Advancing the Role of Gamma-Tocotrienol as Proteasomes Inhibitor: A Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line and Treatment Conditions
2.2. Extraction of Protein Fractions
2.2.1. Isolation of Cytoplasmic Fraction
2.2.2. Isolation of Nuclear Fraction
2.3. Determination of Protein Concentration and Trypsin Digestion
2.4. Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.5. Protein Identification and Label-Free Quantification
2.6. Data Acquisition and Statistical Analysis
2.7. Bioinformatics and Functional Analysis
2.7.1. Venn Diagram Analysis
2.7.2. Protein Set Enrichment Analysis
2.7.3. STRING Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Label-Free Mass Spectrometry Quantification of Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Proteins Isolated from MDA-MB-231 Cells following Treatment with γT3
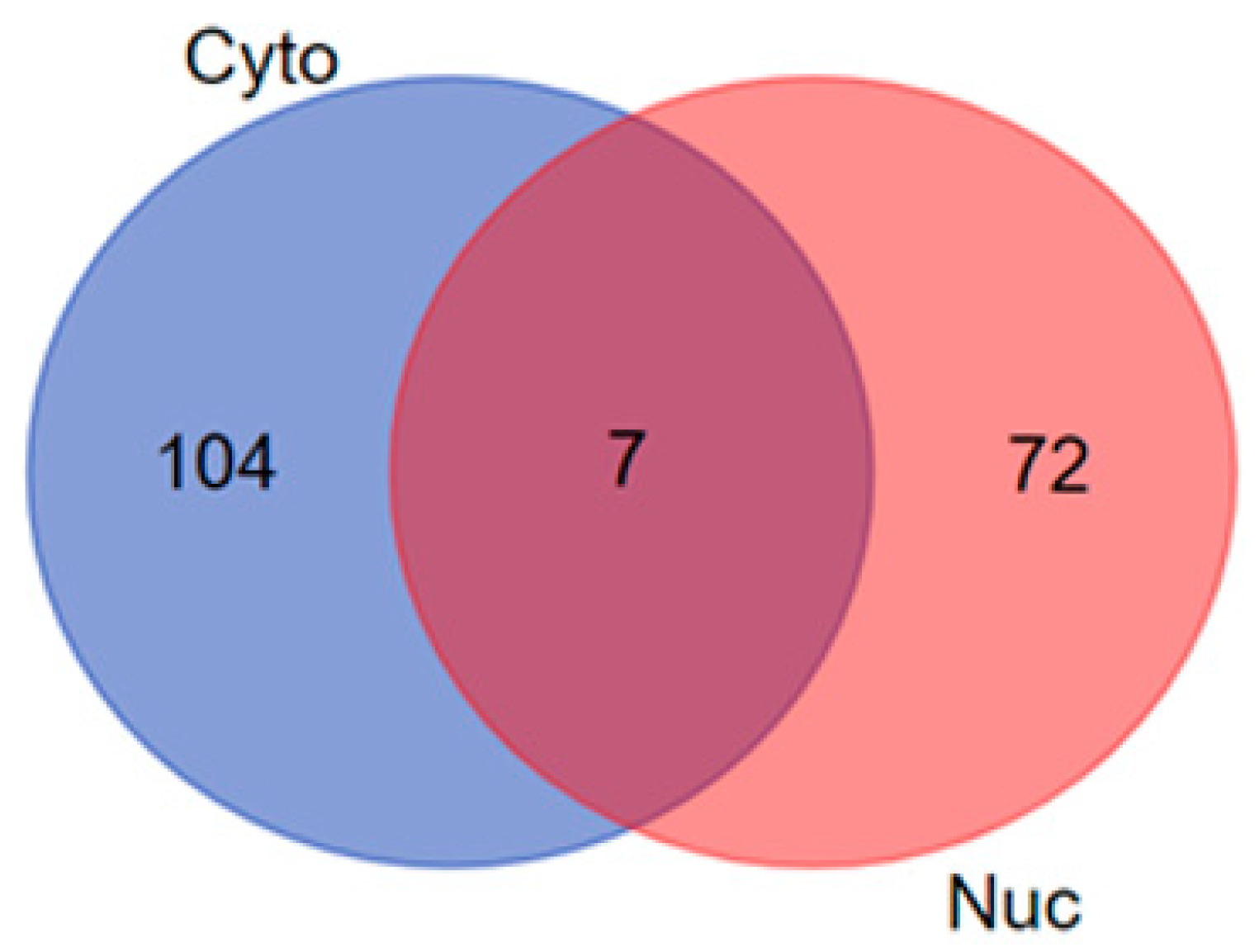
3.2. Venn Diagram Analysis
3.3. Functional Annotation and Pathway Enrichment of Differentially Expressed Proteins of Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Compartment
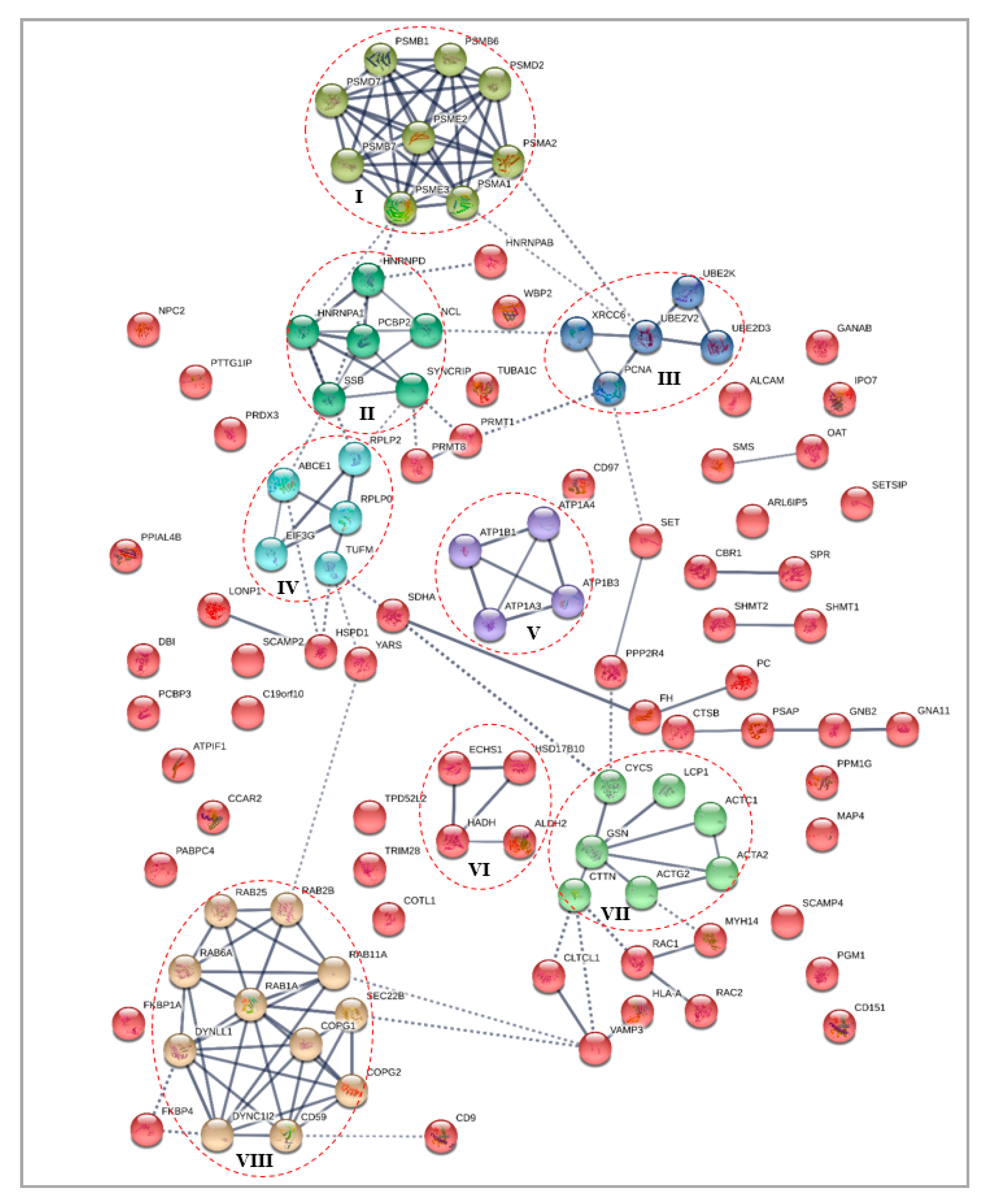
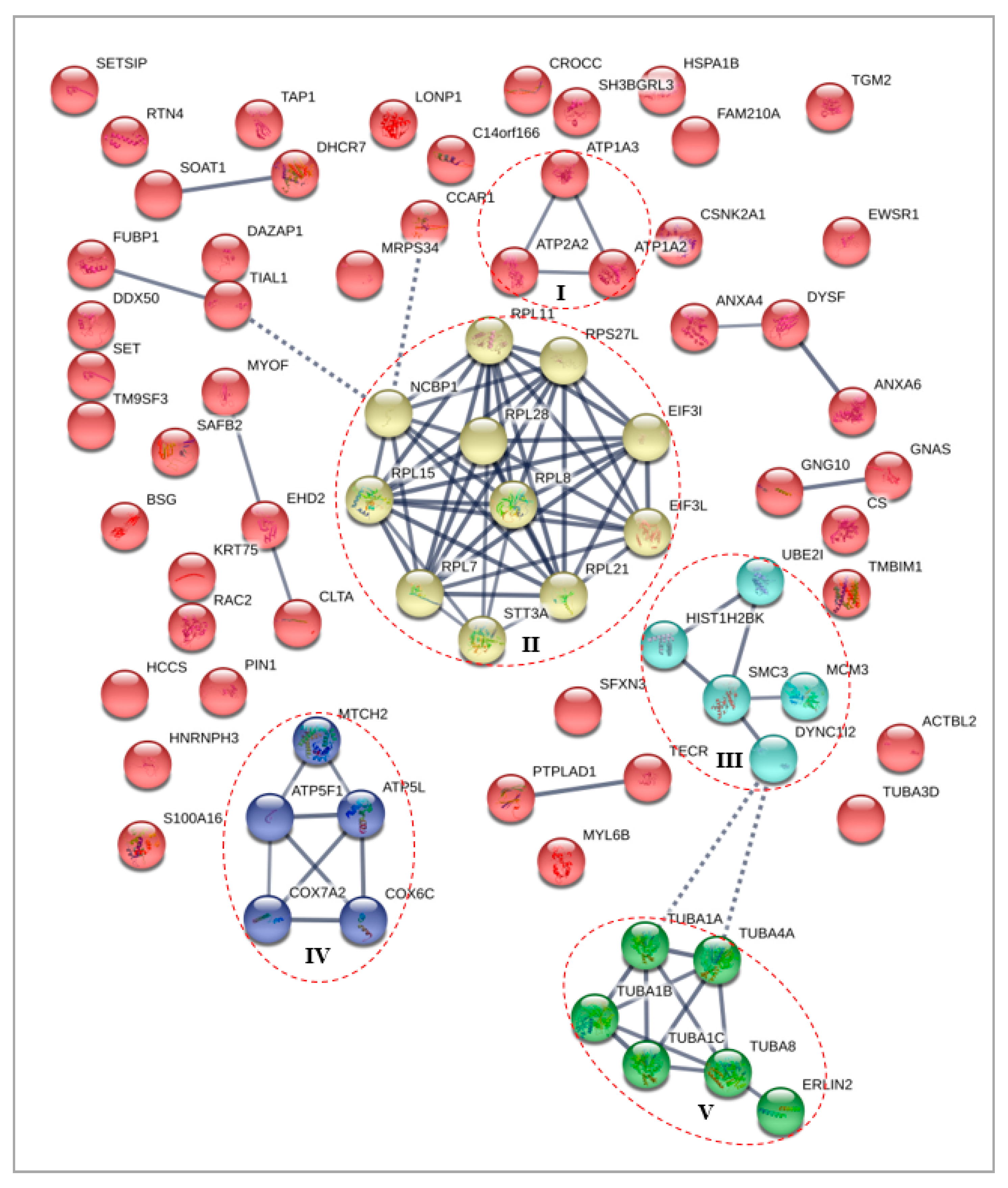
3.4. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
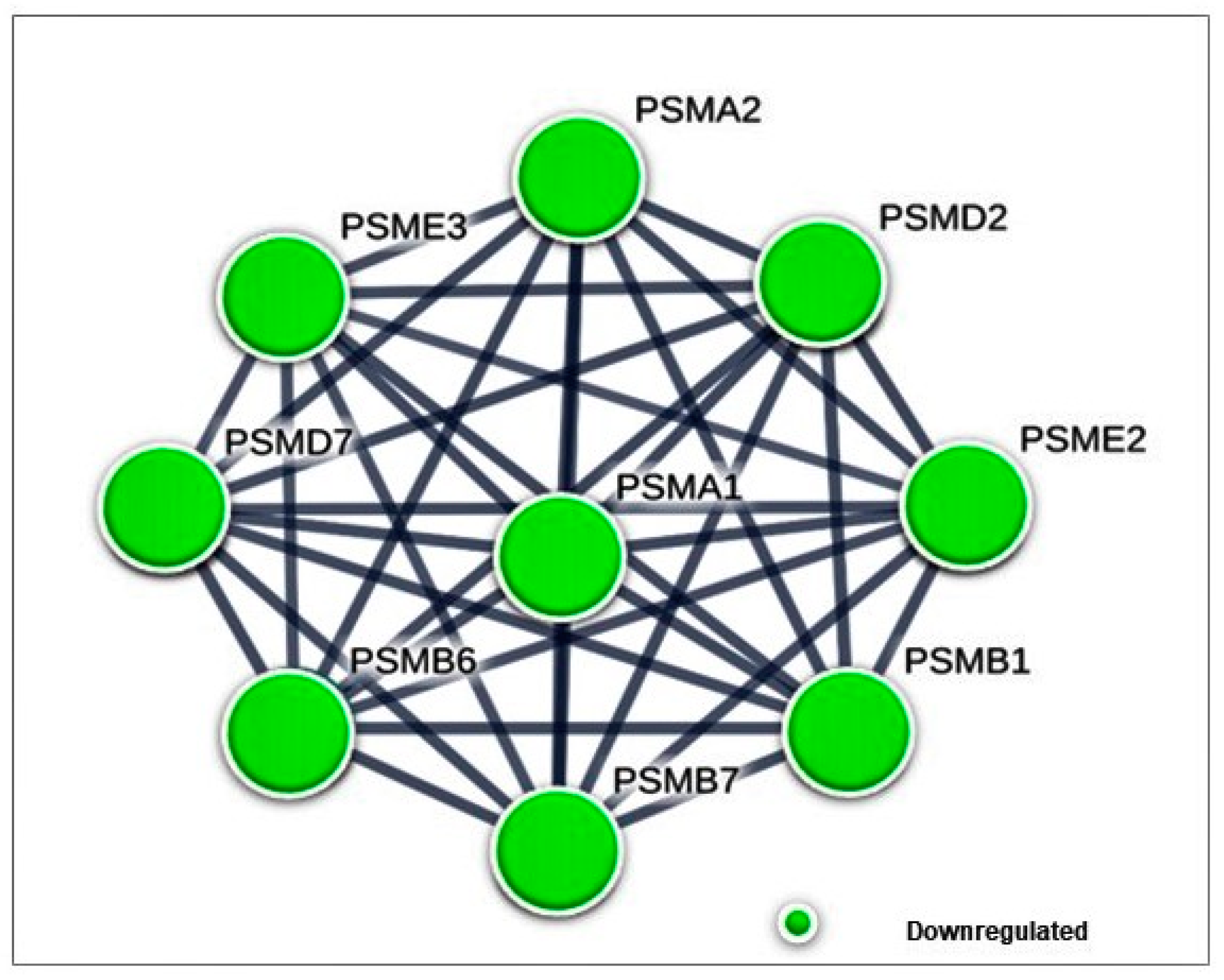
3.4.1. Differentially Expressed Cytoplasmic Proteins STRING Analysis
