Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cellular Material
2.3. Cell Cultures
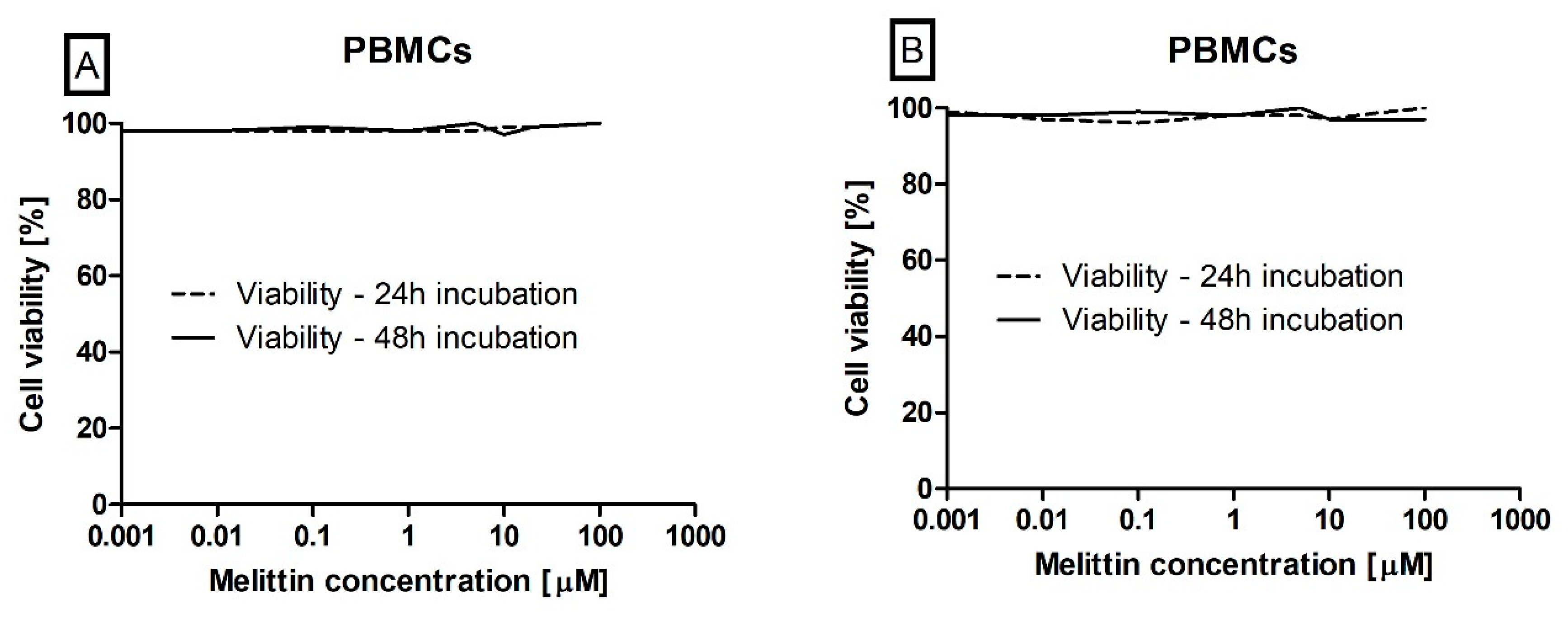
2.4. Cell Viability Determination
2.5. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (MMP)
2.6. Apoptosis Assay—Anexin V Binding
2.7. Determining the Activity of Caspase-3/Caspase-7
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wang, X.R.; Lin, L.T.; Xiao, L.Y.; Zhou, P.; Shi, G.X.; Liu, C.Z. Bee venom therapy: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Toxicon 2018, 148, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, D.J.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Song, H.S.; Lee, C.K.; Hong, J.T. Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis, pain-releasing, and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its constituent compounds. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 115, 246–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ke, T.; He, C.; Cao, W.; Wei, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.R.; et al. The anti-arthritic effects of synthetic melittin on the complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis model in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Gendy, A.; Saber, M.; Daoud, E.; Abdel-Wahhab, K.; el-Rahman, E.; Hegaz, A. Role of bee Venom Acupuncture in improving pain and life quality in Egyptian Chronic Low Back Pain patients. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 7, 168–174. [Google Scholar]
- Rady, I.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Rady, M.; Mukhtar, H. Melittin, a major peptide component of bee venom, and its conjugates in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 2017, 402, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.H.; Gwon, M.G.; Gu, H.M.; Jeon, M.J.; Han, S.M.; Pak, S.C.; Lee, C.K.; Park, I.S.; et al. Therapeutic effects of bee venom and its major component, melittin, on atopic dermatitis in vivo and in vitro. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 175, 4310–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreil, G. Structure and Multistep Activation of the Precursors of Peptides from Honeybee Venom Glands and Frog Skin. Curr. Top. Cell. Regul. 1984, 24, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Brewczyński, Z.; Anczyk, E.; Kasznica-Kocot, J.; Hom, A.; Dąbkowska, B.; Muszyńska-Graca, M.; Pypno, B.; Skiba, M.; Złotkowska, R. Znajomość biologii błonkówek ze szczególnym uwzględnieniem immunochemii ich jadów ma istotne znaczenie we współczesnej medycynie środowiskowej. Medycyna Środowiskowa 2010, 13, 99–111. [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger, T.C.; Eisenberg, D. The structure of melittin. II. Interpretation of the structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 6016–6022. [Google Scholar]
- Terwilliger, T.C.; Weissman, L.; Eisenberg, D. The structure of melittin in the form I crystals and its implication for melittin’s lytic and surface activities. Biophys. J. 1982, 37, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raghuraman, H.; Chattopadhyay, A. Melittin: A membrane-active peptide with diverse functions. Biosci. Rep. 2007, 27, 189–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othon, C.M.; Kwon, O.H.; Lin, M.M.; Zewail, A.H. Solvation in protein (un)folding of melittin tetramer-monomer transition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12593–12598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perekalin, D.S.; Novikov, V.V.; Pavlov, A.A.; Ivanov, I.A.; Anisimova, N.Y.; Kopylov, A.N.; Volkov, D.S.; Seregina, I.F.; Bolshov, M.A.; Kudinov, A.R. Selective ruthenium labeling of the tryptophan residue in the bee venom Peptide melittin. Chemistry 2015, 21, 4923–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: An environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 1997, 18, 2714–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hait, W.N.; Grais, L.; Benz, C.; Cadman, E.C. Inhibition of growth of leukemic cells by inhibitors of calmodulin: Phenothiazines and melittin. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1985, 14, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhakim, Y.M.; Khalil, S.R.; Awad, A.; Al-Ayadhi, L.Y. Combined cytogenotoxic effects of bee venom and bleomycin on rat lymphocytes: An in vitro study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 173903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koumanov, K.; Momchilova, A.; Wolf, C. Bimodal regulatory effect of melittin and phospholipase A2-activating protein on human type II secretory phospholipase A2. Cell Boil. Int. 2003, 27, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, J.F.; Shipman, W.H.; Cole, L.J. Antibacterial action of melittin, a polypeptide from bee venom. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1968, 127, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Chen, Z. Melittin exerts an antitumor effect on non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3581–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.H.; Jeong, Y.J.; Park, K.K.; Cho, H.J.; Chung, I.K.; Min, K.S.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.G.; Yeo, J.H.; Chang, Y.C. Melittin suppresses PMA-induced tumor cell invasion by inhibiting NF-kappaB and AP-1-dependent MMP-9 expression. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.H.; Choi, M.S.; Kwak, D.H.; Oh, K.W.; Yoon, D.Y.; Han, S.B.; Song, H.S.; Song, M.J.; Hong, J.T. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom in prostate cancer cells through activation of caspase pathway via inactivation of NF-κB. Prostate 2011, 71, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Park, M.H.; Kollipara, P.S.; An, B.J.; Song, H.S.; Han, S.B.; Kim, J.H.; Song, M.J.; Hong, J.T. Anti-cancer effect of bee venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 258, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.L.; Ke, Y.Q.; Xu, R.X.; Peng, P. Melittin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of malignant human glioma cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2007, 27, 1775–1777. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Gu, W.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.Q.; Han, K.Q.; Ling, C.Q. Growth arrest and apoptosis of the human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line BEL-7402 induced by melittin. Onkologie 2006, 29, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, B.; Huang, C.; Meng, X.M.; Bian, E.B.; Li, J. Melittin restores PTEN expression by down-regulating HDAC2 in human hepatocelluar carcinoma HepG2 cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Yu, M.; He, Y.; Xiao, L.; Wang, F.; Song, C.; Sun, S.; Ling, C.; Xu, Z. Melittin prevents liver cancer cell metastasis through inhibition of the Rac1-dependent pathway. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1964–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, Y.J.; Choi, Y.; Shin, J.M.; Cho, H.J.; Kang, J.H.; Park, K.K.; Choe, J.Y.; Bae, Y.S.; Han, S.M.; Kim, C.H.; et al. Melittin suppresses EGF-induced cell motility and invasion by inhibiting PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 68, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.M.; Jeong, Y.J.; Cho, H.J.; Park, K.K.; Chung, I.K.; Lee, I.K.; Kwak, J.Y.; Chang, H.W.; Kim, C.H.; Moon, S.K.; et al. Melittin suppresses HIF-1α/VEGF expression through inhibition of ERK and mTOR/p70S6K pathway in human cervical carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Q.; Zhu, Z.A.; Hao, Y.Q.; Dai, K.R.; Zhang, C. Effect of melittin on apoptosis and necrosis of U2 OS cells. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao 2004, 2, 208–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.C.; Wu, C.C.; Hsieh, H.L.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, S.L. Honeybee venom induces calcium-dependent but caspase-independent apoptotic cell death in human melanoma A2058 cells. Toxicon 2008, 52, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, M.; Aydin, C.; Savci, V. Cardiovascular effect of peripheral injected melittin in normotensive conscious rats: Mediation of the central cholinergic system. