MiRNA Profiles of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells—Can They Predict Potential Off-Target Effects?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (i)
- the difficulty in generating a consistent source of cells with a stable phenotype,
- (ii)
- a significant first-pass effect due to entrapment of large cells in the lung and liver microvasculature, and
- (iii)
- patient-specific comorbidities in autologous applications [7].
- (i)
- oncogenic miRNAs,
- (ii)
- tumor suppressor miRNAs, and
- (iii)
- miRNAs with a dual role in cancer progression.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Isolation and Cell Culture
2.2. EV Isolation
2.3. Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis (NTA) and Total Protein Analysis
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.5. Immunofluorescence Staining and Flow Cytometry
2.6. MiRNA Analysis
- (i)
- miRNAs with mean corrected CT (CTcorr) values below 30.00 were considered as detected with certainty,
- (ii)
- miRNAs with mean CTcorr values between 30.00 and 32.99 were considered as detected with uncertainty, and
- (iii)
- miRNAs with mean CTcorr values equal or greater than 33.00 were considered as not detected.
2.7. Literature Search for miRNAs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of EVs
3.2. MiRNA Profile of CB- and AT-MSC-Derived EVs
3.3. Classification of miRNAs: Tumor Suppressor miRNAs, Oncogenic miRNAs, and Cardioprotective miRNAs
4. Discussion
4.1. EV Phenotype
4.2. MiRNA Profile
4.2.1. Anti-fibrotic Signaling via Suppression of the TGF-Beta Pathway
4.2.2. Role of miRNA-Mediated Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Suppression
4.2.3. OncomiRs in MSC-Derived EVs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| MiRNA Function | MiRNA Name | CB-MSC-EV [dCT ± SD] | AT-MSC-EV [dCT ± SD] | Fold Difference | p-Value | Confirmed Target GeneGLOBE ID | Cell/Tissue/Cancer Type | MiRNA Cluster | Biological Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS | miR-127-3p | 4.05 ± 0.24 | 4.98 ± 0.72 | –1.9 | 0.03 | BCL6 | fibroblasts | — | proliferation inhibition in senescent fibroblasts | doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080266 |
| KMT5a | chondrocytes | — | proliferation inhibition in osteoarthritis | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.104 | ||||||
| MMP13 | chondrocytes | — | enhances proliferation of chondrocytes in osteoarthritis | doi:10.1111/jcmm.14400 | ||||||
| ITGA6 | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell growth, invasion) | doi:10.1002/iub.1710 | ||||||
| KIF3B | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell growth) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201901_16877 | ||||||
| KIF3B | pancreatic beta cells | — | proliferation inhibition, diabetes | doi:10.18632/aging.101835 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-30c-5p | 4.01 ± 0.5 | 4.84 ± 0.38 | –1.7 | 0.04 | PAI1 | breast cancer | — | suppression of vasculogenesis | doi:10.1172/JCI123106 |
| CTGF | cardiac fibroblasts | miR-133 | cardioprotection (anti-fibrotic) | doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.182535 | ||||||
| TGFB1, TGFBR2 | cardiac fibroblasts | — | suppression of fibrosis | doi:10.1111/jcmm.13548 | ||||||
| CTGF | fibroblasts | — | suppression of cardiac and renal fibrosis | doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.12.011 | ||||||
| ADAM19 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0120698 | ||||||
| SNAI1 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.095 | ||||||
| BCL9 | prostate cancer | — | tumor suppressor (Wnt signaling suppression, cell proliferation) | doi:10.3892/ol.2016.4161 | ||||||
| TS | miR-99b-5p | 4.45 ± 0.46 | 5.45 ± 0.18 | –2.01 | 0.02 | mTOR, AKT, IGF1 | hepatocytes | — | promotes hepatitis B virus replication | doi:10.1111/cmi.12709 |
| mTOR, AKT, IGF1 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9269 | ||||||
| IGF1 | keratinocytes | — | cell proliferation | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2015.07.013 | ||||||
| PI2K, AKT7, mTOR | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/jcp.27645 | ||||||
| TS | miR-376a-3p | 3.76 ± 0.47 | 5.05 ± 0.51 | –2.45 | 0.01 | c-MYC | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1002/cbin.10828 |
| COA1, PDIA6 | giant cell tumor | miR-127-3p | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.08.029 | ||||||
| NRP1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S173416 | ||||||
| COA1, GLE1, PDIA6 | giant cell tumor | miR-127-3p | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3390/cancers11122019 | ||||||
| TS | mir-376c-3p | 3.98 ± 0.35 | 4.85 ± 0.57 | –1.81 | 0.03 | HOXB7 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.050 |
| BCL2, SYF2 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1155/2016/9604257 | ||||||
| CKD1 | neuroblastoma cells | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9431 | ||||||
| HB-EGF | medullary thyroid carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.5114/aoms.2019.85244 | ||||||
| TS | let-7b-5p | 3.03 ± 0.8 | 1.98 ± 0.36 | 2.07 | 0.04 | FAS | macrophages | — | inhibits clearance of mycobacterium tuberculosis | doi:10.1093/femsle/fny040 |
| KIAA1377 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1002/cbin.11136 | ||||||
| IGF1R | multiple melanoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, enhances apoptosis) | doi:10.1093/abbs/gmu089 | ||||||
| CDC25B, CDK1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1002/jcb.29477 | ||||||
| TS | miR-193b-3p | 3.16 ± 0.45 | 2.21 ± 0.16 | 1.93 | 0.003 | MORC4 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, enhances apoptosis) | doi:10.1002/jcb.27751 |
| p21-AK2 | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.11.086 | ||||||
| HDAC3 | brain | — | suppression of NFkB signaling, reduction of inflammation in brain injury | doi:10.1186/s12974-020-01745-0 | ||||||
| CKD1, AJUBA, HEG1 | lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1042/BSR20190634 | ||||||
| TGFB1 | liver | — | decreases fibrosis | doi:10.1111/jcmm.14210 | ||||||
| TS | mir-143-3p | 3.28 ± 0.49 | 3.48 ± 0.51 | –1.15 | 0.6 | LIMK1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | PMID: 28559978 |
| FOSL2 | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1038/s41598-017-18739-3 | ||||||
| BMPR2 | bone marrow-derived MSCs | — | promotes cartilage differentiation | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201812_16649 | ||||||
| IGF1R, IGFBP5 | synovial cells | — | promotes inflammation and increases apoptosis in RA | doi:10.3892/etm.2018.5907 | ||||||
| BCL2, IGF1R | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.08.075 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-199a-3p | 1.92 ± 0.96 | 1.1 ± 0.45 | 1.82 | 0.16 | ITGB8 | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemoresistance) | doi:10.3892/or.2018.6259 |
| GRP78 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | miR-495 (low detection) | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.gene.2017.03.032 | ||||||
| DDIT4, ING4 | cardiomyocytes | miR-214 | cardioprotective (inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis during injury) | doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00807.2015 | ||||||
| mTOR | kidney | — | induces injury induced apoptosis | doi:10.1002/jcb.29030 | ||||||
| AXL | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | PMID: 25520864 | ||||||
| mTOR | endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | PMID: 31966798 | ||||||
| KL | kidney | — | activation of NFkB signaling in lupus nephritis | doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2018.10.003 | ||||||
| SMAD1 | prostate cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.17191 | ||||||
| mTOR | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1512-5 | ||||||
| AGAP2 | glioma cells | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.18632/aging.102092 | ||||||
| PTGIS | endothelial cells | miR-199a-5p | nitrovasodilatator resistance | doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.029206 | ||||||
| CD44 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.10.130 | ||||||
| SOCS7, STAT3 | kidney | — | suppress renal fibrosis | doi:10.1038/srep43409 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-199a-5p | 2.63 ± 0.92 | 2.35 ± 0.65 | 1.22 | 0.68831 | AA1B | monocytes | — | inhibits differentiation | doi:10.1189/jlb.1A0514-240R |
| MAP3K11 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.7150/jca.29426 | ||||||
| SNAI1 | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.02.051 | ||||||
| HIF1A | hemangioma cells | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, autophagy) | doi:10.1177/0394632017749357 | ||||||
| CCR7 | bladder cancer | — | tumor suppressor (metastasis) | doi:10.1186/s12894-016-0181-3 | ||||||
| ETS1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell invasion) | doi:10.1111/cas.12952 | ||||||
| CLTC | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1002/cbf.3252 | ||||||
| PIAS3 | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (metastasis, suppresses epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.1002/jcb.28631 | ||||||
| ROCK1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1177/1533034618775509 | ||||||
| ECE1 | spinal cord nerves | — | inhibition of ischemia-reperfusion injury | doi:10.1007/s10571-018-0597-2 | ||||||
| TET2 | osteoblasts | — | promote differentiation | doi:10.1016/j.gene.2019.144193 | ||||||
| DDR1 | brain | — | protect against ischemia-reperfusion injury | doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2019.07.203 | ||||||
| DRAM1 | acute myeloid leukemia | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1155/2019/5613417 | ||||||
| CDH1 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell invasion) | doi:10.3892/ol.2016.4602 | ||||||
| MAP4K3 | hepatocellular carcinoma | let-7c | tumor suppressor (invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.14623 | ||||||
| ATF6, GRP78 | cardiomyocytes | — | downregulation in myocardial hypoxic preconditioning | doi:10.1007/s13105-018-0657-6 | ||||||
| MAP3K11 | esophageal cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6752 | ||||||
| ZEB1 | ovarian ectopic endometrial stromal cell | — | inhibition of epithelial–mesenchymal transition | doi:10.1007/s43032-019-00016-5 | ||||||
| HIF1A, OSGIN2 | sarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3892/ol.2016.5320 | ||||||
| PHLPP1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1517/14728222.2015.1057569 | ||||||
| BIP | kidney | — | protect against ischemia-reperfusion injury | doi:10.1096/fj.201801821R | ||||||
| WNT2 | urothelial cells | — | inhibiting smooth muscle cell proliferation | doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.618694 | ||||||
| MAGT1 | gliomal cells | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/jcb.28791 | ||||||
| CD44, SIRT1 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (repress stemness) | doi:10.1080/15384101.2019.1689482 | ||||||
| KL | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.1186/1471-2407-14-218 | ||||||
| Mrz 08 | gliomal cells | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201909_18858 | ||||||
| JunB | cardiomyocytes | — | promotes apoptosis in the failing heart) | doi:10.1038/s41598-018-24932-9 | ||||||
| CAV1 | lung | — | promotes lung fibrosis | doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003291 | ||||||
| NFKB | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9170 | ||||||
| SIRT1, ENOS | endothelial cells | — | promotes migration and tube formation | doi:10.1007/s00705-013-1744-1 | ||||||