3.4.2. Differentially Expressed Nuclear Proteins STRING Analysis
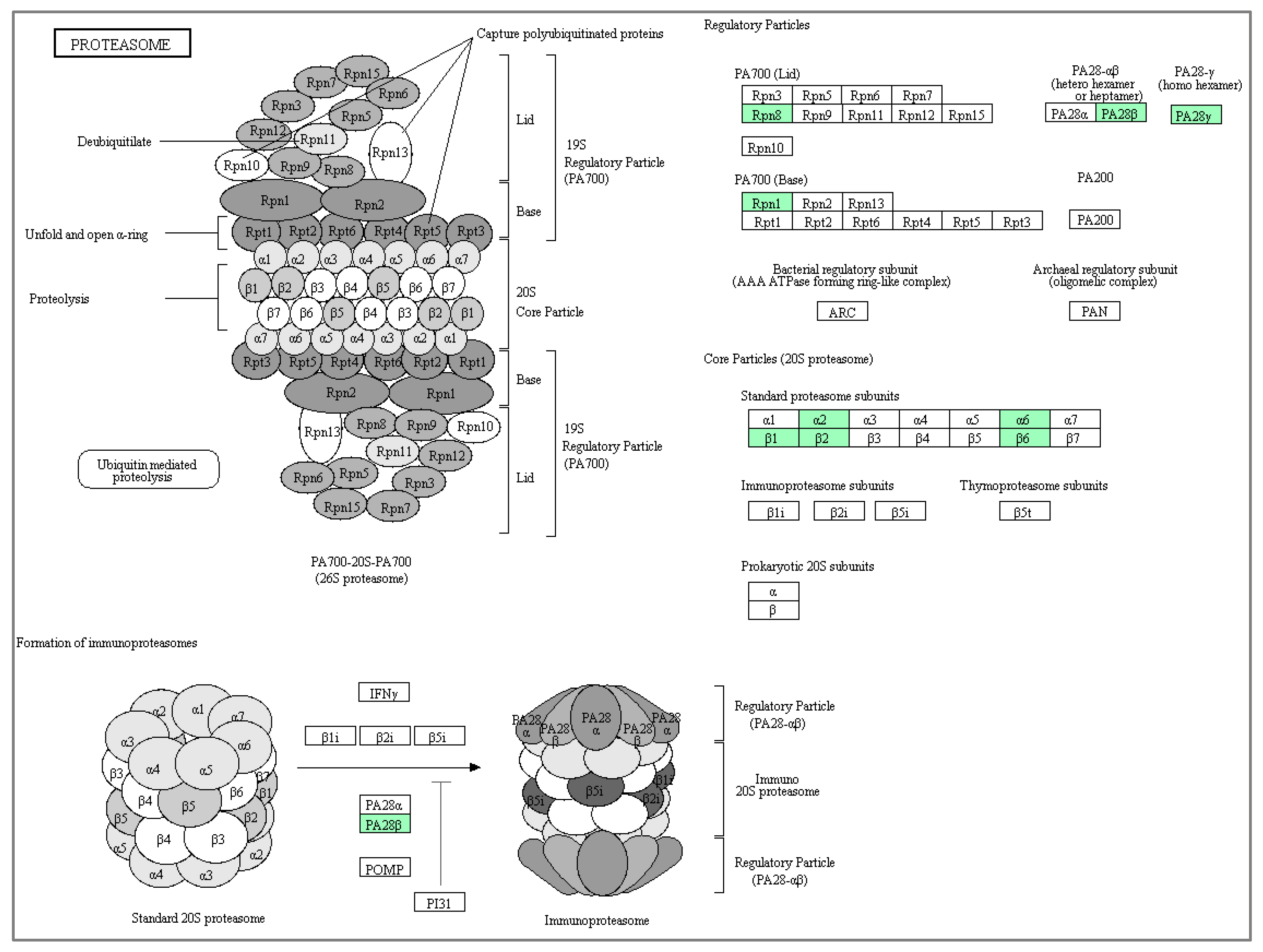
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McLaughlin, S.A. Surgical management of the breast: Breast conservation therapy and mastectomy. Surg. Clin. 2013, 93, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleeland, C.S.; Allen, J.D.; Roberts, S.A.; Brell, J.M.; Giralt, S.A.; Khakoo, A.Y.; Kirch, R.A.; Kwitkowski, V.E.; Liao, Z.; Skillings, J. Reducing the toxicity of cancer therapy: Recognizing needs, taking action. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.B. Triple-negative breast cancers: An updated review on treatment options. Curr. Oncol. 2011, 18, e173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dantzer, R.; Meagher, M.W.; Cleeland, C.S. Translational approaches to treatment-induced symptoms in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yap, W.N.; Chang, P.N.; Han, H.Y.; Lee, D.T.W.; Ling, M.T.; Wong, Y.C.; Yap, Y.L. Gamma-tocotrienol suppresses prostate cancer cell proliferation and invasion through multiple-signalling pathways. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 1832–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, W.N.; Zaiden, N.; Tan, Y.L.; Ngoh, C.P.; Zhang, X.W.; Wong, Y.C.; Ling, M.T.; Yap, Y.L. Id1, inhibitor of differentiation, is a key protein mediating anti-tumor responses of gamma-tocotrienol in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2010, 291, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sznarkowska, A.; Kostecka, A.; Meller, K.; Bielawski, K.P. Inhibition of cancer antioxidant defense by natural compounds. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 15996–16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kannappan, R.; Gupta, S.C.; Kim, J.H.; Aggarwal, B.B. Tocotrienols fight cancer by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways. Genes Nutr. 2012, 7, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Nedelsky, N.B.; Todd, P.K.; Taylor, J.P. Autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system: Collaborators in neuroprotection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2008, 1782, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narayanan, S.; Cai, C.-Y.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Guo, H.-Q.; Cui, Q.; Wei, L.; Huang, J.-J.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S. Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to overcome anti-cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updat. 2020, 48, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Landis-Piwowar, K.R.; Chen, D.; Milacic, V.; Dou, Q.P. Natural compounds with proteasome inhibitory activity for cancer prevention and treatment. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2008, 9, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramdas, P.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Abdu Sani, A.A.; Abdul-Rahman, P.S. Tocotrienols Modulate Breast Cancer Secretomes and Affect Cancer-Signaling Pathways in MDA-MB-231 Cells: A Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ay, C. Nuclear Extraction Kit. Culture 2003, 6642, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Draw Venn Diagram. Available online: http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/ (accessed on 27 November 2019).
- Dennis, G.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; Imamichi, T.; Stephens, R.; Lempicki, R.A. Extracting Biological Meaning from Large Gene Lists with DAVID. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2009, 27, 13.11.1–13.11.13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Available online: https://www.genome.jp/kegg/ (accessed on 27 November 2019).
- STRING: Functional Protein Association Networks. Available online: https://string-db.org/ (accessed on 27 November 2019).
