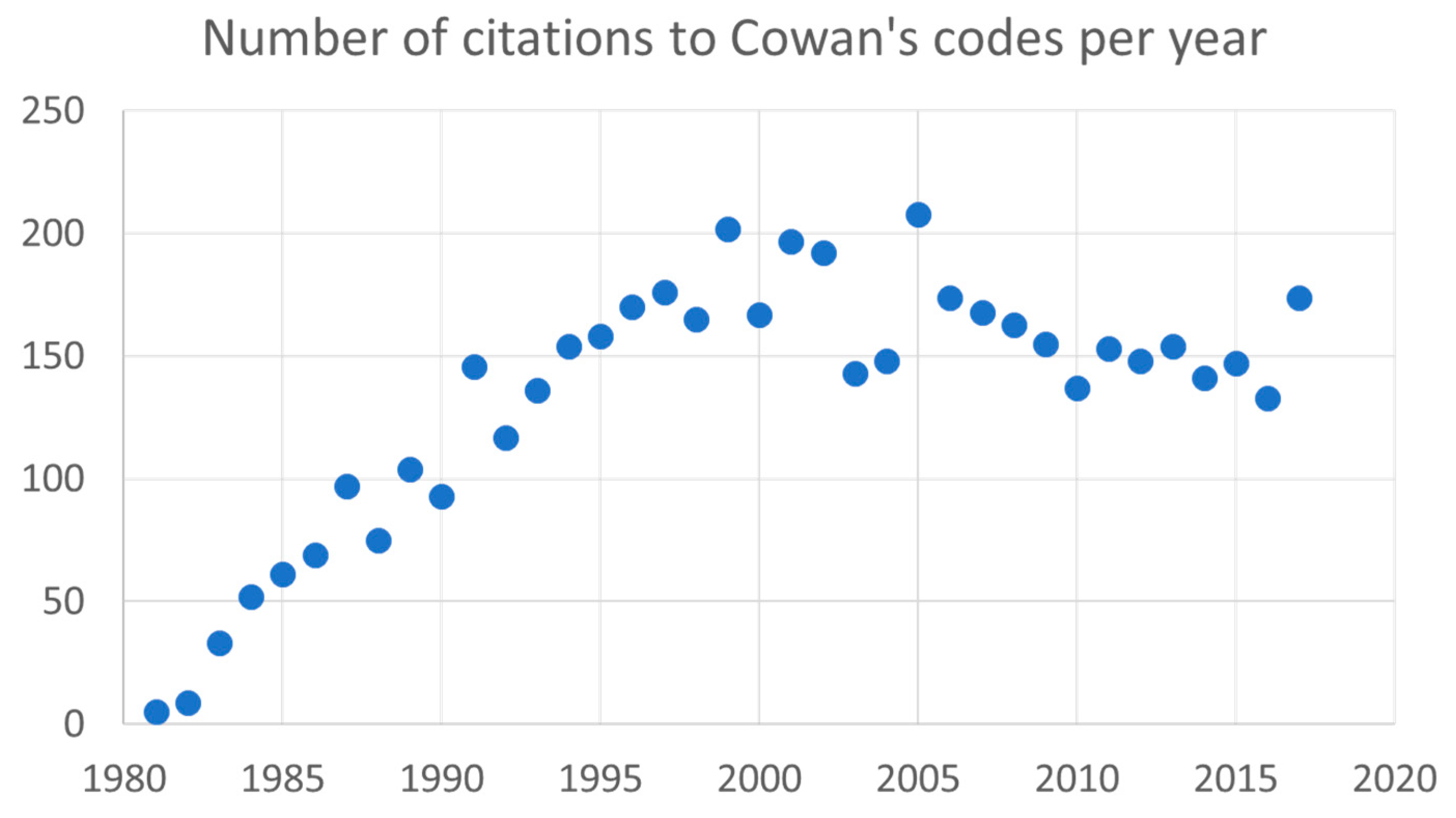
2. Impact of Cowan’s Book and Computer Codes
3. What Cowan’s Codes Do
4. Cowan’s Predecessors
- Compute the wavefunctions.