| HIF1A | prostate adeno-carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.18315 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-99a-5p | 4.11 ± 0.87 | 4.32 ± 0.33 | –1.15 | 0.49 | mTOR | urothelial carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S114276 |
| HOXA1 | smooth muscle cells | — | cardioprotective (inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation and atherosclerosis) | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116664 | ||||||
| mTOR | bladder cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/jcb.27318 | ||||||
| NOX4 | oral cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.4149/neo_2017_503 | ||||||
| CDC25A | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3390/genes11040369 | ||||||
| TS | miR-16-5p | 1.76 ± 0.43 | 1.81 ± 0.33 | –1.03 | 0.84 | AKT3 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1042/BSR20191611 |
| SMAD3 | chordoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0738-z | ||||||
| PIK3R1 | fibroblasts | — | inhibits proliferation | doi:10.3390/ijms20051036 | ||||||
| ANXA11 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1188-x | ||||||
| MYCN | neuroblastoma cells | miR-15a-5p, miR-15b-5p | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/1878-0261.12588 | ||||||
| IGA2 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1002/jcp.28747 | ||||||
| SESN1 | myoblasts | — | myoblast differentiation and proliferation | doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0403-6 | ||||||
| BACH2 | gingival epithelial cells | miR-145-5p | induce apoptosis | PMID: 32509061 | ||||||
| SMAD3 | chondrocytes | — | promotes osteoarthritis | doi:10.2174/1381612821666150909094712 | ||||||
| CARM | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (promotes radiosensitivty) | doi:10.1111/pin.12867 | ||||||
| VEGFA | MSCs | — | suppresses osteogenic potential of MSCs | doi:10.18632/aging.103223 | ||||||
| VEGFA | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, autophagy) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.20398 | ||||||
| VEGFA | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, autophagy) | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.03.006 | ||||||
| EPT1 | preadipocytes | — | promotes differentiation | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.179 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-22-3p | 2.52 ± 0.7 | 1.83 ± 0.31 | 1.62 | 0.09 | HMGB1 | arterial smooth muscle cells | — | inhibits atherosclerosis | doi:10.1159/000480212 |
| MAPK14 | brain | — | prevents Alzheimer’s disease | doi:10.2174/1567202616666191111124516 | ||||||
| WRNIP1 | small cell lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (radiosensitivity) | doi:10.1002/jcb.29032 | ||||||
| AE1 | retinoblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.038 | ||||||
| EIF4EBP3 | cervical cancer | — | oncomiR (tumuorogenesis | doi:10.7150/ijms.21645 | ||||||
| PTEN | kidney | — | suppresses sepsis-induced kidney injury | doi:10.1042/BSR20200527 | ||||||
| AKT3 | Wilm’s tumor | — | tumor suppressor (cell growth) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202006_21493 | ||||||
| SP1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | PMID: 27904693 | ||||||
| SIRT1 | peridontal stem cells | — | increases proliferation and differentiation | doi:10.1002/cbin.11271 | ||||||
| PTAFR | cardiac fibroblasts | — | cardioprotective (reduces activation of cardiac fibroblasts) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_20869 | ||||||
| YAP1 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1111/1759-7714.13280 | ||||||
| DDIT4 | glioblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2020.134896 | ||||||
| SIRT1 | ectopic endometrial cells | — | enhances proliferation and invasion | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202001_20033 | ||||||
| FTO | MSCs | — | promotes osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1186/s13287-020-01707-6 | ||||||
| NFIB | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.4149/neo_2020_190418N350 | ||||||
| TS | miR-152-3p | 4.42 ± 0.66 | 5.16 ± 0.62 | –1.9 | 0.09 | SOS1 | glioblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S210732 |
| p27 | chronic myeloid leukemia | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201812_16646 | ||||||
| KLF4 | prostate cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/jcb.28984 | ||||||
| FOXF1 | fibroblasts | — | promotes cell proliferation, invasion and extracellular matrix production | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116779 | ||||||
| CDK8 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.prp.2019.03.034 | ||||||
| TMEM97 | prostate cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1186/s13148-018-0475-2 | ||||||
| SPIN1 | breast cancer | miR-148 | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1186/s13046-018-0748-9 | ||||||
| PIK3CA | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3727/096504017x14878536973557 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-145-5p | 1.55 ± 0.65 | 1.90 ± 0.37 | –1.28 | 0.3 | FLT1 | trophoblast | — | promote cell proliferation, invasion | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117008 |
| KLF4 | lung | — | promotes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2019.01.011 | ||||||
| CD40 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1007/s11010-017-2982-4 | ||||||
| KLF5 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/jcp.27525 | ||||||
| TAGLN2 | bladder cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9436 | ||||||
| SOX2 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.jss.2018.11.030 | ||||||
| RHBDD1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2019.105641 | ||||||
| FSCN1 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2018.09.018 | ||||||
| TPT1 | prolactinoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1007/s40618-018-0963-4 | ||||||
| TGFB1 | vascular smooth muscle cells | — | inhibits proliferation | doi:10.12659/MSM.910986 | ||||||
| TLR4 | melanoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.1002/jcb.28388 | ||||||
| SEMA3A | AT-MSCs | — | suppresses osteogenic potential of MSCs | doi:10.1007/s11626-019-00318-7 | ||||||
| AKAP12 | prostate cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1111/jcmm.13604 | ||||||
| SMAD2/3 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | reduces extracellular matrix production | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.11.040 | ||||||
| MTDH | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1177/1533033819850189 | ||||||
| NRAS | melanoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1002/cam4.1030 | ||||||
| MTDH | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1096/fj.201701237RR | ||||||
| TS | miR-193a-5p | 4.52 ± 0.67 | 4.35 ± 0.23 | 1.13 | 0.82 | CDK8 | leukemia | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, apoptosis) | doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4671 |
| COL1A1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S255485 | ||||||
| COL1A1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00850 | ||||||
| HOXA1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.18632/aging.103123 | ||||||
| HOXA7 | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, apoptosis) | doi:10.4149/neo_2020_190730N687 | ||||||
| CCNE1 | esophageal cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1007/s13402-019-00493-5 | ||||||
| ERBB2 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S234620 | ||||||
| SRSF6 | pancreatic cancer | — | oncomiR (metastasis) | PMID: 32064152 | ||||||
| DPEP1 | hepatoblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1943-0 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-20a-5p | 4.83 ± 0.27 | 4.72 ± 0.93 | 1.08 | 0.58 | ABCA1 | artery smooth muscle cells | — | promotes cell proliferation and migration | doi:10.1002/jbt.22589 |
| PTEN | endothelial cells | — | pro-angiogenic, inhibits autophagy and apoptosis | doi:10.1038/s41419-020-02745-x | ||||||
| ERBB2 | hepatocellular carcinoma | miR-17-5p | tumor suppressor (metastasis) | doi:10.7150/thno.41365 | ||||||
| TGFBR2 | liver | — | anti-fibrotic | doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00107 | ||||||
| STAT3 | endometrial carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition, invasion) | PMID: 31949657 | ||||||
| STAT3 | bronchial epithelial cells | — | suppresses apoptosis | doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2019.101499 | ||||||
| SRCIN1 | osteoclasts | — | promote proliferation and differentiation | doi:10.1002/cam4.2454 | ||||||
| TGFB1 | endothelial cells | — | anti-angiogenic | doi:10.1002/jcp.29111 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-29c-3p | 3.27 ± 0.92 | 2.48 ± 0.99 | 1.73 | 0.28 | STAT3 | cardiac fibroblasts | — | cardioprotection (inhibits cell proliferation) | doi:10.23736/S0031-0808.20.03975-0 |
| TNFAIP1 | neuroblastoma cells | — | oncomiR (inhibits apoptosis) | doi:10.1007/s11064-020-03096-x | ||||||
| FOS | lens epithelial cells | — | inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110290 | ||||||
| VEGFA | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibit angiogenesis) | doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01594-y | ||||||
| TFAP2C | T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia | miR-29b-3p | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.170. Epub 2020 | ||||||
| NFAT | brain | — | inhibit inflammation in Parkinson’s disease | doi:10.1111/gtc.12764 | ||||||
| CCNA2 | esophageal cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration, and invasion) | doi:10.3389/fbioe.2020.00075 | ||||||
| TRIM31 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3892/or.2020.7469 | ||||||
| FOXP1 | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1080/15384101.2019 | ||||||
| TS, CP | miR-30d-5p | 4.70 ± 0.44 | 5.43 ± 0.63 | 1.66 | 0.09 | SIRT1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibits hypoxia induced apoptosis) | PMID: 32098921 |
| SMAD2 | ovarian granulosa cells | — | promotes apoptosis | doi:10.3892/etm.2019.8184 | ||||||
| NT5E | prostate cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration) | doi:10.1089/cbr.2018.2457 | ||||||
| RUNX2 | colon cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | PMID: 29552759 | ||||||
| TS | miR-320a | 2.51 ± 0.58 | 2.64 ± 0.20 | –1.09 | 0.60 | CXCL9 | synovial cells | — | suppress cell proliferation | doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.00441 |
| SIRT4 | ovaries | — | prevent premature ovarian insufficiency | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2020.05.013 | ||||||
| HIF1A | endometrial carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (anti-angiogenic) | doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112113 | ||||||
| SMAD5 | bone marrow-derived MSCs | — | promote osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202003_20648 | ||||||
| ANRIL | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1016/j.prp.2020.152856 | ||||||
| LOX1 | endothelial cells | — | inhibit apoptosis upon low-density lipoprotein exposure | doi:10.1007/s11010-020-03688-9 | ||||||
| CPEB1 | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (invasion, migration) | doi:10.1002/cam4.2919 | ||||||
| TXNRD1 | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration) | doi:10.1080/15384047.2019.1702405 | ||||||
| FOXM1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition, tumor progression) | doi:10.3390/biom10010020 | ||||||
| PBX3 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.4251/wjgo.v11.i10.842 | ||||||
| PKCG | cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell invasion) | doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1921-6 | ||||||
| MAFB | retina | — | promotes diabetic retinopathy | doi:10.18632/aging.101962 | ||||||
