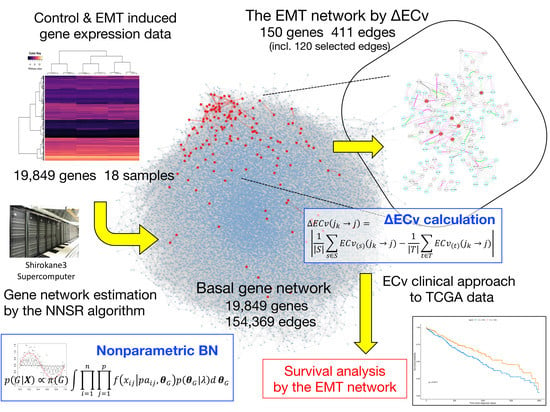
System-Based Differential Gene Network Analysis for Characterizing a Sample-Specific Subnetwork
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nonparametric Bayesian Network
2.2. Proposed Method for Evaluating Sample Specific Edge Contribution Values
2.3. Data Preparation
2.4. Differential Expression Gene Analysis
2.5. Molecular Function Analysis
2.6. ECv Matrix Clustering and Survival Analysis
2.7. Network Analysis and Visualization
2.8. Computation Environment
3. Results
3.1. Basal Gene Network Estimation
3.2. ΔECv Highlights the EMT-Characterized Edges
3.3. ΔECv Unveils the EMT Networks
3.4. Biological Validation for the EMT Network with the Comparison between ΔECv and DEG
3.5. A Clinical Approach Using the EMT Network
4. Discussion
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECv | Edge Contribution value |
| EMT | Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition |
| BN | Bayesian Network |
| DEG | Differentially Expressed Gene |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas project |
| NNSR | the Neighbor Node Sampling and Repeat algorithm |
| NSCLC | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer |
| LUAD | Lung Adenocarcinoma |
| LUSC | Lung Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| X | n-by-p data matrix whose element corresponds to the expression value of the j-th gene at the i-th sample (samples: , genes: ) |
| expression value of the k-th parent of the j-th gene at the i-th sample | |
| parameter vector of the conditional density | |
| value of the regression curve by B-splines, or contribution of the k-th parent of the j-th gene to the expression value of | |
| standard deviation for total observations of the j-th gene | |
| edge contribution value for edge with respect to the i-th sample | |
| E | n-by-m ECv matrix whose element corresponds to ECv of the v-th edge at the i-th sample (samples: , edges: ) |
References
- Lecca, P.; Priami, C. Biological network inference for drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schena, M.; Shalon, D.; Heller, R.; Chai, A.; Brown, P.O.; Davis, R.W. Parallel human genome analysis: microarray-based expression monitoring of 1000 genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10614–10619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rapaport, F.; Khanin, R.; Liang, Y.; Pirun, M.; Krek, A.; Zumbo, P.; Mason, C.E.; Socci, N.D.; Betel, D. Comprehensive evaluation of differential gene expression analysis methods for RNA-seq data. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravind, S.; Pablo, T.; Vamsi, K.M.; Sayan, M.; Benjamin, L.E.; Michael, A.G.; Amanda, P.; Scott, L.P.; Todd, R.G.; Eric, S.L.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.E.; Loh, S.K.; Low, S.T.; Mohamad, M.S.; Deris, S.; Zakaria, Z. A review on the computational approaches for gene regulatory network construction. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 48, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creixell, P.; Reimand, J.; Haider, S.; Wu, G.; Shibata, T.; Vazquez, M.; Mustonen, V.; Gonzalez-Perez, A.; Pearson, J.; Sander, C.; et al. Mutation Consequences and Pathway Analysis Working Group of the International Cancer Genome Consortium. Pathway and network analysis of cancer genomes. Nat. Method 2015, 12, 615–621. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, K.K.; Wang, D.; Sethi, A.; Muir, P.; Kitchen, R.; Cheng, C.; Gerstein, M. Cross-disciplinary network comparison: Matchmaking between hairballs. Cell Syst. 2016, 2, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Margolin, A.A.; Nemenman, I.; Basso, K.; Wiggins, C.; Stolovitzky, G.; Dalla Favera, R.; Califano, A. ARACNE: an algorithm for the reconstruction of gene regulatory networks in a mammalian cellular context. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7 (Suppl. 1), S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araki, H.; Tamada, Y.; Imoto, S.; Dunmore, B.; Sanders, D.; Humphrey, S.; Nagasaki, M.; Doi, A.; Nakanishi, Y.; Yasuda, K.; et al. Analysis of PPARα-dependent and PPARα-independent transcript regulation following fenofibrate treatment of human endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2009, 12, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hurley, D.; Watkins, W.; Araki, H.; Tamada, Y.; Muthukaruppan, A.; Ranjard, L.; Derkac, E.; Imoto, S.; Miyano, S.; et al. Cell cycle gene networks are associated with melanoma prognosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Affara, M.; Sanders, D.; Araki, H.; Tamada, Y.; Dunmore, B.J.; Humphreys, S.; Imoto, S.; Savoie, C.; Miyano, S.; Kuhara, S.; et al. Vasohibin-1 is identified as a master-regulator of endothelial cell apoptosis using gene network analysis. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, A.J.; Ramsey, S.A.; Filtz, T.M.; Kioussi, C. Differential gene regulatory networks in development and disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamada, Y.; Imoto, S.; Araki, H.; Nagasaki, M.; Print, C.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Miyano, S. Estimating genome-wide gene networks using nonparametric Bayesian network models on massively parallel computers. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2011, 8, 683–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimamura, T.; Imoto, S.; Shimada, Y.; Hosono, Y.; Niida, A.; Nagasaki, M.; Yamaguchi, R.; Takahashi, T.; Miyano, S. A novel network profiling analysis reveals system changes in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zeng, T.; Wang, X.; Li, G.; Chen, L. Unravelling personalized dysfunctional gene network of complex diseases based on differential network model. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuijjer, M.L.; Tung, M.G.; Yuan, G.; Quackenbush, J.; Glass, K. Estimating sample-specific regulatory networks. iScience 2019, 14, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Daemen, A.; Hatzivassiliou, G.; Arnott, D.; Wilson, C.; Zhuang, G.; Gao, M.; Liu, P.; Boudreau, A.; Johnson, L.; et al. Metabolic and transcriptional profiling reveals pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 as a mediator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance in tumor cells. Cancer Metab. 2014, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, S.; Goto, T.; Miyano, S. Estimation of genetic networks and functional structures between genes by using Bayesian networks and nonparametric regression. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2002, 7, 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Arima, C.; Kajino, T.; Tamada, Y.; Imoto, S.; Shimada, Y.; Nakatochi, M.; Suzuki, M.; Isomura, H.; Yatabe, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; et al. Lung adenocarcinoma subtypes definable by lung development-related miRNA expression profiles in association with clinicopathologic features. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendelman, R.; Xing, H.; Mirzoeva, O.K.; Sarde, P.; Curtis, C.; Feiler, H.S.; McDonagh, P.; Gray, J.W.; Khalil, I.; Korn, W.M. Bayesian network inference modeling identifies TRIB1 as a novel regulator of cell-cycle progression and survival in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldman, M.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. The UCSC Xena platform for public and private cancer genomics data visualization and interpretation. bioRxiv 2019, 326470. [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krämer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I.; et al. TCGAbiolinks: an R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mounir, M.; Lucchetta, M.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Bontempi, G.; Chen, X.; Noushmehr, H.; Colaprico, A.; Papaleo, E. New functionalities in the TCGAbiolinks package for the study and integration of cancer data from GDC and GTEx. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2019, 15, e1006701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerboth, S.; Housman, G.; Leary, M.; Longacre, M.; Byler, S.; Lapinska, K.; Willbanks, A.; Sarkar, S. EMT and tumor metastasis. Clin. Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. The extracellular matrix: Not just pretty fibrils. Science 2009, 326, 1216–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, K.; Li, Q.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Guo, C.W.; Li, P. Heparan sulfate D-glucosaminyl 3-O-sulfotransferase-3B1, a novel epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Hsu, Y.C.; Hsiao, Y.J.; Su, K.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, J.S.; Chen, Y.J.; et al. FAM198B is associated with prolonged survival and inhibits metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma via blockage of ERK-mediated MMP-1 expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Ding, N.; Li, Y.; Cheng, H.; Wang, D.; Yang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ruan, X.; et al. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) functions as a tumor suppressor in human melanoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20636–20649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzanakakis, G.; Kavasi, R.M.; Voudouri, K.; Berdiaki, A.; Spyridaki, I.; Tsatsakis, A.; Nikitovic, D. Role of the extracellular matrix in cancer-associated epithelial to mesenchymal transition phenomenon. Dev. Dyn. 2018, 247, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| T | Concordance |
|---|---|
| 10,000 | 72.7% |
| 100,000 | 89.0% |
| 500,000 | 94.3% |
| 1,000,000 | 95.6% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanaka, Y.; Tamada, Y.; Ikeguchi, M.; Yamashita, F.; Okuno, Y. System-Based Differential Gene Network Analysis for Characterizing a Sample-Specific Subnetwork. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020306
Tanaka Y, Tamada Y, Ikeguchi M, Yamashita F, Okuno Y. System-Based Differential Gene Network Analysis for Characterizing a Sample-Specific Subnetwork. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020306
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanaka, Yoshihisa, Yoshinori Tamada, Marie Ikeguchi, Fumiyoshi Yamashita, and Yasushi Okuno. 2020. "System-Based Differential Gene Network Analysis for Characterizing a Sample-Specific Subnetwork" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020306
APA StyleTanaka, Y., Tamada, Y., Ikeguchi, M., Yamashita, F., & Okuno, Y. (2020). System-Based Differential Gene Network Analysis for Characterizing a Sample-Specific Subnetwork. Biomolecules, 10(2), 306. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020306