The Many Faces of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Kidney Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
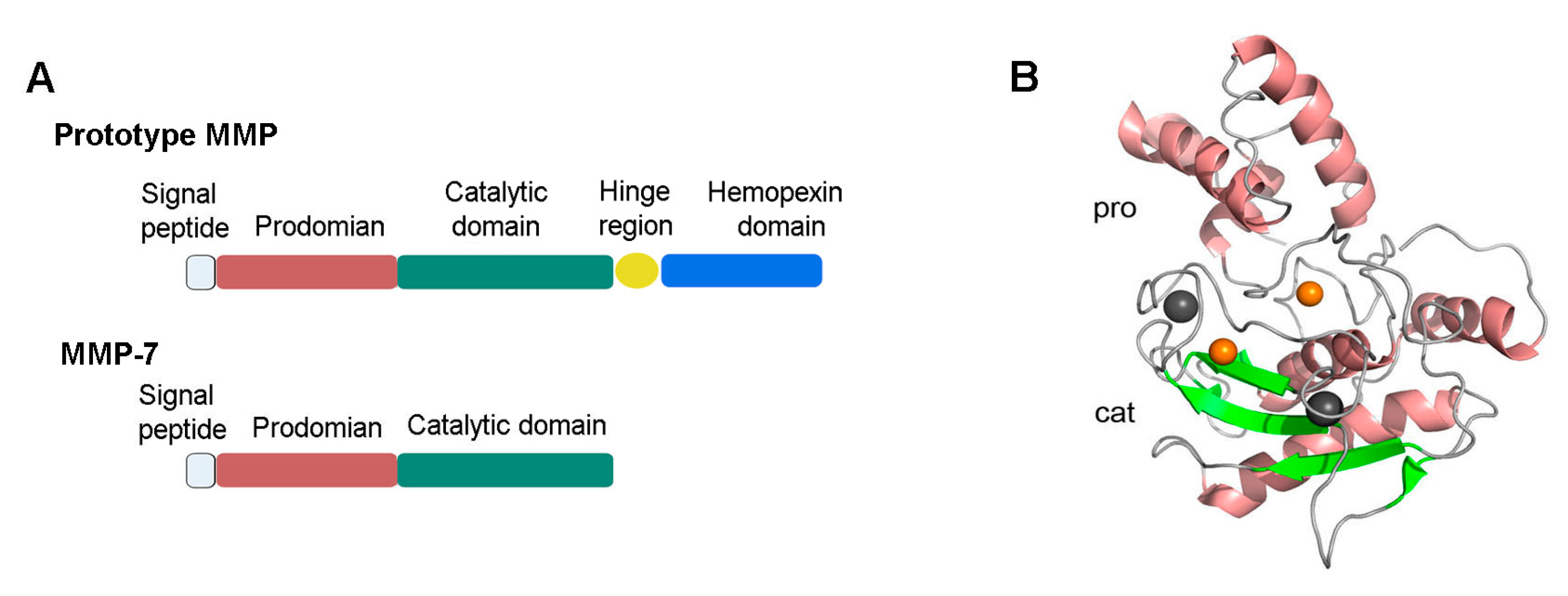
2. MMP-7 Structure, Activation, and Regulation
3. MMP-7 Expression in the Kidney
3.1. Animal Models
| Disease | Location | Expression | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Animal models | |||
| Ischemia–reperfusion -induced AKI 1 | Renal tubular epithelia | Increase | [11] |
| Folic acid-induced AKI | Renal tubular epithelia | Increase | [11,23] |
| Cisplatin-induced AKI | Renal tubular epithelia | Increase | [11] |
| UUO 2 | Renal tubular epithelia, interstitial cells | Increase | [12,21] |
| Human kidney diseases | |||
| FSGS 3 | Renal tubular epithelia, interstitial cells, podocytes | Increase | [12,21] |
| Lupus nephritis | Renal tubular epithelia | Increase | [27] |
| Membranous nephritis | Renal tubular epithelia | Increase | [12] |
| Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease | Epithelial cells lining cysts, atrophic tubules | Increase | [23] |
| Diabetic nephropathy | Renal tubular epithelia, interstitial cells | Increase | [12,21] |
| Hydronephrosis | Cells lining dilated and atrophic tubules | Increase | [23] |
| Thrombotic microangiopathy | Renal tubular epithelia | Increase | [12] |
| IgA nephropathy | Renal tubular epithelia, infiltrated inflammatory cells | Increase | [12,21] |
| Acute renal allograft rejection | Renal tubular epithelia | No change | [28] |
| Chronic allograft nephropathy | Renal tubular epithelia | Increase | [29] |
| Amyloid light-chain amyloidosis | Glomerulus, tubular interstitium, vasculatures | Increase | [30] |
| Light chain deposition disease | Glomerulus, tubular interstitium, vasculatures | No change | [30] |
| Renal cell carcinoma | Cancer cells and endothelial cells | Increase | [22] |
3.2. Human Kidney Biopsies
3.3. Mechanism of MMP-7 Regulation In Vivo
4. MMP-7 As a Biomarker for Kidney Diseases
4.1. uMMP-7 Predicts the Risk of AKI
4.2. uMMP-7 As a Biomarker of CKD Progression
5. Roles of MMP-7 in Kidney Diseases
5.1. MMP-7 Protects Against AKI
5.2. MMP-7 Promotes Kidney Fibrosis and CKD Progression
5.3. MMP-7 Induces Podocyte Dysfunction and Proteinuria
6. Mechanisms and Novel Targets of MMP-7 in Kidney Diseases
6.1. FasL
6.2. E-Cadherin
6.3. Nephrin
6.4. Pro-MMP-2 and -9
7. Conclusion and Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catania, J.M.; Chen, G.; Parrish, A.R. Role of matrix metalloproteinases in renal pathophysiologies. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2007, 292, F905–F911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.J.; Liu, Y. Matrix metalloproteinases in kidney homeostasis and diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 302, F1351–F1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amar, S.; Smith, L.; Fields, G.B. Matrix metalloproteinase collagenolysis in health and disease. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, N.; Hu, M.; Khalil, R.A. Biochemical and Biological Attributes of Matrix Metalloproteinases. Pro. Mol. Biol. Trans. Sci. 2017, 147, 1–73. [Google Scholar]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, J.F., Jr.; Taplin, C.J. Purification and properties of a small latent matrix metalloproteinase of the rat uterus. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 16918–16925. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, R.J.; Li, Y.; Rush, B.M.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Zhou, D.; Fu, H.; Ho, J.; Beer Stolz, D.; Liu, Y. Tubular injury triggers podocyte dysfunction by beta-catenin-driven release of MMP-7. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e122399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, J.K.; Li, Q.; Parks, W.C. Matrilysin (matrix metalloproteinase-7) mediates E-cadherin ectodomain shedding in injured lung epithelium. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1831–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo-Gogola, T.; Crawford, H.C.; Fingleton, B.; Matrisian, L.M. Identification of novel matrix metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) cleavage sites in murine and human Fas ligand. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 408, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsiades, N.; Yu, W.H.; Poulaki, V.; Tsokos, M.; Stamenkovic, I. Matrix metalloproteinase-7-mediated cleavage of Fas ligand protects tumor cells from chemotherapeutic drug cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 577–581. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H.; Zhou, D.; Zhu, H.; Liao, J.; Lin, L.; Hong, X.