Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Fish: Characterization, Isolation, Enrichment, and Recent Advances of In Vitro Culture Systems
Abstract
:1. Overview of Fish Germ Cell Biology
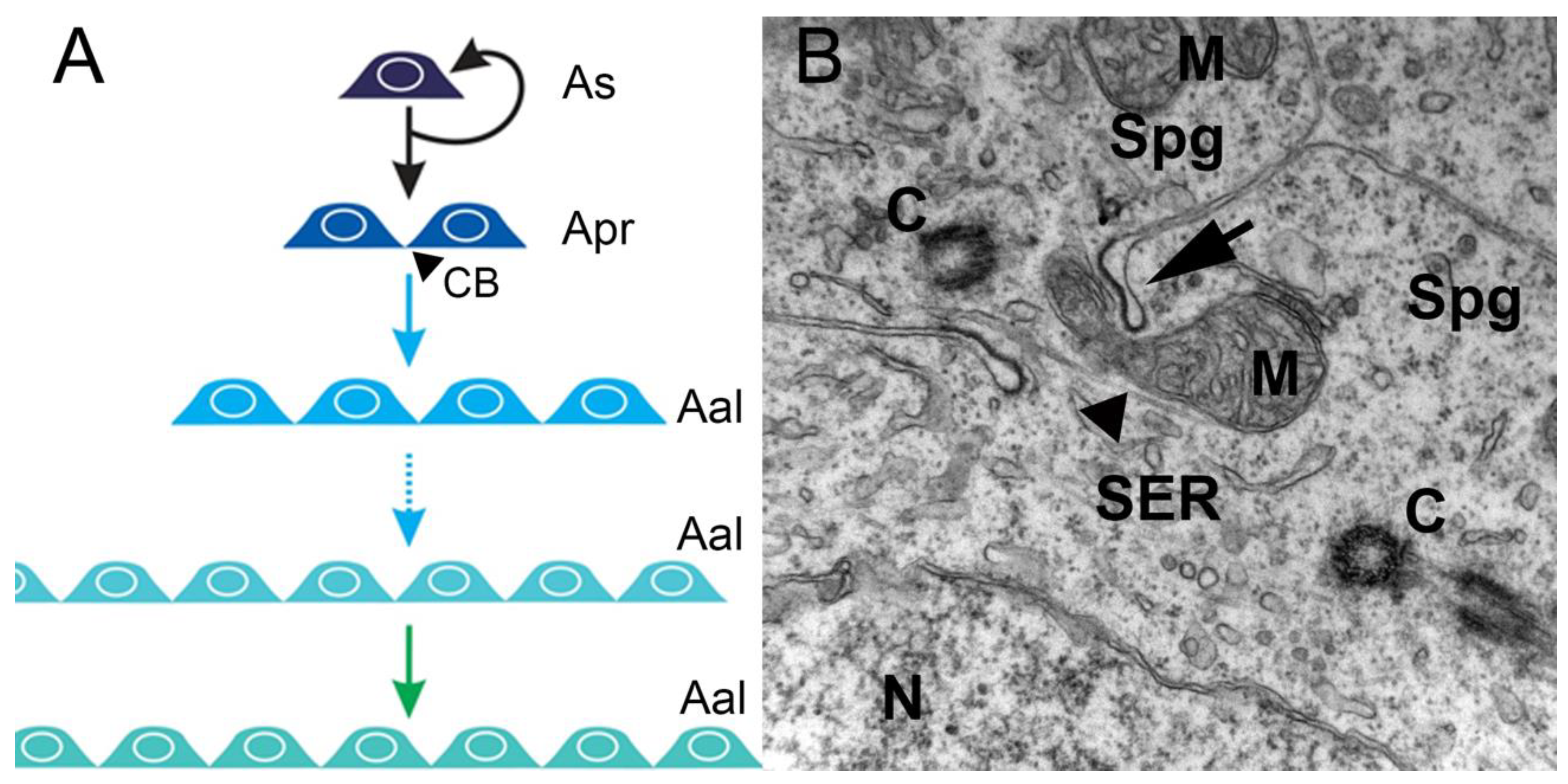
1.1. Spermatogenesis—an Overview
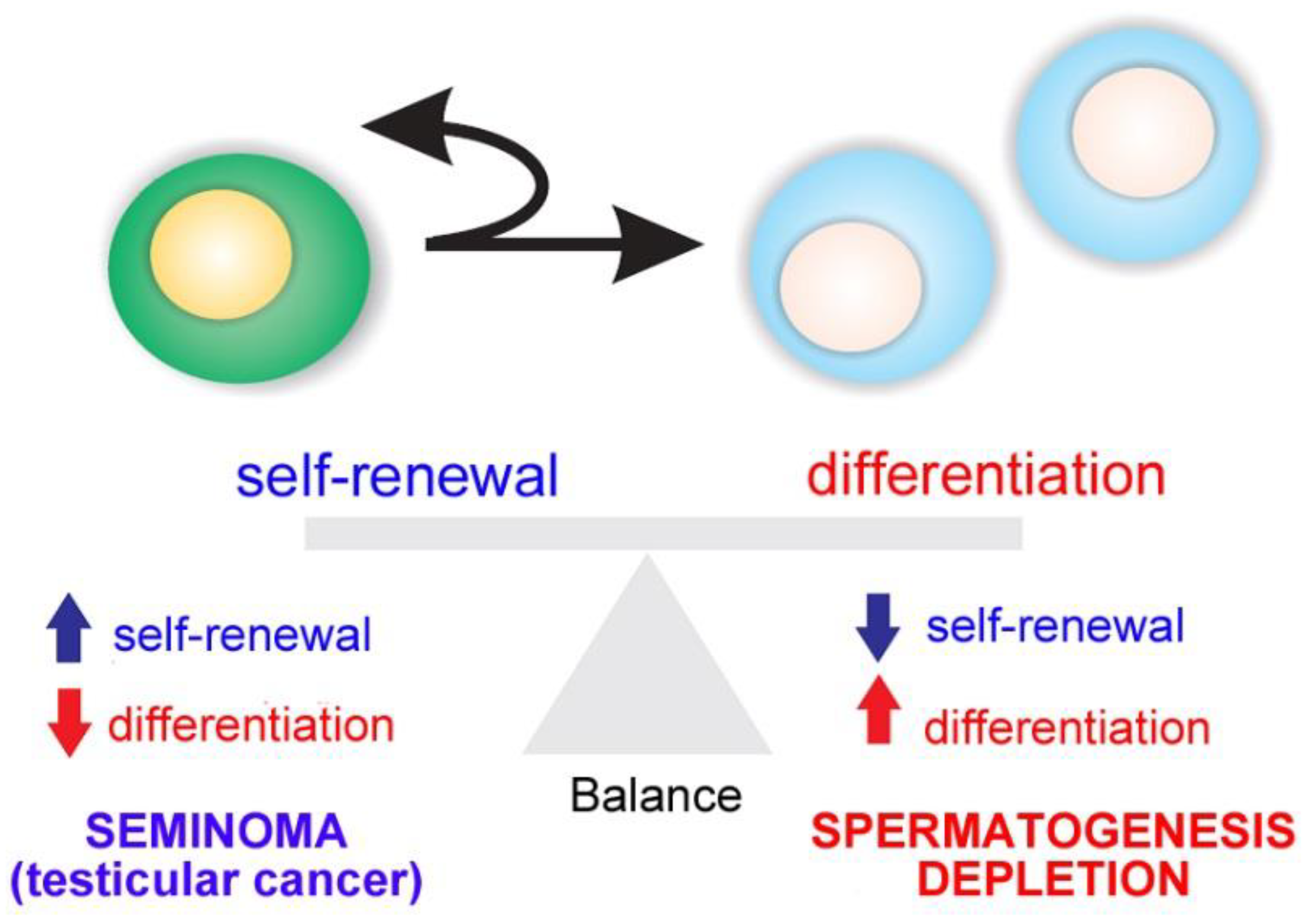
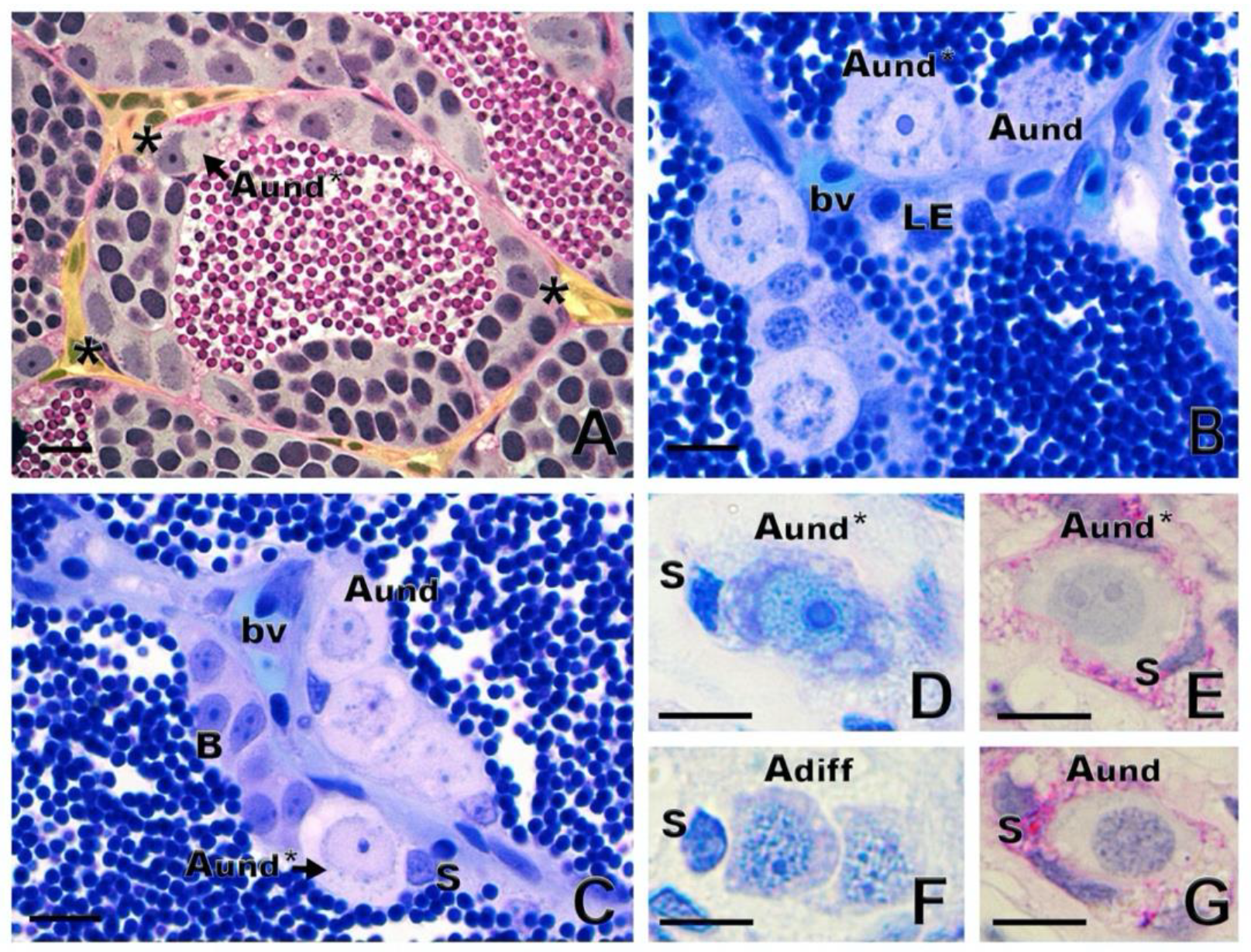
1.2. Spermatogonial Stem Cell Niche
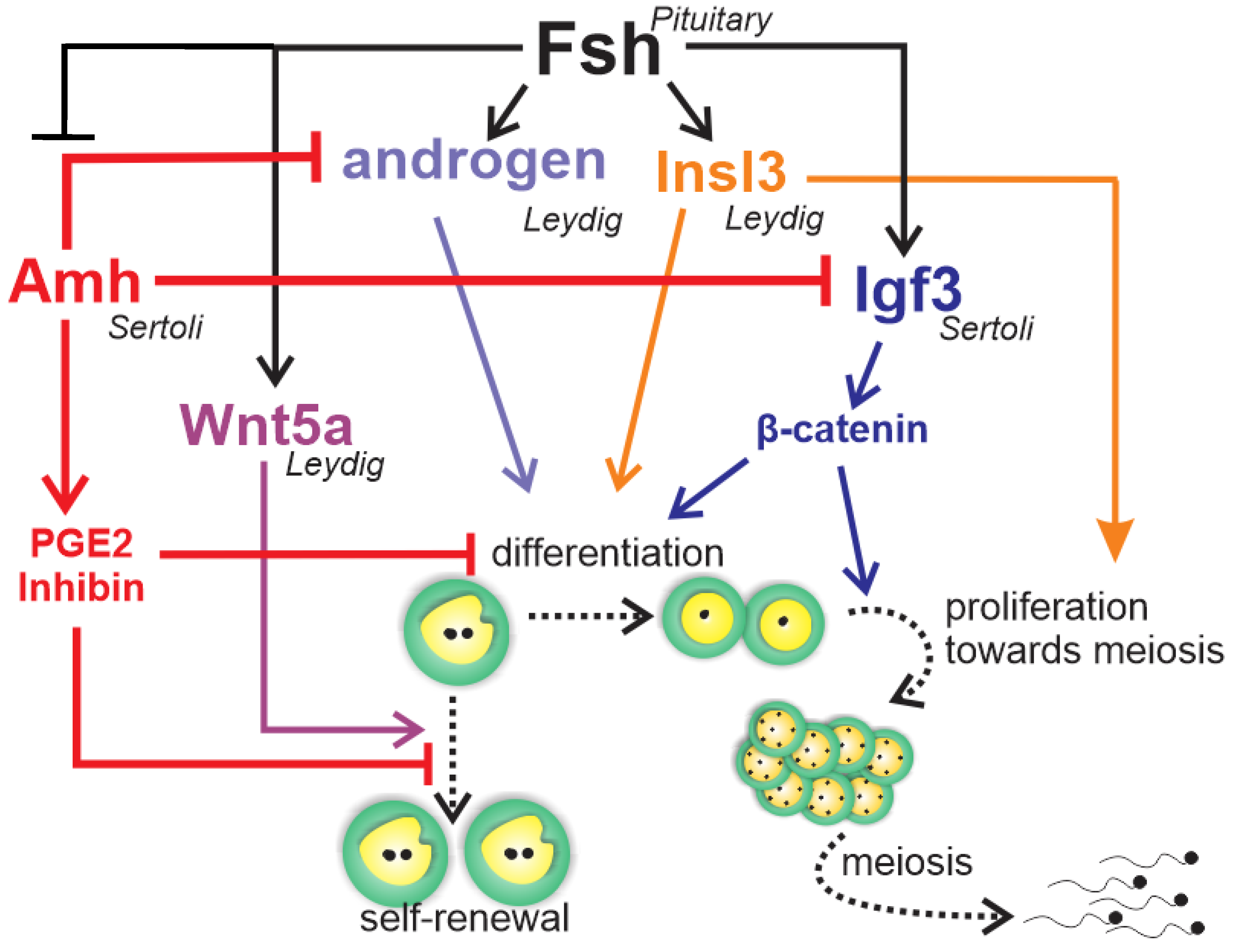
1.3. Endocrine and Paracrine Regulation
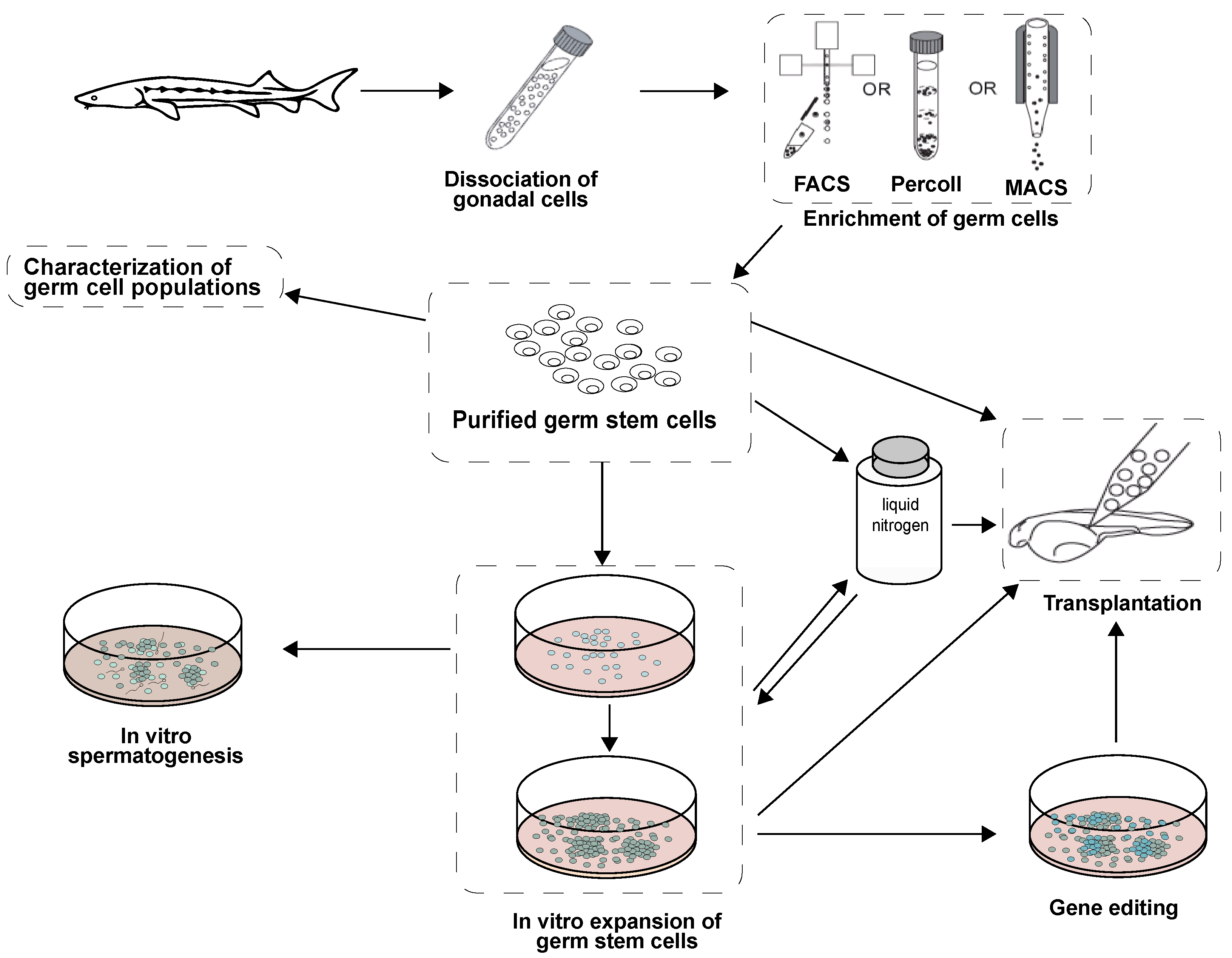
2. Isolation and Enrichment of Germ Cells in Fish
2.1. Enzymatic Digestion
2.2. Germ Cell Purification
2.2.1. Density Gradient Centrifugation
2.2.2. Differential Plating
2.2.3. Flow Cytometric and Magnetically-Activated Cell-Sorting
2.3. Future Trends
3. Germ Cell Cultures
3.1. Serum in Germ Cell Cultures
3.2. Feeder Cells and Growth Factors
3.3. Organ Cultures
3.4. Three-Dimensional Cultures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Rooij, D.G.; Russell, L.D. All you wanted to know about spermatogonia but were afraid to ask. J. Androl. 2000, 21, 776–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Rooij, D.G. Proliferation and differentiation of spermatogonial stem cells. Reproduction-Cambridge- 2001, 121, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rooij, D.G. Rapid expansion of the spermatogonial stem cell tool box. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7939–7940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Rooij, D.G. Regulation of spermatogonial stem cell behavior in vivo and in vitro. Anim. Reprod. 2018, 3, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Ehmcke, J.; Wistuba, J.; Schlatt, S. Spermatogonial stem cells: Questions, models and perspectives. Hum. Reprod. Update 2006, 12, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baloch, A.R.; Franěk, R.; Tichopád, T.; Fučíková, M.; Rodina, M.; Pšenička, M. Dnd1 knockout in sturgeons by CRISPR/Cas9 generates germ cell free host for surrogate production. Animals 2019, 9, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franěk, R.; Marinović, Z.; Lujić, J.; Urbányi, B.; Fučíková, M.; Kašpar, V.; Pšenička, M.; Horváth, Á. Cryopreservation and transplantation of common carp spermatogonia. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0205481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fatira, E.; Havelka, M.; Labbé, C.; Depincé, A.; Iegorova, V.; Pšenička, M.; Saito, T. Application of interspecific Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (iSCNT) in sturgeons and an unexpectedly produced gynogenetic sterlet with homozygous quadruple haploid. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Ferosekhan, S.; Sahoo, S.K.; Sundaray, J.K.; Jayasankar, P.; Barman, H.K. Production of fertile sperm from in vitro propagating enriched spermatogonial stem cells of farmed catfish, Clarias batrachus. Zygote 2016, 24, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, R.W.; de França, L.R.; Lareyre, J.J.; LeGac, F.; Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Nobrega, R.H.; Miura, T. Spermatogenesis in fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 390–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, D.W. Intercellular bridges. Exp. Cell Res. 1961, 8, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grier, H.J. Comparative organization of Sertoli cells including the Sertoli cell barrier. The Sertoli Cell 1993, 703–739. [Google Scholar]
- Loir, M. Trout steroidogenic testicular cells in primary culture: II. Steroidogenic activity of interstitial cells, Sertoli cells, and spermatozoa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1990, 78, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maekawa, M.; Kamimura, K.; Nagano, T. Peritubular Myoid Cells in the Testis: Their Structure and Function. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 1996, 59, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- França, L.R.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Morais, R.D.V.S.; Assis, L.H.D.C.; Schulz, R.W. Sertoli cell structure and function in anamniote vertebrates. In Sertoli Cell Biology; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 385–407. [Google Scholar]
- Hess, R.A.; De Franca, L.R. Spermatogenesis and cycle of the seminiferous epithelium. In Molecular Mechanisms in Spermatogenesis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo, A.F.A.; França, L.R.; Hess, R.A.; Costa, G.M.J. Sertoli cells are capable of proliferation into adulthood in the transition region between the seminiferous tubules and the rete testis in Wistar rats. Cell Cycle 2016, 15, 2486–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Callard, G.V. Endocrinology of Leydig cells in nonmammalian vertebrates. Leydig Cell 1996, 308–331. [Google Scholar]
- Wistuba, J.; Schlatt, S. Transgenic mouse models and germ cell transplantation: Two excellent tools for the analysis of genes regulating male fertility. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2002, 77, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, R.H.; De Souza Morais, R.D.V.; Crespo, D.; De Waal, P.P.; De França, L.R.; Schulz, R.W.; Bogerd, J. Fsh stimulates spermatogonial proliferation and differentiation in zebrafish via Igf3. Endocrinology 2015, 156, 3804–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Safian, D.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Regulation of spermatogonial development by Fsh: The complementary roles of locally produced Igf and Wnt signaling molecules in adult zebrafish testis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 284, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, R.H.; Greebe, C.D.; van de Kant, H.; Bogerd, J.; de França, L.R.; Schulz, R.W. Spermatogonial stem cell niche and spermatogonial stem cell transplantation in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e0012808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Cuevas, M.; Matunis, E.L. The stem cell niche: Lessons from the Drosophila testis. Development 2011, 138, 2861–2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacerda, S.M.S.N.; Aponte, P.M.; Costa, G.M.J.; Segatelli, T.M. An overview of spermatogonial stem cell physiology, niche and transplantation in fish. Anim. Reprod. 2012, 9, 798–808. [Google Scholar]
- De Siqueira-Silva, D.H.; da Silva Rodrigues, M.; Nóbrega, R.H. Testis structure, spermatogonial niche and Sertoli cell efficiency in Neotropical fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 273, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spradling, A.; Drummond-Barbosa, D.; Kai, T. Stem cells find their niche. Nature 2001, 414, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, E.; Tumbar, T.; Guasch, G. Socializing with the neighbors: Stem cells and their niche. Cell 2004, 116, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, A. A glossary for stem-cell biology. Nature 2006, 441, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, D.J. Spermatogonial stem cell transplantation and testicular function. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 322, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, R.A.; Cooke, P.S.; Hofmann, M.-C.; Murphy, K.M. Mechanistic insights into the regulation of the spermatogonial stem cell niche. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooke, P.S.; Hess, R.A.; Simon, L.; Schlesser, H.N.; Carnes, K.; Tyagi, G.; Hofmann, M.C.; Murphy, K.M. The transcription factor Ets-related molecule (ERM) is essential for spermatogonial stem cell maintenance and self-renewal. Anim. Reprod. 