The Guanidine Pseudoalkaloids 10-Methoxy-Leonurine and Leonurine Act as Competitive Inhibitors of Tyrosinase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Extraction and Isolation
2.3. Enzymatic Assay
2.4. Docking Simulation
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Determination of the Tyrosinase Inhibitory Activity of Compounds
3.2. Enzyme Kinetics
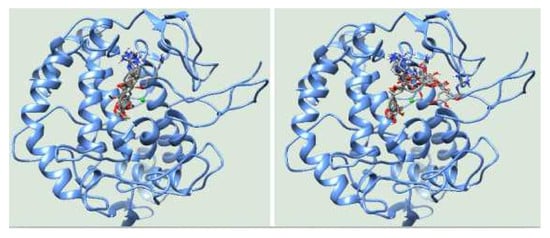
3.3. Molecular Docking
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, M.; Ding, H.; Zhang, G.; Hu, X.; Gong, D. Relationships of dietary flavonoid structure with its tyrosinase inhibitory activity and affinity. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 107, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Lee, J.h.; Hao, H.; Park, Y.-D.; Zhan, Y.; Lü, Z.-R. The effect of oxaloacetic acid on tyrosinase activity and structure: Integration of inhibition kinetics with docking simulation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 101, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Carcelli, M.; Rogolino, D.; Bartoli, J.; Pala, N.; Compari, C.; Ronda, N.; Bacciottini, F.; Incerti, M.; Fisicaro, E. Hydroxyphenyl thiosemicarbazones as inhibitors of mushroom tyrosinase and antibrowning agents. Food Chem. 2020, 303, 125310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.-J.; Liu, Z.; Hu, G.-Z.; Qu, L.-B.; Yang, R. Investigation on the binding of aloe-emodin with tyrosinase by spectral analysis and molecular docking. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 211, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, Z.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Ranjbar, S. Veratric acid derivatives containing benzylidene-hydrazine moieties as promising tyrosinase inhibitors and free radical scavengers. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 27, 2644–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cásedas, G.; Les, F.; González-Burgos, E.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P.; Smith, C.; López, V. Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside inhibits different enzymes involved in central nervous system pathologies and type-2 diabetes. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2019, 120, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.-L.; Liu, T.-L.; Xue, J.-J.; Hong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.-X.; Cui, C.-C.; Liu, M.-C.; Liu, S.-L. Flavanoids derivatives from the root bark of Broussonetia papyrifera as a tyrosinase inhibitor. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 138, 111445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, D.; Seong, S.H.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. Identifying an isoflavone from the root of Pueraria lobata as a potent tyrosinase inhibitor. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.-J.; Xu, D.-Q.; Yue, S.-J.; Tang, Y.-P.; Guo, S.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Z.-H.; Shi, X.-Q.; Chen, Y.-Y.; et al. Comparative analysis of the main active constituents from different parts of Leonurus japonicus Houtt. and from different regions in China by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography with triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 177, 112873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.