- Compute the Slater parameters. It was possible to also compute parameters of additional interactions, such as hyperfine. The user had to construct the input files from the output of the previous code in a laborious semi-manual procedure.
- Assemble the Hamiltonian matrix (extremely tenuous semi-manual task). It was flexible, allowing for introduction of additional interactions.
- Diagonalize the Hamiltonian.
- Use the output of the diagonalization to compute the atomic structure. Calculation of transition rates was not included in the codes. The users had to build their own code extensions to do that.
- Use a least-squares fitting code to adjust the Slater parameters.
5. The Workflow of Cowan’s Suite of Codes
- Specify the atomic configurations and code options in two input files.
- Run RCN (produces input for RCN2).
- Run RCN2 (produces input for RCG).
- Run RCG (cringe at the results, as they are rather inaccurate). This produces the input for RCE and outputs nicely formatted transition data.
- Run RCE. To fit experimental levels, edit an input file and rerun RCE.
- Use utility codes to transfer fitted parameters to the RCG input file.
- Re-run RCG and smile! The results are now very accurate.
6. Why are Cowan’s Codes So Important?
7. Versions of Cowan’s Codes
- P. Quinet’s version with core polarization (private) [23].
- The only codes modified in this version are RCN and RCN2.
- R. L. Kurucz’s version (private).
- Branched from mainstream circa 1970. Designed for very large configuration sets and uses large workstations. The famous Kurucz’s Atoms collection of computed atomic line lists [24] was produced with these codes.
- J. Ruczkowski, M. Elantkowska, and J. Dembczyński’s version (private) [25].
- Incorporates LSF of transition matrix elements in addition to Slater integrals.
- Los Alamos CATS (Cowan ATomic Structure) code (proprietary) [26].
- Parallelized, with dynamic memory allocation, for a large computer cluster. This version does not have an LSF code.
8. My Version of Cowan’s Codes
- ‘printout’: Converts the RCE output to nicely formatted tables of energy levels (including the intermediate quantum numbers omitted in Cowan’s original output) and LSF parameters.
- ‘conv_out’: Converts the RCG output to nicely formatted tables of levels and lines. This code can also create input files for the visual line-identification code IDEN2 [27].
- ‘update11′: Transfers fitted LSF parameters from the RCE output to the RCG input file, re-runs RCG, and runs ‘printout’.
- ‘reorder_ing11′: Converts the RCG input file to change the order of shell summation.
9. Other Codes with Similar or Better Capabilities
9.1. Semiempirical Codes with Parametric Fitting
9.2. Other Ab Initio Codes
- Non-relativistic codes with relativistic corrections:
- Relativistic codes:
- M. F. Gu: FAC (MCDF, MBPT) [18]
- J.P. Desclaux, P. Indelicato: MCDFGME [17]
- Y. Ishikawa: Møller–Plesset many-body perturbation theory (MR-MP; unpublished; see, e.g., [19])
- W.R. Johnson, U. I. Safronova, M.S. Safronova: RMBPT (unpublished, see, e.g., [39])
- M.S. Safronova et al.: RMBPT (all-order; unpublished); see, e.g., [40]
- E. Eliav, U. Kaldor: Coupled-Cluster (unpublished, see, e.g., [41])
- V.A. Dzuba, W.R. Johnson: SD Coupled-Cluster (unpublished, see, e.g., [42])
- I.M. Savukov: parametric CI+MBPT (unpublished, see, e.g., [43])
10. Known Problems in Cowan’s Codes
| (a) | |||||
| 3 | 1Li I s22p | 1s2 5p0 2p | |||
| 3 | 1Li I s23p | 1s2 5p0 3p | |||
| 3 | 1Li I s24p | 1s2 5p0 4p | |||
| 3 | 1Li I 5p23p | 1s0 5p2 3p | |||
| 3 | 1Li I 5p24p | 1s0 5p2 4p | |||
| (b) | |||||
| 3 | 1Li I s22p | 1s2 2p | |||
| 3 | 1Li I s23p | 1s2 2p0 3p | |||
| 3 | 1Li I s24p | 1s2 2p0 3p0 4p | |||
| 3 | 1Li I 5p23p | 1s0 2p0 3p 4p0 5p2 | |||
| 3 | 1Li I 5p24p | 1s0 2p0 3p0 4p 5p2 | |||
- No transformation to jj and jK coupling is available for shells with equivalent electrons. Such shells are always represented in LS coupling.