2018, 3, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Oatley, J.M.; Oatley, M.J.; Avarbock, M.R.; Tobias, J.W.; Brinster, R.L. Colony stimulating factor 1 is an extrinsic stimulator of mouse spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal. Development 2009, 136, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mäkelä, J.-A.; Hobbs, R.M. Molecular regulation of spermatogonial stem cell renewal and differentiation. Reproduction 2019, 1, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayerhofer, A. Peritubular cells of the human testis: Prostaglandin E2 and more. Andrology 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Hornick, J.R.; Griswold, M.D.; Russell, L.D. Distribution of type A spermatogonia in the mouse is not random. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiarini-Garcia, H.; Raymer, A.M.; Russell, L.D. Non-random distribution of spermatogonia in rats: Evidence of niches in the seminiferous tubules. Reproduction-Cambridge- 2003, 126, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Sukeno, M.; Nabeshima, Y. A vasculature-associated niche for undifferentiated spermatogonia in the mouse testis. Science 2007, 317, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rooij, D.G.; Griswold, M.D. Questions about spermatogonia posed and answered since 2000. J. Androl. 2012, 33, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Enomoto, H.; Suzuki, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Simons, B.D.; Yoshida, S. Mouse spermatogenic stem cells continually interconvert between equipotent singly isolated and syncytial states. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitadate, Y.; Jörg, D.J.; Tokue, M.; Maruyama, A.; Ichikawa, R.; Tsuchiya, S.; Segi-Nishida, E.; Nakagawa, T.; Uchida, A.; Kimura-Yoshida, C. Competition for mitogens regulates spermatogenic stem cell homeostasis in an open niche. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Siqueira-Silva, D.H.; Saito, T.; dos Santos-Silva, A.P.; da Silva Costa, R.; Psenicka, M.; Yasui, G.S. Biotechnology applied to fish reproduction: Tools for conservation. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulze, C. Response of the human testis to long-term estrogen treatment: Morphology of Sertoli cells, Leydig cells and spermatogonial stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 1988, 251, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, C. Morphological characteristics of the spermatogonial stem cells in man. Cell Tissue Res. 1979, 198, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Nishimura, T.; Higashijima, S.I.; Tanaka, M. Identification of germline stem cells in the ovary of the teleost medaka. Science 2010, 328, 1561–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paiva Camargo, M.; Cassel, M.; Oliveira de Jesus, L.W.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Borella, M.I. Characterization of undifferentiated spermatogonia and the spermatogonial niche in the lambari fish Astyanax altiparanae. Theriogenology 2017, 96, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinster, R.L.; Zimmermann, J.W. Spermatogenesis following male germ-cell transplantation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11298–11302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majhi, S.K.; Hattori, R.S.; Yokota, M.; Watanabe, S.; Strüssmann, C.A. Germ cell transplantation using sexually competent fish: An approach for rapid propagation of endangered and valuable germlines. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e0006132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lacerda, S.M.S.N.; Batlouni, S.R.; Costa, G.M.J.; Segatelli, T.M.; Quirino, B.R.; Queiroz, B.M.; Kalapothakis, E.; França, L.R. A new and fast technique to generate offspring after germ cells transplantation in adult fish: The nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) model. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e0010740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Li, C.-J.; Yue, H.-M.; Du, H.; Yang, X.-G.; Yoshino, T.; Hayashida, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Wei, Q.-W. Establishment of intraperitoneal germ cell transplantation for critically endangered Chinese sturgeon Acipenser sinensis. Theriogenology 2017, 94, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, R.S.; Yoshinaga, T.T.; Katayama, N.; Hattori-Ihara, S.; Tsukamoto, R.Y.; Takahashi, N.S.; Tabata, Y.A. Surrogate production of Salmo salar oocytes and sperm in triploid Oncorhynchus mykiss by germ cell transplantation technology. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutsu, T.; Shikina, S.; Kanno, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Production of trout offspring from triploid salmon parents. Science 2007, 317, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacerda, S.M.; Dos, S.N.; Costa, G.M.J.; de França, L.R. Biology and identity of fish spermatogonial stem cell. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2014, 207, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagano, M.C.; Yeh, J.R. The identity and fate decision control of spermatogonial stem cells: Where is the point of no return. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2013; Volume 102, pp. 61–95. ISBN 0070-2153. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, A.; Suzuki, K.; Yoshizaki, G. Flow-Cytometric Isolation of Testicular Germ Cells from Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Carrying the Green Fluorescent Protein Gene Driven by Trout vasa Regulatory Regions. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okutsu, T.; Suzuki, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Yoshizaki, G. Testicular germ cells can colonize sexually undifferentiated embryonic gonad and produce functional eggs in fish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buaas, F.W.; Kirsh, A.L.; Sharma, M.; McLean, D.J.; Morris, J.L.; Griswold, M.D.; de Rooij, D.G.; Braun, R.E. Plzf is required in adult male germ cells for stem cell self-renewal. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panda, R.P.; Barman, H.K.; Mohapatra, C. Isolation of enriched carp spermatogonial stem cells from Labeo rohita testis for in vitro propagation. Theriogenology 2011, 76, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozaki, Y.; Saito, K.; Shinya, M.; Kawasaki, T.; Sakai, N. Evaluation of Sycp3, Plzf and Cyclin B3 expression and suitability as spermatogonia and spermatocyte markers in zebrafish. Gene Expr. Patterns 2011, 11, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, C.; Barman, H.K. Identification of promoter within the first intron of Plzf gene expressed in carp spermatogonial stem cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 6433–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautier, A.; Bosseboeuf, A.; Auvray, P.; Sourdaine, P. Maintenance of Potential Spermatogonial Stem Cells In Vitro by GDNF Treatment in a Chondrichthyan Model (Scyliorhinus canicula L.)1. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellaiche, J.; Lareyre, J.-J.; Cauty, C.; Yano, A.; Allemand, I.; Le Gac, F. Spermatogonial Stem Cell Quest: nanos2, Marker of a Subpopulation of Undifferentiated a Spermatogonia in Trout Testis1. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, M.; Su, B.; Lipke, E.A.; Perera, D.A.; Li, C.; Qin, Z.; Li, Y.; Dunn, D.A.; Cek, S.; Peatman, E. Spermatogonial stem cells specific marker identification in channel catfish, Ictalurus punctatus and blue catfish, I. furcatus. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 1545–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, S.M.S.N.; Martinez, E.R.M.; Mura, I.L.D.D.; Doretto, L.B.; Costa, G.M.J.; Silva, M.A.; Digmayer, M.; Nóbrega, R.H.; França, L.R. Duration of spermatogenesis and identification of spermatogonial stem cell markers in a Neotropical catfish, Jundiá (Rhamdia quelen). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 273, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Lindahl, M.; Hyvönen, M.E.; Parvinen, M.; de Rooij, D.G.; Hess, M.W.; Raatikainen-Ahokas, A.; Sainio, K.; Rauvala, H.; Lakso, M. Regulation of cell fate decision of undifferentiated spermatogonia by GDNF. Science 2000, 287, 1489–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, T.; Sharma, M.; Nabeshima, Y.; Braun, R.E.; Yoshida, S. Functional hierarchy and reversibility within the murine spermatogenic stem cell compartment. Science 2010, 328, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costa, G.M.J.; Avelar, G.F.; Guimarães, D.A.; França, L.R. Postnatal testis development in the collared peccary (Tayassu tajacu), with emphasis on spermatogonial stem cells markers and niche. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 273, 98–107. [Google Scholar]
- Savvulidi, F.; Ptacek, M.; Savvulidi Vargova, K.; Stadnik, L. Manipulation of spermatogonial stem cells in livestock species. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos Nassif Lacerda, S.M.; Costa, G.M.J.; da Silva, M.D.A.; Almeida Campos-Junior, P.H.; Segatelli, T.M.; Peixoto, M.T.D.; Resende, R.R.; de França, L.R. Phenotypic characterization and in vitro propagation and transplantation of the Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) spermatogonial stem cells. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 192, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, S.; Hayashi, M.; Kouguchi, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Miwa, M.; Yoshizaki, G. Expression patterns of gdnf and gfrα1 in rainbow trout testis. Gene Expr. Patterns 2014, 14, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Froschauer, A.; Khatun, M.M.; Sprott, D.; Franz, A.; Rieger, C.; Pfennig, F.; Gutzeit, H.O. oct4-EGFP reporter gene expression marks the stem cells in embryonic development and in adult gonads of transgenic medaka. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Sánchez, A.V.; Camp, E.; Mullor, J.L. Fishing pluripotency mechanisms in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Manali, D.; Wang, T.; Bhat, N.; Hong, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, R.; Hong, Y. Identification of pluripotency genes in the fish medaka. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, K. A gated exit from pluripotency. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengner, C.J.; Camargo, F.D.; Hochedlinger, K.; Welstead, G.G.; Zaidi, S.; Gokhale, S.; Scholer, H.R.; Tomilin, A.; Jaenisch, R. Oct4 expression is not required for mouse somatic stem cell self-renewal. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, M.; Ichida, K.; Sadaie, S.; Miwa, M.; Fujihara, R.; Nagasaka, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Establishment of novel monoclonal antibodies for identification of type A spermatogonia in teleosts†. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 101, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichida, K.; Hayashi, M.; Miwa, M.; Kitada, R.; Takahashi, M.; Fujihara, R.; Boonanuntanasarn, S.; Yoshizaki, G. Enrichment of transplantable germ cells in salmonids using a novel monoclonal antibody by magnetic-activated cell sorting. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 1810–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichida, K.; Kawamura, W.; Miwa, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Kubokawa, T.; Hayashi, M.; Yazawa, R.; Yoshizaki, G. Specific visualization of live type A spermatogonia of Pacific bluefin tuna using fluorescent dye-conjugated antibodies†. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 100, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kajiura-Kobayashi, H.; Nagahama, Y. A novel stage-specific antigen is expressed only in early stages of spermatogonia in Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica testis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1998, 51, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, A.; Von Schalburg, K.; Cooper, G.; Koop, B.F.; Yoshizaki, G. Identification of a molecular marker for type A spermatogonia by microarray analysis using gonadal cells from pvasa-GFP transgenic rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mol. Reprod. Dev. Inc. Gamete Res. 2009, 76, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, K.; Shikina, S.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Lymphocyte antigen 75 (Ly75/CD205) is a surface marker on mitotic germ cells in rainbow trout. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 83, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagasawa, K.; Miwa, M.; Yazawa, R.; Morita, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Characterization of lymphocyte antigen 75 (Ly75/CD205) as a potential cell-surface marker on spermatogonia in Pacific bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Ishikawa, Y.; Tanaka, M. Expression and syntenic analyses of four nanos genes in medaka. Zoolog. Sci. 2009, 26, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, J.G.; Parsons, T.F. Glycoprotein hormones: Structure and function. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1981, 50, 465–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, R.I.; Wreford, N.G.; O’donnell, L.; De Kretser, D.M.; Robertson, D.M. The endocrine regulation of spermatogenesis: Independent roles for testosterone and FSH. J. Endocrinol. 1996, 148, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerdoss, S.; Chang, Y.-F.; Buddavarapu, K.C.; Chen, H.-I.H.; Shetty, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Kumar, T.R.; Rao, M.K. Androgen-responsive microRNAs in mouse Sertoli cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e0041146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shirakawa, T.; Yaman-Deveci, R.; Tomizawa, S.; Kamizato, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Sone, H.; Sato, Y.; Sharif, J.; Yamashita, A.; Takada-Horisawa, Y. An epigenetic switch is crucial for spermatogonia to exit the undifferentiated state toward a Kit-positive identity. Development 2013, 140, 3565–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagano, M.; Ryu, B.-Y.; Brinster, C.J.; Avarbock, M.R.; Brinster, R.L. Maintenance of mouse male germ line stem cells in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 68, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, T.; Miyake, H.; Miura, C.; Kamei, H.; Aida, K.; Miura, T. Follicle-stimulating hormone induces spermatogenesis mediated by androgen production in Japanese eel, Anguilla japonica. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-López, Á.; De Jonge, H.; Nóbrega, R.H.; De Waal, P.P.; Van Dijk, W.; Hemrika, W.; Taranger, G.L.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Studies in zebrafish reveal unusual cellular expression patterns of gonadotropin receptor messenger ribonucleic acids in the testis and unexpected functional differentiation of the gonadotropins. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2349–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Lopez, A.; Bogerd, J.; Granneman, J.C.M.; van Dijk, W.; Trant, J.M.; Taranger, G.L.; Schulz, R.W. Leydig cells express follicle-stimulating hormone receptors in African catfish. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chauvigné, F.; Zapater, C.; Gasol, J.M.; Cerdà, J. Germ-line activation of the luteinizing hormone receptor directly drives spermiogenesis in a nonmammalian vertebrate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar]
