Possible Mechanisms of Eosinophil Accumulation in Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. AEP and CEP
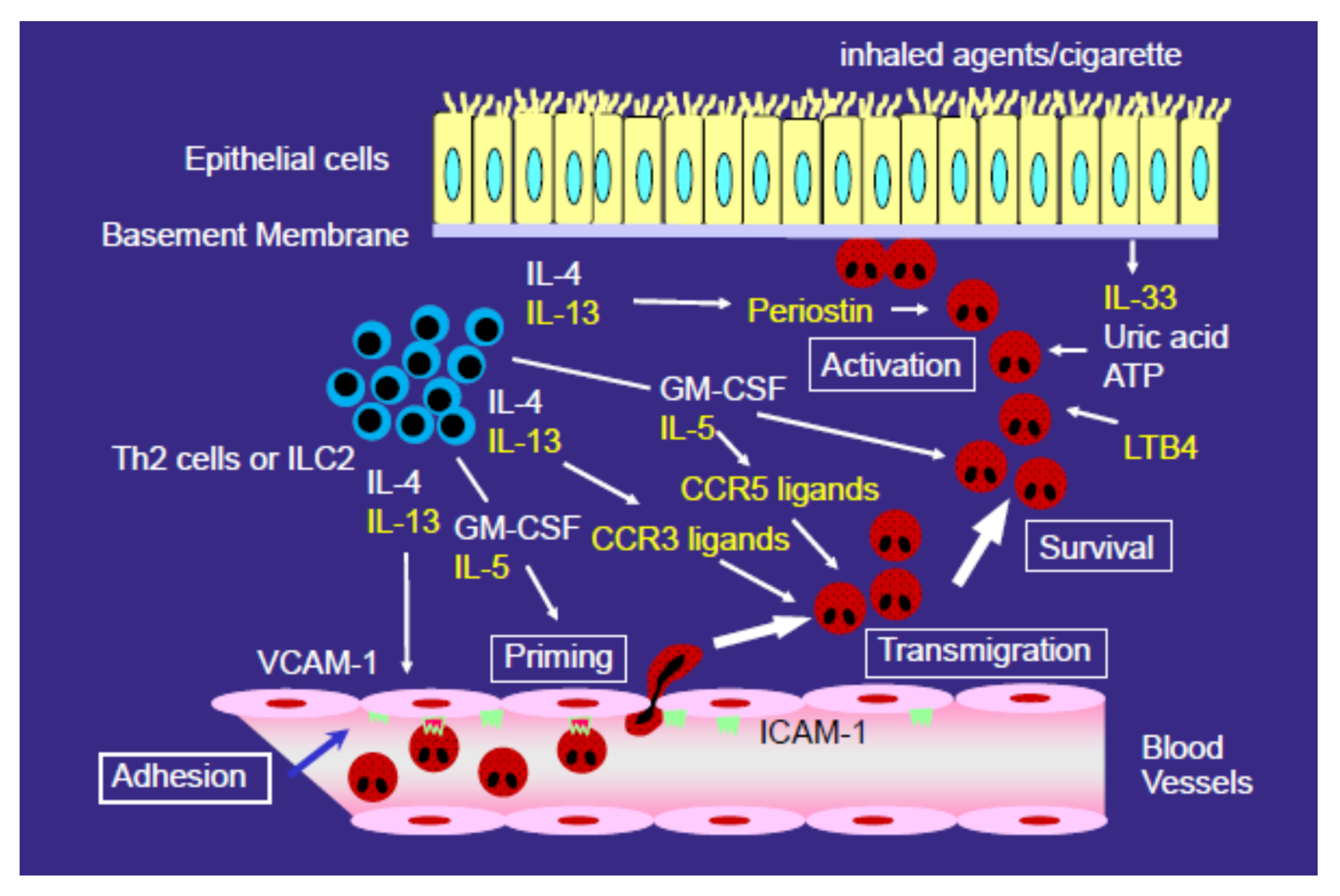
3. Mechanisms for the Development of Eosinophilic Airway Inflammation
4. Role of CCR3 Ligands or CCR5 Ligands in the Eosinophil Accumulation in EP
5. Role of CXCR3 Ligands or CCR4 Ligands in the Development of EP
6. Role of Type 2 Cytokines (IL-4 and IL-13) in the Development of EP
7. Role of Eosinophil Growth Factors/Cytokines in the Development of EP
8. Role of Lipid Mediators in the Development of EP
9. Possible Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Molecules in the Development of EP
10. Possible Role of Extracellular Matrix Protein in the Development of EP
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cottin, V.; Cordier, J.F. Eosinophilic pneumonias. Allergy 2005, 60, 841–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Suda, T. Eosinophilic pneumonia: A review of the previous literature, causes, diagnosis, and management. Allergol. Int. 2019, 68, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.N.; Pacht, E.R.; Gadek, J.E.; Davis, W.B. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia as a reversible cause of noninfectious respiratory failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1989, 321, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrington, C.B.; Addington, W.W.; Goff, A.M.; Madoff, I.M.; Marks, A.; Schwaber, J.R.; Gaensler, E.A. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 1969, 280, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philit, F.; Etienne-Mastroïanni, B.; Parrot, A.; Guérin, C.; Robert, D.; Cordier, J.F. Idiopathic acute eosinophilic pneumonia: A study of 22 patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, H.; Suda, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Shirai, M.; Gemma, H.; Shirai, T.; Toyoshima, M.; Imokawa, S.; Yasuda, K.; Ida, M.; et al. Alterations in smoking habits are associated with acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Chest 2008, 133, 1174–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagome, K.; Kato, J.; Kubota, S.; Kaneko, F.; Hisatomi, T.; Horiuchi, T. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia induced by cigarette smoking. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi 2000, 38, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rom, W.N.; Weiden, M.; Garcia, R.; Yie, T.A.; Vathesatogkit, P.; Tse, D.B.; McGuinness, G.; Roggli, V.; Prezant, D. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia in a New York City firefighter exposed to World Trade Center dust. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorr, A.F.; Scoville, S.L.; Cersovsky, S.B.; Shanks, G.D.; Ockenhouse, C.F.; Smoak, B.L.; Carr, W.W.; Petruccelli, B.P. Acute eosinophilic pneumonia among US Military personnel deployed in or near Iraq. JAMA 2004, 292, 2997–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomeer, M.J.; Costabe, U.; Rizzato, G.; Poletti, V.; Demedts, M. Comparison of registries of interstitial lung diseases in three European countries. Eur. Respir. J. Suppl. 2001, 32, 114s–118s. [Google Scholar]
- Sveinsson, O.A.; Isaksson, H.J.; Gudmundsson, G. Chronic eosinophilic pneumonia in Iceland: Clinical features, epidemiology and review. Laeknabladid 2007, 93, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okubo, Y.; Horie, S.; Hachiya, T.; Momose, T.; Tsukadaira, A.; Takashi, S.; Suzuki, J.; Isobe, M.; Sekiguchi, M. Predominant implication of IL-5 in acute eosinophilic pneumonia: Comparison with chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 1998, 116, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakahara, Y.; Hayashi, S.; Fukuno, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Yatsunami, J. Increased interleukin-5 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid is a major factor for eosinophil accumulation in acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Respiration 