Network Pharmacology-Based Approaches of Rheum undulatum Linne and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer Imply Their Regulation of Liver Failure with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Mice
Abstract
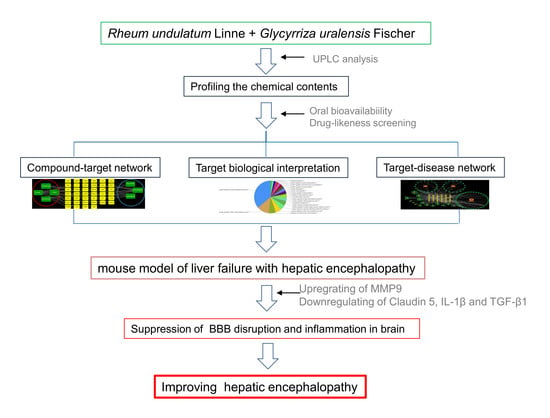
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Preparation of RG Extracts
2.3. Profiling the Chemical Contents of RUE and GUE by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography
2.4. Systems Pharmacology-Based Analysis
2.5. Animals
2.6. Behavioral Tests
2.7. Brain Immunohistochemistry
2.8. Blood Analysis
2.9. Liver Histopathology
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
2.11. Real-Time RT-qPCR Analysis
2.12. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Systems Pharmacology-Based Approach
3.2. RG Improves CCl4-Induced Behavioral Damage
3.3. RG Ameliorates CCl4-Induced Histopathological Changes of Brain
3.4. RG Inhibits the BBB Disruption and Neuroinflammation
3.5. RG Ameliorates CCl4-Induced Liver Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| CCl4 | carbon tetrachloride |
| C-T network | compound–target network |
| H&E | harri’s hematoxylin and eosin |
| HPLC | High-performance liquid chromatography |
| GABA | γ-Aminobutyric acid |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 beta |
| MMP-9 | matrix metallopeptidase 9 |
| OB | Oral bioavailability |
| TGF-β1 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 |
| UPLC | ultra-performance liquid chromatography |
References
- Ferenci, P. Hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterol. Rep. (Oxf). 2017, 5, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilstrup, H.; Amodio, P.; Bajaj, J.; Cordoba, J.; Ferenci, P.; Mullen, K.D.; Weissenborn, K.; Wong, P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology 2014, 60, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F. Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy: A new look at ammonia. Metab. Brain Dis. 2002, 17, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjihambi, A.; Arias, N.; Sheikh, M.; Jalan, R. Hepatic encephalopathy: A critical current review. Hepatol. Int. 2018, 12, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dadsetan, S.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Schousboe, A.; Bak, L.K. Glutamine and ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy. In Glutamine in Clinical Nutrition; Rajendram, R., Preedy, V.R., Patel, V.B., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Stickel, F.; Schuppan, D. Herbal medicine in the treatment of liver diseases. Dig. Liver Dis. 2007, 39, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.M.; Bell, B.P.; Dhotre, K.B.; Manos, M.M.; Terrault, N.A.; Zaman, A.; Murphy, R.C.; Vanness, G.R.; Thomas, A.R.; Bialek, S.R.; et al. Complementary and alternative medicine use in chronic liver disease patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 44, e40–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, C.; Tang, N.; Xie, G.; Zheng, X.; Liu, P.; Fu, L.; Xie, W.; Yao, F.; Li, H.; Jia, W. Management of hepatic encephalopathy by traditional chinese medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 835686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, J.B.; Zhou, G.D.; Shan, L.M.; Xiao, X.H. Investigations of free anthraquinones from rhubarb against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 104, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Lu, G.; Shen, H.M.; Chung, M.C.; Ong, C.N. Anti-cancer properties of anthraquinones from rhubarb. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, E.J.; Ngoc, T.M.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, Y.S.; Jung, Y.S. Chrysophanol-8-O-glucoside, an anthraquinone derivative in rhubarb, has antiplatelet and anticoagulant activities. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 118, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Lee, K.H.; Jang, H.S.; Park, M.J.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Ryu, S.Y.; et al. Rhapontigenin from Rheum undulatum protects against oxidative-stress-induced cell damage through antioxidant activity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2007, 70, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, Z.; Shuangnan, Z.; Xiaohe, X.; Zhen, W.; Yunfeng, B.; Tingting, H.; Chao, Z.; Yao, W.; Zhou, K.; Zhongxia, W.; et al. Rhubarb-based Chinese herbal formulae for hepatic encephalopathy: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 37, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Tang, T.; Fan, R.; Zhang, C.; Huang, Z.; Peng, W.; Gan, P.; Xiong, X.; Huang, W.; et al. Rhein and rhubarb similarly protect the blood–brain barrier after experimental traumatic brain injury via gp91phox subunit of NADPH oxidase/ROS/ERK/MMP-9 signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, F.; Xie, G.; Chen, Z.Q.; Li, H.G.; Tang, T.; Luo, J.K. Rhubarb attenuates blood–brain barrier disruption via increased zonula occludens-1 expression in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, E.H.; Baek, S.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, S.G.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.W. Effect of Rheum undulatum Linne extract and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer extract against arachidonic acid and iron-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cell and CCl4-induced liver injury in mice. Herb. Formula Sci. 2016, 24, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.C.; Yang, Y.S. Simultaneous quantification of flavonoids and triterpenoids in licorice using HPLC. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 850, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, K.H.; Jo, M.J.; Cho, W.J.; Lee, J.R.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.C.; Kim, Y.W.; Jee, S.Y. Bojesodok-eum, a Herbal Prescription, Ameliorates Acute Inflammation in Association with the Inhibition of NF-κB-Mediated Nitric Oxide and ProInflammatory Cytokine Production. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2012, 2012, 457370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Xie, X.Q. GPU accelerated chemical similarity calculation for compound library comparison. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Ling, Y. A novel chemometric method for the prediction of human oral bioavailability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6964–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Huang, C.; Li, P.; Guo, Z.; Tao, W.; Yang, Y.; et al. TCMSP: A database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J. Cheminform. