Anti-Obesity Effect of α-Cubebenol Isolated from Schisandra chinensis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Purification of α-Cubebenol
2.2. Cell Culture, Adipocyte Differentiation, and Treatment of α-Cubebenol
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Oil Red O (ORO) Staining Analysis
2.5. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. ELISA for cAMP Concentration
2.8. Measurement of Free Glycerol Release
2.9. Statistical Significance Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Determination of the Optimal Concentration of α-Cubebenol in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
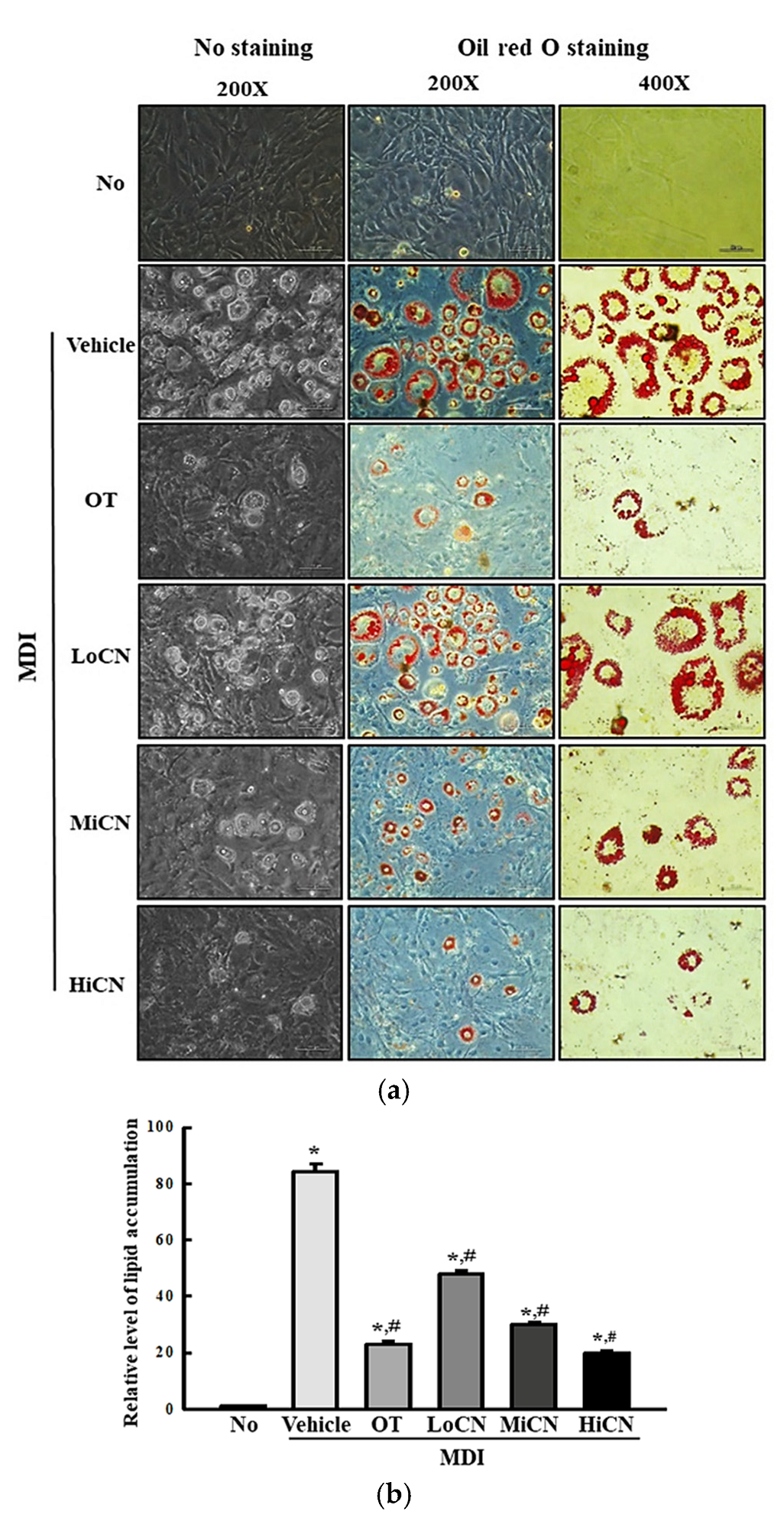
3.2. Inhibitory Effects of α-Cubebenol on Lipid Accumulation
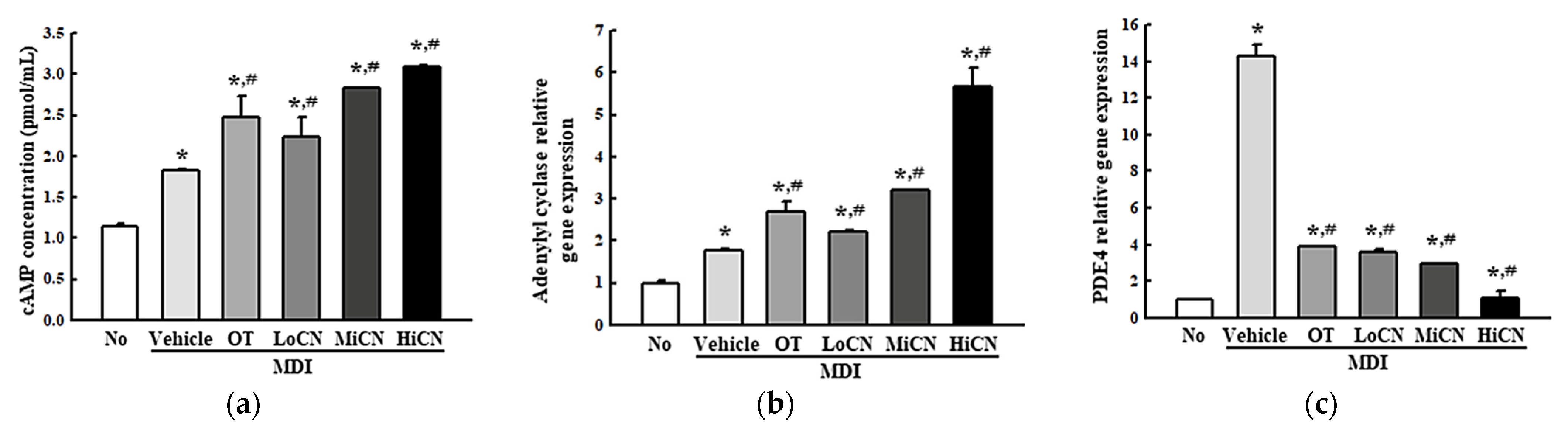
3.3. Effects of α-Cubebenol on the Regulation of Lipogenic Genes Trascription
3.4. Suppressive Effect of α-Cubebenol on the Inflammatory Response
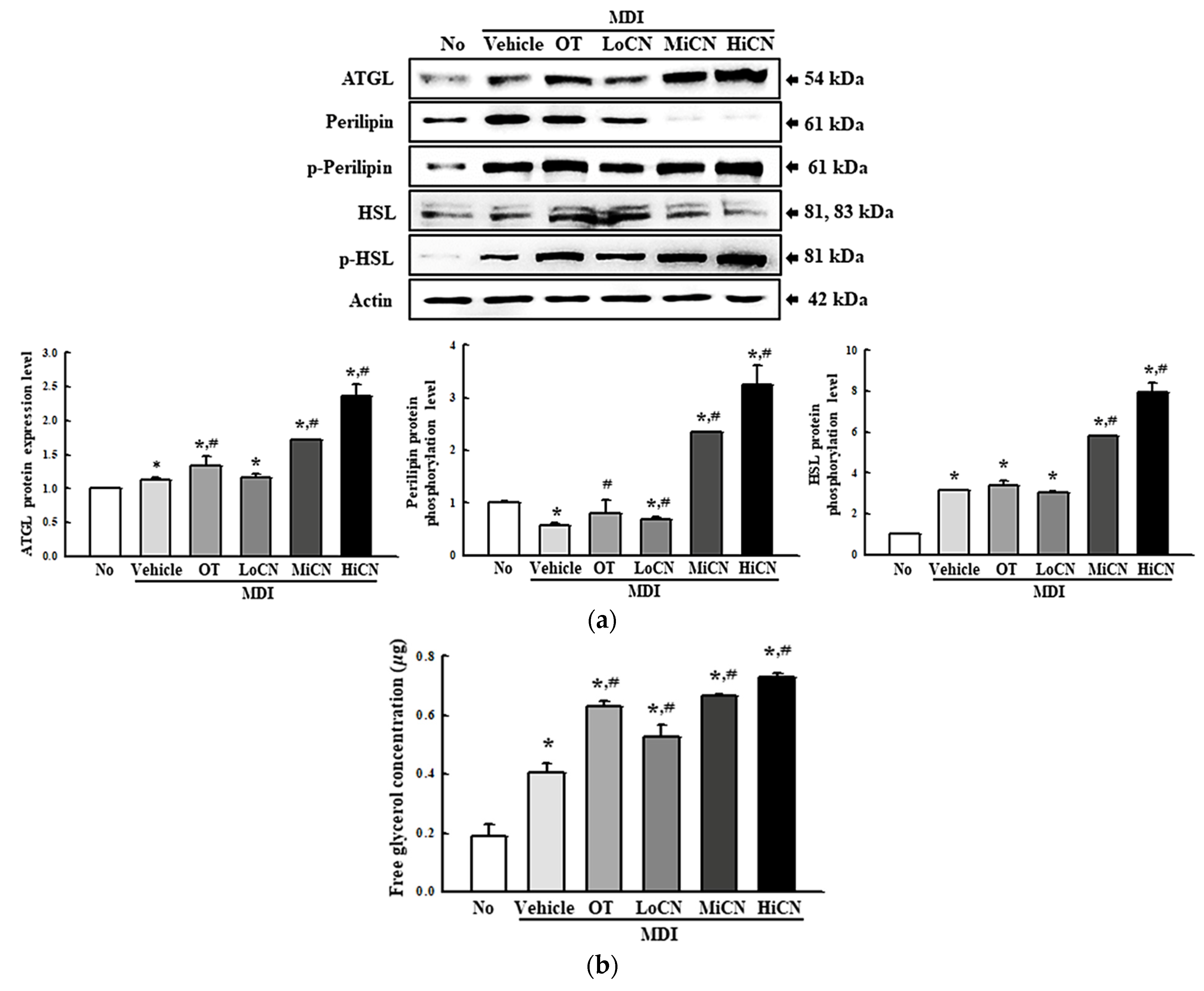
3.5. Effects of α-Cubebenol on the Stimulation of Lipolysis
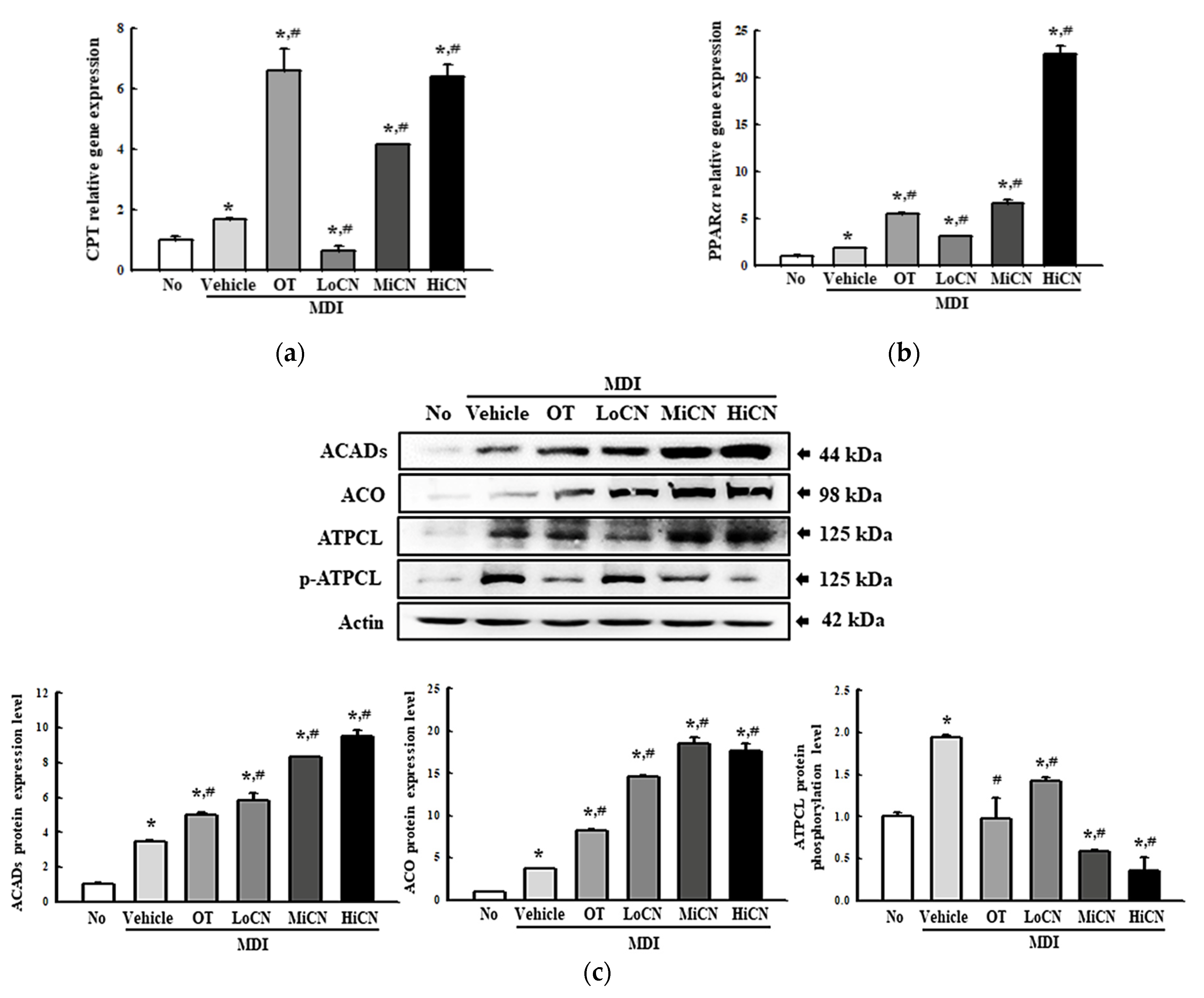
3.6. Stimulatory Effects of α-Cubebenol on the -Oxidation of Lipid
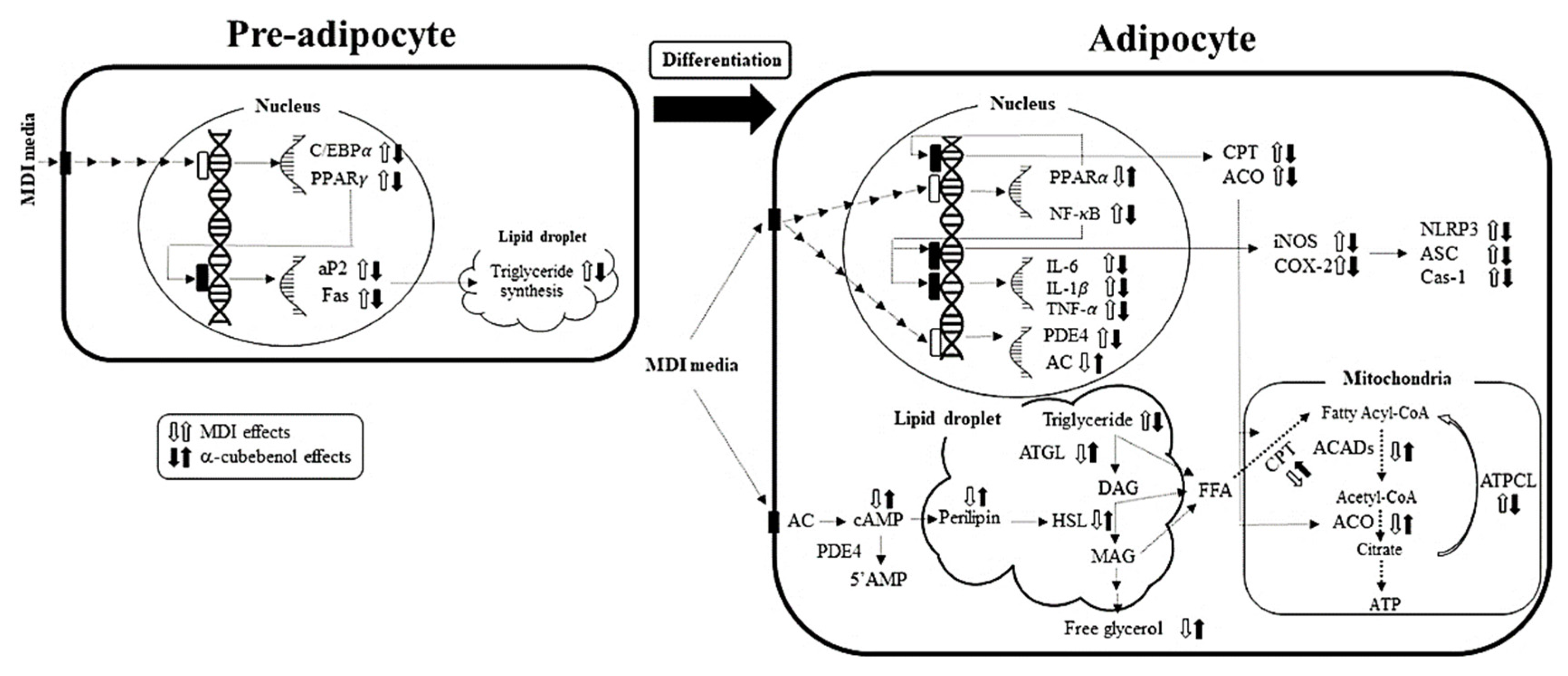
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, L.; Liu, M. Adipose tissue in control of metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 231, R77–R99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, C.; Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Gastaldelli, A. The subtle balance between lipolysis and lipogenesis: A critical point in metabolic homeostasis. Nutrients 2015, 7, 9453–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McArdle, M.; Finucane, O.; Connaughton, R.; McMorrow, A.; Roche, H. Mechanisms of obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance: Insights into the emerging role of nutritional strategies. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lass, A.; Zimmermann, R.; Oberer, M.; Zechner, R. Lipolysis—A highly regulated multi-enzyme complex mediates the catabolism of cellular fat stores. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, M.; Oliveira, T.; Fernandes, R. Biochemistry of adipose tissue: An endocrine organ. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 9, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczak, M.; Wiecek, A. The adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Semin. Nephrol. 2013, 33, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.H.; Wu, Y.X.; Kim, J.S.; Woo, J.H.; Park, K.T.; Kwon, O.J.; Seo, H.J.; Kim, T.; Park, N.H. 6,6′-Bieckol inhibits adipocyte differentiation through downregulation of adipogenesis and lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1830–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.C.; Chi, H.W.; Chin, L.H. Diallyl trisulphide inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes through lipogenesis, fatty acid transport, and fatty acid oxidation pathways. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 16, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Kang, M.; Kim, Y.S. Platycodin D inhibits lipogenesis through AMPKα-PPARγ2 in 3T3-L1 cells and modulates fat accumulation in obese mice. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Kato, T.; Ito, Y.; Yoshida, I.; Harada, T.; Mishima, T.; Fujita, K.; Watai, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Miyazawa, T. Aculeatin, a coumarin derived from Toddalia asiatica (L.) Lam., enhances differentiation and lipolysis of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Agli, M.; Bosisio, E. Biflavones of Ginkgo biloba stimulate lipolysis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, K.Y.; Peng, K.Y.; Day, Y.J.; Hung, L.M. Resveratrol exerts anti-obesity effects in high-fat diet obese mice and displays differential dosage effects on cytotoxicity, differentiation, and lipolysis in 3T3-L1 cells. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-Fabián, S.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D.; Vázquez-Carrera, M.; López-Roa, R.I. Alliin, a garlic (Allium sativum) compound, prevents LPS-induced inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 381815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.L.; Ha, A.W.; Kim, W.K. Effect of saccharin on inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and the related mechanism. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2020, 14, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Lee, B.Y. Fucoidan from the sporophyll of Undaria pinnatifida suppresses adipocyte differentiation by inhibition of inflammation-related cytokines in 3T3-L1 cells. Nutr. Res. 2012, 32, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.W.; Liu, K.L.; Lin, Y.R.; Kuo, W.C. The mechanisms of carnosic acid attenuates tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.; Kim, C.T.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, Y. Effects of capsaicin on lipid catabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 935–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, L.H.; Gow, C.Y. Effects of capsaicin on induction of apoptosis and inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 1730–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isa, Y.; Miyakawa, Y.; Yanagisawa, M.; Goto, T.; Kang, M.S.; Kawada, T.; Morimitsu, Y.; Kubota, K.; Tsuda, T. 6-Shogaol and 6-gingerol, the pungent of ginger, inhibit TNF-alpha mediated downregulation of adiponectin expression via different mechanisms in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 373, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Shim, J.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, S.D.; Choi, Y.W.; Bae, Y.S. Identification of a novel compound that stimulates intracellular calcium increase and CXCL8 production in human neutrophils from Schisandra chinensis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.P.; Kang, S.; Park, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, A.Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, Y.G.; Im, D.S. Anti-allergic effect of α-cubebenoate isolated from Schisandra chinensis using in vivo and in vitro experiments. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 173, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Park, D.J.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, S.J.; Yoon, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Bae, Y.S.; Choi, Y.W. Identification of a novel compound that inhibits iNOS and COX-2 expression in LPS-stimulated macrophages from Schisandra chinensis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1687–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Park, T.G.; Lee, S.J.; Bae, Y.S.; Ko, M.J.; Choi, Y.W. α-Iso-cubebenol inhibits inflammation-mediated neurotoxicity and amyloid beta 1-42 fibril-induced microglial activation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Park, D.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, S.J. Schisandra chinensis α-iso-cubebenol induces heme oxygenase-1 expression through PI3K/Akt and Nrf2 signaling and has anti-inflammatory activity in Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Kang, J.K.; Park, G.; Choi, Y.W. Involvement of activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway in protection against 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cell death by α-iso-cubebenol. Neurotoxicology 2014, 44, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.H.; Choi, S.M.; Kim, J.E.; Sung, J.E.; Lee, H.A.; Choi, Y.H.; Bae, C.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Hwang, D.Y. α-Iso-cubebenol alleviates scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment by repressing acetylcholinesterase activity. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 638, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.G.; Goo, J.S.; Park, D.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Hwang, I.S.; Lee, H.R.; Choi, S.I.; Lee, Y.J.; Oh, C.H.; et al. The α-iso-cubebenol compound isolated from Schisandra chinensis induces p53-independent pathway-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.D.; Kook, M.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, J.S.; Park, Y.H.; Kang, J.S.; Jung, W.J.; Choi, Y.W.; Bae, Y.S. Therapeutic effects of α-iso-cubebenol, a natural compound isolated from the Schisandra chinensis fruit, against sepsis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 427, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.J.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, S.J.; Gong, J.E.; Choi, Y.W.; Hwang, D.Y. Novel function of alpha-Cubebenoate derived from Schisandra chinensis as lipogenesis inhibitor, lipolysis stimulator and inflammasome suppressor. Molecules 2020, 25, 4995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Koh, P.O.; Cho, K.W.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, K.S.; Chung, B.Y.; Kim, G.S.; Cho, J.H. Anti-obesity effect of Schisandra chinensis in 3T3-L1 cells and high fat diet-induced obese rats. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.S.; Jung, H.K.; Cho, K.H.; Youn, K.S.; Hong, J.H. Anti-obesity effect of grape skin extract in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekiert, R.J.; Szopa, A.; Ekiert, H.; Krzek, J.; Dzik, E. Analysis of lignans in Schisandra chinensis fruits, leaves, biomasses from in vitro cultures and food supplements. J. Funct. Foods 2013, 5, 1576–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocan, A.; Crisan, G.; Vlase, L.; Crissan, O.; Vodnar, D.C.; Raita, O.; Gheldiu, A.M.; Toiu, A.; Oprean, R.; Tilea, I. Comparative studies on polyphenolic composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Schisandra chinensis leaves and fruits. Molecules 2014, 19, 15162–15179. [Google Scholar]