- Safian, D.; Ryane, N.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Fsh stimulates Leydig cell Wnt5a production, enriching zebrafish type A spermatogonia. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 239, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assis, L.H.C.; Crespo, D.; Morais, R.D.V.S.; França, L.R.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. INSL3 stimulates spermatogonial differentiation in testis of adult zebrafish (Danio rerio). Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 363, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Planas, J.V.; Swanson, P.; Dickhoff, W.W. Regulation of testicular steroid production in vitro by gonadotropins (GTH I and GTH II) and cyclic AMP in coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch). Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1993, 91, 8–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, D.; Assis, L.H.C.; Furmanek, T.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Expression profiling identifies Sertoli and Leydig cell genes as Fsh targets in adult zebrafish testis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 437, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambroni, E.; Rolland, A.D.; Lareyre, J.J.; Le Gac, F. Fsh and Lh have common and distinct effects on gene expression in rainbow trout testis. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 50, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skaar, K.S.; Nobrega, R.H.; Magaraki, A.; Olsen, L.C.; Schulz, R.W.; Male, R. Proteolytically activated, recombinant Anti-Müllerian hormone inhibits androgen secretion, proliferation, and differentiation of spermatogonia in adult zebrafish testis organ cultures. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 3527–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morais, R.D.V.S.; Crespo, D.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Lemos, M.S.; van de Kant, H.J.G.; de França, L.R.; Male, R.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Antagonistic regulation of spermatogonial differentiation in zebrafish (Danio rerio) by Igf3 and Amh. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017, 454, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adolfi, M.C.; Nakajima, R.T.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Schartl, M. Intersex, hermaphroditism, and gonadal plasticity in vertebrates: Evolution of the Müllerian duct and Amh/Amhr2 signaling. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 149–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfennig, F.; Standke, A.; Gutzeit, H.O. The role of Amh signaling in teleost fish–multiple functions not restricted to the gonads. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2015, 223, 87–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Miura, C.; Konda, Y.; Yamauchi, K. Spermatogenesis-preventing substance in Japanese eel. Development 2002, 129, 2689–2697. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Liu, X.; Dai, S.; Xiao, H.; Qi, S.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Jie, M.; Cheng, C.H.K.; Wang, D. Regulation of spermatogenesis and reproductive capacity by Igf3 in tilapia. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safian, D.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Igf3 activates β-catenin signaling to stimulate spermatogonial differentiation in zebrafish. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 238, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellve, A.; Cavicchia, J.; Millette, C.; O’Brien, D.; Bhatnagar, Y.; Dym, M. Spermatogenic cells of the prepuberal mouse: Isolation and morphological characterization. J. Cell Biol. 1977, 74, 68–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, N. Transmeiotic differentiation of zebrafish germ cells into functional sperm in culture. Development 2002, 129, 3359–3365. [Google Scholar]
- Kossack, N.; Meneses, J.; Shefi, S.; Nguyen, H.N.; Chavez, S.; Nicholas, C.; Gromoll, J.; Turek, P.J.; Reijo-Pera, R.A. Isolation and characterization of pluripotent human spermatogonial stem cell-derived cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaul, G.; Kumar, S.; Kumari, S. Enrichment of CD9+ spermatogonial stem cells from goat (Capra aegagrus hircus) testis using magnetic microbeads. Stem Cell Discov. 2012, 2, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, H.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, R.; Chen, T.; Deng, J.; Gui, J. Establishment of a normal medakafish spermatogonial cell line capable of sperm production in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8011–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakai, N. In vitro male germ cell cultures of zebrafish. Methods 2006, 39, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shikina, S.; Yoshizaki, G. Improved In Vitro Culture Conditions to Enhance the Survival, Mitotic Activity, and Transplantability of Rainbow Trout Type A Spermatogonia1. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 83, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pšenička, M.; Saito, T.; Linhartová, Z.; Gazo, I. Isolation and transplantation of sturgeon early-stage germ cells. Theriogenology 2015, 83, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pšenička, M.; Saito, T.; Rodina, M.; Dzyuba, B. Cryopreservation of early stage Siberian sturgeon Acipenser baerii germ cells, comparison of whole tissue and dissociated cells. Cryobiology 2016, 72, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, G.; Ichikawa, M.; Hayashi, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Miwa, M.; Shikina, S.; Okutsu, T. Sexual plasticity of ovarian germ cells in rainbow trout. Development 2010, 137, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, T.-T.; Saito, T.; Crodian, J.; Collodi, P. Zebrafish Germline Chimeras Produced by Transplantation of Ovarian Germ Cells into Sterile Host Larvae1. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shikina, S.; Ihara, S.; Yoshizaki, G. Culture conditions for maintaining the survival and mitotic activity of rainbow trout transplantable type A spermatogonia. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, K.; Hou, L.; Sun, K.; Xie, W.; Wu, J. Improved efficiency of female germline stem cell purification using fragilis-based magnetic bead sorting. Stem Cells Dev. 2011, 20, 2197–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, T.; Hofmann, M.-C. Isolation of Undifferentiated and Early Differentiating Type A Spermatogonia from Pou5f1-GFP Reporter Mice. In Germline Development; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ohgawara, H.; Iwanaga, T.; Yui, R.; Nishijima, S.; Hirata, Y. Monolayer-forming islet cell culture from neonatal pig pancreas: Using sequential treatment with EDTA-dispase and monoiodoacetic acid for preparation and purification. Tohoku, J. Exp. Med. 1987, 153, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diogo, M.M.; da Silva, C.L.; Cabral, J.M.S. Separation Technologies for Stem Cell Bioprocessing. In Stem Cells and Cell Therapy; Al-Rubeai, M., Naciri, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 157–181. ISBN 978-94-007-7196-3. [Google Scholar]
