Transcriptomically Revealed Oligo-Fucoidan Enhances the Immune System and Protects Hepatocytes via the ASGPR/STAT3/HNF4A Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Oligo-Fucoidan (OF)
2.2. Zebrafish Maintenance
2.3. Oligo-Fucoidan Administration in Adult Wild-Type Zebrafish and Tissue Collection
2.4. Total RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.5. GeneTitan™ Array for Gene Expression Profiling
2.6. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
2.7. Cell Viability and Gene Knockdown
2.8. Western Blots
2.9. Flow Cytometry for In Vitro Completion Assay
2.10. Asialoglycoprotein Receptor (ASGPR) Nuclear Imaging for In Vivo Competition Assay
2.11. Measurement of CYP3A4 activity
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
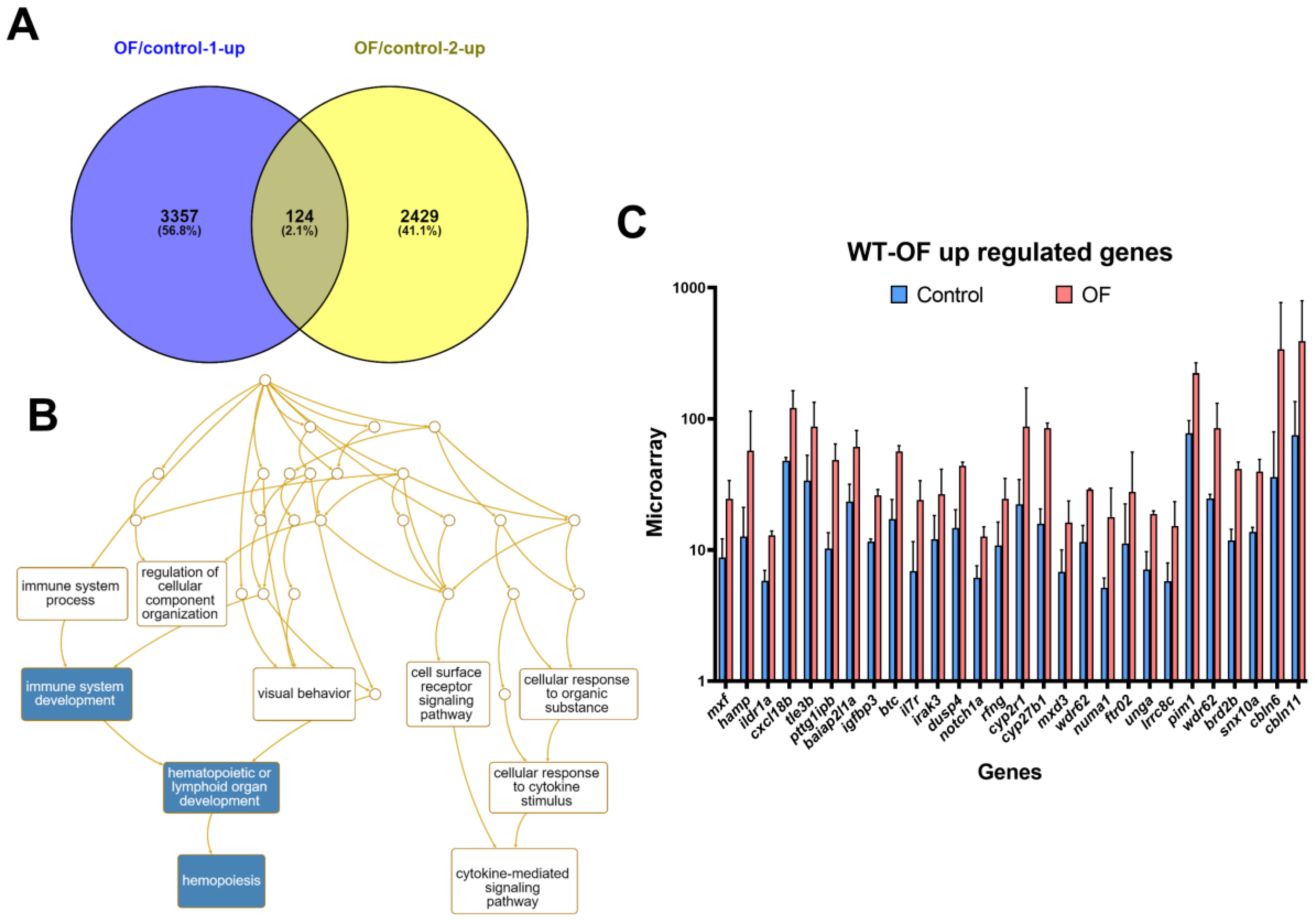
3.1. Oligo-Fucoidan Increases Immune System and Downregulates Lipogenic and Fibrosis-Associated Genes
3.2. Oligo-Fucoidan Enhances the Viability of Normal Hepatocytes
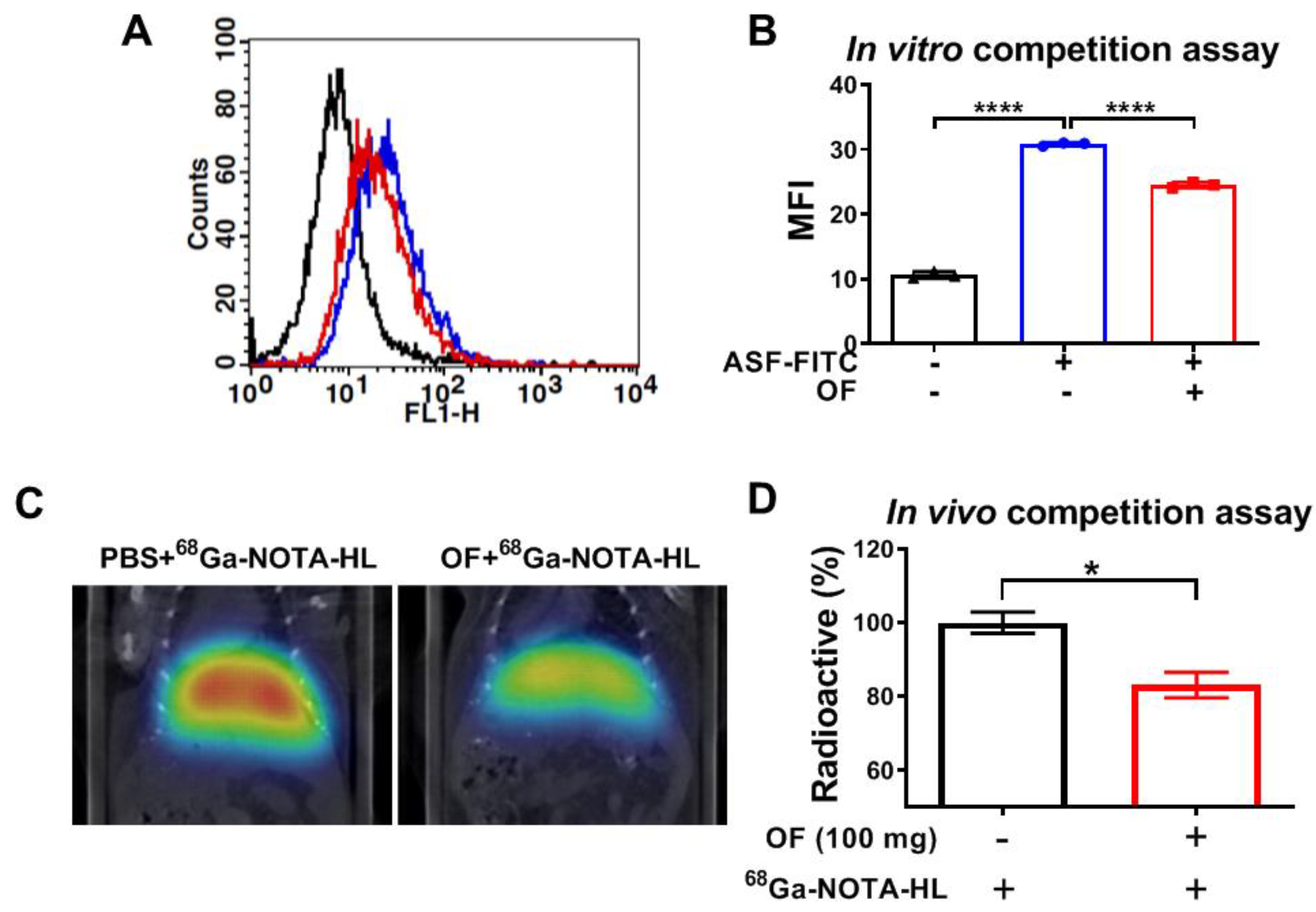
3.3. Oligo-Fucoidan Binds to C-Type Lectin-Like Receptor 2 (CLEC-2)-ASGPR1/2 in Hepatocytes
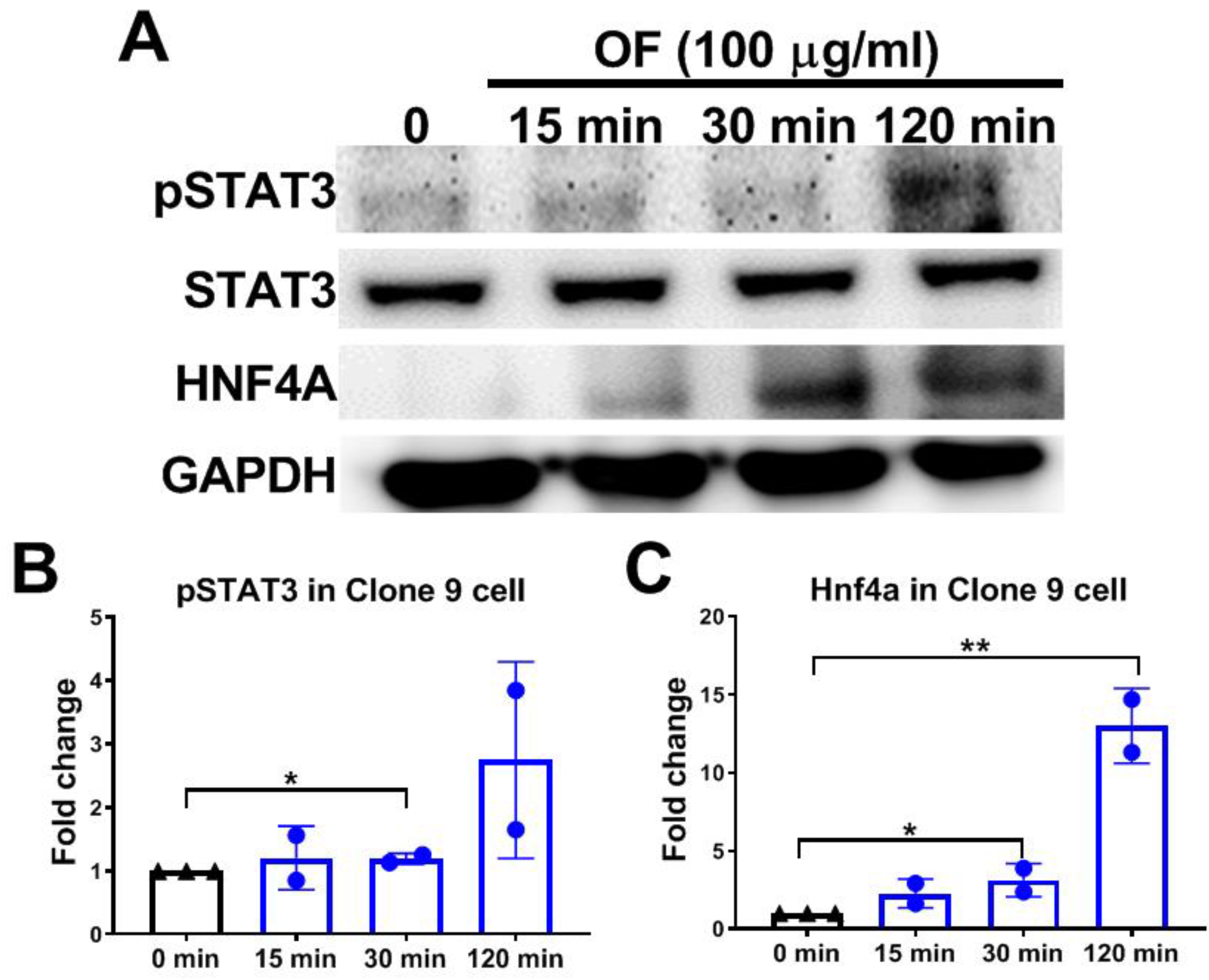
3.4. Oligo-Fucoidan Activates Phosphorylation of STAT3 and Increases Hnf4a Protein Levels in Hepatocytes
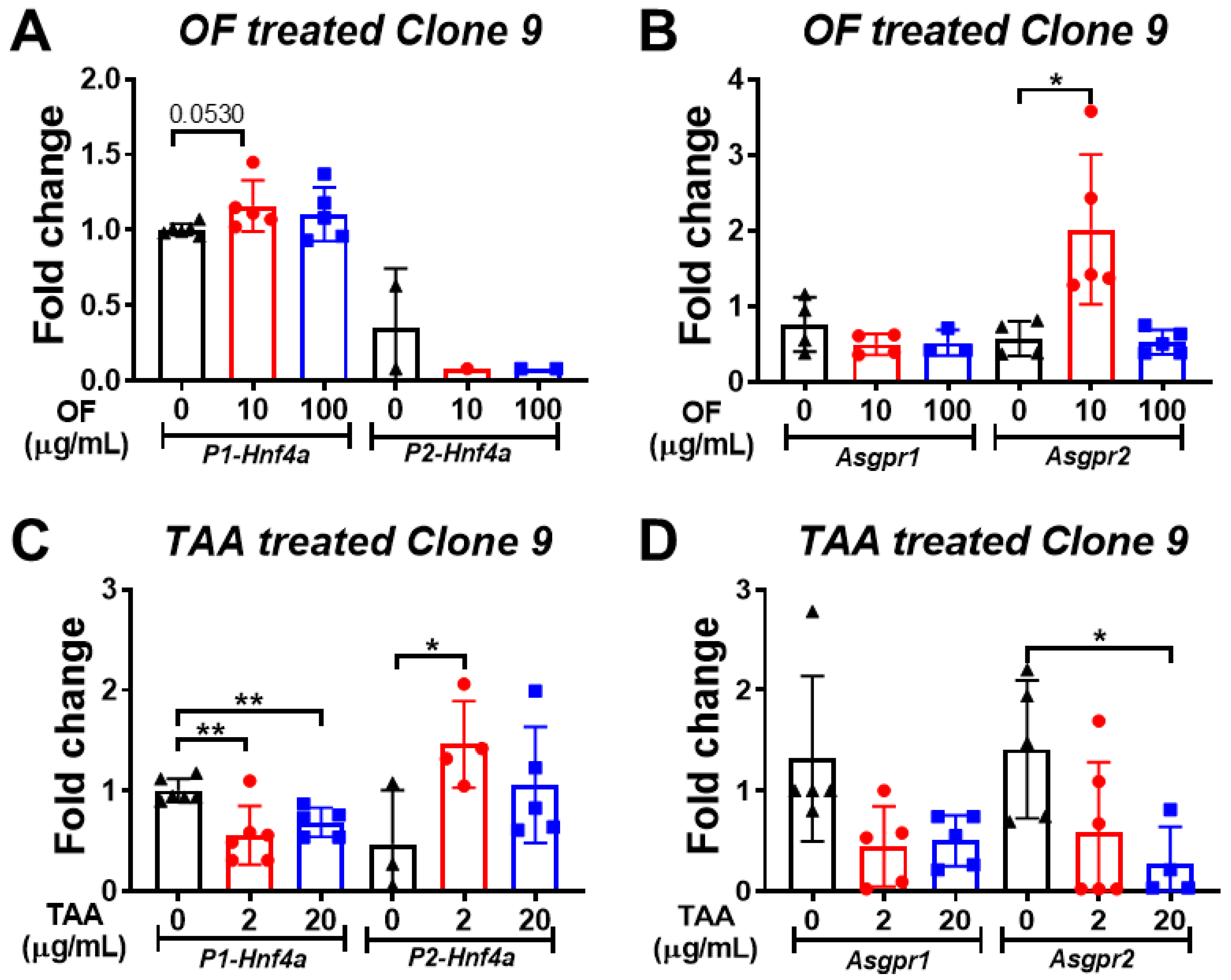
3.5. Oligo-Fucoidan Increases the Expression of P1-Hnf4a in Hepatocytes
3.6. STAT3 Inhibitor Decreases the Viability of Normal Liver Cells
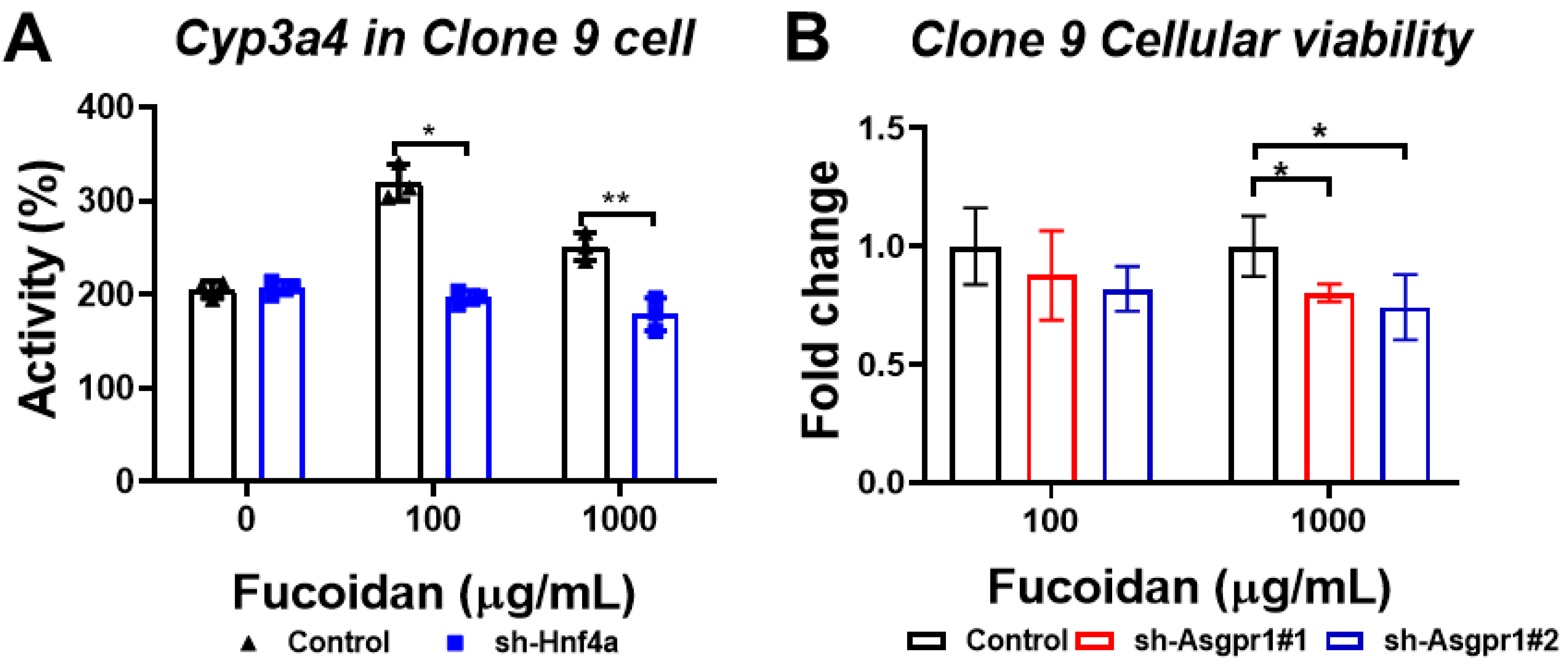
3.7. The Enhancing Effect of Oligo-Fucoidan on CYP3A4 Activity and Cell Viability Could Be Neutralized by the Knockdown of Hnf4a and Asgpr1 in Normal Liver Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Henderson, J.M.; Polak, N.; Chen, J.; Roediger, B.; Weninger, W.; Kench, J.G.; McCaughan, G.W.; Zhang, H.E.; Gorrell, M.D. Multiple liver insults synergize to accelerate experimental hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wang, H. Precision diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer in China. Cancer Lett. 2018, 412, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.-Y.; Hwang, P.