- Manasanch, E.E.; Orlowski, R.Z. Proteasome inhibitors in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Madura, K. Increased proteasome activity, ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes, and eEF1A translation factor detected in breast cancer tissue. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 5599–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J. The proteasome: Structure, function, and role in the cell. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, P.; Tan, J.; Wang, X.; Xiang, T.; Ren, G. miR-7-5p suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells mainly by targeting REGγ. Cancer Lett. 2015, 358, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, Z.; Yang, D.; Liao, X.; Guo, F.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. PSME3 induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition with inducing the expression of CSC markers and immunosuppression in breast cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tu, S.; Tan, J.; Tian, T.; Ran, L.; Rodier, J.-F.; Ren, G. REG gamma: A potential marker in breast cancer and effect on cell cycle and proliferation of breast cancer cell. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, F.; Liang, Y.; Bi, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Y.; Bian, X.; Jiang, J. High expression of REGγ is associated with metastasis and poor prognosis of patients with breast cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7834–7843. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Huang, J.; Zeng, B.; Yang, D.; Sun, J.; Yin, X.; Lu, M.; Qiu, Z.; Peng, W.; Xiang, T.; et al. PSMD2 regulates breast cancer cell proliferation and cell cycle progression by modulating p21 and p27 proteasomal degradation. Cancer Lett. 2018, 430, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhou, H.; Xiong, R.; Lu, Y.; Yan, D.; Xing, T.; Dong, L.; Tang, E.; Yang, H. Over-expression of genes and proteins of ubiquitin specific peptidases (USPs) and proteasome subunits (PSs) in breast cancer tissue observed by the methods of RFDD-PCR and proteomics. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2007, 104, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouette, A.; Trofimov, A.; Haberl, D.; Boucher, G.; Lavallée, V.-P.; D’Angelo, G.; Hébert, J.; Sauvageau, G.; Lemieux, S.; Perreault, C. Expression of immunoproteasome genes is regulated by cell-intrinsic and –extrinsic factors in human cancers. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rho, J.; Qin, S.; Wang, J.Y.; Roehrl, M.H.A. Proteomic Expression Analysis of Surgical Human Colorectal Cancer Tissues: Up-Regulation of PSB7, PRDX1, and SRP9 and Hypoxic Adaptation in Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 2959–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Pan, F.; Li, S.; Huang, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liao, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, L. The prognostic value of the proteasome activator subunit gene family in skin cutaneous melanoma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francia, G.; Mitchell, S.D.; Moss, S.E.; Hanby, A.M.; Marshall, J.F.; Hart, I.R. Identification by differential display of annexin-VI, a gene differentially expressed during melanoma progression. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 3855–3858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Koese, M.; Rentero, C.; Kota, B.P.; Hoque, M.; Cairns, R.; Wood, P.; Vilà de Muga, S.; Reverter, M.; Alvarez-Guaita, A.; Monastyrskaya, K.; et al. Annexin A6 is a scaffold for PKCα to promote EGFR inactivation. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2858–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koumangoye, R.B.; Nangami, G.N.; Thompson, P.D.; Agboto, V.K.; Ochieng, J.; Sakwe, A.M. Reduced annexin A6 expression promotes the degradation of activated epidermal growth factor receptor and sensitizes invasive breast cancer cells to EGFR-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Lam, E.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Feng, L.; Lu, H.; Yu, J.; Jin, H. Annexin A6 is down-regulated through promoter methylation in gastric cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2013, 5, 555–562. [Google Scholar]
- Keklikoglou, I.; Cianciaruso, C.; Güç, E.; Squadrito, M.L.; Spring, L.M.; Tazzyman, S.; Lambein, L.; Poissonnier, A.; Ferraro, G.B.; Baer, C.; et al. Chemotherapy elicits pro-metastatic extracellular vesicles in breast cancer models. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 190–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Widatalla, S.E.; Korolkova, O.Y.; Whalen, D.S.; Goodwin, J.S.; Williams, K.P.; Ochieng, J.; Sakwe, A.M. Lapatinib induced Annexin A6 up-regulation as an adaptive response of triple negative breast cancer cells to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Carcinogenesis 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, A.; Abel, F.; Behboudi, A.; Yhr, M.; Mattsson, J.; Svensson, J.H.; Karlsson, P.; Nordling, M. No germline mutations in supposed tumour suppressor genes SAFB1 and SAFB2in familial breast cancer with linkage to 19p. BMC Med. Genet. 2008, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hammerich-Hille, S.; Bardout, V.J.; Hilsenbeck, S.G.; Osborne, C.K.; Oesterreich, S. Low SAFB levels are associated with worse outcome in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 121, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, F.C.; Teixeira, F.; Reis, I.; Geraldes, N.; Cabrita, A.M.S.; Dias, M.F. Increased transglutaminase 2 and GLUT-1 expression in breast tumors not susceptible to chemoprevention with antioxidants. Tumori 2009, 95, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Lee, S.-H.; Cheong, H.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.-Y. Transglutaminase 2 Promotes Autophagy by LC3 Induction through p53 Depletion in Cancer Cell. Biomol. Ther. (Seoul) 2019, 27, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, S.; Moon, Y.; Choi, J.; Yoon, S.; Jung, K.H.; Cheon, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.H.; Kim, S.