Effect of Sand-Frying-Triggered Puffing on the Multi-Scale Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Cassava Starch in Dry Gel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Dried Cassava Starch Gel and Its Puffing Operation
2.3. Evaluation of Puffing Performance of Dried Cassava Starch Gel
2.4. Characterization of Microstructure of Dried Starch Gel
2.5. Determination of Physicochemical Properties of Starch in Discs
2.6. Characterization of the Ordered Structure of Starch in Discs
2.7. Determination of Molecular Structure of Starch in Discs
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Changes of Physical Properties of Dried Starch Gel upon Puffing
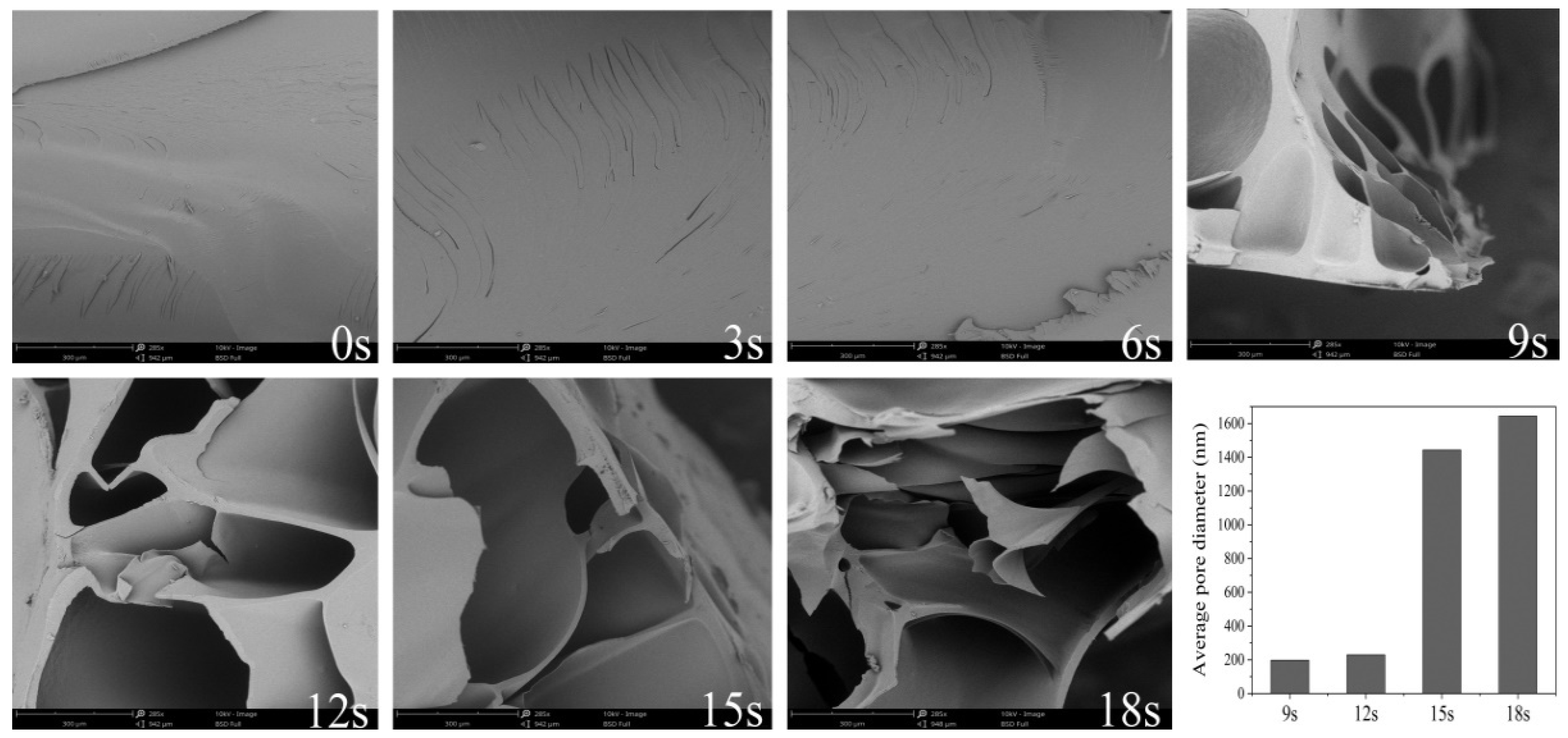
3.2. The Microstructural Evolutions of Dried Starch Gel upon Puffing
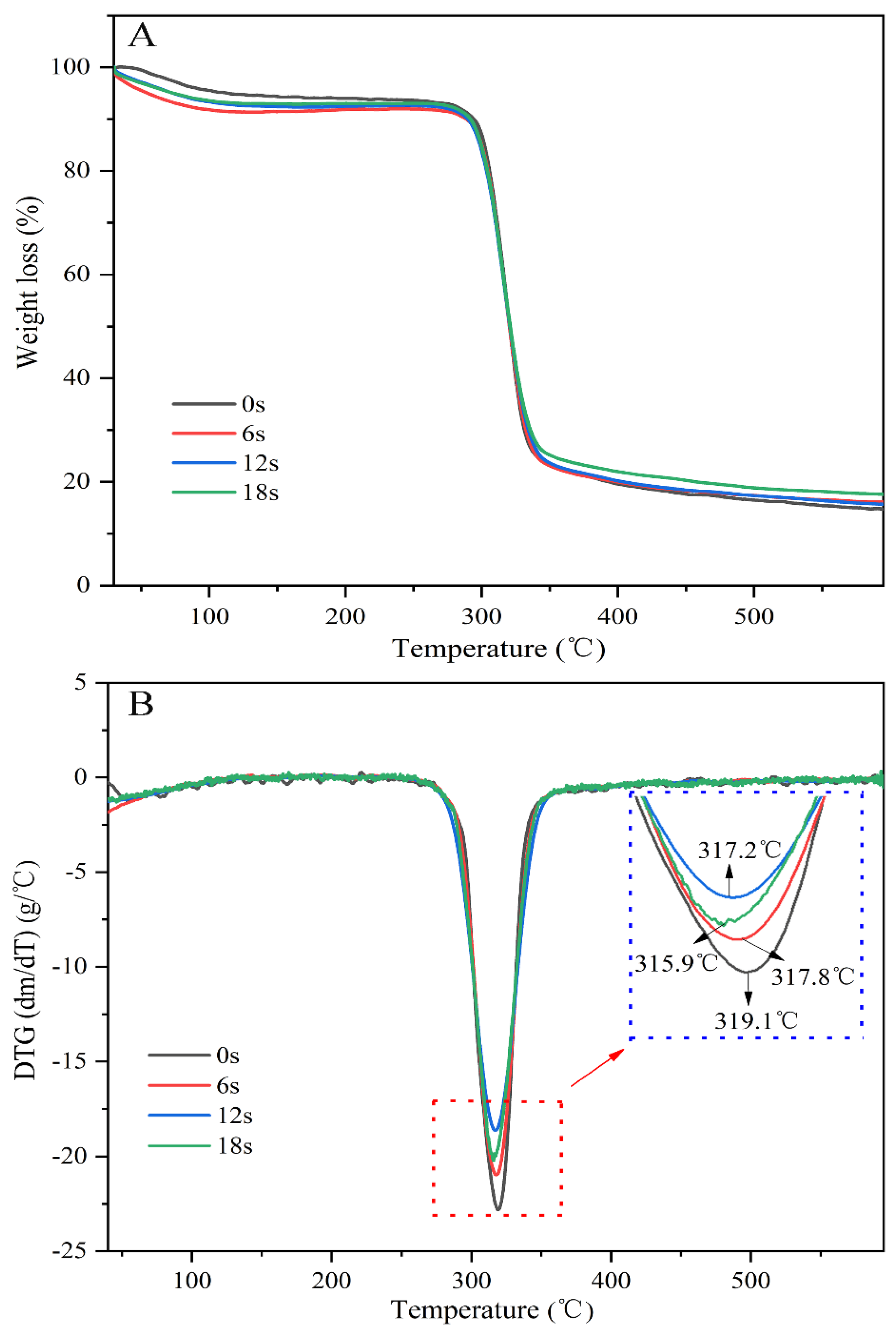
3.3. The Puffing-Induced Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Starch
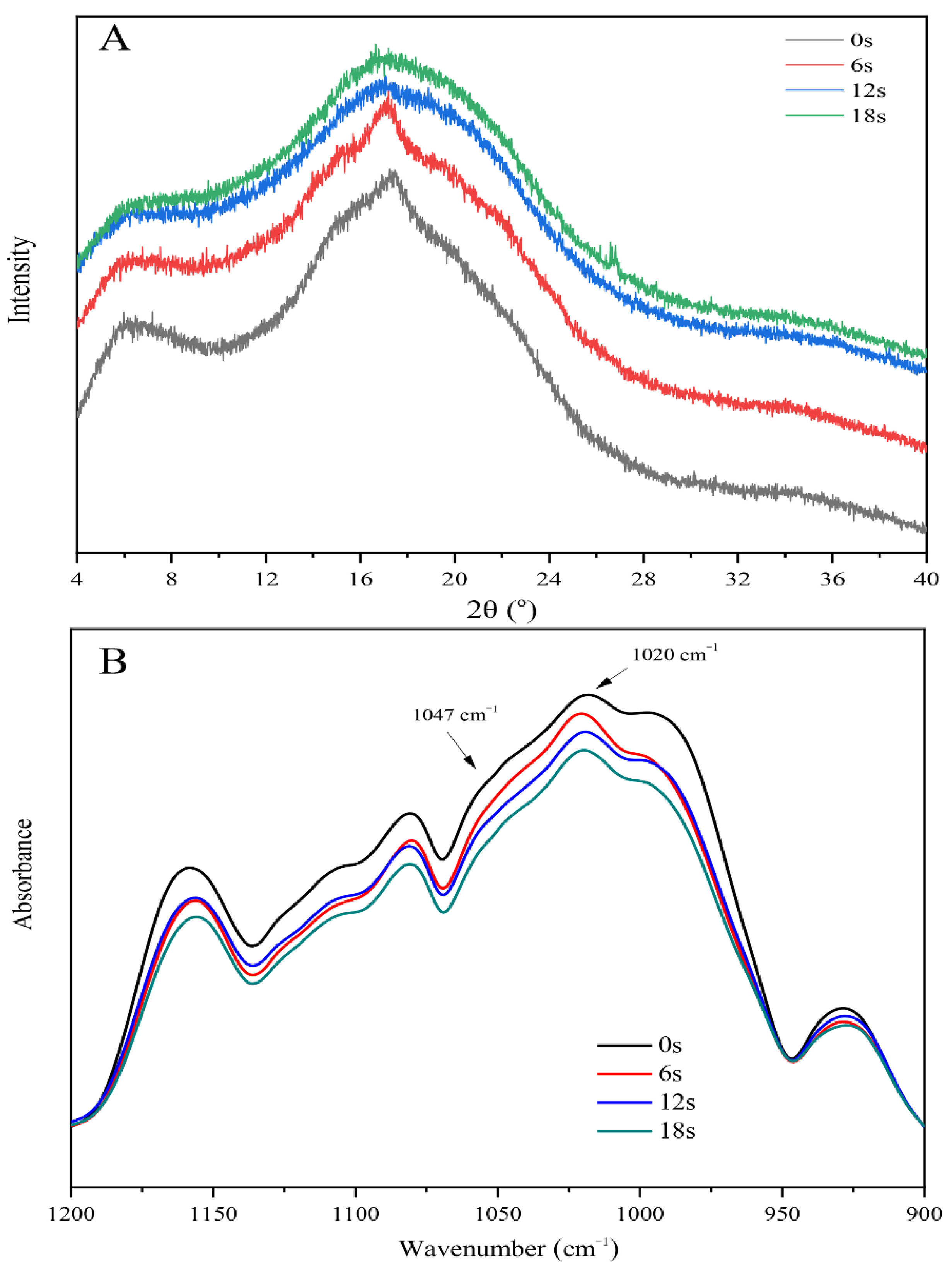
3.4. The Puffing-Induced Changes in the Multi-Scale Structure of Starch
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, T.Y.; Ma, Y.; McClements, D.J.; Ren, F.; Tian, Y.Q.; Jin, Z.Y. A review of structural transformations and properties changes in starch during thermal processing of food. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 113, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.Y.; Luo, H.M.; Hsu, P.H.; Sung, W.C. Effects of calcium supplements on the quality and acrylamide content of puffed shrimp chips. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, J.E.; Perona, M.J. Kinetics of popping of popcorn. Cereal Chem. 2005, 82, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, A.D.; Greenwood, R.W.; Noble, I.; Cox, P.W. Hot air expansion of potato starch pellets with different water contents and salt concentrations. J. Food Eng. 2011, 105, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiamjariyatam, R.; Kongpensook, V.; Pradipasena, P. Effects of amylose content, cooling rate and aging time on properties and characteristics of rice starch gels and puffed products. