Alginate–Halloysite Nanocomposite Aerogel: Preparation, Structure, and Oil/Water Separation Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
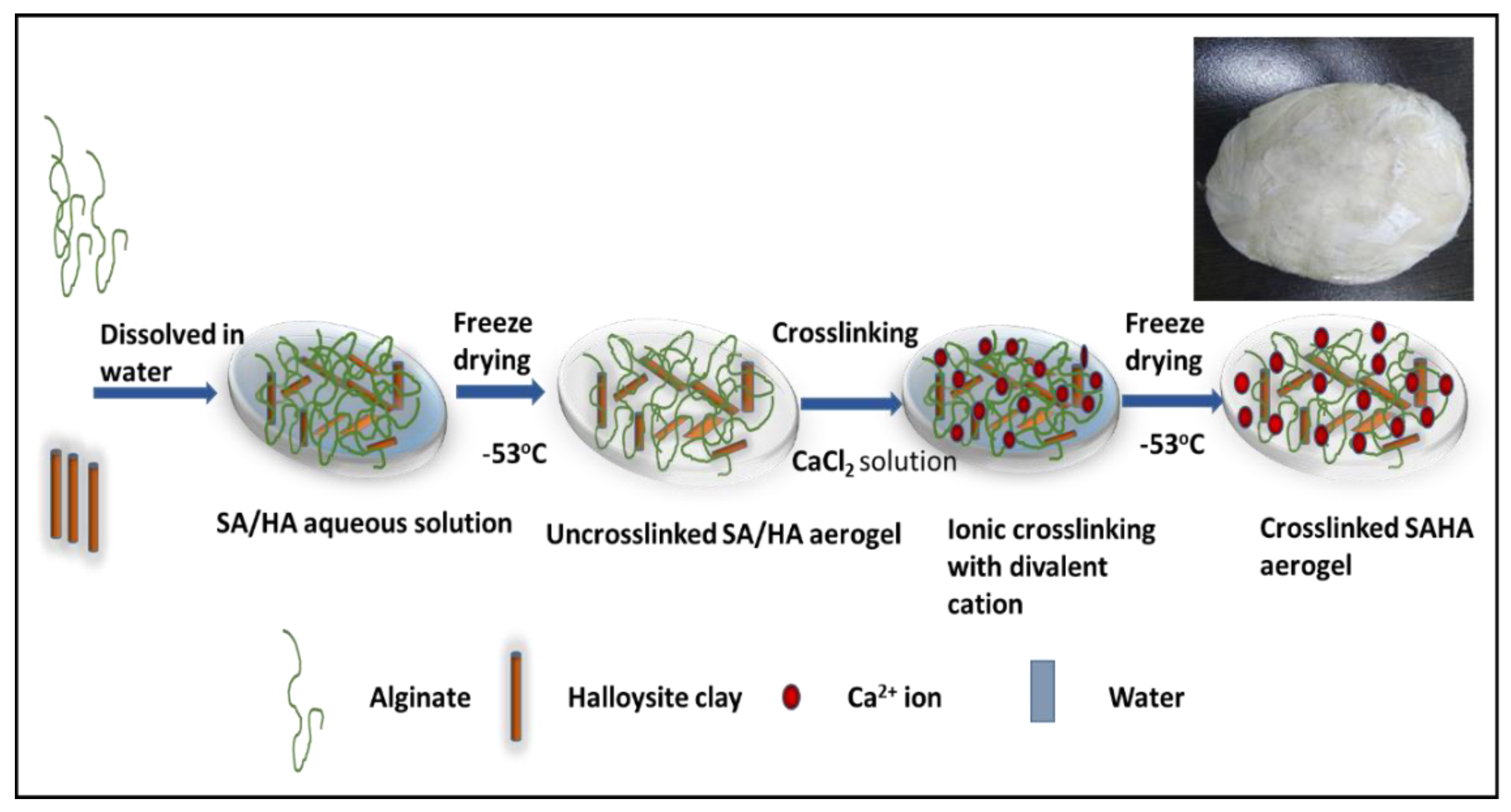
2.2. Preparation of Sodium Alginate Aerogel (SA)
2.3. Preparation of Sodium Alginate–Halloysite Nanocomposite Aerogel (SAHA)
2.4. Characterization
2.4.1. Porosity Measurement
2.4.2. Oil–Water Separation Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Determination of Morphological Properties
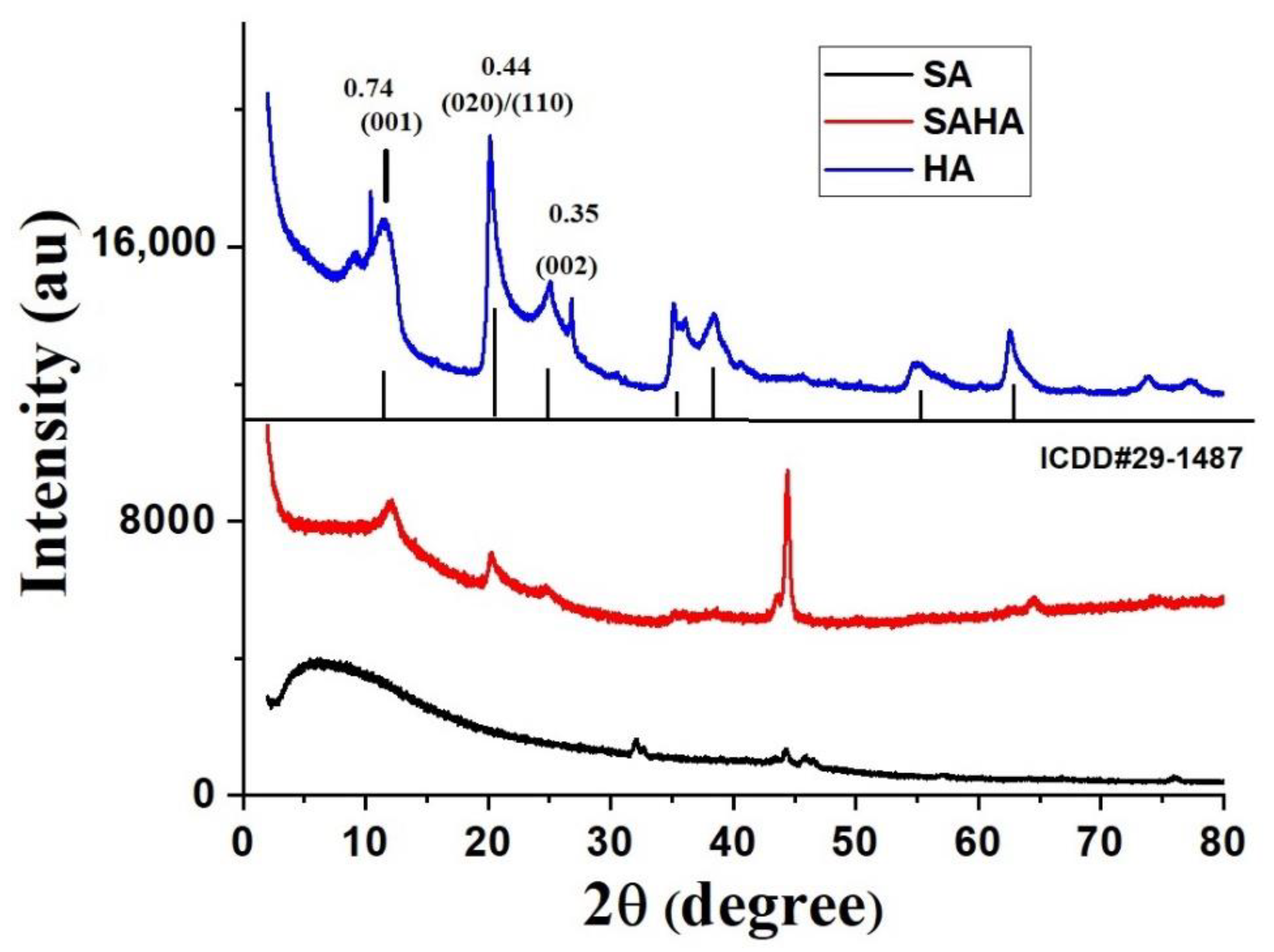
3.1.1. X-ray Diffraction Study
3.1.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
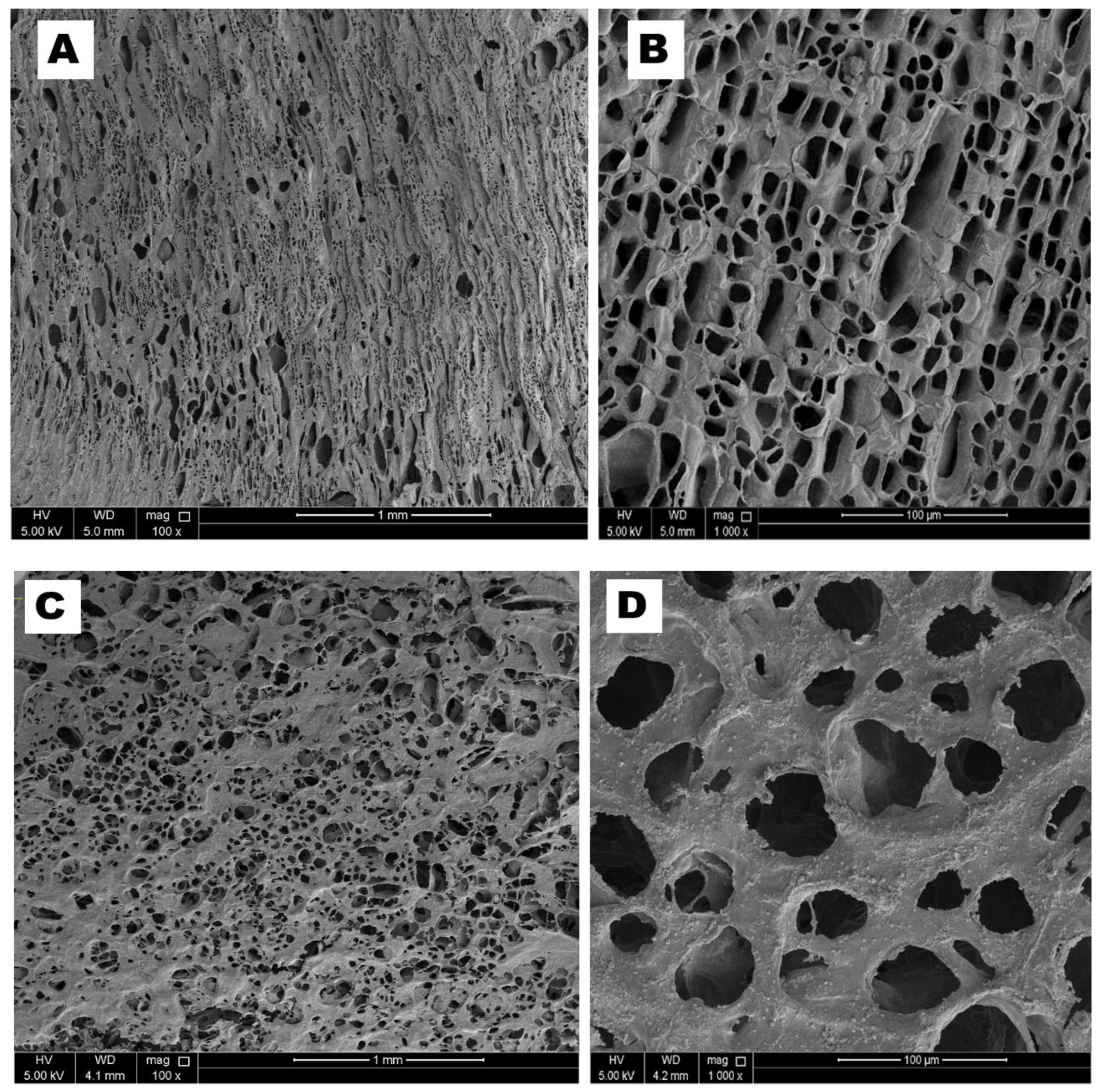
3.1.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
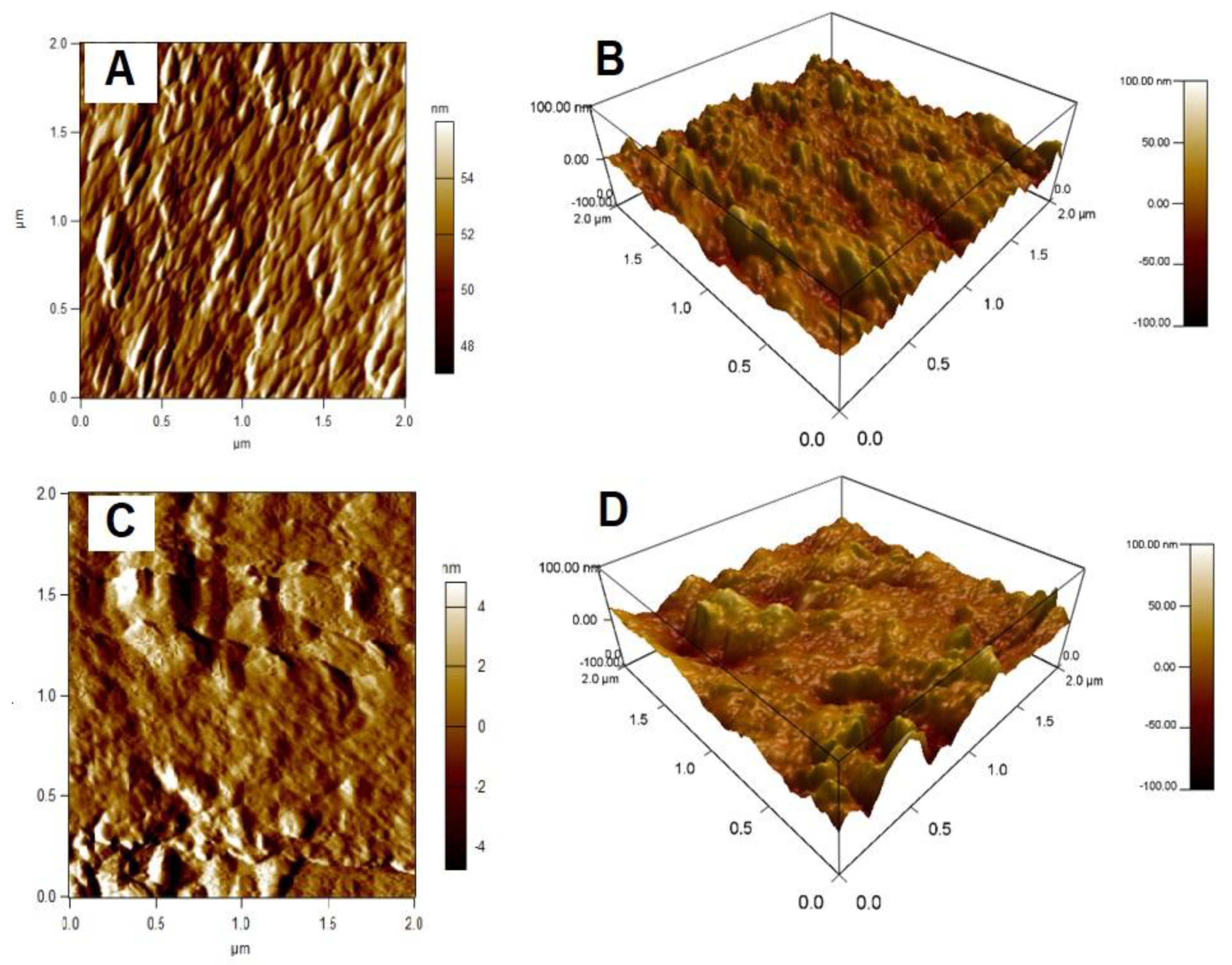
3.1.4. Atomic Force Microscopy Analysis (AFM)
3.1.5. BET Surface Analysis
3.2. Chemical Composition Analysis
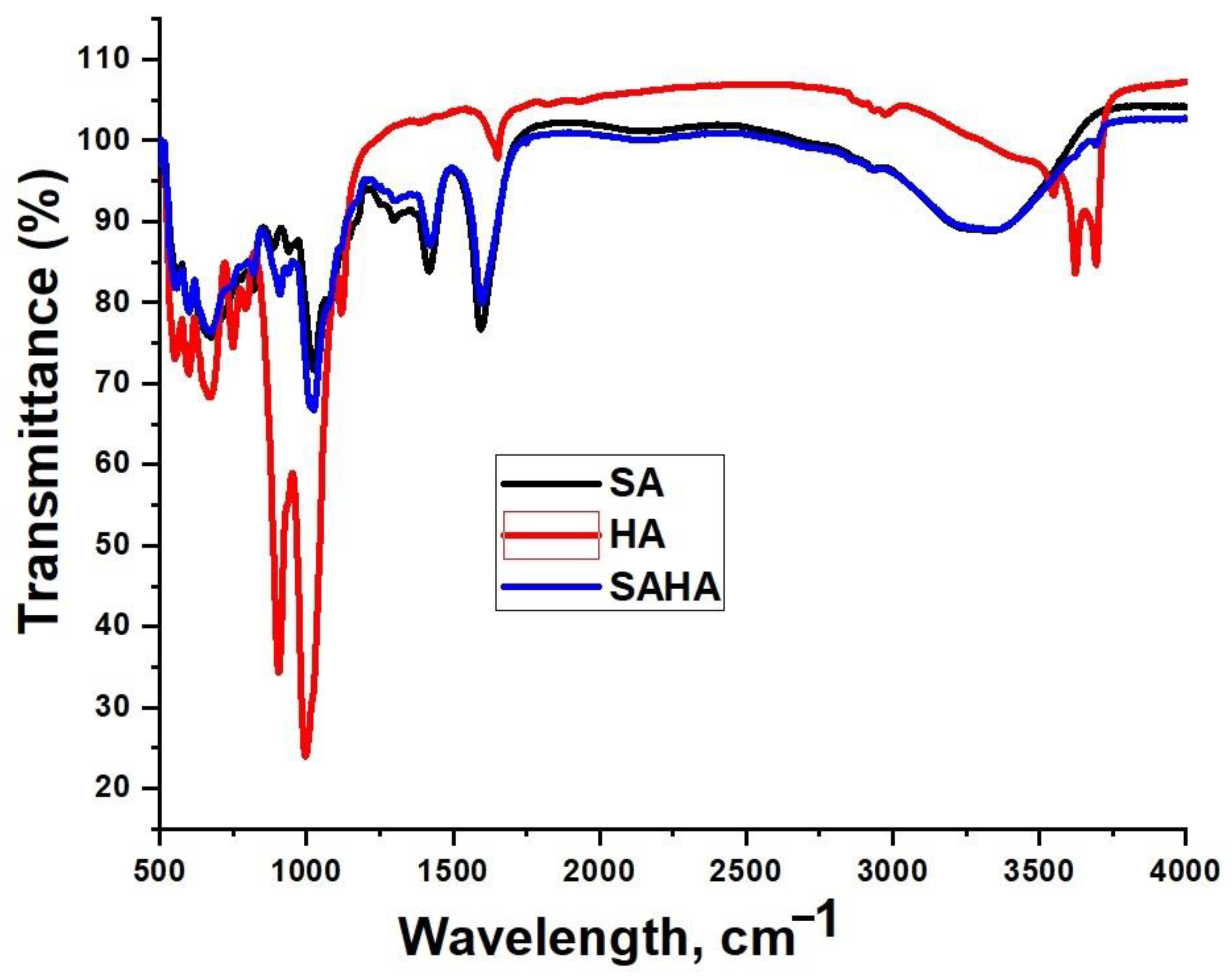
3.2.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
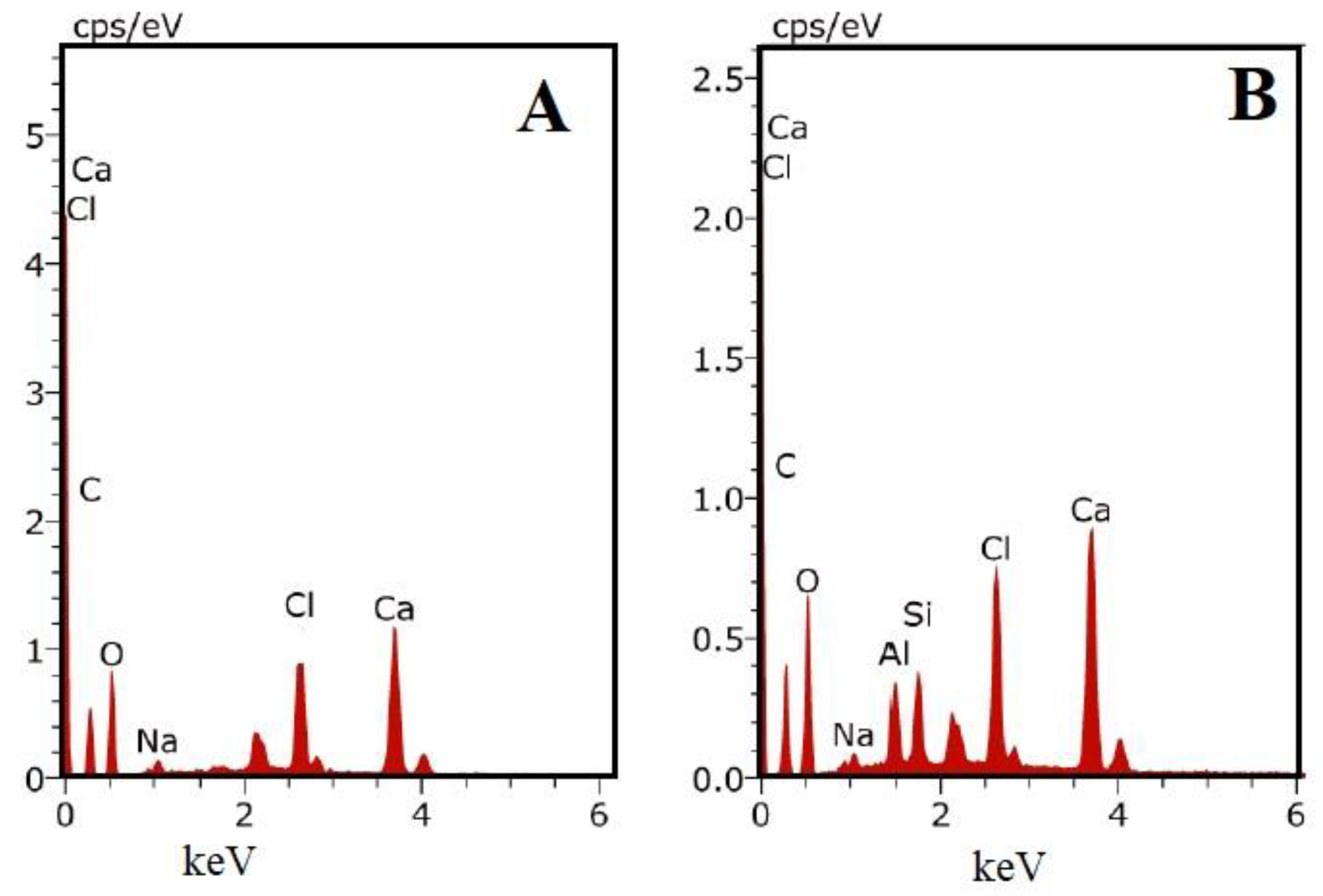
3.2.2. Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectrometry (EDX) Analysis
3.3. Thermal Analysis of the Aerogels
Thermogravimetric Analysis
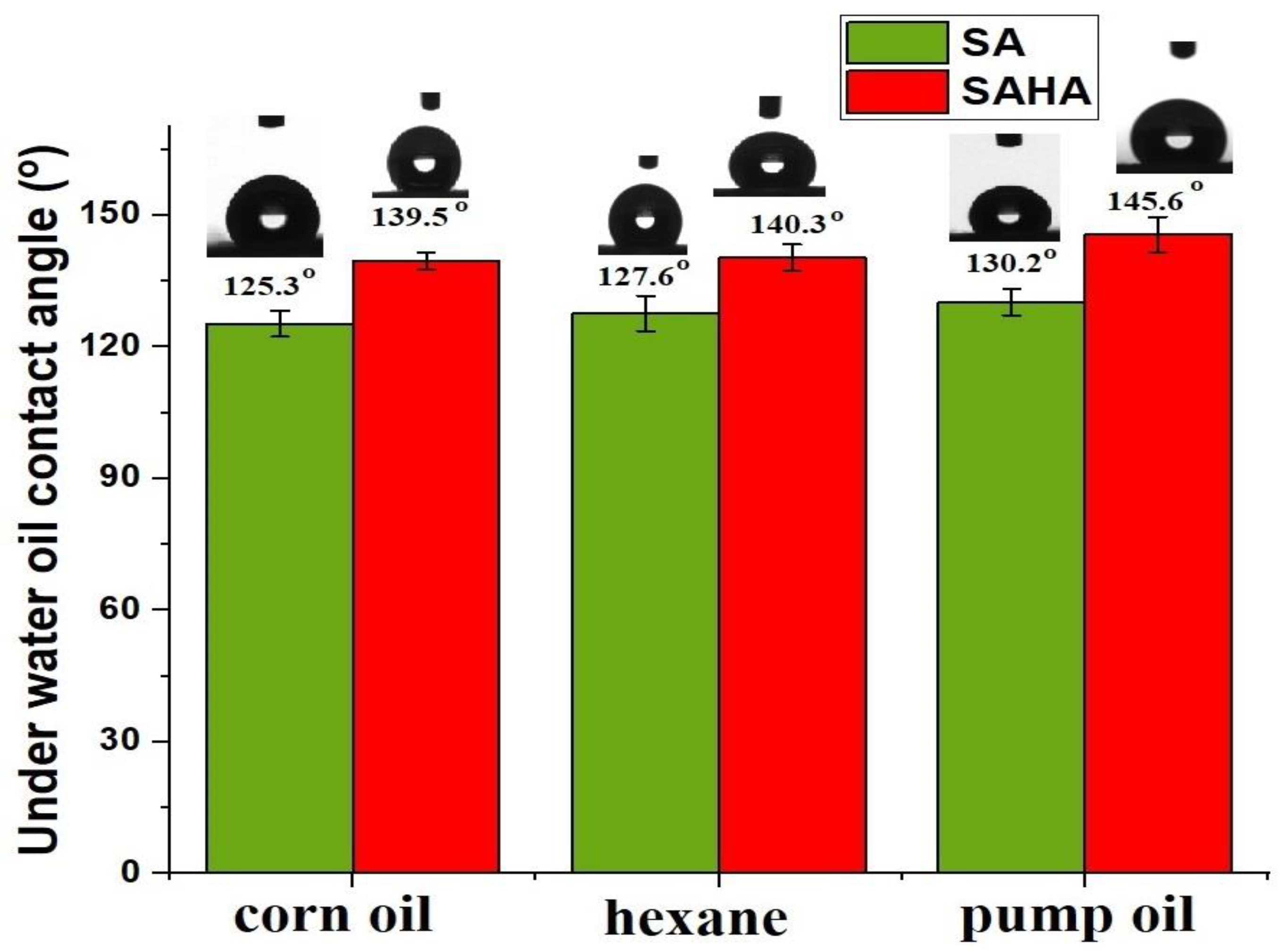
3.4. Oil/Water Wettability by Contact Angle Analysis
3.5. Oil/Water Separation Experiment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al Ameri, K.; Giwa, A.; Yousef, L.; Alraeesi, A.; Taher, H. Sorption and removal of crude oil spills from seawater using peat-derived biochar: An optimization study. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, A.M.; Khalifa, R.E.; Tamer, T.M.; Elnouby, M.; Hamed, A.M.; Ammar, Y.A.; Eldin, M.M. Fabrication of a novel low-cost superoleophilic nonanyl chitosan-poly (butyl acrylate) grafted copolymer for the adsorptive removal of crude oil spills. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 140, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, X.; Wu, S.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z. Toluene diisocyanate based phase-selective supramolecular oil gelator for effective removal of oil spills from polluted water. Chemosphere 2016, 153, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soundarajan, K.; Das, T.M. Sugar-benzohydrazide based phase selective gelators for marine oil spill recovery and removal of dye from polluted water. Carbohydr. Res. 2019, 481, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidli, A.; Huang, Y.; Cherukupally, P.; Bilton, A.M.; Park, C.B. Novel separator skimmer for oil spill cleanup and oily wastewater treatment: From conceptual system design to the first pilot-scale prototype development. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 18, 100598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Sun, G.; Ding, B. Superelastic and superhydrophobic nanofiber-assembled cellular aerogels for effective separation of oil/water emulsions. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3791–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Kim, K.S.; Choi, H. Effect of asymmetric wettability in nanofiber membrane by electrospinning technique on separation of oil/water emulsion. Chemosphere 2018, 204, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Ye, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Q.; Liang, T. Natural flexible superhydrophobic film derived from cajeput bark for oil/water separation. Mater. Lett. 2019, 238, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobolčiak, P.; Tanvir, A.; Popelka, A.; Moffat, J.; Mahmoud, K.A.; Krupa, I. The preparation, properties and applications of electrospun co-polyamide 6, 12 membranes modified by cellulose nanocrystals. Mater. Design 2017, 132, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F. A multifunctional gelatin-based aerogel with superior pollutants adsorption, oil/water separation and photocatalytic properties. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Liu, W.; Dong, Z.; Deng, Y. Underwater superoleophobicity cellulose nanofibril aerogel through regioselective sulfonation for oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 774–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Guo, J.; Zou, X. The preparation of hydrophobic alginate-based fibrous aerogel and its oil absorption property. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2018, 87, 704–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrova, V.A.; Elokhovskiy, V.Y.; Raik, S.V.; Poshina, D.N.; Romanov, D.P.; Skorik, Y.A. Alginate gel reinforcement with chitin nanowhiskers modulates rheological properties and drug release profile. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldino, L.; Cardea, S.; Scognamiglio, M.; Reverchon, E. A new tool to produce alginate-based aerogels for medical applications, by supercritical gel drying. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 146, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, M.P.; Gonçalves, V.S.; Gaspar, F.B.; Nogueira, I.D.; Matias, A.A.; Gurikov, P. Novel alginate-chitosan aerogel fibres for potential wound healing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 156, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J.; Yao, J. Alginate-based attapulgite foams as efficient and recyclable adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 514, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaei, M.; Taran, M.; Imani, M.M. Preparation, structural characterization, thermal properties and antifungal activity of alginate-CuO bionanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, M.; Zheng, P.; Zhuang, J.; Chen, L. A robust salt-tolerant superoleophobic alginate/graphene oxide aerogel for efficient oil/water separation in marine environments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasikiewicz, J.M.; Yoshii, F.; Nagasawa, N.; Wach, R.A.; Mitomo, H. Degradation of chitosan and sodium alginate by gamma radiation, sonochemical and ultraviolet methods. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2005, 73, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Fakhrullin, R. Halloysite clay nanotubes for loading and sustained release of functional compounds. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 1227–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serge, E.J.; Alla, J.P.; Belibi, P.D.B.; Mbadcam, K.J.; Fathima, N.N. Clay/polymer nanocomposites as filler materials for leather. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Milioto, S.; Lazzara, G. Layered composite based on halloysite and natural polymers: A carrier for the pH controlled release of drugs. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 10887–10893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suner, S.S.; Demirci, S.; Yetiskin, B.; Fakhrullin, R.; Naumenko, E.; Okay, O.; Sahiner, N. Cryogel composites based on hyaluronic acid and halloysite nanotubes as scaffold for tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 130, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Wang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Xu, L. High energy density and interfacial polarization in poly (vinylidene fluoride-chlorotrifluoroethylene) nanocomposite incorporated with halloysite nanotube architecture. Colloid Surf. A 2020, 606, 125495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Luo, Y.; Tan, P.; Liu, M.; Zhou, C. Hydrophobically modified chitin/halloysite nanotubes composite sponges for high efficiency oil-water separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 132, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Wang, H.; Han, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y. Halloysite nanotubes functionalized cotton fabric for oil/water separation. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 148, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, C.S.C.; Yeoh, H.K.; Pasbakhsh, P.; Krishnaiah, K.; Poh, P.E.; Tey, B.T.; Chan, E.S. Halloysite/alginate nanocomposite beads: Kinetics, equilibrium and mechanism for lead adsorption. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, T.; Ibarra-Galvan, V.; Song, S. Methylene blue removal from water using the hydrogel beads of poly (vinyl alcohol)-sodium alginate-chitosan-montmorillonite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 198, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Dai, L.; Shi, H.; Xiong, S.; Zhou, C. In vitro evaluation of alginate/halloysite nanotube composite scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 49, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Liu, M.; Long, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhou, C. Effects of halloysite nanotubes on physical properties and cytocompatibility of alginate composite