- Szopa, A.; Ekiert, H. The importance of applied light quality on the production of lignans and phenolic acids in Schisandra chinensis (Turcz.) Baill. cultures in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2016, 127, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kook, M.S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, H.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Choi, Y.W.; Bae, Y.S. Anti-septic activity of α-cubebenoate isolated from Schisandra chinensis. BMB Rep. 2015, 6, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, P.; Schneider, F. Syntheses of tetrahydrolipstatin and absolute configuration of tetrahydrolipstatin and lipstatin. Helv. Chim. 1987, 70, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.R.; Lee, K.P.; Park, S.J.; Noh, D.Y.; Kim, J.M.; Moon, H.R.; Lee, Y.G.; Choi, Y.W.; Im, D.S. Identification of a novel anti-inflammatory compound, α-cubebenoate from Schisandra chinensis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 242–249. [Google Scholar]
- Guerciolini, R. Mode of action of orlistat. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1997, 21, S12–S23. [Google Scholar]
- Ballinger, A.; Peikin, S.R. Orlistat: Its current status as an anti-obesity drug. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 440, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padwal, R.; Li, S.K.; Lau, D.C.; Padwal, R.S. Long-term pharmacotherapy for obesity and overweight. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, 3, CD004094. [Google Scholar]
- Gillies, C.L.; Abrams, K.R.; Lambert, P.C.; Cooper, N.J.; Sutton, A.J.; Hsu, R.T.; Khunti, K. Pharmacological and lifestyle interventions to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes in people with impaired glucose tolerance: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2007, 334, 299. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Rehman, A.U.; Luckett, D.J.; Blanchard, C.L.; Obied, H.K.; Strappe, P. Phenolic compounds with antioxidant properties from canola meal extracts inhibit adipogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, X.; Du, W.; Shi, X.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W.; Gao, M. LKB1-AMPK axis negatively regulates ferroptosis by inhibiting fatty acid synthesis. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2020, 5, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Gu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Chen, Y.Q. Clove extract functions as a natural fatty acid synthesis inhibitor and prevents obesity in a mouse model. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, Y.J.; Gong, J.E.; Jin, Y.J.; Lee, D.W.; Choi, Y.W.; Hwang, D.Y. Anti-Obesity Effect of α-Cubebenol Isolated from Schisandra chinensis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111650
Lee SJ, Kim JE, Choi YJ, Gong JE, Jin YJ, Lee DW, Choi YW, Hwang DY. Anti-Obesity Effect of α-Cubebenol Isolated from Schisandra chinensis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(11):1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111650
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Su Jin, Ji Eun Kim, Yun Ju Choi, Jeong Eun Gong, You Jeong Jin, Da Woon Lee, Young Whan Choi, and Dae Youn Hwang. 2021. "Anti-Obesity Effect of α-Cubebenol Isolated from Schisandra chinensis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes" Biomolecules 11, no. 11: 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111650
APA StyleLee, S. J., Kim, J. E., Choi, Y. J., Gong, J. E., Jin, Y. J., Lee, D. W., Choi, Y. W., & Hwang, D. Y. (2021). Anti-Obesity Effect of α-Cubebenol Isolated from Schisandra chinensis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1650. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111650