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 61, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, T.; Datta, A.K. Coupled multiphase transport, large deformation and phase transition during rice puffing. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 139, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Lee, J.K. Effects of heating methods and kernel characteristics on the expansion of whole grains. Food Eng. Process. 2020, 24, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.R.; Pan, X.D.; Lv, J.G.; Zhong, W.; Yan, F.; Duan, F.X.; Jia, L.R. Effects of explosion puffing on the nutritional composition and digestibility of grains. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 2193–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.Y.; Yang, J.H. Influence of partial gelatinization treatment on the quality changes of puffed rice. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2020, 25, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Giráldez, M.; Fito, P.J.; Prieto, J.M.; Andrés, A.; Fito, P. Study of the puffing process of amaranth seeds by dielectric spectroscopy. J. Food Eng. 2012, 110, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zapana, F.; Bruijn, J.D.; Vidal, L.; Melín, P.; González, M.E.; Cabrera, G.; Williams, P.; Bórquez, R. Physical, chemical and nutritional characteristics of puffed quinoa. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.P.; Wood, J.A.; Saliba, A.J.; Blanchard, C.L.; Carr, B.T.; Prenzler, P.D. Evaluation of puffing quality of Australian desi chickpeas by different physical attributes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Fuente, C.I.A.; Lopes, C.C. HTST puffing in order to produce crispy banana—The effect of the step-down treatment prior to air-drying. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 92, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.J.; Teng, J.W.; Huang, L.; Dai, X.W.; Wei, B.Y. Effect of osmotic pretreatment on quality of mango chips by explosion puffing drying. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Shakila, R.J.; Sivaraman, B.; Ganesan, P.; Velayutham, P. Optimization of the gelatinization conditions to improve the expansion and crispiness of fish crackers using RSM. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.D.; Mohapatra, D.; Joshi, D.C. Varietal selection of some indica rice for production of puffed rice. Food Bioprocess. Technol. 2014, 7, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, A.R.G.; Zavareze, E.D.R.; Elias, M.C.; Helbig, E.; Silva, D.O.D.; Ciacco, C.F. Pasting, expansion and textural properties of fermented cassava starch oxidised with sodium hypochlorite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 84, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junior, M.D.M.; Castanha, N.; Anjos, C.B.P.D.; Augusto, P.E.D.; Sarmento, S.B.S. Ozone technology as an alternative to fermentative processes to improve the oven-expansion properties of cassava starch. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Y.; Gu, B.J.; Ganjyal, G.M. Impacts of the inclusion of various fruit pomace types on the expansion of corn starch extrudates. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 110, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Wandurraga, Z.N.; Igual, M.; García-Segovia, M.; Martínez-Monzó, J. Influence of microalgae addition in formulation on colour, texture, and extrusion parameters of corn snacks. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2020, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Gu, B.J.; Saunders, S.R.; Ganjyal, G.M. High methoxyl pectin enhances the expansion characteristics of the cornstarch relative to the low methoxyl pectin. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarnakar, A.K.; Srivastav, P.P.; Das, S.K. Optimization of preconditioning process of pressure parboiled brown rice (unpolished) for microwave puffing and its comparison with hot sand bed puffing. J. Food Process. Eng. 2019, 42, e13007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.A.; Bosco, S.J.D.; Shah, M.A.; Mir, M.M. Effect of puffing on physical and antioxidant properties of brown rice. Food Chem. 2016, 191, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiawan, M.; Micard, V.; Maladira, P.; Alchamieh, C.; Maigret, J.E.; Réguerre, A.L.; Emin, M.A.; Valle, G.D. Multi-scale structural changes of starch and proteins during pea flour extrusion. Food Res. Int. 2018, 108, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.H.; Shieh, C.J.; Huang, S.M.; Wang, H.M.D.; Huang, C.Y. The effect of extrusion puffing on the physicochemical properties of brown rice used for saccharification and Chinese rice wine fermentation. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 94, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Prasad, K. Effect of parboiling and puffing processes on the physicochemical, functional, optical, pasting, thermal, textural and structural properties of selected Indica rice. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2018, 12, 1707–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.H.; Ye, F.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, L.; Zhao, G.H. Rheological and textural insights into the blending of sweet potato and cassava starches: In hot and cooled pastes as well as in fresh and dried gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, P.; Kumar, A.; Purohit, S.R.; Rao, P.S. Extrusion of fermented rice-black gram flour for development of functional snacks: Characterization, optimization and sensory analysis. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 58, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraman, I.; Wagner, M.E.; Rizvi, S.S.H. Micronutrient and protein-fortified whole grain puffed rice made by supercritical fluid extrusion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 11188–11194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaisangsri, N.; Kowalski, R.J.; Wijesekara, I.; Kerdchoechuen, O.; Laohakunjit, N.; Ganjyal, G.M. Carrot pomace enhances the expansion and nutritional quality of corn starch extrudates. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Thakur, K.; Zhang, J.G.; Wei, Z.J. Structural and physicochemical characteristics of lycoris starch treated with different physical methods. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Bai, B.; Pan, Y.; Li, X.M.; Cheng, J.S.; Chen, H.Q. Effects of pectin with different molecular weight on gelatinization behavior, textural properties, retrogradation and in vitro digestibility of corn starch. Food Chem. 2018, 264, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.Y.; Xiao, L.; Liang, Y.N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, G.H. Spontaneous fermentation tunes the physicochemical properties of sweet potato starch by modifying the structure of starch molecules. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 213, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Roy, A. Puffed rice: A materialistic understanding of rice puffing and its associated changes in physicochemical and nutritional characteristic. J. Food Process. Eng. 2020, 43, e13479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, P.C.; Silva, F.S.D.; Jaren, C.; Junior, P.C.A.; Arana, I. Physical and mechanical properties in rice processing. J. Food Eng. 2007, 79, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotti, M.; Alamprese, C.; Pagani, M.A.; Lucisano, M. Effect of puffing on ultrastructure and physical characteristics of cereal grains and flours. J. Cereal Sci. 2006, 43, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.M.; Cheng, H.H. Properties of pregelatinized rice flour made by hot air or gum puffing. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Scuppa, S.; Brandolini, A. Technological quality and chemical composition of puffed grains from einkorn (Triticum monococcum L. subsp. monococcum) and bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L. subsp. aestivum). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, X.P.; Zhu, R.Z.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.L.; Hu, X.Z. Effect of natural fermentation on the structure and physicochemical properties of wheat starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 218, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.X.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.K.; Jiang, Y.L.; Lv, Y.J.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.R.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhang, H.H. Effect of epigallocatechin gallate on the gelatinisation and retrogradation of wheat starch. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Wu, J.Y.; Luo, S.J.; Zou, P.; Guo, B.Z.; Liu, Y.F.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.M. Improving instant properties of kudzu powder by extrusion treatment and its related mechanism. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, M.; Weglarz, W.P.; Jong, L.D.; Dalen, G.V.; Blonk, J.C.G.; Heussen, P.; Velzen, E.V.; As, H.V.; Duynhoven, J.V. The structural and hydration properties of heat-treated rice studied at multiple length scales. Food Chem. 2010, 120, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambigaipalan, P.; Hoover, R.; Donner, E.; Liu, Q. Starch chain interactions within the amorphous and crystalline domains of pulse starches during heat-moisture treatment at different temperatures and their impact on physicochemical properties. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Sun, M.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.W.; Ouyang, J. Effect of microwave irradiation-retrogradation treatment on the digestive and physicochemical properties of starches with different crystallinity. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Tian, Y.; Wei, B.; Chen, L.; Bi, Y.; Jin, Z. Effect of reaction solvents on the multi-scale structure of potato starch during acid treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Halley, P.J.; Gilbert, R.G. Mechanism of degradation of starch, a highly branched polymer, during extrusion. Macromolecules 2010, 43, 2855–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanashiro, I.; Abe, J.I.; Hizukuri, S. A periodic distribution of the chain length of amylopectin as revealed by high-performance anion-exchange chromatography. Carbohydr. Res. 1996, 283, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.T.; Xu, F.; Khan, M.R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Huang, C.X.; Zhu, K.X.; Tan, L.H.; Chu, Z.; Liu, A.Q. Supramolecular structure of Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam seed starch prepared by improved extrusion cooking technology and its relationship with in vitro digestibility. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters a | Puffing Time (s) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | |
| Puffing ratio | 1.00 ± 0.02 e | 1.01 ± 0.04 e | 1.16 ± 0.03 e | 4.38 ± 0.38 d | 7.07 ± 0.26 c | 10.26 ± 0.53 b | 10.69 ± 0.62 b |