- Recoupling to a non-standard order of shell summation is not exact in the presence of CI.
11. Summary and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cowan, R.D. The Theory of Atomic Structure and Spectra; University of California Press: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Cowan, R.D. Theoretical Calculation of Atomic Spectra Using Digital Computers. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1968, 58, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, R.D. Atomic Self-Consistent-Field Calculations Using Statistical Approximations for Exchange and Correlation. Phys. Rev. 1967, 163, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, R.D.; Andrew, K.L. Coupling Considerations in Two-Electron Spectra. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1965, 55, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.A. Obituary: Robert Duane Cowan 26 July 2018. Available online: https://ladailypost.com/content/obituary-robert-duane-cowan-july-26-2018 (accessed on 9 October 2018).
- Web of Science, Originally Produced by the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI), Now Maintained by Clarivate Analytics. Available online: http://isiknowledge.com/ (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Bordarier, Y.; Vetter, R.; Blaise, J. Étude des structures hyperfines des raies d’arc de 169Tm. J. Phys. 1963, 24, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordarier, Y.; Judd, B.R.; Klapisch, M. Hyperfine Structure of Eu I. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1965, 289, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
- Gluck, G.G.; Bordarier, Y.; Bauche, J.; van Kleef, T.A.M. Deplacement isotopique, calculs theoriques et structure des termes dans le spectre d’arc de l’osmium. Physica 1964, 30, 2068–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, A.; Blaise, J.; Schweighofer, M.-G. Étude des configurations impaires 4f66s6p et 4f55d6s2 de Sm I. J. Phys. 1968, 29, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.E.; Uylings, P.H.M.; Raassen, A.J.J. Parametric Fitting with Orthogonal Operators. Phys. Scr. 1988, 37, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyart, J.-F. On the Interpretation of Complex Atomic Spectra by Means of the Parametric Racah-Slater Method and Cowan Codes. Can. J. Phys. 2011, 89, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramida, A. Critical Evaluation of Data on Atomic Energy Levels, Wavelengths, and Transition Probabilities. Fusion Sci. Technol. 2013, 63, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese Fischer, C.; Tachiev, G.; Gaigalas, G.; Godefroid, M.R. An MCHF Atomic-Structure Package for Large-Scale Calculations. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2007, 176, 559–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbert, A. CIV3—A General Program to Calculate Configuration Interaction Wave Functions and Electric-Dipole Oscillator Strengths. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1975, 9, 141–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, P.; Gaigalas, G.; Bieroń, J.; Froese Fischer, C.; Grant, I.P. New Version: GRASP2K Relativistic Atomic Structure Package. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2013, 184, 2197–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desclaux, J.P.; Indelicato, P. Multiconfiguration Dirac-Fock with General Matrix Elements; Laboratoire Kastler Brossel: Paris, France, 2017; Available online: http://dirac.spectro.jussieu.fr/mcdf/mcdf_code/mcdfgme_accueil.html (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Gu, M.F. The Flexible Atomic Code. Can. J. Phys. 2008, 86, 675–689. [Google Scholar]