| MAPK | synovial cells | — | promote apoptosis, inhibit proliferation | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201903_17228 | ||||||
| IGFR1 | endometrial carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4051 | ||||||
| TS | miR-361-5p | 4.82 ± 0.92 | 5.33 ± 0.31 | –1.43 | 0.34 | ITGB1 | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1007/s43032-019-00008-5 |
| FOXO1 | chondrocytes | — | promotes apoptosis and inhibits cell proliferation | doi:10.1186/s12920-019-0649-6 | ||||||
| SDCBP | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1097/CAD.0000000000000846 | ||||||
| WT1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201910_19277 | ||||||
| ABCA1 | vascular smooth muscle cells | — | inhibits proliferation | PMID: 31312370 | ||||||
| CLDN8 | retinoblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, promotes apoptosis) | doi:10.1007/s00381-019-04199-9 | ||||||
| VEGFA | hemangioma cells | — | tumor suppressor (anti-angiogenic) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.03.084 | ||||||
| FOXM1 | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1577883 | ||||||
| FOXM1 | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1002/jcp.28026 | ||||||
| SIRT1 | liver | — | promotes hepatosteatosis | doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2018.08.007 | ||||||
| SND1 | glioma cells | — | tumor suppressor (invasion, migration) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S171539 | ||||||
| MMP3, MMP9, VEGF | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition, tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.095 | ||||||
| RQCD1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (invasion, migration) | doi:10.17305/bjbms.2018.3399 | ||||||
| ROCK1 | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.03.122 | ||||||
| RPL22L1 | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | PMID: 31938372 | ||||||
| FOXM1 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemoresistance) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.23513 | ||||||
| FGFR1, MMP1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis, metabolism) | doi:10.1186/s13046-017-0630-1 | ||||||
| FOXM1 | lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.4149/neo_2017_406 | ||||||
| TWIST1 | glioma cells | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.3892/or.2017.5406 | ||||||
| TS | miR-708-5p | 5.32 ± 0.62 | 5.41 ± 0.72 | –1.06 | 0.94 | PGE2 | lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.27614 |
| CTNNB1 | colon cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110292 | ||||||
| TLR4 | macrophages | — | immunomodulation of controlling inflammatory factors | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201909_19019 | ||||||
| ZEB1 | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.10013 | ||||||
| URGCP | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.prp.2019.01.026 | ||||||
| TS | let-7c-5p | 3.67 ± 1.01 | 3.94 ± 0.38 | –1.21 | 0.43 | TGFBR1 | kidney | — | chronic kidney disease | doi:10.1155/2020/6960941 |
| PBX3 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1186/s12943-020-01215-4 | ||||||
| CMYC | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.091 | ||||||
| HMGA2 | dental pulp stem cells | — | promotes osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13059 | ||||||
| DMP1MNF | dental pulp stem cells | — | inhibits inflammation | doi:10.12659/MSM.909093 | ||||||
| NAP1L1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration) | doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.08.024 | ||||||
| TS | let-7e-5p | 4.48 ± 1.39 | 5.18 ± 0.15 | –1.63 | 0.28 | CCR7 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.7150/jca.29536 |
| FASLG | endothelial progenitors | — | prevents deep vein thrombosis | doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2015.12.020 | ||||||
| RCN1 | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00352.2019 | ||||||
| TS | let-7g-5p | 4.69 ± 1.15 | 4.60 ± 0.52 | 1.07 | 0.84 | HMGA2 | glioblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1111/jcmm.14884 |
| IGF1R | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell migration, invasion) | doi:10.12659/MSM.914555 | ||||||
| PRKCA | mammary cells | — | regulates differentiation | doi:10.1002/jcp.27676 | ||||||
| VSIG4 | glioblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.3892/or.2016.5098 | ||||||
| TS, CP | let-7i-5p | 1.14 ± 0.89 | 1.39 ± 0.93 | –1.19 | 0.72 | GALE | glioblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S221585 |
| HMGA1 | bladder cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1186/s12894-019-0485-1 | ||||||
| CCND2, E2F2 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (promotes proliferation after injury) | doi:10.1042/CS20181002 | ||||||
| KLK6 | colon cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/or.2018.6577 |
| MiRNA Function | MiRNA Name | CB-MSC-EV [dCT ± SD] | AT-MSC-EV [dCT ± SD] | Fold Difference | p-Value | Confirmed Target GeneGLOBE ID | Cell/Tissue/Cancer Type | MiRNA Cluster | Biological Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O, CP | miR-100-5p | 1.11 ± 0.67 | 2.05 ± 0.28 | –1.9 | 0.05 | ANGPT2 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | suppression of angiogenesis | doi:10.1002/path.4804 |
| p53 | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell growth) | doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03962-x | ||||||
| mTOR | endometrial carcinoma | miR-199a-3p, miR-199b-5p | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | PMID: 31966798 | ||||||
| mTOR | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (anti-angiogenic) | doi:10.1007/s13402-017-0335-7 | ||||||
| mTOR | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201809_15913 | ||||||
| mTOR | vascular smooth muscle cells | — | suppression of angiogenesis | doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.000323 | ||||||
| O | miR-151a-5p | 4.0 ± 0.38 | 5.09 ± 0.2 | –2.14 | 0.007 | CDH1 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition, proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1038/oncsis.2017.66 |
| p53 | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1042/BSR20191357 | ||||||
| O | miR-103a-3p | 2.49 ± 0.64 | 4.24 ± 0.18 | –3.35 | 0.02 | APC/APC2 | colorectal carcinoma | miR-1872 (not tested) | oncomiR (activator of Wnt signaling, cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/jcb.26357 |
| CDK5 | bladder cancer | miR-107 | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1038/emm.2015.39 | ||||||
| CDK6 | AT-MSCs | — | inhibit proliferation | doi:10.1038/srep30919 | ||||||
| GPRC5A | prostate cancer | — | oncomiR, tumor suppressor (depending on cancer type) | doi:10.1261/rna.045757.114 | ||||||
| CDH11, NR3C1 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202006_21505 | ||||||
| PTEN | endothelial progenitor cells | — | promotes migration and angiogenesis | doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2019.10.048 | ||||||
| SNRK | glomerular endothelial cells | — | promotes NFkB/p65 activation, renal inflammation and fibrosis | doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11515-z | ||||||
| O | miR-191-5p | 3.25 ± 0.42 | 4.26 ± 0.42 | –2.01 | 0.02 | SOX4 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1261/rna.060657.117 |
| EGR1, UBE2D3 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | PMID: 31933962 | ||||||
| EGR1 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (activates PI3K/AKT pathway, proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201905_17783 | ||||||
| ENOS, MMP1, MMP9 | endothelial cells | — | antiangiogenic | doi:10.1096/fj.201601263R | ||||||
| O | miR-92a-3p | 3.05 ± 0.75 | 3.12 ± 0.26 | –1.05 | 0.67 | WNT5A | chondrocytes | — | enhance chondrogenesis | doi:10.1186/s13287-018-1004-0 |
| PTEN | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/ijmm.2019.4258 | ||||||
| CDH1 | glioma cells | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.3390/ijms17111799 | ||||||
| PTEN | pancreatic cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2020.180459 | ||||||
| O, CP | miR-423-3p | 4.49 ± 0.12 | 4.47 ± 0.14 | 1.01 | 0.83 | RAP2C | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (in ischemic postconditioning secreted by cardiac fibroblast-EVs) | doi:10.1093/cvr/cvy231 |
| p21CIP1, WAF1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell growth) | doi:10.1159/000430230 | ||||||
| PANX2 | glioma cells | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | PMID: 29928399 | ||||||
| ADIPOR2 | laryngeal cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | PMID: 25337209 | ||||||
| O, CP | miR-21-5p | -0.90 ± 0.52 | -0.78 ± 0.82 | –1.09 | 0.98 | FASLG | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.1089/dna.2018.4529 |
| CCR7 | chondrosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1080/03008207.2019.1702650 | ||||||
| TIAM1 | colon cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1159/000493457 | ||||||
| PDCD4 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.4149/neo_2018_181207N930 | ||||||
| BCL2, TLR4 | macrophages | — | regulates mycobacterial survival | doi:10.1002/1873-3468.13438 | ||||||
| SET, TAF-IA | lung adenocarcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.06.014 | ||||||
| RAB11A | neurons | — | neuroprotection during traumatic brain injury | doi:10.12659/MSM.915727 | ||||||
| PTEN, PDCD4 | lung | — | anti-apoptotic during ischemia-reperfusion injury | doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.01.022 | ||||||
| SOX7 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S146423 | ||||||
| TGFB1 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.3892/etm.2018.6752 | ||||||
| CHL1 | colon adenocarcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1186/s10020-018-0034-5 | ||||||
| PTEN, PDCD4 | lung cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis m2 polarization) | doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1027-0 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S172393 | ||||||
| PI3K | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (improves contractility) | doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312420 | ||||||
| SPRY1 | joints | — | suppresses angiogenesis and matrix degeneration | doi:10.1186/s13075-020-2145-y | ||||||
| PDCD4 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (anti-apoptotic) | doi:10.3892/etm.2019.7970 | ||||||
| MASPIN | endothelial cells | — | suppresses angiogenesis and proliferation | doi:10.1080/09168451.2018.1459179 | ||||||
| CDKN2C | melanoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/2211-5463.12819 | ||||||
| CCL1, TIMP3 | neurons | — | inhibits neuropathic pain development | doi:10.1002/jcb.28920 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | fibroblasts | — | promote fibrosis in tendon injury | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2018.11.006 | ||||||
| FASLG | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1042/BSR20190597 | ||||||
| WWC2 | lung adenocarcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.3233/CBM-201489 | ||||||
| PTEN, mTOR | brain | — | protects against seizure damage | doi:10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2018.05.001 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | fibroblasts | — | activation of spinal fibrosis | doi:10.7150/ijbs.24074 | ||||||
| PDCD4 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/ijo.2017.4127 | ||||||
| HMSH2 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.1159/000481839 | ||||||
| PTEN | smooth muscle cells | — | promotes proliferation and remodeling | doi:10.3390/ijms20040875 | ||||||
| MAPK10 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.1042/BSR20181000 | ||||||
| PTEN | fibroblasts | — | prevents radiation-induced autophagy | doi:10.1038/s41374-019-0323-9 | ||||||