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 protects against acute kidney injury by priming renal tubules for survival and regeneration. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Tian, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Xiao, L.; Tan, R.J.; Tian, J.; Fu, H.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 is a urinary biomarker and pathogenic mediator of kidney fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 598–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Teng, S.; Fu, X.; Zha, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Tian, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Urinary matrix metalloproteinase-7 predicts severe AKI and poor outcomes after cardiac surgery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3373–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afkarian, M.; Zelnick, L.R.; Ruzinski, J.; Kestenbaum, B.; Himmelfarb, J.; de Boer, I.H.; Mehrotra, R. Urine matrix metalloproteinase-7 and risk of kidney disease progression and mortality in type 2 diabetes. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Ou, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Xie, D.; Sun, J.; Zha, Y.; et al. Urinary matrix metalloproteinase 7 and prediction of IgA nephropathy progression. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, H.; Visse, R.; Murphy, G. Structure and function of matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs. Cardiovasc Res. 2006, 69, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Wart, H.E.; Birkedal-Hansen, H. The cysteine switch: A principle of regulation of metalloproteinase activity with potential applicability to the entire matrix metalloproteinase gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 5578–5582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visse, R.; Nagase, H. Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: Structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ. Res. 2003, 92, 827–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Dai, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling mediates transforming growth factor-beta1-driven podocyte injury and proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gan, M.; Zhou, T.; Wang, S. The expression and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase 7 and tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases 2 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 890–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Tan, R.J.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Nie, J.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y. Matrix metalloproteinase-7 as a surrogate marker predicts renal Wnt/beta-catenin activity in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, Y.; Iwata, T.; Ohba, K.; Kanda, S.; Nishikido, M.; Kanetake, H. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7 on cancer cells and tissue endothelial cells in renal cell carcinoma: Prognostic implications and clinical significance for invasion and metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6998–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendran, K.; Simon, T.C.; Liapis, H.; McGuire, J.K. Matrilysin (MMP-7) expression in renal tubular damage: Association with Wnt4. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 2212–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melk, A.; Mansfield, E.S.; Hsieh, S.C.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Grimm, P.; Rayner, D.C.; Halloran, P.F.; Sarwal, M.M. Transcriptional analysis of the molecular basis of human kidney aging using cDNA microarray profiling. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2667–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T.; Jung, A.; Dag, S.; Hlubek, F.; Kirchner, T. beta-catenin regulates the expression of the matrix metalloproteinase-7 in human colorectal cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, H.C.; Fingleton, B.; Gustavson, M.D.; Kurpios, N.; Wagenaar, R.A.; Hassell, J.A.; Matrisian, L.M. The PEA3 subfamily of Ets transcription factors synergizes with beta-catenin-LEF-1 to activate matrilysin transcription in intestinal tumors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 1370–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, H.N.; Landolt-Marticorena, C.; Boutros, P.C.; John, R.; Wither, J.; Fortin, P.R.; Yang, S.; Scholey, J.W.; Herzenberg, A.M. Molecular markers of injury in kidney biopsy specimens of patients with lupus nephritis. J. Mol. Diagn. 2011, 13, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodder, S.; Scherer, A.; Korner, M.; Eisenberger, U.; Hertig, A.; Raulf, F.; Rondeau, E.; Marti, H.P. Meta-analyses qualify metzincins and related genes as acute rejection markers in renal transplant patients. Am. J. Transpl. 