- Vilkas, M.J.; Koc, K.; Ishikawa, Y. Relativistic Multireference Møller-Plesset Perturbation Theory Based on Multiconfigurational Dirac-Fock Reference Functions. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 296, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramida, A.; Ralchenko, Y.; Reader, J.; NIST ASD Team. NIST Atomic Spectra Database (Ver. 5.6.1); National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/asd (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- McGuinness, C.; Robert, D. Cowan’s Atomic Structure Code; Trinity College, University of Dublin: Dublin, Ireland, 2007; Available online: https://www.tcd.ie/Physics/people/Cormac.McGuinness/Cowan/ (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Kramida, A. A Suite of Atomic Structure Codes Originally Developed by RD Cowan Adapted for Windows-Based Personal Computers; National Institute of Standards and Technology: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinet, P.; Palmeri, P.; Biémont, E. On the use of the Cowan’s code for atomic structure calculations in singly ionized lanthanides. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 1999, 62, 625–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurucz, R.L. Atoms; Harvard University: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Available online: http://kurucz.harvard.edu/atoms.html (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Ruczkowski, J.; Elantkowska, M.; Dembczyński, J. An Alternative Method for Determination of Oscillator Strengths: The Example of Sc II. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 145, 20–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, J., Jr.; Clark, R.E.H.; Cowan, R.D. Theoretical Atomic Physics Code Development I. CATS: Cowan Atomic Structure Code; Report LA-11436-M; Los Alamos National Lab: Los Alamos, NM, USA, 1988; Volume I, p. 31. Available online: https://fas.org/sgp/othergov/doe/lanl/docs3/00323386.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2019).
- Azarov, V.I.; Kramida, A.; Vokhmentsev, M.Y. IDEN2–A Program for Visual Identification of Spectral Lines and Energy Levels in Optical Spectra of Atoms and Simple Molecules. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2018, 225, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raassen, A.J.J.; Uylings, P.H.M. The Use of Complete Sets of Orthogonal Operators in Spectroscopic Studies. Phys. Scr. 1996, 65, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van het Hof, G.J.; Raassen, A.J.J.; Uylings, P.H.M. Parametric Description of 3dN4s Configurations using Orthogonal Operators. Phys. Scr. 1991, 44, 343–350. [Google Scholar]
- Azarov, V.I.; Gayasov, R.R. The Third Spectrum of Rhenium (Re III): Analysis of the (5d5+5d46s)–(5d46p+5d36s6p) Transition Array. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2018, 122, 306–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarov, V.I.; Tchang-Brillet, W.-Ü.L.; Gayasov, R.R. Analysis of the Spectrum of the (5d6+5d56s)–(5d56p+5d46s6p) Transitions of Two Times Ionized Osmium (Os III). At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 2018, 122, 345–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyart, J.-F.; Raassen, A.J.J.; Uylings, P.H.M.; Joshi, Y.N. Spectra of High-Z Ions of Stellar Interest. A Theoretical Study of (d + s)8 Mixed Configurations in 5d- and 4d-Elements. Phys. Scr. 1993, 47, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uylings, P.H.M.; (University of Amsterdam). Private communication, 2018.