| CADM1 | tongue cancer | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.1007/s00109-016-1417-0 | ||||||
| O, CP | miR-34a-5p | 3.49 ± 1.45 | 2.09 ± 0.84 | 2.65 | 0.23 | NOTCH1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardiotoxic | doi:10.31083/j.rcm.2019.03.545 |
| BCL2 | endothelial cells | — | hypoxia induced autophagy | doi:10.1002/jcb.29207 | ||||||
| ZEB1 | cardiomyocytes | — | aggravates hypoxia induced apoptosis | doi:10.1515/hsz-2018-0195 | ||||||
| ACSL1 | hepatocytes | — | increases hepatic triglyceride and cholesterol levels | doi:10.3390/ijms20184420 | ||||||
| SIRT1 | kidney | — | promotes injury induced fibrosis | doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0527-8 | ||||||
| SIRT1 | kidney | — | promotes injury induced fibrosis | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.12.048 | ||||||
| DLL1 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.1038/srep44218 | ||||||
| AGTR1 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.1186/s12885-016-3002-x | ||||||
| CD117 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8546 | ||||||
| PD-L1 | ovarian carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresitance) | doi:10.4149/neo_2019_190202N106 | ||||||
| BCL2 | ovarian carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S142446 | ||||||
| O | miR-15b-5p | 4.41 ± 0.46 | 4.88 ± 1.04 | –1.38 | 0.69 | AKT3 | arteries | — | inhibits ateriogenesis, angiogenesis | doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308905 |
| PAQR3 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis) | doi:10.3892/or.2017.5673 | ||||||
| AXIN2 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.3892/ol.2019.11056 | ||||||
| RECK | prostate cancer | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.3892/ol.2019.11056 | ||||||
| SEMA3A | podocytes | — | repressing apoptosis and inflammation in high glucose injury | doi:10.1002/jcp.28691 | ||||||
| PDK4 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.035 | ||||||
| BMPR1A | cardiomyocytes | — | promotes doxorubicin induced injury | doi:10.1007/s12012-018-9495-6 | ||||||
| HPSE2 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.00108 | ||||||
| O | miR-17-5p | 5.57 ± 0.15 | 5.34 ± 0.62 | 1.10 | 0.57 | BAMBI | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes angiogenesis) | doi:10.7150/jca.30757 |
| ETV1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1186/s12885-017-3674-x | ||||||
| RBL2, E2F4 | pancreatic cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.044 | ||||||
| ANKH | fibroblasts | — | increased ostegenesis | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.10.003 | ||||||
| BRCC2 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell growth) | doi:10.3892/or.2016.4542 | ||||||
| NTN4 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis, invasion) | PMID: 31933983 | ||||||
| SKSI1 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.1002/jcb.27832 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | fibroblasts | — | promotes liver fibrosis | doi:10.1111/jcmm.14432 | ||||||
| TGFB2 | cervical cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201804_14712 | ||||||
| E2F1 | granulosa cells | — | promotes cell proliferation | doi:10.1111/rda.13551 | ||||||
| SMAD5 | myoblasts | miR-106b-5p | promotes osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.07.010 | ||||||
| MFN2 | satellite cells | — | modulates mitochondrial function | PMID: 31198013 | ||||||
| P21 | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/cam4.863 | ||||||
| HOXB13 | prostate cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.1186/s12935-019-0994-8 | ||||||
| P21 | astrocytes | — | inhibits apoptosis during hypoxia | doi:10.1186/s12935-019-0994-8 | ||||||
| CMYC | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4355-5 | ||||||
| VEGFA | endothelial cells | — | mitigates endometriosis | doi:10.1007/s12038-020-00049-y | ||||||
| TMOD1 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201907_18430 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | osteoblasts | — | promotes osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1038/emm.2014.43 | ||||||
| RUNX3 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110246 | ||||||
| SOCS6 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.036 | ||||||
| PTEN | thyroid cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.4149/neo_2019_190110N29 | ||||||
| PTEN, GAINT7 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1242/jcs.122895 | ||||||
| PIK3R1 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.1007/s10620-012-2400-4 | ||||||
| P21/PTEN | smooth muscle cells | — | promotes hypoxia induced proliferation | doi:10.1186/s12931-018-0902-0 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | nasal epithelial cells | — | aggravates inflammatory response | doi:10.1186/s12860-018-0152-5 | ||||||
| TGFB2 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8946 | ||||||
| HBP1 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis, invasion) | doi:10.1007/s10549-010-0954-4 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | hepatic stellate cells | — | activates stellate cells | doi:10.1038/labinvest.2015.58 | ||||||
| O, CP | miR-21-3p | 5.28 ± 1.27 | 3.89 ± 1.01 | 2.26 | 0.26 | SPRY1 | fibroblasts | — | promotes wound healing | doi:10.18632/aging.103610 |
| MAT2B | brain | — | attenuate ischemia-reperfusion injury | doi:10.3325/cmj.2019.60.439 | ||||||
| PTEN | vascular smooth muscle cells | — | promote migration and proliferation (pro-atherogenic) | doi:10.7150/thno.37357 | ||||||
| VEGFA | granulosa cells | — | inhibits autophagy | doi:10.1530/REP-19-0285 | ||||||
| TGS4 | retinal pigment epithelial cells | — | modulates apoptosis and inflammation | doi:10.1111/1440-1681.13142 | ||||||
| AKT, CDK2 | kidney | — | regulates metabolic alterations in acute kidney injury | doi:10.1155/2019/2821731 | ||||||
| P53 | multiple cancers | — | oncomiR (inhibit apoptosis) | doi:10.1016/j.abb.2019.05.026 | ||||||
| PTEN | liver cancer | — | oncomiR (inhibit apoptosis) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S183328 | ||||||
| HDAC1 | epithelium | — | inhibits influenca virus replication | doi:10.3389/fcimb.2018.00175 | ||||||
| SORBS2 | cardiomyocytes | — | promoted myocardial dysfunction in sepsis | doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.03.014 | ||||||
| HDAC1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (suppression of myocardial hypertrophy) | doi:10.1093/cvr/cvu254 | ||||||
| O | miR-663a | 4.43 ± 0.38 | 1.49 ± 1.06 | 7.68 | 0.02 | MYL9 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1177/0960327120937330 |
| TGFB1 | liver | — | reduces hepatic stellar cell activation | doi:10.1155/2020/3156267 | ||||||
| ZBTB7A | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (inhibits apoptosis) | doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.01.046 | ||||||
| TGFB1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1186/s12885-018-5016-z | ||||||
| NFIX | spermatogonial stem cells | — | promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2018.05.015 | ||||||
| EMP3 | gallbladder cancer | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2018.05.022 | ||||||
| O | miR-664a-3p | 4.67 ± 1.55 | 4.77 ± 0.54 | –1.07 | 0.44 | FHL1 | lung | — | Progression of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | doi:10.2147/COPD.S224763 |
| FOXP3 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1111/cpr.12567 |
| MiRNA Function | MiRNA Name | CB-MSC-EV [dCT ± SD] | AT-MSC-EV [dCT ± SD] | Fold Difference | p-Value | Confirmed Targets GeneGLOBE ID | Cell/Tissue/Cancer Type | MiRNA Cluster | Biological Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TS/O | miR-31-3p | 4.93 ± 0.56 | 5.08 ± 0.49 | –1.11 | 0.64 | RASA1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, tumor progression) | doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.367763 |
| SEMA4C | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemoresistance) | doi:10.1038/s41598-019-54177-z | ||||||
| TIAM1 | colorectal carcinoma | miR-21 | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition, invasion) | doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.160069 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-199b-5p | 4.39 ± 1.5 | 3.73 ± 0.43 | 1.58 | 0.53 | HER2 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | PMID: 30610808 |
| STON2 | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (metastasis, suppresses epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.1002/iub.1889 | ||||||
| DYRK1A, NOTCH1, JAG1 | — | — | promotes pathological myocardial remodeling | doi:10.1016/j.ncrna.2016.12.002 | ||||||
| KLK10 | cervical cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.165 | ||||||
| mTOR | endometrial endometrial adenocarcinoma | miR-100-5p, miR-199a-3p | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | PMID: 31966798 | ||||||
| GSK3B | monocytes | — | inhibition of NFkB signaling, anti-inflammatory | doi:10.1007/s10753-018-0799-2 | ||||||
| JAG1 | ligamentum flavum cells | — | inhibition of osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1111/jcmm.13047 | ||||||
| CAV1 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1740-9 | ||||||
| ALK1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (angiogenesis) | doi:10.3389/fgene.2019.01397 | ||||||
| DDR1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9255 | ||||||
| BICC1 | oral cancer | miR-101-3p (not detected) | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101567 | ||||||
| MLK | pancreatic beta cells | — | increases cell proliferation | doi:10.2174/2211536605666160607082214 | ||||||
| JAG1, DDR1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1002/path.5238 | ||||||
| PODXL, DDR1 | acute myeloid leukemia | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/ajh.23129 | ||||||
| HES1 | medulloblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (impairs cancer stem cell function) | doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0004998 | ||||||
| ITGA3 | squamous cell carcinoma | miR-199a-3p/5p | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1111/cas.13298 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-221-3p | 1.25 ± 0.67 | 0.65 ± 0.25 | 1.51 | 0.11 | AXIN2 | - | miR-15b-5p | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.3892/ol.2019.11056 |
| THBS2 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes angiogenesis) | doi:10.1007/s10456-019-09665-1 | ||||||
| SDF1 | cartilage | — | prevent cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis | doi:10.1007/s00109-017-1516-6 | ||||||
| VASH1 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis) | doi:10.1038/s41388-018-0511-x | ||||||
| THBS1 | trophoblast | — | promotes invasion and proliferation | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.009 | ||||||
| JAK3 | macrophages | — | regulates M1 to M2 transition | doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.03087 | ||||||
| ARF4 | epithelial ovarian cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.01.002 | ||||||
| THBS2 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis) | doi:10.1038/s41419-017-0077-5 | ||||||
| MMP22 | macrophages | — | prevent low-density lipoprotein-induced oxidative stress | doi:10.1002/jcb.27917 | ||||||
| EIF5A2 | medulloblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, enhances apoptosis) | doi:10.1080/09168451.2018.1553604 | ||||||
| PTEN | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.3727/096504016 × 14756282819385 | ||||||
| TIMP3 | retina | — | promotes microvascular dysfunction | doi:10.1007/s00424-020-02432-y | ||||||
| PARP1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.21561 | ||||||
| RB1 | pancreatic cancer | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.1007/s13277-016-5445-8 | ||||||