-A. Clinical applications of fucoidan in translational medicine for adjuvant cancer therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2019, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Li, J.; Chen, K.; Li, S.; Feng, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R.; Xu, S.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Protective effect of fucoidan from Fucus vesiculosus on liver fibrosis via the TGF-β1/Smad pathway-mediated inhibition of extracellular matrix and autophagy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2016, 10, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Itoh, A.; Isoda, K.; Kondoh, M.; Kawase, M.; Yagi, K. Fucoidan partly prevents CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 580, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazato, K.; Takada, H.; Iha, M.; Nagamine, T. Attenuation of N-nitrosodiethylamine-induced liver fibrosis by high-molecular-weight fucoidan derived fromCladosiphon okamuranus. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 25, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, B.K.; Getz, T.M.; Hughes, C.; AlShehri, O.; Dangelmaier, C.; Naik, U.P.; Watson, S.P.; Kunapuli, S.P. Fucoidan Is a Novel Platelet Agonist for the C-type Lectin-like Receptor 2 (CLEC-2)*. J. Boil. Chem. 2013, 288, 7717–7726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, A.L.T.; Clausen, H.; Wandall, H.H. Carbohydrate clearance receptors in transfusion medicine. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmeister, K.M.; Falet, H. Platelet clearance by the hepatic Ashwell-Morrell receptor: Mechanisms and biological significance. Thromb. Res. 2016, 141, S68–S72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 in Liver Diseases: A Novel Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Boil. Sci. 2011, 7, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettleborough, R.N.W.; Busch-Nentwich, E.M.; Harvey, S.A.; Dooley, C.M.; De Bruijn, E.; Van Eeden, F.; Sealy, I.; White, R.J.; Herd, C.; Nijman, I.; et al. A systematic genome-wide analysis of zebrafish protein-coding gene function. Nature 2013, 496, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The zebrafish reference genome sequence and its relationship to the human genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Wen, Z.-H.; Lin, C.