hydrogels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 70, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Padervand, M.; Jalilian, E.; Seidi, F. Sodium alginate-halloysite nanotube gel beads as potential delivery system for sunitinib malate anticancer compound. Mater. Lett. 2020, 274, 128038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, N.; Bruzzese, C.; Dufresne, A. TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose participating as crosslinking aid for alginate-based sponges. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4948–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brus, J.; Urbanova, M.; Czernek, J.; Pavelkova, M.; Kubova, K.; Vyslouzil, J.; Vysloužil, J. Structure and dynamics of alginate gels cross-linked by polyvalent ions probed via solid state NMR spectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2478–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lisuzzo, L.; Wicklein, B.; Dico, G.L.; Lazzara, G.; Del Real, G.; Aranda, P.; Ruiz-Hitzky, E. Functional biohybrid materials based on halloysite, sepiolite and cellulose nanofibers for health applications. Dalton. Trans. 2020, 49, 3830–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, H.; Liu, X.; Tang, W.; Ma, R. Facile synthesis and characterization of ZnO nanoparticles grown on halloysite nanotubes for enhanced photocatalytic properties. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiewicz, P.; Lutynski, M.; Soltys, J.; Pytlinski, A. Purification of halloysite by magnetic separation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. 2016, 52, 991–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Jurkiewicz, K.; Pawlyta, M.; Burian, A. Structure of Carbon Materials Explored by Local Transmission Electron Microscopy and Global Powder Diffraction Probes. J. Carbon. Res. 2018, 4, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, M.