Contactin-1 Is Reduced in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Parkinson’s Disease Patients and Is Present within Lewy Bodies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. CSF Collection and Assays
2.3. Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Immunofluorescence (IF) and Microscopy
2.4. Statistics
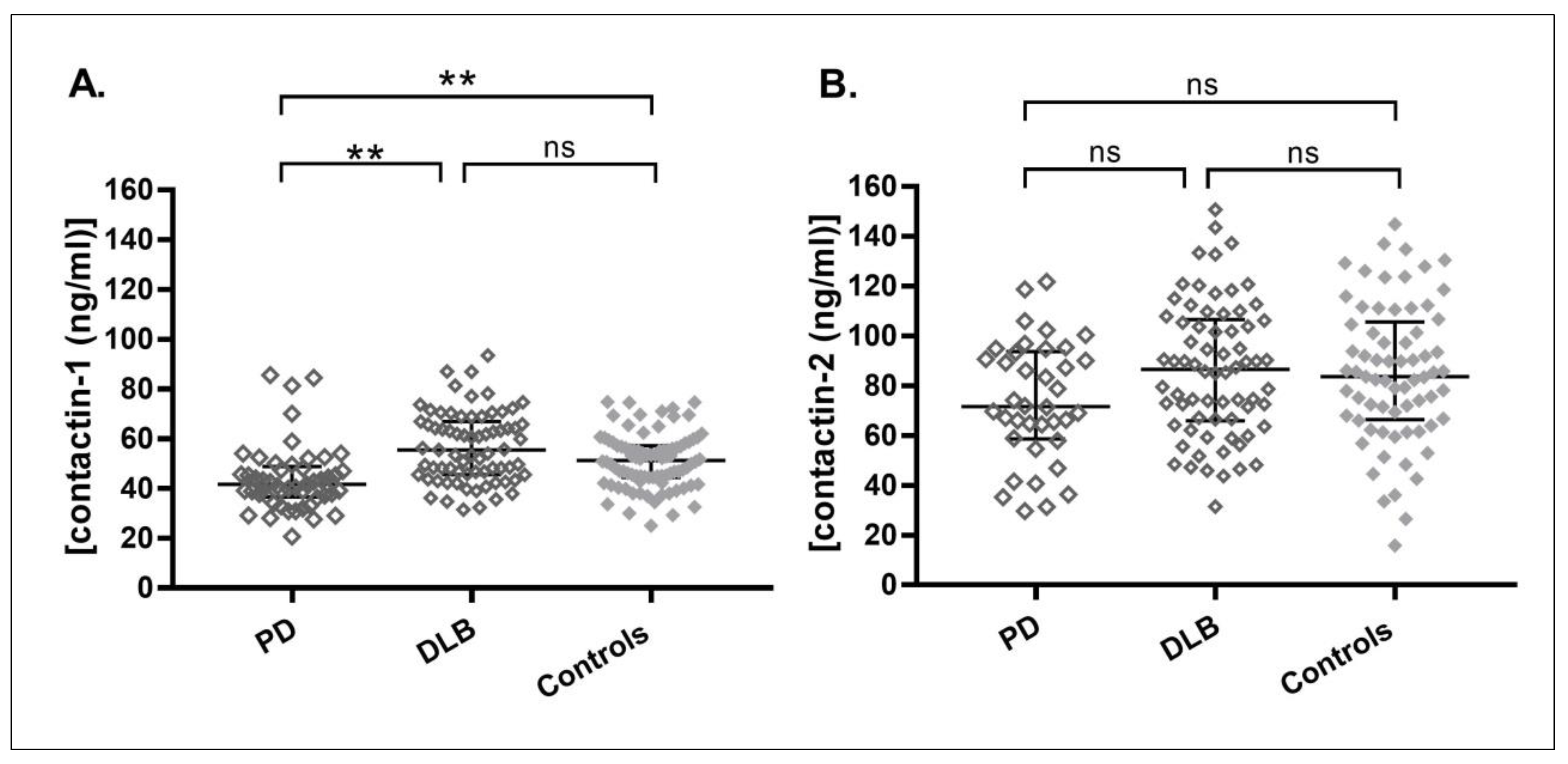
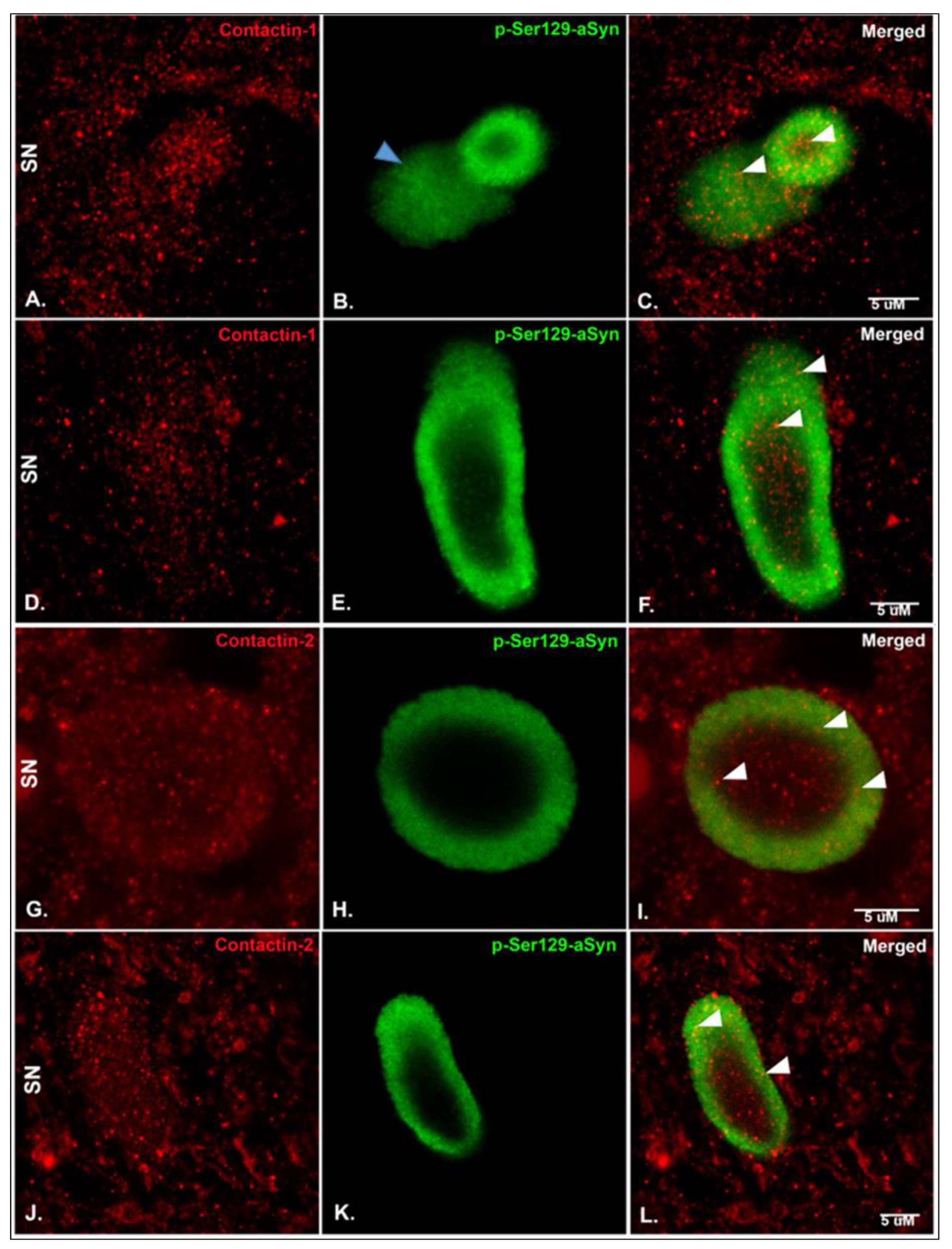
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Clinical Diagnosis
Appendix A.2. Post-Mortem Brain Tissue
| Patient Number | Clinical Diagnosis | Pathological Diagnosis | Sex | Age | Braak NFT Stage | CERAD Amyloid | Braak Alpha-Synuclein Stage | Post Mortem Delay (Hours:Minutes) | pH of CSF | Brain weight (g) | Disease Duration (years) | Cause of Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PD | PD | F | 76 | 1 | O | 6 | 5:30 | 6.16 | 1248 | 15 | Aspiration pneumonia, cardiac arrest |
| 2 | PDD | PDD | M | 80 | 1 | O | 6 | 5:25 | 6.43 | 1180 | 13 | Aspiration pneumonia |
| 3 | PDD | PDD | M | 80 | 2 | B | 6 | 5:30 | 6.29 | 1279 | 13 | |
| 4 | PDD | PDD | M | 72 | 1 | A | 6 | 4:00 | 6.22 | 1210 | 8 | |
| 5 | Control | Control | F | 85 | 3 | A | 0 | 6:25 | 6.60 | 1080 | NA | Euthanasia, ischemic changes in F2 |
| 6 | Control | Control | M | 89 | 2 | O | 0 | 6:50 | 6.23 | 1185 | NA | Urosepsis |
| 7 | Control | Control | M | 80 | 1 | B | 0 | 7:00 | 6.22 | 1354 | NA | Dehydration by epilepsy by brain tumor |
| 8 | Control | Control | F | 78 | 1 | A | 0 | 7:10 | 6.32 | 1120 | NA |
Appendix B
Appendix B.1. Immunohistochemistry (IHC), Immunofluorescence (IF) and Microscopy
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Sherer, T.; Okun, M.S.; Bloem, B.R. The Emerging Evidence of the Parkinson Pandemic. J. Parkinsons. Dis. 2018, 8, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellucci, A.; Mercuri, N.B.; Venneri, A.; Faustini, G.; Longhena, F.; Pizzi, M.; Missale, C.; Spano, P. Parkinson’s disease: From synaptic loss to connectome dysfunction. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2016, 42, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calo, L.; Wegrzynowicz, M.; Santivañez-Perez, J.; Grazia Spillantini, M. Synaptic failure and α-synuclein. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prots, I.; Grosch, J.; Brazdis, R.M.; Simmnacher, K.; Veber, V.; Havlicek, S.; Hannappel, C.; Krach, F.; Krumbiegel, M.; Schütz, O.; et al. α-Synuclein oligomers induce early axonal dysfunction in human iPSC-based models of synucleinopathies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7813–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Adler, C.H.; Bloem, B.R.; Chan, P.; Gasser, T.; Goetz, C.G.; Halliday, G.; Lang, A.E.; Lewis, S.; Li, Y.; et al. Movement disorder society criteria for clinically established early Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnetti, L.; Castrioto, A.; Chiasserini, D.; Persichetti, E.; Tambasco, N.; El-Agnaf, O.; Calabresi, P. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, S.; Hjermind, L.E.; Salvesen, L.; Nielsen, J.E.; Heegaard, N.H.; Jørgensen, H.L.; Rosengren, L.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Winge, K. Amyloid-related biomarkers and axonal damage proteins in parkinsonian syndromes. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Steenoven, I.; Majbour, N.K.; Vaikath, N.N.; Berendse, H.W.; van der Flier, W.M.; van de Berg, W.D.J.; Teunissen, C.E.; Lemstra, A.W.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. α-Synuclein species as potential cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for dementia with lewy bodies. Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1724–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dijk, K.D.; Teunissen, C.E.; Drukarch, B.; Jimenez, C.R.; Groenewegen, H.J.; Berendse, H.J.; van de Berg, W.D.J. Diagnostic cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease: A pathogenetically based approach. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 39, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. The synaptic pathology of α-synuclein aggregation in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, A.A.; Voorn, P.; Berendse, H.W.; Groenewegen, H.J.; Netherlands Brain Bank; Rozemuller, A.J.; van de Berg, W.D. Stage-dependent nigral neuronal loss in incidental Lewy body and parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1244–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milber, J.M.; Noorigian, J.V.; Morley, J.F.; Petrovitch, H.; White, L.; Ross, G.W.; Duda, J.E. Lewy pathology is not the first sign of degeneration in vulnerable neurons in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2012, 79, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, R.E.; O’Malley, K. Axon degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 246, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caminiti, S.P.; Presotto, L.; Baroncini, D.; Garibotto, V.; Moresco, R.M.; Gianolli, L.; Volonté, M.A.; Antonini, A.; Perani, D. Axonal damage and loss of connectivity in nigrostriatal and mesolimbic dopamine pathways in early Parkinson’s disease. NeuroImage Clin. 2017, 14, 734–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Schild, D.; Teunissen, C. Contactins in the central nervous system: Role in health and disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieks, J.K.; Gawinecka, J.; Asif, A.R.; Varges, D.; Gmitterová, K.; Streich, J.; Dihazi, H.; Heinemann, U.; Zerr, I. Low-abundant cerebrospinal fluid proteome alterations in dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 34, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczki, E.; Branca, R.M.; Francis, P.T.; Pereira, J.B.; Baek, J.H.; Hortobágyi, T.; Winblad, B.; Ballard, C.; Lehtiö, J.; Aarsland, D. Synaptic markers of cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases: A proteomic approach. Brain 2018, 141, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Korczyn, A.D. Are dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson’s disease dementia the same disease? BMC Med. 2018, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, F.; Suzuki, M.; Shimada, N.; Kagiya, G.; Ohta, E.; Tamura, K.; Maruyama, H.; Ichikawa, T. Stimulatory effect of α -synuclein on the tau-phosphorylation by GSK-3 β. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4895–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; James, S.; Lei, P. Interactions between α-Synuclein and Tau Protein: Implications to Neurodegenerative Disorders. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 60, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dijk, K.D.; Bidinosti, M.; Weiss, A.; Raijmakers, P.; Berendse, H.W.; van de Berg, W.D. Reduced α-synuclein levels in cerebrospinal fluid in Parkinson’s disease are unrelated to clinical and imaging measures of disease severity. Eur. J. Neurol. 2014, 21, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Flier, W.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L.; Prins, N.; Lemstra, A.W.; Bouwman, F.H.; Teunissen, C.E.; van Berckel, B.N.; Stam, C.J.; Barkhof, F.; Visser, P.J.; et al. Optimizing Patient Care and Research: The Amsterdam Dementia Cohort. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 41, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reijs, B.L.R.; Teunissen, C.E.; Goncharenko, N.; Betsou, F.; Blennow, K.; Baldeiras, I.; Brosseron, F.; Cavedo, E.; Fladby, T.; Froelich, L.; et al. The Central Biobank and Virtual Biobank of BIOMARKAPD: A Resource for Studies on Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Koel-Simmelink, M.J.; Verberk, I.M.; Killestein, J.; Vrenken, H.; Enzinger, C.; Ropele, S.; Fazekas, F.; Khalil, M.; Teunissen, C.E. Contactin-1 and contactin-2 in cerebrospinal fluid as potential biomarkers for axonal domain dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2018, 4, 205521731881953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, C.; Verwey, N.A.; van der Flier, W.M.; Bouwman, F.H.; Kok, A.; van Elk, E.J.; Scheltens, P.; Blankenstein, M.A. Amyloid-beta(1-42), total tau, and phosphorylated tau as cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.P.; Walker, D.E.; Goldstein, J.M.; de Laat, R.; Banducci, K.; Caccavello, R.J.; Barbour, R.; Huang, J.; Kling, K.; Lee, M.; et al. Phosphorylation of Ser-129 is the dominant pathological modification of