-S.; Chakraborty, C. The zebrafish model: Use in studying cellular mechanisms for a spectrum of clinical disease entities. Curr. Neurovascular Res. 2007, 4, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dooley, K.; I Zon, L. Zebrafish: A model system for the study of human disease. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2000, 10, 252–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrighton, P.J.; Oderberg, I.M.; Goessling, W. There’s Something Fishy About Liver Cancer: Zebrafish Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 8, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Yang, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-M.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Yuh, C.-H. Hepatitis B virus X antigen and aflatoxin B1 synergistically cause hepatitis, steatosis and liver hyperplasia in transgenic zebrafish. Acta Histochem. 2013, 115, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Yang, W.-Y.; Tsai, S.-M.; Lin, Y.-M.; Chang, P.-H.; Chen, J.-R.; Wang, H.-D.; Wu, J.-L.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Yuh, C.-H. Liver-Specific Expressions of HBx and src in the p53 Mutant Trigger Hepatocarcinogenesis in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-W.; Liao, C.-Y.; Yang, W.-Y.; Lin, Y.-M.; Jin, S.-L.C.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. Overexpression of Endothelin 1 Triggers Hepatocarcinogenesis in Zebrafish and Promotes Cell Proliferation and Migration through the AKT Pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, Y.-T.; Chen, L.-Y.; Tsai, S.-L.; Tu, H.-C.; Lu, J.-W.; Ciou, S.-C.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. Ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A overexpression promotes liver cancer development in transgenic zebrafish via activation of ERK and β-catenin pathways. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.-L.; Su, C.-W.; Huang, Y.-L.; Yang, W.-Y.; Sampurna, B.P.; Ouchi, T.; Lee, K.-L.; Wu, C.-S.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. A Novel AURKA Mutant-Induced Early-Onset Severe Hepatocarcinogenesis Greater than Wild-Type via Activating Different Pathways in Zebrafish. Cancers 2019, 11, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-Y.; Rao, P.