2001, 68, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Fukushima, K.; Matsukura, S. Elevated interleukin-18 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. Allergy 2004, 59, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, E.; Nureki, S.; Fukami, T.; Shigenaga, T.; Ando, M.; Ito, K.; Ando, H.; Sugisaki, K.; Kumamoto, T.; Tsuda, T. Elevated levels of thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, S.; Nobumoto, A.; Matsumoto, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Ehara, N.; Niki, T.; Inada, H.; Nishi, N.; Yamauchi, A.; Fukushima, K.; et al. Involvement of galectin-9 in lung eosinophilia in patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 153, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mato, N.; Bando, M.; Kusano, A.; Hirano, T.; Nakayama, M.; Uto, T.; Nakaya, T.; Yamasawa, H.; Sugiyama, Y. Clinical significance of interleukin 33 (IL-33) in patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. Allergol. Int. 2013, 62, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Nakagome, K.; Noguchi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Ueda, Y.; Soma, T.; Ikebuchi, K.; Nakamoto, H.; Nagata, M. Elevated uric acid and adenosine triphosphate concentrations in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of eosinophilic pneumonia. Allergol. Int. 2017, 66S, S27–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagome, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Kobayashi, T.; Ohta, S.; Ono, J.; Kobayashi, K.; Ikebuchi, K.; Noguchi, T.; Soma, T.; Yamauchi, K.; et al. Elevated Periostin Concentrations in the Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients with Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 178, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.A.; Bochner, B.S. Eosinophils and eosinophil-associated diseases: An update. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagibashi, T.; Satoh, M.; Nagai, Y.; Koike, M.; Takatsu, K. Allergic diseases: From bench to clinic-Contribution of the discovery of interleukin-5. Cytokine 2017, 98, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.; Pizzichini, M.M.; Kjarsgaard, M.; Inman, M.D.; Efthimiadis, A.; Pizzichini, E.; Hargreave, F.; O’Byrne, P.M. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haldar, P.; Brightling, C.E.; Hargadon, B.; Gupta, S.; Monteiro, W.; Sousa, A.; Marshall, R.P.; Bradding, P.; Green, R.H.; Wardlaw, A.J.; et al. Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory eosinophilic asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 973–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavord, I.D.; Korn, S.; Howarth, P.; Bleecker, E.R.; Buhl, R.; Keene, O.N.; Ortega, H.; Chanez, P. Mepolizumab for severe eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2012, 380, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Akuthota, P.; Jayne, D.; Khoury, P.; Klion, A.; Langford, C.A.; Merkel, P.A.; Moosig, F.; Specks, U.; Cid, M.C.; et al. EGPA Mepolizumab Study Team. Mepolizumab or Placebo for Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkis, E.; Patel, S.; Burns, K.; Batarseh, H.; Mador, M.J. Anti-interleukin (IL)-5 as a steroid-sparing agent in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. J. Asthma. 2018, 57, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, M.; Kono, Y.; Yamawaki, S.; Soeda, S.; Katsube, O.; Kishi, H.; To, Y. A case of chronic eosinophilic pneumonia successfully treated with mepolizumab. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2018, 6, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagome, K.; Nagata, M. Involvement and Possible Role of Eosinophils in Asthma Exacerbation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 18, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagome, K.; Nagata, M. Pathogenesis of airway inflammation in bronchial asthma. Auris. Nasus. Larynx. 