-M.; Cui, Z.-M.; Liu, Z.-K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, D.-R.; Liu, S.-H.; Long, H.; Sun, H.-D.; Dang, Y.-J.; Xiao, W.-L. Three minor new compounds from the aerial parts of Leonurus japonicas. Chinese Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 1000–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-Y.; Peng, X.; Jin, X.J.; Wei, W.-J.; Ma, K.-L.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.-J.; Gao, K. Labadane-type diterpenoids from Leonurus japonicus and their plant-growth regulatory activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2568–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Z.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, J.S.; Zhang, P.C. Hepatoprotective glycosides from Leonurus japonicas Houtt. Carbohydr. Res. 2012, 348, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-m.; Peng, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, L.-S.; Yang, Y.-T.; Xie, X.-F.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.-H.; Xiong, L. Steroids from the aerial parts of Leonurus japonicus. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Q.-M.; Guo, L.; Liu, Z.-H.; Xiong, L. Alkaloids and flavonoid glycosides from the aerial parts of Leonurus japonicas and their opposite effects on uterine smooth muscle. Phytochemistry 2018, 145, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.-Y.; Hu, H.-C.; Chiang, H.-M.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yang, J.-C.; Lin, Y.-A.; Chen, C.-J.; Chang, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-L. New diterpenes leojaponins G-L from Leonurus japonicas. Fitoterapia 2018, 130, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, M.D.; Bouzidi, C.; Gorod, N.S.; Puiatti, M.; Michel, S.; Grougnet, R.; Ortega, M.G. In vitro biological evaluation and molecular docking studies of natural and semisynthetic flavones from Gardenia oudiepe (Rubiaceae) as tyrosinase inhibitors. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 82, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leem, H.H.; Lee, G.Y.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, H.N.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, Y.H. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitory activity of components from Leonurus japonicas. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Qin, P.; Shan, F.; Ren, G. Flavonoid composition, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of tartary buckwheat bran extract. Ind. Crops. Prod. 2013, 49, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafary, S.; Ranjbar, S.; Larijani, B.; Amini, M.; Biglar, M.; Mahdavi, M.; Bakhshaei, M.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Sakhteman, A.; Khoshneviszadeh, M. Novel morpholine containing cinnamoyl amides as potent tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 135, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, S.A.N.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 147, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, Y.C.; Yeung, H.W.; Cheung, Y.M.; Phil, M.; Hwang, J.C.; Chan, Y.W.; Law, Y.P.; Ng, K.H.; Yeung, C.H. Isolation of the uterotonic principle from Leonurus artemisia, the Chinese Motherwork. Am. J. Chin. Med. 1976, 4, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.; Lei, Y. Leonurine inhibits IL-1β induced inflammation in murine chondrocytes and ameliorates murine osteoarthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 65, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, H.; Liu, X.H.; Zhu, Y.Z. Herba leonurine attenuates doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiacmuscle cell. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2009, 612, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Reddy, P.H. Structure based design and molecular docking studies for phosphorylated tau inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease. Cells 2019, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pradeepkiran, J.A.; Reddy, A.P.; Reddy, P.H. Pharmacophore-based models fro therapeutic drugs against phosphorylated tau in Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
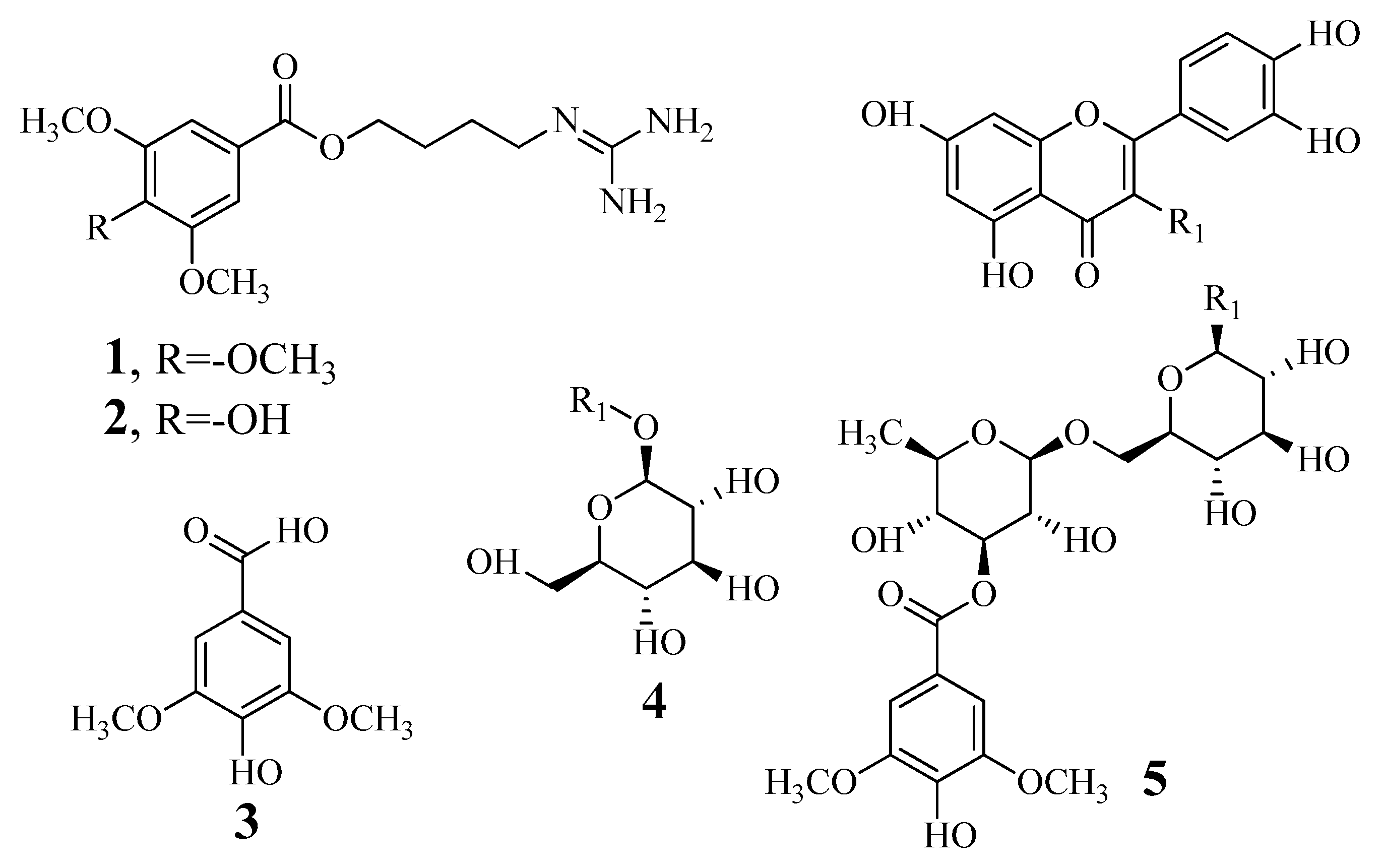



| Inhibitor | Inhibition Rate (%) at 100 μM a | IC50 Value (μM) | Binding Type (Ki, μM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91.8 ± 2.9 | 7.4 ± 0.4 | Competitive (1.6 ± 0.7) |
| 2 | 85.6 ± 1.8 | 12.4 ± 0.8 | Competitive (11.4 ± 1.1) |
| 3 | 11.6 ± 0.1 | N.T c | N.T c |
| 4 | 1.8 ± 5.9 | N.T c | N.T c |
| 5 | 8.3 ± 0.6 | N.T c | N.T c |
| Kojic acid b | 79.4 ± 2.5 | 25.7 ± 1.3 |
| Ranks | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autodock Score (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bonds (Å) | Autodock Score (kcal/mol) | Hydrogen Bonds (Å) | |
| 1 | −6.83 | His85 (2.69), His244(2.68), Gly245(3.05) | −6.16 | Glu322(2.78) |
| 2 | −6.82 | His244(2.99), Gly245(2.71) | −6.12 | Ala246(2.67) |
| 3 | −6.78 | His244(2.81), Gly245(2.97) | −6.12 | His244(3.01), Ala246(2.67) |
| 4 | −6.76 | His244(2.91), Gly245(2.65) | −6.1 | Tyr78(3.07), Asn81(2.98), His85(2.50, 2.82) |
| 5 | −6.60 | His244(2.95), Gly245(2.72) | −5.99 | Asn81(2.64, 2.92), His85(2.67, 3.26), His244(3.02) |
| 6 | −6.58 | Gly245(2.93) | −5.91 | Asn81(2.84), Cys83(2.67) His85(3.01), Gly86(2.88), |
| 7 | −6.54 | His85(2.82), His244(2.99), Glu322(2.56) | −5.85 | His85(3.01), Gly86(3.04), Ala323(3.18) |
| 8 | −6.52 | His244(2.87), Ala246(3.16) | −5.83 | His85(3.03), Asn320(2.96) |
| 9 | −6.40 | His85(3.05), His244(3.14), Asn320(3.01) | −5.80 | His244(2.96), Glu322(2.68) |
| 10 | −6.38 | His244(2.69), Gly245(3.08), Asn260(3.25) | −5.80 | Asn81(2.63), Cys83(3.14), His85(2.85) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.H.; Leem, H.H.; Lee, G.Y. The Guanidine Pseudoalkaloids 10-Methoxy-Leonurine and Leonurine Act as Competitive Inhibitors of Tyrosinase. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020174
Kim JH, Leem HH, Lee GY. The Guanidine Pseudoalkaloids 10-Methoxy-Leonurine and Leonurine Act as Competitive Inhibitors of Tyrosinase. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020174
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jang Hoon, Hyun Hee Leem, and Ga Young Lee. 2020. "The Guanidine Pseudoalkaloids 10-Methoxy-Leonurine and Leonurine Act as Competitive Inhibitors of Tyrosinase" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020174
APA StyleKim, J. H., Leem, H. H., & Lee, G. Y. (2020). The Guanidine Pseudoalkaloids 10-Methoxy-Leonurine and Leonurine Act as Competitive Inhibitors of Tyrosinase. Biomolecules, 10(2), 174. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020174