-S.; Luo, Y.-C.; Lin, H.-K.; Huang, S.-H.; Yang, J.-M.; Yuh, C.-H. Yang Omics-based Investigation of Diet-induced Obesity Synergized with HBx, Src, and p53 Mutation Accelerating Hepatocarcinogenesis in Zebrafish Model. Cancers 2019, 11, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, H.; Hsiao, Y.; Yang, W.; Tsai, S.; Lin, H.; Liao, C.; Lu, J.; Chou, Y.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. Up-regulation of golgi α-mannosidase IA and down-regulation of golgi α-mannosidase IC activates unfolded protein response during hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatol. Commun. 2017, 1, 230–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collymore, C.; Rasmussen, S.; Tolwani, R.J. Gavaging Adult Zebrafish. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 78, e50691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.-S.; Huang, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-R.S.; Hsiao, E.; Hsu, T.-A.; Shiao, H.-Y.; Jiaang, W.-T.; Sampurna, B.; Lin, K.-H.; Wu, M.-S.; et al. Identification of Novel Anti-Liver Cancer Small Molecules with Better Therapeutic Index than Sorafenib via Zebrafish Drug Screening Platform. Cancers 2019, 11, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.-T.; Jiang, J.-K.; Yang, M.-H.; Lu, J.-W.; Lin, H.-K.; Wang, H.-D.; Yuh, C.-H. Identification of a noncanonical function for ribose-5-phosphate isomerase A promotes colorectal cancer formation by stabilizing and activating β-catenin via a novel C-terminal domain. PLoS Boil. 2018, 16, e2003714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Lin, H.-C.; Tsai, K.-J.; Chiang, Y.-W.; Lim, K.-H.; Chen, C.G.-S.; Su, Y.-W.; Peng, C.-L.; Ho, A.; Huang, L.; et al. Epidermal growth factor induces STAT1 expression to exacerbate the IFNr-mediated PD-L1 axis in epidermal growth factor receptor-positive cancers. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.-M.; Chan, C.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Chien, C.-Y.; Wang, P.-Y.; Juan, W.-C.; Yang, C.-H.; Hsia, H.-T.; Wang, M.-H.; Lin, W.-J.; et al. Development of single vial kits for preparation of68Ga-labelled hexavalent lactoside for PET imaging of asialoglycoprotein receptor. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2018, 61, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Von Der Malsburg, A.; Dick, A.; Faelber, K.; Schröder, G.F.; Haller, O.; Kochs, G.; Daumke, O. Structure of Myxovirus Resistance Protein A Reveals Intra- and Intermolecular Domain Interactions Required for the Antiviral Function. Immunity 2011, 35, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, K.R.; Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T.; Mehrad, B. Hepcidin and Host Defense against Infectious Diseases. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmy, Y.A.; Fawzy, M.; Elaswad, A.; Sobieh, A.; Kenney, S.P.; Shehata, A.A. The COVID-19 Pandemic: A Comprehensive Review of Taxonomy, Genetics, Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Control. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladeira, M.M.; Schoonmaker, J.P.; Swanson, K.C.; Duckett, S.; Gionbelli, M.P.; Rodrigues, L.M.; Teixeira, P.D. Review: Nutrigenomics of marbling and fatty acid profile in ruminant meat. Animal 2018, 12, s282–s294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Baselli, G.; Bassani, G.A.; Rametta, R.; Pietrelli, A.; Maggioni, M.; Facciotti, F.; Trunzo, V.; Badiali, S.; et al. Insulin resistance promotes Lysyl Oxidase Like 2 induction and fibrosis accumulation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatib, S.A.; Wang, X.W. Proteomic heterogeneity reveals SOAT1 as a potential biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drescher, H.K.; Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Current Status in Testing for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH). Cells 2019, 8, 845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoud, O.; Charlton, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, C.D.; Lickteig, A.; Augustine, L.M.; Ranger-Moore, J.; Jackson, J.P.; Ferguson, S.S.; Cherrington, N.J. Hepatic cytochrome P450 enzyme alterations in humans with progressive stages of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, R.; De La Monte, S.M.; Ogasawara, K.; Adusumalli, S.; Barlock, B.; Akhlaghi, F. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes Are Associated with Decreased CYP3A4 Protein Expression and Activity in Human Liver. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 2621–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, T.; Bell, A.; Brooks, J.M.; Setoyama, K.; Melis, M.; Han, B.; Fukumitsu, K.; Handa, K.; Tian, J.; Kaestner, K.H.; et al. Resetting the transcription factor network reverses terminal chronic hepatic failure. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekry, B.; Ribas-Latre, A.; Baumgartner, C.; Deans, J.R.; Kwok, C.; Patel, P.; Fu, L.; Berdeaux, R.; Sun, K.; Kolonin, M.G.; et al. Incompatibility of the circadian protein BMAL1 and HNF4α in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babeu, J.-P.; Jones, C.; Geha, S.; Carrier, J.C.; Boudreau, F. P1 promoter-driven HNF4α isoforms are specifically repressed by β-catenin signaling in colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell Sci. 2018, jcs.214734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Yoon, J.-H.; Yoo, J.-J.; Lee, M.; Lee, D.H.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Yu, S.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, C.Y. Fucoidan protects hepatocytes from apoptosis and inhibits invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by up-regulating p42/44 MAPK-dependent NDRG-1/CAP43. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan-Loy, C.; Phang, S.-M. Marine Algae as a Potential Source for Anti-Obesity Agents. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atashrazm, F.; Lowenthal, R.; Woods, G.M.; Holloway, A.; Dickinson, J.L. Fucoidan and Cancer: A Multifunctional Molecule with Anti-Tumor Potential. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2327–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Ko, C.-I.; Jee, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.-S.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava in zebrafish model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-Y.; Yan, M.-D.; Wu, A.T.; Yuan, K.S.-P.; Liu, S.