α-synuclein in familial and sporadic lewy body disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29739–29752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Dohmae, N.; Kawashima, A.; Masliah, E.; Goldberg, M.S.; Shen, J.; Takio, K.; Iwatsubo, T. Alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, M.; Del Campo, M.; Morrema, T.H.J.; de Waal, M.; van der Flier, W.M.; Hoozemans, J.J.M.; Teunissen, C.E. Contactin-2, a synaptic and axonal protein, is reduced in cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers. Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiglieri, V.; Calabrese, V.; Calabresi, P. Alpha-Synuclein: From Early Synaptic Dysfunction to Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahmoradian, S.H.; Genoud, C.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Hench, J.; Moors, T.E.; Navarro, P.P.; Castaño-Díez, D.; Schweighauser, G.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Goldie, K.N.; et al. Lewy Pathology in Parkinson’s Disease Consists of Crowded Organelles and Lipid Membranes. Nat Neurosci. 2019, 22, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhena, F.; Faustini, G.; Varanita, T.; Zaltieri, M.; Porrini, V.; Tessari, I.; Poliani, P.L.; Missale, C.; Borroni, B.; Padovani, A.; et al. Synapsin III is a key component of α-synuclein fibrils in Lewy bodies of PD brains. Brain Pathol. 2018, 28, 875–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiasserini, D.; Biscetti, L.; Eusebi, P.; Salvadori, N.; Frattini, G.; Simoni, S.; De Roeck, N.; Tambasco, N.; Stoops, E.; Vanderstichele, H.; et al. Differential role of CSF fatty acid binding protein 3, α-synuclein, and Alzheimer’s disease core biomarkers in Lewy body dis.orders and Alzheimer’s dementia. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majbour, N.K.; Chiasserini, D.; Vaikath, N.N.; Eusebi, P.; Tokuda, T.; van de Berg, W.; Parnetti, L.; Calabresi, P.; El-Agnaf, O.M. Increased levels of CSF total but not oligomeric or phosphorylated forms of alpha-synuclein in patients diagnosed with probable Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majbour, N.K.; Vaikath, N.N.; Van Dijk, K.D.; Mustafa, A.T.; Varghese, S.; Vesterager, L.B.; Montezinho, L.P.; Poole, S.; Safieh-Garabedian, B.; Tokuda, T.; et al. Oligomeric and phosphorylated alpha-synuclein as potential CSF biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2016, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, K.K.; Misner, D.; Ranscht, B. Contactin supports synaptic plasticity associated with hippocampal long-term depression but not potentiation. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ishizawa, T.; Mattila, P.; Davies, P.; Wang, D.; Dickson, D.W. Colocalization of tau and alpha-synuclein epitopes in Lewy bodies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, K.; Hirai, S.; Sunohara, N.; Aoto, K.; Izumiyama, Y.; Uéda, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawai, M. Cellular co-localization of phosphorylated tau- and NACPra-synuclein-epitopes in Lewy bodies in sporadic Parkinson’s disease and in dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Res. 1999, 843, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, G.G. Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) and Movement Disorder Society Revision of the UPDRS (MDS-UPDRS). In Rating Scales in Parkinson’s Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; pp. 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankovic, J.; McDermott, M.; Carter, J.; Gauthier, S.; Goetz, C.; Golbe, L.; Huber, S.; Koller, W.; Olanow, C.; Shoulson, I.; et al. Variable expression of Parkinson’s disease: A baseline analysis of the DATATOP cohort. The Parkinson Study Group. Neurology 1990, 40, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeith, I.G.; Dickson, D.W.; Lowe, J.; Emre, M.; O’Brien, J.T.; Feldman, H.; Cummings, J.; Duda, J.E.; Lippa, C.; Perry, E.K.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: Third report of the DLB consortium. Neurology 2005, 65, 1863–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppert, F.A.; Brayne, C.; Gill, C.; Paykel, E.S.; Beardsall, L. CAMCOG—A concise neuropsychological test to assist dementia diagnosis: Socio-demographic determinants in an elderly population sample. Br. J. Clin. Psychol. 1995, 34, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafuzoff, I.; Thal, D.R.; Arzberger, T.; Bogdanovic, N.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Bodi, I.; Boluda, S.; Bugiani, O.; Duyckaerts, C.; Gelpi, E.; et al. Assessment of β-amyloid deposits in human brain: A study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafuzoff, I.; Ince, P.G.; Arzberger, T.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Bell, J.; Bodi, I.; Bogdanovic, N.; Bugiani, O.; Ferrer, I.; Gelpi, E.; et al. Staging/typing of Lewy body related α-synuclein pathology: A study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 635–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafuzoff, I.; Arzberger, T.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Bodi, I.; Bogdanovic, N.; Braak, H.; Bugiani, O.; Del-Tredici, K.; Ferrer, I.; Gelpi, E.; et al. Staging of Neurofibrillary Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Study of the BrainNet Europe Consortium. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| PD | DLB | Controls | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 58 | 72 | 90 |
| Sex (female %) | 38 | 10 | 41 |
| Age (years) (mean ± SD) | 63 ± 10 e | 68 ± 6 c | 64 ± 7 |
| MMSE (mean ± SD) | 29 ± 2 | 23 ± 4 a,d | 29 ± 1 |