| JNK1, TGFBR1, ETS-1 | cardiac fibroblasts | — | cardioprotective (inhibits fibroblast activation) | doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10094 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-25-3p | 4.52 ± 0.53 | 4.8 ± 0.13 | –1.21 | 0.33 | BTG2 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1186/s12943-017-0754-0 |
| PTEN | retinoblastoma | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109111 | ||||||
| FBXW7, DKK3 | glioma cells | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/etm.2019.7583 | ||||||
| BTG2 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1155/2019/7024675 | ||||||
| SEMA4C | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (suppresses EMT) | doi:10.1111/cas.13104 | ||||||
| ADAM10 | endothelial cells | — | inhibit NFkB Signaling and reduces inflammation | doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02205 | ||||||
| EZH2 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotective (inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis during injury) | doi:10.1080/0886022X.2020.1745236 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-23b-3p | 0.73 ± 0.69 | 1.02 ± 0.26 | –1.23 | 0.307825 | SIRT1 | lens epithelial cells | — | reduces apoptosis in oxidative stress | doi:10.1002/jcb.29270 |
| TGFBR3 | atrial fibroblasts | miR-27b-3p | promote atrial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation | doi:10.1111/jcmm.14211 | ||||||
| CB1R | gastric cancer | miR-130a-5p (not detected) | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S181706 | ||||||
| ANXA2 | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1159/000494468 | ||||||
| ETS1 | hepatocytes | — | downregulate Apo(a) expression | doi:10.1002/cbin.10896 | ||||||
| PGC1A | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1038/s41419-019-1614-1 | ||||||
| EBF3 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1093/abbs/gmy049 | ||||||
| ZEB1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (suppresses epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.1016/j.gene.2018.05.061 | ||||||
| CMET | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1038/s41598-020-60143-x | ||||||
| ATG12, HMGB2 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.123 | ||||||
| HS6ST2 | chondrocytes | — | enhances matrix degradation in osteoarthritis | doi:10.1038/s41419-018-0729-0 | ||||||
| TGIF1 | keratinocytes | — | regulation of keratinocyte differentiation | doi:10.1111/exd.13119 | ||||||
| PTEN | renal cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050203 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-27b-3p | 2.97 ± 0.79 | 2.77 ± 0.5 | 1.15 | 0.84 | TGFBR3 | atrial fibroblasts | miR-27b-3p | promote atrial fibrosis in atrial fibrillation | doi:10.1111/jcmm.14211 |
| HOXA10 | colorectal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1042/BSR20191087 | ||||||
| CBLB, GRB2 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, chemoresistance) | doi:10.1038/s41419-017-0211-4 | ||||||
| WNT3A | atrial fibroblasts | — | cardioprotection (reduces atrial fibrosis during atrial fibrillation) | doi:10.1155/2019/5703764 | ||||||
| MARCH7 | endometrial carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1093/abbs/gmz030 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | endothelial cells | — | suppresses endothelial cell proliferation and migration in Kawasaki disease | doi:10.1159/000492354 | ||||||
| HIPK2 | chondrocytes | — | inhibits apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis | doi:10.1080/21691401.2019.1607362 | ||||||
| PPARG | thyroid cancer | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.1111/bcpt.13076 | ||||||
| FZD7 | lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | PMID: 29028088 | ||||||
| SP7 | maxillary sinus membrane stem cells | — | suppress osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1097/ID.0000000000000637 | ||||||
| LIMK1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | PMID: 31966797 | ||||||
| GSPT1 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109417 | ||||||
| YAP1 | glioma cells | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1139/bcb-2019-0300 | ||||||
| ROR1 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1186/s13046-015-0253-3 | ||||||
| PPARG | oocytes | — | maturation | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.046 | ||||||
| GSPT1 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S196865 | ||||||
| NRF2 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1007/s13577-020-00329-7 | ||||||
| TRAF3 | chondrocytes | — | inhibits IL1B-induced injury | doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106052 | ||||||
| NR5A2, CREB1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1038/cddis.2016.361 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-24-3p | 0.43 ± 0.62 | 1.48 ± 0.56 | –2.05 | 0.091 | KEAP1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1155/2018/7042105 |
| FGF11 | T-cells | — | oncomiR (immune evasion) | doi:10.1002/path.4781 | ||||||
| SOX7 | lung cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis, invasion) | doi:10.1002/jcb.26553 | ||||||
| SOCS6 | prostate cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis, invasion, proliferation) | PMID: 31938287 | ||||||
| p27KIP1 | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes metastasis, invasion, proliferation) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201907_18327 | ||||||
| BIM | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.1002/jcb.28568 | ||||||
| RIPK1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1159/000495161 | ||||||
| DEDD | bladder cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.3892/or.2016.5326 | ||||||
| PRKCH | Lacrimal adenoid cystic carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0158433 | ||||||
| MTT1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/cbf.3213 | ||||||
| SMAD5 | peridontal stem cells | — | inhibit osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1002/jcp.27499 | ||||||
| JAB1/CSN5 | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (radiosensitivity) | doi:10.1038/onc.2016.147 | ||||||
| ATG4A | small cell lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.2787 | ||||||
| IGFBP5 | intervertebrate discs | — | induces disc degeneration | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117288 | ||||||
| NOTCH1, DLL1 | endothelial cells | — | inhibit angiogenesis after myocardial infarction | doi:10.3390/ijms21051733 | ||||||
| LAMB3 | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.01499 | ||||||
| CHD5 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, chemoresistance) | doi:10.2217/fon-2016-0179 | ||||||
| FGF11 | fibroblasts | — | activation of fibrosis and proliferation in renal fibrosis | doi:10.1002/jcp.29329 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-23a-3p | -0.14 ± 0.54 | 0.06 ± 0.95 | –1.14 | 0.99 | PNRC2 | renal cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.11.065 |
| KLF3 | melanoma | — | oncomiR (promotes tumor progression) | doi:10.1186/s12935-019-0927-6 | ||||||
| FGF2 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.prp.2018.12.021 | ||||||
| CHD17 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1007/s13105-020-00726-4 | ||||||
| SMAD3 | chondrocytes | — | promotes osteoarthritis | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.071 | ||||||
| PTEN | gliomal cells | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation) | doi:10.1002/ar.24410 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-130a-3p | 4.86 ± 0.83 | 5.01 ± 0.74 | –1.11 | 0.75 | PDE4D | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (improves cardiac cell proliferation after myocardial infarction) | doi:10.1002/jcp.26327 |
| SMAD4 | esophageal cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.1002/cam4.1981 | ||||||
| RAB5B | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor ( invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.018 | ||||||
| SOX4 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1080/15384047.2017.1385679 | ||||||
| SMAD4 | hepatoma cells | — | tumor suppressor (invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1186/s13046-016-0296-0 | ||||||
| SNON | kidney | — | inhibition of renal fibrosis | doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.104358 | ||||||
| TGFBR1/2 | hepatic stellate cells | — | decreases hepatic fibrosis | doi:10.1038/cddis.2017.10 | ||||||
| BACH2 | nasopharyngeal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.1042/BSR20160576 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-15a-5p | 5.52 ± 2.85 | 4.42 ± 1.07 | 2.14 | 0.73 | VEGFA | chondrocytes | — | aggravates osteoarthritis | doi:10.5582/bst.2016.01187 |
| VEGFA | peritoneal mesothelial cells | — | suppresses inflammation and fibrosis | doi:10.1002/jcp.27660 | ||||||
| WNT3A | endometrial carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell growth) | PMID: 29164582 | ||||||
| CXCL10 | chronic myeloid leukemia | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy), metastasis | PMID: 28979704 | ||||||
| MYCN | neuroblastoma cells | miR-15b-5p, miR-16-5p | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/1878-0261.12588 | ||||||
| PTHrP | chondrocytes | — | promotes osteoarthritis | doi:10.1155/2019/3904923 | ||||||
| FASN | arteries | — | alleviates atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation | doi:10.1042/BSR20181852 | ||||||
| PHLPP2 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.4149/neo_2020_190904N861 | ||||||
| TP53INP1 | cervical cancer | — | oncomiR (anti-apoptotic) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201910_19129 | ||||||
| BDNF | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1007/s13277-015-4427-6 | ||||||
| TGFB3, VEGF | retinal endothelial cells | — | promote endothelial cell tight junction formation | doi:10.1016/j.visres.2017.07.007 | ||||||
| VEGFA | endometrial mesenchymal stem cells | — | promote endometriosis | PMID: 27608888 | ||||||
| HOXA3 | thyroid cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1089/hum.2018.109 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-181a-5p | 5.5 ± 0.68 | 6.54 ± 0.7 | –1.09 | 0.9 | PBX1 | ligaments | — | promotes osteogenesis | doi:10.7150/thno.44309 |
| CBLB | esophageal cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S251264 | ||||||
| E2F7 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S240964 | ||||||
| ESM1 | retina | — | anti-angiogenesis | doi:10.1002/jcp.29733 | ||||||
| SIRT1 | cardiomyocytes | — | promotes apoptosis in hypoxic injury | doi:10.1080/09168451.2020.1750943 | ||||||
| KLF17 | prostate cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | PMID: 32195032 | ||||||
| PDGFRA | endothelial cells | — | anti-angiogenesis | doi:10.1002/cbf.3472 | ||||||
| AKT3 | gastric adenocarcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, apoptosis) | doi:10.1098/rsob.190095 | ||||||
| p53 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (reduces high glucose induced apoptosis) | doi:10.1538/expanim.19-0058 | ||||||
| ATG7 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (inhibits autophagy) | doi:10.1002/jcb.29064 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-106a-5p | 5.19 ± 0.76 | 5.42 ± 1.07 | –1.17 | 0.97 | HK2 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1007/s11010-020-03840-5 |
| STAT3 | endothelial cells | — | allelviates atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation | doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11147 | ||||||
| RBM24 | prostate cancer | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S246274 | ||||||
| TGFBR2 | colorectal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | PMID: 31949649 | ||||||