-H. Brown Seaweed Fucoidan Inhibits Cancer Progression by Dual Regulation of mir-29c/ADAM12 and miR-17-5p/PTEN Axes in Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 2408–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthuli, S.; Wu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wu, M.; Tong, H. Therapeutic Effects of Fucoidan: A Review on Recent Studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xing, M.; Cao, Q.; Ji, A.; Liang, H.; Song, S. Biological Activities of Fucoidan and the Factors Mediating Its Therapeutic Effects: A Review of Recent Studies. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.; Kuang, H.; Ansari, S.; Liu, T.; Gong, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, C.; Guo, L.; et al. Landscape of Intercellular Crosstalk in Healthy and NASH Liver Revealed by Single-Cell Secretome Gene Analysis. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 644–660.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Weelden, G.; Bobiński, M.; Okła, K.; Van Weelden, W.J.; Romano, A.; Pijnenborg, J.M. Fucoidan Structure and Activity in Relation to Anti-Cancer Mechanisms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walesky, C.; Edwards, G.; Borude, P.; Gunewardena, S.; O’Neil, M.; Yoo, B.; Apte, U. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha deletion promotes diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rodents. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2480–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecker, A.; Hoelbl-Kovacic, A. The dark and the bright side of Stat3: Proto-oncogene and tumor-suppressor. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, K.-C.; Chang, K.-S.; Hsu, S.-Y.; Sung, H.-C.; Feng, T.-H.; Chao, M.; Juang, H.-H. Human Heme Oxygenase-1 Induced by Interleukin-6 via JAK/STAT3 Pathways Is a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Hepatoma Cells. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, H.H.; Ng, N.H.J.; Loo, L.S.W.; Jasmen, J.B.; Teo, A.K.K. The molecular functions of hepatocyte nuclear factors—In and beyond the liver. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1033–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Primer Name | sequence | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|
| mxf-F | CGACTGGGGAGGATGTTAAA | NM_182942.4 |
| mxf-R | CCCCGGTACTTGACTTCGTA | |
| hamp-F | CAGCAGGTACAGGATGAGCA | NM_205583.2 |
| hamp-R | AGCCTTTATTGCGACAGCAT | |