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monteggia, L.M.; Luikart, B.; Barrot, M.; Theobold, D.; Malkovska, I.; Nef, S.; Parada, L.F.; Nestler, E.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor conditional knockouts show gender differences in depression-related behaviors. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, C. Pharmacokinetic analysis of rhein in Rheum undulatum L. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 84, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, T.; Miyawaki, Y.; Nishikawa, A.; Horiyama, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Kuwano, S. Prostaglandin E2-mediated stimulation of mucus synthesis and secretion by rhein anthrone, the active metabolite of sennosides A and B, in the mouse colon. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1990, 42, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströhle, A.; Höfler, M.; Pfister, H.; Müller, A.G.; Hoyer, J.; Wittchen, H.U.; Lieb, R. Physical activity and prevalence and incidence of mental disorders in adolescents and young adults. Psychol. Med. 2007, 37, 1657–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingawale, D.K.; Mandlik, S.K.; Naik, S.R. Models of hepatotoxicity and the underlying cellular, biochemical and immunological mechanism(s): A critical discussion. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 37, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giebel, S.J.; Menicucci, G.; McGuire, P.G.; Das, A. Matrix metalloproteinases in early diabetic retinopathy and their role in alteration of the blood-retinal barrier. Lab. Investig. 2005, 85, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.B.; You, N.; Zheng, L.; Li, J. Fecal microbiota transplantation prevents hepatic encephalopathy in rats with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic dysfunction. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6983–6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.M. Improvement of carbon tetrachloride-induced acute hepatic failure by transplantation of induced pluripotent stem cells without reprogramming factor c-Myc. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3598–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. MMP-mediated disruption of claudin-5 in the blood–brain barrier of rat brain after cerebral ischemia. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 762, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhanda, S.; Sandhir, R. Blood–brain Barrier Permeability Is Exacerbated in Experimental Model of Hepatic Encephalopathy via MMP-9 Activation and Downregulation of Tight Junction Proteins. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 3642–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spindler, K.R.; Hsu, T.H. Viral disruption of the blood–brain barrier. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Ohashi, N.; Li, W.; Eckman, C.; Nguyen, J.H. Disruptions of occludin and claudin-5 in brain endothelial cells in vitro and in brains of mice with acute liver failure. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1914–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhalala, U.S.; Koehler, R.C.; Kannan, S. Neuroinflammation and neuroimmune dysregulation after acute hypoxic-ischemic injury of developing brain. Front. Pediatr. 2015, 2, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bémeur, C.; Butterworth, R.F. Liver-brain proinflammatory signalling in acute liver failure: Role in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy and brain edema. Metab. Brain Dis. 2013, 28, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, R.F. The liver-brain axis in liver failure: Neuroinflammation and encephalopathy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Sample | Identity | Chemical Formula | Mass Accuracy (ppm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RUE (Rheum undulatum Linne) | Sennoside A | C42H38O20 | 145.85 ± 7.080 |
| Emodin | C15H10O5 | 1.20 ± 0.012 | |
| Chrysophanol | C15H10O4 | 0.064 ± 0.001 | |
| Aloe-emodin | C15H10O5 | 2.11 ± 0.616 | |
| Rhein | C15H8O6 | 29.47 ± 0.447 | |
| GUE (Glycyrriza uralensis) | Glycyrrhizin acid | C42H62O16 | 325.91 ± 6.8 |
| Liquiritigenin | C15H12O4 | 124.25 ± 3.7 | |
| Isoliquiritigenin | C15H12O4 | 6.08 ± 0.7 |
| Genes | Sense | Antisense |
|---|---|---|
| MMP-9 | 5′-TCCCTCTGAATAAAGTCGACA-3′ | 5′-AGGTGACAAGGTGGACCATG-3′ |
| IL-1β | 5′-CAGGATGAGGACATGAGC-3′ | 5′-CTCTGCAGACTCAAACTCCA-3′ |
| TGF- β1 | 5′-GAGGTTTGCTGGGGTGAG-3′ | 5′-CAGCACGAGGAGGAGCAG-3′ |
| GAPDH | 5′-AACGACCCCTTCATTGAC-3′ | 5′-TCCACGACATACTCAGCAC-3′ |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baek, S.Y.; Lee, E.H.; Oh, T.W.; Do, H.J.; Kim, K.-Y.; Park, K.-I.; Kim, Y.W. Network Pharmacology-Based Approaches of Rheum undulatum Linne and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer Imply Their Regulation of Liver Failure with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Mice. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030437
Baek SY, Lee EH, Oh TW, Do HJ, Kim K-Y, Park K-I, Kim YW. Network Pharmacology-Based Approaches of Rheum undulatum Linne and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer Imply Their Regulation of Liver Failure with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Mice. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(3):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030437
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaek, Su Youn, Eun Hye Lee, Tae Woo Oh, Hyun Ju Do, Kwang-Youn Kim, Kwang-Il Park, and Young Woo Kim. 2020. "Network Pharmacology-Based Approaches of Rheum undulatum Linne and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer Imply Their Regulation of Liver Failure with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Mice" Biomolecules 10, no. 3: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030437
APA StyleBaek, S. Y., Lee, E. H., Oh, T. W., Do, H. J., Kim, K.-Y., Park, K.-I., & Kim, Y. W. (2020). Network Pharmacology-Based Approaches of Rheum undulatum Linne and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer Imply Their Regulation of Liver Failure with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Mice. Biomolecules, 10(3), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10030437