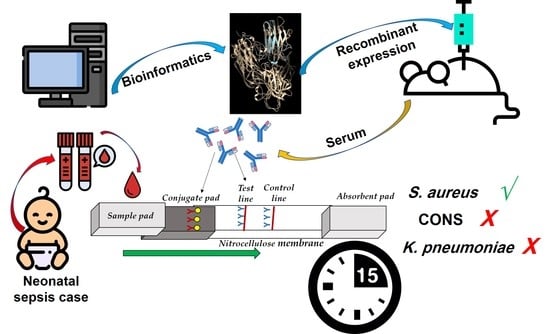
A Novel Surface-Exposed Polypeptide Is Successfully Employed as a Target for Developing a Prototype One-Step Immunochromatographic Strip for Specific and Sensitive Direct Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Neonatal Sepsis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Statement of Ethical Approval
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
2.3. Screening for Potential Targets for Development of Immunochromatographic Strip
2.3.1. Bioinformatics Analyses of the S. aureus Proteome to Identify Potential Targets
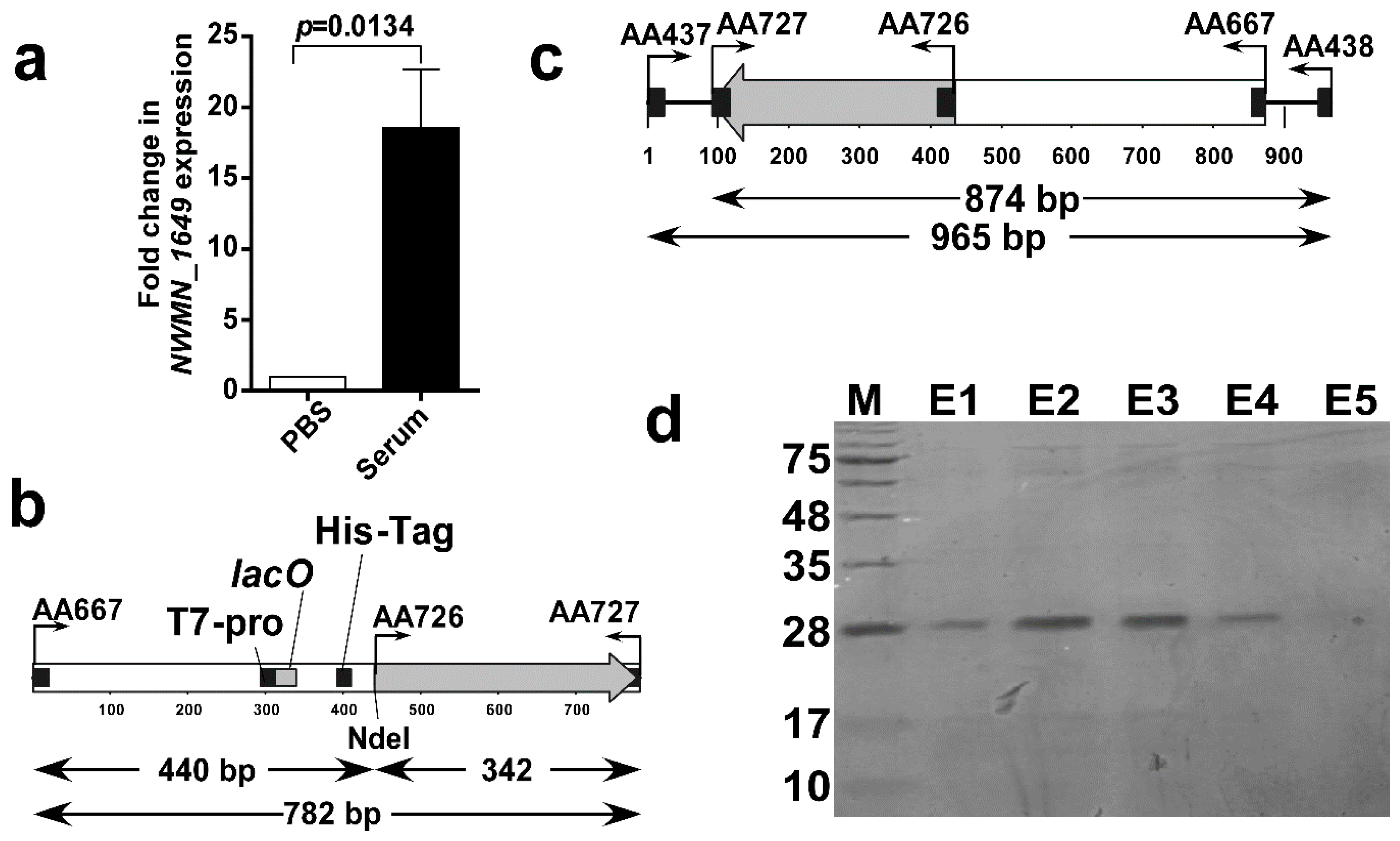
2.3.2. In Vitro Assessment of the Expression of the Selected Protein Using Real-Time RT-PCR
2.4. Cloning, Expression and Purification of Recombinant NWMN_1649 Polypeptide
2.5. Development of an Immunochromatographic Strip(ICS)
2.5.1. Animal Immunization and Production of Immunoglobulins
2.5.2. Specificity Evaluation of the Produced Antibodies using Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.5.3. Synthesis and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles (GNPs)
2.5.4. Preparation of GNP-Antibody Conjugate and Assembly of ICS
2.5.5. Testing the Sensitivity and Specificity of the Constructed ICS
2.6. Assessment of the Developed ICS Using Clinical Specimens Obtained from Neonatal Sepsis Patients
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Identification of Potential Targets for ICS
3.2. Successful Cloning, Expression, and Purification of NWMN_1649 (46–157) Polypeptide
3.3. Assessment of the Obtained Anti-Sera and Construction of the ICS
3.4. The Developed ICS Specifically Detects S. aureus in Neonatal Sepsis Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oestergaard, M.Z.; Inoue, M.; Yoshida, S.; Mahanani, W.R.; Gore, F.M.; Cousens, S.; Lawn, J.E.; Mathers, C.D.; United Nations Inter-Agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation; Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group. Neonatal mortality levels for 193 countries in 2009 with trends since 1990: A systematic analysis of progress, projections, and priorities. PLoS Med. 2011, 8, e1001080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gebremedhin, D.; Berhe, H.; Gebrekirstos, K. Risk Factors for Neonatal Sepsis in Public Hospitals of Mekelle City, North Ethiopia, 2015: Unmatched Case Control Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, N.C.; Chen, S.J.; Tang, R.B.; Hwang, B.T. Neonatal bacteremia in a neonatal intensive care unit: Analysis of causative organisms and antimicrobial susceptibility. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2004, 67, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mussap, M.; Molinari, M.P.; Senno, E.; Gritti, P.; Soro, B.; Mannelli, S.; Fabris, C. New diagnostic tools for neonatal sepsis: The role of a real-time polymerase chain reaction for the early detection and identification of bacterial and fungal species in blood samples. J. Chemother. 2007, 19 (Suppl. 2), 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruno, J.G. Application of DNA Aptamers and Quantum Dots to Lateral Flow Test Strips for Detection of Foodborne Pathogens with Improved Sensitivity versus Colloidal Gold. Pathogens 2014, 3, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.; Wang, R.; Gu, X.; Wen, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Q.A.; Xiao, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; et al. Rapid detection of fumonisin B1 using a colloidal gold immunoassay strip test in corn samples. Toxicon 2015, 108, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Shukla, S.; Lee, G.; Kim, M. Immunochromatographic Strip Assay for Detection of Cronobacter sakazakii in Pure Culture. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1855–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Shi, B.; Meng, F.; Ma, R.; Hu, Q.; Qin, T.; Chen, S.; Peng, D.; Liu, X. Development of a Colloidal Gold-Based Immunochromatographic Strip for Rapid Detection of H7N9 Influenza Viruses. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindayna, K.M.; Jamsheer, A.; Farid, E.; Botta, G.A. Neonatal sepsis 1991–2001: Prevalent bacterial agents and antimicrobial susceptibilities in Bahrain. Med. Prin. Pract. 2006, 15, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohammady, M.N.; Eltahlawy, E.M.; Reda, N.M. Pattern of bacterial profile and antibiotic susceptibility among neonatal sepsis cases at Cairo University Children Hospital. J. Taibah Univ. Med Sci. 2020, 15, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishk, R.M.; Mandour, M.F.; Farghaly, R.M.; Ibrahim, A.; Nemr, N.A. Pattern of blood stream infections within neonatal intensive care unit, Suez Canal University hospital, Ismailia, Egypt. Int. J. Microbiol. 2014, 2014, 276873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohammed, D.; El Seifi, O.S. Bacterial nosocomial infections in neonatal intensive care unit, Zagazig University Hospital, Egypt. Gaz. Egypt Paediatr. Assoc. 2014, 62, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Kaur, P.; Aggarwal, A. Staphylococcus aureus- the predominant pathogen in the neonatal ICU of a tertiary care hospital in amritsar, India. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2013, 7, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- G/Eyesus, T.; Moges, F.; Eshetie, S.; Yeshitela, B.; Abate, E. Bacterial etiologic agents causing neonatal sepsis and associated risk factors in Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia. BMC Pediatr. 2017, 17, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, T.; Chen, L.P.; Liu, H.; Xie, S.; Luo, Y.; Wu, D.C. The Analysis of Etiology and Risk Factors for 192 Cases of Neonatal Sepsis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 8617076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duthie, E.S.; Lorenz, L.L. Staphylococcal coagulase; mode of action and antigenicity. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1952, 6, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambrook, J.; Russell, D.W. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 3rd ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Studier, F.W.; Moffatt, B.A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 189, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peabody, M.A.; Laird, M.R.; Vlasschaert, C.; Lo, R.; Brinkman, F.S. PSORTdb: Expanding the bacteria and archaea protein subcellular localization database to better reflect diversity in cell envelope structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D663–D668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Park, Y.M.; Lee, J.; Buso, N.; Gur, T.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Basutkar, P.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Potter, S.C.; Finn, R.D.; et al. The EMBL-EBI search and sequence analysis tools APIs in 2019. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W636–W641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okonechnikov, K.; Golosova, O.; Fursov, M.; Team, U. Unipro UGENE: A unified bioinformatics toolkit. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1166–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Webb, B.; Sali, A. Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2016, 54, 5.6.1–5.6.37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, H. Predicting secretory proteins with SignalP. In Protein Function Prediction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Lu, C.H.; Hwang, J.K. Prediction of protein subcellular localization. Proteins 2006, 64, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, L.; Reményi, I.; Tusnády, G.E. CCTOP: A Consensus Constrained TOPology prediction web server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W408–W412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Elghanam, M.S.; Attia, A.S.; Shoeb, H.A.; Hashem, A.E. Expression and purification of hepatitis B surface antigen S from Escherichia coli; a new simple method. BMC Res. Notes 2012, 5, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, F.