-W.; et al. The GTP binding activity of transglutaminase 2 promotes bone metastasis of breast cancer cells by downregulating microRNA-205. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Chai, N.; Tian, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Tian, Z.; Yi, X.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; et al. Novel peptide GX1 inhibits angiogenesis by specifically binding to transglutaminase-2 in the tumorous endothelial cells of gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Varambally, S.; Creighton, C.J. Molecular Correlates of Metastasis by Systematic Pan-Cancer Analysis Across The Cancer Genome Atlas. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Ichikawa-Tomikawa, N.; Shishito, N.; Nishiura, K.; Miura, T.; Hozumi, A.; Chiba, H.; Yoshida, S.; Ohtake, T.; Sugino, T. Co-expression of S100A14 and S100A16 correlates with a poor prognosis in human breast cancer and promotes cancer cell invasion. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Zhu, X.; Li, A.; Yang, S.; Qiao, R.; Zhang, J. S100A16 regulated by Snail promotes the chemoresistance of nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer through the AKT/Bcl-2 pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 2449–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C.; Ning, K.; Guan, Z.-R.; Chen, S.-X.; Hong, T.-T.; Hua, D. S100A16 is a prognostic marker for colorectal cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 117, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Xue, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Su, D.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; et al. S100A16 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis via AKT and ERK cell signaling pathways in human prostate cancer. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 12241–12250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomiyama, N.; Ikeda, R.; Nishizawa, Y.; Masuda, S.; Tajitsu, Y.; Takeda, Y. S100A16 up-regulates Oct4 and Nanog expression in cancer stem-like cells of Yumoto human cervical carcinoma cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9929–9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| (A) Up-Regulated Cytoplasmic Proteins | |||
| Accession | Protein Description | Gene Symbol | * Fold-Change |
| P10809 | 60 kDa heat shock protein, mitochondrial protein | HSPD1 | 1.45 |
| Q9BQE3 | Tubulin alpha-1C chain | TUBA1C | 2.98 |
| P68032 | Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 | ACTC1 | 1.81 |
| P63267 | Actin, gamma-enteric smooth muscle | ACTG2 | 1.81 |
| P62736 | Actin, aortic smooth muscle | ACTA2 | 1.81 |
| P62820 | Ras-related protein Rab-1A | RAB1A | 1.71 |
| P30048 | Thioredoxin-dependent peroxide reductase | PRDX3 | 1.64 |
| P30084 | Enoyl-CoA hydratase, mitochondrial | ECHS1 | 2.15 |
| P34897 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, mitochondrial | SHMT2 | 1.36 |
| Q99714 | 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase type-2 | HSD17B10 | 1.42 |
| P48960 | CD97 antigen | CD97 | 1.36 |
| P13637 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit α-3 | ATP1A3 | 1.2 |
| P62879 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(T) subunit beta-2 | GNB2 | 2.16 |
| P04181 | Ornithine aminotransferase, mitochondrial | OAT | 2.47 |
| P36776 | Lon protease homolog, mitochondrial | LONP1 | 1.45 |
| P05091 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | ALDH2 | 1.97 |
| Q15366 | Poly(rC)-binding protein 2 | PCBP2 | 2.13 |
| Q14697 | Neutral alpha-glucosidase AB | GANAB | 2.27 |
| P16152 | Carbonyl reductase [NADPH] 1 | CBR1 | 1.43 |
| P06396 | Gelsolin | GSN | 1.18 |
| P07954 | Fumarate hydratase, mitochondrial | FH | 1.46 |
| P31040 | Succinate dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein subunit | SDHA | 1.49 |
| P11498 | Pyruvate carboxylase, mitochondrial | PC | 1.12 |
| P07602 | Prosaposin | PSAP | 1.85 |
| P49411 | Elongation factor Tu, mitochondrial | TUFM | 1.7 |
| Q09160 | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen | HLA-A | 3.62 |
| P62942 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | FKBP1A | 3.02 |
| Q13733 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit α-4 | ATP1A4 | 2.58 |
| P04439 | HLA class I histocompatibility antigen | HLA-A | 3.36 |
| O43399 | Tumor protein D54 | TPD52L2 | 1.68 |
| O75396 | Vesicle-trafficking protein SEC22b | SEC22B | 1.12 |
| Q8WUD1 | Ras-related protein Rab-2B | RAB2B | 2.17 |
| P57721 | Poly(rC)-binding protein 3 | PCBP3 | 2.31 |
| Q14247 | Src substrate cortactin | CTTN | 1.61 |
| P20340 | Ras-related protein Rab-6A | RAB6A | 1.92 |
| Q15836 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 3 | VAMP3 | 2.19 |
| Q7Z406 | Myosin-14 | MYH14 | 2.33 |
| P21926 | CD9 antigen | CD9 | 3.74 |
| P05026 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit β-1 | ATP1B1 | 1.74 |
| Q14019 | Coactosin-like protein | COTL1 | 3.35 |
| P62491 | Ras-related protein Rab-11A | RAB11A | 3.44 |
| Q13740 | CD166 antigen | ALCAM | 1.26 |
| P63000 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 | RAC1 | 1.62 |
| P15153 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2 | RAC2 | 2.41 |
| P53801 | Pituitary tumor-transforming gene 1 protein-interacting protein | PTTG1IP | 3.76 |
| Q9Y536 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase A-like 4A | PPIAL4A | 1.15 |
| P61916 | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2 | NPC2 | 2.8 |
| P54709 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit β-3 | ATP1B3 | 2.65 |
| Q969H8 | Myeloid-derived growth factor | MYDGF | 2.75 |
| P63167 | Dynein light chain 1, cytoplasmic | DYNLL1 | 1.85 |
| O15127 | Secretory carrier-associated membrane protein 2 | SCAMP2 | 1.78 |
| Q15819 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 variant 2 | UBE2V2 | 1.72 |
| P13987 | CD59 glycoprotein | CD59 | 1.84 |