2011, 38, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Bates, M.E.; Kita, H.; Busse, W.W. Eosinophil adhesion to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 activates superoxide anion generation. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 2194–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Nagata, M.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Kita, H.; Busse, W.W. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor augments ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 activation of eosinophil function. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 19, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, M.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Vrtis, R.; Busse, W.W. Endothelial cells upregulate eosinophil superoxide generation via VCAM-1 expression. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 1999, 29, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Tabe, K.; Sakamoto, Y. Eosinophil transmigration across VCAM-1-expressing endothelial cells is upregulated by antigen-stimulated mononuclear cells. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 125 (Suppl 1), 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, S.; Robinson, D.S.; Meng, Q.; Rottman, J.; Kennedy, R.; Ringler, D.J.; Mackay, C.R.; Daugherty, B.L.; Springer, M.S.; Durham, S.R.; et al. Enhanced expression of eotaxin and CCR3 mRNA and protein in atopic asthma. Association with airway hyperresponsiveness and predominant co-localization of eotaxin mRNA to bronchial epithelial and endothelial cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1997, 27, 3507–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Fukushima, K.; Mukae, H.; Kadota, J.I.; Kohno, S.; Matsukura, S. Elevated chemokine levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 106, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tateno, H.; Nakamura, H.; Minematsu, N.; Amakawa, K.; Terashima, T.; Fujishima, S.; Luster, A.D.; Lilly, C.M.; Yamaguchi, K. Eotaxin and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2001, 17, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagome, K.; Shoda, H.; Shirai, T.; Nishihara, F.; Soma, T.; Uchida, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Nagata, M. Eosinophil transendothelial migration induced by the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of acute eosinophilic pneumonia. Respirology 2017, 22, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Konno, Y.; Kanda, A.; Yamada, Y.; Yasuba, H.; Sakata, Y.; Fukuchi, M.; Tomoda, K.; Iwai, H.; Ueki, S. Critical role of CCL4 in eosinophil recruitment into the airway. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2019, 49, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Bates, M.E.; Vrtis, R.F.; Gern, J.E.; Kita, H.; Jarjour, N.N.; Busse, W.W.; Kelly, E.A. Decreased expression of membrane IL-5 receptor alpha on human eosinophils: I. Loss of membrane IL-5 receptor alpha on airway eosinophils and increased soluble IL-5 receptor alpha in the airway after allergen challenge. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6452–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Sedgwick, J.B.; Bates, M.E.; Vrtis, R.F.; Gern, J.E.; Kita, H.; Jarjour, N.N.; Busse, W.W.; Kelly, E.A. Decreased expression of membrane IL-5 receptor alpha on human eosinophils: II. IL-5 down-modulates its receptor via a proteinase-mediated process. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6459–6466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M.; Saito, K.; Tsuchiya, T.; Sakamoto, Y. Leukotriene D4 upregulates eosinophil adhesion via the cysteinyl leukotriene 1 receptor. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 109, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, K.; Nagata, M.; Kikuchi, I.; Sakamoto, Y. Leukotriene D4 and eosinophil transendothelial migration, superoxide generation, and degranulation via β2 integrin. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004, 93, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaura, M.; Nakajima, T.; Imai, T.; Harada, S.; Combadiere, C.; Tiffany, H.L.; Murphy, P.M.; Yoshie, O. Molecular cloning of human eotaxin, an eosinophil-selective CC chemokine, and identification of a specific eosinophil eotaxin receptor, CC chemokine receptor 3. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7725–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, H.; Miyamasu, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Fujisawa, T.; Ohta, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Morita, Y.; Hirai, K. Expression of CXCR4 in eosinophils: Functional analyses and cytokine-mediated regulation. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5935–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jinquan, T.; Jing, C.; Jacobi, H.H.; Reimert, C.M.; Millner, A.; Quan, S.; Hansen, J.B.; Dissing, S.; Malling, H.J.; Skov, P.S.; et al. CXCR3 expression and activation of eosinophils: Role of IFN-γ-inducible protein-10 and monokine induced by IFN-γ. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1548–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkerson, E.M.; Johansson, M.W.; Hebert, A.S.; Westphall, M.S.; Mathur, S.K.; Jarjour, N.N.; Schwantes, E.A.; Mosher, D.F.; Coon, J.J. The Peripheral Blood Eosinophil Proteome. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 1524–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larose, M.C.; Archambault, A.S.; Provost, V.; Laviolette, M.; Flamand, N. Regulation of Eosinophil and Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Trafficking in Asthma. Front Med. 2017, 4, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Kato, Y.; Atsuta, J.; Terada, A.; Iguchi, K.; Kamiya, H.; Yamada, H.; Nakajima, T.; Miyamasu, M.; Hirai, K. Chemokine production by the BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells: Differential regulation of eotaxin, IL-8, and RANTES by TH2- and TH1-derived cytokines. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000, 105, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Imburgia, C.; Dul, E.; Appelbaum, E.; O’Donnell, K.; O’Shannessy, D.J.; Brawner, M.; Fornwald, J.; Adamou, J.; Elshourbagy, N.A.; et al. Cloning and functional characterization of a novel human CC chemokine that binds to the CCR3 receptor and activates human eosinophils. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1997, 62, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamkhioued, B.; Garcia-Zepeda, E.A.; Abi-Younes, S.; Nakamura, H.; Jedrzkiewicz, S.; Wagner, L.; Renzi, P.M.; Allakhverdi, Z.; Lilly, C.; Hamid, Q.; et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-4 expression in the airways of patients with asthma. Induction in epithelial cells and mononuclear cells by proinflammatory cytokines. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.; Strange, P.G. The chemokine receptor, CCR5. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, T.N.; Power, C.A.; Shaw, J.P.; Proudfoot, A.E. Chemokine blockers-therapeutics in the making? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchimoto, Y.; Kanehiro, A.; Miyahara, N.; Koga, H.; Ikeda, G.; Waseda, K.; Tanimoto, Y.; Ueha, S.; Kataoka, M.; Gelfand, E.W.; et al. Requirement for chemokine receptor 5 in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 45, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaku, Y.; Nakagome, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Hagiwara, K.; Kanazawa, M.; Nagata, M. IFN-γ-inducible protein of 10 kDa upregulates the effector functions of eosinophils through β2 integrin and CXCR3. Respir. Res. 2011, 12, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, S.; Fukushima, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Ehara, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Hirashima, M. Accumulation of CXCR3-expressing eosinophils and increased concentration of its ligands (IP10 and Mig) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with chronic eosinophilic pneumonia. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 137, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, S.; Fukushima, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Abe, K.; Onai, N.; Matsushima, K.; Matsukura, S. Accumulation of CCR4-expressing CD4+ T cells and high concentration of its ligands (TARC and MDC) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. Allergy 2003, 58, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, E.; Nureki, S.; Ono, E.; Ando, M.; Matsuno, O.; Fukami, T.; Ueno, T.; Kumamoto, T. Circulating thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine/CCL17 is a useful biomarker for discriminating acute eosinophilic pneumonia from other causes of acute lung injury. Chest 2007, 131, 1726–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Jarjour, N.N.; Busse, W.W.; Kelly, E.A. Chemokine receptor expression on human eosinophils from peripheral blood and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid after segmental antigen challenge. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, H.; Kudo, K.; Izumi, S.; Ohta, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Yamaguchi, M.; Matsushima, K.; Morita, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Hirai, K. Chemokine receptor expression profile of eosinophils at inflamed tissue sites: Decreased CCR3 and increased CXCR4 expression by lung eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 108, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochner, B.S.; Bickel, C.A.; Taylor, M.L.; MacGlashan, D.W., Jr.; Gray, P.W.; Raport, C.J.; Godiska, R. Macrophage-derived chemokine induces human eosinophil chemotaxis in a CC chemokine receptor 3- and CC chemokine receptor 4-independent manner. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1999, 103, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Corren, J.; Pavord, I.D.; Maspero, J.; Wenzel, S.; Rabe, K.F.; Busse, W.W.; Ford, L.; Sher, L.; FitzGerald, J.M.; et al. Dupilumab Efficacy and Safety in Moderate-to-Severe Uncontrolled Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Han, J.K.; Desrosiers, M.; Hellings, P.W.; Amin, N.; Lee, S.E.; Mullol, J.; Greos, L.S.; Bosso, J.V.; Laidlaw, T.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): Results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials. Lancet 2019, 394, 1638–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.T.; Mosher, D.F. IL-5 induces suspended eosinophils to undergo unique global reorganization associated with priming. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sannohe, S.; Adachi, T.; Hamada, K.; Honda, K.; Yamada, Y.; Saito, N.; Cui, C.H.; Kayaba, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Chihara, J. Upregulated response to chemokines in oxidative metabolism of eosinophils in asthma and allergic rhinitis. Eur. Respir. J. 2003, 21, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, E.; Taniguchi, M.; Mita, H.; Higashi, N.; Fukutomi, Y.; Tanimoto, H.; Sekiya, K.; Oshikata, C.; Tsuburai, T.; Tsurikisawa, N.; et al. Increased urinary leukotriene E4 concentration in patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medzhitov, R. Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenfeldt, A.L.; Wenneras, C. Danger signals derived from stressed and necrotic epithelial cells activate human eosinophils. Immunology 2004, 112, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kouzaki, H.; Kita, H. Human eosinophils recognize endogenous danger signal crystalline uric acid and produce proinflammatory cytokines mediated by autocrine ATP. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6350–6358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Soma, T.; Noguchi, T.; Nakagome, K.; Nakamoto, H.; Kita, H.; Nagata, M. ATP drives eosinophil effector responses through P2 purinergic receptors. Allergol. Int. 2015, 64 (Suppl 1), 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussion, C.