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L. A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.X.; Niu, H.M.; Chen, X.L.; Zhan, H.B. Natural cellulose microfiltration membranes for oil/water nanoemulsions separation. Colloid Surf. A 2019, 564, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulker, Z.; Erkey, C. A novel hybrid material: An inorganic silica aerogel core encapsulated with a tunable organic alginate aerogel layer. Rsc Adv. 2014, 4, 62362–62366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vinokurov, V.; Stavitskaya, A.; Glotov, A.; Ostudin, A.; Sosna, M.; Gushchin, P.; Lvov, Y. Halloysite nanotube-based cobalt mesocatalysts for hydrogen production from sodium borohydride. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 268, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Ulker, Z.; Erkey, C. A novel composite of alginate aerogel with PET nonwoven with enhanced thermal resistance. J Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 491, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Southon, P.D.; Liu, Z.; Green, M.E.; Hook, J.M.; Antill, S.J.; Kepert, C.J. Functionalization of halloysite clay nanotubes by grafting with γ-aminopropyltriethoxysilane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 15742–15751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos-Ramírez, S.; Ramos-Fernández, E.V.; Silvestre-Albero, J.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Pastor-Blas, M.M.; González-Montiel, A. Use of nanotubes of natural halloysite as catalyst support in the atom transfer radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate. Micropor. Mesopor. Mater. 