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 12.33 ± 1.19 b | 12.23 ± 1.21 b | 11.97 ± 1.35 b | 8.04 ± 0.18 c | 6.37 ± 1.19 cd | 4.08 ± 0.65 d | 3.25 ± 0.05 de |
| Porosity (%) | 5.77 ± 1.54 f | 5.89 ± 0.88 f | 5.96 ± 1.04 f | 41.11 ± 8.40 e | 71.29 ± 1.37 d | 84.55 ± 1.19 c | 89.04 ± 0.89 b |
| Surface temperature (°C) | 31.67 ± 1.53 f | 111.67 ± 3.06 e | 129.33 ± 4.93 d | 162.67 ± 4.51 c | 177.33 ± 2.08 b | 181.33 ± 2.52 b | 181.67 ± 4.93 b |
| L* | 37.82 ± 1.86 e | 37.78 ± 2.11 e | 38.21 ± 1.72 e | 53.29 ± 1.38 d | 61.81 ± 0.59 c | 67.47 ± 2.15 b | 66.84 ± 1.35 b |
| a* | 3.08 ± 0.18 b | 3.09 ± 0.40 b | 3.09 ± 0.31 b | 2.41 ± 0.14 c | 1.76 ± 0.08 d | 1.47 ± 0.09 e | 1.35 ± 0.04 e |
| b* | 6.39 ± 0.30 b | 6.27 ± 0.12 b | 6.26 ± 0.45 bc | 5.62 ± 0.29 cd | 5.42 ± 0.26 d | 4.84 ± 0.20 e | 4.64 ± 0.55 e |
| C | 7.11 ± 0.35 b | 7.01 ± 0.28 b | 6.99 ± 0.33 b | 6.11 ± 0.32 c | 6.02 ± 0.34 c | 5.07 ± 0.19 d | 4.84 ± 0.54 d |
| H | 64.23 ± 0.37 d | 63.79 ± 2.61 d | 63.64 ± 3.56 d | 66.81 ± 0.95 c | 71.93 ± 1.31 b | 73.08 ± 1.12 b | 73.63 ± 1.47 b |
| ΔE* | − | 1.94 ± 0.89 d | 2.66 ± 0.77 d | 15.52 ± 0.72 c | 24.05 ± 1.74 b | 29.73 ± 3.74 b | 29.13 ± 2.93 b |
| Bulk density (g/mL) | 2.69 ± 0.09 b | 2.80 ± 0.10 b | 2.79 ± 0.05 b | 0.60 ± 0.04 c | 0.38 ± 0.05 d | 0.26 ± 0.02 e | 0.21 ± 0.01 f |
| True density (g/mL) | 2.85 ± 0.06 b | 2.94 ± 0.12 b | 2.95 ± 0.09 b | 1.04 ± 0.18 ef | 1.32 ± 0.12 de | 1.74 ± 0.25 cd | 1.95 ± 0.05 c |
| Hardness (N) | 67.45 ± 20.54 b | 65.64 ± 12.77 b | 66.01 ± 16.16 b | 44.14 ± 4.41 c | 40.33 ± 5.65 c | 24.52 ± 4.52 d | 24.55 ± 2.48 d |
| First peak force (N) | 51.69 ± 2.99 b | 52.81 ± 6.52 b | 50.47 ± 10.14 b | 34.09 ± 1.69 c | 14.07 ± 2.83 d | 10.51 ± 1.35 e | 9.98 ± 0.78 e |
| WSI (%) | 5.95 ± 0.47 g | 6.96 ± 0.25 f | 7.98 ± 0.12 de | 8.01 ± 0.37 cd | 8.26 ± 0.71 bd | 8.90 ± 0.47 bc | 9.01 ± 0.45 b |
| Parameters a | Puffing Time (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 12 | 18 | |
| RC (%) | 7.06 ± 0.21 b | 3.49 ± 0.42 c | 0.38 ± 0.08 d | 0.31 ± 0.04 e |
| 1047/1020 (cm−1) | 0.88 ± 0.01 b | 0.83 ± 0.00 c | 0.79 ± 0.00 d | 0.78 ± 0.00 d |
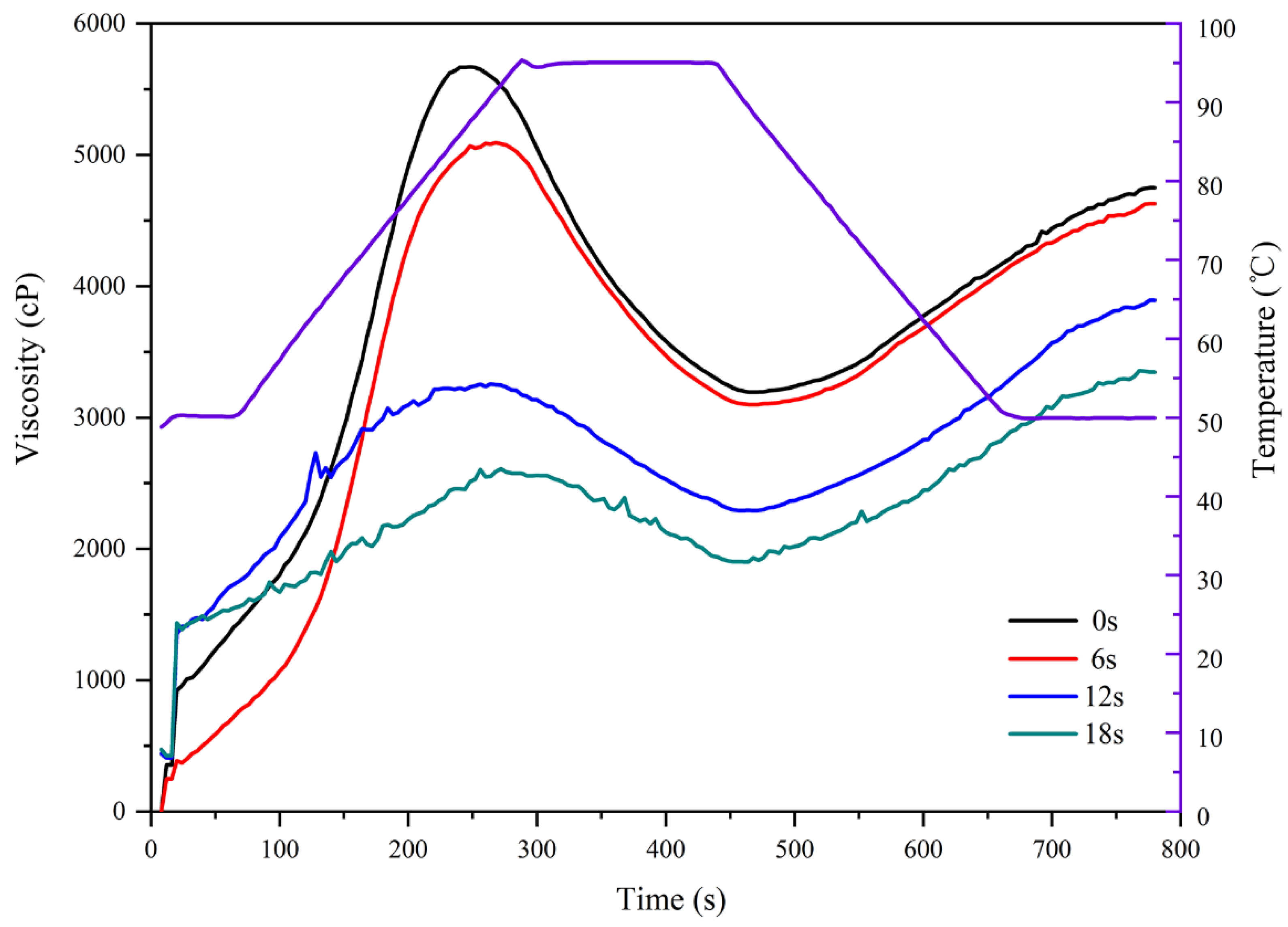