| P07108 | Acyl-CoA-binding protein | DBI | 2.14 |
| Q5JXB2 | Putative ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 N-like | UBE2NL | 1.96 |
| P34896 | Serine hydroxymethyltransferase, cytosolic | SHMT1 | 2.59 |
| Q969E2 | Secretory carrier-associated membrane protein 4 | SCAMP4 | 1.68 |
| P48509 | CD151 antigen | CD151 | 1.78 |
| P57735 | Ras-related protein Rab-25 | RAB25 | 2.33 |
| P99999 | Cytochrome c | CYCS | 1.79 |
| (B) Down-Regulated Cytoplasmic Proteins | |||
| Accession | Protein Description | Gene Symbol | * Fold-Change |
| Q99873 | Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 1 | PRMT1 | -1.23 |
| P12956 | X-ray repair cross-complementing protein 6 | XRCC6 | -1.57 |
| Q01105 | Protein SET | SET | -1.62 |
| P12004 | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen | PCNA | -1.46 |
| P19338 | Nucleolin | NCL | -1.51 |
| Q13200 | 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 2 | PSMD2 | -1.08 |
| Q9Y678 | Coatomer subunit gamma-1 | COPG1 | -2.17 |
| Q9UL46 | Proteasome activator complex subunit 2 | PSME2 | -1.63 |
| Q13263 | Transcription intermediary factor 1-β | TRIM28 | -1.82 |
| P05387 | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P2 | RPLP2 | -1.06 |
| P20618 | Proteasome subunit beta type-1 | PSMB1 | -1.02 |
| P25787 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-2 | PSMA2 | -2.04 |
| P05455 | Lupus La protein | SSB | -1.65 |
| P05388 | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P0 | RPLP0 | -1.46 |
| P0DME0 | Protein SETSIP | SETSIP | -1.49 |
| P36871 | Phosphoglucomutase-1 | PGM1 | -2.65 |
| Q16836 | Hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | HADH | -1.55 |
| Q8NHW5 | 60S acidic ribosomal protein P0-like | RPLP0P6 | -1.43 |
| Q02790 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase | FKBP4 | -2.2 |
| P35270 | Sepiapterin reductase | SPR | -2.13 |
| P25786 | Proteasome subunit alpha type-1 | PSMA1 | -1.23 |
| Q8N163 | Cell cycle and apoptosis regulator protein 2 | CCAR2 | -2.38 |
| P13796 | Plastin-2 | LCP1 | -4.72 |
| P27816 | Microtubule-associated protein 4 | MAP4 | -1.21 |
| P52788 | Spermine synthase | SMS | -1.8 |
| P61289 | Proteasome activator complex subunit 3 | PSME3 | -3.47 |
| P61077 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D3 | UBE2D3 | -2.15 |
| Q14103 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein D0 | HNRNPD | -1.64 |
| Q99436 | Proteasome subunit beta type-7 | PSMB7 | -3.68 |
| P53675 | Clathrin heavy chain 2 | CLTCL1 | -2.3 |
| Q13310 | Polyadenylate-binding protein 4 | PABPC4 | -1.39 |
| P54577 | Tyrosine-tRNA ligase, cytoplasmic | YARS | -2.15 |
| Q15257 | Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A activator | PTPA | -3.18 |
| O60506 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein Q | SYNCRIP | -1.69 |
| O75915 | PRA1 family protein 3 | ARL6IP5 | -3.35 |
| O95373 | Importin-7 | IPO7 | -2.37 |
| P51665 | 26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 7 | PSMD7 | -1.22 |
| Q99729 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B | HNRNPAB | -1.48 |
| O15355 | Protein phosphatase 1G | PPM1G | -3.2 |
| P28072 | Proteasome subunit beta type-6 | PSMB6 | -1.31 |
| P29992 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein subunit alpha-11 | GNA11 | -2.59 |
| Q9UBF2 | Coatomer subunit gamma-2 | COPG2 | -2.84 |
| O75821 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit G | EIF3G | -2.04 |
| P61086 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K | UBE2K | -2.08 |
| P09651 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 | HNRNPA1 | -1.52 |
| O14602 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 1A | EIF1AY | -1.42 |
| P61221 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family E member 1 | ABCE1 | -2.82 |
| Q13409 | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 2 | DYNC1I2 | -2.05 |
| Q9UII2 | ATPase inhibitor, mitochondrial | ATP5IF1 | -3.86 |
| Q969T9 | WW domain-binding protein 2 | WBP2 | -1.7 |
| Q9NR22 | Protein arginine N-methyltransferase 8 | PRMT8 | -1.57 |
| P07858 | Cathepsin B | CTSB | -1.76 |
| (A) Upregulated Nuclear Proteins | |||
| Accession | Protein Description | Gene Symbol | * Fold-change |
| P08133 | Annexin A6 | ANXA6 | 2.24 |
| Q9NZM1 | Myoferlin | MYOF | 1.08 |
| Q562R1 | Beta-actin-like protein 2 | ACTBL2 | 7.96 |
| P16615 | Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 | ATP2A2 | 1.2 |
| P68363 | Tubulin alpha-1B chain | TUBA1B | 3.83 |
| Q9BQE3 | Tubulin alpha-1C chain | TUBA1C | 2.37 |
| Q71U36 | Tubulin alpha-1A chain | TUBA1A | 2.82 |
| P09525 | Annexin A4 | ANXA4 | 2.31 |
| P68366 | Tubulin alpha-4A chain | TUBA4A | 2.43 |
| Q13748 | Tubulin alpha-3C/D chain | TUBA3C | 1.79 |
| P46977 | Dolichyl-diphosphooligosaccharide-protein glycosyltransferase subunit STT3A | STT3A | 2.44 |
| P35610 | Sterol O-acyltransferase 1 | SOAT1 | 2.79 |
| O94905 | Erlin-2 | ERLIN2 | 1.25 |
| Q9NY65 | Tubulin alpha-8 chain | TUBA8 | 1.2 |
| P50993 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-2 | ATP1A2 | 1.74 |
| P13637 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-3 | ATP1A3 | 1.6 |
| Q9Y6C9 | Mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 | MTCH2 | 1.33 |
| Q9BWM7 | Sideroflexin-3 | SFXN3 | 1.17 |
| Q9P035 | Very-long-chain (3R)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase 3 | HACD3 | 2.34 |
| Q5JWF2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(s) subunit alpha isoforms XLas | GNAS | 2.31 |
| Q14151 | Scaffold attachment factor B2 | SAFB2 | 3.14 |
| Q9NZ01 | Very-long-chain enoyl-CoA reductase | TECR | 2.12 |
| Q9HD45 | Transmembrane 9 superfamily member 3 | TM9SF3 | 2.38 |
| Q9NQC3 | Reticulon-4 | RTN4 | 2.81 |
| P14406 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A2, mitochondrial | COX7A2 | 4.23 |
| P18124 | 60S ribosomal protein L7 | RPL7 | 3.08 |
| P62917 | 60S ribosomal protein L8 | RPL8 | 3.71 |
| P46778 | 60S ribosomal protein L21 | RPL21 | 3.6 |
| P15153 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 2 | RAC2 | 2.78 |