2010, 10, 286–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodder, S.; Scherer, A.; Raulf, F.; Berthier, C.C.; Hertig, A.; Couzi, L.; Durrbach, A.; Rondeau, E.; Marti, H.P. Renal allografts with IF/TA display distinct expression profiles of metzincins and related genes. Am. J. Transpl. 2009, 9, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeling, J.; Herrera, G.A. Matrix metalloproteinases and mesangial remodeling in light chain-related glomerular damage. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 1590–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henger, A.; Kretzler, M.; Doran, P.; Bonrouhi, M.; Schmid, H.; Kiss, E.; Cohen, C.D.; Madden, S.; Porubsky, S.; Grone, E.F.; et al. Gene expression fingerprints in human tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis as prognostic markers of disease progression. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.; Liang, L.; Qin, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhou, Q.; Feng, S.; Yip, S.H.; et al. Functional networks of aging markers in the glomeruli of IgA nephropathy: A new therapeutic opportunity. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 33616–33626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, C.D.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Eichinger, F.; Hahn, A.; Seifert, M.; Moll, A.G.; Schmid, H.; Kiss, E.; Grone, E.; Grone, H.J.; et al. Improved elucidation of biological processes linked to diabetic nephropathy by single probe-based microarray data analysis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Liu, Y. New insights into the role and mechanism of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling in kidney fibrosis. Nephrology 2018, 23 (Suppl. 4), 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Tan, R.J.; Fu, H.; Liu, Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in kidney injury and repair: A double-edged sword. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angers, S.; Moon, R.T. Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signalling and podocyte dysfunction in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2015, 11, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, P.; Williams, E.O.; Bell, E.L.; Gong, J.J.; Bonkowski, M.; Guarente, L. SIRT1 suppresses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis and organ fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 1175–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Chen, C.; Meng, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Q. Resveratrol attenuates renal injury and fibrosis by inhibiting transforming growth factor-beta pathway on matrix metalloproteinase 7. Exp. Biol. Med. 2016, 241, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetshina, A.; Palumbo, K.; Dees, C.; Bergmann, C.; Venalis, P.; Zerr, P.; Horn, A.; Kireva, T.; Beyer, C.; Zwerina, J.; et al. Activation of canonical Wnt signalling is required for TGF-beta-mediated fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nlandu-Khodo, S.; Neelisetty, S.; Phillips, M.; Manolopoulou, M.; Bhave, G.; May, L.; Clark, P.E.; Yang, H.; Fogo, A.B.; Harris, R.C.; et al. Blocking TGF-beta and beta-catenin epithelial crosstalk exacerbates CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3490–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, T.; Wu, J.; Liu, X. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via an MMP-7/ syndecan-1/TGF-β autocrine loop. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63324–63337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Liu, X.; Yan, Z.; Xie, L. Sphingosine 1-phosphate regulates proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via syndecan-1. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2019, 148, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, H.A.; Ishani, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Greer, N.L.; MacDonald, R.; Rossini, D.; Sadiq, S.; Lankireddy, S.; Kane, R.L.; Wilt, T.J. Screening for, monitoring, and treatment of chronic kidney disease stages 1 to 3: A systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force and for an American College of Physicians Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2012, 156, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rysz, J.; Gluba-Brzózka, A.; Franczyk, B.; Jabłonowski, Z.; Ciałkowska-Rysz, A. Novel Biomarkers in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease and the Prediction of Its Outcome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2019, 394, 1949–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanaye, P.; Cavalier, E.; Pottel, H. Serum creatinine: Not so simple! Nephron 2017, 136, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronco, C.; Bellomo, R.; Kellum, J. Understanding renal functional reserve. Inten. Care Med. 2017, 43, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Luo, W.; Yang, M.; Yang, P.; Yang, X. Urinary matrix metalloproteinase-7 and prediction of AKI progression post cardiac surgery. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 9217571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, C.R.; Devarajan, P.; Zappitelli, M.; Sint, K.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Li, S.; Kim, R.W.; Koyner, J.L.; Coca, S.G.; Edelstein, C.L.; et al. Postoperative biomarkers predict acute kidney injury and poor outcomes after pediatric cardiac surgery. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 1737–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, C.; Tian, J.; Zha, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Ma, C.; et al. Urinary angiotensinogen level predicts AKI in acute decompensated heart failure: A prospective, two-Stage Study. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alge, J.L.; Karakala, N.; Neely, B.A.; Janech, M.G.; Tumlin, J.A.; Chawla, L.S.; Shaw, A.D.; Arthur, J.M. Urinary angiotensinogen and risk of severe AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, A.O.; Parikh, C.R.; Sint, K.; Coca, S.G.; Koyner, J.; Patel, U.D.; Butrymowicz, I.; Shlipak, M.; Garg, A.X. Association of postoperative proteinuria with AKI after cardiac surgery among patients at high risk. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, A.B.; Alpers, C.E. What is the best way to measure renal fibrosis?: A pathologist’s perspective. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2014, 4, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farris, A.B.; Adams, C.D.; Brousaides, N.; Della Pelle, P.A.; Collins, A.B.; Moradi, E.; Smith, R.N.; Grimm, P.C.; Colvin, R.B. Morphometric and visual evaluation of fibrosis in renal biopsies. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.J.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2014, 4, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Stolz, D.B.; Kiss, L.P.; Monga, S.P.; Holzman, L.B.; Liu, Y. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte dysfunction and albuminuria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.J.; von Toerne, C.; Grone, H.J. Wnt-signaling pathways in progressive renal fibrosis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2011, 15, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Toerne, C.; Schmidt, C.; Adams, J.; Kiss, E.; Bedke, J.; Porubsky, S.; Gretz, N.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Cohen, C.D.; Grone, H.J.; et al. Wnt pathway regulation in chronic renal allograft damage. Am. J. Transpl. 2009, 9, 2223–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Chuang, J.H.; Chou, M.H.; Wu, C.L.; Chen, C.M.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, C.L.; Tai, M.H. Matrilysin (MMP-7) is a major matrix metalloproteinase upregulated in biliary atresia-associated liver fibrosis. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtinghagen, R.; Michels, D.; Haberkorn, C.I.; Arndt, B.; Bahr, M.; Flemming, P.; Manns, M.P.; Boeker, K.H. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-7, and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 are closely related to the fibroproliferative process in the liver during chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2001, 34, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujishima, S.; Shiomi, T.; Yamashita, S.; Yogo, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Inoue, T.; Nakamura, M.; Tasaka, S.; Hasegawa, N.; Aikawa, N.; et al. Production and activation of matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin 1) in the lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2010, 134, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosas, I.O.; Richards, T.J.; Konishi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Gibson, K.; Lokshin, A.E.; Lindell, K.O.; Cisneros, J.; Macdonald, S.D.; Pardo, A.; et al. MMP1 and MMP7 as potential peripheral blood biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, T.M.; Oballa, E.; Simpson, J.K.; Porte, J.; Habgood, A.; Fahy, W.A.; Flynn, A.