- Bellaïche, J.; Goupil, A.-S.; Sambroni, E.; Lareyre, J.-J.; Le Gac, F. Gdnf-Gfra1 Pathway Is Expressed in a Spermatogenetic-Dependent Manner and Is Regulated by Fsh in a Fish Testis1. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, H.; Morishima, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Saito, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamaha, E.; Arai, K. Chromosome Doubling in Early Spermatogonia Produces Diploid Spermatozoa in a Natural Clonal Fish1. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 80, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, T.T.; Tesfamichael, A.; Collodi, P. Production of Zebrafish Offspring from Cultured Female Germline Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0062660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shikina, S.; Nagasawa, K.; Hayashi, M.; Furuya, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Short-term in vitro culturing improves transplantability of type A spermatogonia in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kise, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Sato, M.; Tashiro, M.; Yazawa, R.; Nagasaka, Y.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Flow-Cytometric Isolation and Enrichment of Teleost Type A Spermatogonia Based on Light-Scattering Properties1. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 86, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ichida, K.; Kise, K.; Morita, T.; Yazawa, R.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Flow-cytometric enrichment of Pacific bluefin tuna type A spermatogonia based on light-scattering properties. Theriogenology 2017, 101, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abascal, F.J.; Megina Martínez, C.; Medina, A. Testicular development in migrant and spawning bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus (L.)) from the eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean. Fish. Bull. 2004, 102, 407–417. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Sosa, J.R.; Dobson, H.; Hahnel, A. Isolation and transplantation of spermatogonia in sheep. Theriogenology 2006, 66, 2091–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, B.P.; Sukhwani, M.; Winkler, F.; Pascarella, J.N.; Peters, K.A.; Sheng, Y.; Valli, H.; Rodriguez, M.; Ezzelarab, M.; Dargo, G.; et al. Spermatogonial stem cell transplantation into rhesus testes regenerates spermatogenesis producing functional sperm. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Tang, Z.; Xiong, T.; Tang, W. Isolation and characterization of human spermatogonial stem cells. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rolland, A.D.; Lareyre, J.J.; Goupil, A.S.; Montfort, J.; Ricordel, M.J.; Esquerré, D.; Hugot, K.; Houlgatte, R.; Chalmel, F.; Le Gac, F. Expression profiling of rainbow trout testis development identifies evolutionary conserved genes involved in spermatogenesis. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linhartová, Z.; Rodina, M.; Guralp, H.; Gazo, I.; Saito, T.; Pšenička, M. Isolation and cryopreservation of early stages of germ cells of tench (Tinca tinca). Czech, J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 59, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, M.; Morita, T.; Katayama, N.; Yoshizaki, G. Production of genetically diversified fish seeds using spermatogonial transplantation. Aquaculture 2014, 422, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkouby, Y.M.; Mullins, M.C. Methods for the analysis of early oogenesis in Zebrafish. Dev. Biol. 2017, 430, 310–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.-T.; Tesfamichael, A.; Collodi, P. Identification of promoter elements responsible for gonad-specific expression of zebrafish Deadend and its application to ovarian germ cell derivation. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2013, 57, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanatsu-Shinohara, M.; Inoue, K.; Ogonuki, N.; Morimoto, H.; Ogura, A.; Shinohara, T. Serum- and Feeder-Free Culture of Mouse Germline Stem Cells1. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.; Megee, S.; Rathi, R.; Dobrinski, I. Protein gene product 9.5 is a spermatogonia-specific marker in the pig testis: Application to enrichment and culture of porcine spermatogonia. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2006, 73, 1531–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aponte, P.M.; De Rooij, D.G. Biomanipulation of bovine spermatogonial stem cells. Anim. Reprod. 2018, 5, 16–22. [Google Scholar]
- Julius, M.H.; Herzenberg, L.A. Isolation of antigen-binding cells from unprimed mice: Demonstration of antibody-forming cell precursor activity and correlation between precursor and secreted antibody avidities. J. Exp. Med. 1974, 140, 904–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, S.F.; Van Den Engh, G. Flow cytometry and cell sorting. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2007, 106, 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, S.F.; Van Den Engh, G. High-speed cell sorting: Fundamentals and recent advances. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003, 14, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Engh, G. High speed cell sorting. Emerg. Tools Single Cell Anal. Adv. Opt. Meas. Technol. 2000, 8, 21–48. [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara, T.; Orwig, K.E.; Avarbock, M.R.; Brinster, R.L. Spermatogonial stem cell enrichment by multiparameter selection of mouse testis cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8346–8351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oatley, J.M.; Brinster, R.L. Regulation of spermatogonial stem cell self-renewal in mammals. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2008, 24, 263–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanatsu-Shinohara, M.; Morimoto, H.; Shinohara, T. Enrichment of mouse spermatogonial stem cells by melanoma cell adhesion molecule expression. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinaki, M.; Djourabtchi, A.; Golestaneh, N. Long-term culture of human SSEA-4 positive spermatogonial stem cells (SSCs). J. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altman, E.; Yango, P.; Moustafa, R.; Smith, J.F.; Klatsky, P.C.; Tran, N.D. Characterization of human spermatogonial stem cell markers in fetal, pediatric, and adult testicular tissues. Reproduction 2014, 148, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Valli, H.; Sukhwani, M.; Dovey, S.L.; Peters, K.A.; Donohue, J.; Castro, C.A.; Chu, T.; Marshall, G.R.; Orwig, K.E. Fluorescence- and magnetic-activated cell sorting strategies to isolate and enrich human spermatogonial stem cells. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hermann, B.P.; Sukhwani, M.; Salati, J.; Sheng, Y.; Chu, T.; Orwig, K.E. Separating spermatogonia from cancer cells in contaminated prepubertal primate testis cell suspensions. Hum. Reprod. 2011, 26, 3222–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokalov, S.V.; Gutzeit, H.O. Spermatogenesis in testis primary cell cultures of the tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Dev. Dyn. 2005, 233, 1238–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, K.