| P50151 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-10 | GNG10 | 1.52 |
| P22090 | 40S ribosomal protein S4, Y isoform 1 | RPS4Y1 | 2.29 |
| P62913 | 60S ribosomal protein L11 | RPL11 | 3.31 |
| Q9UBM7 | 7-dehydrocholesterol reductase | DHCR7 | 2.51 |
| Q9BQ39 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX50 | DDX50 | 2.11 |
| P35613 | Basigin | BSG | 1.28 |
| Q9H299 | SH3 domain-binding glutamic acid-rich-like protein 3 | SH3BGRL3 | 1.62 |
| P09669 | Cytochrome c oxidase subunit 6C | COX6C | 4.24 |
| P46779 | 60S ribosomal protein L28 | RPL28 | 1.39 |
| P09496 | Clathrin light chain A | CLTA | 2.84 |
| Q5TZA2 | Rootletin | CROCC | 3.44 |
| Q13409 | Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 2 | DYNC1I2 | 1.47 |
| Q13526 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase NIMA-interacting 1 | PIN1 | 1.25 |
| Q969 × 1 | Protein lifeguard 3 | TMBIM1 | 1.14 |
| Q8TD47 | 40S ribosomal protein S4, Y isoform 2 | RPS4Y2 | 2.3 |
| O75964 | ATP synthase subunit g, mitochondrial | ATP5L | 2 |
| P61313 | 60S ribosomal protein L15 | RPL15 | 3.87 |
| Q6NVV1 | Putative 60S ribosomal protein L13a protein RPL13AP3 | RPL13AP3 | 3.53 |
| P14649 | Myosin light chain 6B | MYL6B | 2.51 |
| Q96EP5 | DAZ-associated protein 1 | DAZAP1 | 3.1 |
| Q71UM5 | 40S ribosomal protein S27-like | RPS27L | 3.3 |
| O95678 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 75 | KRT75 | 1.78 |
| P24539 | ATP synthase F(0) complex subunit B1, mitochondrial | ATP5F1 | 2.78 |
| (B) Down-Regulated Nuclear Proteins | |||
| Accession | Protein Description | Gene Symbol | * Fold-change |
| P31942 | Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H3 | HNRNPH3 | -1.03 |
| Q09161 | Nuclear cap-binding protein subunit 1 | NCBP1 | -1.62 |
| Q9NZN4 | EH domain-containing protein 2 | EHD2 | -1.06 |
| Q9Y262 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit L | EIF3L | -1.21 |
| Q01105 | Protein SET | SET | -1.36 |
| P0DMV9 | Heat shock 70 kDa protein 1B | HSPA1B | -1.89 |
| Q9Y224 | UPF0568 protein C14orf166 | RTRAF | -1.09 |
| O75390 | Citrate synthase, mitochondrial | CS | -1.73 |
| Q01844 | RNA-binding protein EWS | EWSR1 | -1.29 |
| P68400 | Casein kinase II subunit alpha | CSNK2A1 | -1.23 |
| P36776 | Lon protease homolog, mitochondrial | LONP1 | -1.44 |
| Q13347 | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit I | EIF3I | -1.32 |
| Q96AE4 | Far upstream element-binding protein 1 | FUBP1 | -1.29 |
| P0DME0 | Protein SETSIP | SETSIP | -1.45 |
| Q9UQE7 | Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 3 | SMC3 | -1.11 |
| P63279 | SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 | UBE2I | -2.08 |
| Q96FQ6 | Protein S100-A16 | S100A16 | -1.06 |
| P25205 | DNA replication licensing factor MCM3 | MCM3 | -1.51 |
| Q03518 | Antigen peptide transporter 1 | TAP1 | -1.81 |
| Q8IX12 | Cell division cycle and apoptosis regulator protein 1 | CCAR1 | -1.38 |
| P53701 | Cytochrome c-type heme lyase | HCCS | -1.82 |
| P82930 | 28S ribosomal protein S34, mitochondrial | MRPS34 | -1.28 |
| O60814 | Histone H2B type 1-K | HIST1H2BK | -1.88 |
| Q01085 | Nucleolysin TIAR | TIAL1 | -1.89 |
| O75923 | Dysferlin | DYSF | -1.23 |
| Q96ND0 | Protein FAM210A | FAM210A | -3.82 |
| M2P21980 | Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase 2 | TGM2 | -1.54 |
| Compartment | Total | Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Cytoplasmic and Nuclear | 7 | ATP1A3, TUBA1C, LONP1, DYNC1I2, SET, RAC2 and SETSIP |
| Cytoplasmic Proteins | 104 | SMS, HSPD1, PSMA2, PSMB1, MAP4, CCAR2, FH, PRMT1, UBE2V2, DBI, ACTA2, CLTCL1, ATP1A4, ECHS1, CD151, PTTG1IP, CD9, PSMB6, HSD17B10, PPIAL4A, COPG1, RAC1, UBE2NL, ALCAM, ACTG2, EIF1AY, CYCS, PABPC4, SSB, HADH, ARL6IP5, CTSB, UBE2K, PRDX3, PSME3, COPG2, XRCC6, DYNLL1, RAB25, GANAB, PCBP3, HNRNPD, RPLP0, PSME2, SEC22B, HNRNPAB, YARS, COTL1, RPLP0P6, GSN, SYNCRIP, MYH14, TUFM, PTPA, IPO7, TPD52L2, GNA11, RAB11A, CD59, PRMT8, GNB2, PGM1, ACTC1, ATP1B3, RPLP2, PSAP, SPR, PCNA, MYDGF, ABCE1, HLA-A, WBP2, LCP1, SCAMP4, PSMA1, NCL, PC, HNRNPA1, SCAMP2, VAMP3, ATP5IF1, FKBP1A, CTTN, EIF3G, PSMB7, SHMT1, PPM1G, RAB1A, TRIM28, UBE2D3, SHMT2, PSMD7, SDHA, FKBP4, RAB2B, PCBP2, NPC2, RAB6A, CD97, PSMD2, CBR1, ALDH2, ATP1B1 and OAT |
| Nuclear Proteins | 72 | RPL13AP3, PIN1, CCAR1, STT3A, MCM3, EIF3I, RTN4, ACTBL2, ATP5F1, MYL6B, TM9SF3, ANXA6, TUBA4A, EWSR1, DAZAP1, ERLIN2, RTRAF, RPL28, RPL7, MYOF, SH3BGRL3, DHCR7, GNG10, TMBIM1, RPS27L, COX6C, ANXA4, TUBA3C, RPS4Y1, ATP2A2, MTCH2, TUBA1A, S100A16, HSPA1B, TAP1, NCBP1, COX7A2, CS, ATP5L, ATP1A2, SOAT1, CROCC, CSNK2A1, TGM2, HNRNPH3, TECR, RPL21, HACD3, CLTA, SMC3, RPL11, SFXN3, RPL8, DDX50, MRPS34, EHD2, GNAS, EIF3L, DYSF, TUBA8, FUBP1, HIST1H2BK, FAM210A, TUBA1B, KRT75, HCCS, UBE2I, BSG, SAFB2, TIAL1, RPS4Y2 and RPL15 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramdas, P.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Abdu Sani, A.A.; Kumari, M.; Anandha Rao, J.S.; Abdul-Rahman, P.S. Advancing the Role of Gamma-Tocotrienol as Proteasomes Inhibitor: A Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010019
Ramdas P, Radhakrishnan AK, Abdu Sani AA, Kumari M, Anandha Rao JS, Abdul-Rahman PS. Advancing the Role of Gamma-Tocotrienol as Proteasomes Inhibitor: A Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamdas, Premdass, Ammu Kutty Radhakrishnan, Asmahani Azira Abdu Sani, Mangala Kumari, Jeya Seela Anandha Rao, and Puteri Shafinaz Abdul-Rahman. 2020. "Advancing the Role of Gamma-Tocotrienol as Proteasomes Inhibitor: A Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells" Biomolecules 10, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010019
APA StyleRamdas, P., Radhakrishnan, A. K., Abdu Sani, A. A., Kumari, M., Anandha Rao, J. S., & Abdul-Rahman, P. S. (2020). Advancing the Role of Gamma-Tocotrienol as Proteasomes Inhibitor: A Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomolecules, 10(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10010019