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherry, W.B.; Yoon, J.; Bartemes, K.R.; Iijima, K.; Kita, H. A novel IL-1 family cytokine, IL-33, potently activates human eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izuhara, K.; Arima, K.; Ohta, S.; Suzuki, S.; Inamitsu, M.; Yamamoto, K. Periostin in allergic inflammation. Allergol. Int. 2014, 63, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, G.; Erickson, R.W.; Choy, D.F.; Mosesova, S.; Wu, L.C.; Solberg, O.D.; Shikotra, A.; Carter, R.; Audusseau, S.; Hamid, Q.; et al. Bronchoscopic Exploratory Research Study of Biomarkers in Corticosteroid-refractory Asthma (BOBCAT) Study Group: Periostin is a systemic biomarker of eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthmatic patients. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanemitsu, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Izuhara, K.; Tohda, Y.; Kita, H.; Horiguchi, T.; Kuwabara, K.; Tomii, K.; Otsuka, K.; Fujimura, M.; et al. Increased periostin associates with greater airflow limitation in patients receiving inhaled corticosteroids. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.W.; Annis, D.S.; Mosher, D.F. αMβ2 integrin-mediated adhesion and motility of IL-5-stimulated eosinophils on periostin. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 48, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, T.; Nakagome, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Uchida, Y.; Soma, T.; Nakamoto, H.; Nagata, M. Periostin upregulates the effector functions of eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1449–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.W.; Khanna, M.; Bortnov, V.; Annis, D.S.; Nguyen, C.L.; Mosher, D.F. IL-5-stimulated eosinophils adherent to periostin undergo stereotypic morphological changes and ADAM8-dependent migration. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Tanaka, H.; Yasokawa, N.; Kittaka, M.; Kurose, K.; Abe, M.; Yoshioka, D.; Shirai, R.; Nakazato, M.; et al. Elevated levels of periostin and TGF-β1 in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with idiopathic eosinophilic pneumonia. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto, Y.; Hirahara, K.; Kiuchi, M.; Wada, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Kanno, T.; Okano, M.; Kokubo, K.; Onodera, A.; Sakurai, D.; et al. Amphiregulin-Producing Pathogenic Memory T Helper 2 Cells Instruct Eosinophils to Secrete Osteopontin and Facilitate Airway Fibrosis. Immunity 2018, 49, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puxeddu, I.; Berkman, N.; Ribatti, D.; Bader, R.; Haitchi, H.M.; Davies, D.E.; Howarth, P.H.; Levi-Schaffer, F. Osteopontin is expressed and functional in human eosinophils. Allergy 2010, 65, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, A.; Kurokawa, M.; Konno, S.; Ito, K.; Kon, S.; Ashino, S.; Nishimura, T.; Uede, T.; Hizawa, N.; Huang, S.K.; et al. Osteopontin is involved in migration of eosinophils in asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 39, 1152–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, T.; Miyazaki, E.; Ando, M.; Nureki, S.; Kumamoto, T. Osteopontin levels are elevated in patients with eosinophilic pneumonia. Respirology 2010, 15, 1111–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakagome, K.; Nagata, M. Possible Mechanisms of Eosinophil Accumulation in Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040638
Nakagome K, Nagata M. Possible Mechanisms of Eosinophil Accumulation in Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040638
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakagome, Kazuyuki, and Makoto Nagata. 2020. "Possible Mechanisms of Eosinophil Accumulation in Eosinophilic Pneumonia" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040638
APA StyleNakagome, K., & Nagata, M. (2020). Possible Mechanisms of Eosinophil Accumulation in Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Biomolecules, 10(4), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040638