| ARHGAP24 | ovarian carcinoma | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117296 | ||||||
| TGFBR2 | palate | — | promotes cleft palate formation | doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2019 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-125a-5p | 2.3 ± 0.54 | 2.64 ± 0.22 | –1.27 | 0.27 | FUT4 | osteosarcoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.00672 |
| LIN28B | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11223 | ||||||
| MACC1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | miR-34a | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.4149/neo_2020_191019N1062 | ||||||
| FNDC3B | colorectal carcinoma | miR-217 | oncomiR (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S226520 | ||||||
| HK2 | lung | — | inhibits glycolysis and improved pulmonary arterial hypertension | doi:10.18632/aging.103163 | ||||||
| TRAF6 | macrophages | — | promotes M2 polarization | doi:10.1007/s10753-020-01231-y | ||||||
| GALNT7 | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.1186/s12935-020-01209-8 | ||||||
| VEGFA | trophoblast | — | suppresses migration and proliferation | doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.02.137 | ||||||
| GAB2 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion) | doi:10.3934/mbe.2019347 | ||||||
| SIRT7 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (radioresistance) | doi:10.3233/CBM-190381 | ||||||
| TAZ | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.3233/CBM-190381 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-125b-5p | −1.36 ± 0.51 | −1.21 ± 0.36 | –1.11 | 0.58 | p53, BAK1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.7150/thno.28021 |
| p53, BNIP3 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.312758 | ||||||
| SMAD7 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardiotoxic (increase hypoxia induced injury signaling) | doi:10.3892/ijmm.2018.3496 | ||||||
| BAK1, KLF13 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.11.003 | ||||||
| EIF5A2 | melanoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis) | doi:10.1186/s13046-020-01599-7 | ||||||
| BTG2 | lung adenocarcinoma | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation, migration and promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_20841 | ||||||
| PAK3 | prenatal follicles | — | inhibits steroidogenesis | doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154241 | ||||||
| BACE1 | neurons | — | attenuate neurotoxicity | doi:10.1016/j.jns.2020.116793 | ||||||
| TRIB2 | squamous cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1042/BSR20193172 | ||||||
| PDK1 | cervical cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1155/2020/4351671 | ||||||
| NLRC5 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.3892/etm.2019.8309 | ||||||
| STAT3 | embryonic stem cells | — | tumor suppressor (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.7150/jca.33696 | ||||||
| TRAF6 | skeletal muscle | — | relieves skeletal muscle atrophy | doi:10.21037/atm.2019.08.39 | ||||||
| HK2 | bladder cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1007/s13577-019-00285-x | ||||||
| AKT3 | keratinocytes | miR-181b-5p (not tested) | inhibit proliferation | doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172659 | ||||||
| LIMK1 | brain | — | neuroprotection | doi:10.2174/1567202616666190906145936 | ||||||
| TXNRD1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.1186/s12935-019-0919-6 | ||||||
| TRAF6 | chondrocytes | — | anti-inflammatory in the setting of osteoarthritis | doi:10.1038/s41598-019-42601-3 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-19a-3p | 3.07 ± 0.62 | 3.29 ± 1.04 | –1.16 | 0.99 | PTEN | brain | — | alleviates ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced apoptosis | doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.04.020 |
| IGFBP3 | brain | — | alleviates ischemia-reperfusion injury | doi:10.1186/s40659-020-00280-9 | ||||||
| FAS | rectal cancer | — | tumor suppressor (induces apoptosis) | doi:10.1177/1533033820917978 | ||||||
| PIK3IP1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.7150/jca.37748 | ||||||
| FOXF2 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibits epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.627 | ||||||
| IGFBP3 | ovarian carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/mc.23113 | ||||||
| SOCS3 | synovial cells | — | promote cell proliferation | 10.1002/jcb.28442 | ||||||
| PTEN | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9592 | ||||||
| PFN1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.prp.2018.12.012 | ||||||
| PTEN | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance, metastasis) | doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.06.097 | ||||||
| PITX1 | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.1159/000489590 | ||||||
| TSC1 | osteoblasts | — | mediates dexamethasone resistance | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.23326 | ||||||
| SMAD2/4 | prostate cancer | — | tumor suppressor (invasion, metastasis) | doi:10.3892/or.2017.6096 | ||||||
| TGFBR2 | cardiac fibroblasts | miR-19b-3p | cardioprotection: anti-fibrotic | doi:10.1038/srep24747 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-19b-3p | 3.29 ± 0.35 | 3.07 ± 0.81 | 1.16 | 0.47 | NRP1 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1186/s12935-020-01257-0 |
| CCDC6 | cholangiosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes proliferation, epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.1016/j.abb.2020.108367 | ||||||
| HIF1A | endothelial cells | — | anti-angiogenic after hypoxia | doi:10.1096/fj.201902434R | ||||||
| BACE1 | brain | miR-16-5p | prevent amyloid beta induced apoptosis | doi:10.1097/WNR.0000000000001379 | ||||||
| TNFAIP3 | endothelial cells | — | pro-inflammatory in the setting of meningitis | doi:10.3390/pathogens8040268 | ||||||
| HOXA9 | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes proliferation, migration, invasion) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S216320 | ||||||
| PTEN | pancreatic cancer | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation) | doi:10.21037/atm.2019.04.61 | ||||||
| GRK6 | chondrocytes | — | reduces inflammation and matrix degradation | doi:10.1007/s11010-019-03563-2 | ||||||
| PTEN | muscle cells | — | osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1002/cbin.11133 | ||||||
| TS/O CP | miR-214-3p | 2.19 ± 1.04 | 1.96 ± 0.59 | 1.17 | 0.99 | PTEN | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection: inhibiting autophagy in sepsis | doi:10.1155/2020/1409038 |
| ATM | lung | — | reduce radiation induced pulmonary injury | doi:10.1089/ars.2019.7965 | ||||||
| CENPM | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor supressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1093/jb/mvaa073 | ||||||
| PLAGL2 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.18632/aging.103233 | ||||||
| LIVIN | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor supressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1080/21655979.2020 | ||||||
| IL17 | myocardium | — | cardioprotective (anti-fibrotic) | doi:10.3389/fcell.2020.00243 | ||||||
| WNT23 | vascular smooth muscle cells | — | inhibits cell proliferation | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202003_20696 | ||||||
| ABCB1, XIAP | retinoblastoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S235862 | ||||||
| PSMD10 | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/jcp.29557 | ||||||
| TWIST1 | endometrial carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibit epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S181037 | ||||||
| LHX6 | ovarian carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.3390/cancers11121917 | ||||||
| ST6GAL1 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation, inhibit apoptosis) | doi:10.1007/s10616-019-00352-z | ||||||
| FOXP3 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201910_19156 | ||||||
| HDGF | pancreatic cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S222703 | ||||||
| BIRC5 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201909_18856 | ||||||
| NLRC5 | myocardium | — | cardioprotection: anti-fibrotic | doi:10.1042/CS20190203 | ||||||
| CTNNB1 | preadipocytes | — | promote differentiation | doi:10.3390/ijms20081816 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-222-3p | 2.34 ± 1.60 | 1.61 ± 0.57 | 1.66 | 0.50 | PUMA | non-small cell lung carcinoma | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation, inhibit apoptosis) | doi:10.1177/1533033820922558 |
| PDCD10 | ovarian carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (inhibit epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.7150/thno.43198 | ||||||
| GILZ | airway epithelial cells | — | ameliorates glucocorticoid induced inhibition of cell repair | doi:10.1080/10799893.2020.1742739 | ||||||
| IGF1 | bone marrow-derived MSCs | — | promote osteogenic differentiation | doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108121 | ||||||
| TMP2 | renal clear cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.3233/CBM-190264 | ||||||
| IRF2, INPP4B | acute myeloid leukemia | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101513 | ||||||
| CDKN1B | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1111/jop.12986 | ||||||
| PPP2R2A | large B-cell lymphoma | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation, inhibit apoptosis) | doi:10.1177/1533033819892256 | ||||||
| GAS5, PTEN | colorectal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, migration, invasion) | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.06.009 | ||||||
| PDE3A | endothelial cells | miR-27a-3p | promote vascular integrity | doi:10.1007/s12035-018-1446-5 | ||||||
| TIMP3 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promote metastasis and invasion) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S175745 | ||||||
| PTEN | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | oncomiR (inhibit apoptosis) | doi:10.18632/oncotarget.23336 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-26a-5p | 3.75 ± 0.54 | 4.06 ± 0.72 | –1.24 | 0.53 | RANBP9 | brain | — | inhibit injury induced apoptosis | doi:10.1016/j.acthis.2020.151571 |
| TLR4 | kidney | — | protect against diabetic nephropathy | doi:10.1074/jbc.RA120.012522 | ||||||
| HMGA2 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, promote apoptosis) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S237752 | ||||||
| CTGF | macrophages | — | modulates TLR signaling upon activation | doi:10.1042/BSR20192598 | ||||||
| CREB1 | renal cell carcinoma | miR-27a-3p, miR-221-3p | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, promote apoptosis) | doi:10.1038/s41598-020-63403-y | ||||||
| DYRK1A | brain | — | inhibit development Alzheimer’s disease | doi:10.2174/1567202617666200414142637 | ||||||
| WNT5A | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S241199 | ||||||
| ADAM17 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibit apoptosis) | doi:10.1007/s10863-020-09829-5 | ||||||
| COL10A1 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration, and invasion) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202002_20170 | ||||||
| HOXA5 | osteosarcoma | — | oncomiR (promotes cell proliferation, migration) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S232100 | ||||||
| PTEN | myocardium | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1590/1414-431 × 20199106 | ||||||
| PTGS2 | joints | — | alleviate osteoarthritis | doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105946 | ||||||
| AURKA | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1177/1533033819851833 | ||||||