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Braybrooke, R.; Divyateja, H.; et al. An epithelial biomarker signature for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: An analysis from the multicentre PROFILE cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017, 5, 946–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuka, Y.; Handa, T.; Nakashima, R.; Tanizawa, K.; Kubo, T.; Murase, Y.; Sokai, A.; Ikezoe, K.; Hosono, Y.; Watanabe, K.; et al. Serum matrix metalloproteinase levels in polymyositis/dermatomyositis patients with interstitial lung disease. Rheumatology 2019, 58, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, T.; Didier, M.; Boubaya, M.; Moya, L.; Sutton, A.; Carton, Z.; Baran-Marszak, F.; Sadoun-Danino, D.; Israël-Biet, D.; Cottin, V.; et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea and related comorbidities in incident idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.N.; Tang, S.C.; Schena, F.P.; Novak, J.; Tomino, Y.; Fogo, A.B.; Glassock, R.J. IgA nephropathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzenberg, A.M.; Fogo, A.B.; Reich, H.N.; Troyanov, S.; Bavbek, N.; Massat, A.E.; Hunley, T.E.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Julian, B.A.; Fervenza, F.C.; et al. Validation of the Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.C.; Haas, M.; Reich, H.N. IgA nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Li, Y.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.G.; Novak, J.; Zhang, H. The level of galactose-deficient IgA1 in the sera of patients with IgA nephropathy is associated with disease progression. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthoux, F.; Suzuki, H.; Thibaudin, L.; Yanagawa, H.; Maillard, N.; Mariat, C.; Tomino, Y.; Julian, B.A.; Novak, J. Autoantibodies targeting galactose-deficient IgA1 associate with progression of IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundberg, S.; Qureshi, A.R.; Olivecrona, S.; Gunnarsson, I.; Jacobson, S.H.; Larsson, T.E. FGF23, albuminuria, and disease progression in patients with chronic IgA nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 7, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ren, P.; Wang, Y.; Feng, S.; Wang, C.; Shen, X.; Weng, C.; Lang, X.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, H.; et al. Serum matrix metalloproteinase-7 level is associated with fibrosis and renal survival in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2017, 42, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Nakagawa, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ohashi, N.; Fukasawa, H.; Fujigaki, Y.; Kato, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuki, F.; Hishida, A. Urinary angiotensinogen as a marker of intrarenal angiotensin II activity associated with deterioration of renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, W.; Nair, V.; Smith, S.; Zhu, L.; Shedden, K.; Song, P.X.K.; Mariani, L.H.; Eichinger, F.H.; Berthier, C.C.; Randolph, A.; et al. Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 316ra193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, H.P.; Waanders, F.; Meijer, E.; van den Brand, J.; Steenbergen, E.J.; van Goor, H.; Wetzels, J.F. High urinary excretion of kidney injury molecule-1 is an independent predictor of end-stage renal disease in patients with IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 3581–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musial, K.; Bargenda, A.; Zwolinska, D. Urine matrix metalloproteinases and their extracellular inducer EMMPRIN in children with chronic kidney disease. Ren Fail. 2015, 37, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrailkill, K.M.; Clay Bunn, R.; Fowlkes, J.L. Matrix metalloproteinases: Their potential role in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Endocrine 2009, 35, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonventre, J.V.; Yang, L. Cellular pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 4210–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuncewitch, M.; Yang, W.L.; Corbo, L.; Khader, A.; Nicastro, J.; Coppa, G.F.; Wang, P. WNT agonist decreases tissue damage and improves renal function after ischemia-reperfusion. Shock 2015, 43, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang-Panesso, M.; Humphreys, B.D. Cellular plasticity in kidney injury and repair. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boor, P.; Ostendorf, T.; Floege, J. Renal fibrosis: Novel insights into mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2010, 6, 643–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Neilson, E.G. Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Tan, R.J.; Liu, Y. Myofibroblast in kidney fibrosis: Origin, activation, and regulation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1165, 253–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.J.; Zhou, D.; Fu, H.; Zhang, R.; Wang, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Xing, J. Sequential Wnt agonist then antagonist treatment accelerates tissue repair and minimizes fibrosis. iScience 2020, 23, 101047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, B.; Fan, C.; Yang, L.; Fang, X. Matrix Metalloproteinases-7 and Kidney Fibrosis. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriz, W.; LeHir, M. Pathways to nephron loss starting from glomerular diseases-insights from animal models. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y.; Grunebach, F.; Schmidt, S.M.; Heine, A.; Hantschel, M.; Stevanovic, S.; Rammensee, H.G.; Brossart, P. Matrilysin (MMP-7) is a novel broadly expressed tumor antigen recognized by antigen-specific T cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 5503–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenschwender, M.; Wajant, H. The role of FasL and Fas in health and disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 647, 64–93. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, C.Y.; Huang, S.; Yang, T.; Dong, Z. Cisplatin-induced apoptosis in p53-deficient renal cells via the intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009, 296, F983–F993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havasi, A.; Borkan, S.C. Apoptosis and acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2011, 80, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waring, P.; Mullbacher, A. Cell death induced by the Fas/Fas ligand pathway and its role in pathology. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1999, 77, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nareznoi, D.; Konikov-Rozenman, J.; Petukhov, D.; Breuer, R.; Wallach-Dayan, S.B. Matrix Metalloproteinases Retain Soluble FasL-mediated Resistance to Cell Death in Fibrotic-Lung Myofibroblasts. Cells 2020, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Tan, R.J.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Kidney tubular beta-catenin signaling controls interstitial fibroblast fate via epithelial-mesenchymal communication. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadsworth, S.J.; Atsuta, R.; McIntyre, J.O.; Hackett, T.L.; Singhera, G.K.; Dorscheid, D.R. IL-13 and TH2 cytokine exposure triggers matrix metalloproteinase 7-mediated Fas ligand cleavage from bronchial epithelial cells. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Lin, L.; Tan, X.; Yang, J.; Bu, G.; Mars, W.M.; Liu, Y. tPA protects renal interstitial fibroblasts and myofibroblasts from apoptosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roucou, X.; Antonsson, B.; Martinou, J.C. Involvement of mitochondria in apoptosis. Cardiol. Clin. 2001, 19, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Liu, Z.; Niu, B.; Zhang, J.; Tan, T.K.; Lee, S.R.; Zhao, Y.; Harris, D.C.; Zheng, G. E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex and the epithelial barrier. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 567305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noe, V.; Fingleton, B.; Jacobs, K.; Crawford, H.C.; Vermeulen, S.; Steelant, W.; Bruyneel, E.; Matrisian, L.M.; Mareel, M. Release of an invasion promoter E-cadherin fragment by matrilysin and stromelysin-1. J. Cell. Sci 2001, 114, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Liao, J.; Zhou, X.; Hong, X.; Song, D.; Hou, F.F.; Liu, Y.; Fu, H. Tenascin-C promotes acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease progression by impairing tubular integrity via alphavbeta6 integrin signaling. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 1017–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelec-Butuner, B.; Alapinar, C.; Ertunc, N.; Gonen-Korkmaz, C.; Yörükoğlu, K.; Korkmaz, K.S. TNFα-mediated loss of β-catenin/E-cadherin association and subsequent increase in cell migration is partially restored by NKX3.1 expression in prostate cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Parajuli, K.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, K.; Mo, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Wang, A.R.; et al. Interleukin-17 promotes prostate cancer via MMP7-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 2017, 36, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in renal fibrogenesis: Pathologic significance, molecular mechanism, and therapeutic intervention. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendonsa, A.M.; Na, T.Y.; Gumbiner, B.M. E-cadherin in contact inhibition and cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4769–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motti, M.L.; Califano, D.; Baldassarre, G.; Celetti, A.; Merolla, F.; Forzati, F.; Napolitano, M.; Tavernise, B.; Fusco, A.; Viglietto, G. Reduced E-cadherin expression contributes to the loss of p27kip1-mediated mechanism of contact inhibition in thyroid anaplastic carcinomas. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Croix, B.; Sheehan, C.; Rak, J.W.; Florenes, V.A.; Slingerland, J.M.; Kerbel, R.S. E-Cadherin-dependent growth suppression is mediated by the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(KIP1). J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watabe, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Tsukita, S.; Takeichi, M. Induction of polarized cell-cell association and retardation of growth by activation of the E-cadherin-catenin adhesion system in a dispersed carcinoma line. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 127, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahammer, F.; Schell, C.; Huber, T.B. The podocyte slit diaphragm--from a thin grey line to a complex signalling hub. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2013, 9, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabbe, T.; Smith, B.; O’Connell, J.; Docherty, A. Human progelatinase A can be activated by matrilysin. FEBS Lett. 1994, 345, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barille, S.; Bataille, R.; Rapp, M.J.; Harousseau, J.L.; Amiot, M. Production of metalloproteinase-7 (matrilysin) by human myeloma cells and its potential involvement in metalloproteinase-2 activation. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 5723–5728. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.Q.; So, J.; Reierstad, S.; Fishman, D.A. Matrilysin (MMP-7) promotes invasion of ovarian cancer cells by activation of progelatinase. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 114, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Bredow, D.C.; Cress, A.E.; Howard, E.W.; Bowden, G.T.; Nagle, R.B. Activation of gelatinase-tissue-inhibitors-of-metalloproteinase complexes by matrilysin. Biochem J. 1998, 331 (Pt 3), 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, K.; Yokohama, Y.; Nakanishi, I.; Ohuchi, E.; Fujii, Y.; Nakai, N.; Okada, Y. Matrix metalloproteinase 7 (matrilysin) from human rectal carcinoma cells. Activation of the precursor, interaction with other matrix metalloproteinases and enzymic properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 6691–6697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Limbu, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P.; Liu, B. MMP-2 and 9 in chronic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Lovett, D.H. Gelatinase A (MMP-2) is necessary and sufficient for renal tubular cell epithelial-mesenchymal transformation. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1937–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Disease | Role of MMP-7 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| AKI 1 | Protecting against AKI by priming tubular cells for proliferation and survival | [11] |
| UUO 2 | Promoting renal fibrosis by activating partial EMT and β-catenin | [12] |
| Proteinuric CKD 3 | Increasing urinary albumin excretion by impairing the glomerular filtration barrier | [7] |
| Diabetic nephropathy | Initiating diabetic nephropathy by expanding glomerular mesangium and thickening glomerular basement membrane | [79] |
| Chronic allograft nephropathy | MMPs, including MMP-7, contribute to the deregulation of extracellular matrix remodeling and possibly EMT. | [29] |
| Light chain deposition disease | The decrease of MMPs, including MMP-7, leads to the accumulation of tenascin and extracellular matrix | [30] |
| Amyloid light- chain amyloidosis | The increase of MMPs, including MMP-7, leads to the reduction of extracellular matrix | [30] |
| Renal cell carcinoma | Affecting tumor progression by regulating invasion and angiogenesis | [22] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Tan, R.J.; Liu, Y. The Many Faces of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Kidney Diseases. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060960
Liu Z, Tan RJ, Liu Y. The Many Faces of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Kidney Diseases. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(6):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060960
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zhao, Roderick J. Tan, and Youhua Liu. 2020. "The Many Faces of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Kidney Diseases" Biomolecules 10, no. 6: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060960
APA StyleLiu, Z., Tan, R. J., & Liu, Y. (2020). The Many Faces of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Kidney Diseases. Biomolecules, 10(6), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10060960