| Disease duration (median(IQR)) | 4 (2–10) | 2.5 (2.0–4.0) | – |
| H&Y (mean ± SD) | 2 ± 0.5 | – | – |
| UPDRS-III (mean ± SD) | 23 ± 9 | – | – |
| tTau (pg/mL) (median(IQR)) | 190 (157–274) | 306 (224–369) a,d | 229 (174–272) |
| pTau (pg/mL) (median(IQR)) | 40 (28–51) | 47 (35–61) | 44 (34–50) |
| Aβ42 (pg/mL) (median(IQR)) | 967 (794–1076) | 710 (560–937) a,d | 1009 (848–1139) |
| Contactin-1(ng/mL) (median(IQR)) | 42 (36–49) b | 56 (46–67) e | 52 (45–58) |
| Contactin-2 (ng/mL) (median(IQR)) | 72 (59–94) | 87 (66–106) | 84 (66–106) |
| t-α-syn (pg/mL) (median(IQR)) | 1.47 (1.25–1.77) c | 1.40 (1.10–1.70) b | 1.71 (1.40–1.93) |
| DLB | Controls | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contactin-1 | Contactin-2 | Contactin-1 | Contactin-2 | |
| t-α-syn | r = 0.55 p = 0.001 | r = 0.26 p = 0.13 | r = 0.66 p < 0.001 | r = 0.41 p = 0.02 |
| tTau | r = 0.55 p < 0.001 | r = 0.46 p < 0.001 | r = 0.62 p < 0.001 | r = 0.44 p < 0.001 |
| pTau | r = 0.58 p < 0.001 | r = 0.43 p < 0.001 | r = 0.67 p < 0.001 | r = 0.50 p < 0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatterjee, M.; van Steenoven, I.; Huisman, E.; Oosterveld, L.; Berendse, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Del Campo, M.; Lemstra, A.W.; van de Berg, W.D.J.; Teunissen, C.E. Contactin-1 Is Reduced in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Parkinson’s Disease Patients and Is Present within Lewy Bodies. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081177
Chatterjee M, van Steenoven I, Huisman E, Oosterveld L, Berendse H, van der Flier WM, Del Campo M, Lemstra AW, van de Berg WDJ, Teunissen CE. Contactin-1 Is Reduced in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Parkinson’s Disease Patients and Is Present within Lewy Bodies. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(8):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081177
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatterjee, Madhurima, Inger van Steenoven, Evelien Huisman, Linda Oosterveld, Henk Berendse, Wiesje M. van der Flier, Marta Del Campo, Afina W. Lemstra, Wilma D. J. van de Berg, and Charlotte E. Teunissen. 2020. "Contactin-1 Is Reduced in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Parkinson’s Disease Patients and Is Present within Lewy Bodies" Biomolecules 10, no. 8: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081177
APA StyleChatterjee, M., van Steenoven, I., Huisman, E., Oosterveld, L., Berendse, H., van der Flier, W. M., Del Campo, M., Lemstra, A. W., van de Berg, W. D. J., & Teunissen, C. E. (2020). Contactin-1 Is Reduced in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Parkinson’s Disease Patients and Is Present within Lewy Bodies. Biomolecules, 10(8), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10081177