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Liang, S.; Li, X.J. High expression level of soluble SARS spike protein mediated by adenovirus in HEK293 cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Sultana, I.; Couzens, L.K.; Mindaye, S.; Eichelberger, M.C. Assessment of influenza A neuraminidase (subtype N1) potency by ELISA. J. Virol. Methods 2017, 244, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabar, K.C.; Brown, K.R.; Keating, C.D.; Stranick, S.J.; Tang, S.L.; Natan, M.J. Nanoscale characterization of gold colloid monolayers: A comparison of four techniques. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailes, J.; Mayoss, S.; Teale, P.; Soloviev, M. Gold nanoparticle antibody conjugates for use in competitive lateral flow assays. In Nanoparticles in Biology and Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 45–55. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, C.; Rautelin, H.; Kaden, R. Staphylococcus argenteus and Staphylococcus schweitzeri are cytotoxic to human cells in vitro due to high expression of alpha-hemolysin Hla. Virulence 2019, 10, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stepanović, S.; Dakić, I.; Morrison, D.; Hauschild, T.; Ježek, P.; Petráš, P.; Martel, A.; Vuković, D.; Shittu, A.; Devriese, L.A. Identification and characterization of clinical isolates of members of the Staphylococcus sciuri group. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekizuka, T.; Niwa, H.; Kinoshita, Y.; Uchida-Fujii, E.; Inamine, Y.; Hashino, M.; Kuroda, M. Identification of a mecA/mecC-positive MRSA ST1-t127 isolate from a racehorse in Japan. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClure, J.A.; Zhang, K. Complete Genome Sequences of Two USA300-Related Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Clinical Isolates. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Shao, F.; Wang, P.; Duan, G.; Yang, H. Analysis of the features of 45 identified CRISPR loci in 32 Staphylococcus aureus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stinear, T.P.; Holt, K.E.; Chua, K.; Stepnell, J.; Tuck, K.L.; Coombs, G.; Harrison, P.F.; Seemann, T.; Howden, B.P. Adaptive change inferred from genomic population analysis of the ST93 epidemic clone of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Genome Biol. Evol. 2014, 6, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howden, B.P.; McEvoy, C.R.; Allen, D.L.; Chua, K.; Gao, W.; Harrison, P.F.; Bell, J.; Coombs, G.; Bennett-Wood, V.; Porter, J.L.; et al. Evolution of multidrug resistance during Staphylococcus aureus infection involves mutation of the essential two component regulator WalKR. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, K.; Jularic, M.; Horsburgh, S.M.; Hirschhausen, N.; Neumann, C.; Bertling, A.; Schulte, A.; Foster, S.; Kehrel, B.E.; Peters, G. Molecular characterization of a novel Staphylococcus aureus surface protein (SasC) involved in cell aggregation and biofilm accumulation. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehab El-Din, E.M.; El-Sokkary, M.M.; Bassiouny, M.R.; Hassan, R. Epidemiology of Neonatal Sepsis and Implicated Pathogens: A Study from Egypt. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 509484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakayama, T.; Zhao, J.; Takeuchi, D.; Kerdsin, A.; Chiranairadul, P.; Areeratana, P.; Loetthong, P.; Pienpringam, A.; Akeda, Y.; Oishi, K. Colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic strip test compromising optimised combinations of anti-S. suis capsular polysaccharide polyclonal antibodies for detection of Streptococcus suis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilela Rodrigues, T.C.; Jaiswal, A.K.; de Sarom, A.; de Castro Oliveira, L.; Freire Oliveira, C.J.; Ghosh, P.; Tiwari, S.; Miranda, F.M.; de Jesus Benevides, L.; Ariston de Carvalho Azevedo, V. Reverse vaccinology and subtractive genomics reveal new therapeutic targets against Mycoplasma pneumoniae: A causative agent of pneumonia. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2019, 6, 190907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, J.; Song, E.H.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, S.R.; Park, S.J.; Sung, H.; Kim, M.N.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.O.; Choi, S.H.; et al. Emergence of Panton-Valentine leucocidin-positive ST8-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (USA300 clone) in Korea causing healthcare-associated and hospital-acquired bacteraemia. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 35, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlemann, A.C.; Otto, M.; Lowy, F.D.; DeLeo, F.R. Evolution of community- and healthcare-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gowda, H.; Norton, R.; White, A.; Kandasamy, Y. Late-onset Neonatal Sepsis-A 10-year Review From North Queensland, Australia. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, E.K.; West, T.E.; Day, N.P.; Peacock, S.J. Staphylococcus aureus disease and drug resistance in resource-limited countries in south and east Asia. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.R.; Westh, H.; de Lencastre, H. Origins and evolution of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clonal lineages. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3237–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, O.-H.; Park, K.-H.; Song, J.Y.; Hong, J.M.; Kim, T.; Hong, S.I.; Kim, S.; Bae, I.-G. Prevalence and microbiological characteristics of qacA/B-positive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in a surgical intensive care unit. Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.L.; Grassmann, A.A.; Schuch, R.A.; Neto, A.C.P.S.; Mendonca, M.; Hartwig, D.D.; McBride, A.J.A.; Dellagostin, O.A. Evaluation of the Leptospira interrogans outer membrane protein OmpL37 as a vaccine candidate. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.L.; Britton, Z.T.; Robinson, A.S. Recombinant protein expression and purification: A comprehensive review of affinity tags and microbial applications. Biotechnol. J. 2012, 7, 620–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlenfein, T.J.; Murphy, R.M. Expression, purification, and characterization of human cystatin C monomers and oligomers. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 117, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Filutowicz, M. Hexahistidine (His6)-tag dependent protein dimerization: A cautionary tale. Acta Biochim. Pol. 1999, 46, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sysoeva, T.A.; Zepeda-Rivera, M.A.; Huppert, L.A.; Burton, B.M. Dimer recognition and secretion by the ESX secretion system in Bacillus subtilis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7653–7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiriyachaiporn, S.; Howarth, P.H.; Bruce, K.D.; Dailey, L.A. Evaluation of a rapid lateral flow immunoassay for Staphylococcus aureus detection in respiratory samples. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 75, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Sekiguchi, J.-I.; Watanabe, S.; Kuwahara-Arai, K.; Mizutani, N.; Yanagisawa, I.; Hishinuma, T.; Zan, K.N.; Mya, S.; Tin, H.H. Assessment of a newly developed immunochromatographic assay for NDM-type metallo-β-lactamase producing Gram-negative pathogens in Myanmar. BMC Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brakstad, O.G.; Aasbakk, K.; Maeland, J.A. Detection of Staphylococcus aureus by polymerase chain reaction amplification of the nuc gene. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 1654–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.-C.; Yang, C.-Y.; Sun, R.-L.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Kao, W.-C.; Yang, P.-C. Rapid single cell detection of Staphylococcus aureus by aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, srep01863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregson, D.; Low, D.E.; Skulnick, M.; Simor, A.E. Problems with rapid agglutination methods for identification of Staphylococcus aureus when Staphylococcus saprophyticus is being tested. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1398–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasawa, Y.; Kiku, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Yabusaki, N.; Oono, K.; Fujii, K.; Suzuki, T.; Maehana, K.; Hayashi, T. Rapid Staphylococcus aureus Detection From Clinical Mastitis Milk by Colloidal Gold Nanoparticle-Based Immunochromatographic Strips. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, K.; Zheng, X.; Huang, C.; Xu, K.; Zhi, Y.; Shen, H.; Jia, N. A colloidal gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic test strip for rapid and convenient detection of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2014, 14, 5151–5156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gan, M.; Xu, H.; Chen, F.; Ming, X.; Xu, H.; Wei, H.; Xu, F.; Liu, C. Development of a rapid and sensitive quantum dot-based immunochromatographic strip by double labeling PCR products for detection of Staphylococcus aureus in food. Food Control 2014, 46, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-H. Gold nanoparticle-based immunochromatographic assay for the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Sensor Actuat. B Chem. 2007, 127, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Kong, H.; Cheng, J.; Yan, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q.; Qu, H.; Zhao, Y. A Highly Sensitive Immunochromatographic Strip Test for Rapid and Quantitative Detection of Saikosaponin d. Molecules 2018, 23, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, S.A.; Samir, T.M.; Helmy, O.M.; Elhosseiny, N.M.; Ali, A.A.; El-Kholy, A.A.; Attia, A.S. A Novel Surface-Exposed Polypeptide Is Successfully Employed as a Target for Developing a Prototype One-Step Immunochromatographic Strip for Specific and Sensitive Direct Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Neonatal Sepsis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111580
Mohamed SA, Samir TM, Helmy OM, Elhosseiny NM, Ali AA, El-Kholy AA, Attia AS. A Novel Surface-Exposed Polypeptide Is Successfully Employed as a Target for Developing a Prototype One-Step Immunochromatographic Strip for Specific and Sensitive Direct Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Neonatal Sepsis. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(11):1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111580
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Sally A., Tamer M. Samir, Omneya M. Helmy, Noha M. Elhosseiny, Aliaa A. Ali, Amani A. El-Kholy, and Ahmed S. Attia. 2020. "A Novel Surface-Exposed Polypeptide Is Successfully Employed as a Target for Developing a Prototype One-Step Immunochromatographic Strip for Specific and Sensitive Direct Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Neonatal Sepsis" Biomolecules 10, no. 11: 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111580
APA StyleMohamed, S. A., Samir, T. M., Helmy, O. M., Elhosseiny, N. M., Ali, A. A., El-Kholy, A. A., & Attia, A. S. (2020). A Novel Surface-Exposed Polypeptide Is Successfully Employed as a Target for Developing a Prototype One-Step Immunochromatographic Strip for Specific and Sensitive Direct Detection of Staphylococcus aureus Causing Neonatal Sepsis. Biomolecules, 10(11), 1580. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10111580