| WNT5A | papillary thyroid carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration, and invasion) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S205994 | ||||||
| PTEN | myocardium | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201908_18661 | ||||||
| PTEN | synovial cells | — | promote cell proliferation and inhibit apoptosis | doi:10.1042/BSR20182192 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-27a-3p | 1.87 ± 0.98 | 1.80 ± 0.88 | 1.05 | 0.96 | SLIT2 | endothelial cells | — | promotes apoptosis, autophagy during inflammation | doi:10.1016/j.jss.2020.05.102 |
| SP7 | preosteoblasts | — | promotes differentiation | doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.11246 | ||||||
| TAB3 | kidney | — | promotes apoptosis during kidney injury | doi:10.1080/09168451.2020.1792760 | ||||||
| PDL1 | macrophages | — | oncomiR (promotes immune evasion of breast cancer) | doi:10.1111/jcmm.15367 | ||||||
| BNIP3 | pancreatic cancer | — | oncomiR (inhibits apoptosis) | doi:10.3892/ijmm.2020.4632 | ||||||
| SMURF2 | lung | — | anti-fibrotic after bleomycin exposure | PMID: 32538751 | ||||||
| TGFBR1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1155/2020/2016259 | ||||||
| FBXW7 | cervical cancer | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S234897 | ||||||
| ICOS | lung adenocarcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (promotes antitumor immunity) | doi:10.1111/1759-7714.13411 | ||||||
| NOVA | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.3892/mmr.2020.10949 | ||||||
| BNIP3 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotection (inhibits apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion injury) | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.11.017 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-29a-3p | 2.50 ± 0.87 | 1.64 ± 0.66 | 1.82 | 0.19 | E2F1 | ovarian carcinoma | — | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.18632/aging.103388 |
| PTEN | aorta | — | promotes development of aortic aneurysms | doi:10.1002/jcp.29746 | ||||||
| DRP1 | myocardium | — | cardioprotection (prevent myocardial hypertrophy) | doi:10.2174/0929866527666200416144459 | ||||||
| COL4A2 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration, and invasion) | doi:10.1039/c9mt00266a | ||||||
| COL5A1 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration) | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117179 | ||||||
| TNFR1 | endothelial cells | — | reduces TNF-alpha injury response | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.10.014 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-30b-5p | 5.04 ± 1.10 | 4.56 ± 0.62 | 1.40 | 0.62 | KIF18A | prostate cancer | — | oncomiR (radioresistance) | doi:10.1089/cbr.2019.3538. |
| MYBL2 | medulloblastoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, promotes apoptosis) | doi:10.1136/jim-2020-001354 | ||||||
| CAMK2D | dermal papilla cells | — | inhibits proliferation | doi:10.1186/s12864-020-06799-1 | ||||||
| ASPP2 | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (cell proliferation, migration, and invasion) | doi:10.1155/2020/7907269 | ||||||
| PTAFR | myocardium | — | cardioprotection: anti-fibrotic | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_20869 | ||||||
| PPARGC1A | Huh-7 cells | — | regulate lipid metabolism | doi:10.1186/s12944-020-01261-3 | ||||||
| CTNNB1 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardiotoxic (increased apoptosis during myocardial injury) | doi:10.23736/S00264806.20.06565-9 | ||||||
| AVEN | cardiomyocytes | — | cardiotoxic (increased apoptosis during myocardial injury) | doi:10.1186/s11658-019-0187-4 | ||||||
| TS/O, CP | miR-31-5p | 1.42 ± 0.46 | 2.24 ± 0.74 | –1.76 | 0.15 | YAP | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, metastasis, chemosensitivity) | doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112176 |
| FLOT1 | renal clear cell carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, promote apoptosis) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S254634 | ||||||
| HOXA7 | trophoblast | — | inhibit proliferation | doi:10.1111/jog.14344 | ||||||
| PEX5 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (radioresistance) | doi:10.7150/thno.42371 | ||||||
| TNS1 | colon adenocarcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.18632/aging.103096 | ||||||
| PKCG | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotective, inhibit cardiomyocyte hypertrophy | doi:10.26355/eurrev_202002_20351 | ||||||
| PAN3 | cardiomyocytes | — | cardioprotective: attenuates doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity | doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2020.02.009 | ||||||
| ETBR, VEGFA | endothelial cells | — | anti-angiogenic | doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117306 | ||||||
| MEGEA3 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance, cell proliferation) | doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2019.10.035 | ||||||
| LATS2 | colorectal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.3390/cancers11101576 | ||||||
| MLH1 | renal cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.1002/ijc.32543 | ||||||
| VEGFA | gliomal cells | — | tumor suppressor (anti-angiogenic) | doi:10.1002/ijc.32483 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-365a-3p | 3.99 ± 0.84 | 4.34 ± 0.67 | –1.27 | 0.43 | ABCC4 | gastric cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.2147/OTT.S245557 |
| ADAM10 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration) | doi:10.7150/jca.42731 | ||||||
| CREL | pancreatic cancer | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.03.025 | ||||||
| TET1 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression, invasion) | doi:10.4149/neo_2018_171119N752 | ||||||
| USP33 | lung cancer | — | oncomiR (tumorigenesis) | doi:10.1186/s12935-018-0563-6 | ||||||
| TS/O | miR-93-5p | 5.04 ± 0.59 | 5.43 ± 0.62 | –1.31 | 0.39 | MAP3K2 | hepatocellular carcinoma | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.1038/s41388-020-01401-0 |
| RGMB | squamous cell carcinoma | — | oncomiR (migration and invasion) | doi:10.7150/jca.43854 | ||||||
| FOXA1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | oncomiR (radioresistance) | doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1507-2 | ||||||
| AHNAK | gastric cancer | — | oncomiR (promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition) | doi:10.1186/s12935-019-1092-7 | ||||||
| PD-L1 | colorectal carcinoma | — | tumor suppressor (tumor progression) | doi:10.1002/cbin.11323 | ||||||
| FOXK2 | cervical cancer | — | oncomiR (tumor progression) | doi:10.1007/s43032-020-00140-7 | ||||||
| CASC2 | chondrocytes | — | inhibits apoptosis in osteoarthritis | doi:10.1186/s12891-019-3025-y | ||||||
| MMP2 | gliomal cells | — | tumor suppressor (cell proliferation, migration) | doi:10.26355/eurrev_201911_19446 | ||||||
| TS/O | let-7a-5p | 2.46 ± 0.96 | 2.79 ± 0.46 | –1.26 | 0.40 | SMAD2 | chondrocytes | — | promotes hypertrophic differentiation | doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00039.2020 |
| SAMD2 | lens epithelial cells | — | inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion | PMID: 32345785 | ||||||
| DUSP7 | breast cancer | — | tumor suppressor (chemoresistance) | doi:10.2147/CMAR.S238513 | ||||||
| BCLXL | lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (cell autophagy) | doi:10.1016/j.omto.2019.08.010 | ||||||
| BCL2L1 | lung cancer | — | tumor suppressor (induce apoptosis) | doi:10.3389/fonc.2019.00808 | ||||||
| EGFR | breast cancer | — | oncomiR (chemoresistance) | doi:10.1002/iub.2075 | ||||||
| HMGA2 | kidney | — | promotes diabetic nephropathy | doi:10.3892/mmr.2019.10057 |
References
- Han, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Chang, F.; Ding, J. Mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine. Cells 2019, 8, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karantalis, V.; Hare, J.M. Use of mesenchymal stem cells for therapy of cardiac disease. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1413–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spees, J.L.; Lee, R.H.; Gregory, C.A. Mechanisms of mesenchymal stem/stromal cell function. Curr. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Spoel, T.I.; Jansen of Lorkeers, S.J.; Agostoni, P.; van Belle, E.; Gyöngyösi, M.; Sluijter, J.P.; Cramer, M.J.; Doevendans, P.A.; Chamuleau, S.A. Human relevance of pre-clinical studies in stem cell therapy: Systematic review and meta-analysis of large animal models of ischaemic heart disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 91, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen of Lorkeers, S.J.; Eding, J.E.; Vesterinen, H.M.; van der Spoel, T.I.; Sena, E.S.; Duckers, H.J.; Doevendans, P.A.; Macleod, M.R.; Chamuleau, S.A. Similar effect of autologous and allogeneic cell therapy for ischemic heart disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis of large animal studies. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambria, E.; Pasqualini, F.S.; Wolint, P.; Günter, J.; Steiger, J.; Bopp, A.; Hoerstrup, S.P.; Emmert, M.Y. Translational cardiac stem cell therapy: Advancing from first-generation to next-generation cell types. NPJ Regen. Med. 2017, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendt, M.; Rezvani, K.; Shpall, E. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for clinical use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019, 54, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.; Wollert, K.C.; Meyer, G.P.; Menke, A.; Arseniev, L.; Hertenstein, B.; Ganser, A.; Knapp, W.H.; Drexler, H. Monitoring of bone marrow cell homing into the infarcted human myocardium. Circulation 2005, 111, 2198–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Hu, Q.; Wang, X.; Mansoor, A.; Lee, J.; Feygin, J.; Zhang, G.; Suntharalingam, P.; Boozer, S.; Mhashilkar, A.; et al. Bioenergetic and functional consequences of bone marrow-derived multipotent progenitor cell transplantation in hearts with postinfarction left ventricular remodeling. Circulation 2007, 115, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, L.M.; Wang, M.Z. Overview of extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells 2019, 8, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moghaddam, A.S.; Afshari, J.T.; Esmaeili, S.A.; Saburi, E.; Joneidi, Z.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A.A. Cardioprotective microRNAs: Lessons from stem cell-derived exosomal microRNAs to treat cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis. 2019, 285, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Felekkis, K.; Touvana, E.; Stefanou, C.H.; Deltas, C. microRNAs: A newly described class of encoded molecules that play a role in health and disease. Hippokratia 2010, 14, 236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Latysheva, N.S.; Babu, M.M. Discovering and understanding oncogenic gene fusions through data intensive computational approaches. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4487–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nazari-Shafti, T.Z.; Exarchos, V.; Biefer, H.R.; Cesarovic, N.; Meyborg, H.; Falk, V.; Emmert, M.Y. MicroRNA Mediated Cardioprotection–Is There a Path to Clinical Translation? Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Serocki, M.; Bartoszewska, S.; Janaszak-Jasiecka, A.; Ochocka, R.J.; Collawn, J.F.; Bartoszewski, R. miRNAs regulate the HIF switch during hypoxia: A novel therapeutic target. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meng, X.M.; Nikolic-Paterson, D.J.; Lan, H.Y. TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowen, A.; Shahjin, F.; Chand, S.; Odegaard, K.E.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Challenges in Clinical Applications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandergriff, A.; Huang, K.E.; Shen, D.; Hu, S.; Hensley, M.T.; Caranasos, T.G.; Qian, L.; Cheng, K. Targeting regenerative exosomes to myocardial infarction using cardiac homing peptide. Theranostics 2018, 8, 1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Meng, Q.; Yu, Y.; Sun, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; et al. Engineered Exosomes with Ischemic Myocardium-Targeting Peptide for Targeted Therapy in Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marzi, M.J.; Ghini, F.; Cerruti, B.; De Pretis, S.; Bonetti, P.; Giacomelli, C.; Gorski, M.M.; Kress, T.; Pelizzola, M.; Muller, H.; et al. Degradation dynamics of microRNAs revealed by a novel pulse-chase approach. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.I.; Mizuno, H.; Huang, J.; Futrell, J.W.; Katz, A.J.; Benhaim, P.; Lorenz, H.P.; Hedrick, M.H. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bieback, K.; Netsch, P. Isolation, Culture, and Characterization of Human Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press Inc.: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 1416, pp. 245–258. [Google Scholar]