- Blaise, J.; Wyart, J.-F.; Conway, J.G.; Worden, E.F. Generalized Parametric Study of 5fN and 5fN7s Configurations. Phys. Scr. 1980, 22, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyart, J.-F.; Raassen, A.J.J.; Joshi, Y.N.; Uylings, P.H.M. The 5d96p-5d9(6d+7s) Transitions in the Isoelectronic Sequence Au II-Bi VI. J. Phys. II 1992, 2, 895–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissner, W.; Jones, M.; Nussbaumer, H. Techniques for the Calculation of Atomic Structures and Radiative Data Including Relativistic Corrections. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1974, 8, 270–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanovich, P.; Rancova, O. Quasirelativistic Hartree-Fock Equations Consistent with Breit-Pauli Approach. Phys. Rev. 2006, 74, 052501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese Fischer, C.; Gaigalas, G.; Jönsson, P.; Bieroń, J. GRASP2018—A Fortran 95 version of the General Relativistic Atomic Structure Package. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2019, 237, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, M.S.; Johnson, W.R.; Safronova, U.I. Relativistic Many-Body Calculations of the Energies of n = 2 States for the Berylliumlike Isoelectronic Sequence. Phys. Rev. 1996, 53, 4036–4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safronova, U.I.; Safronova, M.S.; Kozlov, M.G. Relativistic All-Order Calculations of In I and Sn II Atomic Properties. Phys. Rev. 2007, 76, 022501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliav, E.; Kaldor, U.; Ishikawa, Y. Ionization Potentials and Excitation Energies of the Alkali-Metal Atoms by the Relativistic Coupled-Cluster Method. Phys. Rev. A 1994, 50, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzuba, V.A.; Johnson, W.R. Coupled-Cluster Single-Double Calculations of the Relativistic Energy Shifts in C IV, Na I, Mg II, Al III, Si IV, Ca II, and Zn II. Phys. Rev. A 2007, 76, 062510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savukov, I.M. Parametric CI+MBPT Calculations of Th I Energies and g-Factors for Even States. J. Phys. B 2007, 50, 165001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramida, A. Configuration Interactions of Class 11: An Error in Cowan’s Atomic Structure Theory. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2017, 215, 47–48, Erratum2018, 232, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaigalas, G. Coupling: The program for searching optimal coupling scheme in atomic theory. Submitted to Comput. Phys. Commun. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Safronova, M.S.; Dzuba, V.A.; Flambaum, V.V.; Safronova, U.I.; Porsev, S.G.; Kozlov, M.G. Highly Charged Ions for Atomic Clocks, Quantum Information, and Search for α variation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 030801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banine, V.Y.; Koshelev, K.N.; Swinkels, G.H.P.M. Physical Processes in EUV Sources for Microlithography. J. Phys. D 2011, 44, 253001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenzer, S.H.; Fournier, K.B.; Wilson, B.G.; Lee, R.W.; Suter, L.J. Ionization Balance in Inertial Confinement Fusion Hohlraums. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 045002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Conf.: | 3d4s | 3d24s | 3d34s | 3d44s | 3d54s | 3d64s | 3d74s | 3d84s | 3d94s |
| Nc: | 4 | 16 | 38 | 63 | 74 | 63 | 38 | 16 | 4 |
| N0: | 5 | 17 | 30 | 42 | 42 | 42 | 30 | 17 | 5 |
| Spectrum: | Ti III | V III | Cr III | Mn III | Fe III | Co III | Ni III | Cu III | Zn III |
| Ne: | 4 | 16 | 37 | 54 | 65 | 58 | 38 | 16 | 4 |
| σ [cm−1]: | 0 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 1.4 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0 |
| Spectrum: | V IV | Cr IV | Mn IV | Fe IV | Co IV | Ni IV | Cu IV | Zn IV | Ga IV |
| Ne: | 4 | 16 | 17 | 62 | 59 | 51 | 37 | 16 | 4 |
| σ [cm−1]: | 0 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 1.8 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0 |
| Spectrum: | Cr V | Mn V | Fe V | Co V | Ni V | Cu V | Zn V | Ga V | Ge V |
| Ne: | 4 | 16 | 36 | 57 | 68 | 47 | 37 | 15 | 4 |
| σ [cm−1]: | 0 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0 |
| Spectrum: | Mn VI | Fe VI | Co VI | Ni VI | As VI | ||||
| Ne: | 4 | 15 | 36 | 57 | 4 | ||||
| σ [cm−1]: | 0 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kramida, A. Cowan Code: 50 Years of Growing Impact on Atomic Physics. Atoms 2019, 7, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7030064
Kramida A. Cowan Code: 50 Years of Growing Impact on Atomic Physics. Atoms. 2019; 7(3):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7030064
Chicago/Turabian StyleKramida, Alexander. 2019. "Cowan Code: 50 Years of Growing Impact on Atomic Physics" Atoms 7, no. 3: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7030064
APA StyleKramida, A. (2019). Cowan Code: 50 Years of Growing Impact on Atomic Physics. Atoms, 7(3), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms7030064