| PV (cP) | 5655 ± 85 b | 5134 ± 35 c | 3208 ± 211 d | 2639 ± 225 e |
| TV (cP) | 3226 ± 69 b | 3111 ± 53 b | 1962 ± 292 c | 1910 ± 35 c |
| BD (cP) | 2429 ± 47 b | 2023 ± 53 c | 1245 ± 275 d | 729 ± 191 d |
| FV (cP) | 4730 ± 49 b | 4611 ± 19 c | 3781 ± 178 d | 3256 ± 124 e |
| SB (cP) | 1504 ± 49 bd | 1499 ± 50 bc | 1818 ± 199 b | 1346 ± 108 cd |
| PTemp (°C) | 50.12 ± 0.03 b | 50.23 ± 0.14 b | 50.27 ± 0.16 b | 50.57 ± 0.52 b |
| PT (min) | 4.16 ± 0.04 cd | 4.47 ± 0.07 bd | 4.53 ± 0.13 b | 4.51 ± 0.23 bc |
| Parameters a | Puffing Time (s) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 6 | 12 | 18 | |
| Mw (kDa) | 94,574.5 | 44,506.9 | 35,144.1 | 33,769.2 |
| Mn (kDa) | 20,350.9 | 10,378.8 | 8829.1 | 7182.1 |
| DP 6–12 (A) | 32.3 | 34.5 | 35.2 | 35.9 |
| DP 13–24 (B1) | 49.7 | 50.4 | 52.3 | 53.3 |
| DP 25–36 (B2) | 11.1 | 10.3 | 9.6 | 8.2 |
| DP ≥ 37 (B3) | 6.9 | 4.8 | 2.9 | 2.6 |
| CL | 18.4 | 17.4 | 16.9 | 16.6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Y.; Ye, F.; Li, S.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G. Effect of Sand-Frying-Triggered Puffing on the Multi-Scale Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Cassava Starch in Dry Gel. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121872
He Y, Ye F, Li S, Wang D, Chen J, Zhao G. Effect of Sand-Frying-Triggered Puffing on the Multi-Scale Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Cassava Starch in Dry Gel. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(12):1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121872
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Yonglin, Fayin Ye, Sheng Li, Damao Wang, Jia Chen, and Guohua Zhao. 2021. "Effect of Sand-Frying-Triggered Puffing on the Multi-Scale Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Cassava Starch in Dry Gel" Biomolecules 11, no. 12: 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121872
APA StyleHe, Y., Ye, F., Li, S., Wang, D., Chen, J., & Zhao, G. (2021). Effect of Sand-Frying-Triggered Puffing on the Multi-Scale Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Cassava Starch in Dry Gel. Biomolecules, 11(12), 1872. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11121872