- Beez, C.M.; Haag, M.; Klein, O.; Van Linthout, S.; Sittinger, M.; Seifert, M. Extracellular vesicles from regenerative human cardiac cells act as potent immune modulators by priming monocytes. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Théry, C.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G.; Clayton, A. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2006, 30, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesompele, J.; De Preter, K.; Pattyn, F.; Poppe, B.; Van Roy, N.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F. Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 2002, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of exosome composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buschmann, D.; Kirchner, B.; Hermann, S.; Märte, M.; Wurmser, C.; Brandes, F.; Kotschote, S.; Bonin, M.; Steinlein, O.K.; Pfaffl, M.W.; et al. Evaluation of serum extracellular vesicle isolation methods for profiling miRNAs by next-generation sequencing. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1481321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, A.E.; Sneider, A.; Witwer, K.W.; Bergese, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Cocks, A.; Cocucci, E.; Erdbrügger, U.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Freeman, D.W.; et al. Biological membranes in EV biogenesis, stability, uptake, and cargo transfer: An ISEV position paper arising from the ISEV membranes and EVs workshop. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2019, 8, 1684862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stranska, R.; Gysbrechts, L.; Wouters, J.; Vermeersch, P.; Bloch, K.; Dierickx, D.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R. Comparison of membrane affinity-based method with size-exclusion chromatography for isolation of exosome-like vesicles from human plasma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Fehér, B.; Kitka, D.; Wacha, A.; Bóta, A.; Berényi, S.; Pipich, V.; Fraikin, J.L. Size Measurement of Extracellular Vesicles and Synthetic Liposomes: The Impact of the Hydration Shell and the Protein Corona. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 19, 111053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklander, O.P.; Bostancioglu, R.B.; Welsh, J.A.; Zickler, A.M.; Murke, F.; Corso, G.; Felldin, U.; Hagey, D.W.; Evertsson, B.; Liang, X.M.; et al. Systematic methodological evaluation of a multiplex bead-based flow cytometry assay for detection of extracellular vesicle surface signatures. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragni, E.; Orfei, C.P.; De Luca, P.; Lugano, G.; Viganò, M.; Colombini, A.; Valli, F.; Zacchetti, D.; Bollati, V.; De Girolamo, L. Interaction with hyaluronan matrix and miRNA cargo as contributors for in vitro potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in a model of human osteoarthritic synoviocytes. Stem Cell Res. Therapy. 2019, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragni, E.; Perucca, O.C.; De Luca, P.; Colombini, A.; Viganò, M.; de Girolamo, L. Secreted Factors and EV-miRNAs Orchestrate the Healing Capacity of Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2020, 21, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reis, M.; Mavin, E.; Nicholson, L.; Green, K.; Dickinson, A.M.; Wang, X.N. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate dendritic cell maturation and function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, V.; Noureddine, L. MicroRNAs and fibrosis. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, H.; Kanisicak, O.; Prasad, V.; Correll, R.N.; Fu, X.; Schips, T.; Vagnozzi, R.J.; Liu, R.; Huynh, T.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Fibroblast-specific TGF-β–Smad2/3 signaling underlies cardiac fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3770–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Du, J.; Niu, X.; Fu, N.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Sun, D.; Nan, Y. MiR-130a-3p attenuates activation and induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells in nonalcoholic fibrosing steatohepatitis by directly targeting TGFBR1 and TGFBR2. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Qin, S.; Liu, J.; Su, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q. MiR-130a-3p regulates cell migration and invasion via inhibition of Smad4 in gemcitabine resistant hepatoma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, K.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Tang, X.; Guo, W. miR-16-5p inhibits chordoma cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis by targeting Smad3. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Fei, Q.; Du, M.; Zhu, H.; Ye, J.; Qian, L.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Peng, F.; et al. miR-130a-3p regulated TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition depends on SMAD4 in EC-1 cells. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svoronos, A.A.; Engelman, D.M.; Slack, F.J. OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of microRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3666–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Guo, H.; Fang, X.; Liang, J.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, H.; Pan, R.; Yuan, S.; et al. Novel role of the clustered miR-23b-3p and miR-27b-3p in enhanced expression of fibrosis-associated genes by targeting TGFBR3 in atrial fibroblasts. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3246–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Luo, T.; Jiang, Y. Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easton, J.B.; Houghton, P.J. mTOR and cancer therapy. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6436–6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grundmann, S.; Hans, F.P.; Kinniry, S.; Heinke, J.; Helbing, T.; Bluhm, F.; Sluijter, J.P.; Hoefer, I.; Pasterkamp, G.; Bode, C.; et al. MicroRNA-100 regulates neovascularization by suppression of mammalian target of rapamycin in endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells. Circulation 2011, 123, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, A.; Liu, F.; Guan, B.; Luo, Z.; Lin, J.; Fang, W.; Liu, L.; Zuo, W. p53 induces miR-199a-3p to suppress mechanistic target of rapamycin activation in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 17625–17634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, J.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, Y. miR-143-3p regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by targeting IGF1R and IGFBP5 and regulating the Ras/p38 MAPK signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 3781–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Ma, M.; Zheng, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lin, X. mTOR and Beclin1: Two key autophagy-related molecules and their roles in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12562–12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalhoub, N.; Baker, S.J. PTEN and the PI3-kinase pathway in cancer. Annual Review of Pathology. Mech. Dis. 2009, 4, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, Q.; Gong, K.; Long, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, X. Downregulation of miR-103a-3p Contributes to Endothelial Progenitor Cell Dysfunction in Deep Vein Thrombosis Through PTEN Targeting. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 64, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.C.; Hou, B.; Zhou, D.; Liu, Q.X.; Zhang, K.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, H.; Dai, J.G. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-103a-2-5p facilitates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 6097–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, N.; Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Xu, L. MicroRNA-221-3p plays an oncogenic role in gastric carcinoma by inhibiting PTEN expression. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Guo, S.; Min, L.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, S. miR-92a-3p promotes the proliferation, migration and invasion of esophageal squamous cell cancer by regulating PTEN. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Ao, J.; Li, H.; Li, M. Role of miR-92a-3p/PTEN Axis in Regulation of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Proliferation and Metastasis. J. Cent. South Univ. Med. Sci. 2020, 45, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, W.; Han, Y.; Lu, L.; Yang, K.; Cao, J. Effect of HIF-1α/miR-10b-5p/PTEN on Hypoxia-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e011948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, X.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Li, C.; Zhong, G. Overexpression of miR-27b-3p targeting Wnt3a regulates the signaling pathway of Wnt/β-catenin and attenuates atrial fibrosis in rats with atrial fibrillation. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5703764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
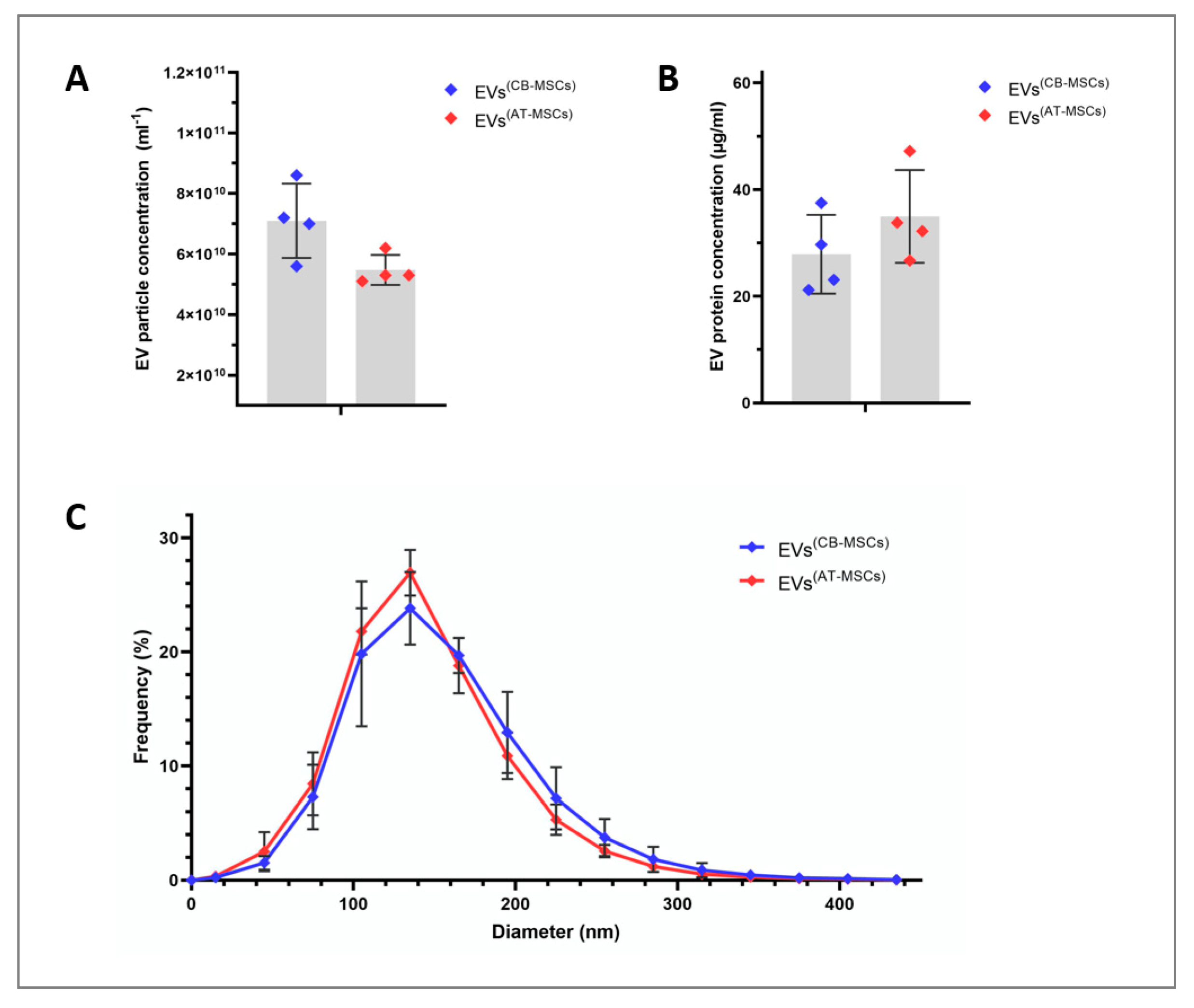


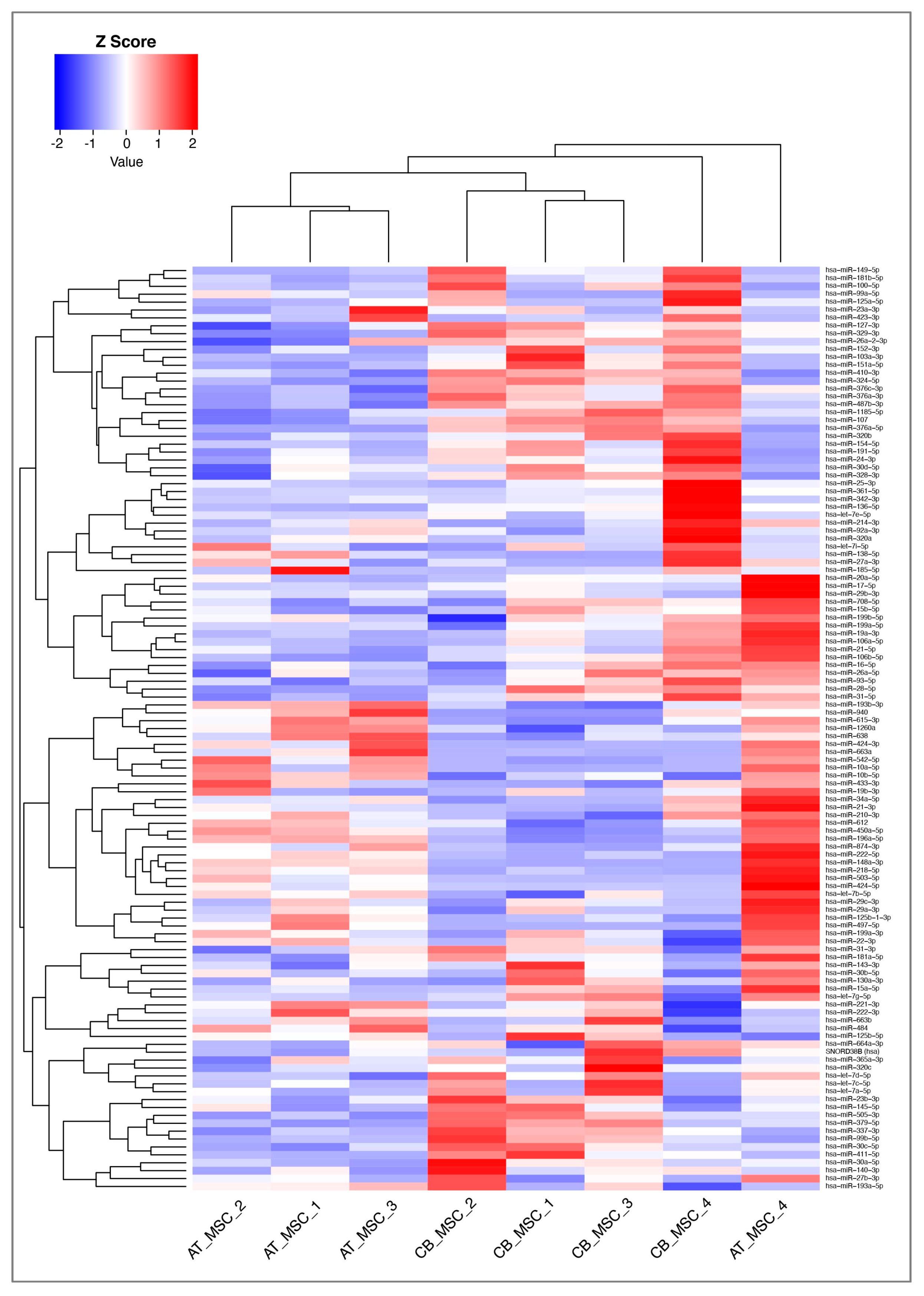




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nazari-Shafti, T.Z.; Neuber, S.; Duran, A.G.; Exarchos, V.; Beez, C.M.; Meyborg, H.; Krüger, K.; Wolint, P.; Buschmann, J.; Böni, R.; et al. MiRNA Profiles of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells—Can They Predict Potential Off-Target Effects? Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091353
Nazari-Shafti TZ, Neuber S, Duran AG, Exarchos V, Beez CM, Meyborg H, Krüger K, Wolint P, Buschmann J, Böni R, et al. MiRNA Profiles of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells—Can They Predict Potential Off-Target Effects? Biomolecules. 2020; 10(9):1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091353
Chicago/Turabian StyleNazari-Shafti, Timo Z., Sebastian Neuber, Ana G. Duran, Vasileios Exarchos, Christien M. Beez, Heike Meyborg, Katrin Krüger, Petra Wolint, Johanna Buschmann, Roland Böni, and et al. 2020. "MiRNA Profiles of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells—Can They Predict Potential Off-Target Effects?" Biomolecules 10, no. 9: 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091353
APA StyleNazari-Shafti, T. Z., Neuber, S., Duran, A. G., Exarchos, V., Beez, C. M., Meyborg, H., Krüger, K., Wolint, P., Buschmann, J., Böni, R., Seifert, M., Falk, V., & Emmert, M. Y. (2020). MiRNA Profiles of Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells—Can They Predict Potential Off-Target Effects? Biomolecules, 10(9), 1353. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10091353