2009, 120, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Huo, J.; Chen, F.; Yang, Q.; Hou, X. Oil/water separation based on natural materials with super-wettability: Recent advances. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 25140–25163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspired superoleophobic and smart materials: Design, fabrication, and application. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2013, 58, 503–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Desorption Average Pore Radius (BJH) (nm) | t-Plot Micropore Volume Cc/g |
|---|---|---|---|
| SA aerogel | 12.1 | 10.6 | 0.035 |
| SAHA aerogel | 2.9 | 37.6 | 0.0115 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhagyaraj, S.; Krupa, I. Alginate–Halloysite Nanocomposite Aerogel: Preparation, Structure, and Oil/Water Separation Applications. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121632
Bhagyaraj S, Krupa I. Alginate–Halloysite Nanocomposite Aerogel: Preparation, Structure, and Oil/Water Separation Applications. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(12):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121632
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhagyaraj, Sneha, and Igor Krupa. 2020. "Alginate–Halloysite Nanocomposite Aerogel: Preparation, Structure, and Oil/Water Separation Applications" Biomolecules 10, no. 12: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121632
APA StyleBhagyaraj, S., & Krupa, I. (2020). Alginate–Halloysite Nanocomposite Aerogel: Preparation, Structure, and Oil/Water Separation Applications. Biomolecules, 10(12), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10121632