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Yoshizaki, G.; Miwa, M.; Babiak, I. Identification and migration of primordial germ cells in Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar: Characterization of vasa, dead end, and lymphocyte antigen 75 genes. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kobayashi, T.; Yoshizaki, G.; Takeuchi, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Isolation of highly pure and viable primordial germ cells from rainbow trout by GFP-dependent flow cytometry. Mol. Reprod. Dev. Inc. Gamete Res. 2004, 67, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, C.S.; Sykes, N.L. Magnetic labeling and cell sorting. J. Immunol. Methods 1984, 73, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, H.; Tahmoorespur, M.; Hosseini, S.M.; Nasiri, Z.; Bahadorani, M.; Hajian, M.; Nasiri, M.R.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. THY1 as a reliable marker for enrichment of undifferentiated spermatogonia in the goat. Theriogenology 2013, 80, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Avarbock, M.R.; Brinster, R.L. Culture Conditions and Single Growth Factors Affect Fate Determination of Mouse Spermatogonial Stem Cells1. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 71, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gassei, K.; Ehmcke, J.; Schlatt, S. Efficient enrichment of undifferentiated GFR alpha 1+ spermatogonia from immature rat testis by magnetic activated cell sorting. Cell Tissue Res. 2009, 337, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Murthy, S.K. Stem cell separation technologies. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schönfeldt, V.; von Krishnamurthy, H.; Foppiani, L.; Schlatt, S. Magnetic Cell Sorting Is a Fast and Effective Method of Enriching Viable Spermatogonia from Djungarian Hamster, Mouse, and Marmoset Monkey Testes1. Biol. Reprod. 1999, 61, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buageaw, A.; Sukhwani, M.; Ben-Yehudah, A.; Ehmcke, J.; Rawe, V.Y.; Pholpramool, C.; Orwig, K.E.; Schlatt, S. GDNF Family Receptor alpha1 Phenotype of Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Immature Mouse Testes1. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 73, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alipoor, F.J.; Gilani, M.A.S.; Eftekhari-Yazdi, P.; Hampa, A.D.; Hosseinifar, H.; Alipour, H.; Panah, M.L. Achieving high survival rate following cryopreservation after isolation of prepubertal mouse spermatogonial cells. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2009, 26, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nickkholgh, B.; Mizrak, S.C.; Korver, C.M.; van Daalen, S.K.M.; Meissner, A.; Repping, S.; van Pelt, A.M.M. Enrichment of spermatogonial stem cells from long-term cultured human testicular cells. Fertil. Steril. 2014, 102, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatsu-Shinohara, M.; Mori, Y.; Shinohara, T. Enrichment of Mouse Spermatogonial Stem Cells Based on Aldehyde Dehydrogenase Activity1. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 89, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohni, K.; Zhang, X.; Tan, S.L.; Chan, P.; Nagano, M. CD9 Is Expressed on Human Male Germ Cells That Have a Long-Term Repopulation Potential after Transplantation into Mouse Testes1. Biol. Reprod. 2012, 87, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, H.; Avarbock, M.R.; Brinster, R.L. Growth factors essential for self-renewal and expansion of mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16489–16494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reding, S.C.; Stepnoski, A.L.; Cloninger, E.W.; Oatley, J.M. THY1 is a conserved marker of undifferentiated spermatogonia in the pre-pubertal bull testis. Reproduction 2010, 139, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poudineh, M.; Aldridge, P.M.; Ahmed, S.; Green, B.J.; Kermanshah, L.; Nguyen, V.; Tu, C.; Mohamadi, R.M.; Nam, R.K.; Hansen, A.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of circulating tumour cell phenotypes using nanoparticle-mediated magnetic ranking. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2017, 12, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nery, A.A.; Wrenger, C.; Ulrich, H. Recognition of biomarkers and cell-specific molecular signatures: Aptamers as capture agents. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creemers, L.B.; den Ouden, K.; van Pelt, A.M.M.; de Rooij, D.G. Maintenance of adult mouse type A spermatogonia in vitro: Influence of serum and growth factors and comparison with prepubertal spermatogonial cell culture. Reproduction 2002, 124, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.; Sato, G. Serum-free cell culture: A unifying approach. Cell 1980, 22, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatsu-Shinohara, M.; Miki, H.; Inoue, K.; Ogonuki, N.; Toyokuni, S.; Ogura, A.; Shinohara, T. Long-Term Culture of Mouse Male Germline Stem Cells Under Serum-or Feeder-Free Conditions1. Biol. Reprod. 2005, 72, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurita, K.; Burgess, S.M.; Sakai, N. Transgenic zebrafish produced by retroviral infection of in vitro-cultured sperm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1263–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClusky, L.M. Fetal bovine serum simultaneously stimulates apoptosis and DNA synthesis in premeiotic stages of spermatogenesis in spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias) in vitro: Modulation by androgen and spermatogenic activity status. Apoptosis 2008, 13, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolero, F.; Kaighn, M.E.; Camalier, R.F.; Saffiotti, U. Effects of serum and serum-derived factors on growth and differentiation of mouse keratinocytes. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. 1986, 22, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Baker, H.; Hancock, W.S.; Fawaz, F.; McCaman, M.; Pungor, E. Proteomic analysis for the assessment of different lots of fetal bovine serum as a raw material for cell culture. Part IV. Application of proteomics to the manufacture of biological drugs. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1294–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodaira, K.; Imada, M.; Goto, M.; Tomoyasu, A.; Fukuda, T.; Kamijo, R.; Suda, T.; Higashio, K.; Katagiri, T. Purification and identification of a BMP-like factor from bovine serum. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.T.; Collodi, P. Dorsomorphin Promotes Survival and Germline Competence of Zebrafish Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Culture. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0071332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, J.C.; Chandler, G.L.; Damoulis, V.A.; Fustino, N.J.; Lillard, K.; Looijenga, L.; Margraf, L.; Rakheja, D.; Amatruda, J.F. Mutation in the type IB bone morphogenetic protein receptor Alk6b impairs germ-cell differentiation and causes germ-cell tumors in zebrafish. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13153–13158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pellegrini, M.; Grimaldi, P.; Rossi, P.; Geremia, R.; Dolci, S. Developmental expression of BMP4/ALK3/SMAD5 signaling pathway in the mouse testis: A potential role of BMP4 in spermatogonia differentiation. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3363–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aoshima, K.; Baba, A.; Makino, Y.; Okada, Y. Establishment of Alternative Culture Method for Spermatogonial Stem Cells Using Knockout Serum Replacement. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0077715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawasaki, T.; Saito, K.; Sakai, C.; Shinya, M.; Sakai, N. Production of zebrafish offspring from cultured spermatogonial stem cells. Genes Cells 2012, 17, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Miura, C.; Yamauchi, K. Spermatogenesis in the Japanese eel. In Eel biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003; pp. 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, H.; Yomogida, K.; Dohmae, K.; Nishimune, Y. Regulation of proliferation and differentiation in spermatogonial stem cells: The role of c-kit and its ligand SCF. Development 2000, 127, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, S.; Segretain, D.; Nishikawa, S.; Nishikawa, S.-I.; Sage, J.; Cuzin, F.; Rassoulzadegan, M. Stage-specific expression of the Kit receptor and its ligand (KL) during male gametogenesis in the mouse: A Kit-KL interaction critical for meiosis. Development 1998, 125, 4585–4593. [Google Scholar]
- Loir, M.; Sourdaine, P. Testes cells: Isolation and culture. Anal. Tech. 1994, 3, 249–272. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, C.; Miura, T.; Yamashita, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Nagahama, Y. Hormonal induction of all stages of spermatogenesis in germ-somatic cell coculture from immature Japanese eel testis. Dev. Growth Differ. 1996, 38, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, K.; Sakai, N. Functionally Distinctive Testicular Cell Lines of Zebrafish to Support Male Germ Cell Development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2004, 67, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.; Gutzeit, H.O. Primary culture of medaka (Oryzias latipes) testis: A test system for the analysis of cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell Tissue Res. 2003, 313, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamra, F.K.; Schultz, N.; Chapman, K.M.; Grellhesl, D.M.; Cronkhite, J.T.; Hammer, R.E.; Garbers, D.L. Defining the spermatogonial stem cell. Dev. Biol. 2004, 269, 393–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nasiri, Z.; Hosseini, S.M.; Hajian, M.; Abedi, P.; Bahadorani, M.; Baharvand, H.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. Effects of different feeder layers on short-term culture of prepubertal bovine testicular germ cells in-vitro. Theriogenology 2012, 77, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G.; Takeuchi, T. Biotechnology: Surrogate broodstock produces salmonids. Nature 2004, 430, 629–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutsu, T.; Yano, A.; Nagasawa, K.; Shikina, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Takeuchi, Y.; Yoshizaki, G. Manipulation of Fish Germ Cell: Visualization, Cryopreservation and Transplantation. J. Reprod. Dev. 2006, 52, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hong, Y.; Winkler, C.; Schartl, M. Pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cell lines from the medakafish (Oryzias latipes). Mech. Dev. 1996, 60, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatsu-Shinohara, M.; Ogonuki, N.; Inoue, K.; Miki, H.; Ogura, A.; Toyokuni, S.; Shinohara, T. Long-term proliferation in culture and germline transmission of mouse male germline stem cells. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, J.; Liu, L.; Fan, Z.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D. Identification, Prokaryote Expression of Medaka gdnfa/b and Their Biological Activity in a Spermatogonial Cell Line. Stem Cells Dev. 2017, 26, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Li, P.; Pšenička, M.; Ye, H.; Steinbach, C.; Li, C. Optimization of in vitro culture conditions of sturgeon germ cells for purpose of surrogate production. Animals 2018, 106, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, R.; Bando, H.; Sakai, N.; Kotani, T.; Yamashita, M. Function of leukaemia inhibitory factor in spermatogenesis of a teleost fish, the medaka Oryzias latipes. Zygote 2019, 2, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Siegfried, K.R.; Sakai, N. Differentiation of zebrafish spermatogonial stem cells to functional sperm in culture. Development 2016, 143, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Nam, Y.K.; Gong, S.P.; Kang, S.M. Enhanced adhesion of fish ovarian germline stem cells on solid surfaces by mussel-inspired polymer coating. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loir, M.; Sourdaine, P.; Mendis-Handagama, S.M.L.C.; Jégou, B. Cell-cell interactions in the testis of teleosts and elasmobranchs. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1995, 32, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batlouni, S.R.; Carreno, F.R.; Romagosa, E.; Borella, M.I. Cell junctions in the germinal epithelium may play an important role in spermatogenesis of the catfish P. fasciatum (Pisces, Siluriformes). J. Mol. Histol. 2005, 36, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Lopes, J.P.; Söder, O.; Stukenborg, J.B. Testicular organoid generation by a novel in vitro three-layer gradient system. Biomaterials 2017, 130, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeya, M.; Sato, T.; Ogawa, T. In vitro spermatogenesis: A century-long research journey, still half way around. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2018, 17, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowell, O.A. The culture of mature organs in a synthetic medium. Exp. Cell Res. 1959, 16, 118–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, A.; Steinberg, E.; Perloff, W.H. Growth of rat testes fragments in organ culture. Aamer. Soc. Exp. Biol. Bethesda 1963, 22, 372. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberger, A.; Steinberger, E.; Perloff, W.H. Mammalian testes in organ culture. Exp. Cell Res. 1964, 36, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberger, A.; Steinberger, E. Differentiation of rat seminiferous epithelium in organ culture. Reproduction 1965, 9, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curtis, D. In vitro differentiation of diakinesis figures in human testis. Hum. Genet. 1981, 59, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, T.; Yamauchi, K.; Takahashi, H.; Nagahama, Y. Hormonal induction of all stages of spermatogenesis in vitro in the male Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5774–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leal, M.C.; de Waal, P.P.; García-López, Á.; Chen, S.X.; Bogerd, J.; Schulz, R.W. Zebrafish primary testis tissue culture: An approach to study testis function ex vivo. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2009, 162, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komeya, M.; Hayashi, K.; Nakamura, H.; Yamanaka, H.; Sanjo, H.; Kojima, K.; Sato, T.; Yao, M.; Kimura, H.; Fujii, T.; et al. Pumpless microfluidic system driven by hydrostatic pressure induces and maintains mouse spermatogenesis in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15459–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amer, M.A.; Miura, T.; Miura, C.; Yamauchi, K. Involvement of Sex Steroid Hormones in the Early Stages of Spermatogenesis in Japanese Huchen (Hucho perryi )1. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miura, C.; Higashino, T.; Miura, T. A Progestin and an Estrogen Regulate Early Stages of Oogenesis in Fish1. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, R.D.V.S.; Nóbrega, R.H.; Gómez-González, N.E.; Schmidt, R.; Bogerd, J.; França, L.R.; Schulz, R.W. Thyroid hormone stimulates the proliferation of sertoli cells and single type A spermatogonia in adult zebrafish (danio rerio) testis. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 4365–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T. In vitro germ cell differentiation during sex differentiation in a teleost fish. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2010, 54, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loir, M. Spermatogonia of rainbow trout: I. Morphological characterization, mitotic activity, and survival in primary cultures of testicular cells. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1999, 53, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komeya, M.; Kimura, H.; Nakamura, H.; Yokonishi, T.; Sato, T.; Kojima, K.; Hayashi, K.; Katagiri, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Sanjo, H. Long-term ex vivo maintenance of testis tissues producing fertile sperm in a microfluidic device. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21472–21481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haycock, J.W. 3D Cell Culture: Methods & Protocols; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781607619833. [Google Scholar]
- Parent-Massin, D. Relevance of clonogenic assays in hematotoxicology. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2001, 17, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.J.; Gye, M.C. In vitro spermatogenesis by three-dimensional culture of rat testicular cells in collagen gel matrix. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 2845–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Gye, M.C.; Choi, K.W.; Hong, J.Y.; Lee, Y.B.; Park, D.W.; Lee, S.J.; Min, C.K. In vitro differentiation of germ cells from nonobstructive azoospermic patients using three-dimensional culture in a collagen gel matrix. Fertil. Steril. 2007, 87, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukenborg, J.B.; Wistuba, J.; Luetjens, C.M.; Elhija, M.A.; Huleihel, M.; Lunenfeld, E.; Gromoll, J.; Nieschlag, E.; Schlatt, S. Coculture of spermatogonia with somatic cells in a novel three-dimensional Soft-Agar-Culture-System. J. Androl. 2008, 29, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stukenborg, J.-B.; Schlatt, S.; Simoni, M.; Yeung, C.-H.; Elhija, M.A.; Luetjens, C.M.; Huleihel, M.; Wistuba, J. New horizons for in vitro spermatogenesis? An update on novel three-dimensional culture systems as tools for meiotic and post-meiotic differentiation of testicular germ cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2009, 15, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abu Elhija, M.; Lunenfeld, E.; Schlatt, S.; Huleihel, M. Differentiation of murine male germ cells to spermatozoa in a soft agar culture system. Asian J. Androl. 2012, 14, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huleihel, M.; Nourashrafeddin, S.; Plant, T.M. Application of three-dimensional culture systems to study mammalian spermatogenesis, with an emphasis on the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta). Asian J. Androl. 2015, 17, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legendre, A.; Froment, P.; Desmots, S.; Lecomte, A.; Habert, R.; Lemazurier, E. An engineered 3D blood-testis barrier model for the assessment of reproductive toxicity potential. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4492–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.J.; Choi, S.M.; Kang, H.Y.; Min, H.J.; Lee, R.; Ikram, M.; Subhan, F.; Jin, S.W.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kwak, J.Y.; et al. Bioactive fish collagen/polycaprolactone composite nanofibrous scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for 3D cell culture. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 205, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaoka, Y.; Kishimura, H.; Adachi, S.; Takagi, Y. Collagen peptides derived from the triple helical region of sturgeon collagen improve glucose tolerance in normal mice. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Ookawa, M.; Tan, Y.; Ura, K.; Adachi, S.; Takagi, Y. Biochemical characterisation and assessment of fibril-forming ability of collagens extracted from Bester sturgeon Huso huso × Acipenser ruthenus. Food Chem. 2014, 160, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mredha, M.T.I.; Kitamura, N.; Nonoyama, T.; Wada, S.; Goto, K.; Zhang, X.; Nakajima, T.; Kurokawa, T.; Takagi, Y.; Yasuda, K.; et al. Anisotropic tough double network hydrogel from fish collagen and its spontaneous in vivo bonding to bone. Biomaterials 2017, 132, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, H.; Yunoki, S.; Kondo, E.; Ikoma, T.; Tanaka, J.; Yasuda, K. In vivo biological responses and bioresorption of tilapia scale collagen as a potential biomaterial. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2009, 20, 1353–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Marker | Specification | Species | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SGSA-1 | Spermatogonia specific-antigen-1 | Japanese eel | [78] |
| Notch1 | Notch homolog protein 1 | Rainbow trout | [79] |
| Pou5/2 (Oct-4) | POU domain, class 5/2 | Medaka Common carp | [71] Nobrega et al. unpublished observations |
| Ly75 (CD205) | Lymphocyte antigen 75 | Rainbow trout Pacific bluefin tuna | [80] [81] |
| PLZF | Promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger | Zebrafish Carpa rohu Dogfish Rainbow trout Catfish (several species) | [58] [57] [60] [61] [9,62,63] |
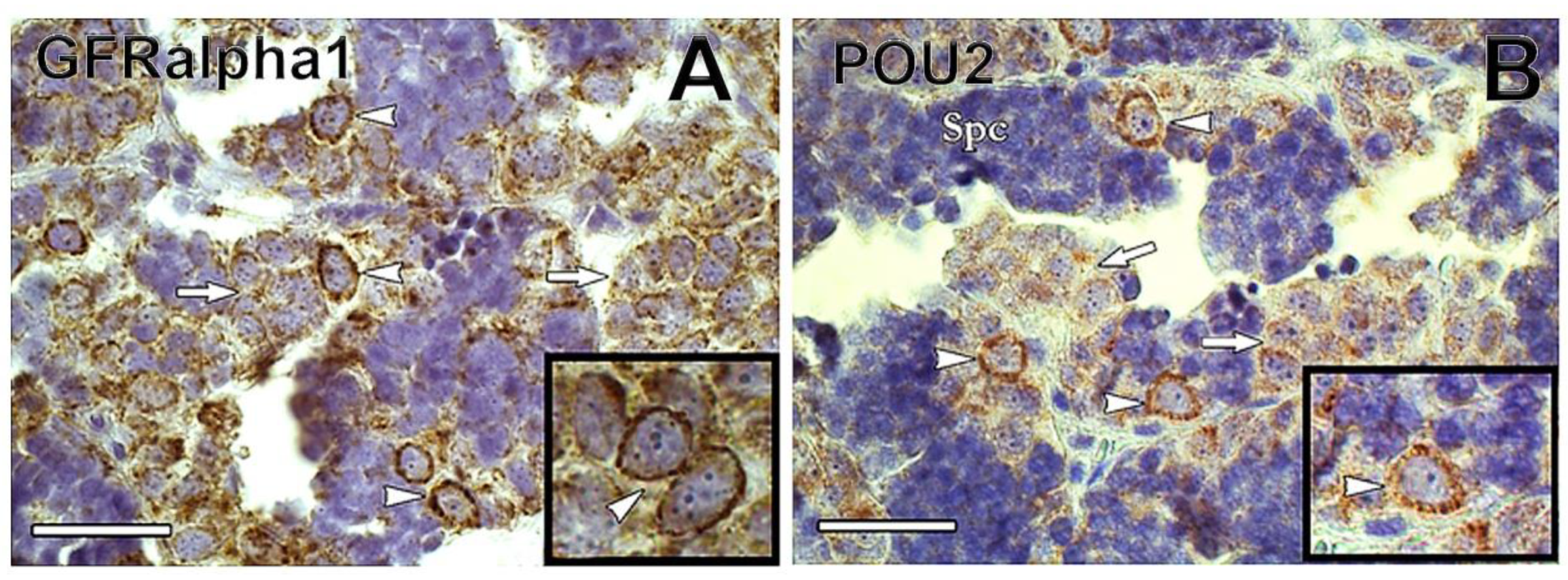
| GFRα1 | GDNF-family receptor α1 | Nile tilapia Dogfish Rainbow trout Common carp | [68] [60] [69] Nobrega et al. unpublished observations |
| NANOG | NANOG homeobox | Medaka Nile tilapia | [72] [68] |
| NANOS2 | NANOS homolog 2 | Medaka Nile tilapia Rainbow trout | [82] [68] [61] |
| NANOS3 | NANOS homolog 3 | Rainbow trout | [61] |
| Antibodies numbers 80 and 95 | Not identified | Rainbow trout Also applied in Zebrafish Salmonids | [75] [75] [77] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, X.; Nóbrega, R.; Pšenička, M. Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Fish: Characterization, Isolation, Enrichment, and Recent Advances of In Vitro Culture Systems. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040644
Xie X, Nóbrega R, Pšenička M. Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Fish: Characterization, Isolation, Enrichment, and Recent Advances of In Vitro Culture Systems. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040644
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Xuan, Rafael Nóbrega, and Martin Pšenička. 2020. "Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Fish: Characterization, Isolation, Enrichment, and Recent Advances of In Vitro Culture Systems" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040644
APA StyleXie, X., Nóbrega, R., & Pšenička, M. (2020). Spermatogonial Stem Cells in Fish: Characterization, Isolation, Enrichment, and Recent Advances of In Vitro Culture Systems. Biomolecules, 10(4), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040644