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 2009, 81, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.J.; Ha, S.J.; Song, H.S.; Lim, Y.; Yun, Y.P.; Lee, J.W.; Moon, D.C.; Park, Y.H.; Park, B.S.; Song, M.J.; et al. Melittin inhibits vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation through induction of apoptosis via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB and Akt activation and enhancement of apoptotic protein expression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 317, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bijak, M.; Synowiec, E.; Sitarek, P.; Sliwiński, T.; Saluk-Bijak, J. Evaluation of the Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Flavonolignans in Different Cellular Models. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sitarek, P.; Synowiec, E.; Kowalczyk, T.; Śliwiński, T.; Skała, E. An In Vitro Estimation of the Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of Root Extract from. Molecules 2018, 23, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bijak, M.; Kolodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Ponczek, M.B.; Saluk, J.; Nowak, P. Protective effects of grape seed extract against oxidative and nitrative damage of plasma proteins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 51, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbikowska, H.M.; Antosik, A.; Szejk, M.; Bijak, M.; Olejnik, A.K.; Saluk, J.; Nowak, P. Does quercetin protect human red blood cell membranes against γ-irradiation? Redox Rep. 2014, 19, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijak, M.; Saluk, J.; Antosik, A.; Ponczek, M.B.; Zbikowska, H.M.; Borowiecka, M.; Nowak, P. Aronia melanocarpa as a protector against nitration of fibrinogen. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 55, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.H.; Jeha, S. New therapeutic strategies for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartledge Wolf, D.M.; Langhans, S.A. Moving Myeloid Leukemia Drug Discovery Into the Third Dimension. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terwilliger, T.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jabbour, E.; O’Brien, S.; Konopleva, M.; Kantarjian, H. New insights into the pathophysiology and therapy of adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer 2015, 121, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flis, S.; Chojnacki, T. Chronic myelogenous leukemia, a still unsolved problem: Pitfalls and new therapeutic possibilities. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Śladowska, K.; Handzlik, J.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; Mazur, L. In vitro cytotoxic activity evaluation of phenytoin derivatives against human leukemia cells. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2016, 54, 553–559. [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Andrews, D.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; et al. Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: Recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watala, C.; Gwoździński, K. Melittin-induced alterations in dynamic properties of human red blood cell membranes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1992, 82, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panina, S.B.; Baran, N.; Brasil da Costa, F.H.; Konopleva, M.; Kirienko, N.V. A mechanism for increased sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia to mitotoxic drugs. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yun, H.D.; Schirm, D.K.; Felices, M.; Miller, J.S.; Eckfeldt, C.E. Dinaciclib enhances natural killer cell cytotoxicity against acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2448–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Fang, F.; Li, B. Anti-Tumor Effects of Melittin and Its Potential Applications in Clinic. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.T.; Cheng, H.H.; Huang, C.J.; Chang, H.C.; Chi, C.C.; Su, H.H.; Hsu, S.S.; Wang, J.L.; Chen, I.S.; Liu, S.I.; et al. Phospholipase A2-independent Ca2+ entry and subsequent apoptosis induced by melittin in human MG63 osteosarcoma cells. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.S.; Jang, B.H.; Jo, Y.S.; Kim, S.J.; Eom, T.I.; Kim, M.C.; Ko, H.J.; Sim, S.S. The effect of acteoside on intracellular Ca(2+) mobilization and phospholipase C activity in RBL-2H3 cells stimulated by melittin. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratton, D.L.; Fadok, V.A.; Richter, D.A.; Kailey, J.M.; Guthrie, L.A.; Henson, P.M. Appearance of phosphatidylserine on apoptotic cells requires calcium-mediated nonspecific flip-flop and is enhanced by loss of the aminophospholipid translocase. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 26159–26165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aubry, J.P.; Blaecke, A.; Lecoanet-Henchoz, S.; Jeannin, P.; Herbault, N.; Caron, G.; Moine, V.; Bonnefoy, J.Y. Annexin V used for measuring apoptosis in the early events of cellular cytotoxicity. Cytometry 1999, 37, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Synowiec, E.; Hoser, G.; Wojcik, K.; Pawlowska, E.; Skorski, T.; Błasiak, J. UV Differentially Induces Oxidative Stress, DNA Damage and Apoptosis in BCR-ABL1-Positive Cells Sensitive and Resistant to Imatinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18111–18128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pfeffer, C.M.; Singh, A.T.K. Apoptosis: A Target for Anticancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ly, J.D.; Grubb, D.R.; Lawen, A. The mitochondrial membrane potential (deltapsi(m)) in apoptosis; an update. Apoptosis 2003, 8, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.G. Melittin triggers apoptosis in Candida albicans through the reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondria/caspase-dependent pathway. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 355, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| The Biological Effect of Melittin | Reference |
|---|---|
| Inhibits clonogenicity and growth in leukemic cells of humans and mice | [15] |
| Activates of secretory phospholipase A2 | [17] |
| Demonstrates antibacterial activity against strain of Staphylococcus aureus (strain 80) resistant to penicillin | [18] |
| Inhibits invasion and migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells induced by the epidermal growth factor | [19] |
| Inhibits human renal carcinoma invasion | [20] |
| Inhibits growth of human prostate cancer cells | [21] |
| Induces apoptotic cell death in ovarian cancer cells | [22] |
| Inhibits proliferation and induction of apoptosis in malignant human glioma cells. | [23] |
| Inhibits proliferation and induction of apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells | [24,25,26] |
| Inhibits breast cancer cell invasion and migration | [27] |
| Inhibits human cervical cancer progression and angiogenesis. | [28] |
| Inhibits proliferation of the osteosarcoma cells | [29] |
| Induces apoptosis in human melanoma cells | [30] |
| Exerts tachycardic effects by activating COX pathway | [31] |
| Increasing blood pressure and reversing hypotension in haemorrhagic shock | [32] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceremuga, M.; Stela, M.; Janik, E.; Gorniak, L.; Synowiec, E.; Sliwinski, T.; Sitarek, P.; Saluk-Bijak, J.; Bijak, M. Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247
Ceremuga M, Stela M, Janik E, Gorniak L, Synowiec E, Sliwinski T, Sitarek P, Saluk-Bijak J, Bijak M. Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeremuga, Michal, Maksymilian Stela, Edyta Janik, Leslaw Gorniak, Ewelina Synowiec, Tomasz Sliwinski, Przemyslaw Sitarek, Joanna Saluk-Bijak, and Michal Bijak. 2020. "Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247
APA StyleCeremuga, M., Stela, M., Janik, E., Gorniak, L., Synowiec, E., Sliwinski, T., Sitarek, P., Saluk-Bijak, J., & Bijak, M. (2020). Melittin—A Natural Peptide from Bee Venom Which Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukaemia Cells. Biomolecules, 10(2), 247. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020247