| irak3-F | GGCATTTCCACCAGGACTTA | XM_017355295.2 |
| irak3-R | AGAAGCGATCCGAATCTGAA | |
| fasn-F | ATCTGTTCCTGTTCGATGGC | XM_682295 |
| fasn-R scd-F scd-R loxl2a-F loxl2a-R foxo3b-F foxo3b-R soat1-F soat1-R | AGCATATCTCGGCTGACGTT ACGCTCCTCAGATACGCACT AGTCGTAGGGAAACGTGTGG CGAATTCCTGGTCACAGGTT TCGGCTGTTTAAAGGTGTCC AGAGAGCACCCCTGACAAGA CACGAGCTCTTTCCAGTTCC GCTCTCATAAGGTGGCTTCG GCCTCATCAGGTCTGCTTTC | NM_198815 XM_009305250.3 NM_131085.1 NM_001123272.1 |
| actin-F | CTCCATCATGAAGTGCGACGT | NM_131031.1 |
| actin-F | CAGACGGAGTATTTGCGCTCA | |
| P1-Hnf4α-Q-F | CATGGATATGGCCGACTACAGCGC | NM_008261.3 |
| Hnf4α-Q-R | GCCCGAATGTCGCCATTGATCC | |
| P2-Hnf4α-Q-F | CAGGGGTTCCTGCAGATCACATCA | NM_001312907.1 |
| Hnf4α-Q-R | GCCCGAATGTCGCCATTGATCC | |
| Asgr1-F | ATCCCAAAATTCCCAACTCC | XM_017314231.1 |
| Asgr1-R | TTTCCAGCTTCGACTCCACT | |
| Asgr2-F | CCTGTTGGTGGTCATCTGTG | NM_001313925.1 |
| Asgr2-R | GGTCTGCCTTTAGCTGTTGC |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, C.-C.; Yang, W.-Y.; Hsiao, M.-C.; Lin, K.-H.; Lee, H.-W.; Yuh, C.-H. Transcriptomically Revealed Oligo-Fucoidan Enhances the Immune System and Protects Hepatocytes via the ASGPR/STAT3/HNF4A Axis. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060898
Cheng C-C, Yang W-Y, Hsiao M-C, Lin K-H, Lee H-W, Yuh C-H. Transcriptomically Revealed Oligo-Fucoidan Enhances the Immune System and Protects Hepatocytes via the ASGPR/STAT3/HNF4A Axis. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(6):898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060898
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Chun-Chia, Wan-Yu Yang, Ming-Chen Hsiao, Kuan-Hao Lin, Hao-Wei Lee, and Chiou-Hwa Yuh. 2020. "Transcriptomically Revealed Oligo-Fucoidan Enhances the Immune System and Protects Hepatocytes via the ASGPR/STAT3/HNF4A Axis" Biomolecules 10, no. 6: 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060898
APA StyleCheng, C.-C., Yang, W.-Y., Hsiao, M.-C., Lin, K.-H., Lee, H.-W., & Yuh, C.-H. (2020). Transcriptomically Revealed Oligo-Fucoidan Enhances the Immune System and Protects Hepatocytes via the ASGPR/STAT3/HNF4A Axis. Biomolecules, 10(6), 898. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060898






